Lab Exam-2
1/288
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
289 Terms
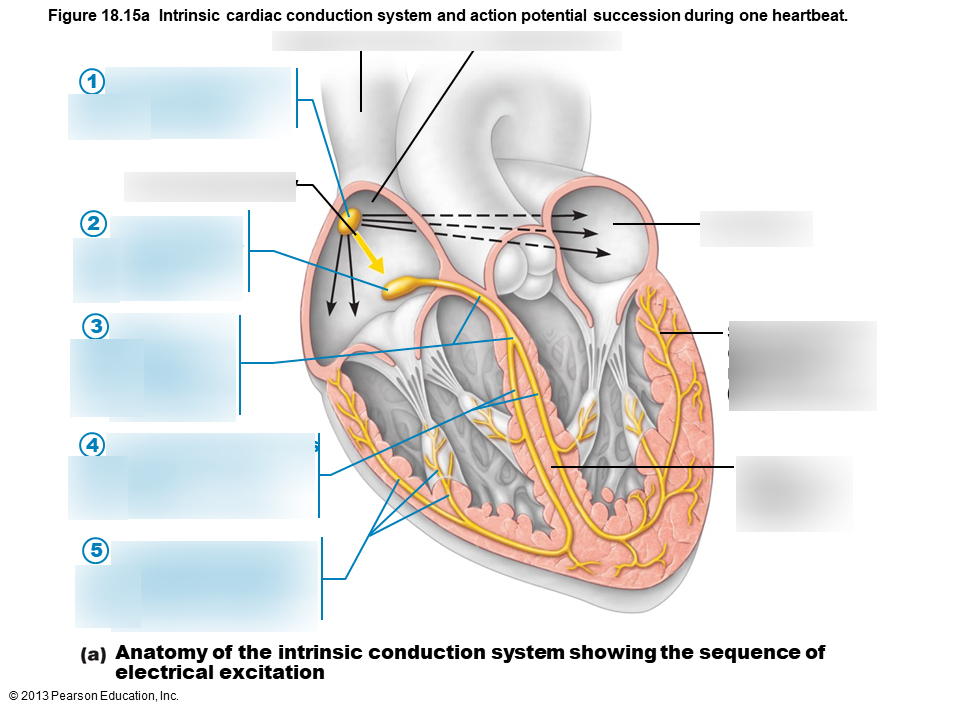
1
sinoatrial node
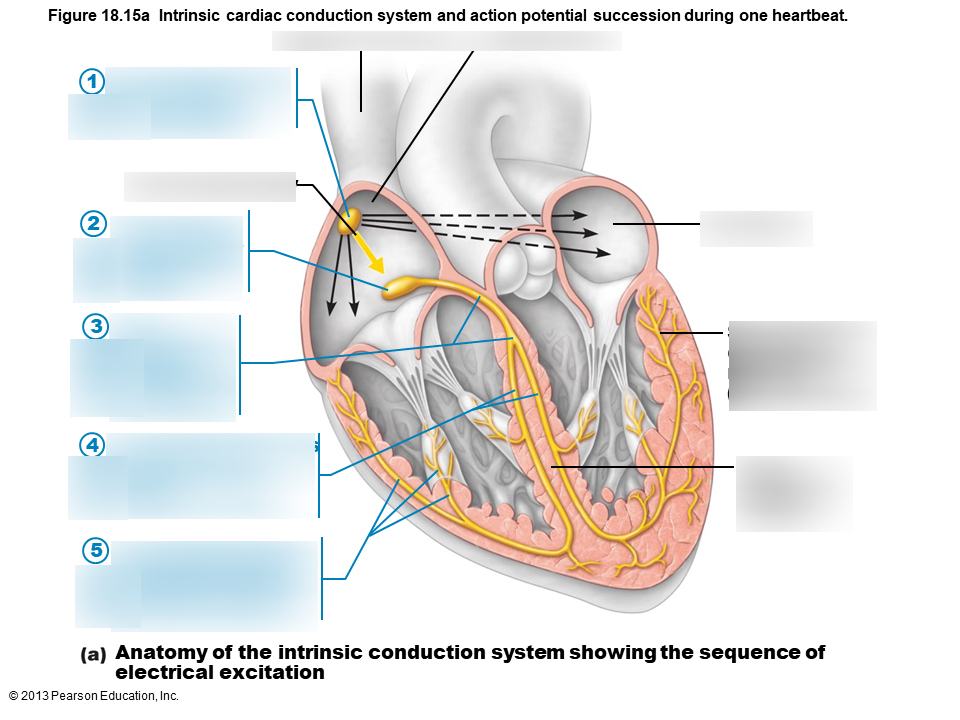
2
atrioventricular node
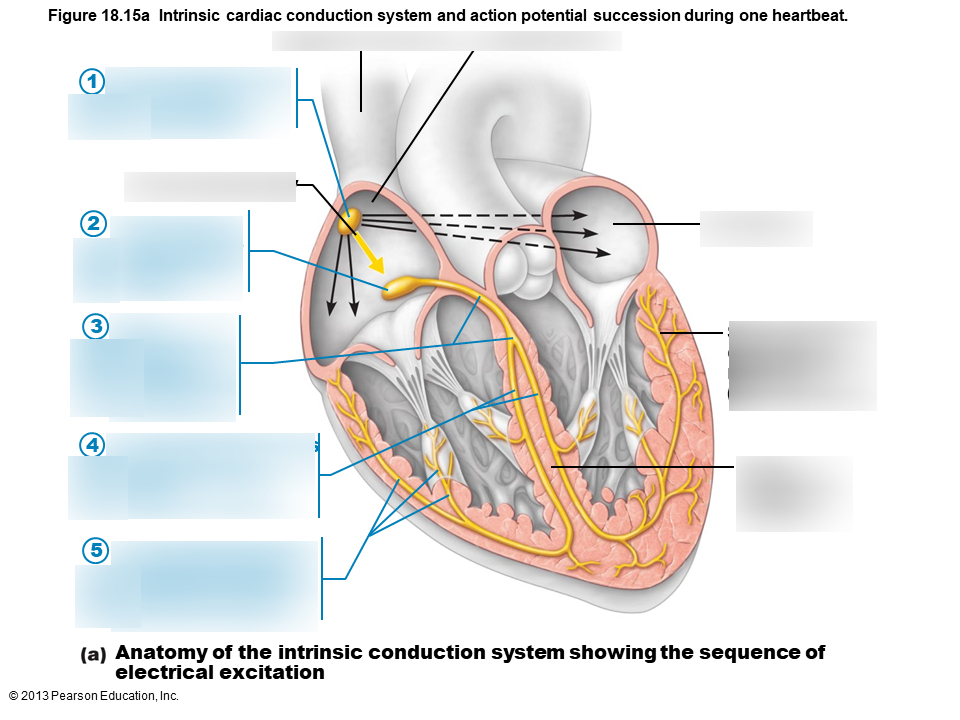
3
atrioventricular bundle
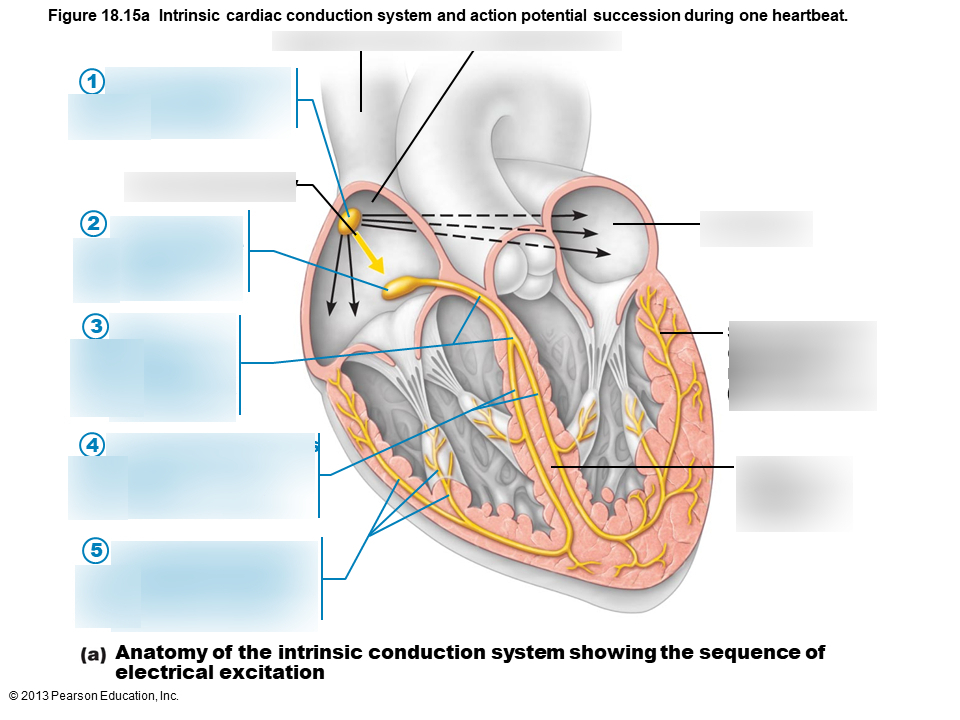
4
bundle branches
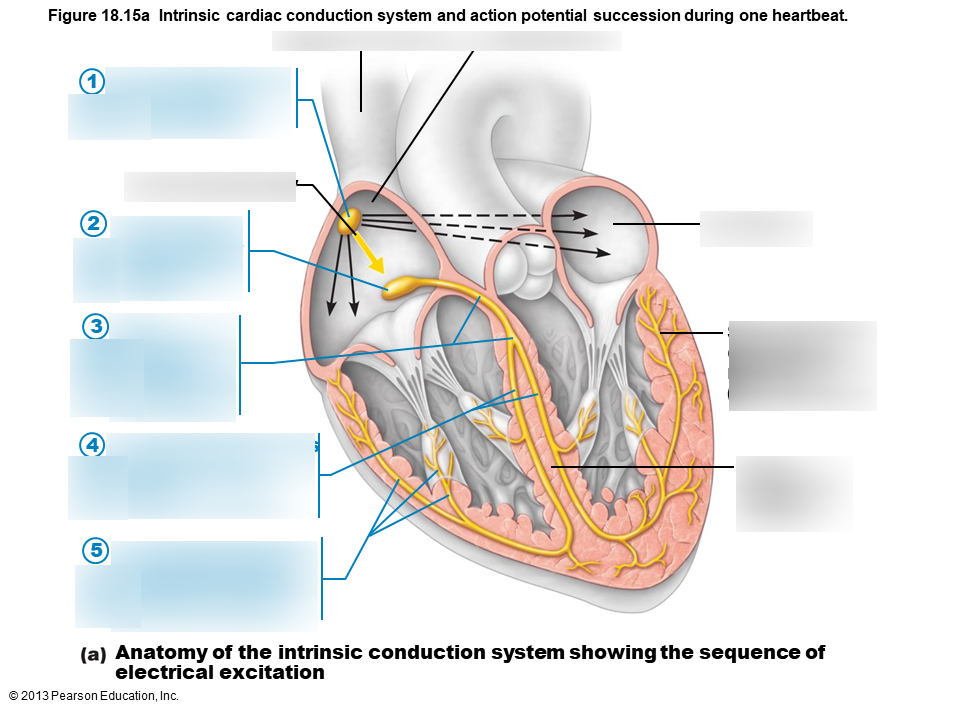
5
Purkinje fibers
function of SA node
generates action potentials
function of AV node
impulses pause before moving to AV bundle
function of AV bundle
electrical connection between left and right ventricles
function of bundle branches
conducts impulses to the ventricles
function of purkinje fibers
depolarizes the contractile cells of the ventricle
p wave represents
atrial depolarization
QRS complex represents
ventricular depolarization
T wave represents
ventricular repolarization
U wave
small wave associated with repolarization
P-R segment represents
Time interval from end of atrial depolarization to beginning of ventricular depolarization
S-T segment represents
Time interval from end of ventricular depolarization to beginning of ventricular repolarization
P-R interval represents
Time interval from beginning of atrial depolarization to beginning of ventricular depolarization
Q-T interval represents
From beginning of ventricular depolarization to end of ventricular repolarization
on EKG: a big square is ___ seconds
0.2
on EKG: a small square is ___ seconds
0.04
normal P wave should be no more than ___ to ___ seconds in duration
0.08 to 0.10 seconds
in adults, the normal QRS duration is ___ seconds or less
0.12
T wave duration in seconds
0.1- 0.25
PR segment should be no longer than ___ second
0.1
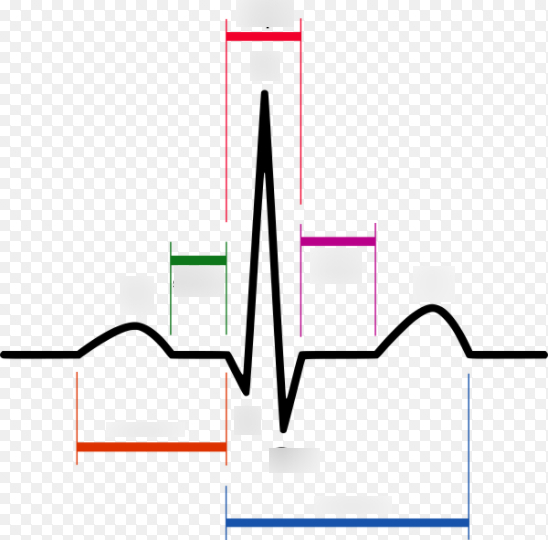
red (middle)
QRS complex
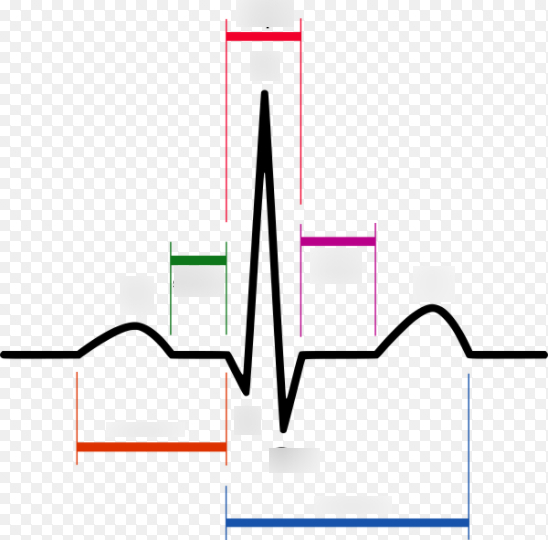
pink/purple
ST segment
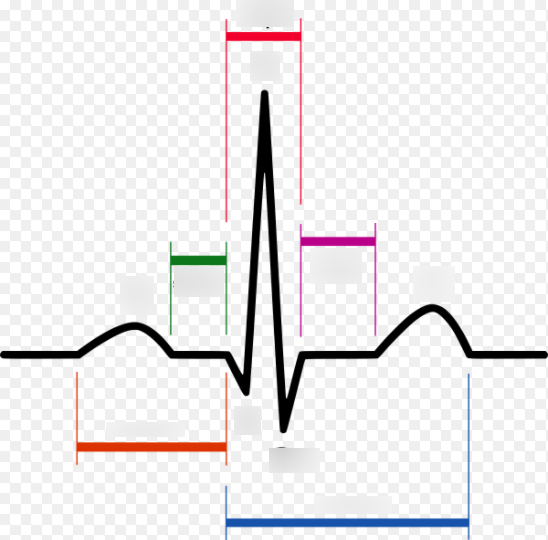
green
PR segment
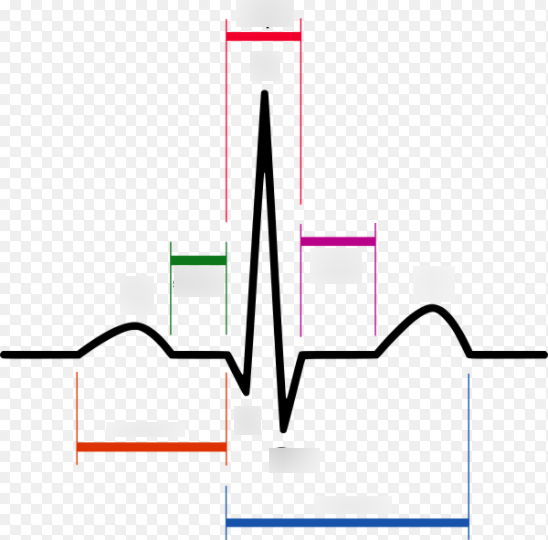
blue
QT interval
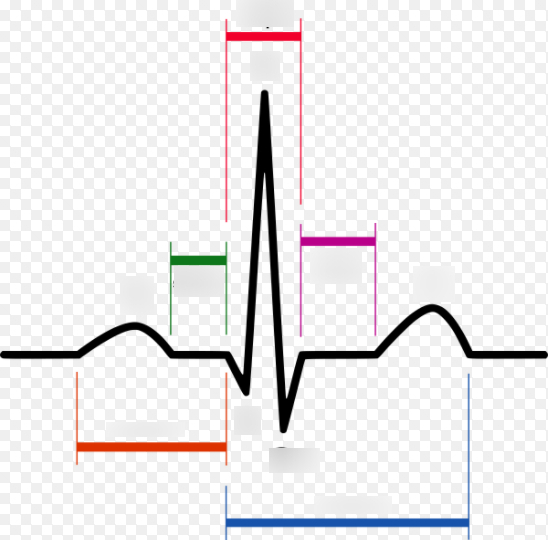
orange
PR interval
Heart rate from EKG formula
# of small boxes * 0.04/ 60
impact of exercise on EKG
all intervals shorten; increased conduction and increased heart rate shorten duration of intervals
Location of sound: aortic valve
second intercostal space, right sternal border
Timing of sound: aortic valve
heard during S2
Location of sound: tricuspid valve
fifth intercostal space, left sternal border
Timing of sound: tricuspid valve
heard during S1
Location of sound: mitral valve
fifth intercostal space, mid-clavicular line
Timing of sound: mitral valve
heart during S1
Location of sound: pulmonary valve
second intercostal space, left sternal border
Timing of sound: pulmonary valve
heard during S2
S1 makes ___ sound
lub
S2 makes ___ sound
dub
The parasympathetic nervous system releases _______ to affect heart rate.
acetylcholine
A cholinergic drug that worked the same as acetylcholine would _______.
be an agonist and decrease heart rate.
Norepinephrine affects the heart rate by _________.
increasing the rate of depolarization and increasing the frequency of action potentials.
The __________ receptor binds norepinephrine and epinephrine.
B-1 adrenergic
Pilocarpine is a cholinergic drug, an acetylcholine agonist. Predict the effect that pilocarpine will have on heart rate.
decrease HR
Atropine is another cholinergic drug, an acetylcholine antagonist. Predict the effect that atropine will have on heart rate.
increase HR
What increases the heart rate and mimics the sympathetic nervous system?
epinephrine
Individuals with weakened hearts need to allow maximum time for venous return and increased stroke volume and would therefore most likely benefit from ______.
increased force of contraction and decreased heart rate
Pilocarpine decreased the heart rate. Typical of cholinergic agonists, it _________.
decreased the frequency of action potentials.
The effect of atropine was to ________.
mimic the sympathetic nervous system.
The modifiers tested that decrease the heart rate were ______.
digitalis and pilocarpine.
To increase the heart rate, the best choices would be ______
epinephrine and atropine.
normal BP
120/80
instruments used to get BP
stethoscope, Sphygmomanometer
causes for increased BP
increased resistance, vasoconstriction, increased viscosity
T/F: Longer vessels have higher peripheral resistance than shorter vessels.
true
causes for decreased BP
decreased resistance, vasodilation, decreased viscosity
Cardiac output formula
CO= SV x HR
systolic pressure
the maximum pressure exerted on the wall of an artery (during ventricular contraction)
diastolic pressure
The minimum pressure exerted on the wall of an artery (during ventricular relaxation)
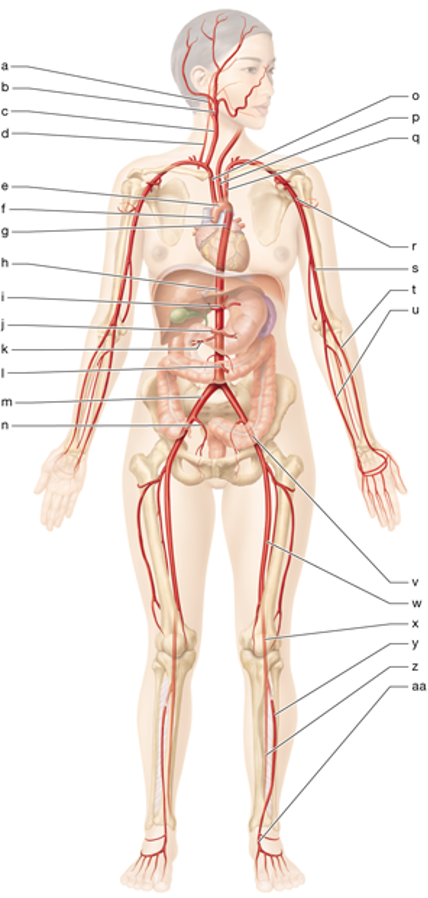
e
aortic arch
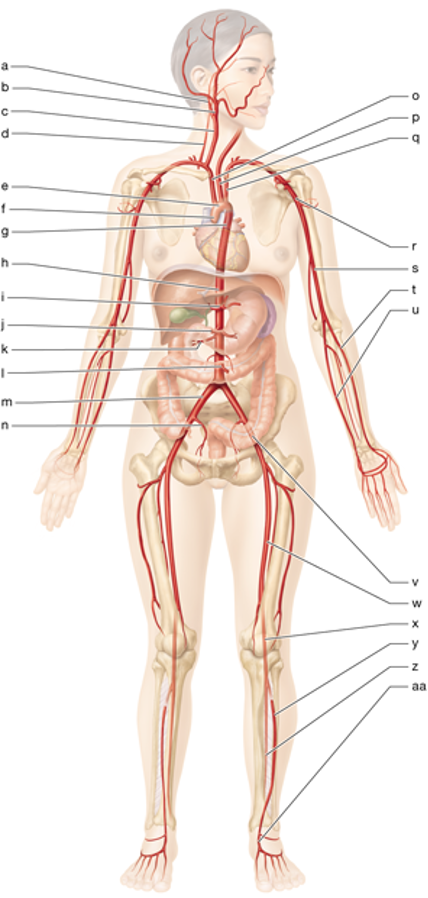
g
thoracic aorta
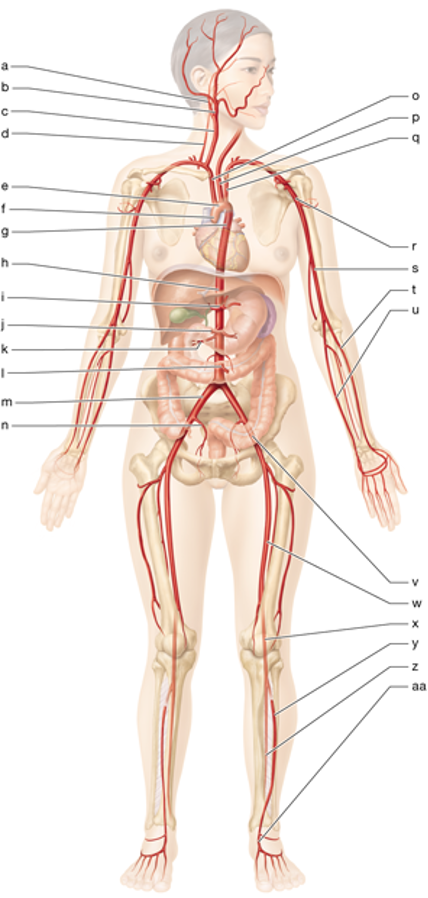
h
abdominal aorta
c
right common carotid
p
left common carotid
o
brachiocephalic trunk
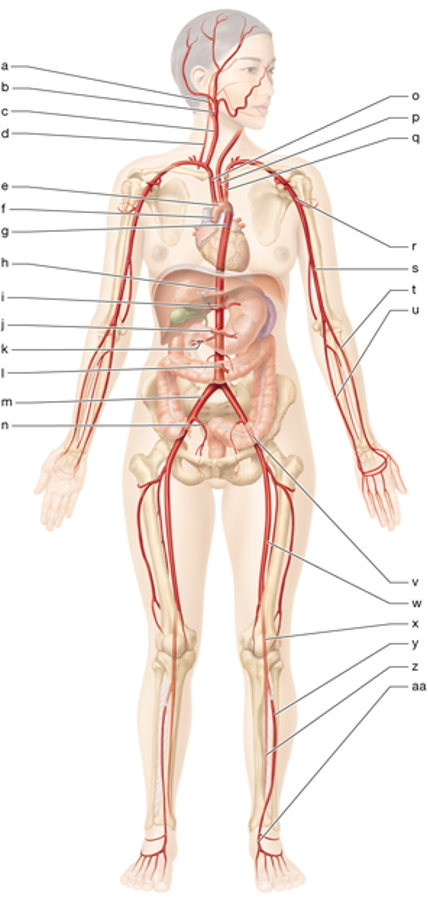
q
left subclavian artery
r
left axillary artery
s
left brachial artery
u
left ulnar artery
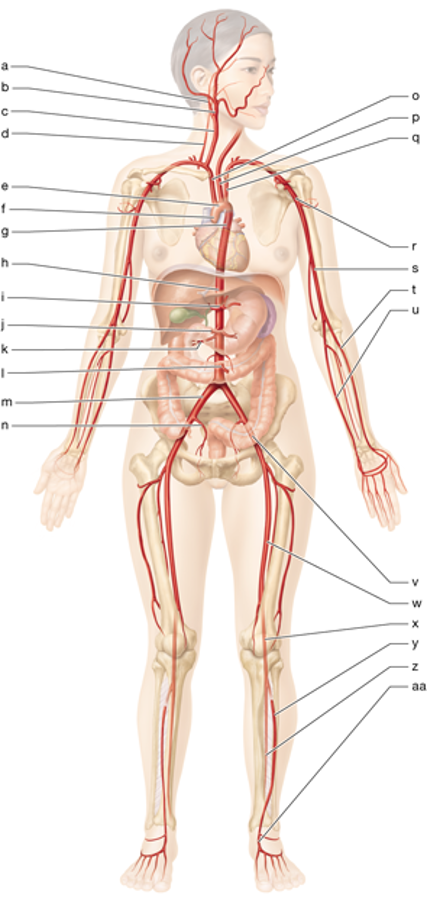
t
left radial artery
m
right common iliac artery
n
right internal iliac artery
w
left femoral artery
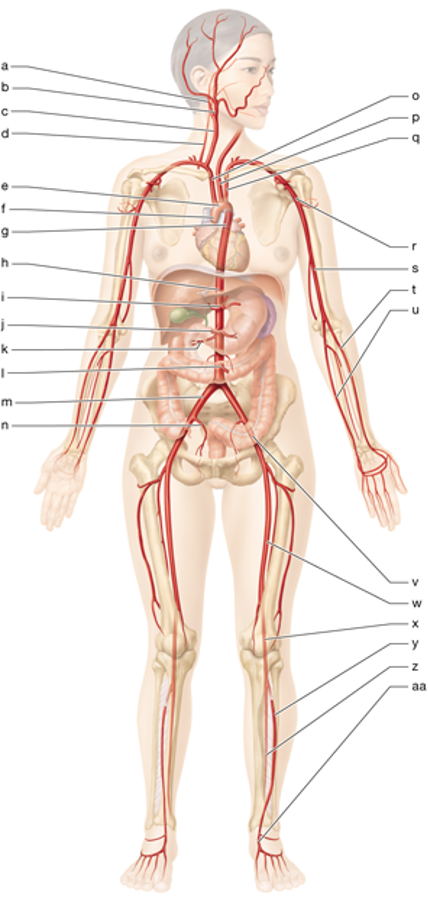
x
left popliteal artery
y
left anterior tibial artery
z
left posterior tibial artery
i
celiac trunk
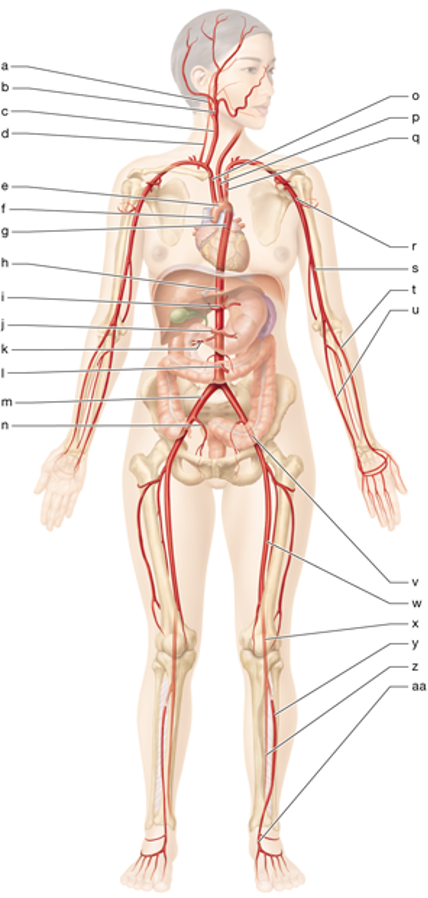
J
superior mesenteric artery
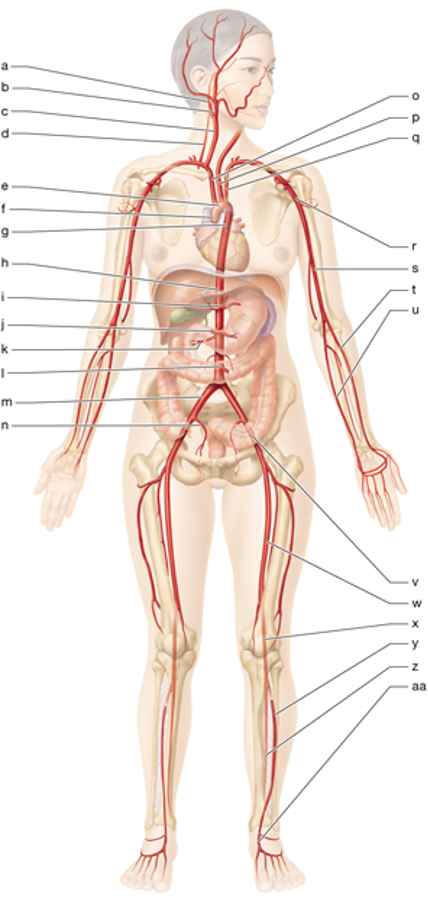
l
inferior mesenteric artery
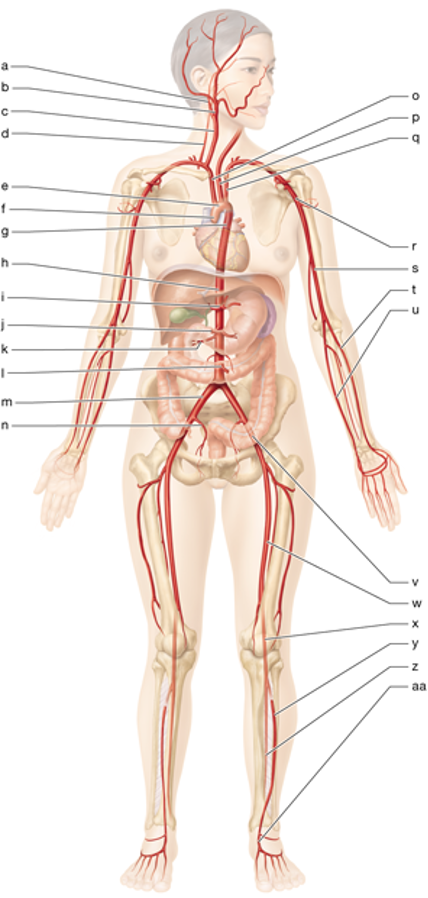
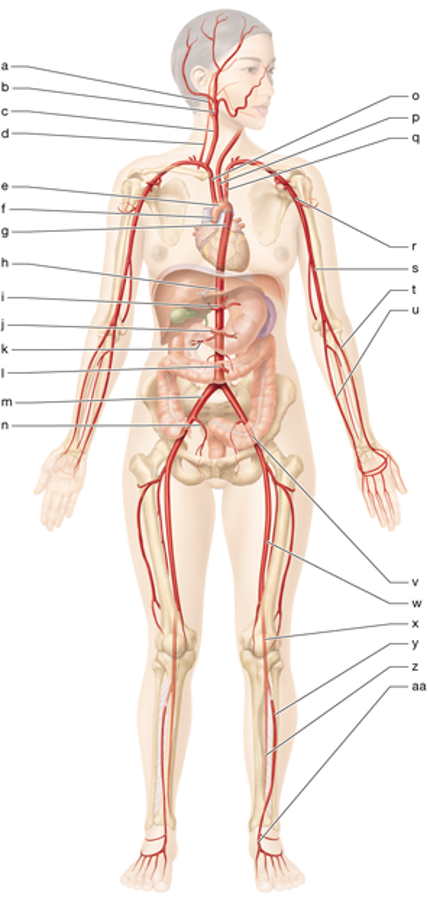
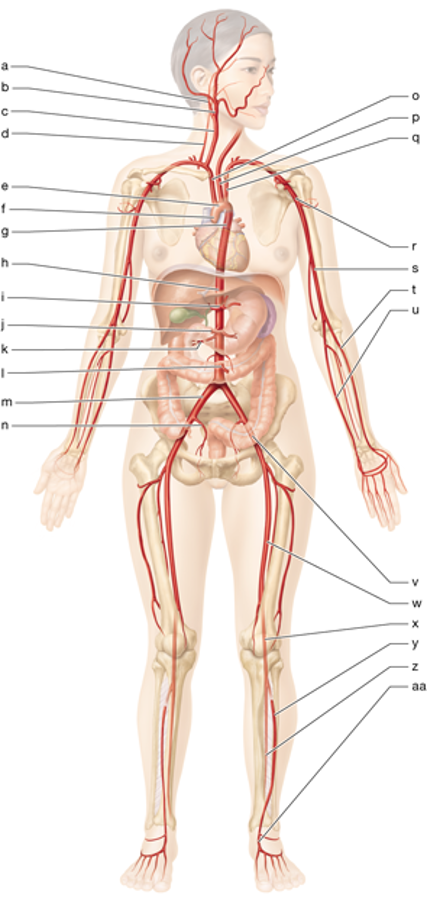
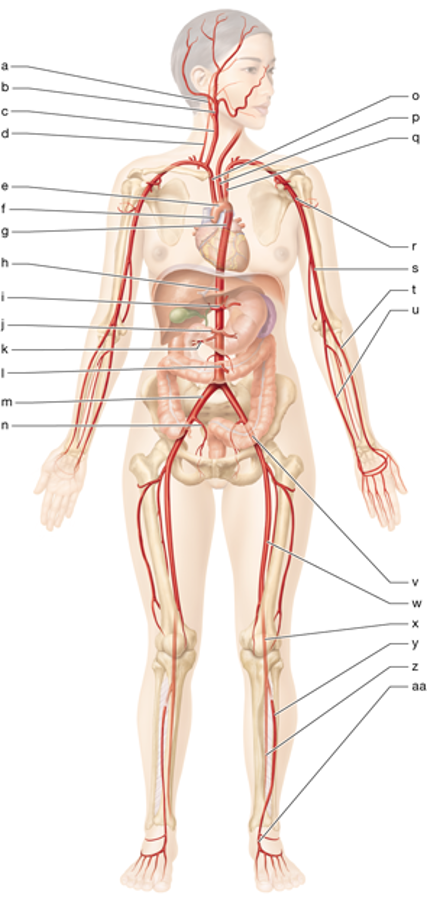
u
superior vena cava
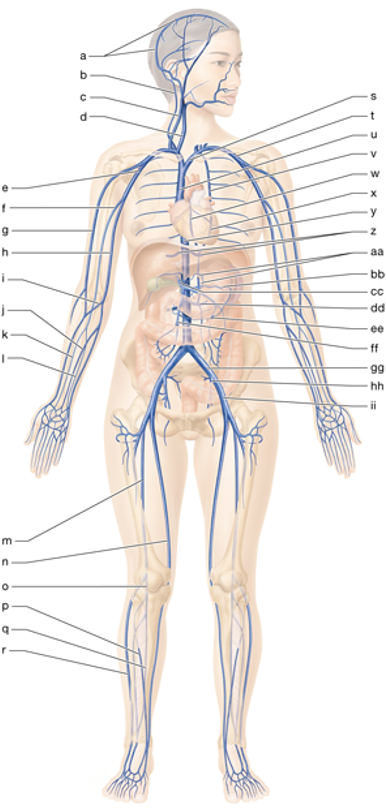
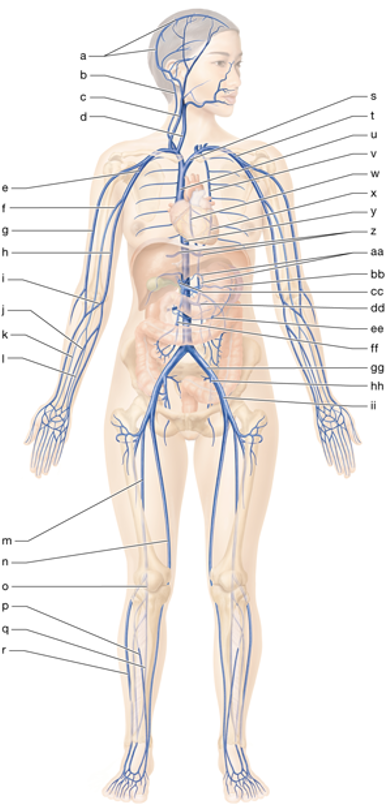
ee
inferior mesenteric vein
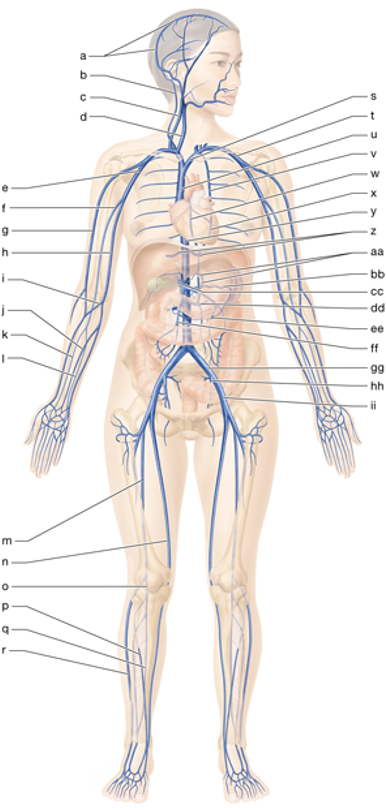
ff
superior mesenteric vein
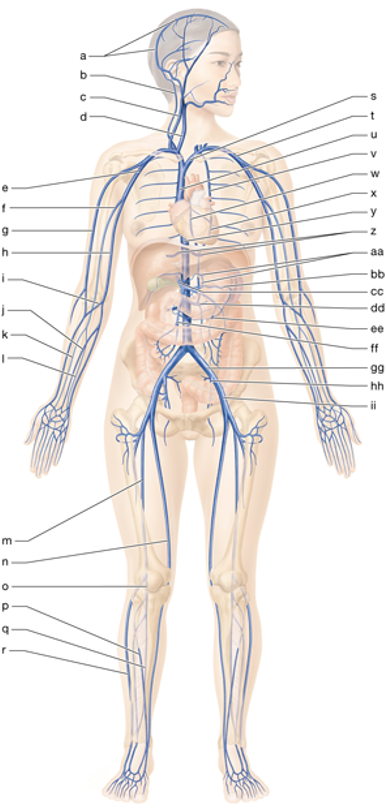
s
left brachiocephalic vein
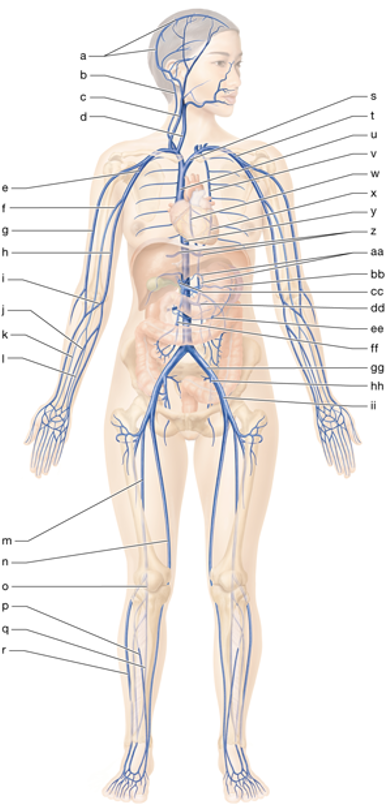
t
left subclavian vein
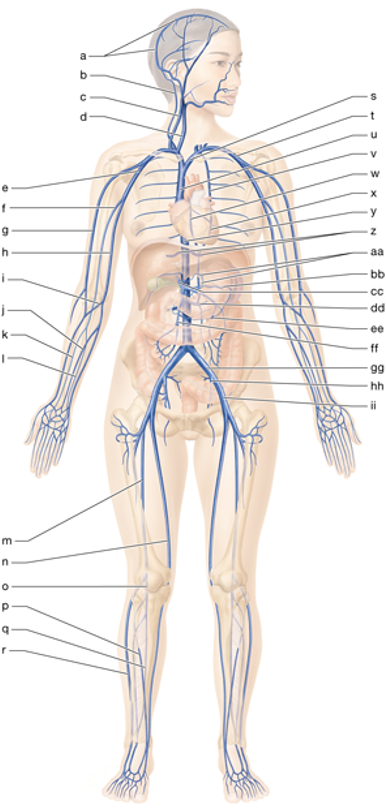
e
right axillary vein
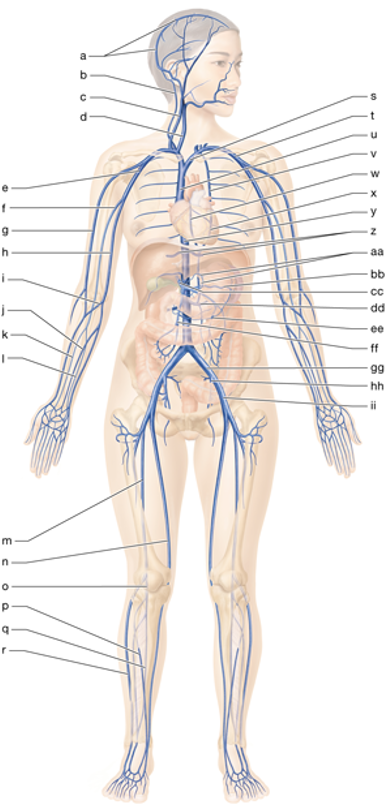
d
right internal jugular vein
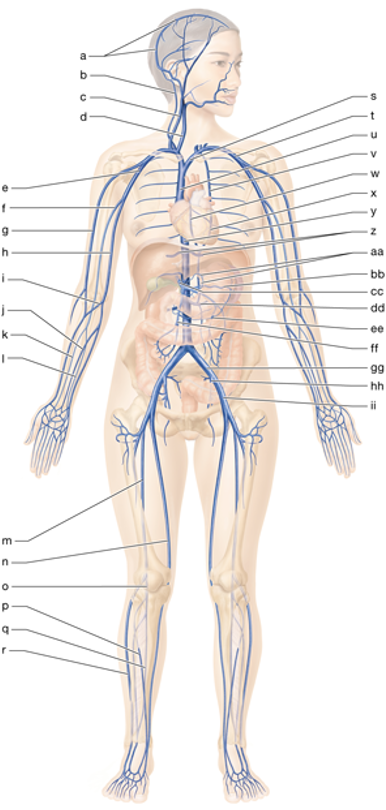
gg
left common iliac vein
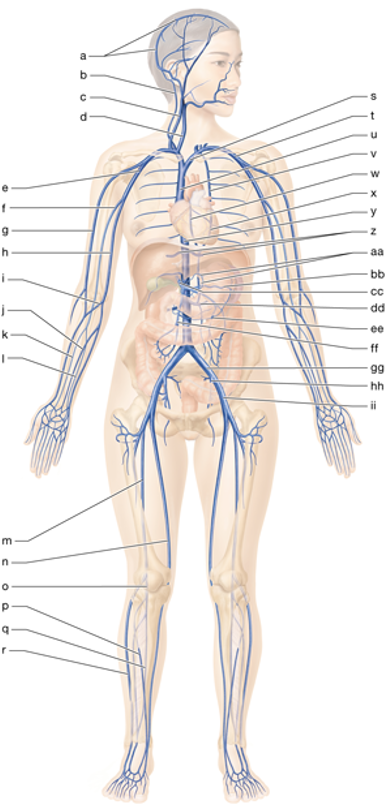
hh
left internal iliac vein
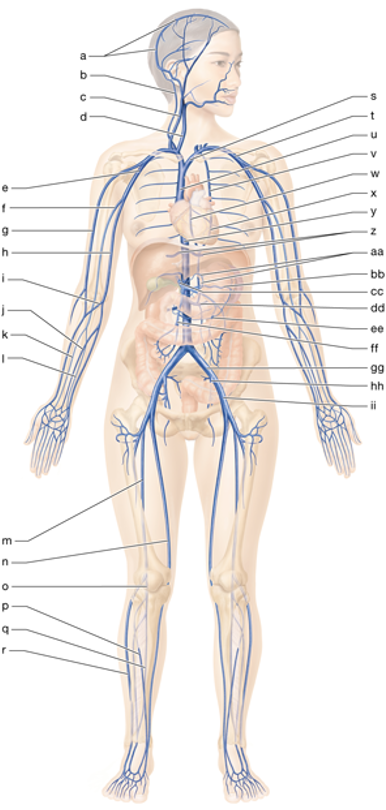
m
right femoral vein
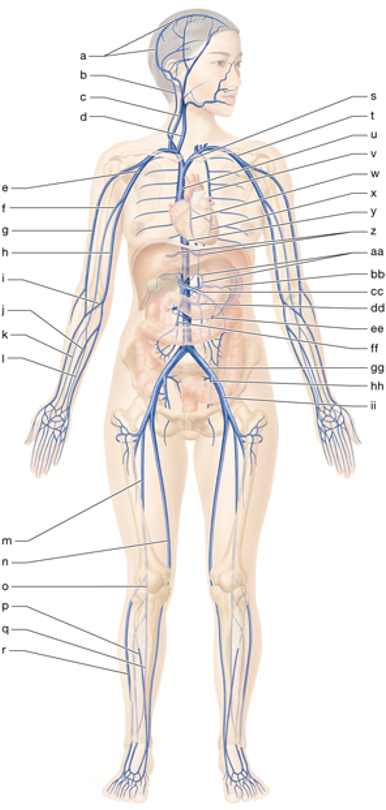
n
right great saphenous vein
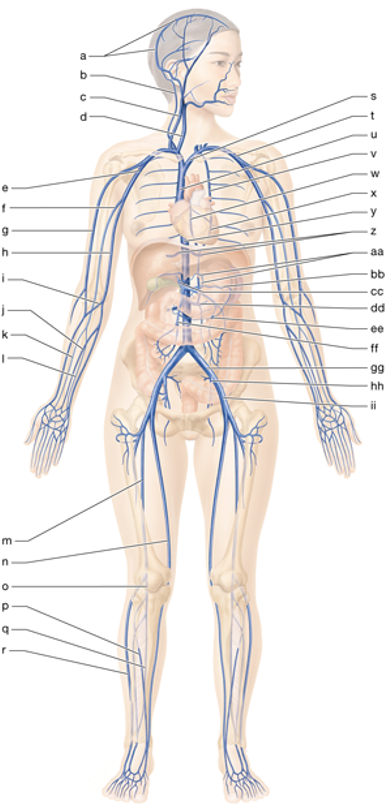
r
right small saphenous vein
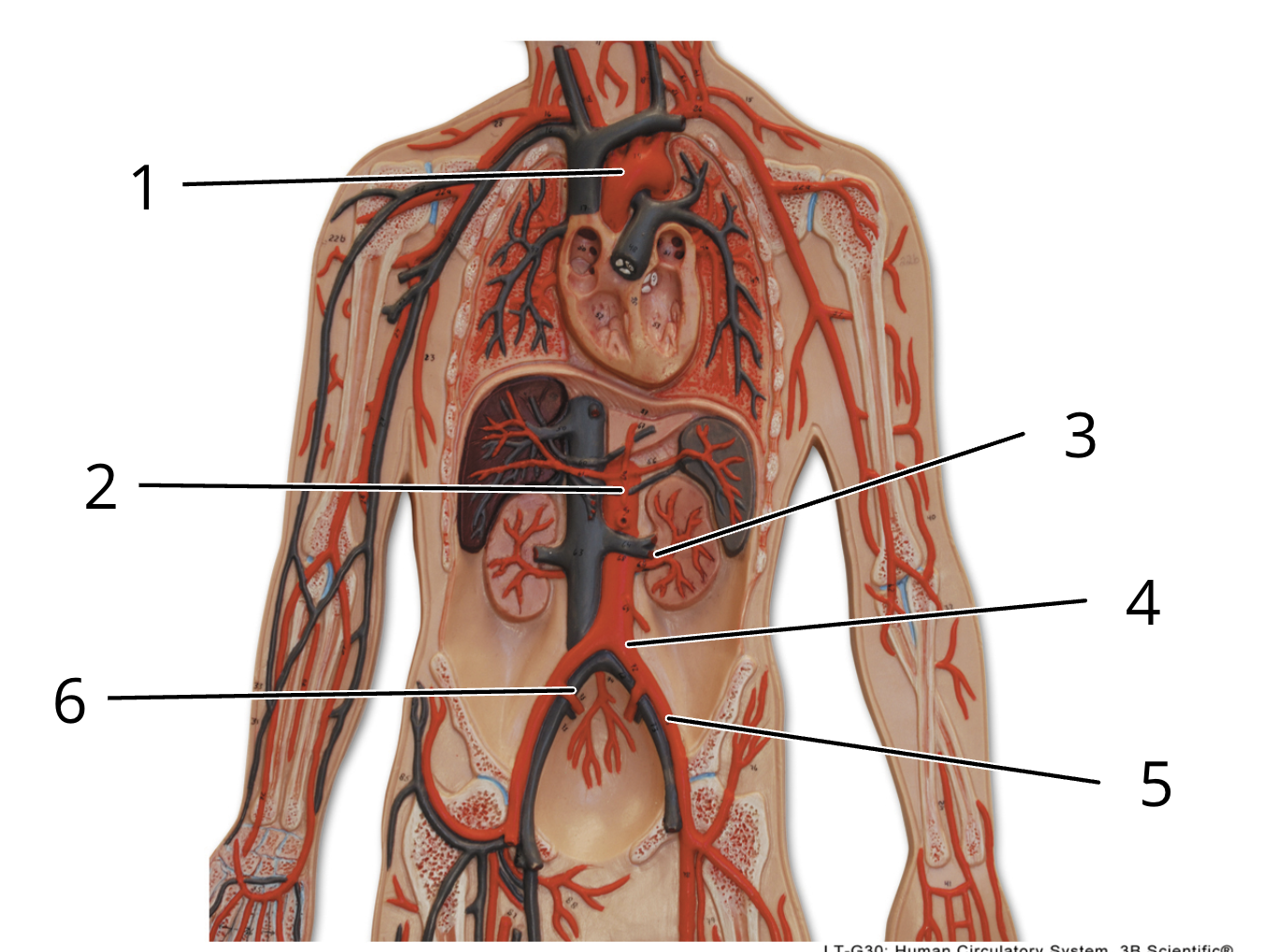
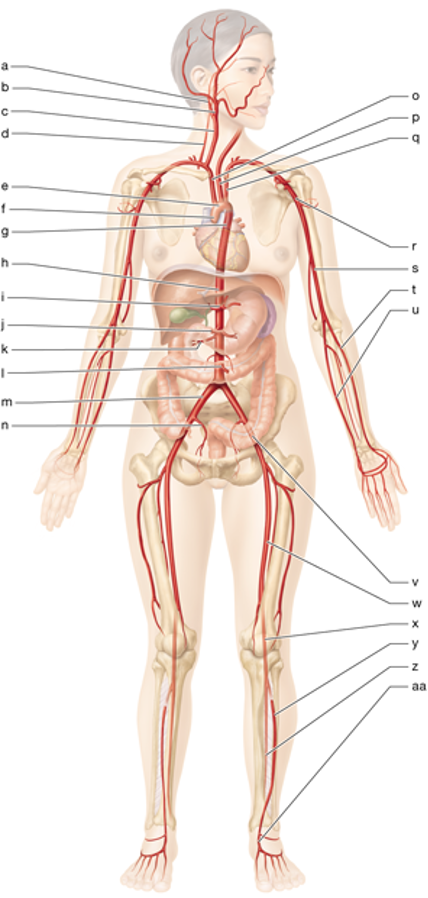
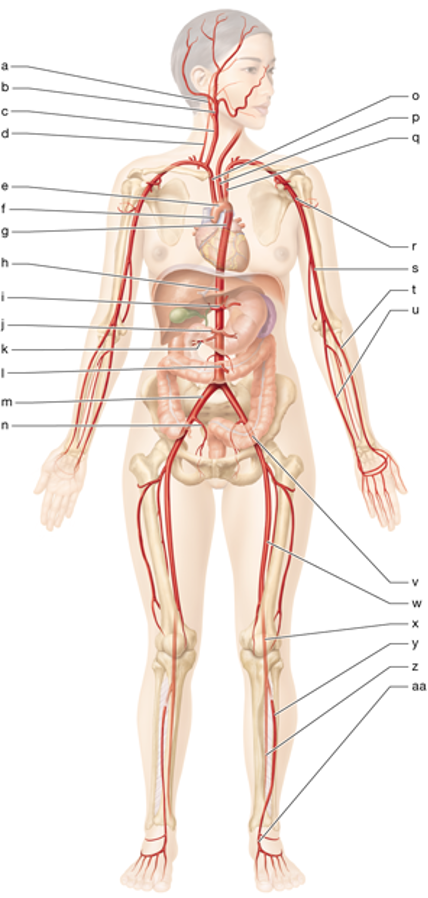
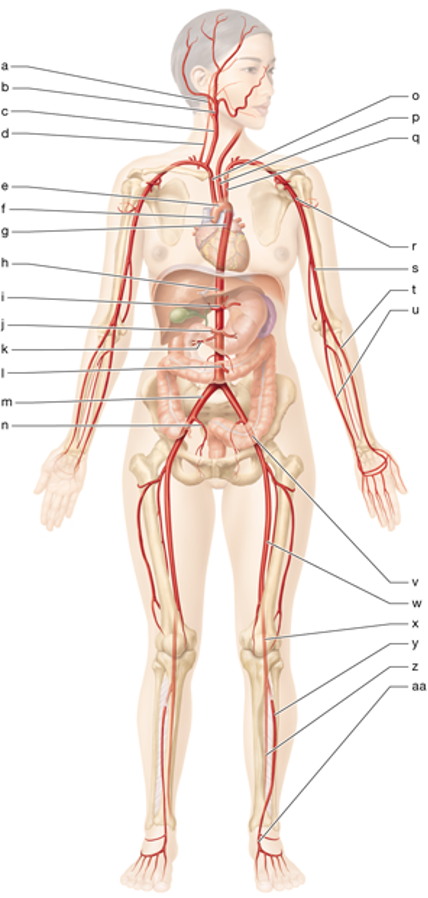
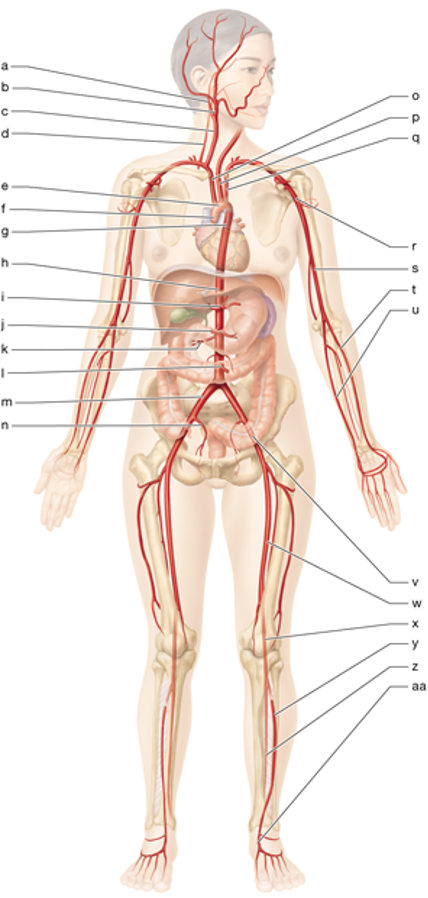
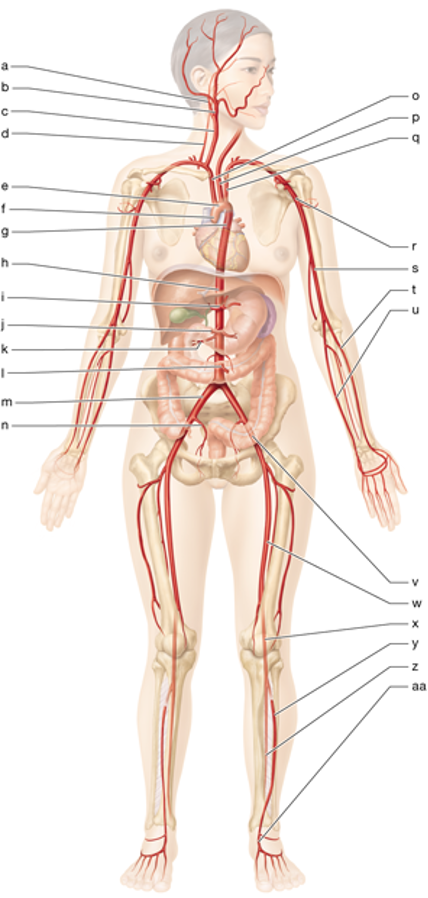
2
abdominal aorta
4
left common iliac artery
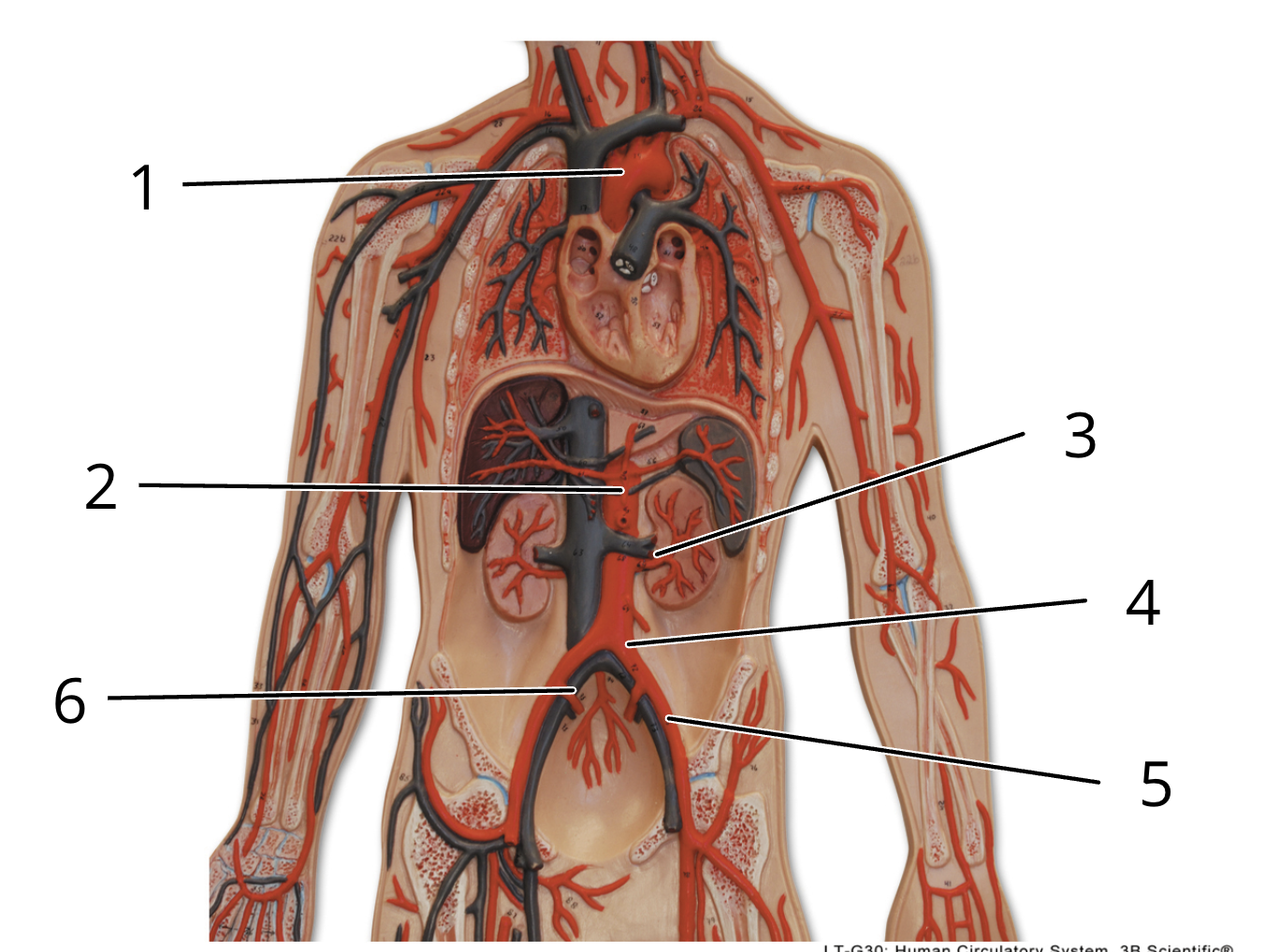
6
right internal iliac artery
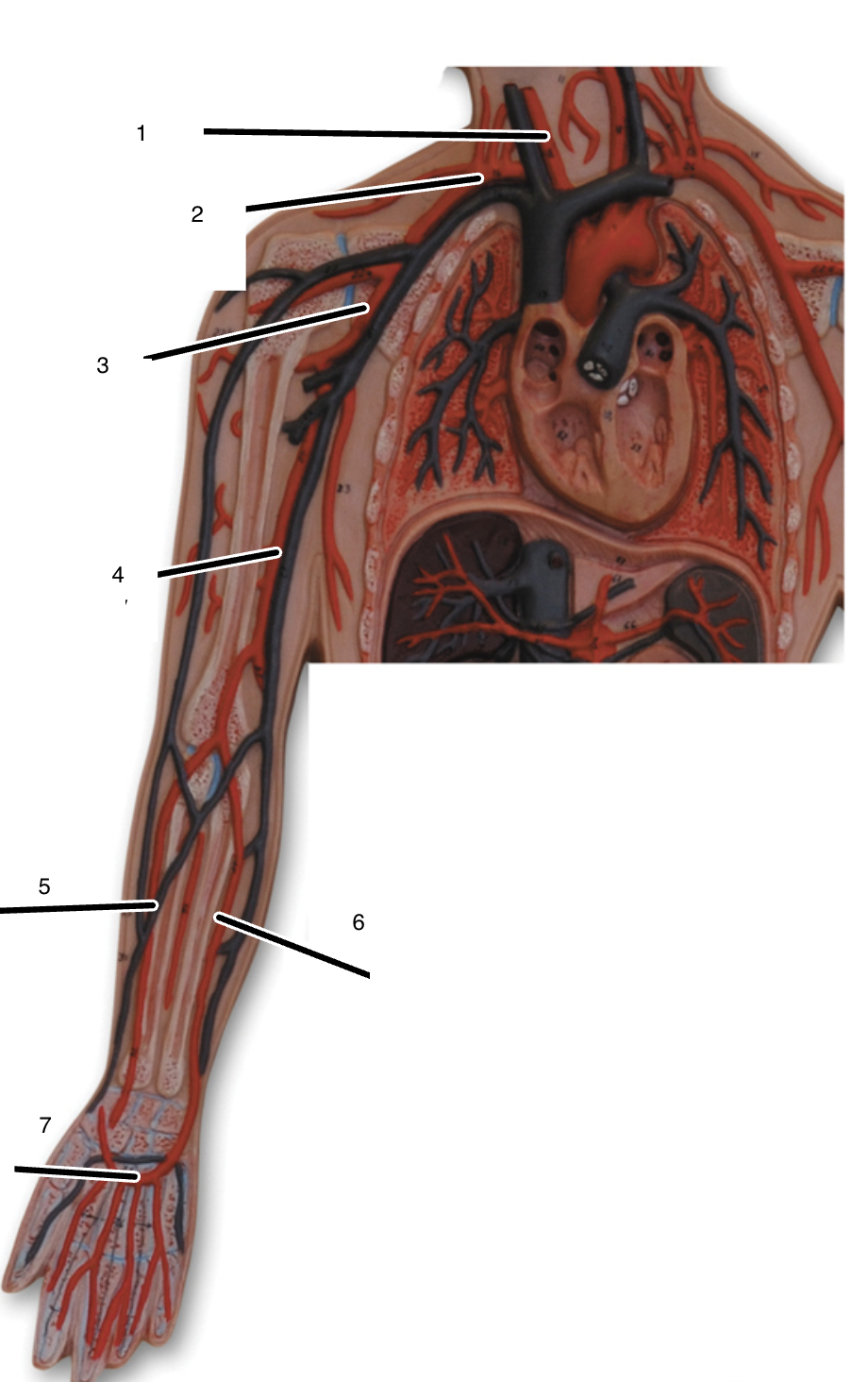
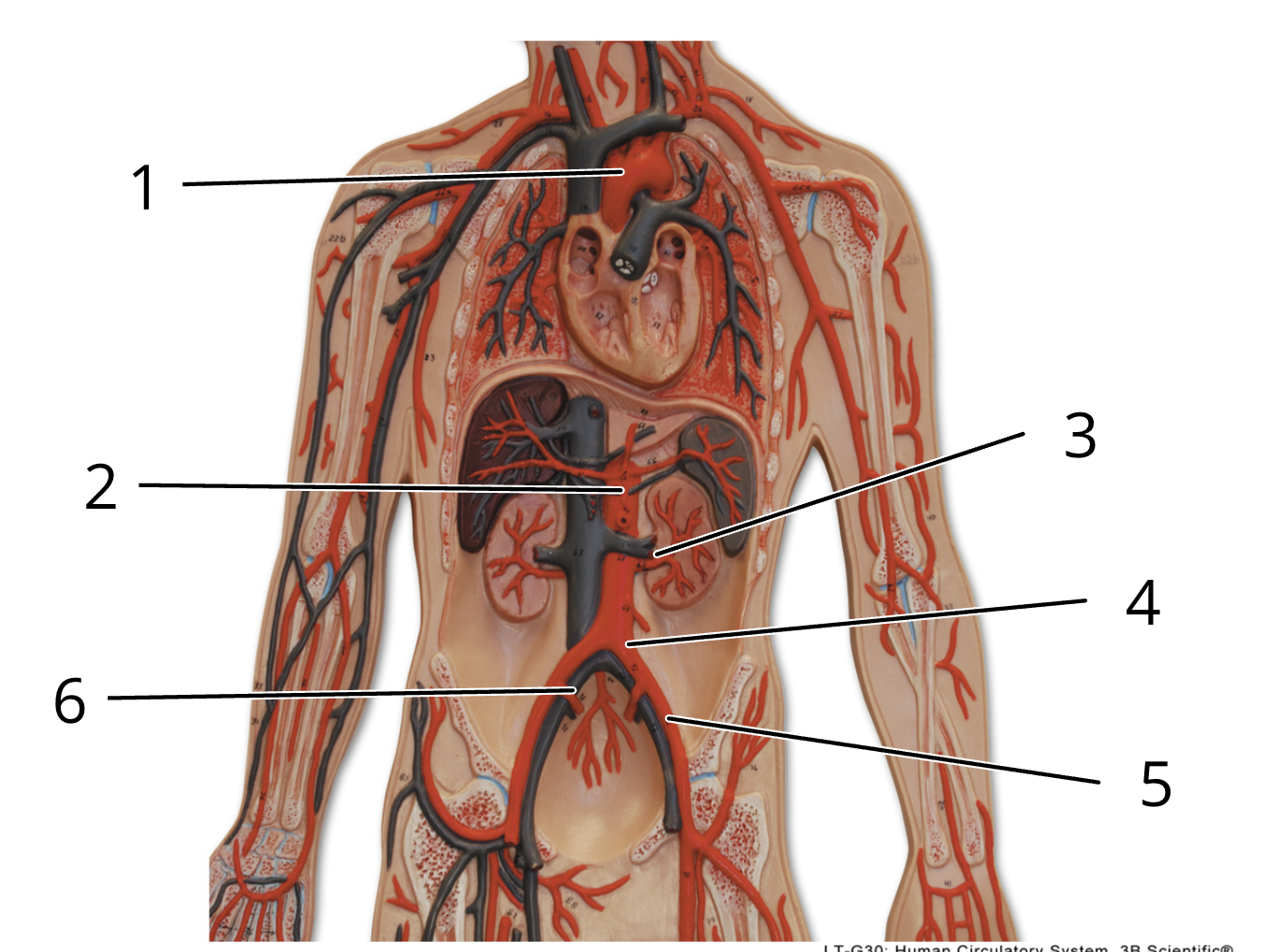
1
right common carotid artery
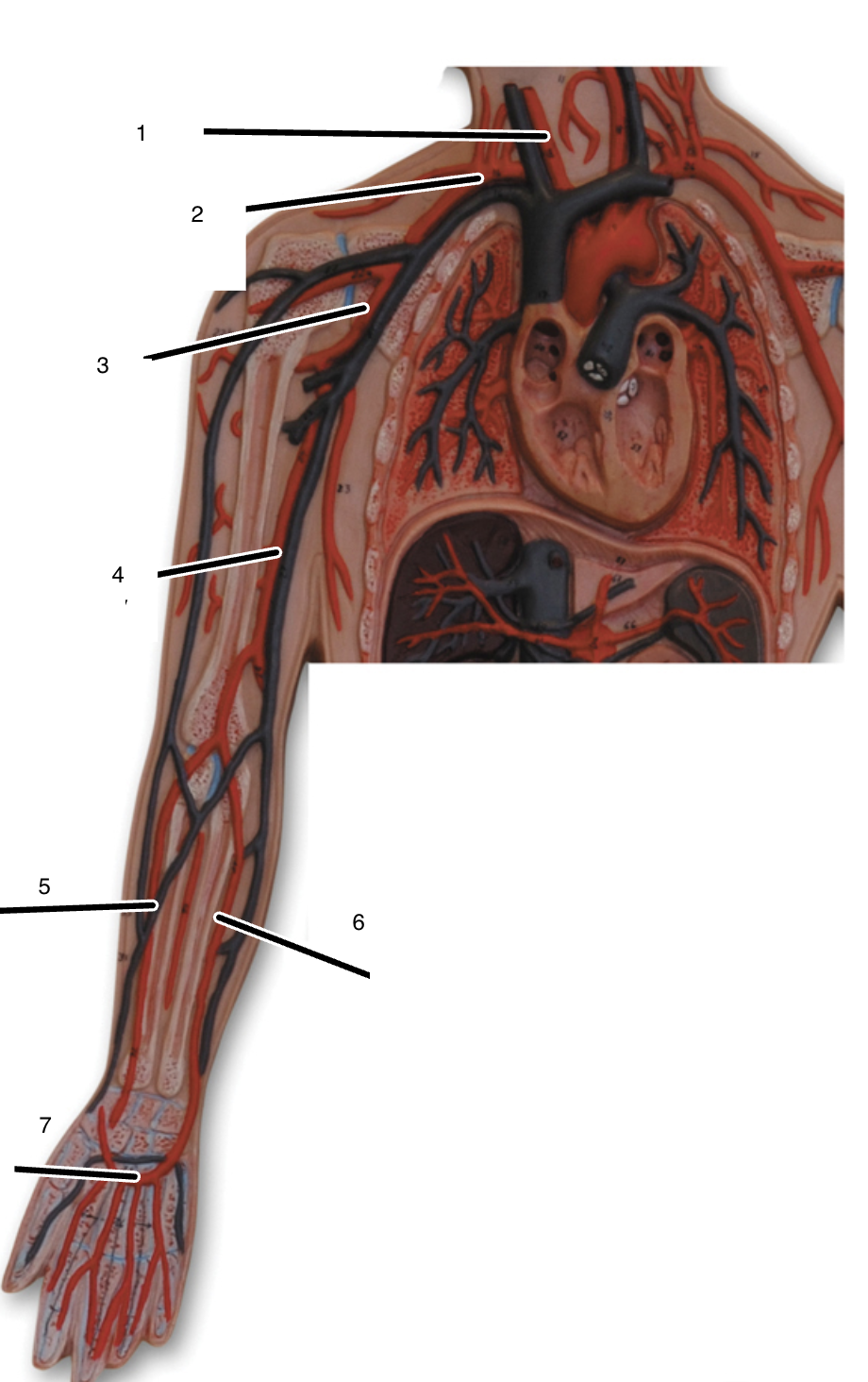
2
right subclavian artery
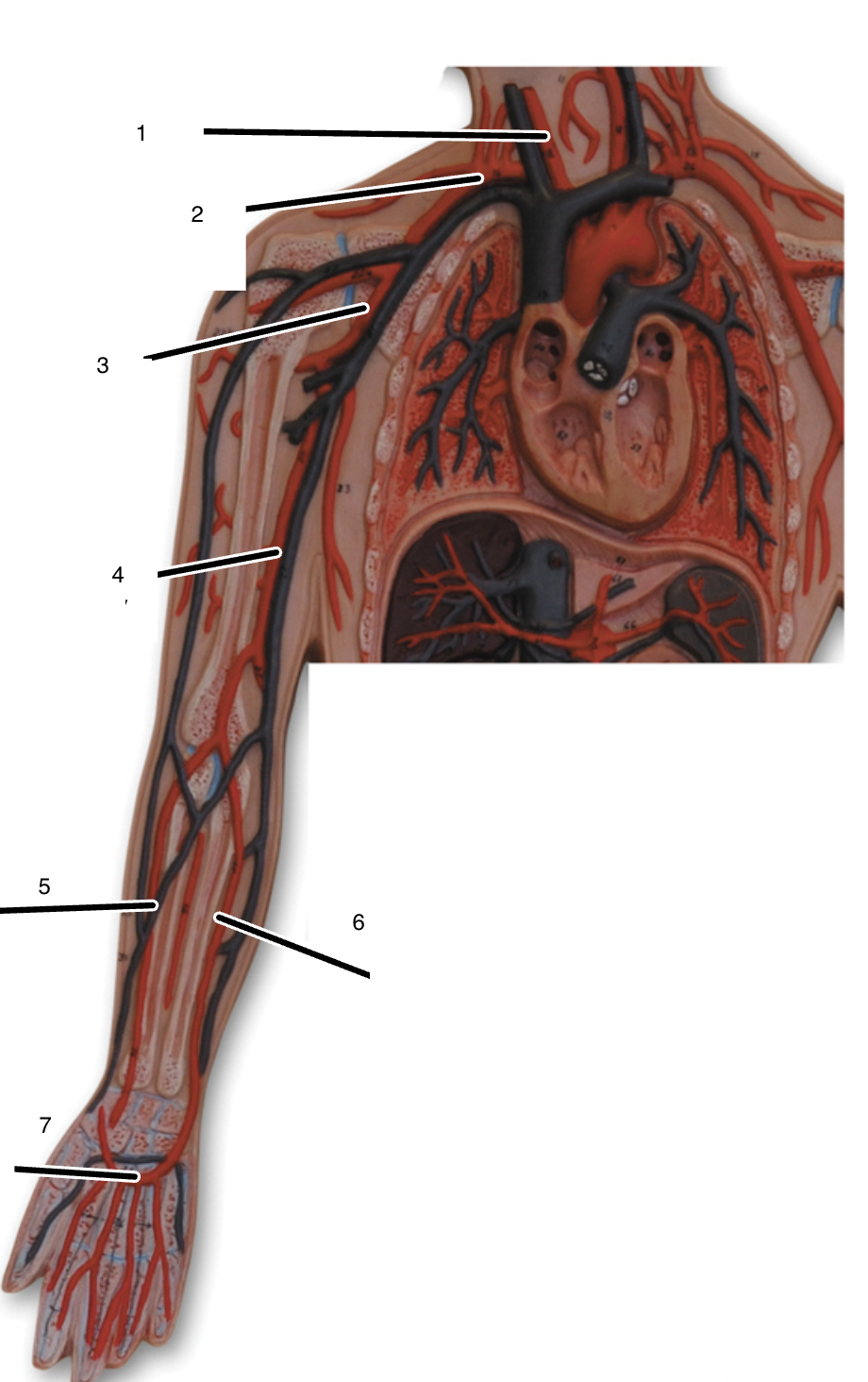
3
right axillary artery
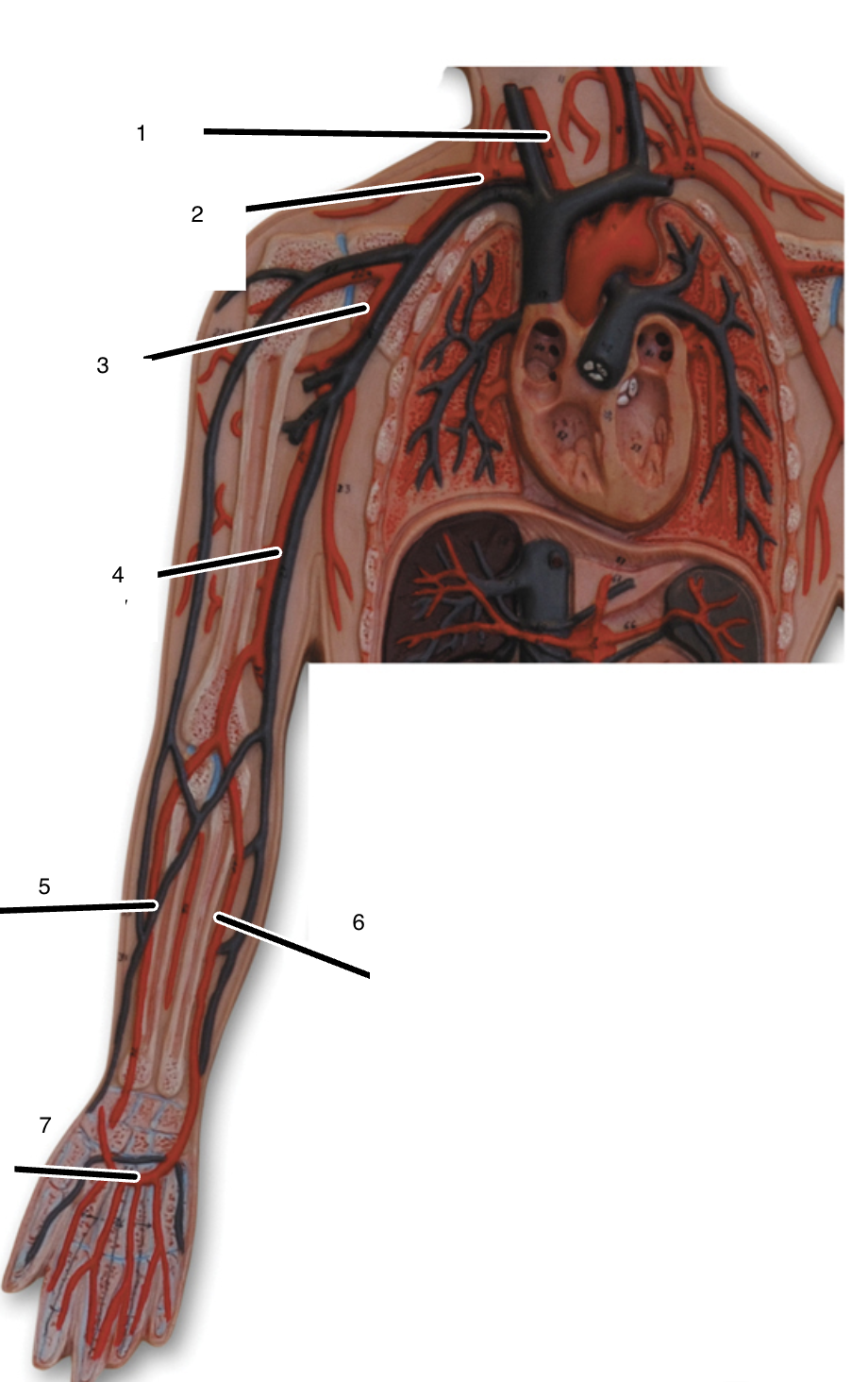
4
right brachial artery