Hemorrhage
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
Hemorrhage, thrombosis, and embolisms are all examples of altered ________
Hemostasis
Define Hemorrhage
Escape of blood from the cardiovascular system (can be internal or external)
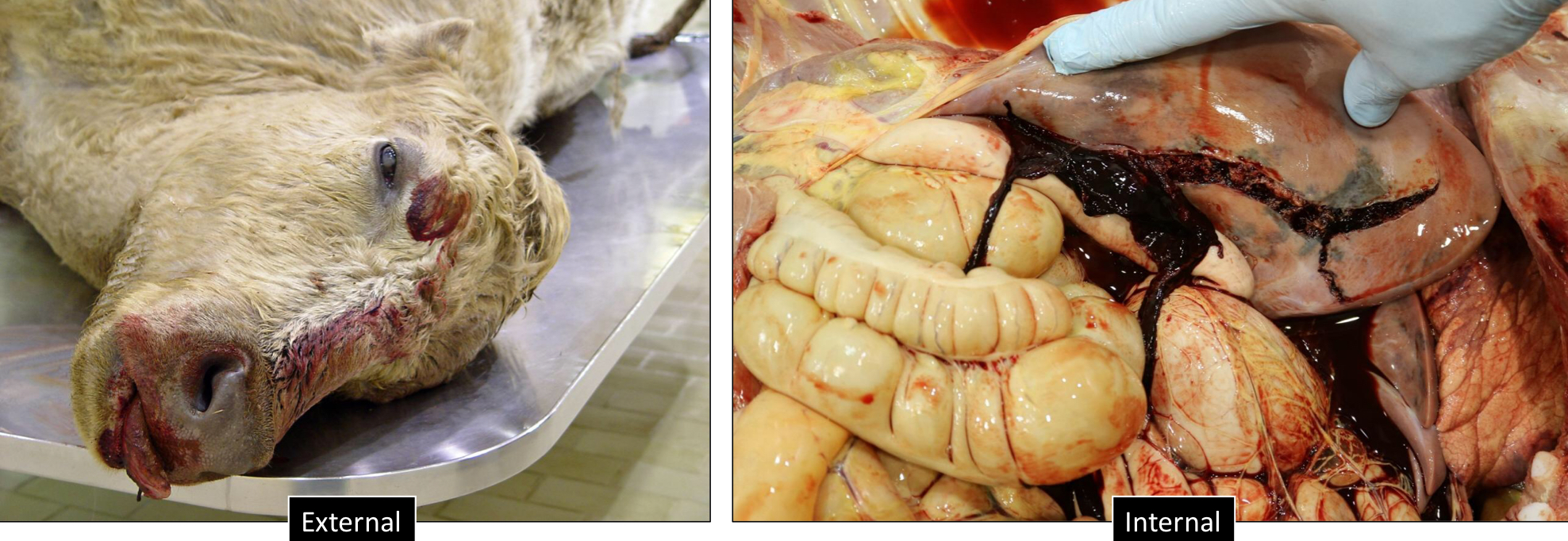
Hemorrhage from a tear in the blood vessel or heart is called what?
Hemorrhage by Rhexis
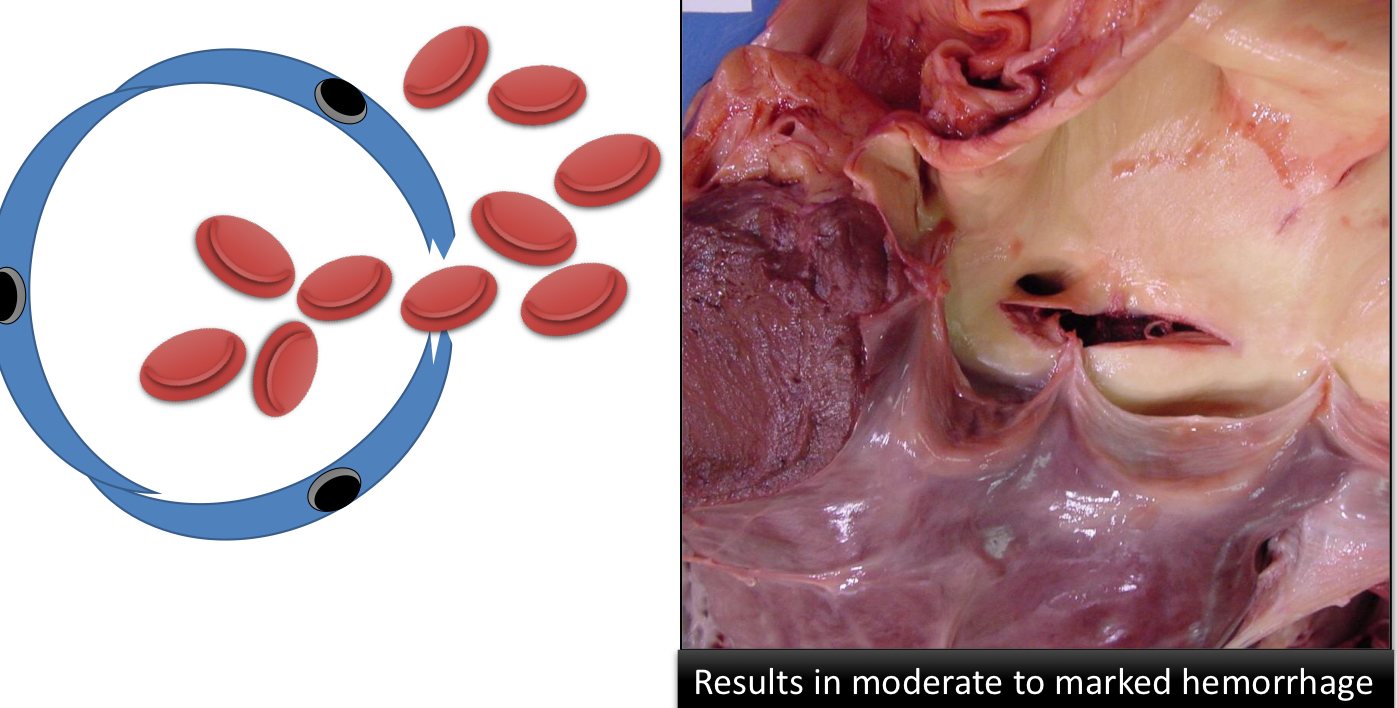
Define Hemorrhage by Diapedesis, what causes it?
Bleeding from a small defect
Caused by increased permeability in the vasculature
If a patient has bleeding diathesis, what does that mean?
They have an increased tendency to hemorrhage (aka more prone to bleeding)
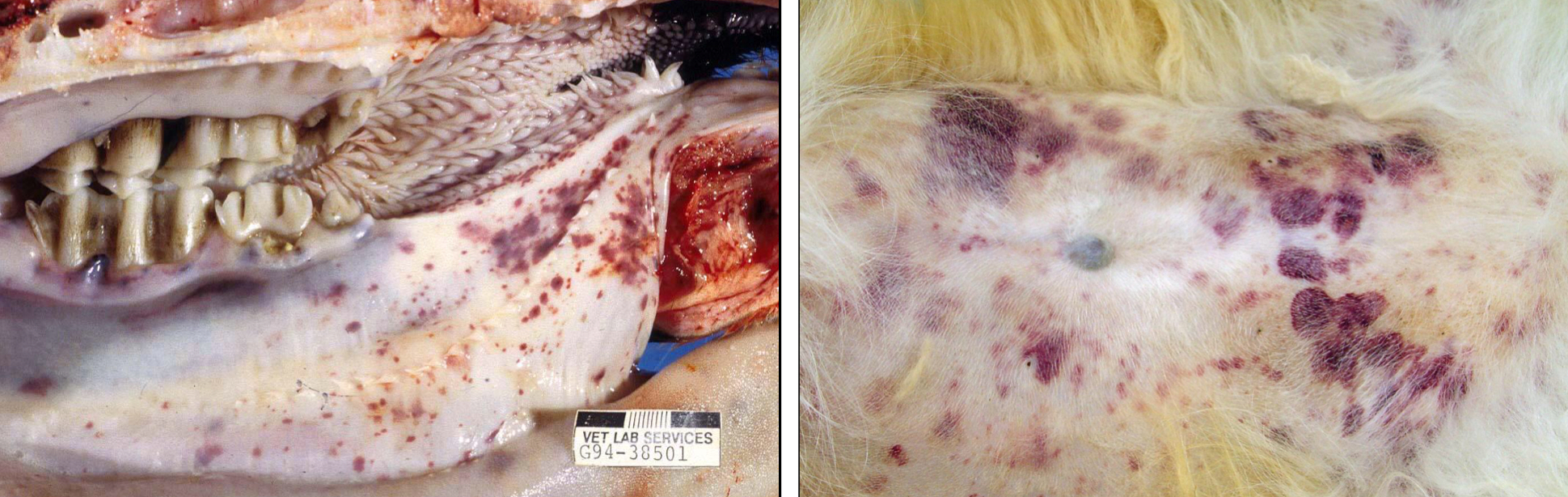
What type of damage or dysfunction do these lesions indicate?
The lesions are small foci of hemorrhage on mucosal surfaces and skin
They indicate platelet defects
Define Thrombocytopenia and Thrombocytopathy
Decreased # of circulating platelets
<200 × 109
Defective platelet function
If a patient has
History of bleeding
Normal Platelet counts
Abnormal platelet function tests
A defect in adhesion
Defect in release of granules from platelets
Defect in aggregation
What type of platelet disorder does this describe?
Thrombocytopathy
In general, large hemorrhages or hematomas in the absence of trauma suggest a _________ disorder
Coagulation
What are the two ways that coagulation disorders can be acquired?
Inherited (rare)
Acquired (more common)
Animals with a coagulation defect may have ________ clotting times, what are the 2 ways we test for clotting time?
Prolonged
PT (prothrombin time) and aPTT (activated partial thromboplastin time)
Acquired coagulation defects can results from a ____ in the production of coagulation factors
Decrease
Vitamin _ deficiency and ____ failure will cause decreased production of coagulation factors, which results in an inability of the animal to perform coagulation
Vitamin K
Liver failure
What is disseminated Intravascular Coagulation (DIC)
Sudden onset of widespread thrombosis in the microcirculation
Pathological activation/disequilibria of hemostasis
Increased use of Coagulation factors
Excessive clotting throughout the body
What are some potential causes of DIC?
Severe burns
Heat stroke
Systemic viral disease
Shock
Malignant neoplasia
Heartworm
Pancreatitis
Tissue factor is released from tissue when it is ______, it triggers coagulation
Damaged
What are the 2 ways that DIC causes hemorrhage?
Depletion of clotting factors → Hemorrhage
Activation of plasmin → Fibrinolysis → FDPs → Inhibition of clot formation → Hemorrhage
DIC is associated with excess ______ production, it can be caused by ________ activation/ _________ of hemostasis
Thrombin
Pathological
Disequilibrium
Define subdural/epidural hemorrhage
Blood accumulation beneath/above the dura
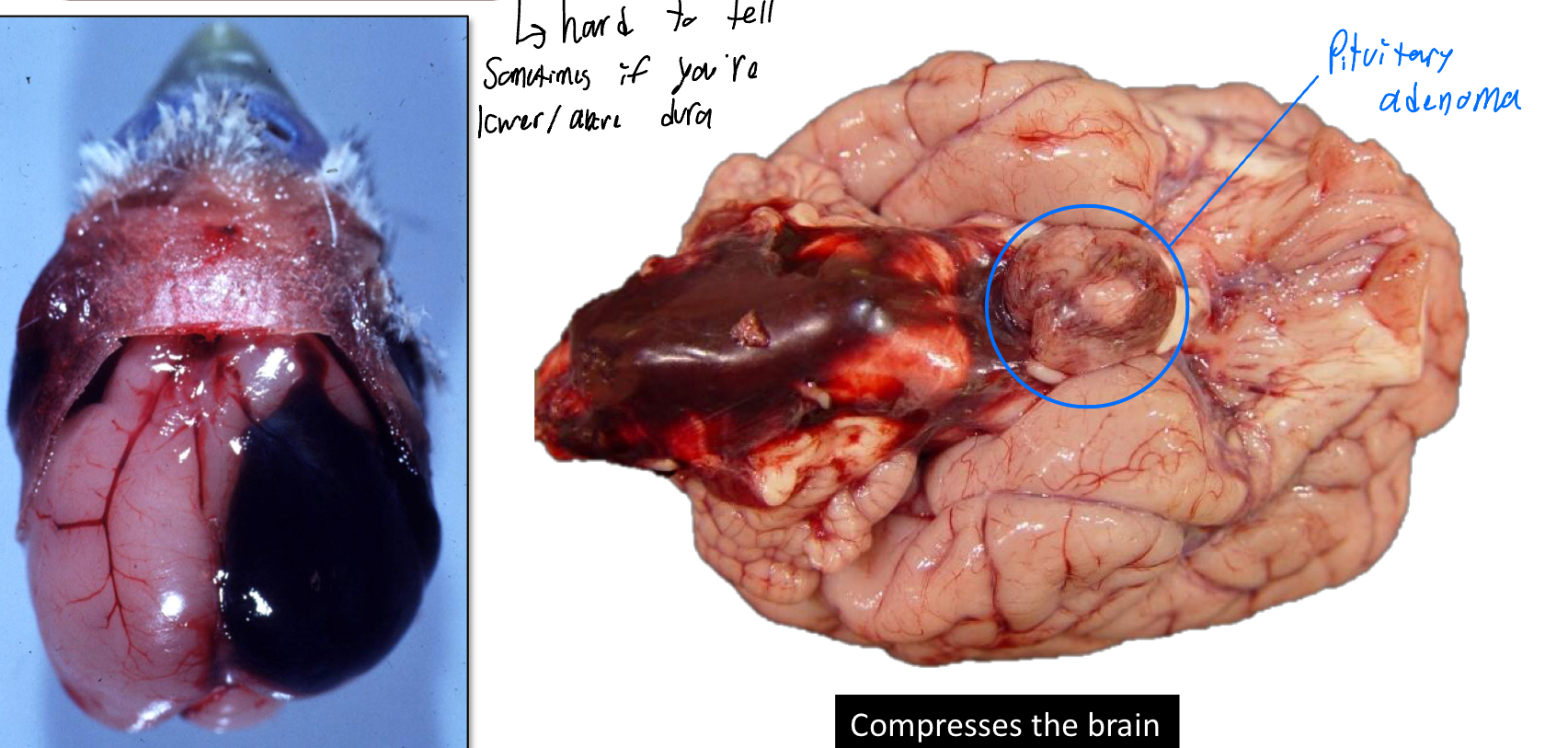
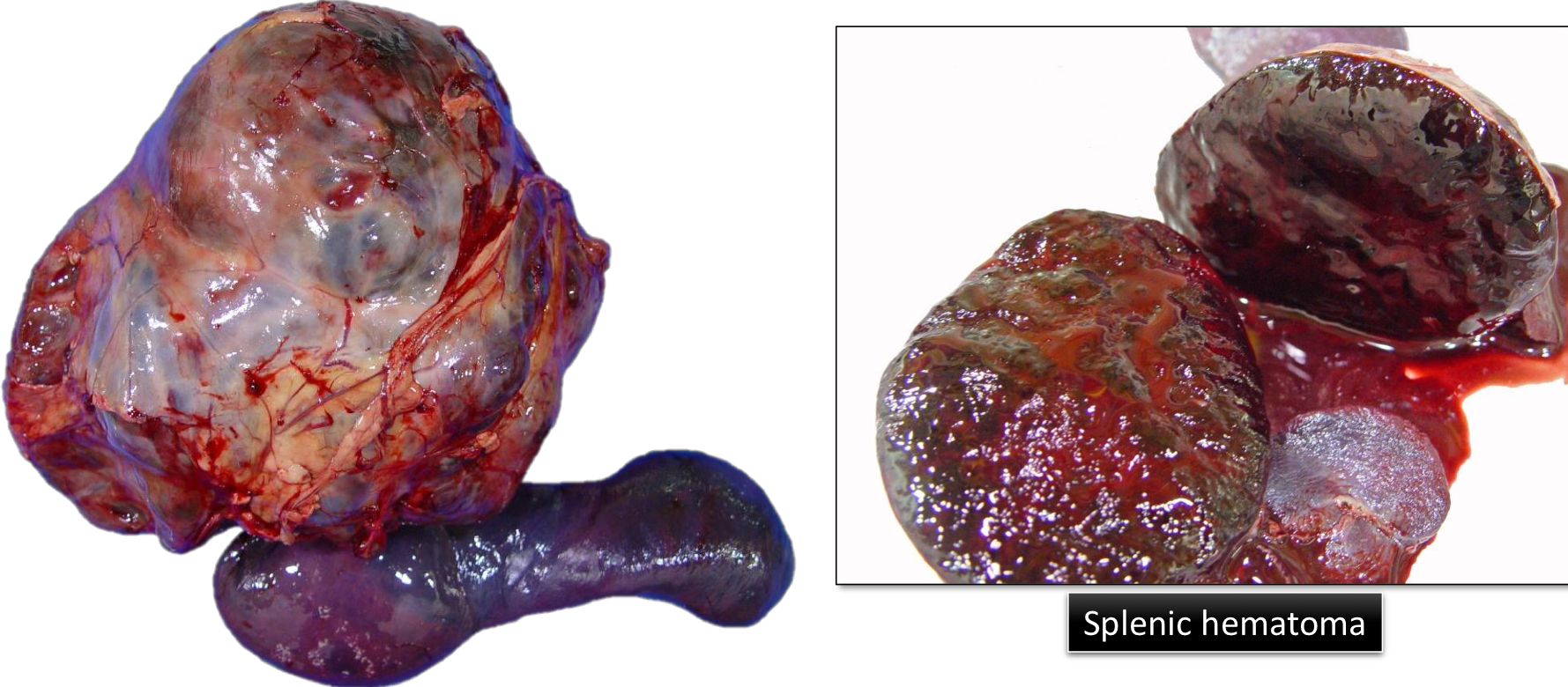
Define Hematoma
Hemorrhage enclosed within a tissue
Extravascular 3-dimensional blood clot
Define Hemopericardium
Blood in the pericardial sac
Can be acute/chronic (tissue will appear red because blood is an irritant)
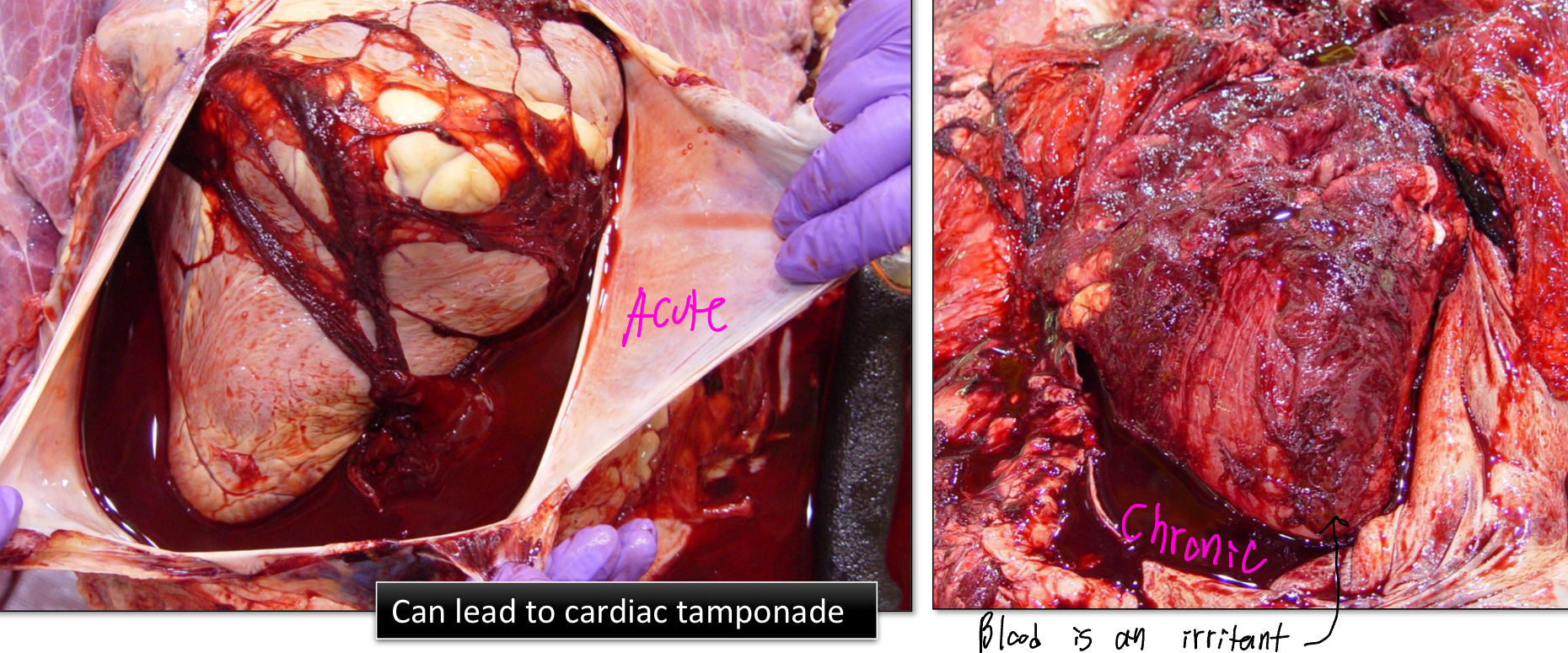
T/F: Hemopericardium can lead to cardiac tamponade
True
Define Cardiac Tamponade
Compression of the heart due to accumulation of blood in the pericardial sac
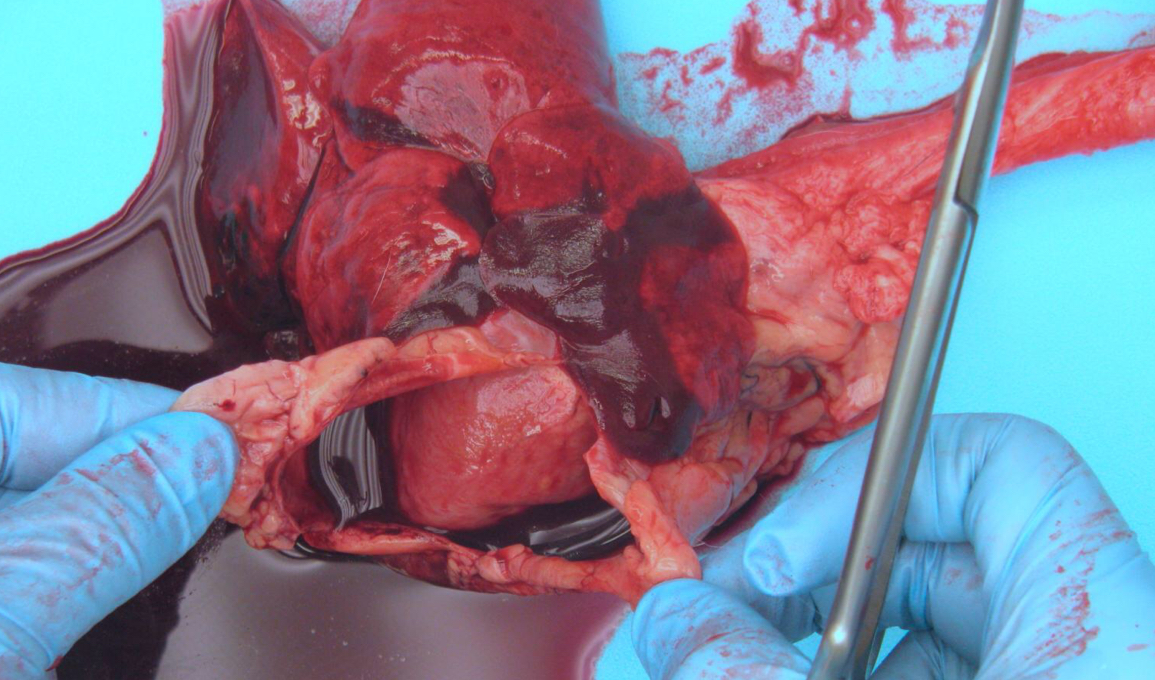
If an animal has cardiac tamponade, which side of the heart would be more affected, if at all?
The right side since it is less muscular than the left
Define Hemothorax
Blood in the thorax (pleural cavity)
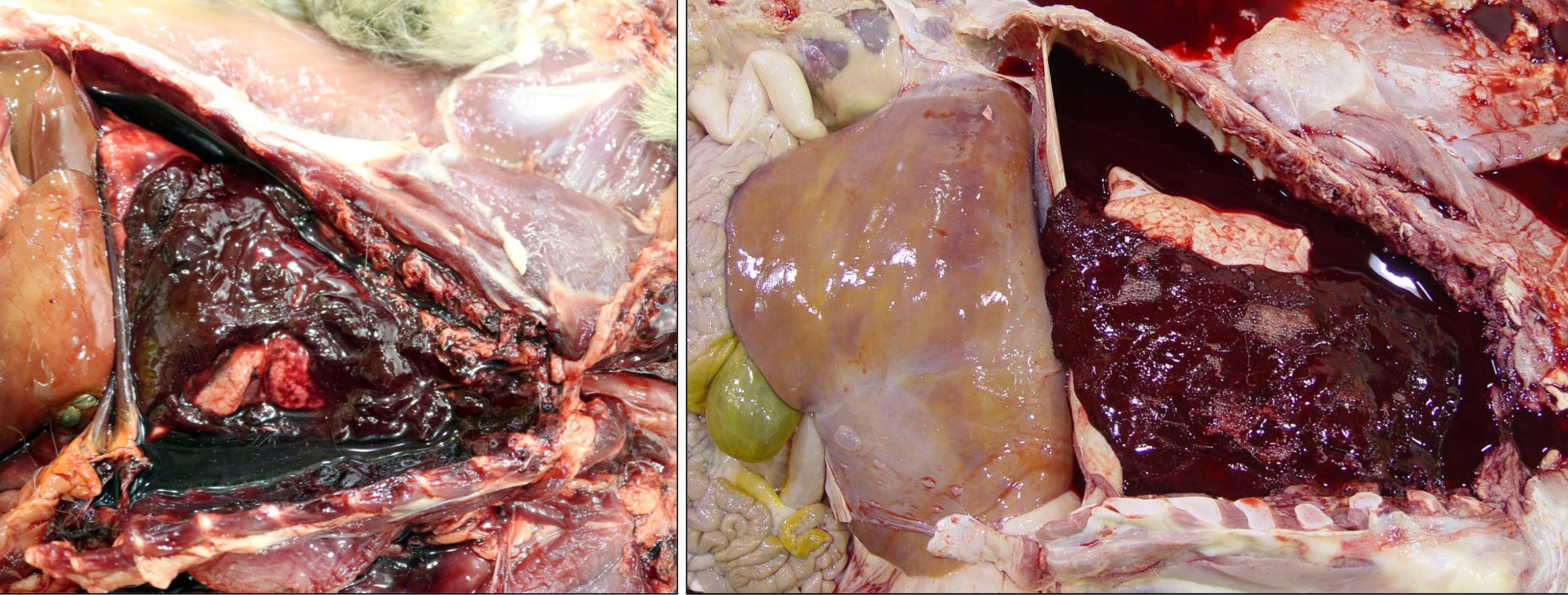
Define Hemoabdomen (Hemoperitoneum)
Blood in the abdomen (peritoneal cavity)
T/F: Clotting of blood is a good indicator of chronicity
False, blood clots can break down post-mortem
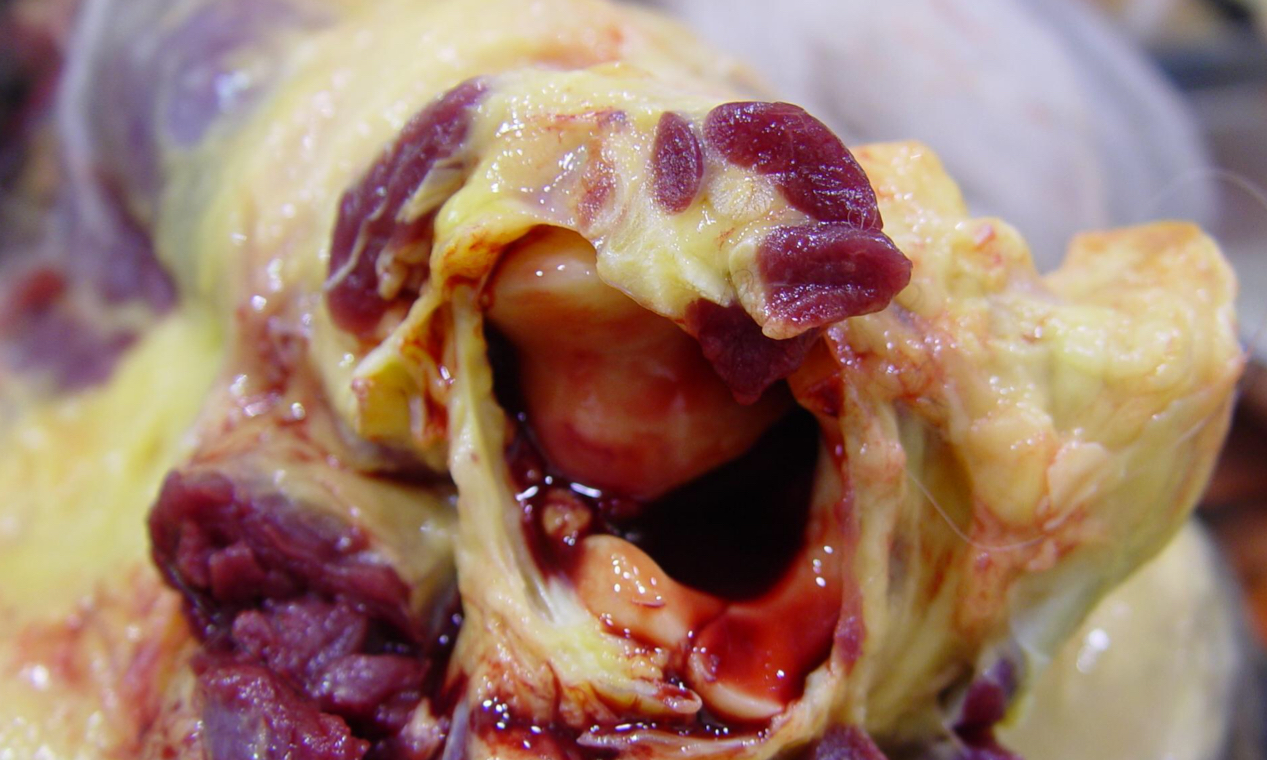
Define Hemarthrosis
Blood in the joint spaces

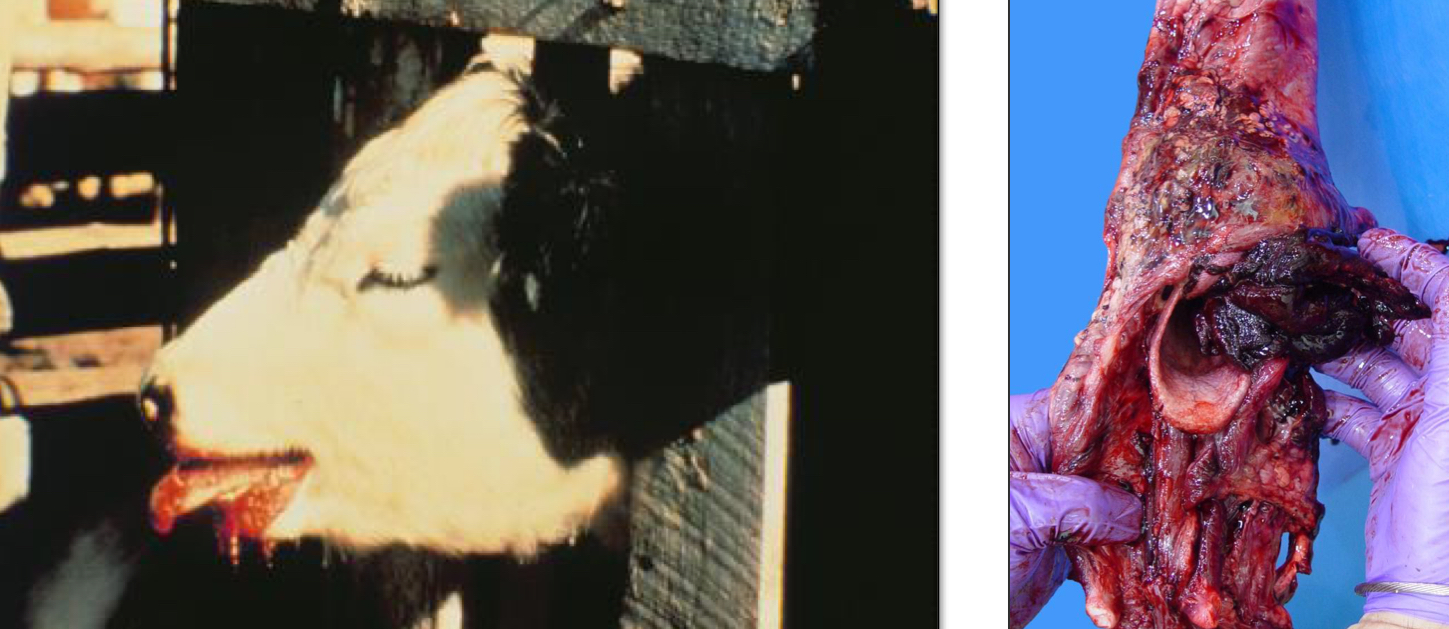
Define Hemoptysis
Coughing blood from the lungs or airways

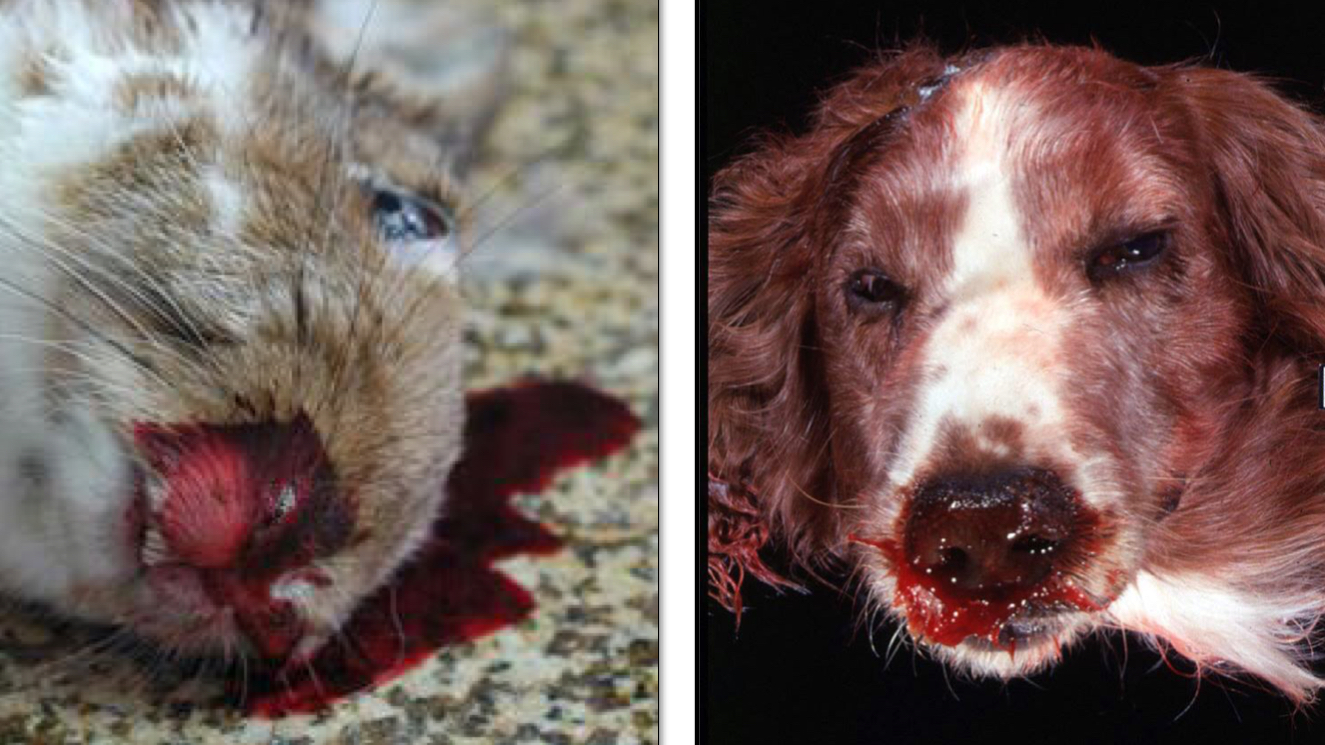
Define Epistaxis
Bleeding from the nose

Define Hematemesis
Vomiting up blood
What is the difference between Hematochezia and Melena?
Hematochezia
The presence of fresh blood in the stool (red color, indicates lower G.I bleed)
Melena
Presence of tarry blood in the stool (black blood, indicates upper G.I bleed)
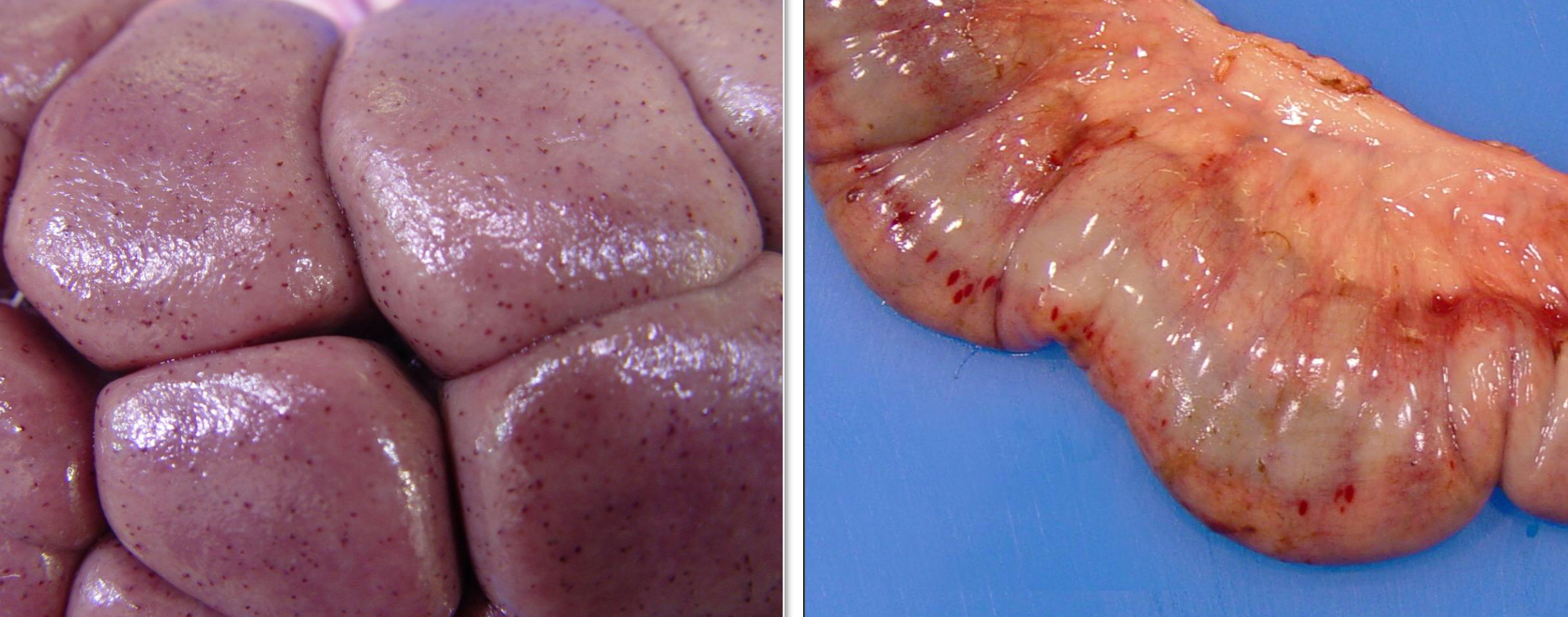
Define petechia(e), where is it most commonly observed?
Pinpoint hemorrhages (1-2mm)
Most common in the skin, mucosa, and serosa
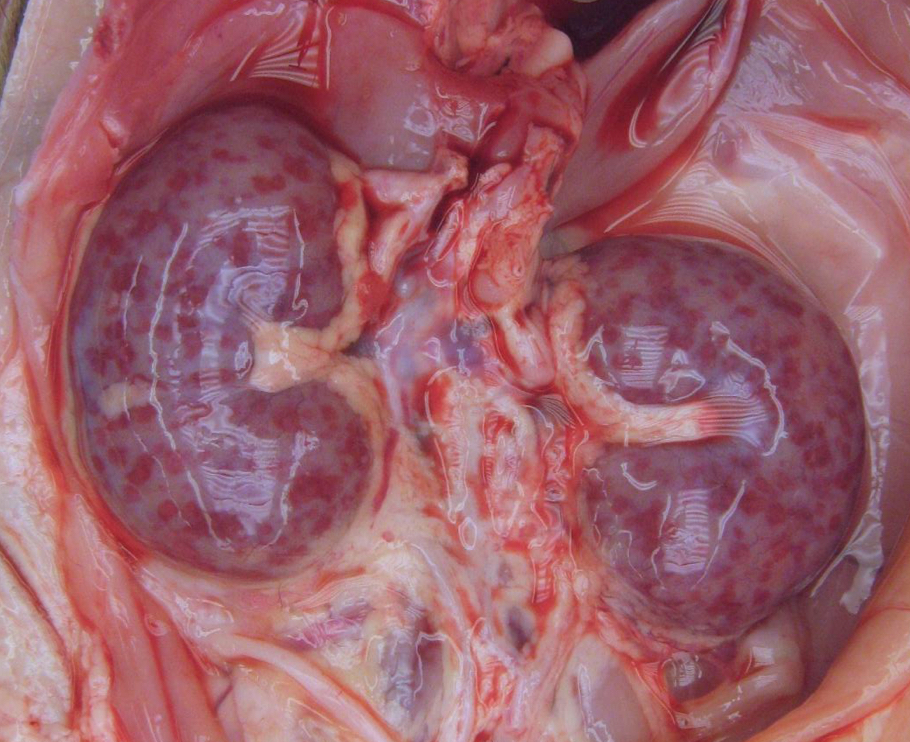
Define Purpura
3mm-1cm hemorrhages
Most common in the skin, mucosa, and serosa
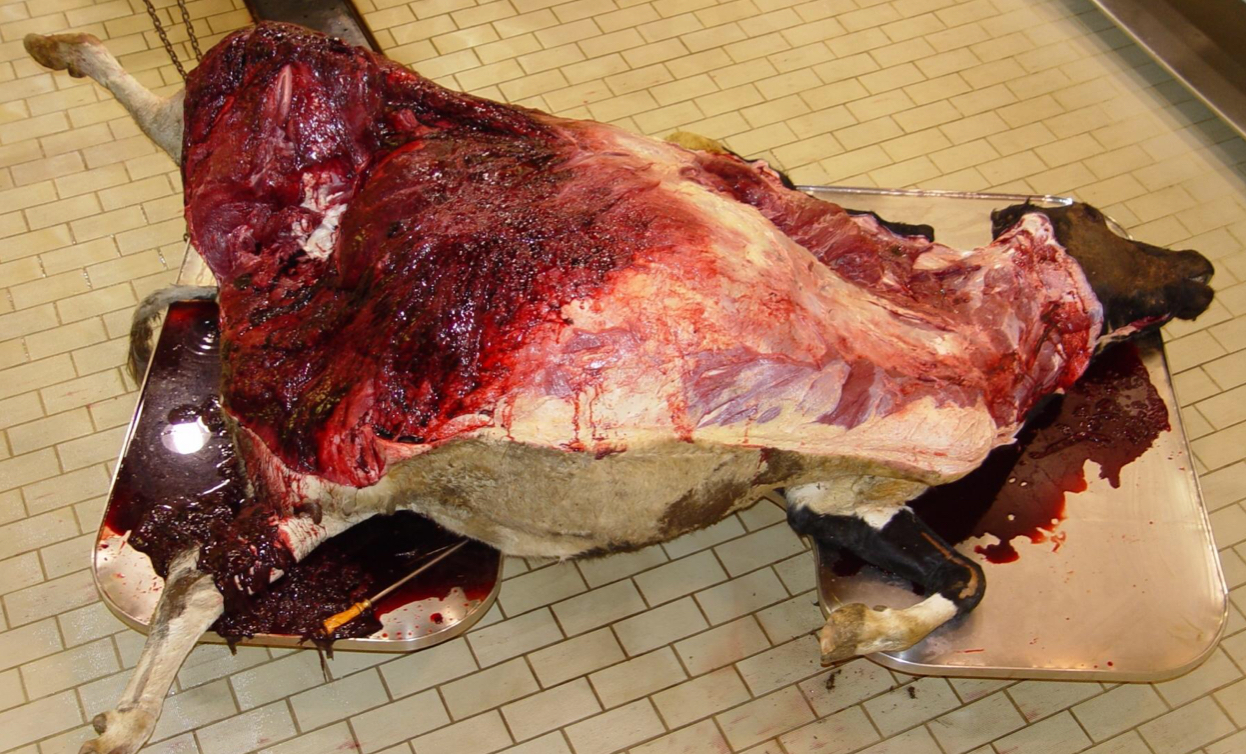
Define Ecchymosis (Ecchymoses)
hemorrhages larger than 1cm
Often blotchy and irregular
Define paint brush hemorrhage
Hemorrhage, which looks like red paint was applied with a brush
Define Suffusive hemorrhage
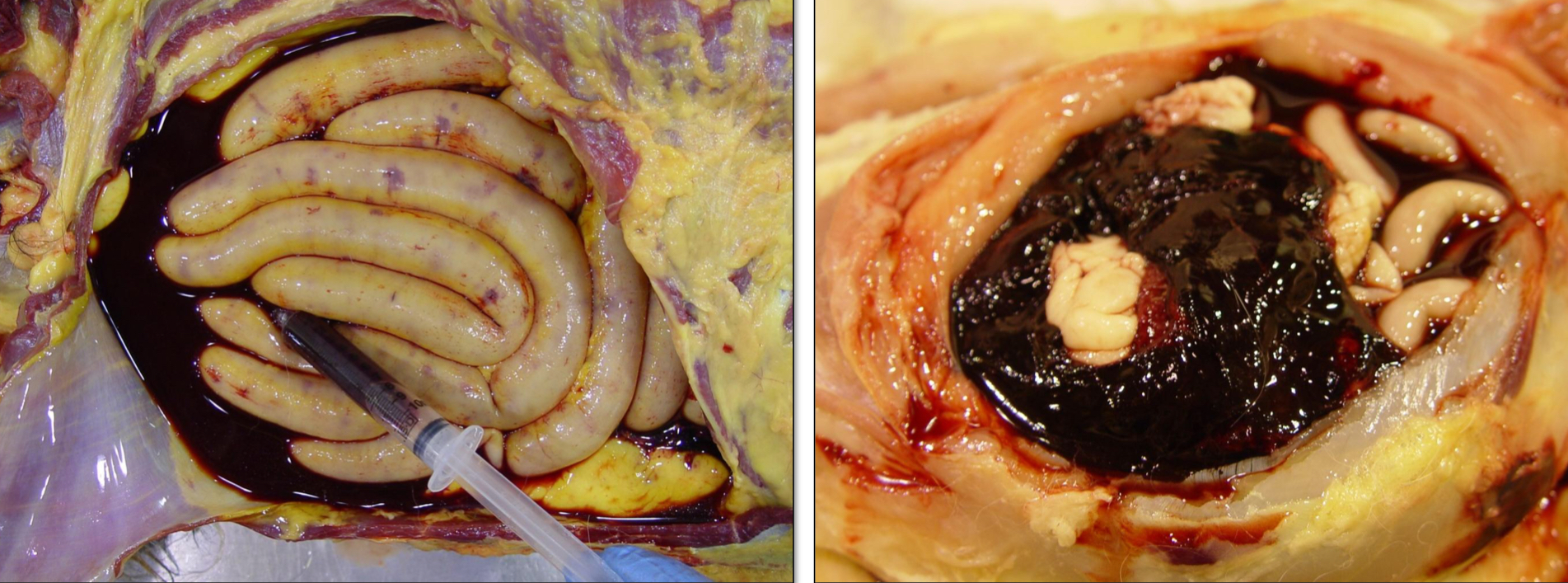
Area of hemorrhage larger than ecchymoses and contiguous (sharing a common border; touching)
What type of hemorrhage is this?
Suffusive Hemorrhage
What type of hemorrhage is this?
Petechia(e)
What type of hemorrhage is this?
Purpura
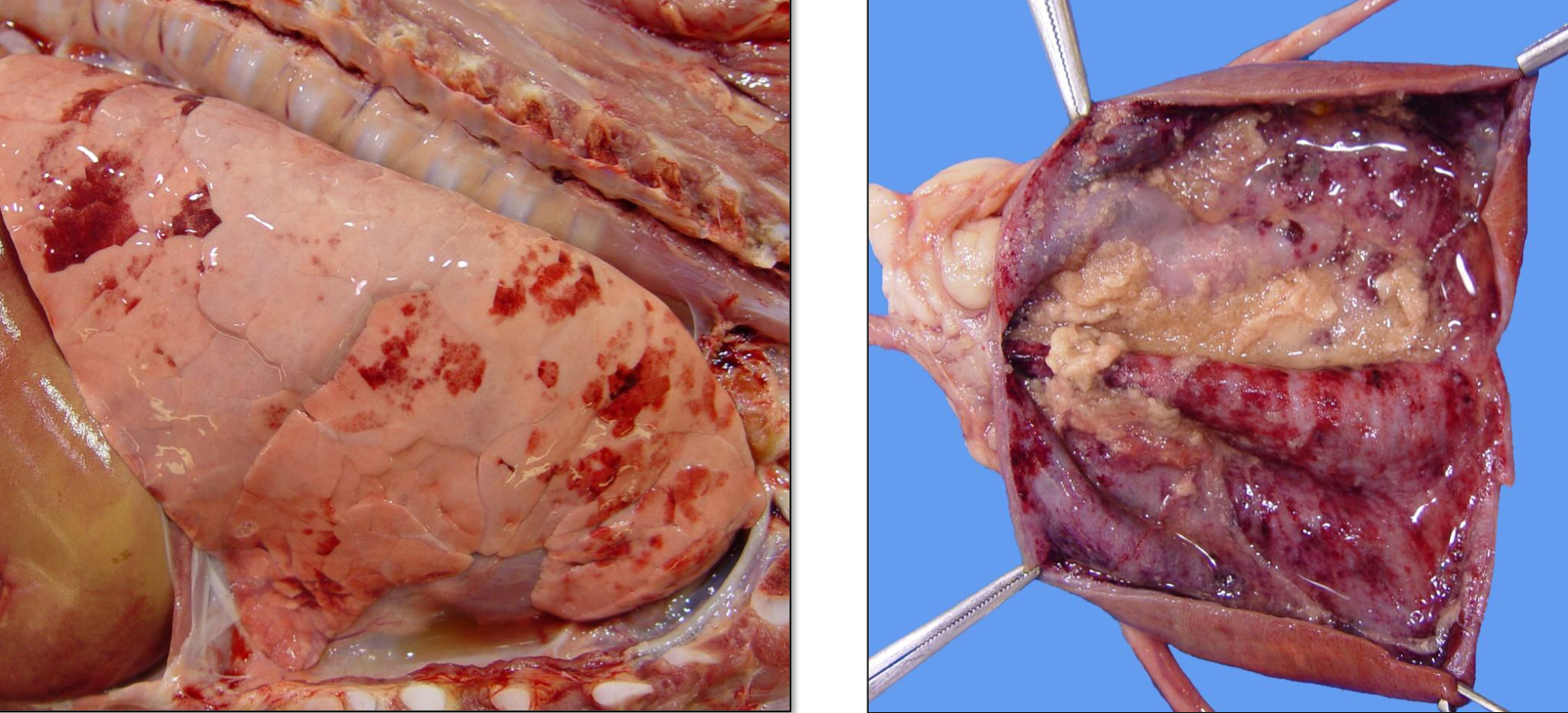
What type of hemorrhage is this?
Ecchymosis/Ecchymoses
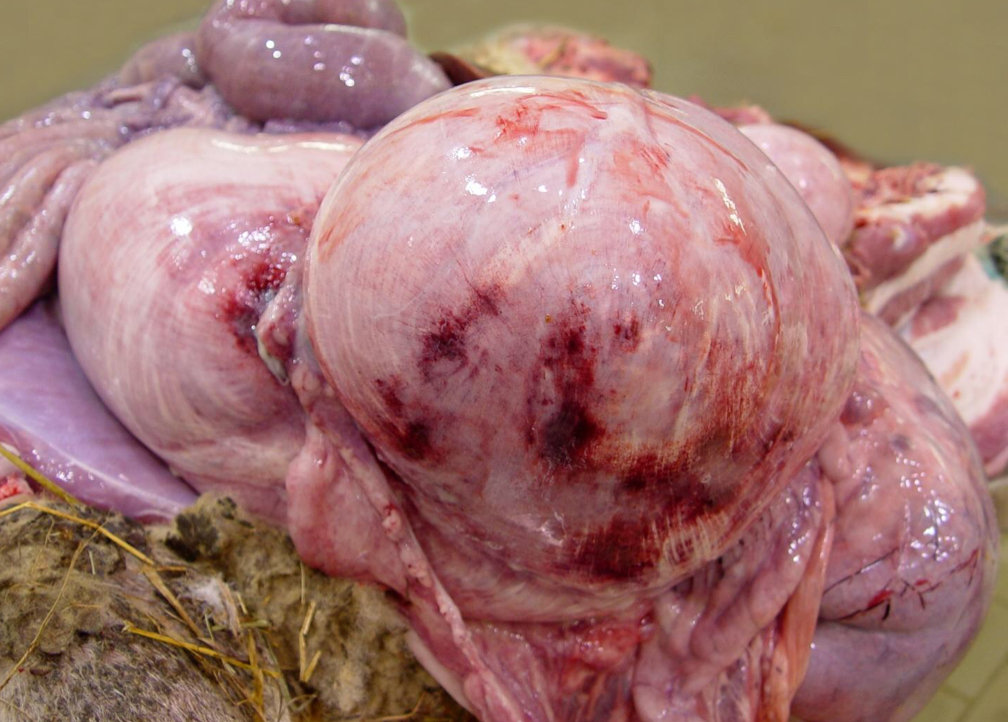
What type of hemorrhage is this?
Paint Brush Hemorrhage
Define Agonal Hemorrhage
Petechiae and ecchymoses that are associated with terminal hypoxia (bleeding associated with dying cells)
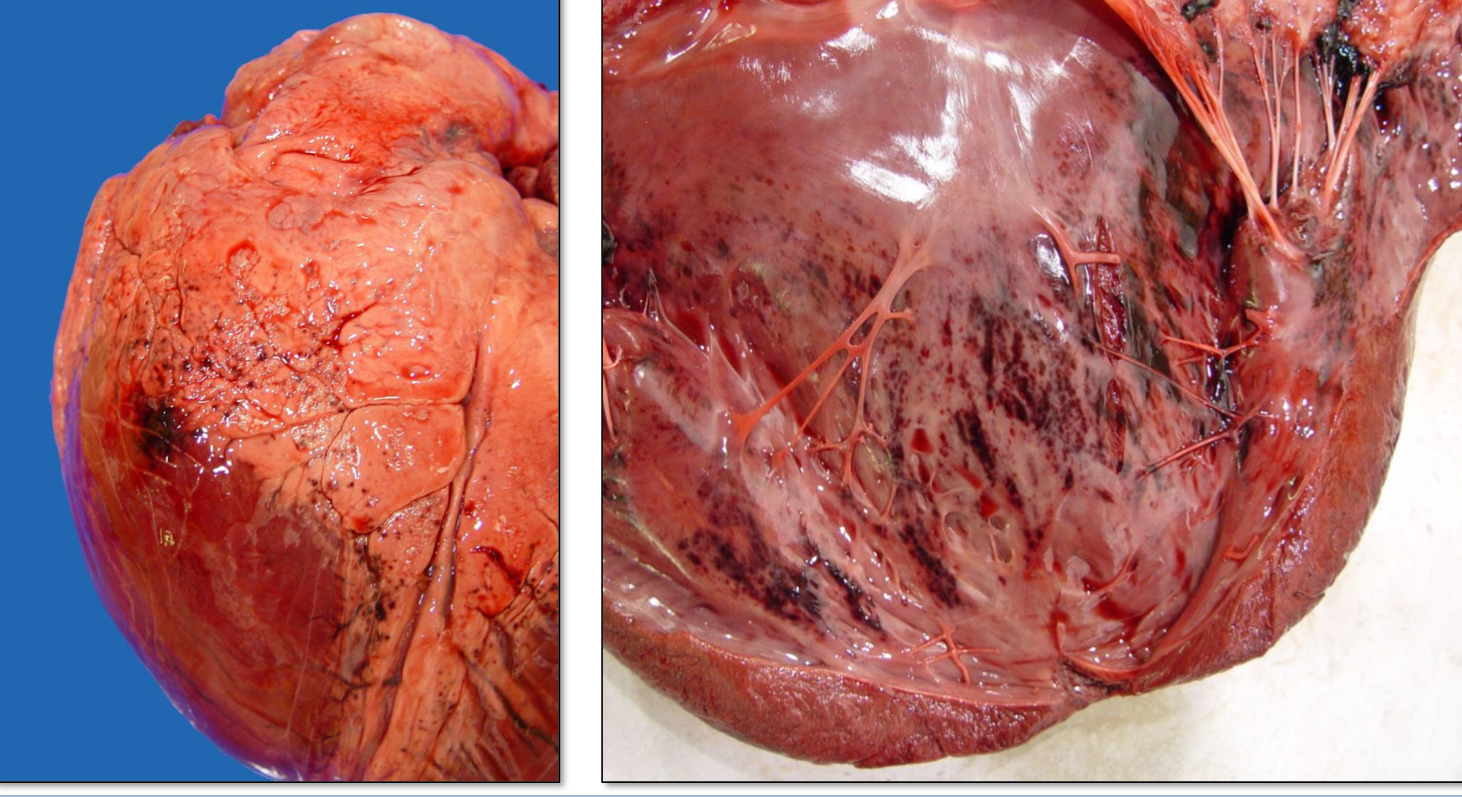
The arrest of hemorrhage occurs as a result of _______
Hemostasis
The resolution of hemorrhage depends on the amount of hemorrhage, what are the two ways hemorrhage can be arrested?
Resorption
Only small amounts
Organization
Larger amounts
Breakdown and removal of RBCs by macrophages
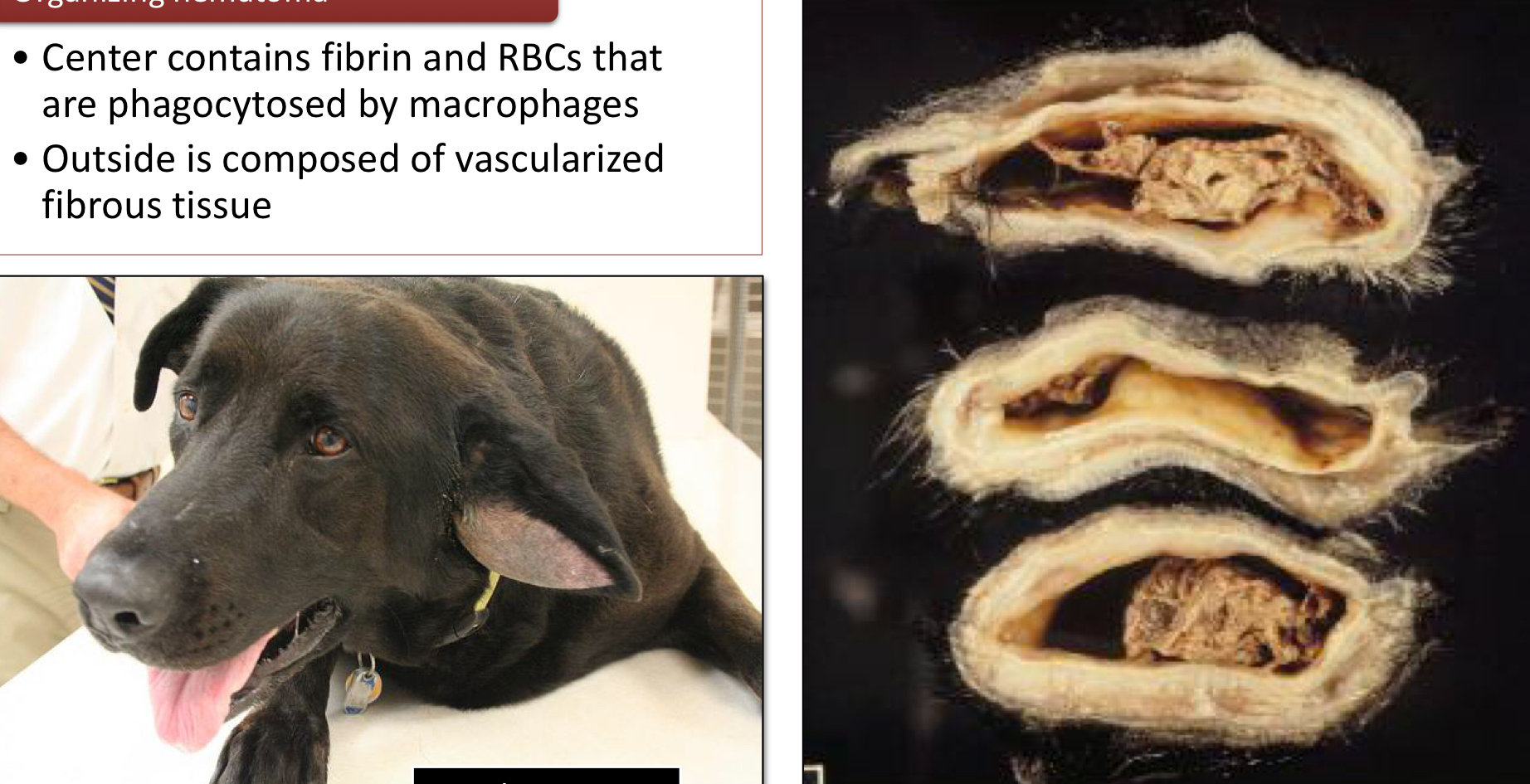
What makes up an organizing hematoma?
Center contains fibrin and RBCs that are phagocytosed by macrophages
Outside is composed of vascularized fibrous tissue
Define Thrombosis
Inappropriate activation of hemostasis resulting in the formation of a solid mass (thrombus) within the blood vessels or heart
Define Thrombus
An aggregate of platelets, fibrin, and other blood elements (RBCs/WBCs) formed on the endothelial surface
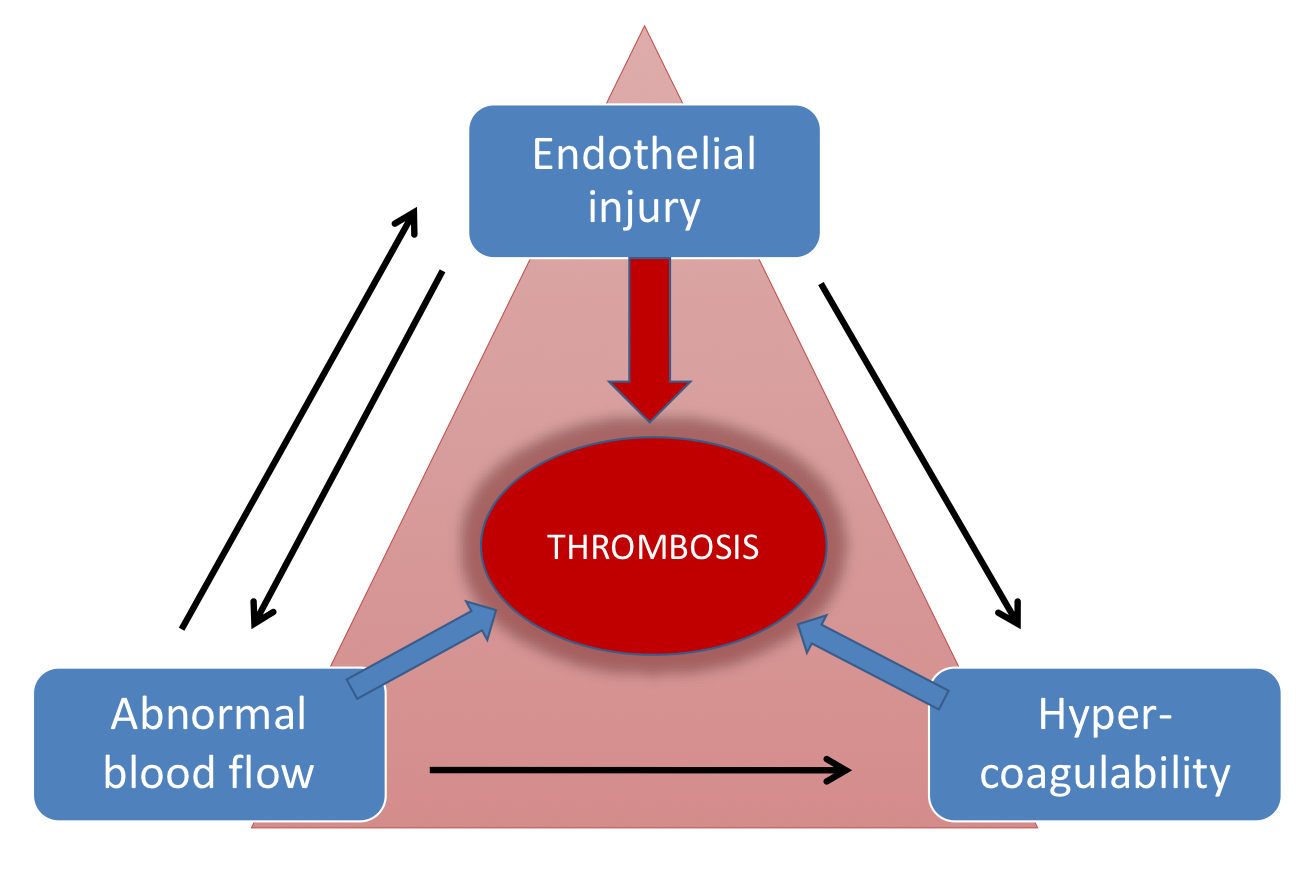
What is Virchow’s Triad?
A theory that explains three main factors that can lead to blood clots, or thrombosis
Hypercoagulability: When blood is more likely to clot
Stasis: When blood flow is abnormal
Endothelial injury: When the lining of blood vessels is damaged
What are the 3 main locations that thrombi can be found int he cardiovascular system?
Blood vessels
Cardiac Chambers
Cardiac Valves