StemUp: AQA A level Biology 3.5.4 Nutrient cycles
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
What are the two cycles you need to know that exemplify how nutrients are recycled in an ecosystem? (2)
- Nitrogen cycle
- Phosphorus cycle
Draw a simplified diagram of the nitrogen cycle (10)
NOTE: Practise drawing this out to memorise it, exam questions will usually only ask you for parts of this diagram as its so big!
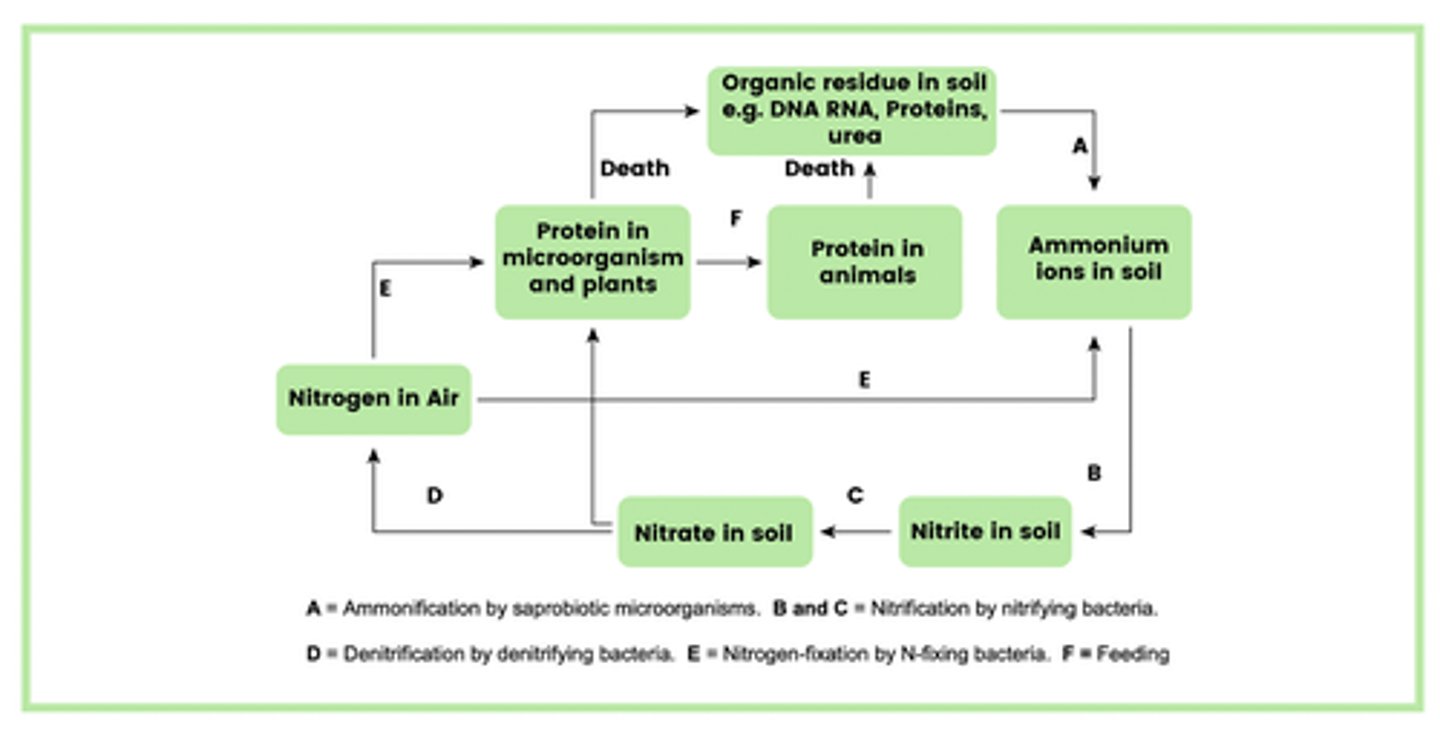
What is the role of saprobiotic microorganisms in decomposition? (3)
- Use enzymes to break down proteins in animals
- To form organic residues (ammonia) in soil
- That can be recycled
What are the sources of proteins that saprobiotic microorganisms break down? (2)
- Waste products e.g. urea and faeces
- Dead animal remains
What is the role of saprobiotic microorganisms in ammonification? (2)
- Ammonia in the soil
- Will then form ammonium ions via ammonification
What is the role of nitrogen fixing bacteria? (1)
Live free in the soil and 'fix' nitrogen into ammonia/ammonium compounds
What is the role of nitrifying bacteria? (2)
- They will oxidise ammonia and ammonium ions in the soil into nitrites and then nitrates
- Nitrates are absorbed by plant roots by active transport
What are the nitrates that are absorbed by plant roots via active transport used for? (2)
- Provide the source of nitrogen for plants
- So that they can synthesise proteins and nucleic acids
What is the role of denitrifying bacteria? (1)
Convert nitrites and nitrates in the soil back into atmospheric nitrogen after a plant has decomposed
Draw a simplified diagram of the phosphorus cycle (10)
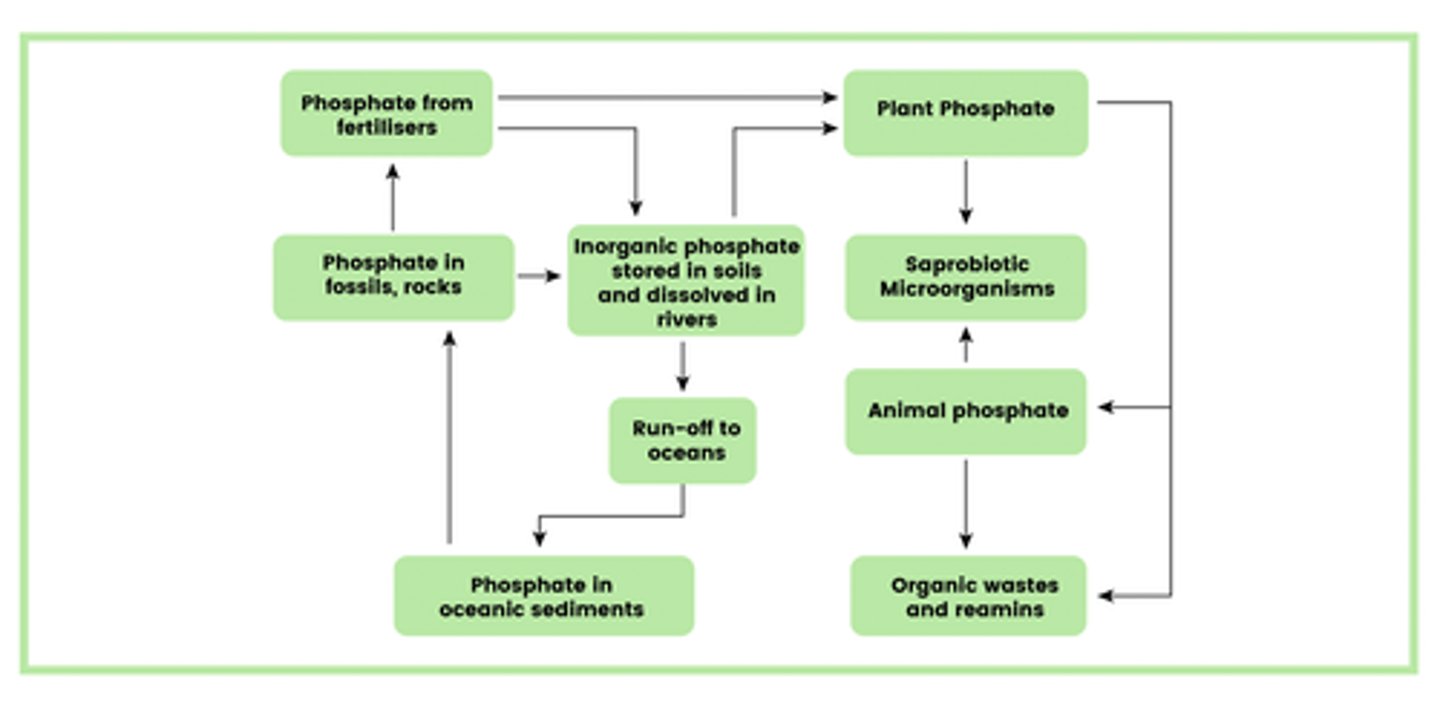
How are phosphorus ions released into the soil and water sources? (2)
- Phosphorus in rocks
- Slowly released into soil and water sources
- In the form of phosphate ions (PO₄³⁻)
- By weathering
How do plants and algae acquire phosphate ions? (2)
- Plants take it up from the soil through their roots
- Algae absorb them from the water
How are phosphate ions transferred to consumers? (1)
Through feeding
What happens to phosphate ions in waste products and dead organisms? (2)
- Released into water sources or soil
- By saprobionts
What happens to phosphate ions after decomposition? (3)
- Can be taken up and used again by producers
- May be trapped in sediments that, over very long geological time periods
- Turn into phosphorus-containing rocks
What happens once phosphate ions is taken in through the roots of plants? (2)
- Some fungi form symbiotic or mutualistic relationships with plant roots
- These relationships are known as mycorrhizae
How do the fungi in mycorrhizae benefit the plant? (4)
- Fungi consists of yphae - long, thin strands
- Which connect with the plant roots and extend into the soil
- To increase the surface area of plant roots
- For absorption of water and of ions such as phosphate
How do the plants in mycorrhizae benefit the fungi? (3)
- Fungi receive organic compounds
- Such as glucose
- Produced by the plant during photosynthesis
What is the use of fertilisers? (1)
Replace the nutrients removed by the growth and harvesting of crops and feeding
What are natural fertilisers? (2)
- Dead and decaying remains of plants and animals, manure and bone meal
- As they decay, mineral ions are released which are taken up by crop plants
What are artificial fertilisers? (2)
- Mixture of inorganic compounds of nitrogen, phosphorous and potassium (NPK)
- Which are given to the crop for growth
What is a major issue for use of fertilisers? (1)
Leaching - which causes eutrophication
How does leeching by fertilisers occur? (2)
1. Large amounts of fertilisers can be washed away (leached) into rivers and lakes
2. This may result in eutrophication (particularly overused)
Describe what happens during eutrophication (9)
1. Leaching and runoff of inorganic fertilisers occurs
2. So there is an increased concentration of nitrates and phosphates in lake
3. Algae bloom on surface of water
4. Which means there is no light for plants on water bed
5. So they can't photosynthesise which causes the death of plants
6. So there will be large quantities of decaying organic matter
7. Therefore, Increased numbers of aerobic saprobionts
8. Aerobic bacteria, fish and invertebrates die as dissolved oxygen is used up by saprobionts and they cannot respire
9. This causes a reduction in species diversity
What happens to the concentration of nitrates and phosphates in a lake during eutrophication? (1)
There is an increased concentration of nitrates and phosphates in the lake
What occurs as a result of the increased nutrient concentrations in the lake? (1)
Algae bloom on the surface of the water
How does the algae bloom affect plants on the water bed? (2)
- Blocks light from reaching the plants on the water bed
- Plants cannot photosynthesise, which leads to their death
What happens to the organic matter from the dead plants? (2)
- Large quantities of decaying organic matter accumulate
- So the number of aerobic saprobionts increases
What is the effect of the increased number of aerobic saprobionts on the lake's ecosystem? (2)
- Aerobic bacteria, fish, and invertebrates die
- As dissolved oxygen is used up by saprobionts
- And so they cannot respire
What is the final outcome of eutrophication on species diversity? (1)
Causes a reduction in species diversity