What is a catabolic reaction?
Breaking larger molecules down into smaller ones
What is an anabolic reaction?
Building smaller molecules up into larger ones
What is an isomer?
A molecule with the same chemical formula but appears differently in atomic space
What is a condensation reaction?
Water is released when joining two monomers together.
What is a hydrolysis reaction?
Water is used to break apart monomers.
Monomer
A molecules most basic unit.
Polymer
Large complex molecule made up of long chains of monomers joined together
Polymerisation
Monomers bind to each other to form repeating chain molecules called polymers
Macromolecules
Large molecules with a high molecular mass and specific 3D structures and functions such as proteins.
Are all macromolecules polymers?
No
Are all polymers macromolecules?
Yes
What is the monomer of protein?
Amino acids
What is the polymer of protein?
polypeptide chain
Examples of proteins
Enzymes, Antibodies, Structural (Keratin/Collagen), Haemoglobin
What are the three groups found in the structure of an amino acid?
An amine or amino group
A carboxyl group
A variable side group
What is the formula for an amino group?
NH2
What is the formula for a carboxyl group?
COOH
What is the formula for a variable side group?
R
What is a Dipeptide?
It is two amino acids joined by a peptide bond
What is a polypeptide?
More than two amino acids joined together
What is a peptide bond?
It is a bond that connects two amino acids together
How many amino acids are there?
20
How many non essential amino acids are there?
9
How many essential amino acids are there?
9
What is the primary structure of protein formation?
The initial sequence of amino acids bonded by peptide bonds in a polypeptide chain
What is the Secondary structure of protein formation?
Hydrogen bonds form between nearby amino acids between the amine group of one amino acid to the carboxyl group of another within the polypeptide chain. The interaction causes folding of the chain.
What is the Tertiary structure of protein formation?
The folded polypeptide chain coils and folds resulting from interactions between the R groups with giving the protein a 3D structure.
What is the Quaternary structure of protein formation? (only some proteins)
This structure results from the interaction of multiple polypeptide chains held together by bonds.
What are the two shapes which can be formed from folding in the secondary structure of protein formation?
Alpha helix or beta-pleated sheet
What are the five types of bond which can be formed between the R groups int he tertiary structure of protein formation?
Hydrogen bonds, disulphide bonds, ionic bonds and polar interactions, hydrophobic interactions
What are the two groups of protein?
Globular and Fibrous
Describe globular proteins
Spherical, hydrophobic inside and hydrophilic outside, water-soluble, enzymes hormones and transport proteins, can denature easily
Describe fibrous proteins
Long and thin, strong and insoluble, do not denature as easily, structural proteins, collagen, keratin, elastin
What does an Alpha-glucose look like?
What does a Beta-glucose look like?
What does Ribose look like?
What does Deoxyribose look like?
What is the structure and function of Alpha-glucose?
Hexose, energy source/store
What is the structure and function of Beta-glucose?
Hexose, structural
What is the structure and function of ribose?
Pentose, RNA, ATP,NAD
What is the general formula for carbohydrates?
Cn(H2O)n
What are the monomers of carbohydrates?
monosaccharides
What is the polymer of carbohydrates?
polysaccharides
What is a polysaccharide?
A long chain of sugar molecules
What are the subunits of polysaccharides called?
monosaccharides
Give three examples of monosaccharides?
Glucose, fructose, galactose
What are two monosaccharides called?
disaccharide
What reaction forms a disaccharide?
Condensation (lost of water)
What bond connects monosaccharides?
glycosidic
Give two examples of disaccharides?
Sucrose, lactose
What monosaccharides are sucrose made from?
Alpha-Glucose and fructose
What monosaccharides are lactose made from?
Alpha-Glucose and Beta-galactose
What monosaccharides are maltose made from?
Alpha-glucose and Alpha-glucose
Give three examples of polysaccharides?
glycogen, amylose and cellulose
What two polysaccharides make up starch?
Amylose and amylopectin
What glucose is amylose made from?
Alpha
What glucose is amylopectin made from?
Alpha
What glucose is glycogen made from?
Alpha
What glucose is cellulose made from?
Beta
Where is starch found and what is it used for?
Energy source and store in plants
Where is glycogen found and what is it used for?
As an energy source and store in the liver and muscles of animals
Where is cellulose found and what is it used for?
Structural support in the cell wall of plants
What is the shape of Amylose?
Coiled
What is the shape of Amylopectin?
branched every 20
What is the shape of glycogen?
branched every 10
What is the shape of cellulose?
linear structure
What are the bonds in amylose?
1,4
What are the bonds in amylopectin?
1,4 and 1,6
What are the bonds in glycogen?
1,4 and 1,6
What are the bonds in cellulose?
1,4
Why are starch and glycogen good storage polymers?
They are compact and insoluble
What are 4 examples of reducing sugars?
Galactose, glucose, fructose, maltose
Give an example of a reducing sugar?
Sucrose
What is the test for reducing sugars?
Add benedicts and heat
What is the test for non-reducing sugars?
Add HCL heat solution, add sodium hydrogencarbonate, re-test with benedicts
What is the positive result for a sugar test?
Blue to brick-red
Are lipids polymers?
No
Are lipids macromolecules?
Yes
What are the monomers of lipids?
Fatty acids
What is the definition of saturated?
When the carbon atoms are bonded to the maximum number of hydrogens ad there are no carbon-carbon double bonds.
What is the definition of unsaturated?
When the carbons are not bonded to the maximum number of hydrogens and there are double or triple bonds, this causes the chains to bend.
What are the properties of saturated fats?
High melting point, forms solids at room temperature.
What are the properties of unsaturated fats?
Low melting point, more likely to be liquid at room temperature, used as energy stores in plants, healthier.
What are the three types of lipids?
Triglycerides, phospholipids and cholesterol
What is the structure of a triglyceride?
One glycerol molecule and three fatty acids joined with ester bonds
What is the function of triglycerides?
They are the main part of body fat found in animals, they are good stores of energy
What is the structure of phospholipids?
One glycerol, one phosphate group, and two fatty acids joined to the glycerol with ester bonds
What do the glycerol and phosphate group make up in a phospholipid?
the external hydrophilic head
What do the fatty acids make up in a phospholipid?
the internal hydrophobic tail
What is the function of phospholipids?
They make up the bilayer of cell membranes. The hydrophilic head and hydrophobic tail allows them to form this.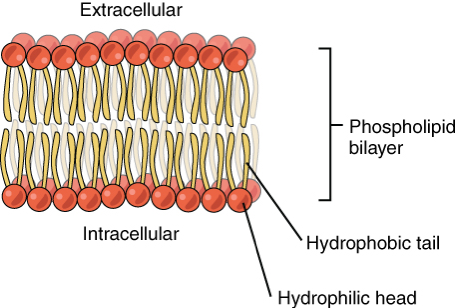
What is cholesterol?
A waxy, fat-like steroid hormone produced by the liver.
What is cholesterol made from?
4 carbon based rings called isoprene units
Where is cholesterol found?
in the middle of the hydrophobic bilayer of the cell membrane
What does cholesterol do?
Regulate the fluidity of the cell membrane
Where is cholesterol found in plants and what is different about it?
In the derivative membranes, it has an extra carbon double bond and is called stigmasterol.
What are three examples of steroid hormones made from cholesterol?
Oestrogen, testosterone, Vitamin D
What is the test for lipids?
The emulsion test (ethanol)
What is the positive result of a lipid test?
Colourless to milky
What is the monomer of nucleic acid?
nucleotides
What is the polymer of nucleic acid?
DNA or RNA