RITE imaging
1/91
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
92 Terms
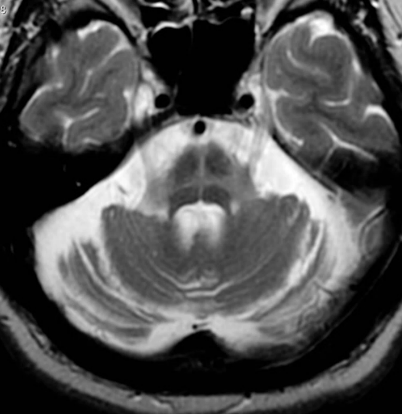
MSA
hot cross bun sign
hyperintensities of cerebellar peduncles
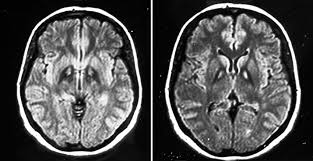
eye of the tiger sign
globus pallidus T2 hypointensity with central hyperintensity
PKAN
iron deposition disorder
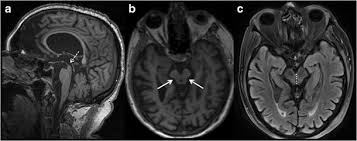
PSP imaging findings
micky mouse & hummingbird signs from midbrain atrophy
cerebellar atrophy, particularly in vermis
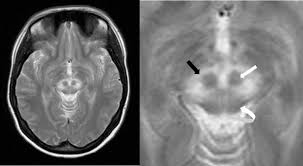
panda sign
symmetric hyperintensities of putamen > caudate, thalamus, brainstem; red nuclei are eyes
wilson’s disease
from copper deposition
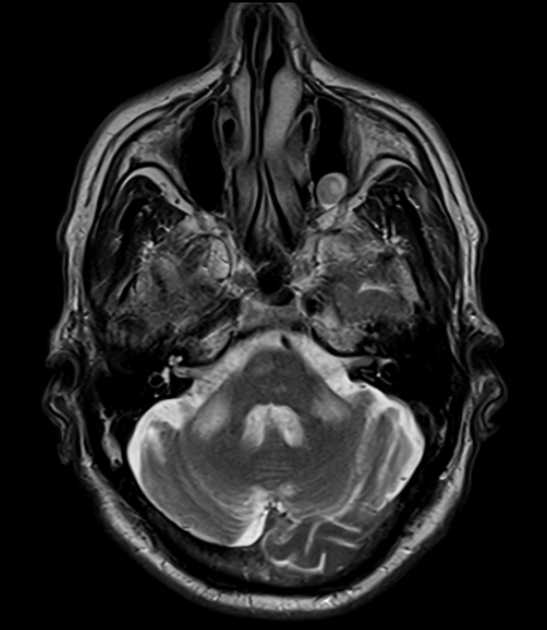
bilateral MCP sign
fragile X-associated tremor/ataxia syndrome (FXTAS)
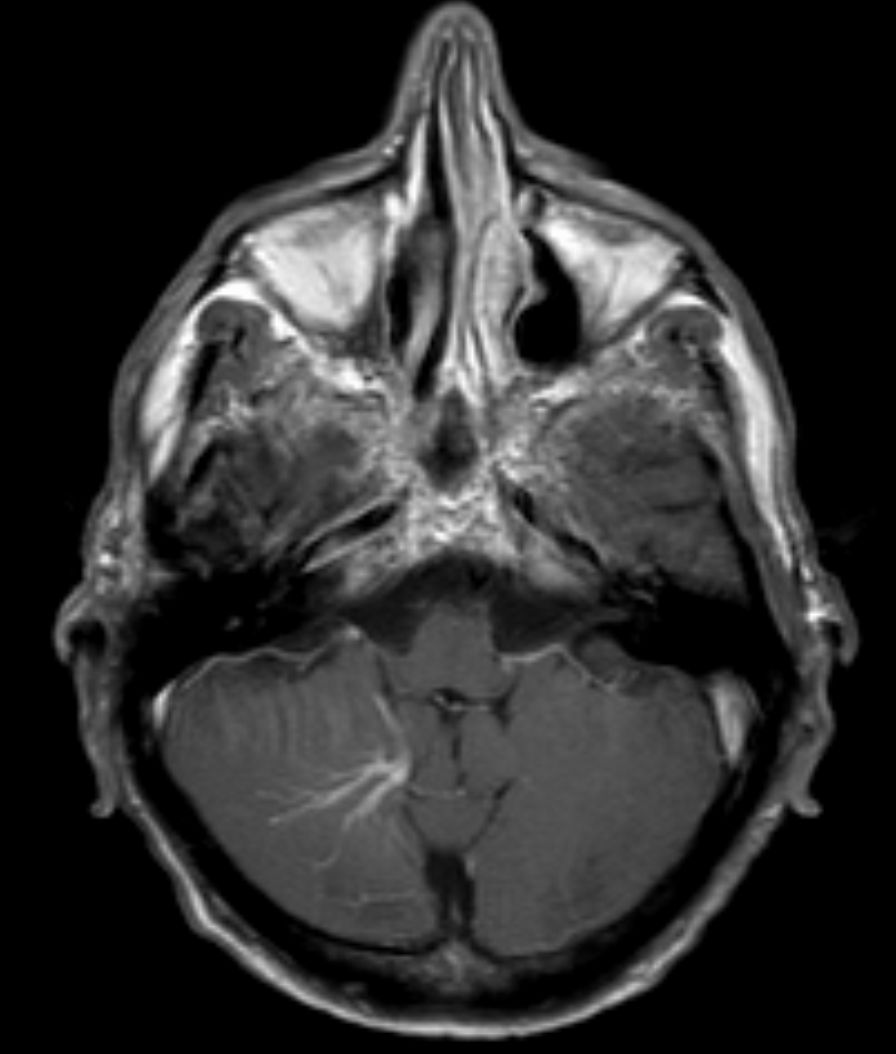
developmental venous anomaly
network of dilated veins
caput medusae sign
typically asymptomatic, rarely cause hemorrhage
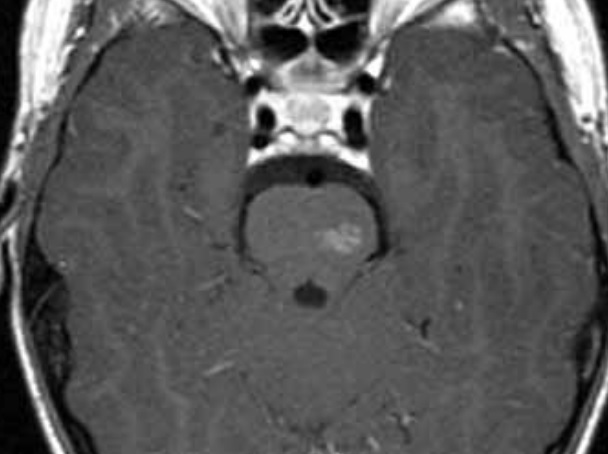
capillary telangiectasia
dilated capillaries
most common in pons
typically asymptomatic, rarely cause hemorrhage
slightly bright on T2, subtle enhancement
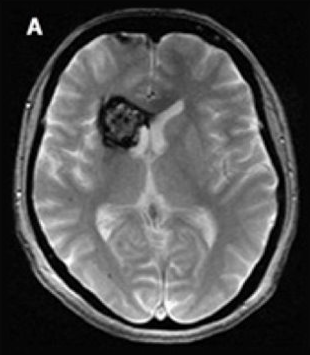
cavernoma
dilated vascular cavity lined by vascular endothelium
typically supratentorial
popcorn appearance on MRI, core can be hyperintense, dark rim on T2
can cause seizures, can bleed
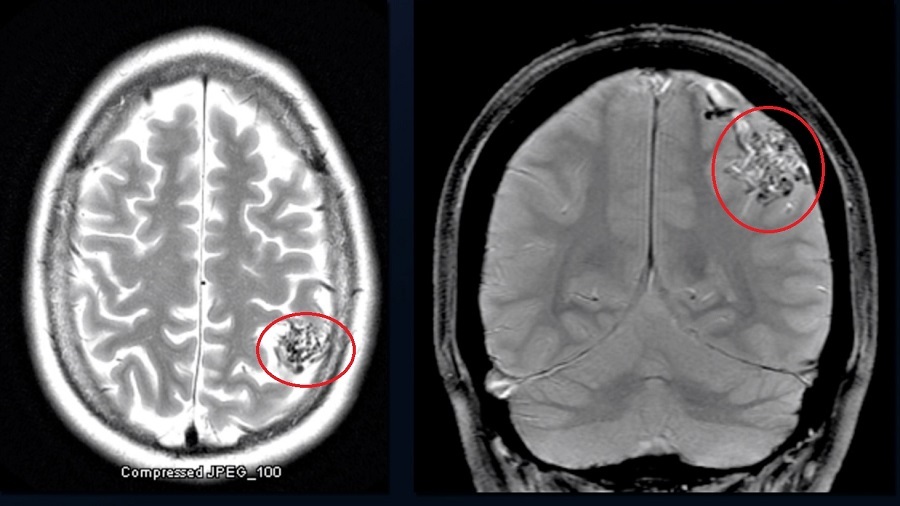
cerebral AVM
tangle of connected arteries & veins
can cause bleed, seizures, headaches, ischemic stroke (steal phenomenon)
bag of worms appearance on MRI
requires angiography for diagnosis
resection can be curative
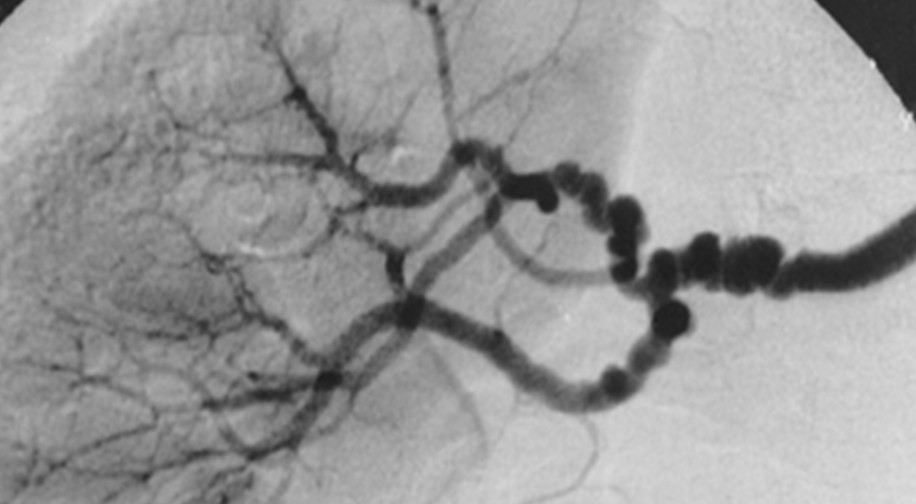
fibromuscular dysplasia
string of beads
commonly affects ICAs and verts
more common in females
slight incr risk TIA/stroke and dissection but often asymptomatic
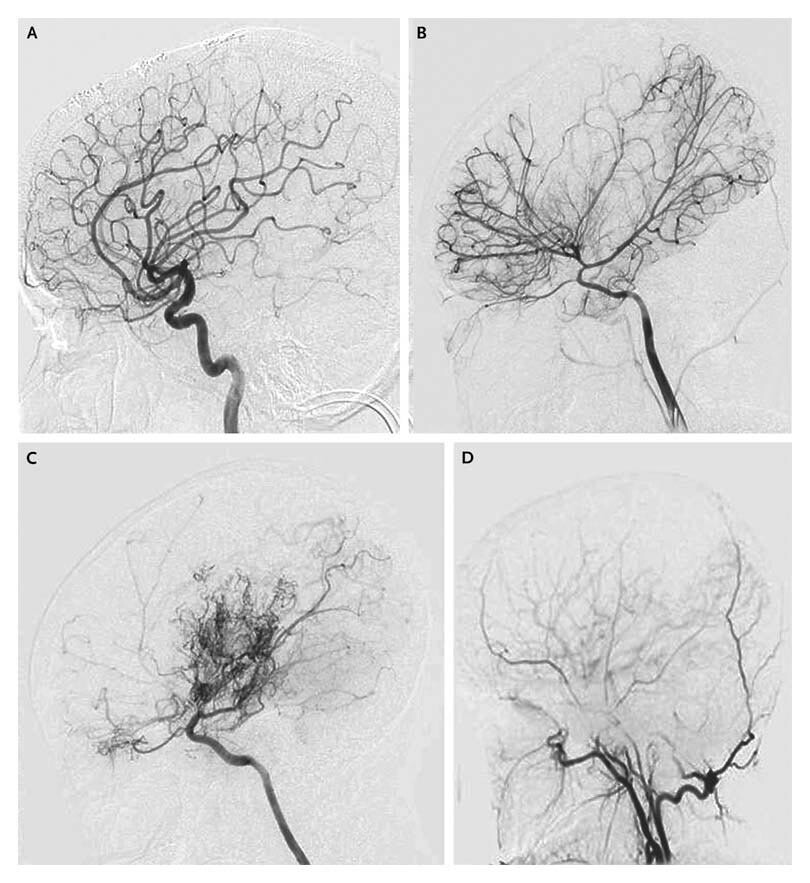
moyamoya
stenosis & occlusion of distal ICA and proximal MCA with prominent collateralization over time
treated with antiplatelets, EC-IC bypass
“puff of smoke” appearance on angio due to collateralization
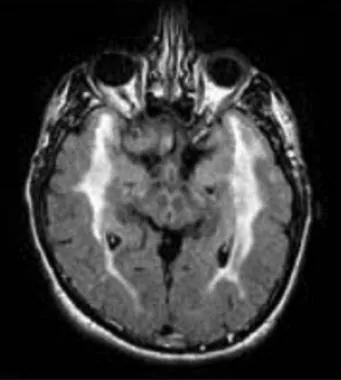
CADASIL/CARASIL
cerebral autosomal dominant/recessive arteriopathy with subcortical infarcts and leukoencephalopathy
NOTCH3 mutations
causes progressive cognitive decline, recurrent ischemic strokes (often lacunar), migraines
MRI features symmetric WM hyperintensities, including in anterior temporal poles
… are bright on CT
acute blood (hyperacute can be isodense, old is hypodense)
bone
choroid plexus
minerals
calcification
… are dark on CT
old blood
CSF
air
what structures are dark & bright on T1 MRI
bright: fat (lipoma), mineral deposition, cortical necrosis, melanin, proteinacous stuff
My Best Friend is Pretty Cool (melanin, blood - subacute, fat, protein, cholesterol/calcium)
dark: CSF, edema, bone, most pathology (incr water content)
white matter brighter than grey matter
what structures are dark & bright on T2 MRI
bright: fat, CSF, edema, most pathology
dark: fat, bone
gray matter brighter than white matter
how to age blood on MRI
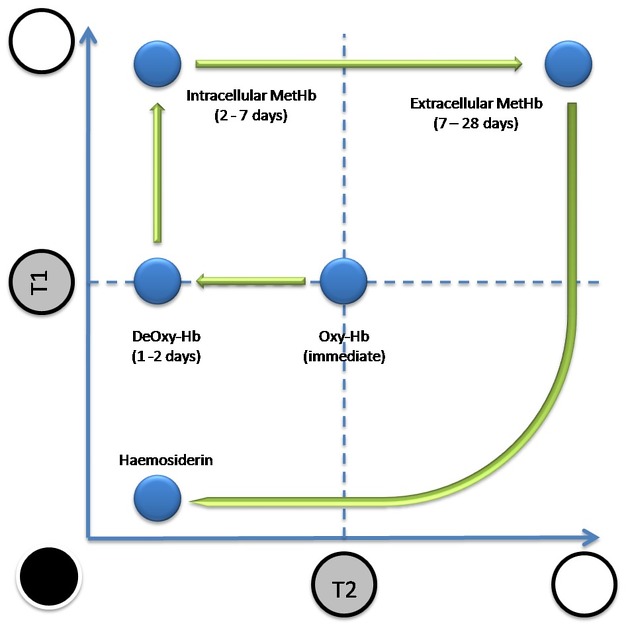
T1 generally goes from iso > bright > dark
T2 more complicated
hyperacute: isodense on both
acute: isodense on T1, dark on T2
early subacute (1 week): bright on T1, dark on T2
late subacute (>1w, <1mo): bright on both
chronic: dark on both
FLAIR same as T2
alternative way to remember: I Be IdDy BiDy BaBy Doo Doo
differential for FLAIR non-suppression
CSF spaces still bright
hyperoxygenation
SAH
meningitis
differential for diffusion restriction
acute-subacute infarct (arterial or venous)
abscess (core)
tumors (rim)
PRES
CJD (cortical)
diffuse anoxic injury
lymphoma
ODS
carbon monoxide toxicity
acute demyelination
hypoglycemia (cortical)
what structures enhance on T1-post contrast MRI
blood vessels
venous sinuses
choroid plexus
pineal gland
sinuses (the nose knows)
tumors, abscess, infections, subacute stroke, active demyelination, inflammation
… are dark on GRE
blood
iron, calcium, manganese
possibilities for bright lesion on DWI
dark on ADC > restricted diffusion
iso on ADC > T2 shine through
bright on ADC > facilitated diffusion
imaging findings in intracranial hypotension
sagging brainstem
downward displacement of cerebellar tonsils
slit ventricles
diffuse pachymeningeal (dural) enhancement
subdurals, can be bilateral
imaging findings in IIH
partially empty sella
optic nerve tortuosity, dilated optic nerve sheaths, visible protrusion of optic head into eyeballs
stenosis of transverse sinus
differential for pituitary mass
pituitary adenoma: homogeneously enhancing
craniopharyngiomas: cystic/calcified
rathke cleft cyst: non-enhancing
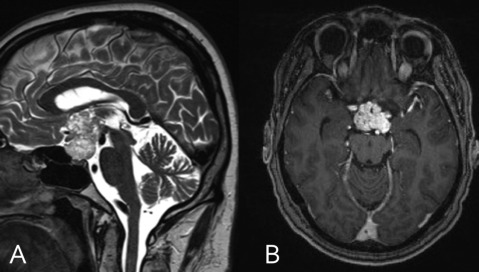
craniopharyngioma
suprasellar
cystic/calcified
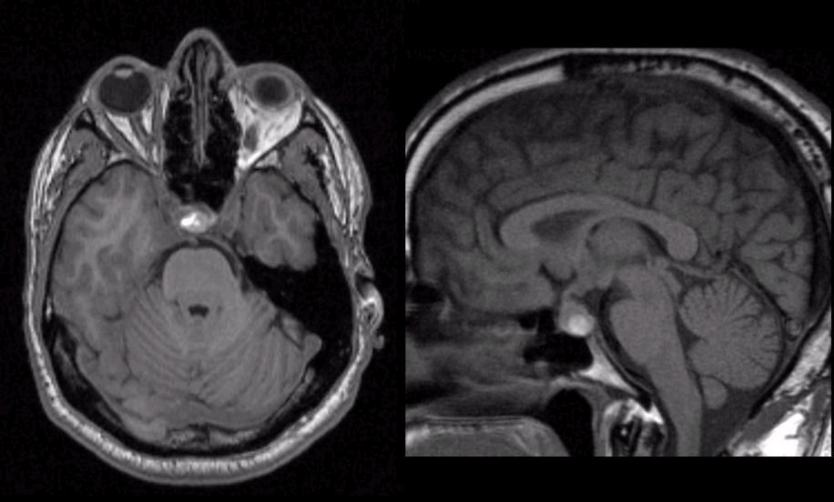
pituitary apoplexy
ischemia/hemorrhage of pituitary gland
higher risk if existing macroadenoma
often postpartum
p/w HA, CN deficits, panhypopituitarism
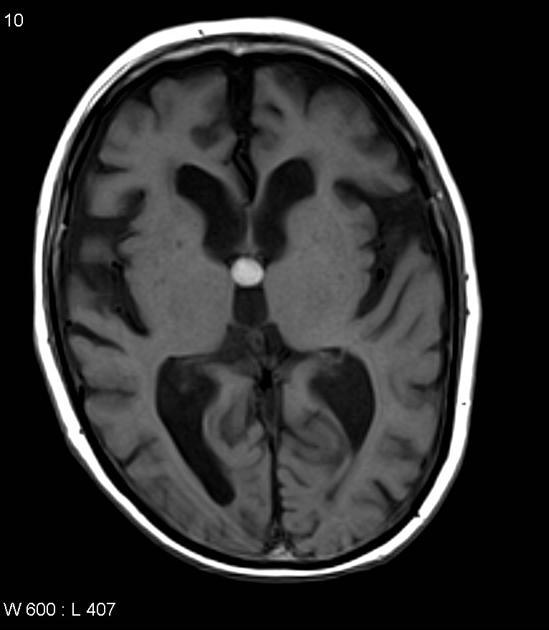
colloid cyst
benign but can cause acute hydrocephalus
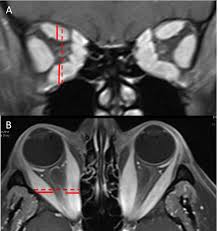
EOM enlargement
can be caused by thyroid eye disease, ocular myositis, orbital pseudotumor
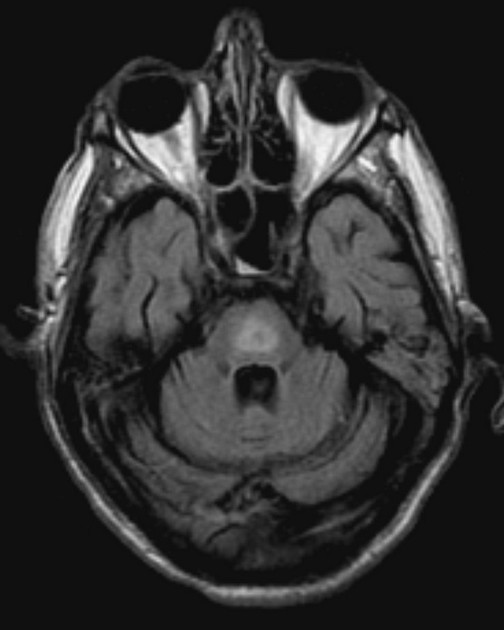
ODS
central pons
hypodense on CT
can be diffusion restricting
hyperintense on T2/FLAIR
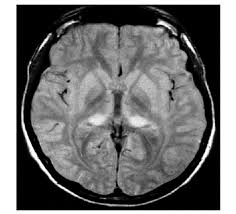
pulvinar sign - bilateral FLAIR hyperintensities of pulvinar thalamic nuclei
can be seen in CJD, Fabry, status, ADEM
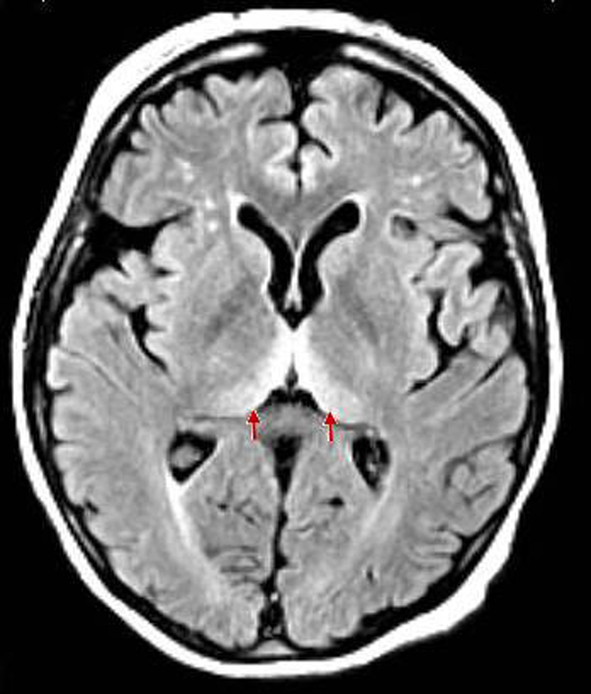
hockey stick sign
bilateral hyperintensity of pulvinar nuclei and medial thalamus
can be seen in CJD or Wernicke’s
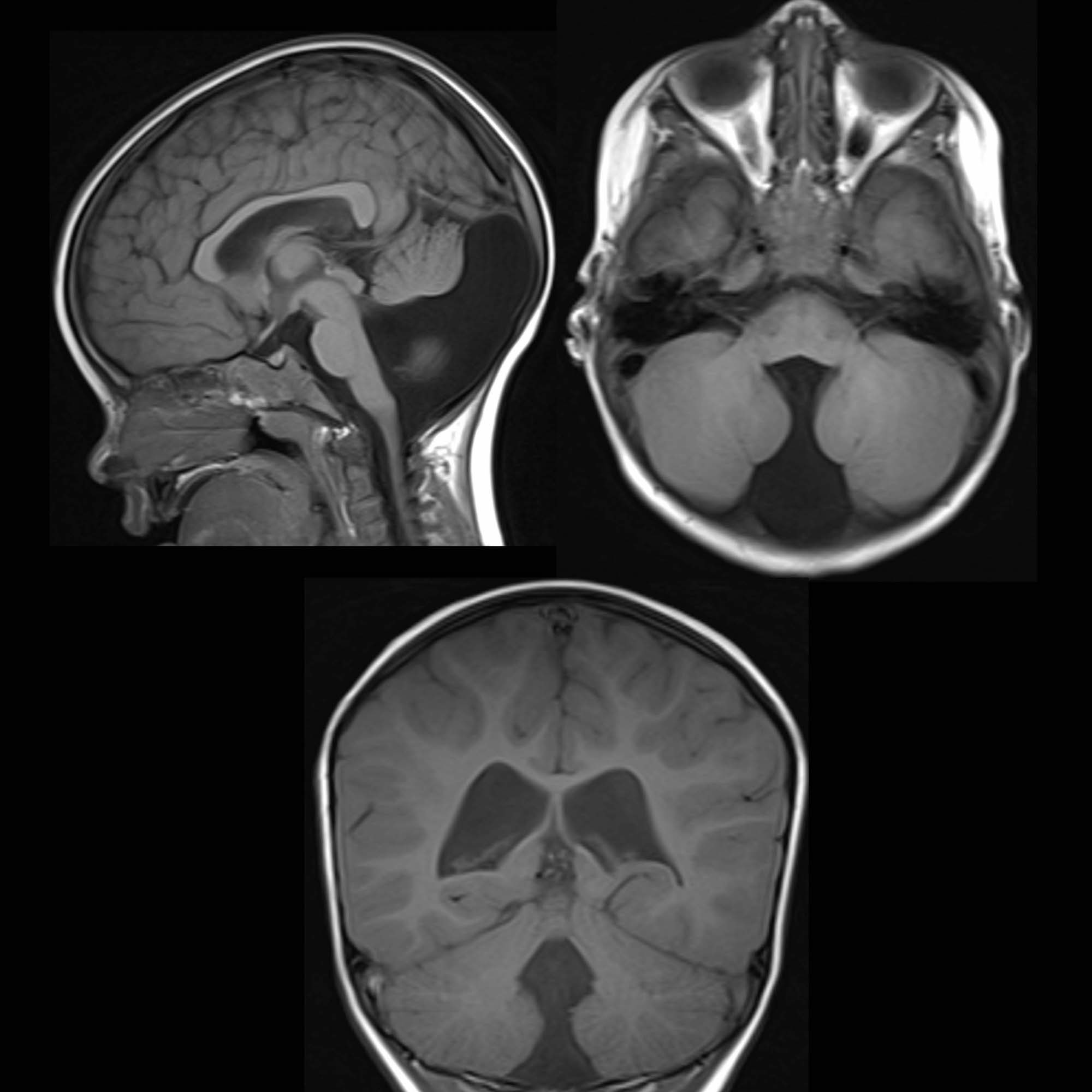
Dandy Walker malformation
agenesis/hypoplasia of cerebellar vermis resulting in cystic enlargement of 4th ventricle
can exist with or without hydrocephalus
can be hypotonic & ataxic
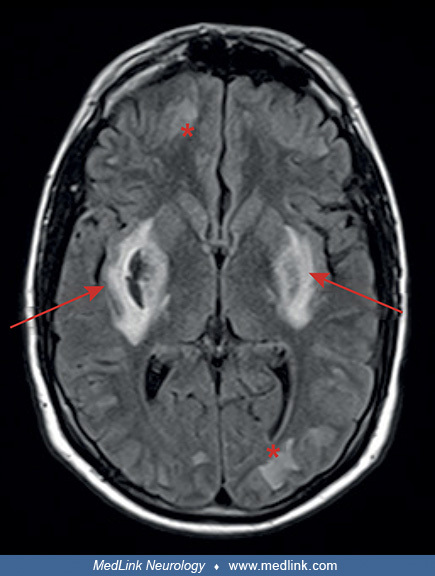
methanol toxicity
bilateral putaminal hemorrhages/necrosis
can also see damage to optic nerves
lissencephaly
pachy or agyria (smooth brain)
enlarged ventricles
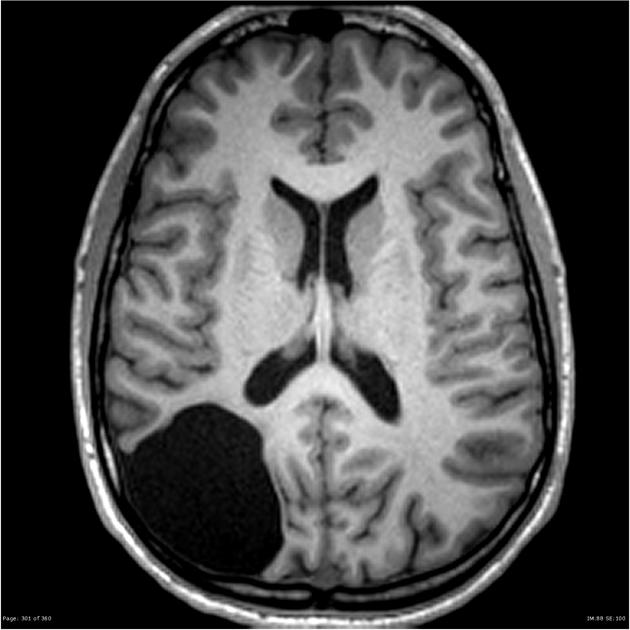
porencephaly
“pore” lined with white matter, not communicating with ventricles
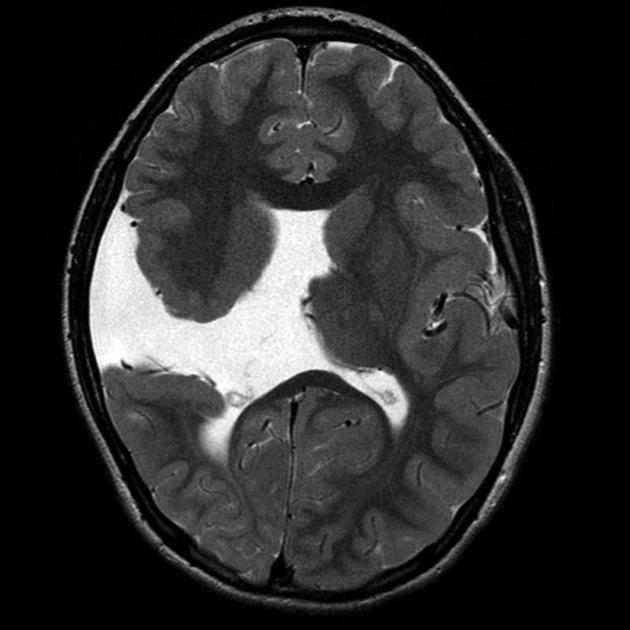
schizencephaly
fluid-filled cleft that communicates with lateral ventricles
lined with gray matter
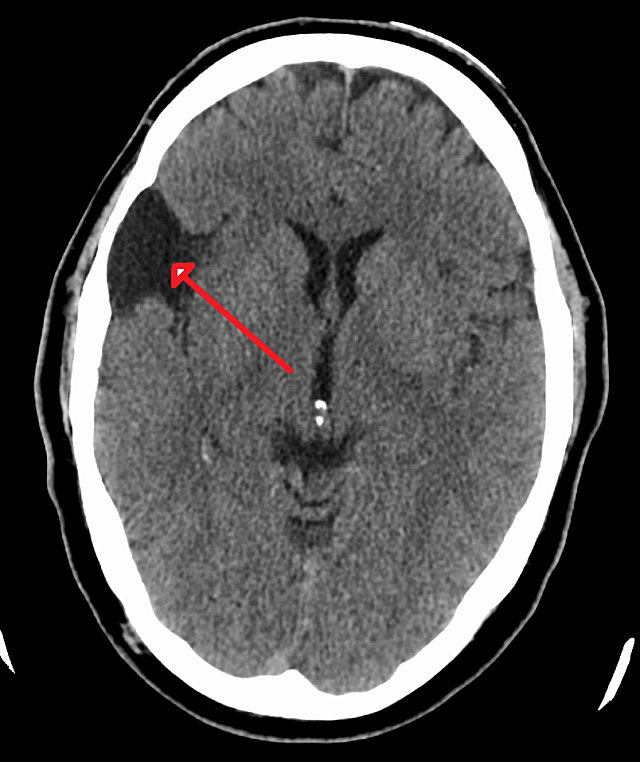
arachnoid cyst
often congenital
extra-axial
same as CSF signal
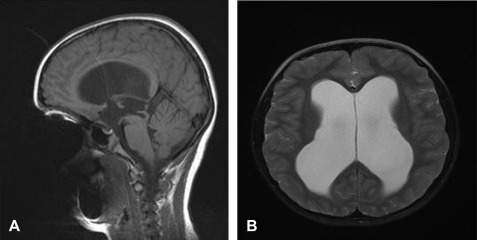
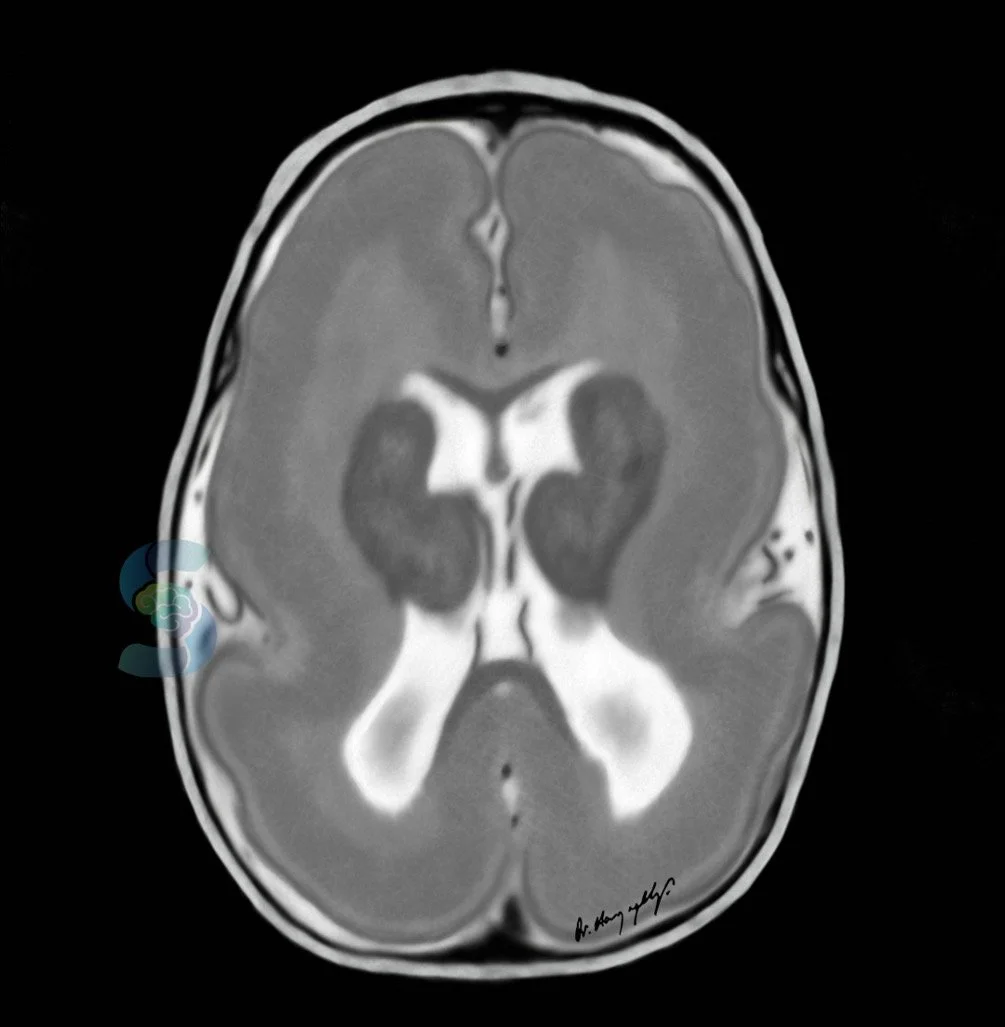
aqueductal stenosis
can be congenital or acquired
narrowing/obstruction of cerebral aqueduct between 3rd & 4th ventricles
marked enlargement of 3rd and lateral
effacement of cortical sulci
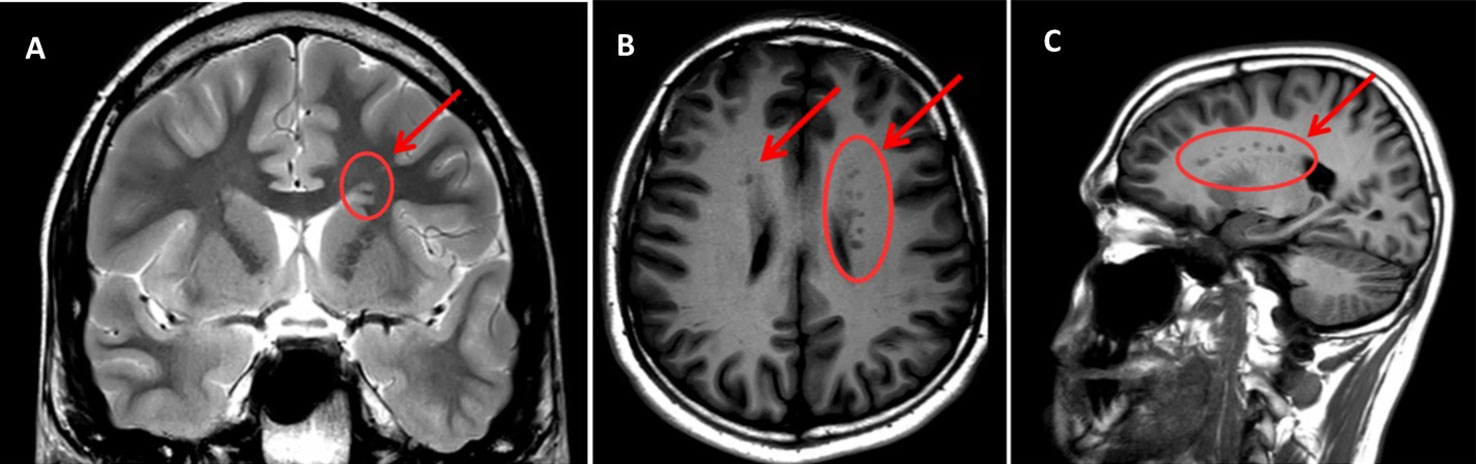
gray matter heterotopia
disorder of neuronal migration
nodules/bands of gray matter in abnormal locations, can be periventricular, subcortical or lobar
isodense on T1/T2/FLAIR
cause seizures
includes subependymal nodules (seen in tuberous sclerosis)
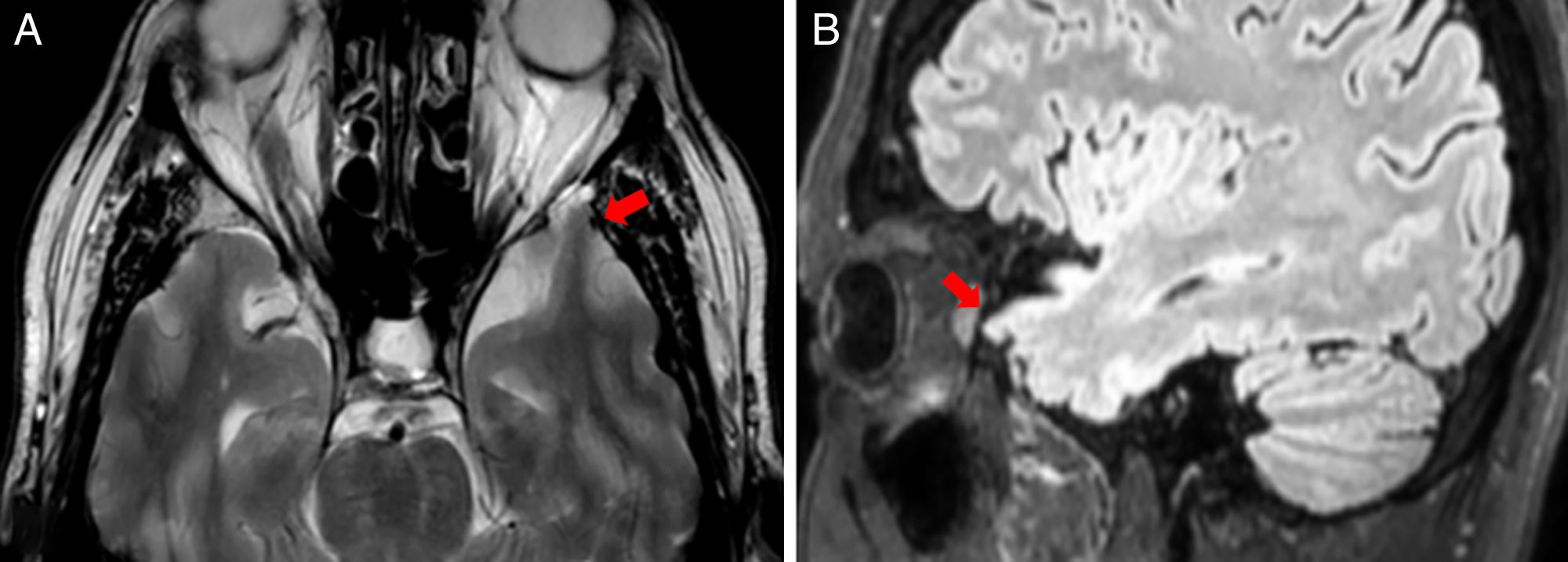
temporal lobe encephalocele
outpouching through skull defect
associated with epilepsy
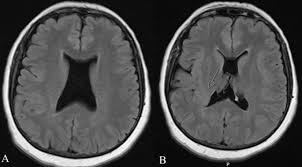
septo-optic dysplasia
hypoplastic or absent septum pellucidum
hypoplastic corpus callosum
hypoplastic optic nerves
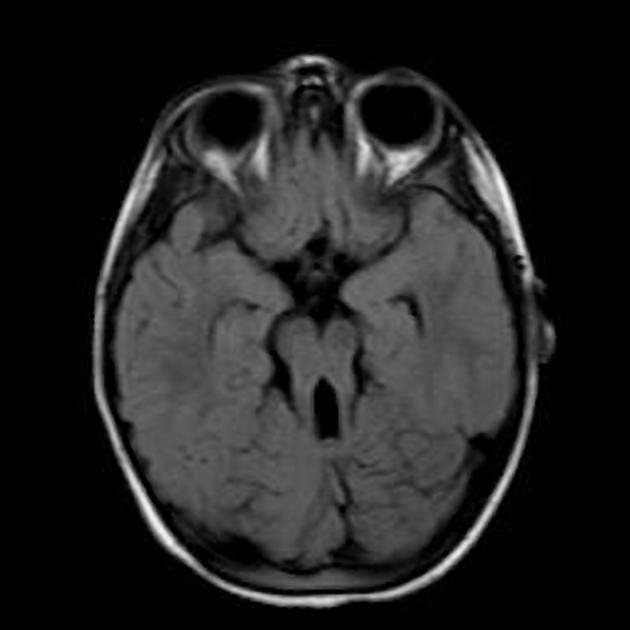
molar tooth sign
associated with Joubert syndrome (cerebellar vermis hypoplasia)
superior cerebellar peduncles horizontal & thick
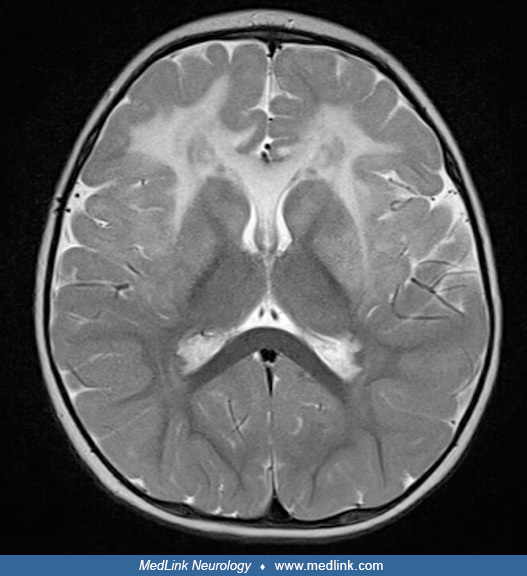
Alexander disease, type of genetic demyelinating leukodystrophy with bifrontal predominance
imaging findings in CJD
pulvinar & hockey stick signs (bilateral FLAIR hyperintensities in pulvinar & medial thalamus)
cortical diffusion restriction
imaging findings in Alzheimer’s
atrophy, particularly of temporal lobes
PET hypometabolism in parietal & temporal lobes
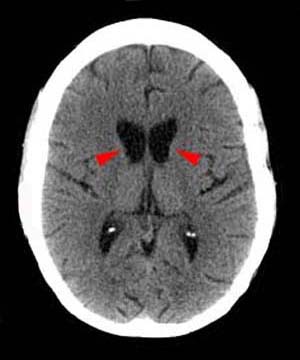
Huntington’s disease
atrophy of caudate head causes enlargement of frontal horns
Neuroacanthocytosis
also cause BG degeneration
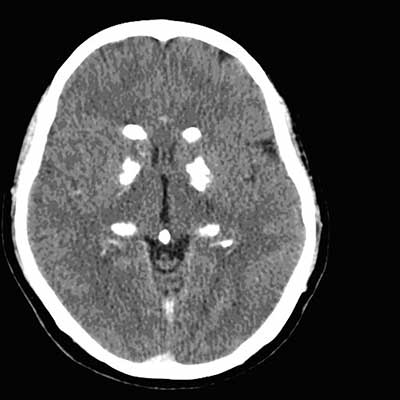
Fahr disease
disorder of calcium deposition and cell loss
primarily in BG and cortex
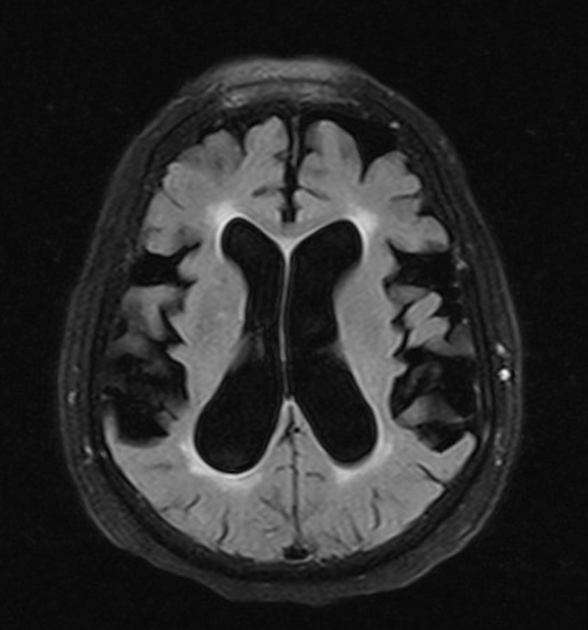
DESH (disproportionally enlarged subarachnoid space hydrocephalus)
associated with NPH
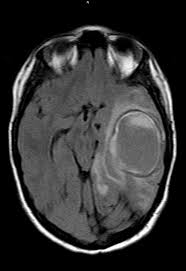
abscess with double rim sign
outer rim hypointense
inner rim hyperintense
can diffusion restrict in core
can have surrounding vasogenic edema
differentiate from glioma which also has hypodense rim but more heterogenous enhancement and peripheral diffusion restriction
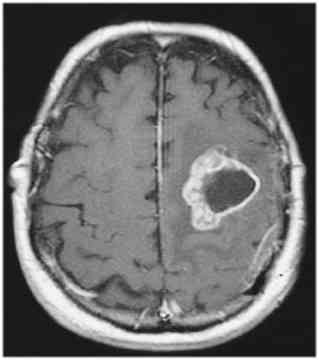
glioblastoma
multicystic
heterogeneously enhancing
vasogenic edema
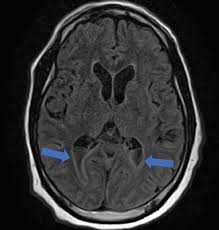
ventriculitis
enhancement lining ventricles
can occur with EVD, bacterial meningitis, ruptured brain abscess, skull infection
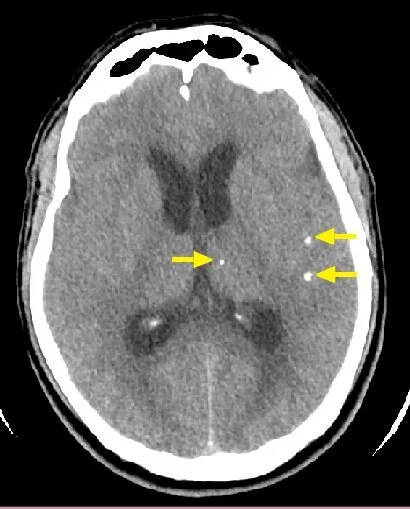
neurocysticercosis
hyperdense/calcified on CTH
hypointense core on MRI with edema, can rim-enhance
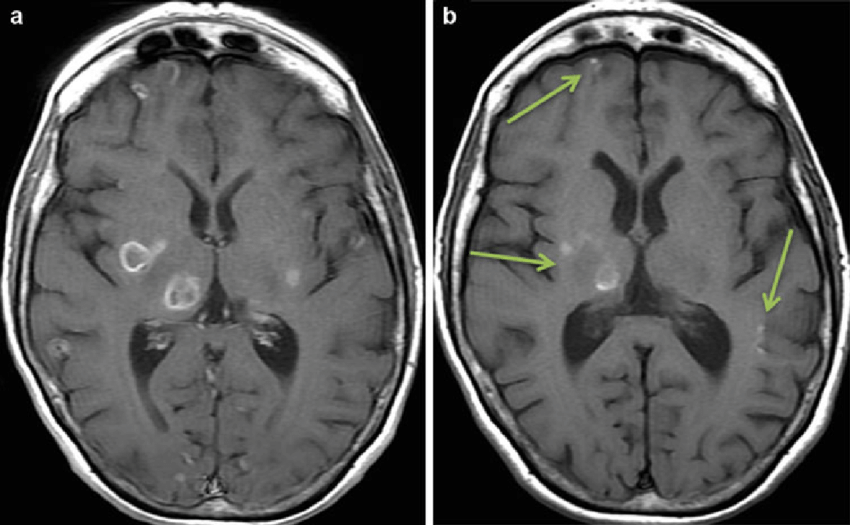
toxoplasmosis
tend to be in BG but can be anywhere
rim or nodular enhancement
often with surrounding edema
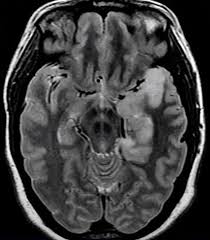
HSV encephalitis
affects temporal lobes & limbic structures
swollen, hyperintense, can be diffusion restricting or hemorrhagic
can see leptomeningeal enhancement
differential includes autoimmune (NMDAr) and paraneoplastic (LGI1) encephalitis which also favor temporal lobes
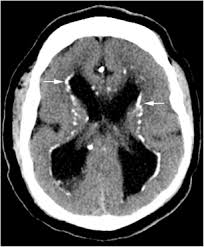
congenital CMV
ventriculomegaly/hydrocephalus
periventricular calcifications
microcephaly
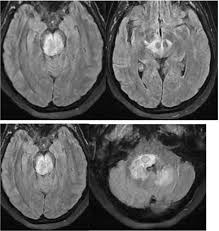
rhombencephalitis
infection/inflammation of brainstem & cerebellum
most common infectious cause is listeria, also enterovirus 71 and HSV. can also be autoimmune (Behcet’s, SLE) or paraneoplastic
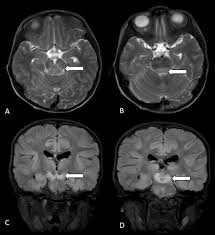
bickerstaff brainstem encephalitis
AMS, ataxia, ophthalmoplegia
post-infectious
+GQ1b antibodies
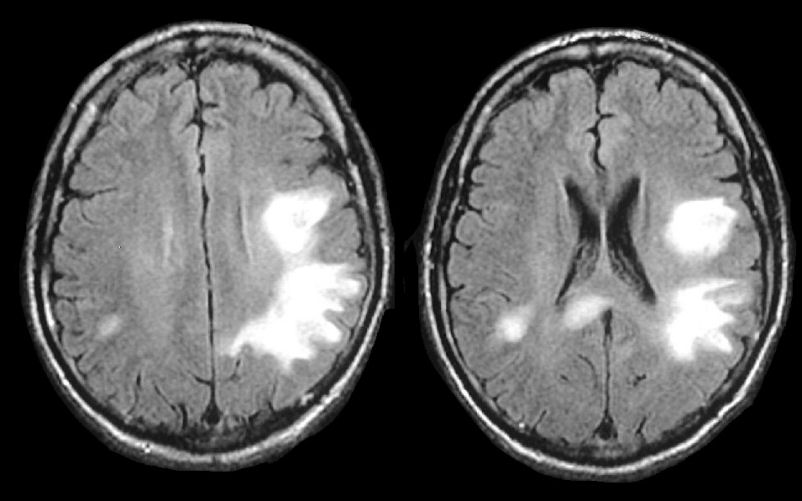
progressive multifocal leukencephalopathy (PML)
hypointense on T1, hyperintense on T2, can see peripheral patchy diffusion restriction, typically non-enhancing
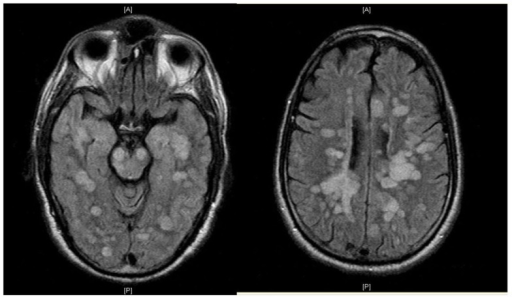
ADEM
large multifocal demyelinating lesions, can have tumefactive appearance
often involving cortex, subcortical grey matter, thalamus, brainstem
presents acutely in child with viral illness, typically monophasic
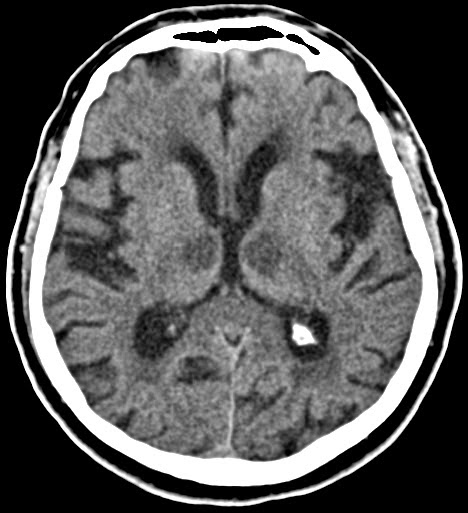
bilateral thalamic infarct
artery of percheron stroke or straight sinus thrombosis
core vs penumbra on perfusion imaging
rCBG < 30% = core = infarcted tissue
Tmax >6s = penumbra = tissue at risk
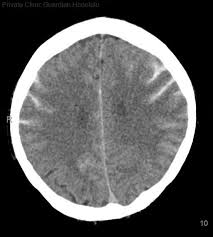
subarachnoid hemorrhage
best seen on CTH
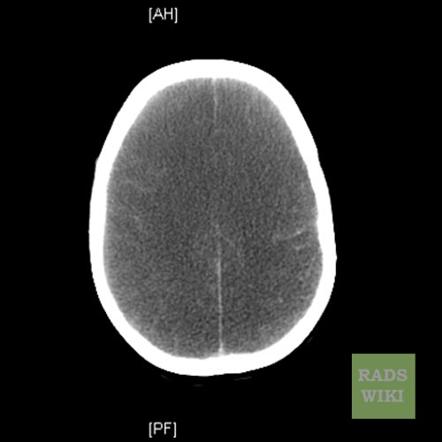
anoxic brain injury post-arrest
loss of gray-white differentiation
swollen sulci, small ventricles
pseudo-SAH from proteinacous leakage into subarach space
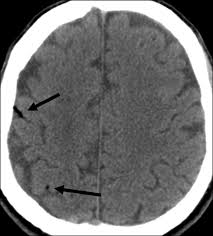
air embolism
punctate or curvilinear hypodensities
air darker than CSF
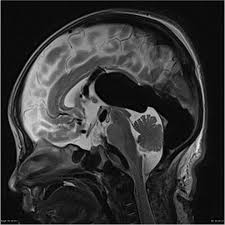
vein of Galen malformation
presents in babies with high output heart failure
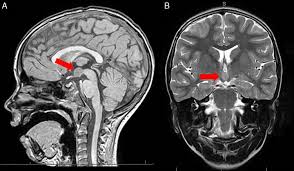
hypothalamic hamartoma
benign malformation/tumor
p/w refractory gelastic seizures, precocious puberty
spinal imaging
T1: CSF dark, pathology often dark
T2: CSF bright, pathology often bright
STIR (short tau inversion recovery): T2 with suppression of fat
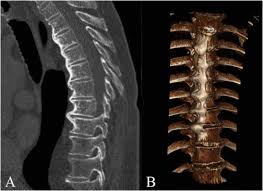
diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis
calcification and ossification of anterior longitudinal ligament
can accelerate spondylosis
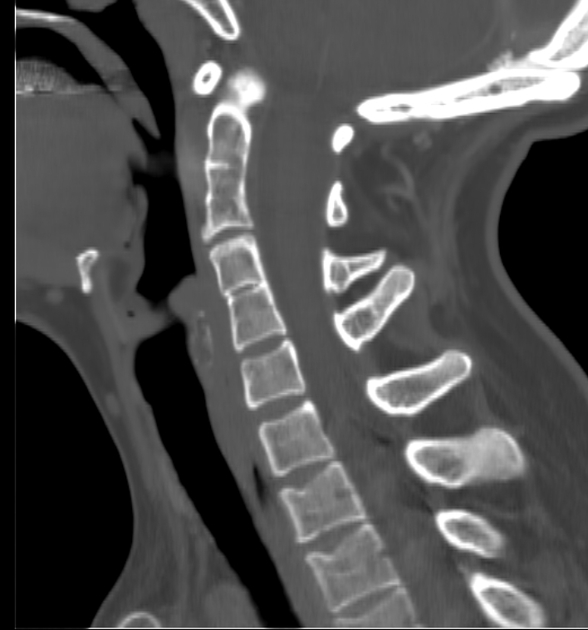
klippel fiel syndrome
incomplete segmentation of C-spine
congenital
limited mobility of neck and upper spine
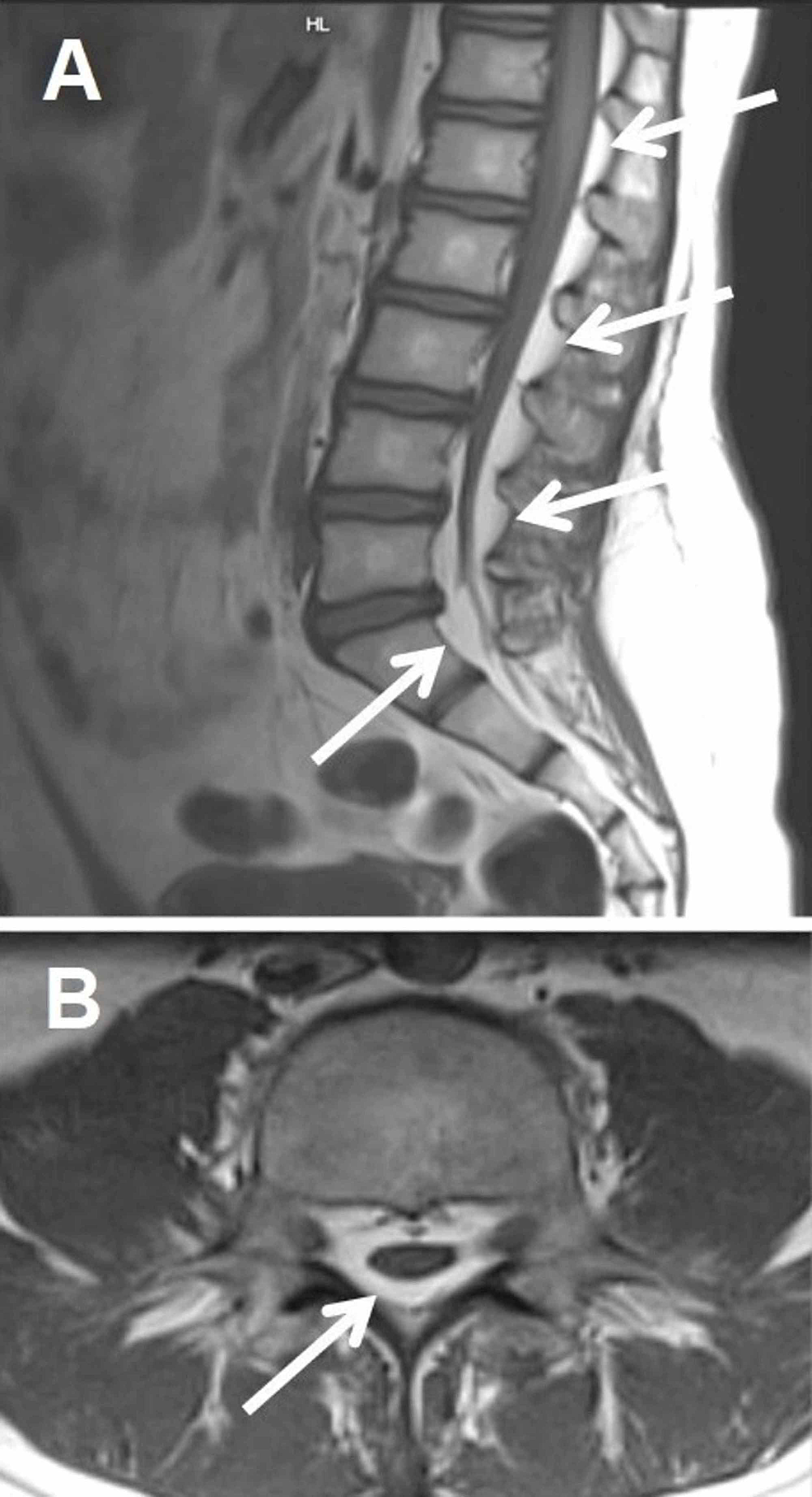
epidural lipomatosis
accumulation of excess fat in spinal epidural space resulting in spinal cord compression
associated with long-term steroid use
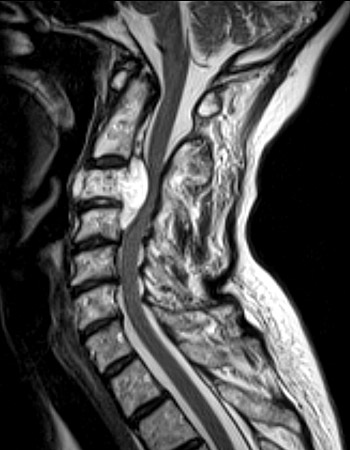
chordoma
slow growing
thought to arise from cellular remnants of notocord
can cause cord compression
can grow along cord or in brain adjacent to sphenoid bone
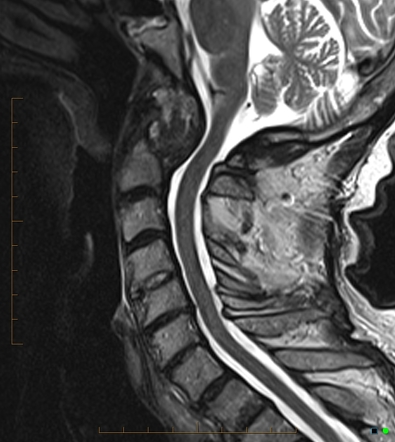
rheumatoid pannus
inflammatory synovial tissue commonly growing in cervical spine around C1-2, can cause neck pain/instability and cord compression
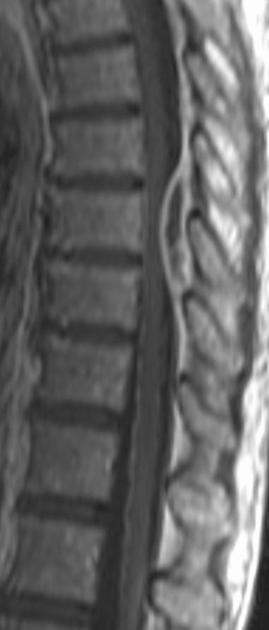
spinal epidural abscess
non-enhancing core w rim of enhancement
can be diffusion restricting in core
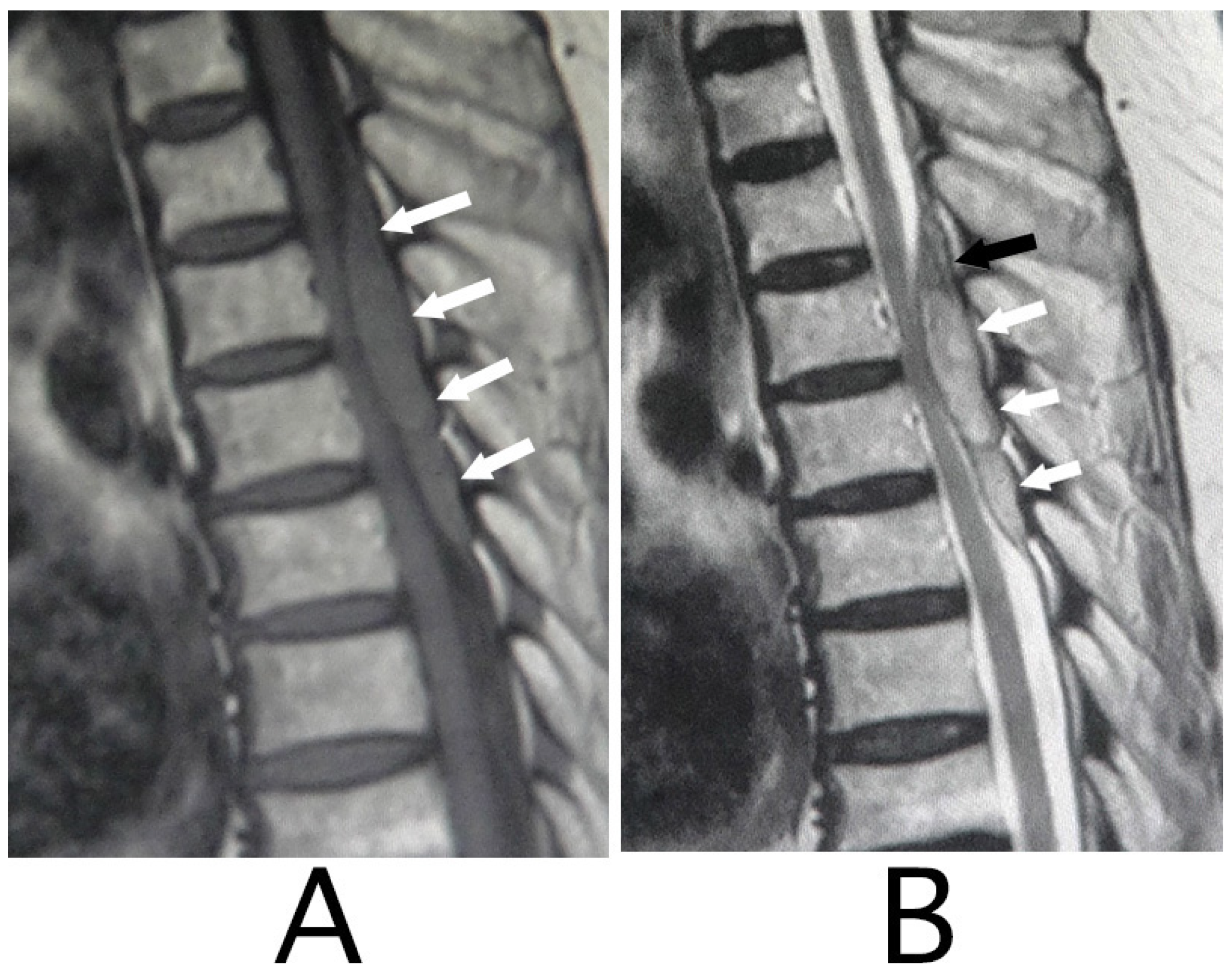
spinal epidural hematoma
heterogeneous appearance but mostly hyperintense on T1/2
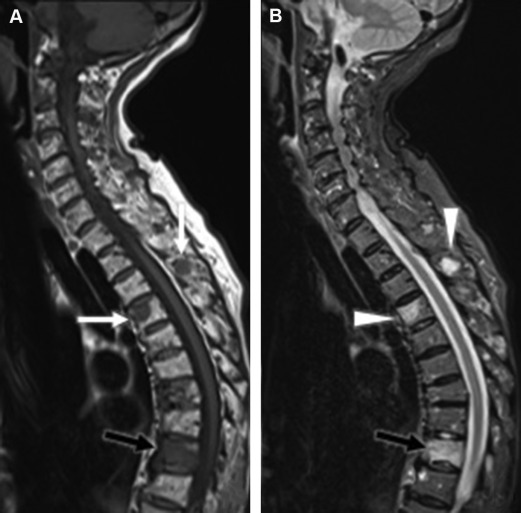
multiple myeloma vertebral lesions
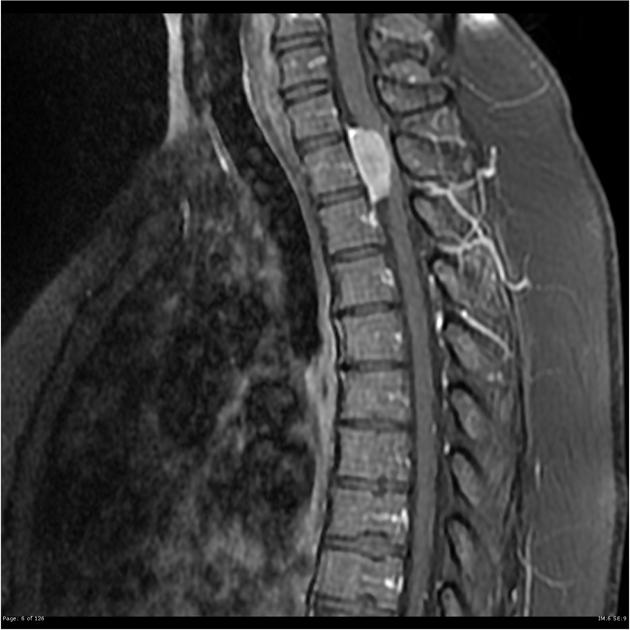
spinal meningioma
well circumscribed
dural attachment (dural tail sign)
homogeneous enhancement
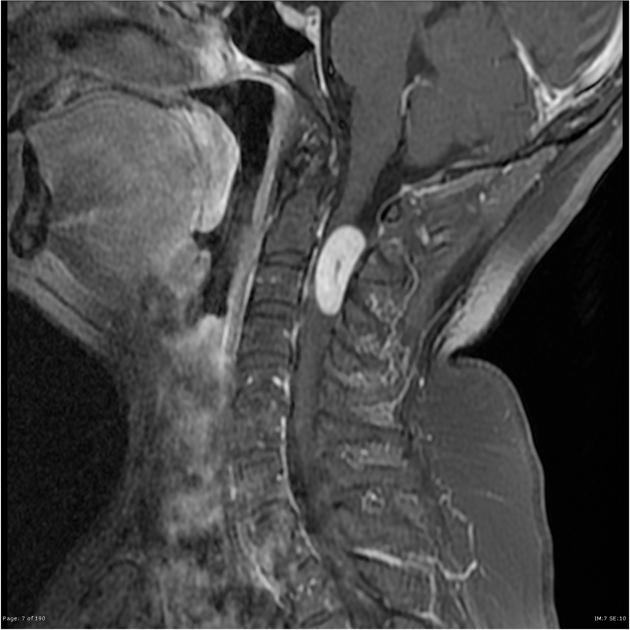
spinal schwannoma
arise from spinal nerve roots
homogeneous enhancement
differentiated from spinal meningioma by lack of dural tail
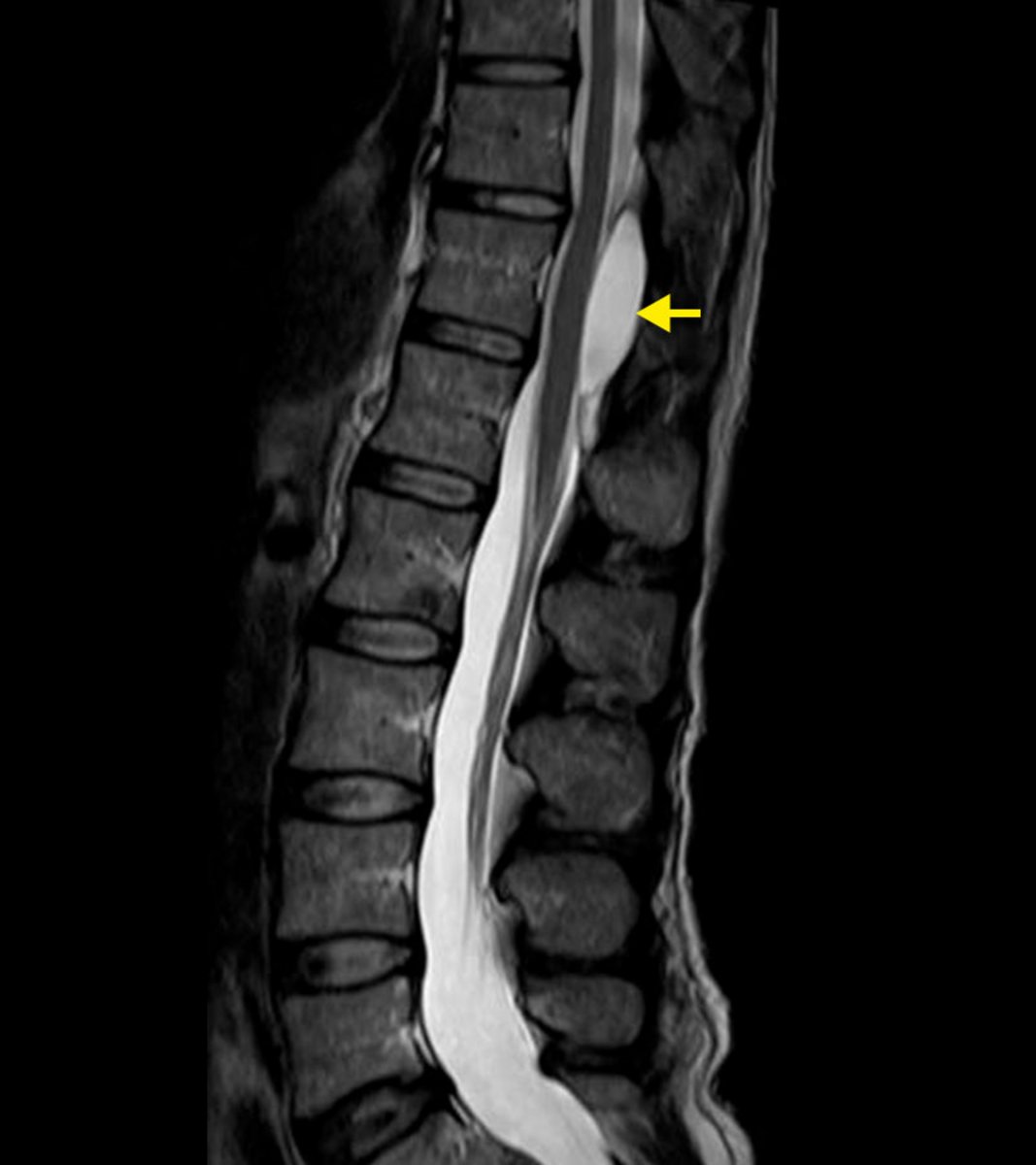
spinal arachnoid cyst
CSF-filled cyst within arachnoid space
can be congenital or from trauma (most commonly T spine)
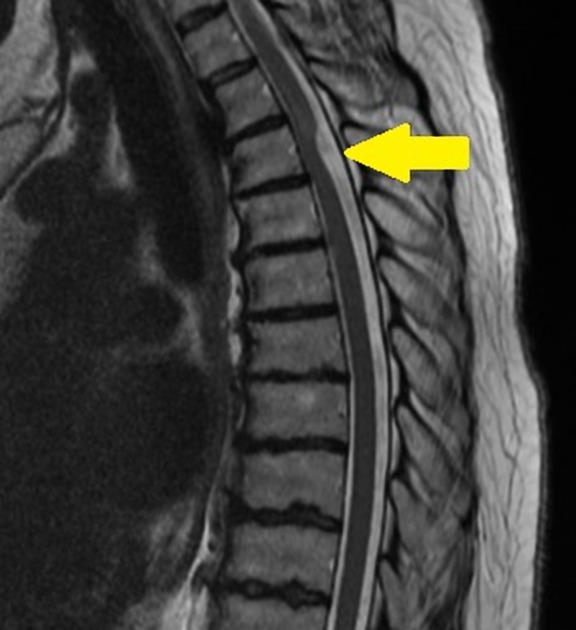
arachnoid web
scalpel sign
thickened band of arachnoid over dorsal cord
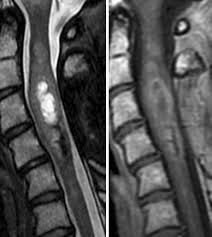
spinal ependymoma
central cord (arise from central canal)
enhancing
often cystic looking
often associated syrinx
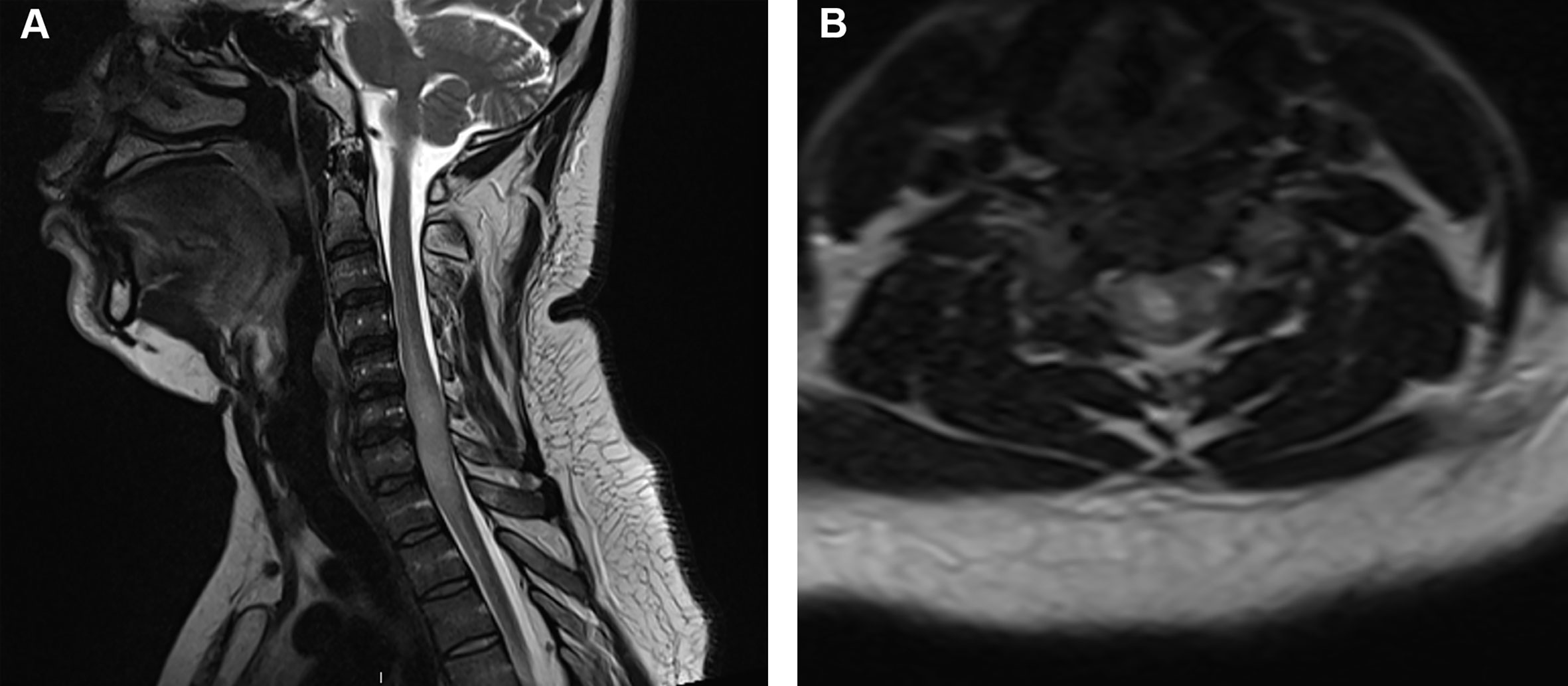
spinal astrocytoma
intramedullary
often eccentric (arise from cord parenchyma)
poorly defined margins
most enhance
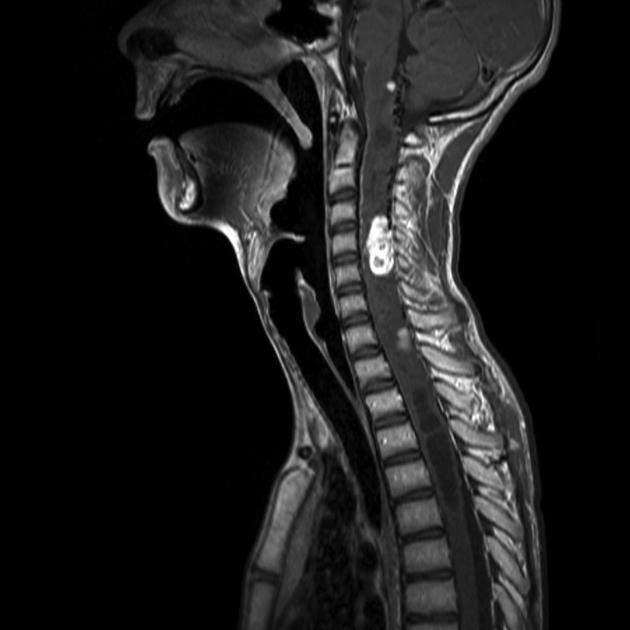
spinal hemangioblastoma
intramedullary
nodular appearance
may see vascular flow voids
vividly enhancing
features of different causes of LETM
NMO - central often involving gray & white matter, bright & spotty, patchy enhancement, can see prominent swelling
MOG - central, sometimes restricted to gray (H sign), often non-enhancing, can involve conus
sarcoid - central, “trident” sign
paraneoplastic - tract-specific (often dorsal/lateral columns)
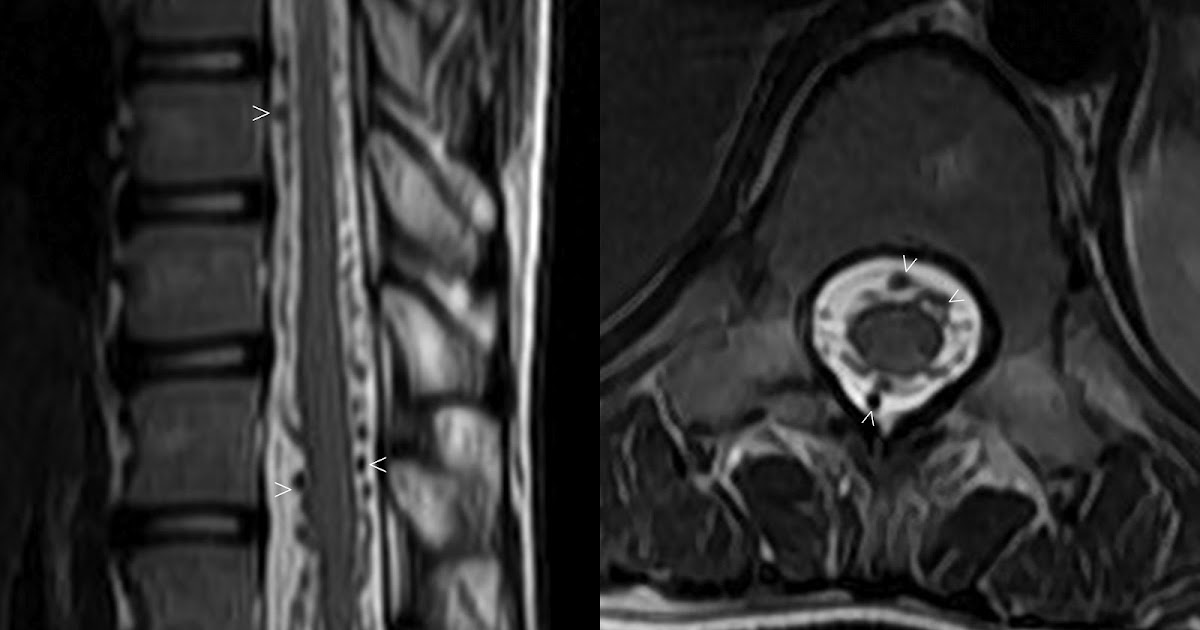
H sign of grey matter restricted myelitis
associated with MOGAD
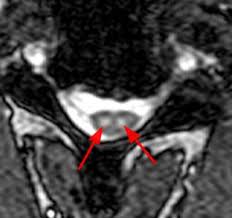
trident sign
associated with neurosarcoid
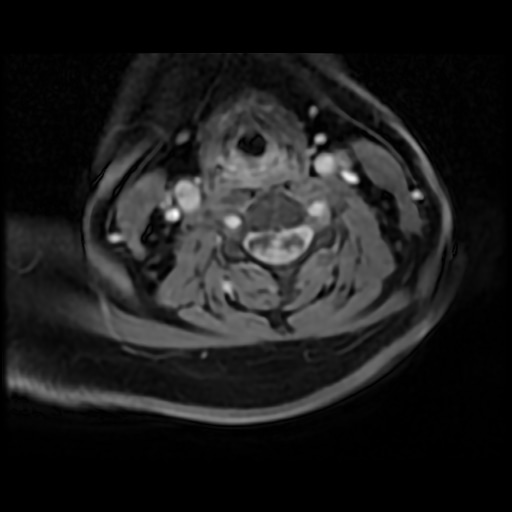
spinal dural AVF
present with gradual but progressive pain, leg weakness/numbness, bladder/bowel changes
flow voids on T2
can see intramedullary hyperintensity due to edema, often involving conus
confirmed with DSA
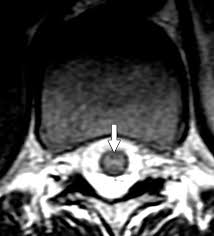
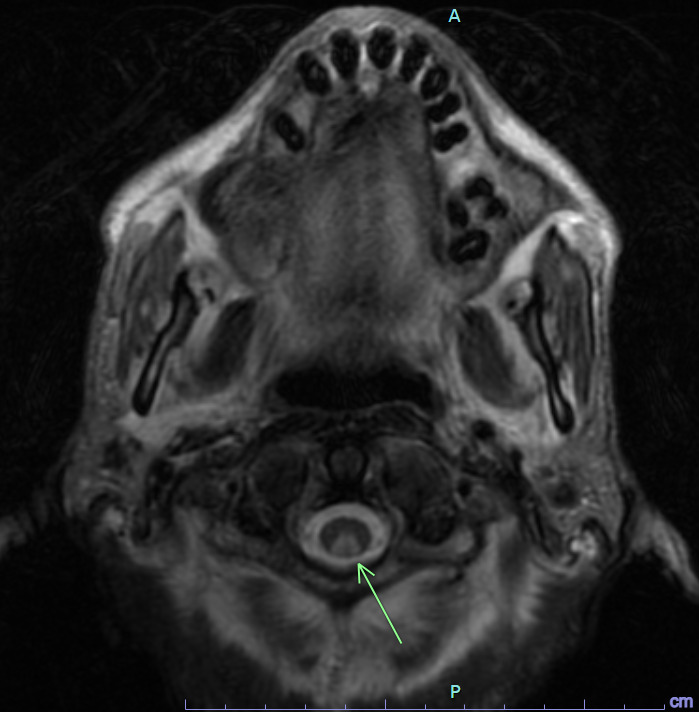
owl eye sign
spinal cord infarct
anterior horn cells
can also be seen in ALS, polio
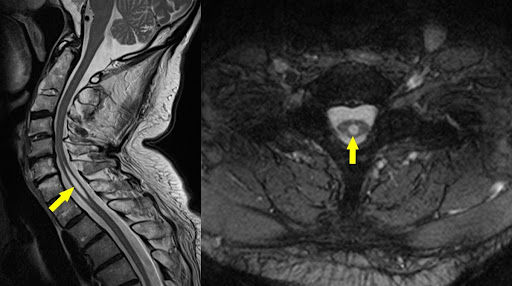
subacute combined degeneration
demyelination of dorsal columns
B12 deficiency, syphilis, copper deficiency, methotrexate toxicity
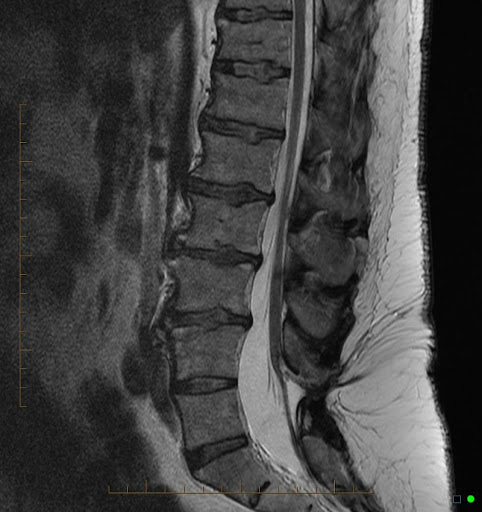
syringomyelia
collection of CSF in central cord around central canal
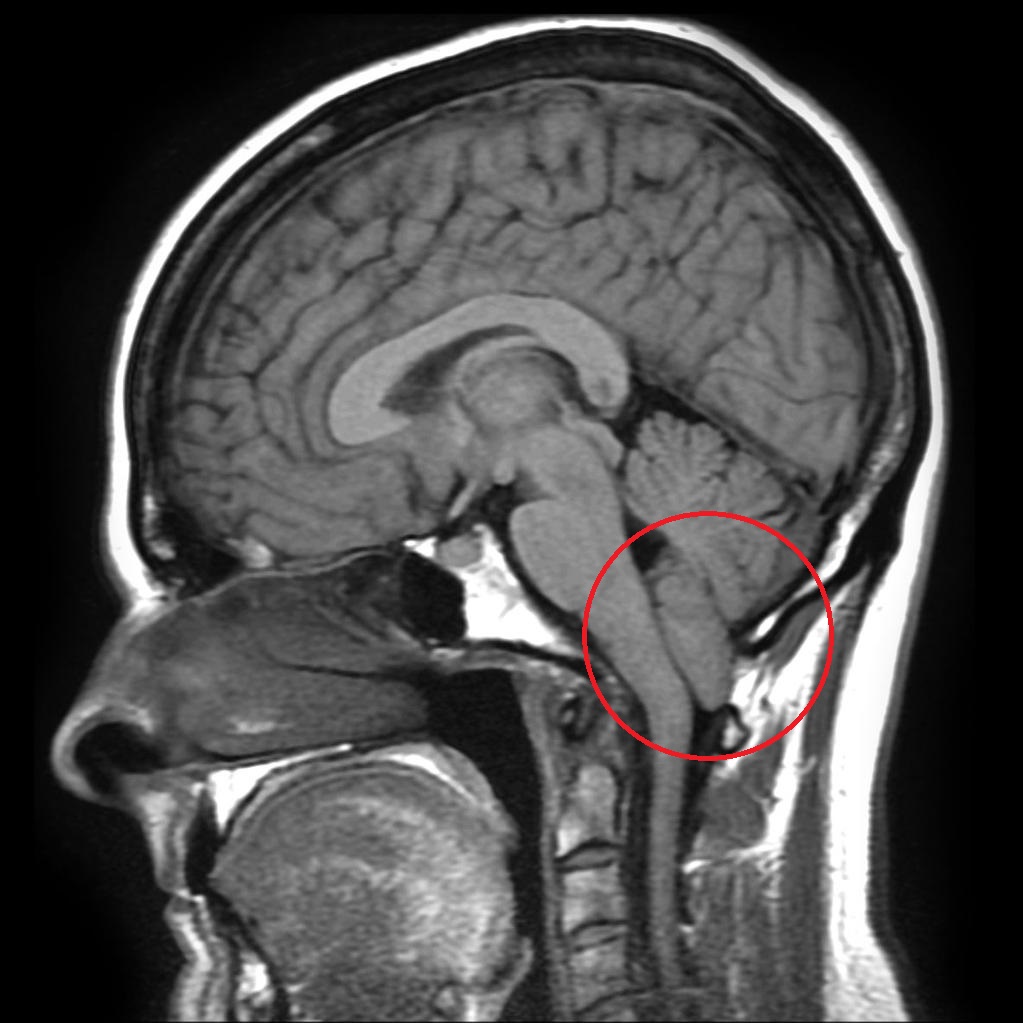
chiari malformation
I: downward displacement of cerebellar tonsils, often associated with syringomyelia
II: downward displacement of medulla, 4th ventricle and cerebellum through foramen magnum, often associated with myelomeningocele
tethered cord
progressive stretching from lengthening of spinal column
conus terminates at low position
can see other imaging findings of spinal dysraphism
can be associated with terminal lipoma (lipmeningocele)