Ways of the World Chapter 3
1/84
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
85 Terms
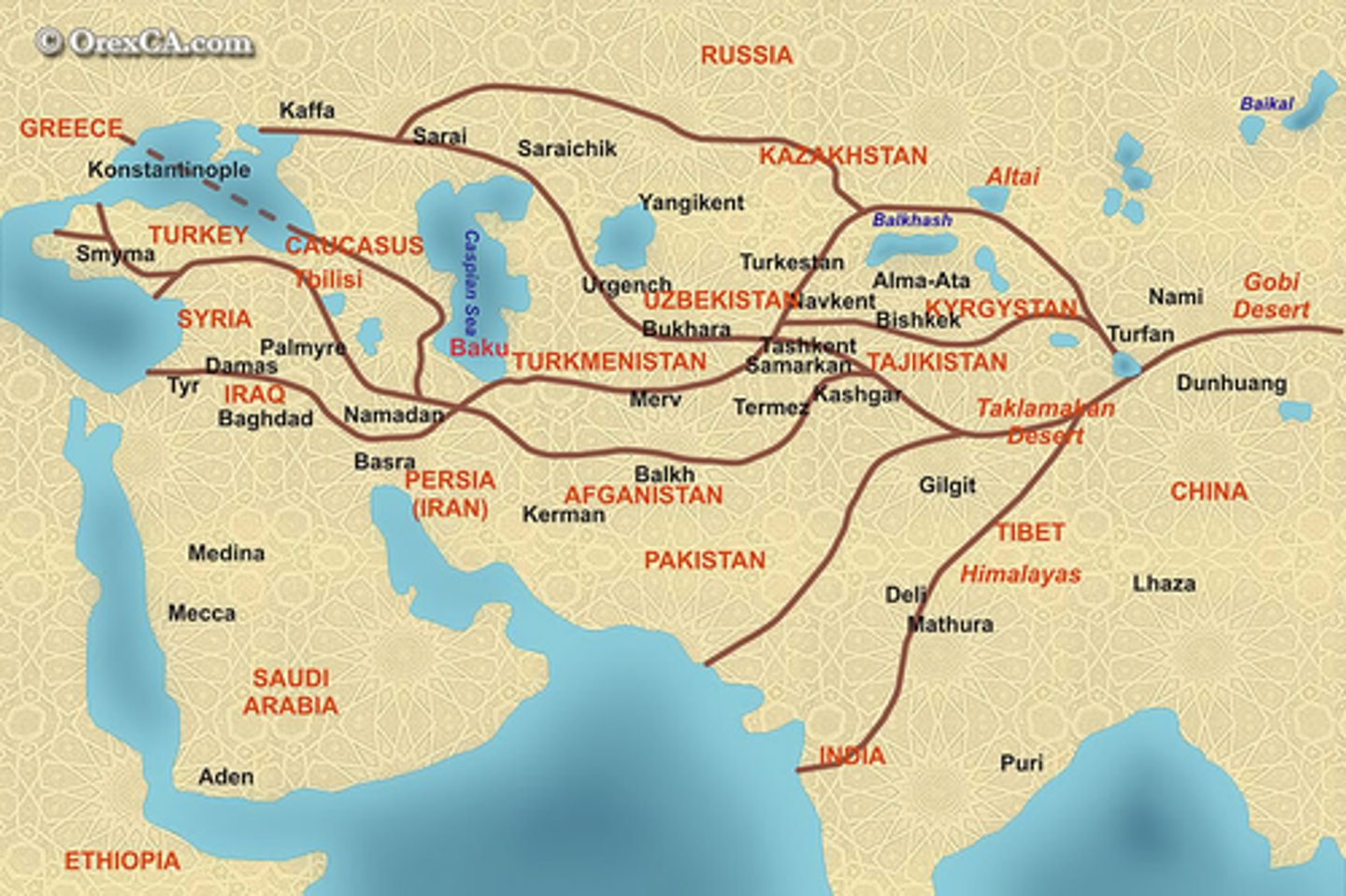
Silk Road
An ancient trade route between China and the Mediterranean Sea extending some 6,440 km (4,000 mi) and linking China with the Roman Empire
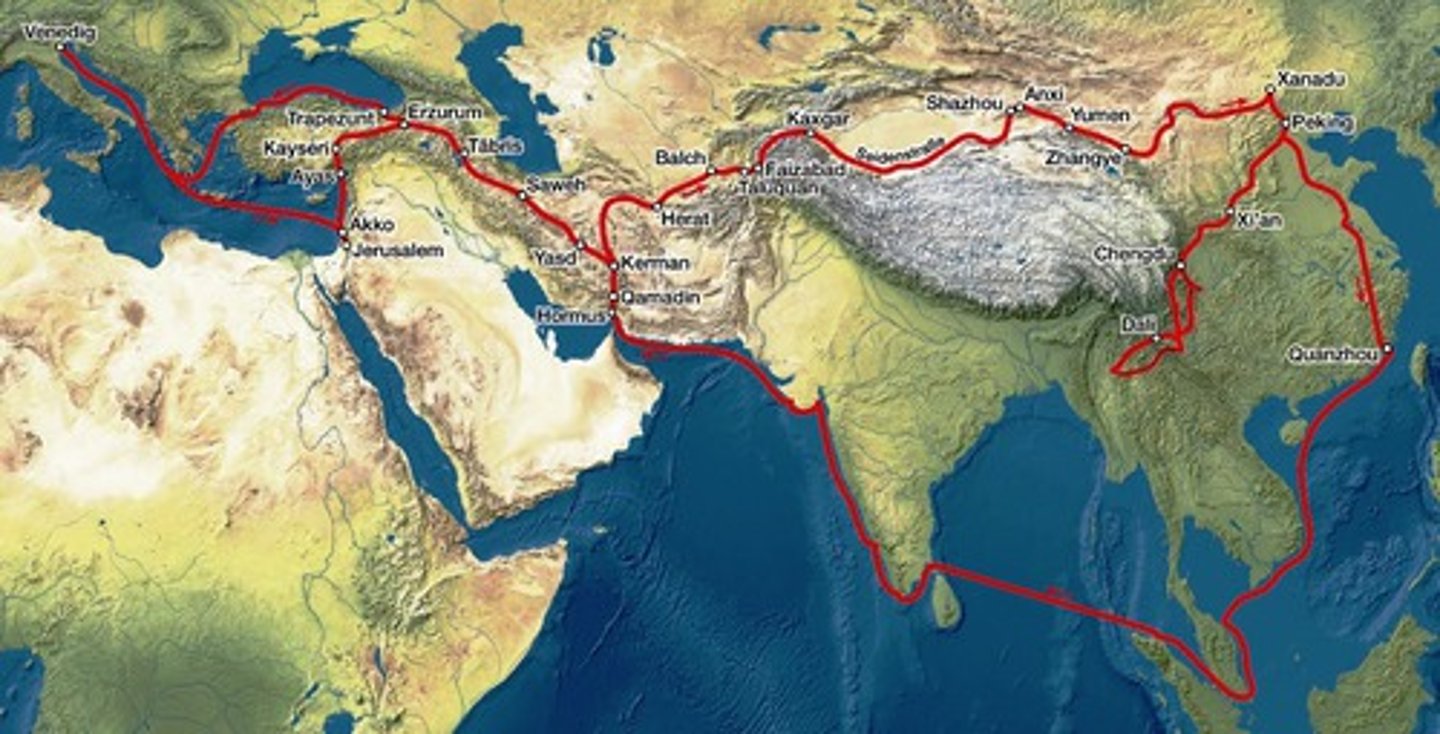
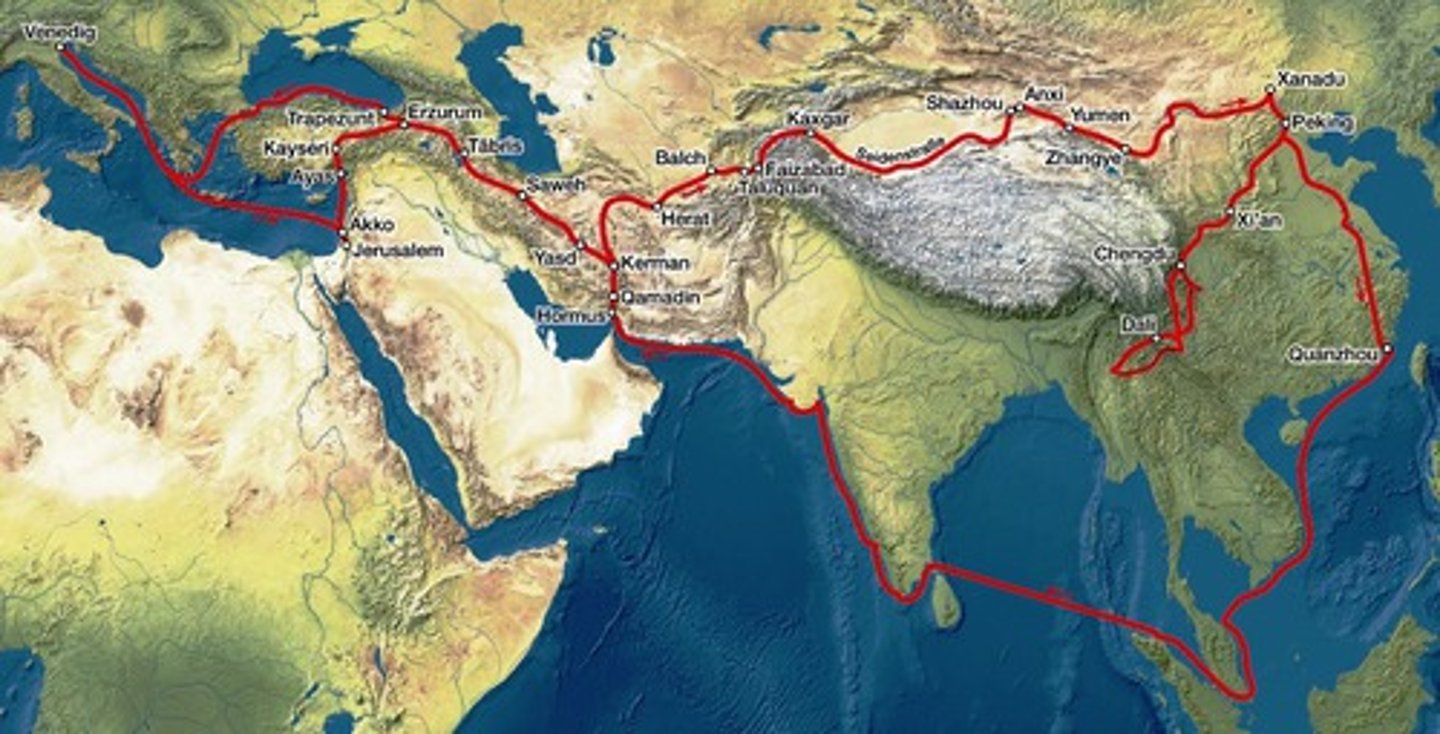
Marco Polo
Venetian merchant and traveler. His accounts of his travels to China offered Europeans a firsthand view of Asian lands and stimulated interest in Asian trade.
Ibn Battuta
Moroccan Muslim scholar, the most widely traveled individual of his time. He wrote a detailed account of his visits to Islamic lands from China to Spain and the western Sudan.
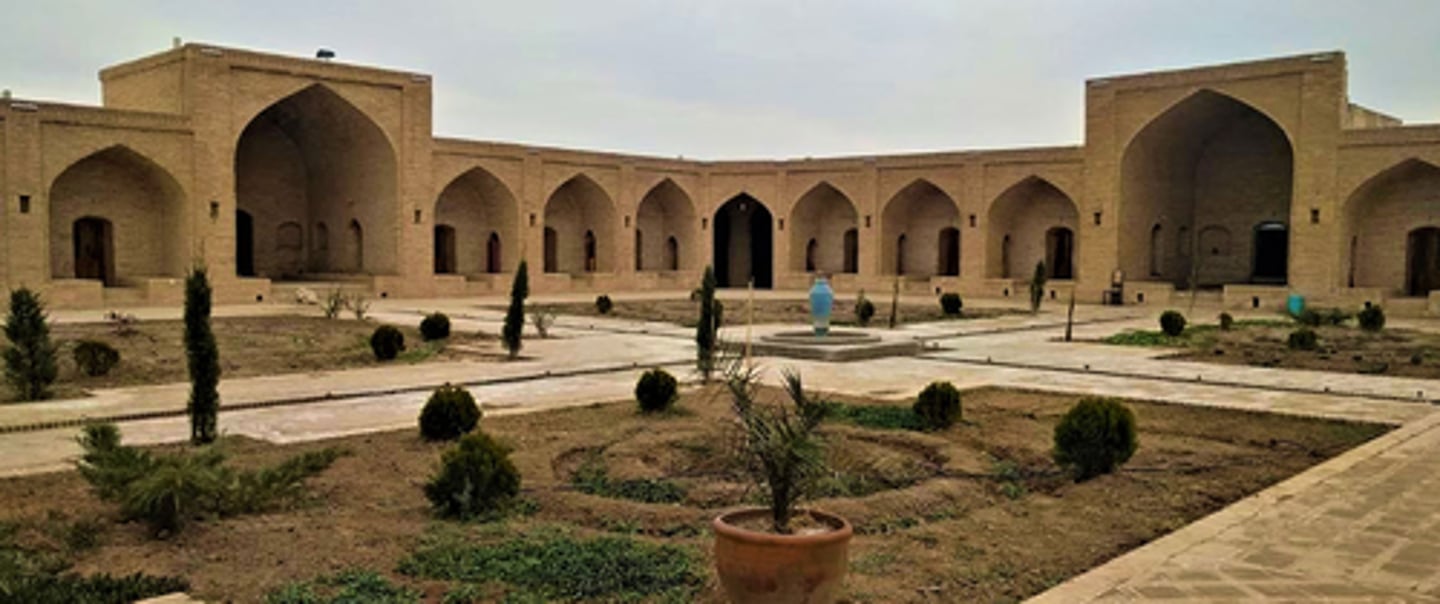
Caravanserai
an inn with a central courtyard for travelers in the desert regions of Asia or North Africa.
They grew into big commerce cities with diversity

Caravanserai Cities
Bukhara
Samarkand
Khotan
Kashgar
Dunhuang
What were some very important imports and their affects?
-silk(China):
social status, gift, valuable
-saddle/yoke/stirrup(China,Arab)
helped carry load efficiently
-paper money/flaying cash(China)
silk
a valuable cloth, originally made only in China from threads spun by caterpillars called silkworms
showed social status
showed religious importance as monasteries / devotion and peity
Monasteries
Communities of monks
Pierty
Religous devotion and reverence to God
saddles and stirrups
these Chinese inventions allowed soldiers to fight on horseback

Yokes
a device that allows animals (horses, oxen) to pull heavy carts or plows. This of course increases crop yields and the amount of trade
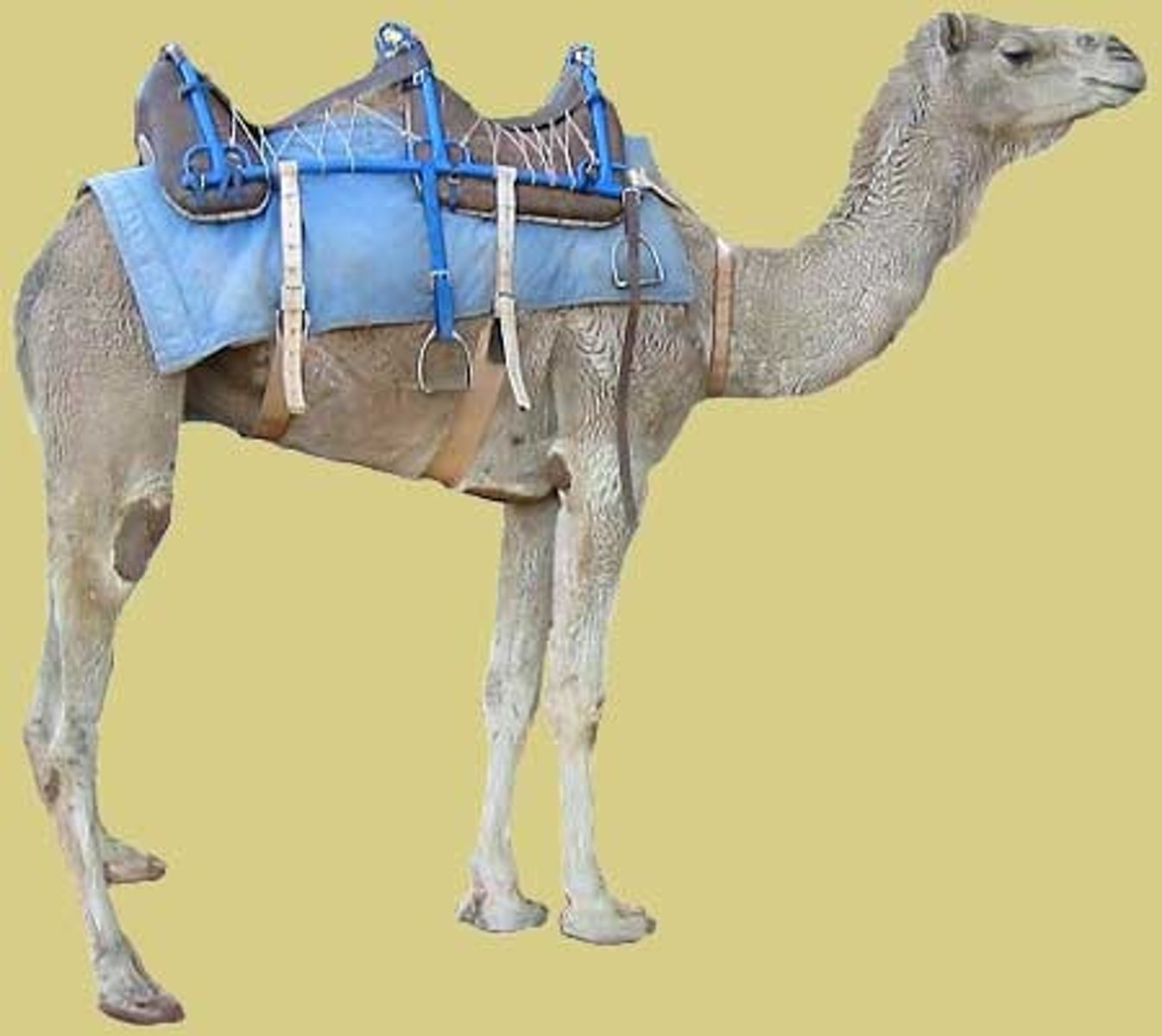
Arab invented for camels

frame and mattress saddle
saddle that helped Arab Camels carry items

paper money
-legal currency issued on paper; it developed in China as a convenient alternative to metal coins
-also were used as letters of credit came into common use during the early Tang period
-It enabled merchants to deposit good or cash at one location and draw the equivalent in cash or merchandise elsewhere in China.

What economic consequences did the Silk Road have on average people? How did this impact their choices?
people started to create supplies more for long distance commerce rather than for themselves. For example, farmers grew silk farms for silk production rather than food for themselves and their community.
-items like silk, iron tools, porcelain, spices
Under what circumstances did the Silk Road trading networks prosper?
The government helped and protected traders so the stronger the states the more efficient the trade.
How did the original faith of Buddhism change along the Silk Road?
-the ascetic Buddhist religion became more secular and materialistic as societies got richer. It was more Mahayanan
-other religious influences were incorporated as Bohisattvas
material world
consumer society
Secular
Concerned with worldly rather than spiritual matters
Asceticism
severe self-discipline and avoidance of all forms of indulgence, typically for religious reasons.
Mahayana
Sect of Buddhism that offers salvation to all and allows popular worship
The name of the more mystical and larger of the two main Buddhist sects. This one originated in India in the 400s CE and gradually found its way north to the Silk road and into Central and East Asia.
Bohisattva
In mahayan buddhism, a saint or semi-divine being who has voluntarily renounced nirvana in order to help others to salvation
Pure Land Buddhism
-A denomination of Buddhism that taught that believers would be reborn in a blissful, pure land or paradise.
-Emphasized salvationist aspects of Chinese Buddhism; popular among masses of Chinese society.
-Ensured rebirth without the strict practices
What did China's government do to Buddhism?
-They didn't like the incorporation of another religion due to the impact it can have on the religious based political system
-Buddhism was frequently attacked and called as an evil religion. They passed laws making lives for monks harder and came under state control.
-eventually it became assimilated
Chan School of Buddhism
school for Buddhism and emphasize its practice. it became dominant in the Song dynasty and was favored by court officials and scholars.
Neoconfucianism
term that describes the resurgence of Confucianism and the influence of Confucian scholars during the T'ang Dynasty; a unification of Daoist or Buddhist metaphysics/morals with Confucian pragmatism(philosophy)
Metaphysics
a branch of philosophy that investigates the ultimate nature of reality
How did other eastern Asian countries react to Buddhism
Korea
-got most of its influence from China. They modeled government morals/structure
-tributes spread Buddhism and education was very influenced in the spreading too
Japan
-at first, elite people were more influenced but later was incorporated
what items were traded in the Indian ocean
textiles, pepper, timber, rice, sugar, wheat
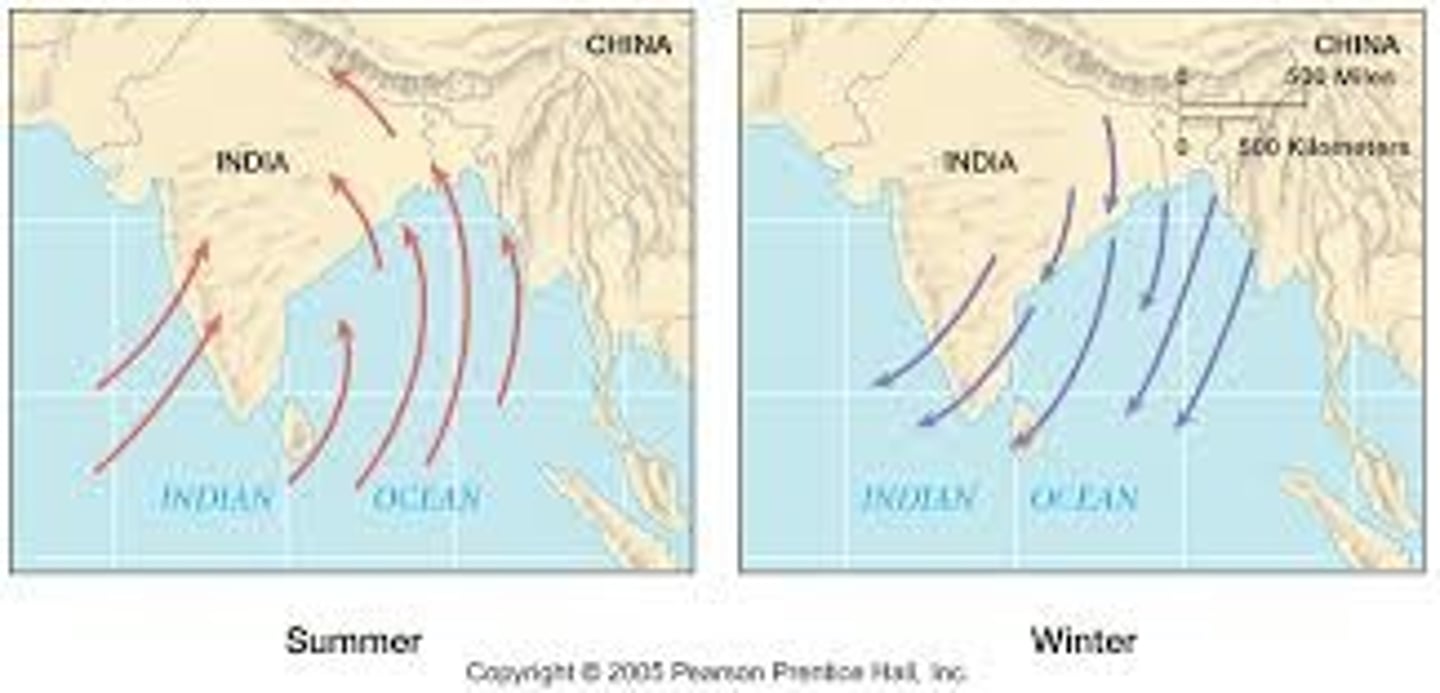
Sea Roads
The world's largest sea based system before 1500. Took place on the Indian Ocean and was made possible by the push from the predictable monsoons. Sea roads were not only limited to luxury goods like the silk roads, and could carry more bulk.
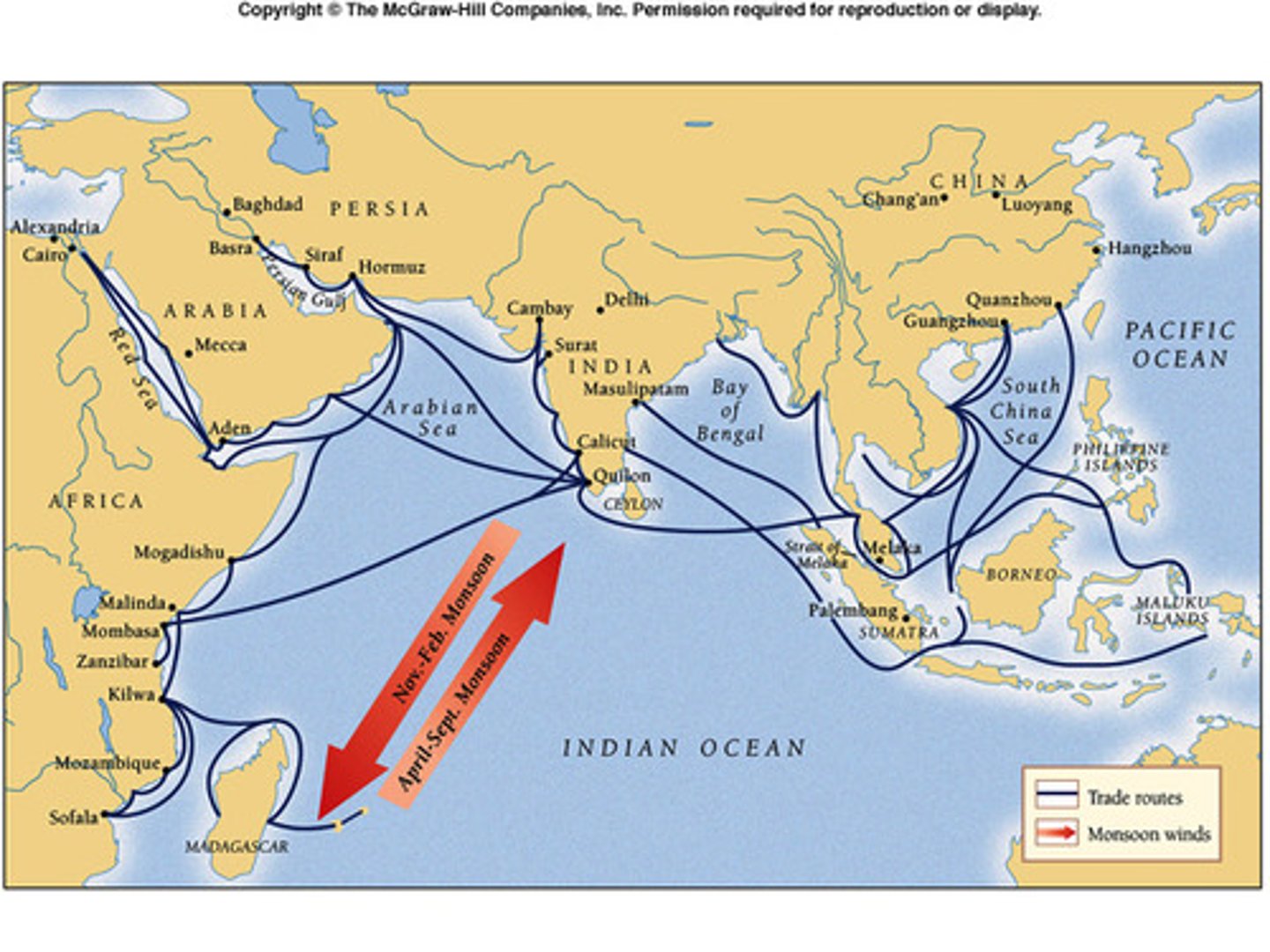
Monsoons
seasonal wind patterns that cause wet and dry seasons
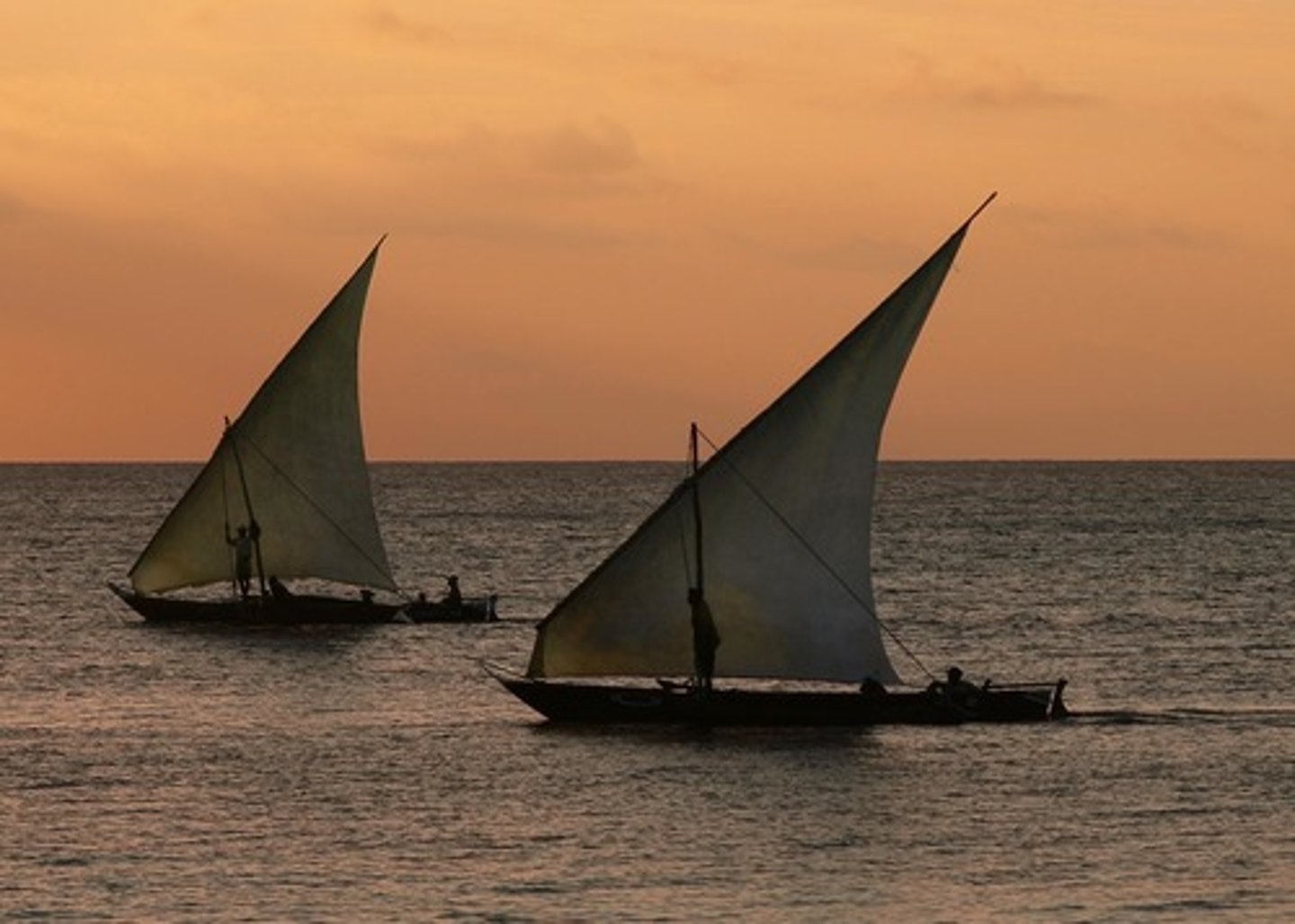
Dhows
Large ships favored by Indian, Persian, and Arab sailors that could carry up to four hundred tons of cargo.

Junk Ships (Treasure Ships)
A junk is an ancient Chinese sailing vessel/ship design still in use today. Junks were developed during the Song Dynasty (960-1129)[1] and were used as seagoing vessels as early as the 2nd century CE.
![<p>A junk is an ancient Chinese sailing vessel/ship design still in use today. Junks were developed during the Song Dynasty (960-1129)[1] and were used as seagoing vessels as early as the 2nd century CE.</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/e66837c2-57e9-4a87-8027-8148fd64e9b3.jpg)
magnet compass
invented by the Chinese determines direction by indicating north
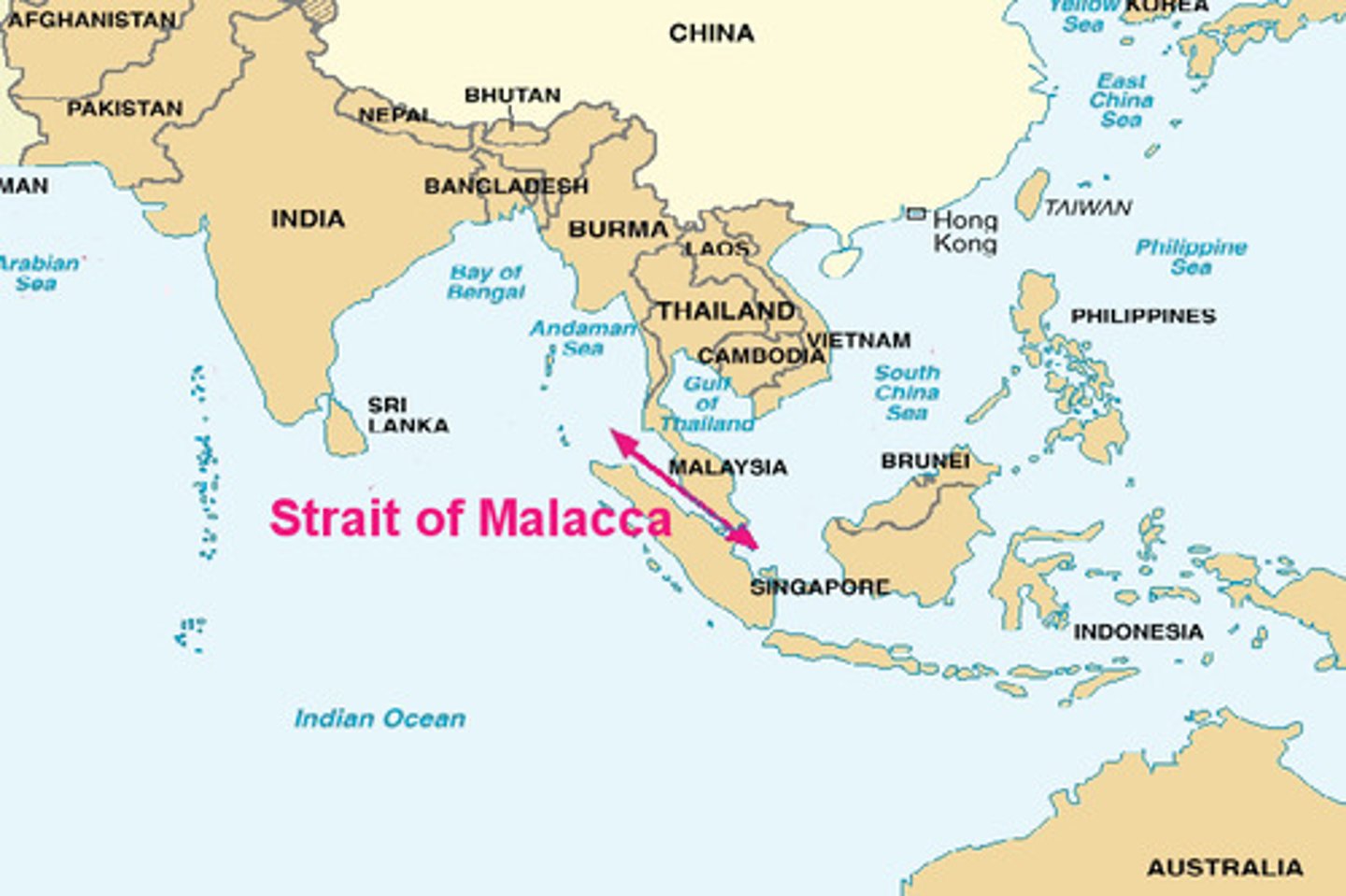
Straits of MalaccaWhat was the appeal of Islam to merchants? Monarchs?
well-traveled stretch of water between Malaysia and Indonesia used for trade along the Spice Route
What was the impact of Srivijaya in trade
-Malay Kingdom that dominated the Strait of Malacca from 670-1025 C.E.
-Was abundant in spices(cloves, nutmeg, mace) and gold.
-They taxed passing ships
-Major Buddhist center
Palembang
Capital of Sumatra/Srivijaya; Buddhist based city
-was very cosmopolitan with language and culture
-rulers were said to be magical
-Indian based area helped with the social power of rulers
cosmpolitan
sophisticated and not limited by a narrow point of view; diverse and containing a variety of people
Sailendra
a kingdom of central Java that flourished from the 8th century to the 10th century
noted for being deeply influenced by Indian Culture
allied with Srivijaya
featured Hindu and Buddhist temples(Borobudur Temple)
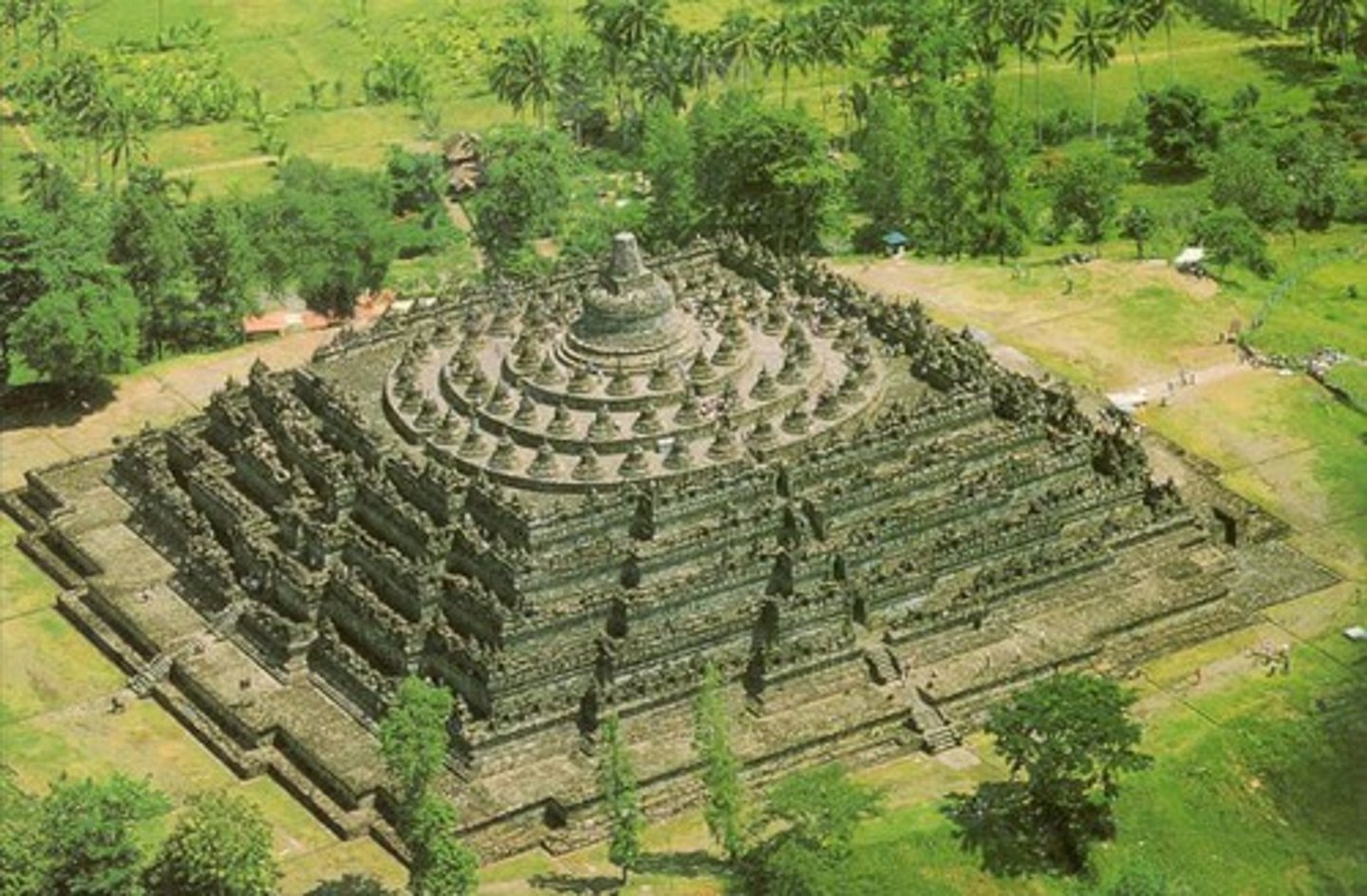
Borobudur Temple
Central Java, Sailendra(Indonesia) made of Volcanic stone masonry with Islamic influence of using government riches for religious importance/purposes
temple is a Buddhist monument with carving special to java due to the Javanese figures and backgrounds

How did Hinduism develop in east and southeast Asia
Vietnam
-well established, worshipped, and prominent
Khmer Kingdom(Cambodia)
-temples like Angkor Wat
Angkor Wat
-A temple complex built in the Khmer Empire
-dedicated to the understanding of the cosmos and to the Hindu God, Vishnu.
-later used by the Buddhists
-largest of its time
Malacca
-Flourishing trading city in Malaya(powerful influence due to its position); established a trading empire after the fall of Shrivijaya.
-Cosmopolitan style(diverse languages)
-attracted Muslim traders with a sultan and overall Muslim based society
-very rich and connected to China
-Portuguese came and it fell
What did the relationship with China do for Malacca?
-Had tributes with China
-They served as China's naval expeditions and overall helped China's influence in the strait
-Pepper was heavily bought by the Chinese which benefited the Malays
Swahili city-states
-Waring states that were always competing for control of trade routes and each other. established by swahili., --Many of these city-states were Muslim and very cosmopolitan.
-used to live in small villages speaking the bantu language
-grew from the Indian Ocean trade by selling gold, ivory, quartz, leopard skins, iron, timber, and slaves
-Lamu, Mombasa, Kilwa, Sofala
-later become more Islamic based(voluntarily)
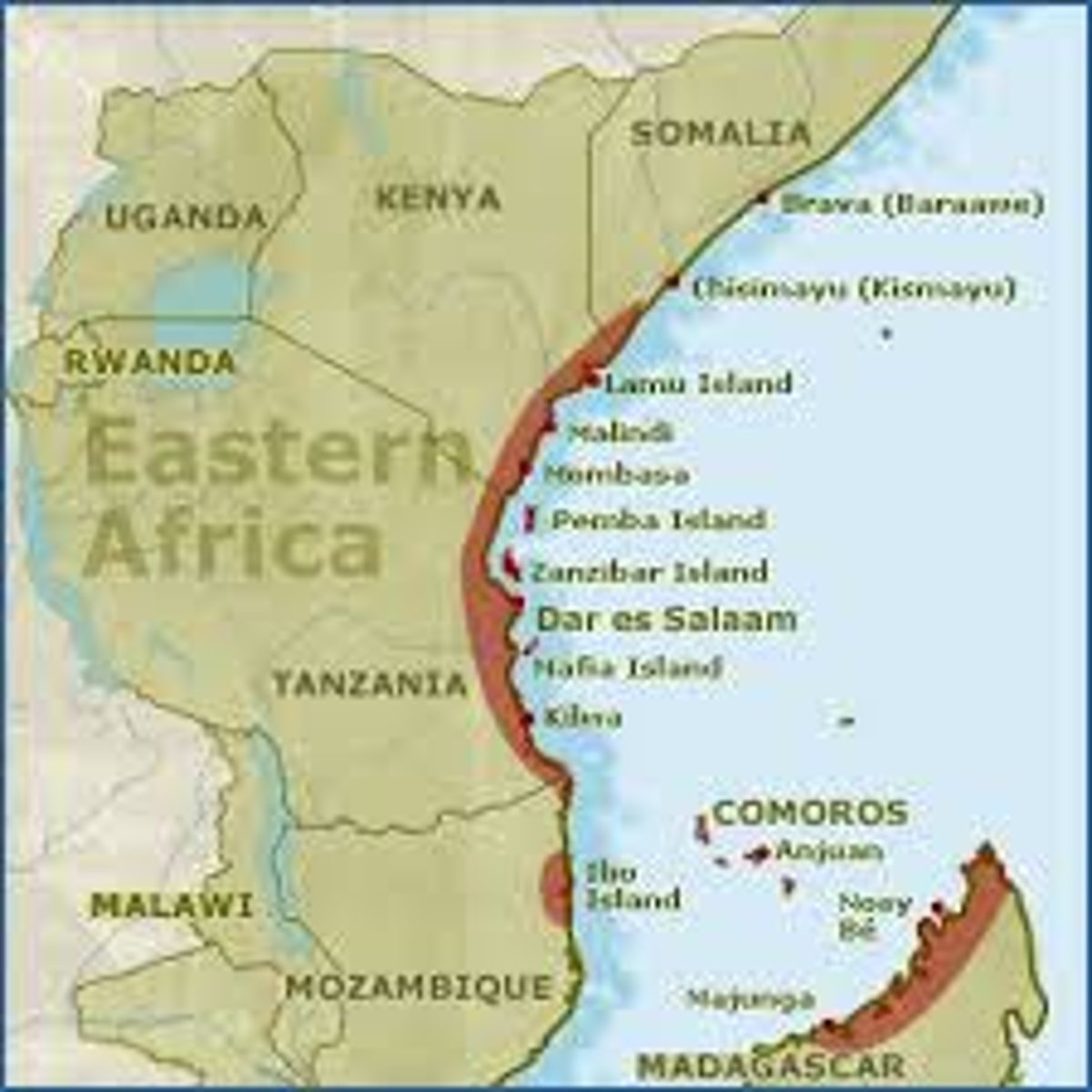
What was unique about the cities of the Swahili kingdom?
-they were each independent and very competitive with each other
-shipping boats were divided up socially and were more organized together.
What examples of cultural integration prove the importance of the Swahili Kingdom's connection to the Indian Trade Routes?
-Non-native merchants/traders were very welcome, even to settle.
-Sometimes elites would boast about their Arab or Persian origins as prestige
-The Swahili language was written with Arab influences(scripts/words)
-art was integrated with their own existing cultures too
What proof exists that the Indian Ocean commerce system impacted the southern parts of the Swahili kingdom?
-less Muslim based but still lots of trade
-places like Great Zimbabwe prospered with giant structures and gold
-bananas helped the cultivation, population growth, and supported the power of the political state
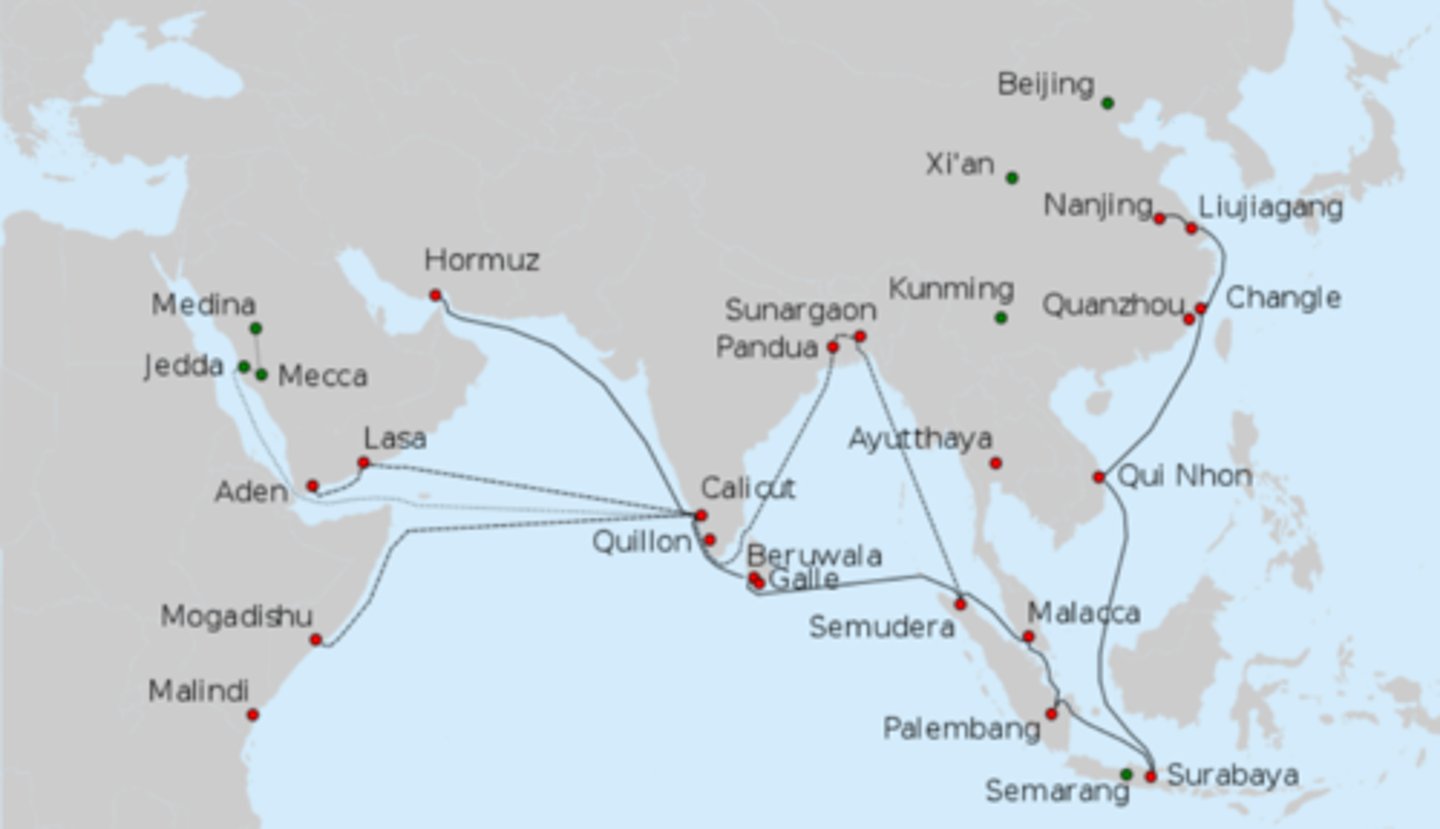
Zheng He
-An imperial eunuch and Muslim, entrusted by the Ming emperor Yongle with a series of state voyages that took his gigantic ships through the Indian Ocean(very powerful ships)
-from Southeast Asia to Africa
-to enroll other countries to China's tributary system
-it showed China's power but did not intervene or create hostility
-it suddenly ended tho
eunuch
a castrated man
Why did the expeditions abruptly end?
1: The Ming emperor Yongle had died. He was the main patron/supporter
2: High ranking officials thought it was a waste since they already were the "middle kingdom"
3: They wanted to focus more on the Northern threats because other areas already know their power and presence
4: Officials viewed the voyage as a project of the eunuch, who they despised
What was the long term consequence on the Indian Ocean trade network of the decision to stop the expeditions?
The take away of the big Chinese influence made it possible for the European entry, like the Portuguese. And then the Ottoman Empire
Sand Roads
A term used to describe the routes of the trans-Sahara trade in Africa.
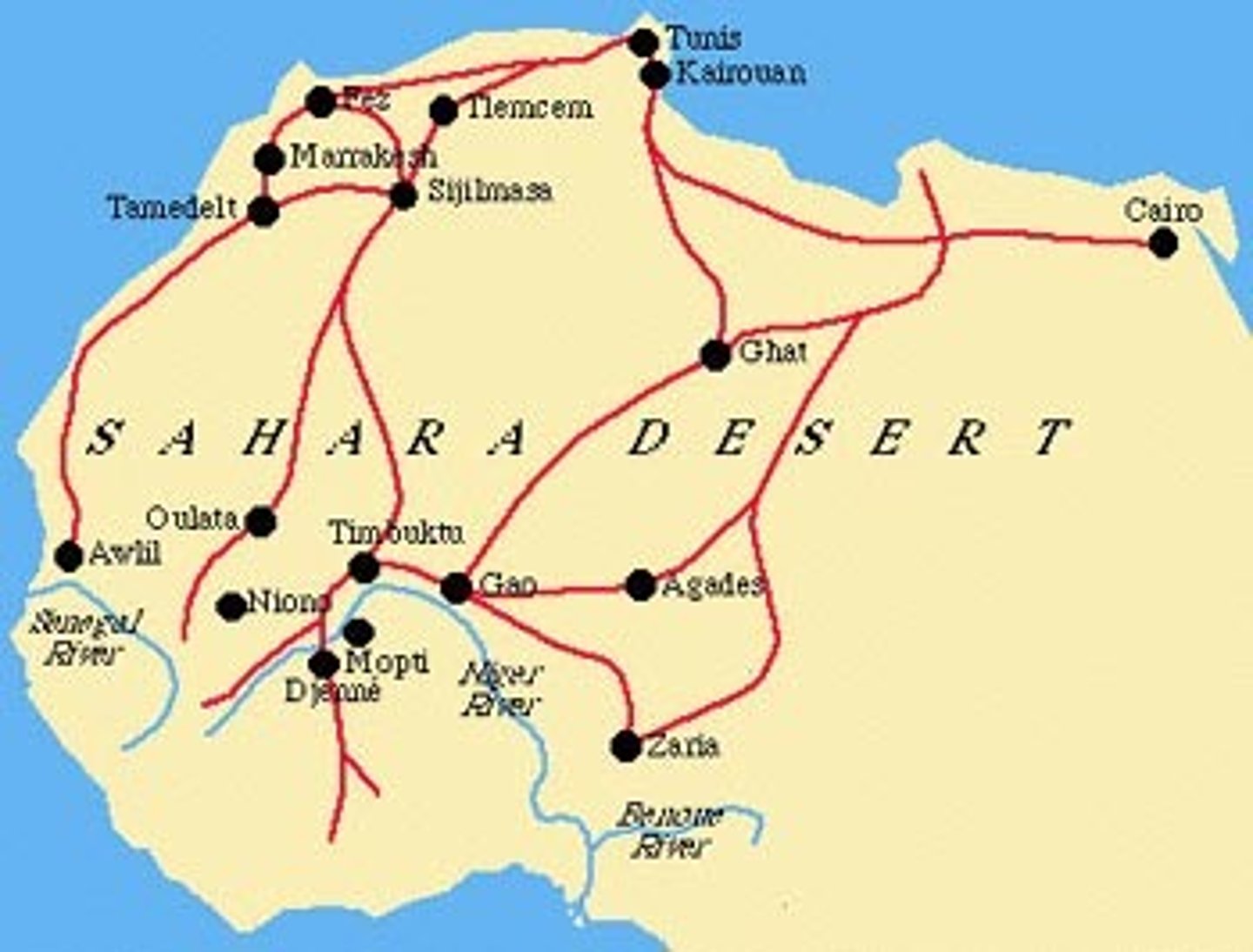
How did geography and environmental variation impact the emergence of the Sand Roads?
different variations of things to sell like
gold, salt, ivory, slaves, food, material
Arabian Camel
A domesticated animal that was widely used in the Sand Roads due to its ability to hold water in it's humps for extended periods of time. These animals only need water every 10 days.
the domesticated one-humped camel, probably native to the deserts of North Africa and southwestern Asia.
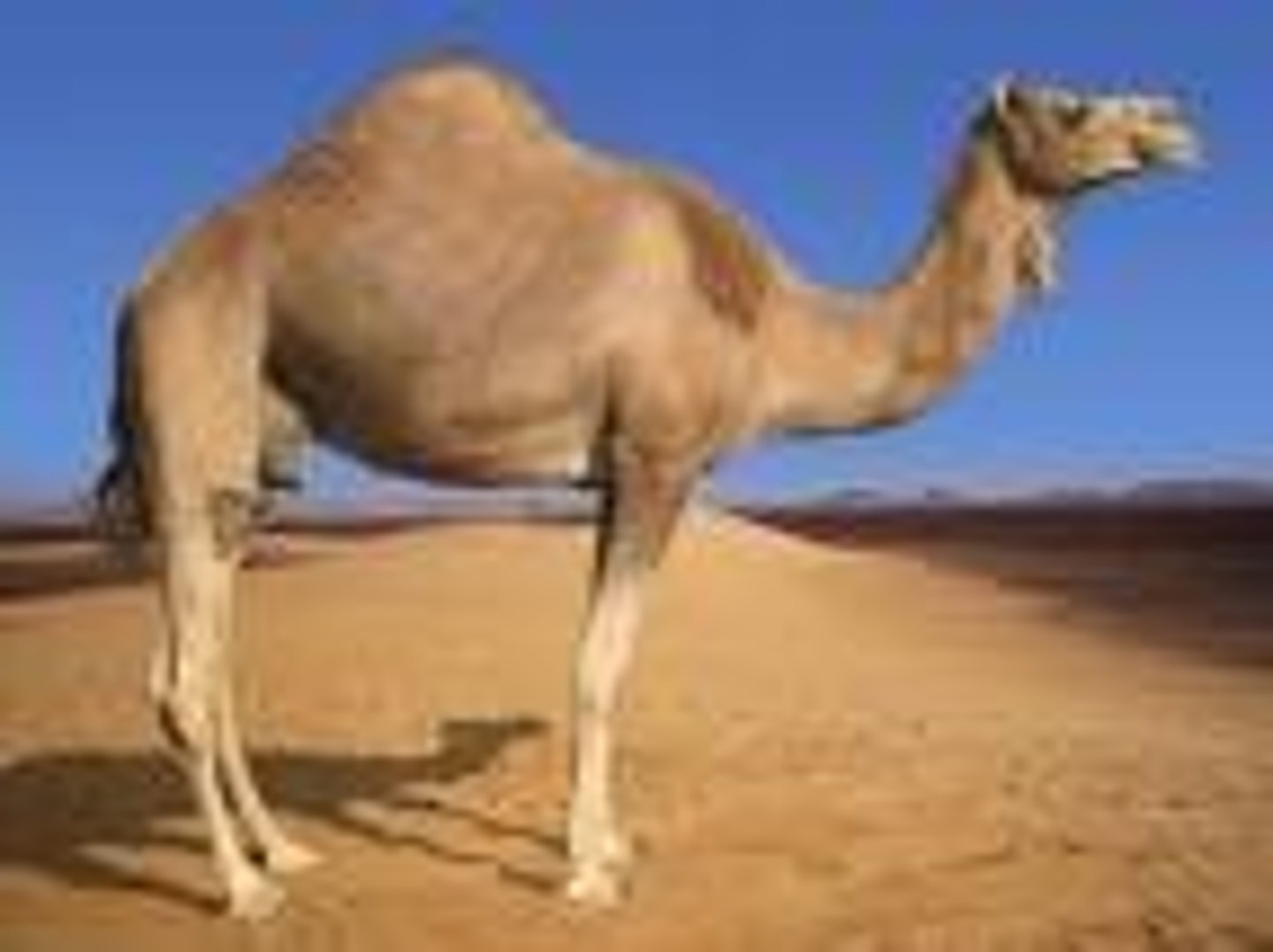

West African Civilizations
-Mali, Ghana, Songhai engaged in salt and gold trade through the Sahara
-Timbuktu: center of learning and trade
-Mansa Musa: spread Islam
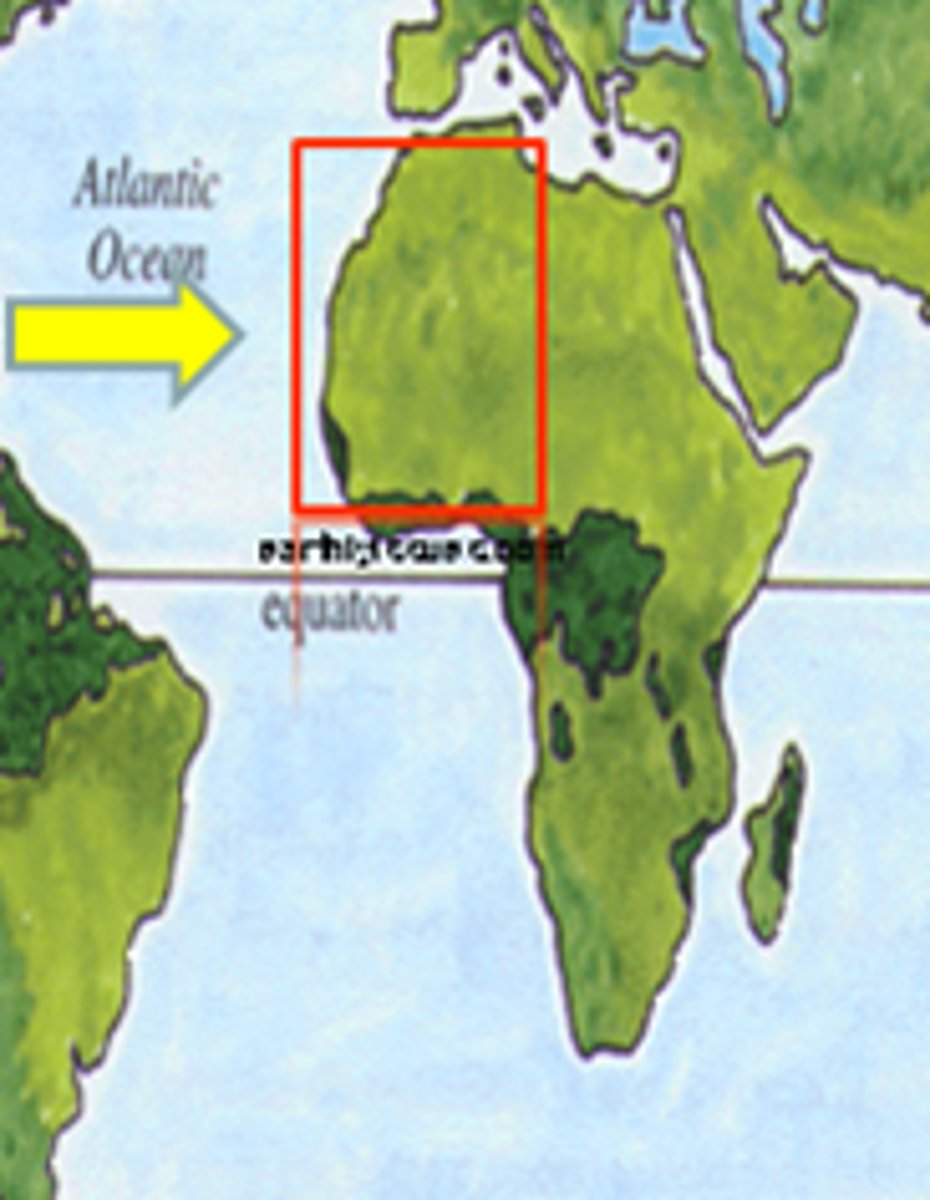
Hausa City-States
Kano, Katsina, Gobir
people of northern Nigeria formed these states;
lived east of Songhai. they built a society based on independent city-states
Economy was based on farming manufacturing and trade.
Mali
Empire created by indigenous Muslims in western Sudan of West Africa from the thirteenth to fifteenth century. It was famous for its role in the trans-Saharan gold trade. Monopolized the trade making them rich
How did the growing integration into the international commerce world impact the development of social hierarchies in West Africa?
what were the lives of women like in West Africa
There was more of a patriarchy stance in higher positions but women were not ass suppressed and had importance in making items, farming, and carrying babies
also most slaves were women working as concubines and domestic servants
trans-Saharan slave trade
A fairly small-scale trade that developed in the twelfth century C.E., exporting West African slaves captured in raids across the Sahara for sale mostly as household servants in Islamic North Africa; the difficulty of travel across the desert limited the scope of this trade.
where were african slaves taken
further south from raids of non-Islamic and stateless societies
Diasporic communities in West Africa
merchant communities that introduced their own cultures into other areas and helped facilitate trade
What was the appeal of Islam to merchants in West Africa? Monarchs?
How was Islam introduced into West Africa?
By Muslim merchants
Peaceful and voluntary from already Islamized North Africa
Mosque
A Muslim place of worship
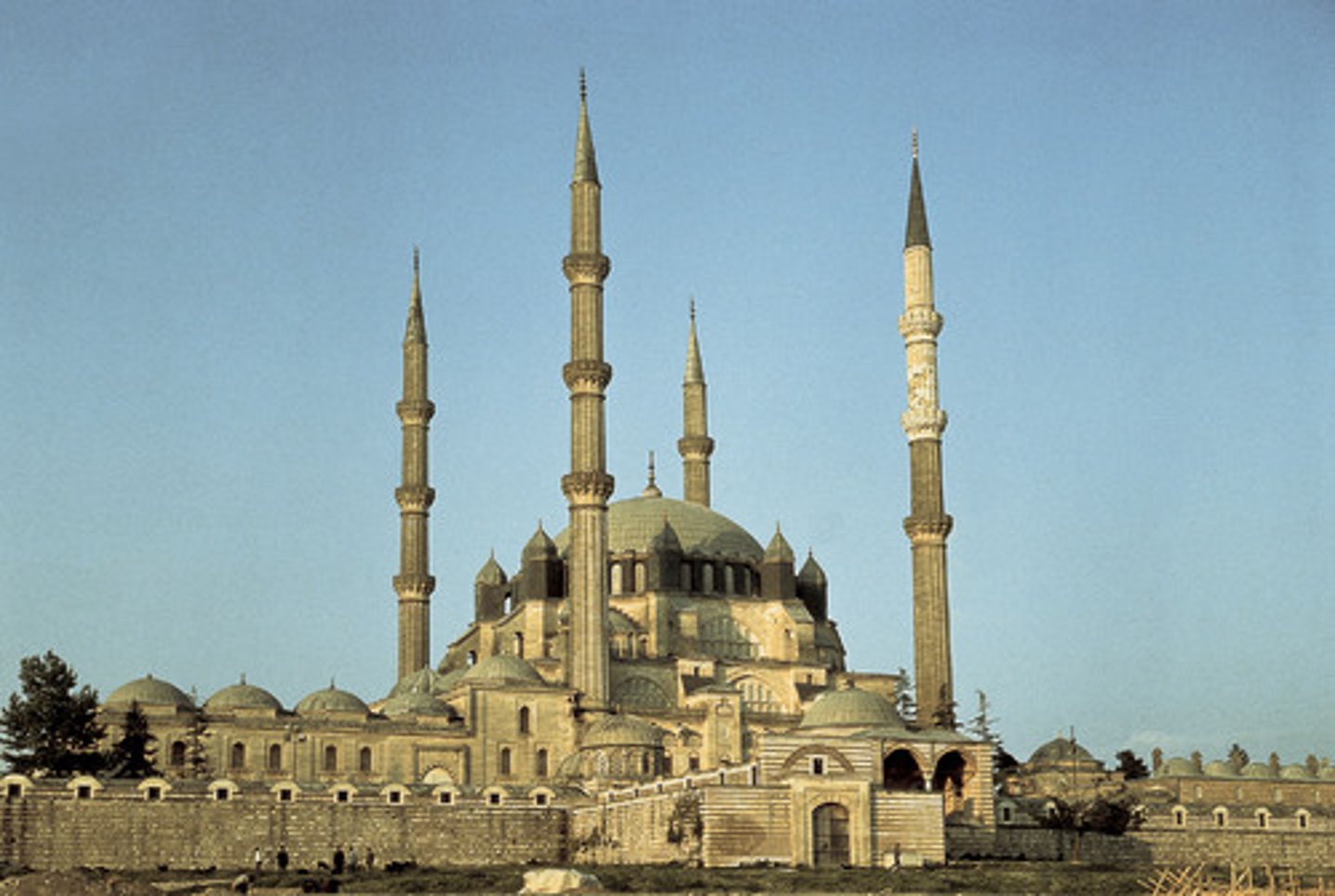

What was the geographic reach of the Muslim merchant network?
-------------
middle, religion, political, center, commerce, pilgrimage, elite
sharia
Islamic law
helped influence commerce
What ecological changes did the Muslim trade network contribute to?
--------------
banking partners, business contracts, credit,
What new technologies, ideas and achievements did the spreading Islamic world contribute to?
-----------
improving, rockets, paper(writing)
What agricultural changes did the Muslim trade network contribute to?
--------------
products, practices, crops, water, urbanization, production, growth
House of Wisdom
An academic center for research and translation of foreign texts that was established in Baghdad in 830 C.E. by the Abbasid caliph al-Mamun.
Mutazalite
Islamic thinkers
reason over revelation
revelation
an enlightening or astonishing disclosure
What factors limited the development of a regional trade network similar to the Silk, Sand and Sea Roads of Afro-Eurasia in the Americas?
---------------------------------------------
not much cultural exchange
no long distance/global commerce or contact
absence of tools to help exploration and long distance trade(boats,animals)
geography(travel,farming)
at least some loose long distance diffusion
American Web
The network of trade that linked parts of the pre-Columbian Americas. Provided a means of exchange for luxury goods and ideas over large areas
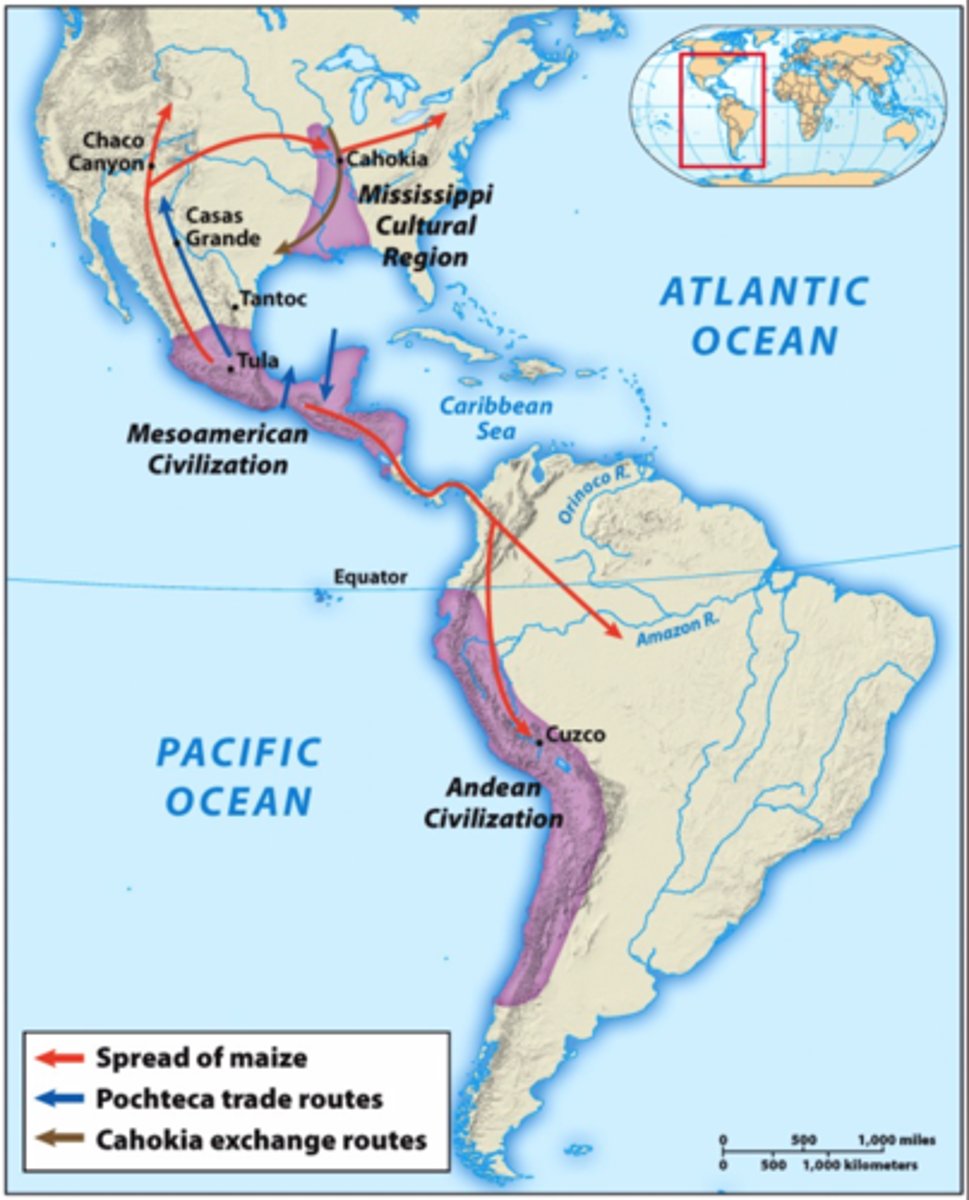
What are the four main nodes of the loose American web of trade?
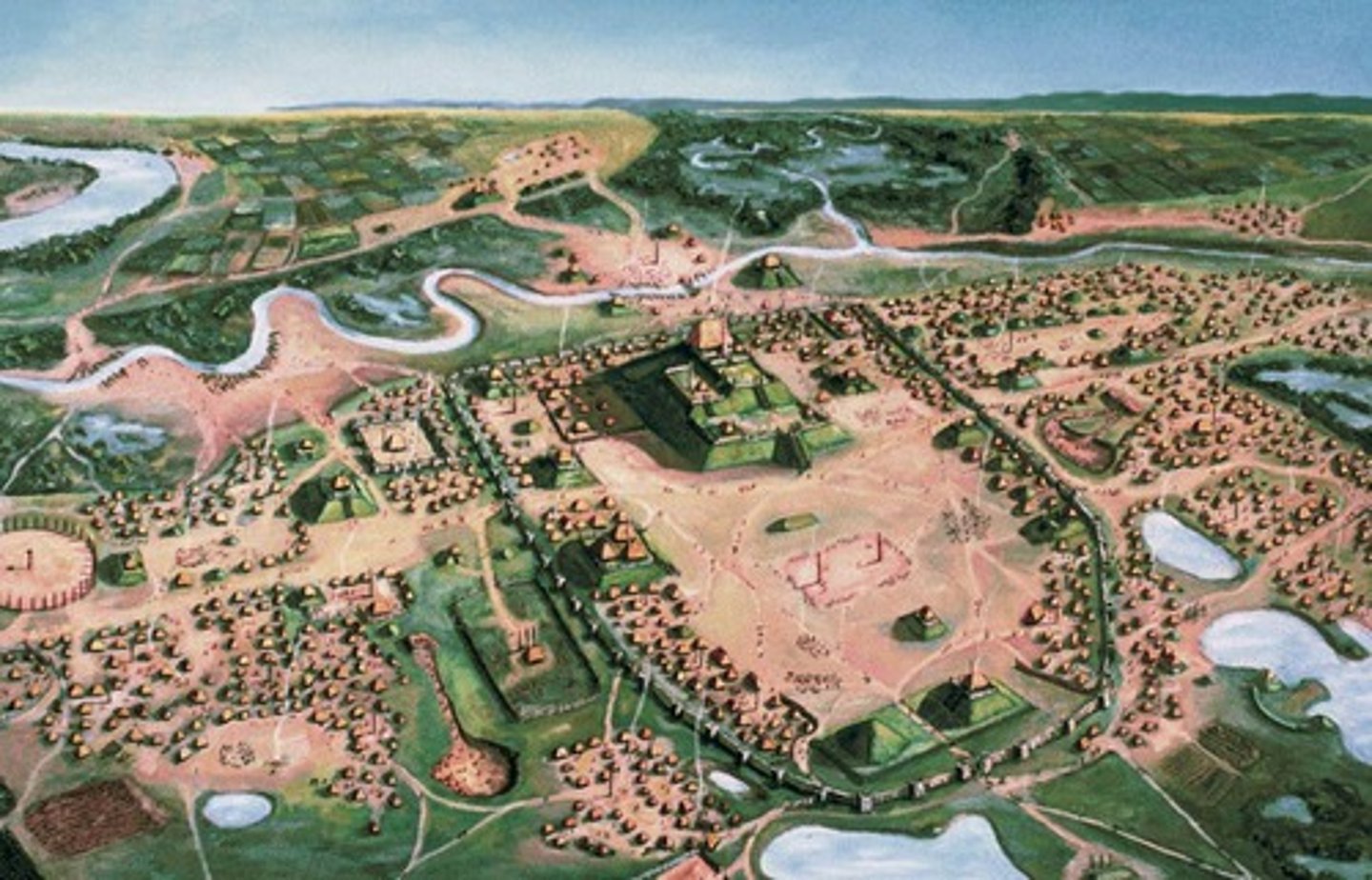
Cahokia
(Mississippians)
-The dominant center of an important Mississippi valley mound-building culture
-located near present-day St. Louis, Missouri
-flourished from about 900 to 1250 C.E.
-Center of the American Web
-they had trade items from all over the area
Chaco Canyon
(Anasazi )
Important ancient Anasazi Indian center in New Mexico that included a pueblo of six hundred interconnected rooms
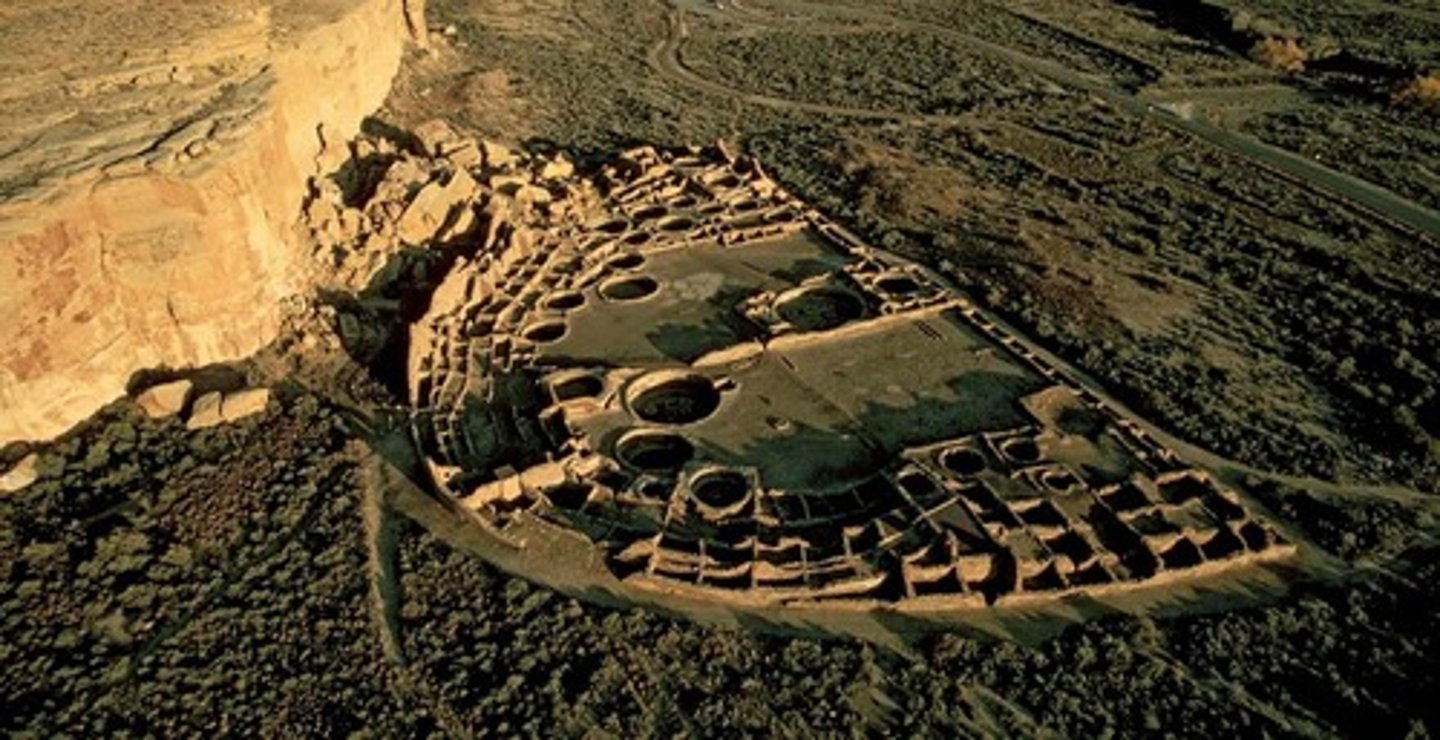

Anasazi
Important culture of what is now the southwest (1000-1300 C.E.). Centered on Chaco Canyon in New Mexico and Mesa Verde in Colorado, the Anasazi culture built multistory residences and worshipped in subterranean buildings called kivas. (pg 308)
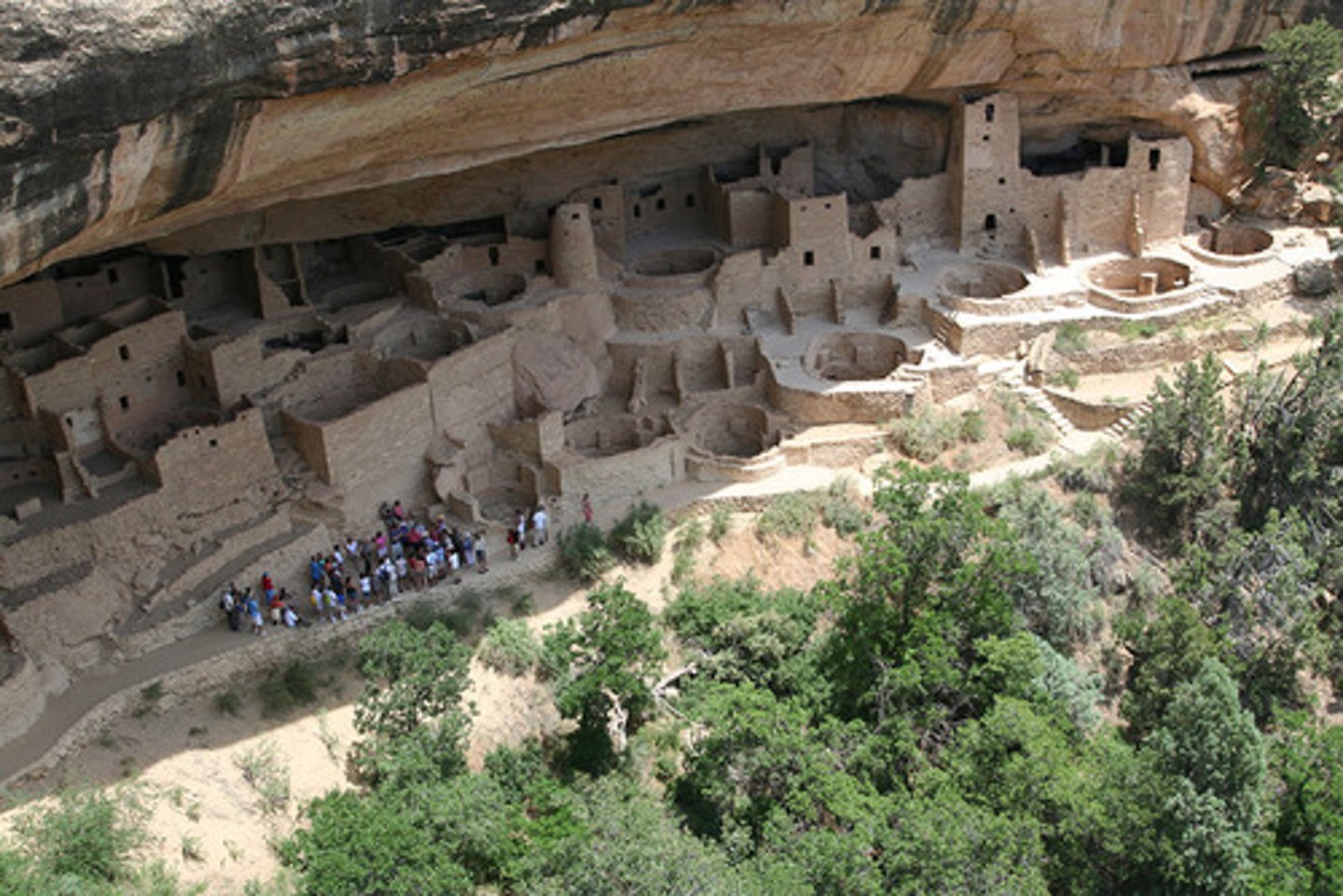

Chaco Phenomenon
Name given to a main process of settlement and societal organization that occurred in the period 860-1130 C.E. among the peoples of Chaco canyon, in what is now Northwestern New Mexico; the society formed there is notable for its settlements in large pueblos and for the building of hundreds of miles of roads. Maybe suggesting trade routes?
Pochteca
Special merchant class in Aztec society; specialized in long-distance trade in luxury items
What evidence exists contributing to the influence of the Cahokia trade network?
What evidence seems to prove the existence of a trade network around Chaco canyon?
How did the trade networks function in the Mesoamerican node of the American web?
How was trade different in the Inca node?
What are the differences between the pre-modern and modern globalized world of trade?
Most people still produced for consumption rather than sale
A much smaller range of goods were traded at market
Fewer people had to sell their labor for wages
Most trade as in luxury goods due to cost
Circuits of trade were geographically limited
Trade was not dominated by one region and inequality was less obvious between regions of the world
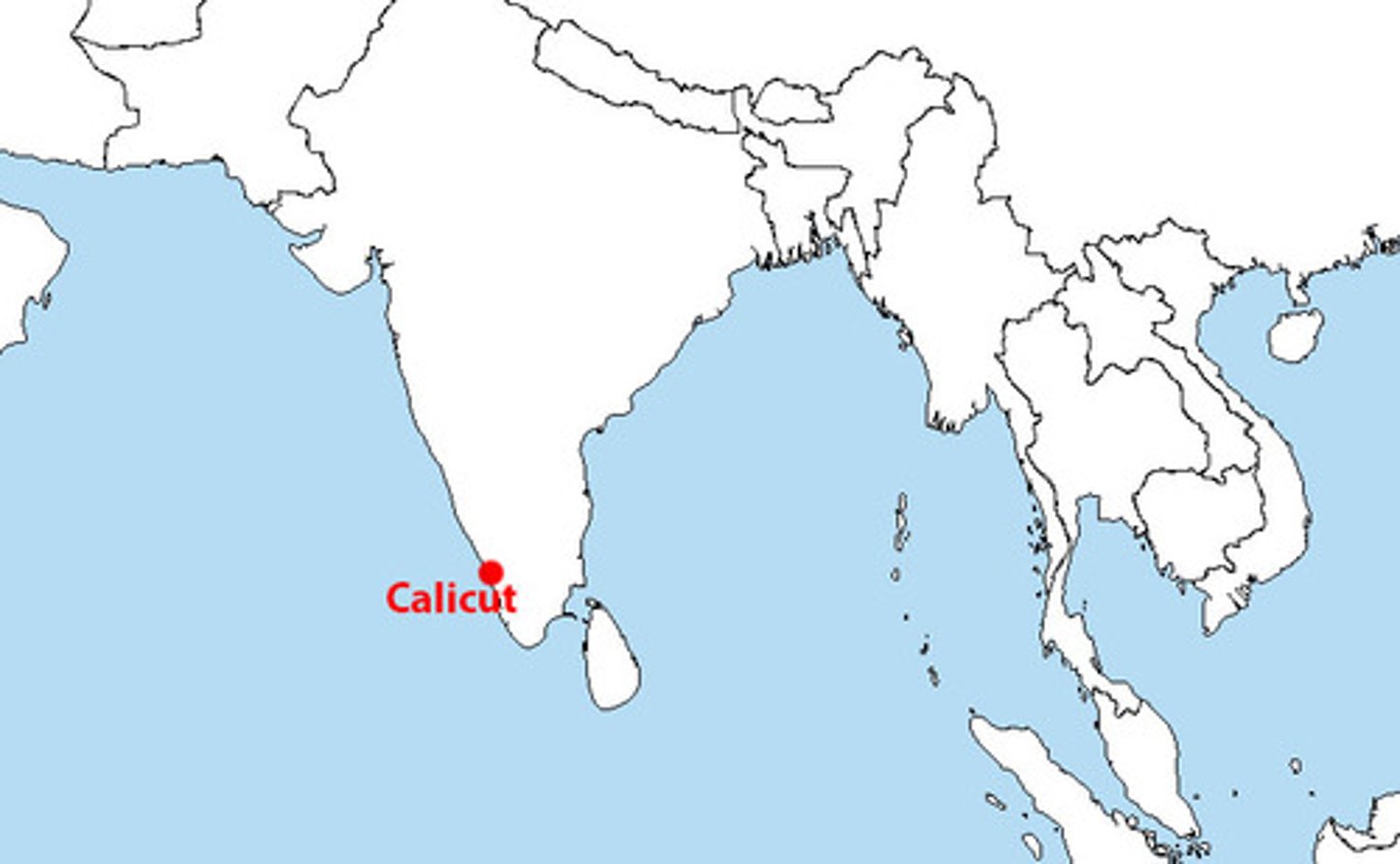
Calicut
A city of southwest India on the Malabar Coast southwest of Bangalore
Tenochtitlan