Hazardous Exam 1
1/79
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
80 Terms
The major concerns with hazardous materials is the involvement in a ________, ________/toxicity, or in a ________.
fire, ingestion, spill
Wet chemicals like (KOAc) are used for Class K fires because they turn the grease into _______ (saponification)
soap
Flammability by state is ________ > ________ > _____.
gas, liquid, solid
1 lb = ________ g
1 qt = _______ mL
454, 946
Density defines the ____________ of an object.
compactness
Specific gravity = density/d(________)
water
Immiscible liquids with d > 1 will ________.
sink
Vapor density = d(gas)/d(_____)
air
Gases with vd > 1 will ____.
sink
Kelvin and Rankin are ________ scales.
absolute
Pressure = ________/area
force
A psig = 0 does not mean the container is ________.
empty
Normal boiling occurs when the VP = _(___)
P(atm)
BP _______ as external pressure increases.
increases
Kinetic energy is due to ________ motion.
molecular
Black body radiation is the EM energy that is emitted by an object due to ________. The higher the temp, the longer the ____________.
temperature, wavelength
Class 1 - _________
Explosives
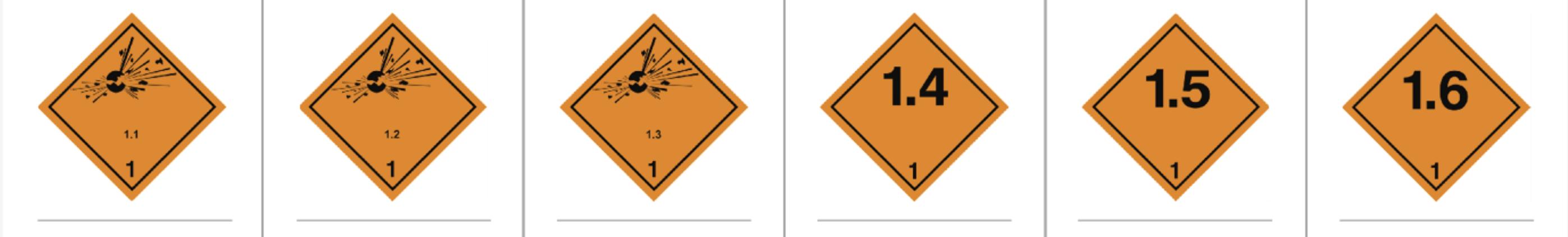
Class 2 - ____________ _______
compressed gases

Class 3 - ____________ _______ (based on ___ and ___)
Flammable liquids, bp, fp

Class 4 - ____________ _______ (based on ______ test and _____ reaction)
flammable solids, flame, water
Class 5 - ____________ (_______ or reaction compared to ________/oxidizer mixture)
oxidizer, pressure, cellulose
Class 6 - __________/_______ (based on _____)
poison/toxic, ld50

Class 7 - ____________ (based on _________ _____________)
radioactive, surface activity

Class 8 - ____________ (based on _____ or ________ reactivity)
corrosive, skin, steel

Class 9 - ____________
miscellaneous
Types of thermal energy transport:
conduction: the transfer through ____ ______ between objects. (ex. touching a stove)
convention: the transfer through a ________. (ex. fireplace)
radiation: ___ electromagnetic waves emitted by warm objects.
flashover
direct contact, medium, IR
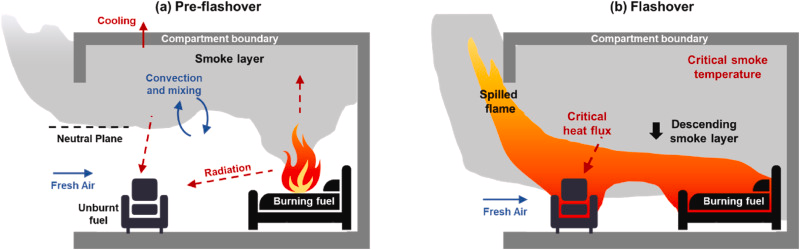
First Aid - Burns
first degree: red skin (______)
second degree: outer layer is damaged
third degree: skin is charred and requires skin grafts
2nd and 3rd first aid: flush with ___ _____ for at least 10-15 mins.
ice, cool water
__________ _________ is when solids/liquids/gases expand when heated due to increased molecular motion.
thermal expansion
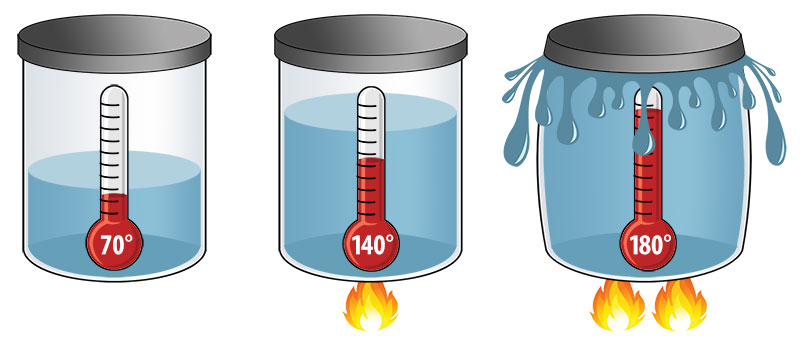
BLEVE - boiling liquid __________ __________ explosion
expanding vapor
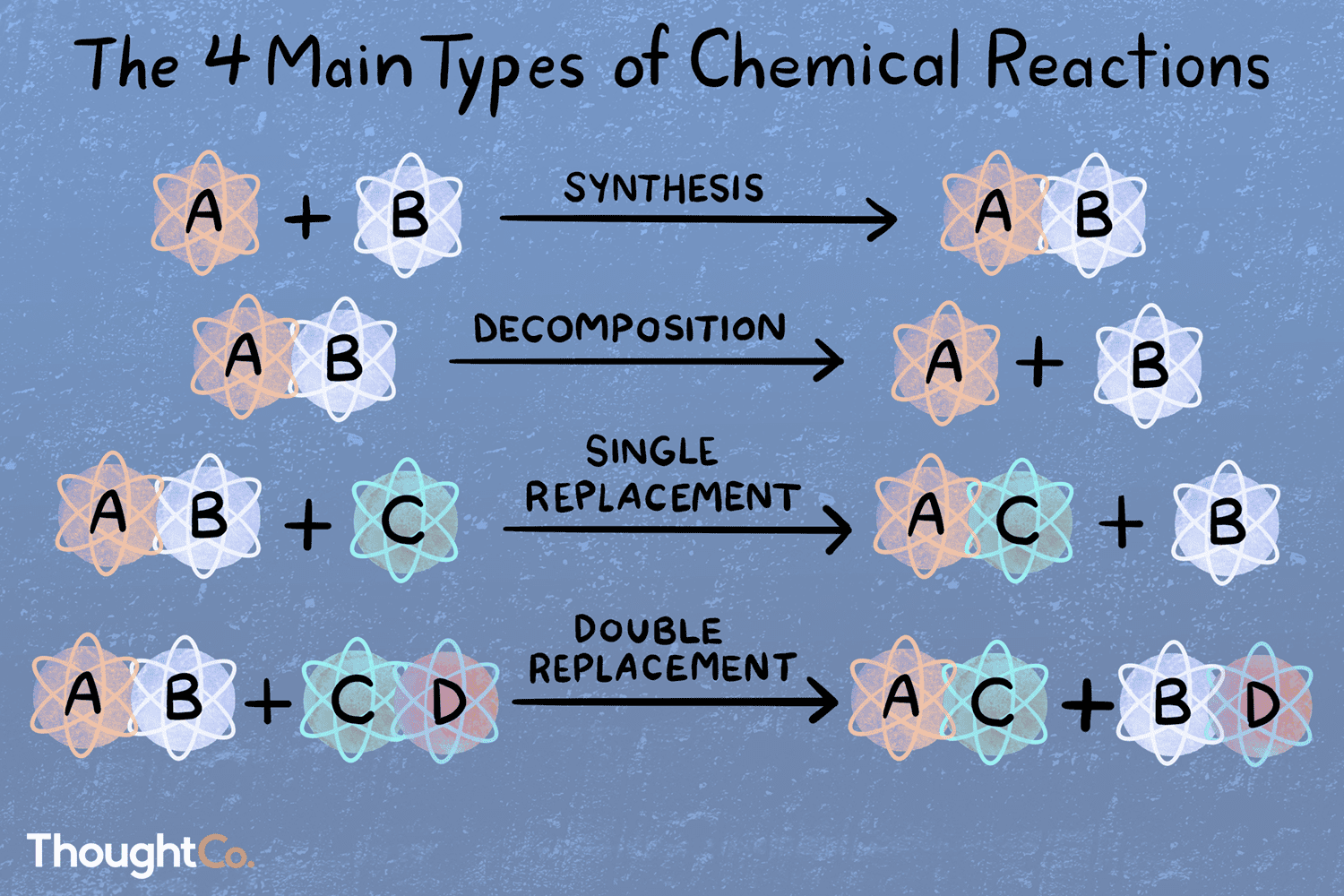
Types of chemical reactions:
________
____________
________ replacement
________ replacement
synthesis, decomposition, single, double
Factors affecting the rate of reaction:
______________
rate doubles for each 10 C
_______ of the reactants
the larger the surface area —> the faster the reaction
state of __________
gas > liquid » solid
concentration of _________
rate increases with []
_____________ energy (Ea)
temperature, subdivision, aggregation, reactants, activation
RCRA characteristics of reactivity
undergoes a _________ change without _____________.
reacts violently with __________
forms explosive mixtures with ________
is capable of detonating at _____________ temperature and pressure.
is capable of detonating by a catalyst or _______.
violent, detonating, water, water, regular, heat
Statues involving Household Products
CPSC - Federal Hazardous Substance Act —> _________ household products
FDA - Food, Drug, & Cosmetic Act —> prohibits __________
EPA - Insecticide, Fungicide, & Rodenticide Act —> regulates __________
EPA - Toxic Substance Act —> regulates current and new __________
labeling, carcinogens, pesticides, chemicals
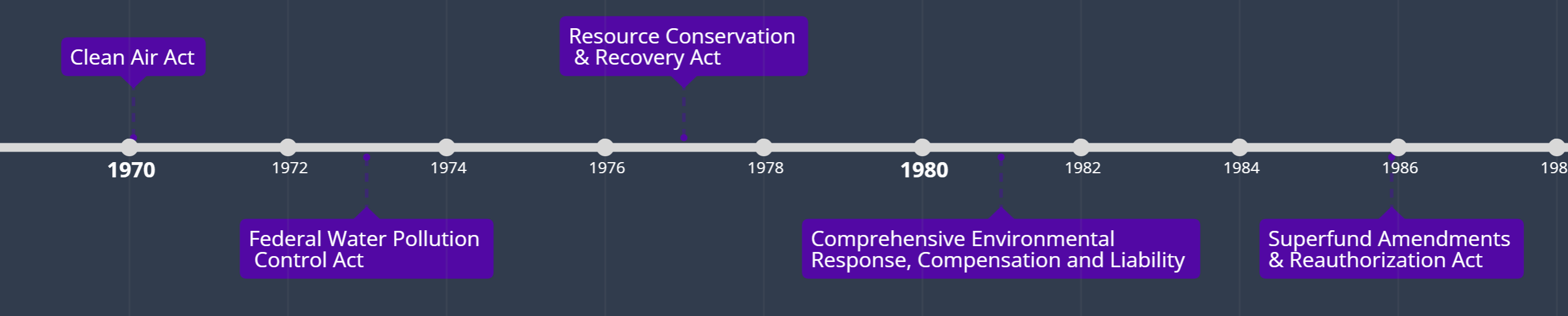
Federal Statues Involving Pollutants and Wastes
EPA - Clean Air Act —> established national ______ quality standards. (SO2, CO, O3, NOx, Pb)
EPA - Federal Water Pollution Control Act —> established national ________ quality standards
established the ________ ___________ Center (Coast Guard).
sole federal point of contact for reporting ___-___ _______.
EPA - Resource Conservation & Recovery Act (RCRA) —> regulates ______________ _______.
EPA - Comprehensive Environmental Response, Compensation and Liability
legislation for the ________ of hazardous waste sites. (paid for by the manufacturers)
EPA - Superfund Amendments & Reauthorization Act (SARA) (Love Canal)
establishes programs for __________ and __________.
air, water, national response, haz-mat spills, hazardous waste, cleanup, training, education
Federal Statues Involving the Workplace
________ (1970)
Warning Labels, and ___s
OSHA, SDS
Federal Statues Involving Transportation
DOT —> Hazardous Materials Transportation Act (1970)
regulates __________ ________
chemical shipping
Four US authorities that have jurisdiction over labeling:
___
___
____
____
DOT, EPA, OSHA, CPCS
Federal Statues involving Communities
EPA - ______-____-______ Act (1986) —> established ___________ _________ _________ __________ (LEPC)
right-to-know, local emergency planning committee
EPA - National Environmental Policy Act (1969) —> requires ______________ ______ _____________ (EIS)
big projects need to petition the government by sending in a statement
Title I: EIS
Title II: provides rules for federal agencies
Title III: provides advice for the EPA/Senate.
environmental impact statements
CHEMTREC (______________ ___________ _________ ______) - 24/7 help with emergencies and contracts
chemical transportation emergency center
CFR Titles
Title 21: ________ and ______ (schedule I & II)
Title 29: ____ (OSHA)
Title 37: ________, _______, and ____________
Title 40: Protection of ____________ (EPA)
Title 44: Emergency _____________ and ________ (RTK/LEPC)
Title 49: ____________ (DOT/HAZMAT)
food, drug, labor, patents, trademarks, copyrights, environment, management, assistance, Transportation
49 CFR
Part 172: ____________ ________ ______
Part 173: Hazardous ______ Definitions
hazardous materials table, class
29 CFR
Part _____/______ - safety and health regulations.
1910, 1926
40 CFR
Part 261 - List of ____________ ________
Part 262 - classification of waste generators (_ levels: amount of waste per year)
hazardous wastes, 4
704 Hazard System Symbols
OX: __________
W: reacts __________ with waterCOR: __________
☢: __________
SA: simple __________ ____
ACD: __________
ALK: __________
P: __________ __________________ (hot monomers)
oxidizer, violently, corrosive, radioactive, asphyxiant gas, acidic, alkaline, exothermic autopolymerization
HSSQ Rating: dangerous when it is greater or equal to ___.
15
the official ___________ ______ is listed in the Hazardous Materials Table (49 CFR)
shipping name
shipping papers fall into _______ hazardous classes (_>__>___)
three
__ CFR ___.___ requires carriers to obtain Hazardous Materials Safety Permits for interstate/intrastate commerce.
49, 385.400
Class 7 is categorized by SA which is _________ (mSv).
7.1: SA < ________ mSv
7.2: SA < ________ mSv < (7.3)
millisieverts, 0.005, 0.5
Class 8 includes acids/bases with pH≤ _ or pH ≥ ___
2, 12.5
Class 9 includes ____ ____ and _______ ___________.
dry ice, marine pollutants
Companies must report releases of hazardous substance to the ___________ _____________ ____________ if:
amount is above ________ quantity
release involves ________ or _________________
damage exceeds $___________
accident involves ____________ material
release of _________ pollutant above threshold quantity.
national response center, threshold, death, injury, 50000, radioactive, marine
Fire Classification
Class A: ordinary _______ materials (embers/coals)
extinguish with: ___________
Class B: ____________ liquids and gases
_______ (vroom), _________ (ABC Store), methane
extinguish with: ____, dry chemicals
Class C: combustion due to live __________ ________
extinguish with: ____, dry chemicals
cellulose, water, flammable, gasoline, alcohol, co2, electrical circuits, co2
Fire Classification
Class D: combustion of certain _______
__, Mg, Zr, __
extinguish with: graphite, _____
Class E: “__________” media
_________ and animal oils/fats
extinguish with: wet chemicals (water + KOAc)
metals, Ti, Na, NaCl, kitchen, vegetable
Carbon Combustion
complete combustion produces mainly carbon _______
incomplete combustion produces mainly carbon ____________.
Soot is unburnt fine ___________ particles
dioxide, monoxide, carbon
The Fire Tetrahedron includes ____ + ________ + Heat + ______ ____________.
fuel, oxidizer, free radicals
Fire Extinguishers
water extracts ______
foam extracts ______ ______ and O2
CO2 extracts O2 and ______
Halons (CFCs) remove ______ ________
Dry chemicals/powders remove ______ and ______ ________
Wet Chemicals remove ______.
heat, free radicals, heat, free radicals, heat, free radicals, air
Flammability: for liquids and solids, the amount of vapors depends on ____________ and ______ pressure.
temperature, vapor
The ______ the flammability range (UEL-LEL) the more dangerous the material.
larger
Flash Point is the ____________ temperature of a liquid that produces sufficient vapors for ignition. The Fire Point is usually ______ than the FP.
minimum, higher

Class ____
__, acetylene, ___
2.1, H2, CH4

Class ___
___, He, __
2.2, CO2, O2

Class ___
___, phosphine, __
2.3, HCN, F2
Responding to Disaster (compressed gases) (must know):
contents/size of ___
_________ of contents
overall _______ of gas
availability of ________
Population _________
_________ conditions
contents support ____________ (fire) or are ______ (vial of murder)
leak, hazard, volume, water, density, weather, combustion, toxic
Responding to Disaster (general response) (compressed gases):
no fire: _______ the leak
near a fire: _________ the tank and keep _____
In/On Fire: __________
control, remove, cool, evacuate
Cryogenic Liquid - ___________ at reduced temperatures (BP < _______ F)
examples: He, N2
need _______ _______ valves
_________: double-walled vessel under vacuum
hazard: high ___________ rate, tissue damage
First Aid: flush with tepid ________.
liquefied, -130, pressure relief, dewar, expansion, water

Class __-_
FP < ______ F
IA-C, 100

Class __ and ___-_
FP ≥ _____ F
II, IIIA-B, 100
For Class 3I, the liquids should be dispersed from ________________ ___________ containers.
electrically grounded
Transporting Flammable Liquids (DOT regulations)
pressurized or non —> prevents _________
shielded or non —> prevents ______________
single or double walled —> prevents __________
boiling, overheating, punctures

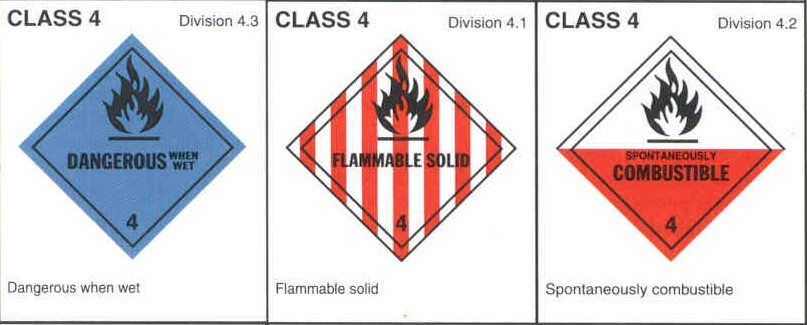
Class __ - Flammable Solid
4.1

Class ___ - Spontaneously Combustible
4.2

Class ___ - Dangerous When Wet
4.3

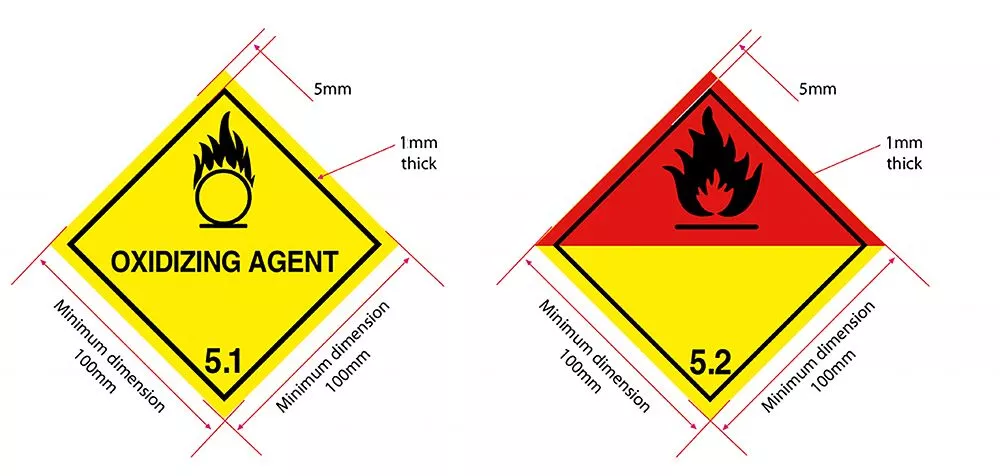
Class 5.1 - __________
oxidizer

Class 5.2 - ____________ ___________
Organic Peroxide

Class ___ - Poisonous Material
6.1

Class ___ - infectious material
6.2

Radioactive Class has ________ sections.
three