American Heritage Readings
1/19
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Based on textbook notes and weekly reading assignment comprehension questions.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
How does the example of the two Koreas support the authors’ argument about institutions?
(The Making of Prosperity and Poverty-Acemoglu)
Same region, different institutions → drastically different outcomes. South Korea (free market) = prosperous; North Korea (closed market) = poor and starving. Proves institutions determine prosperity.
What is an Inclusive Institution? Add an example
(The Making of Prosperity and Poverty-Acemoglu)
Inclusive: Encourage broad participation in economic activities using talents/skills (ex: South Korea, USA)
What is an Extractive Institution? Add an example
(The Making of Prosperity and Poverty-Acemoglu)
Extractive: Extract wealth from some to benefit others (ex: North Korea, colonial Latin America)
Why are inclusive political institutions necessary for prosperity?
Foster economic growth, productivity growth, and economic prosperity.
Why is equality in property essential?
(Commonwealth of Oceana-Harrington)
Equality of property → equality of power → freedom/liberty
What happens to true monarchy/aristocracy/democracy?
(Commonwealth of Oceana-Harrington)
Each degrades into evil form: monarchy → tyranny; aristocracy → oligarchy; democracy → anarchy
"Empire of laws, not men" connection to modern democracy?
(Commonwealth of Oceana-Harrington)
Laws (not individual rulers) govern, which is the foundation of modern constitutional democracy and rule of law. Prevents leader corruption from power lust, protecting people's liberties.
Why were founders uncertain about success?
(The Pursuit of Happiness-Rosen)
Required all citizens to practice daily self-mastery toward moral perfection, which is a difficult standard to maintain. Questioned whether common people could sustain this level of virtue and self-discipline long-term.
Jefferson/Franklin's pursuit of happiness vs. modern view?
(The Pursuit of Happiness-Rosen)
Founders: Self-mastery and virtue
Modern: Being happy (hedonism/materialism)
Role of self-mastery/virtue in political stability?
(The Pursuit of Happiness-Rosen)
Must overcome destructive emotions (jealousy, anger, fear) to be virtuous citizens capable of maintaining a republic.
Founders' concerns vs. modern social media?
(The Pursuit of Happiness-Rosen)
Madison feared factions driven by passion over reason. Social media amplifies passion over reason and creates factions through echo chambers, which is exactly what Madison feared would destroy the republic.
What is a “Good Society”?
A kind of society that will benefit everyone
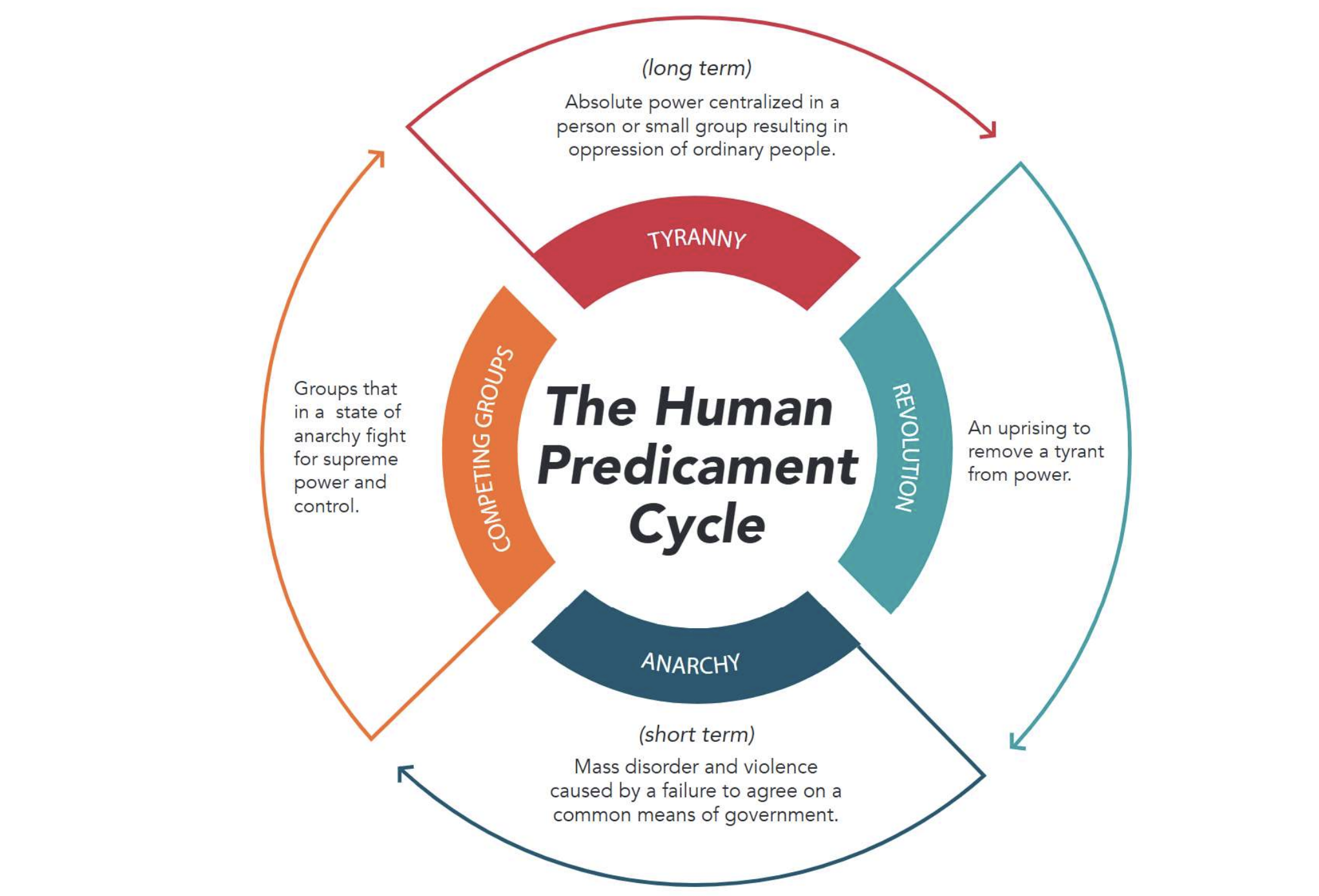
What are the four main terms in the Human Predicament Cycle?
Tyranny, Revolution, Anarchy, Competing Groups
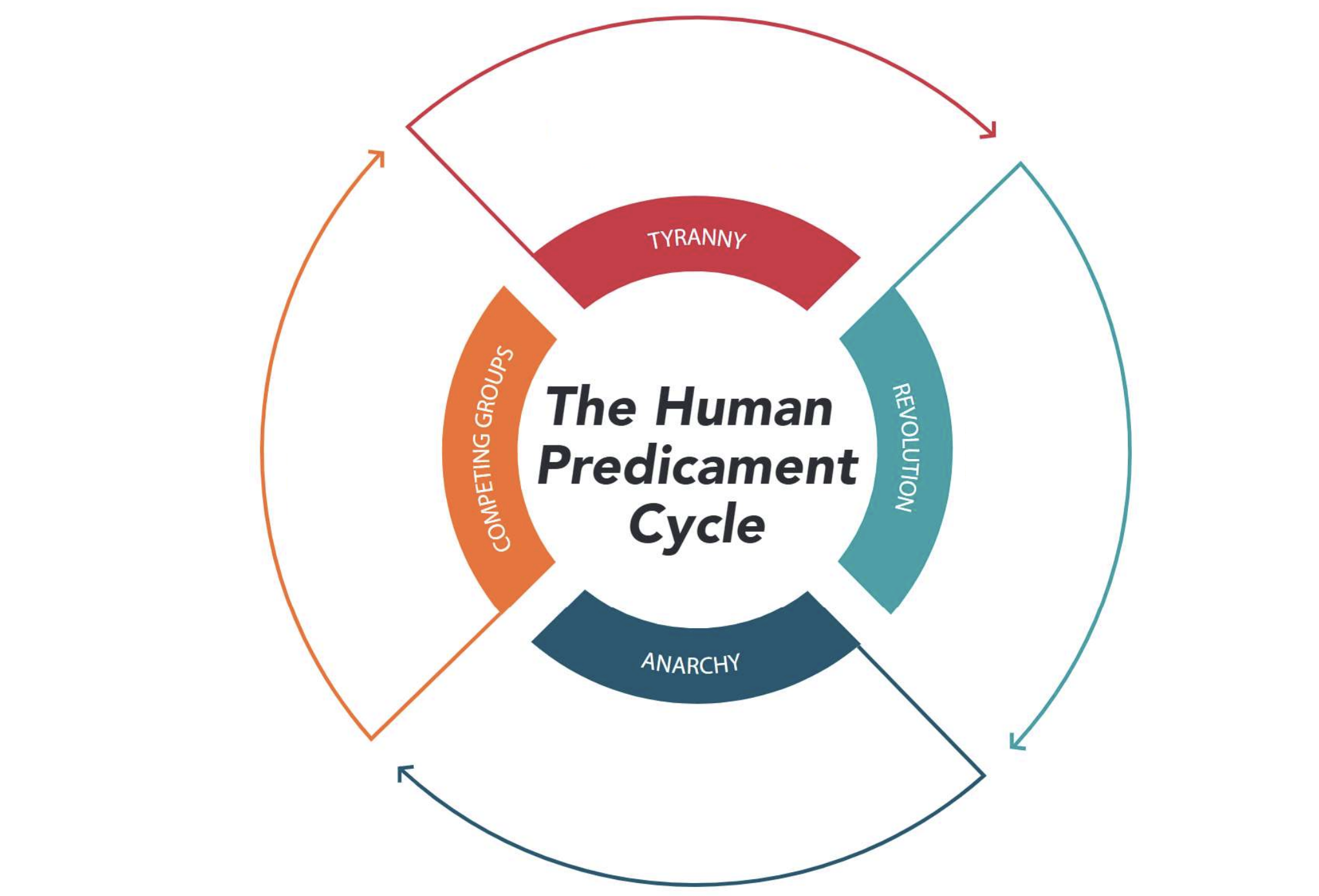
Explain the Human Predicament Cycle
A repeating pattern where societies swing between two dangers:
Too much freedom → chaos/anarchy → people demand order
Too much order → tyranny/oppression → people demand freedom
Back to step 1
What is the equality of result?
Everyone should end with about the same wealth, status, resources, etc.
What did ancient Greek philosophers believe was the best way to build a government? Include examples
Virtue and structure. Platonic virtues: wisdom, courage, temperance(self-control).
What is distributive justice?
Positive things will be distributed by society will be given to you.
What is justice?
The ability to fully participate in society. AKA: Communal, social, and not individual.
What did aristotle think the best gov’t was? Think about the branches of the US gov’t.
A mix of all forms of gov’t. The one, few, and many.