ECON exam 2
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
74 Terms
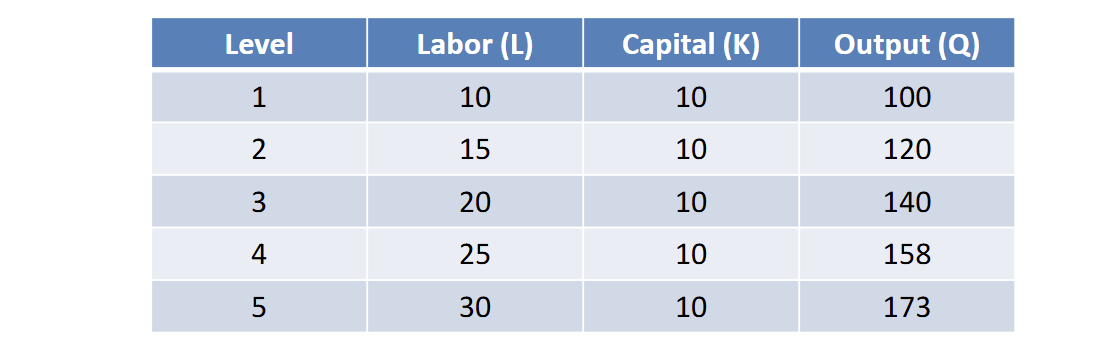
Is this short run or long run and how would you tell
its short run because capital stays constant
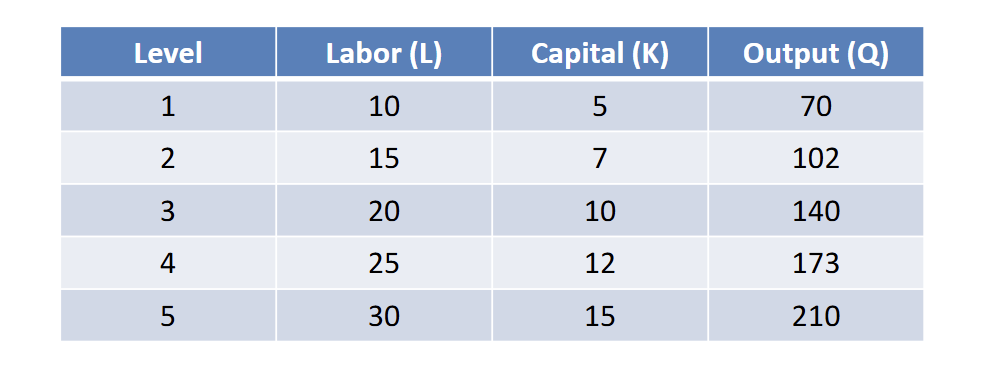
is this short run or long run
This is long run because variables like capital can change
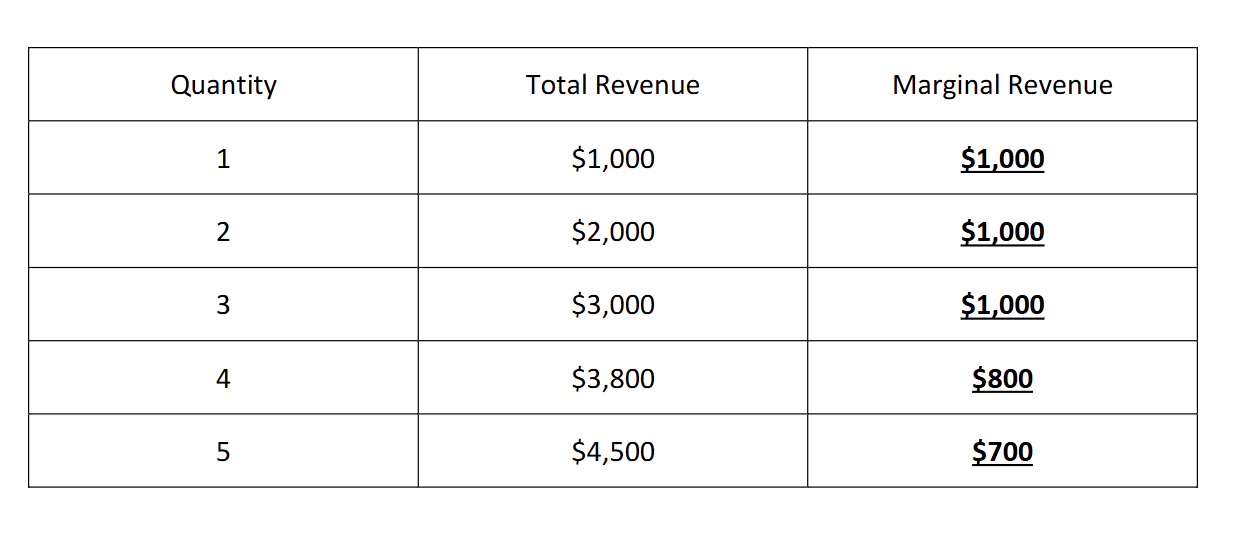
how would you calculate Marginal revenue in a graph like this
subtract the difference of total revenue, ex 1000-2000
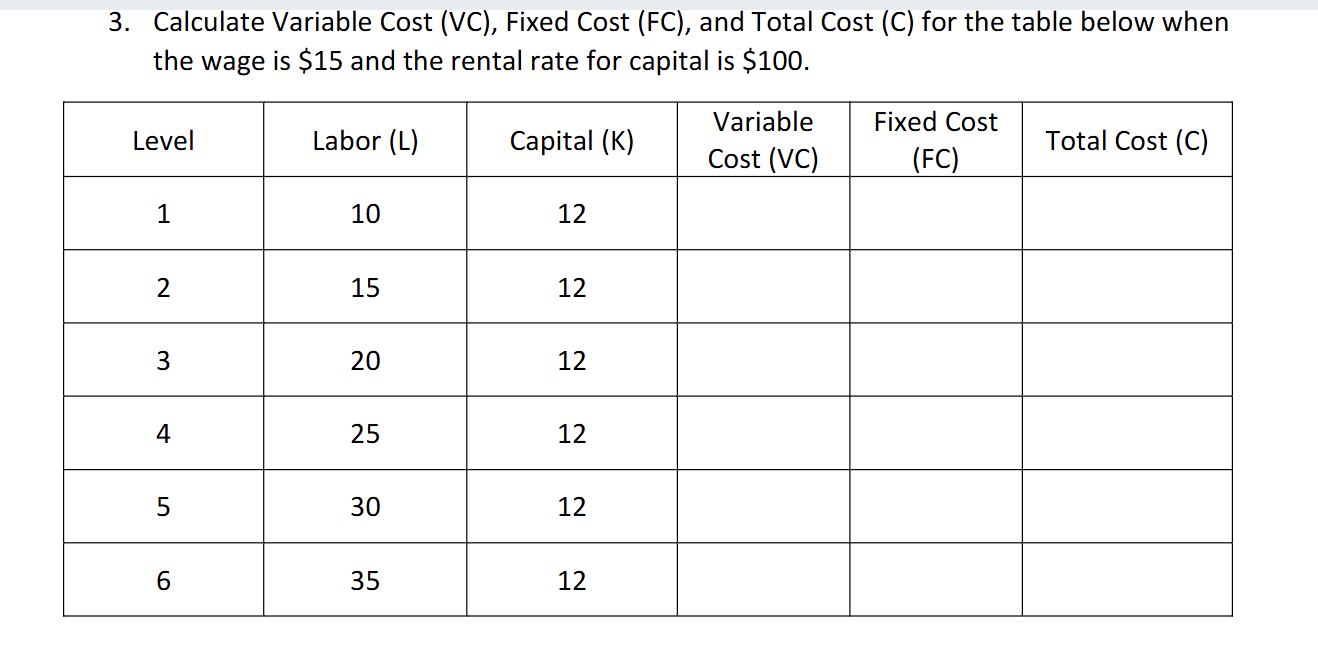
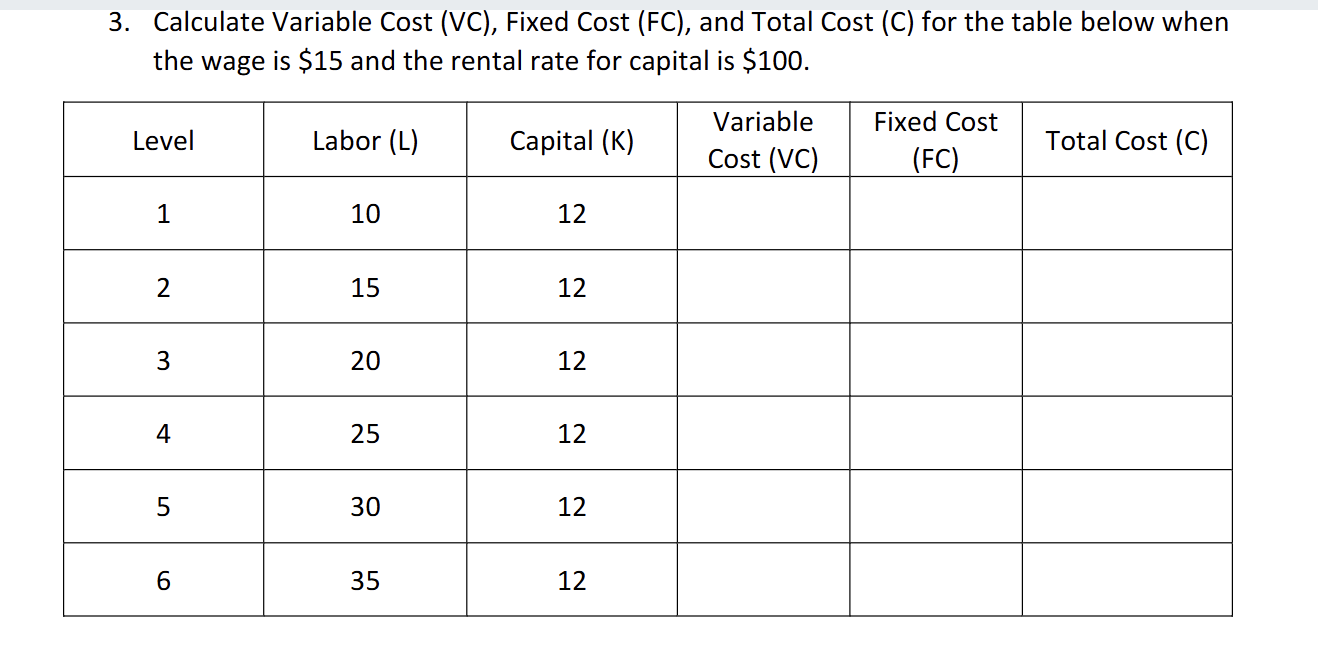
How would you find variable cost like in this question
you would do wage X labor so 15 X 10 here
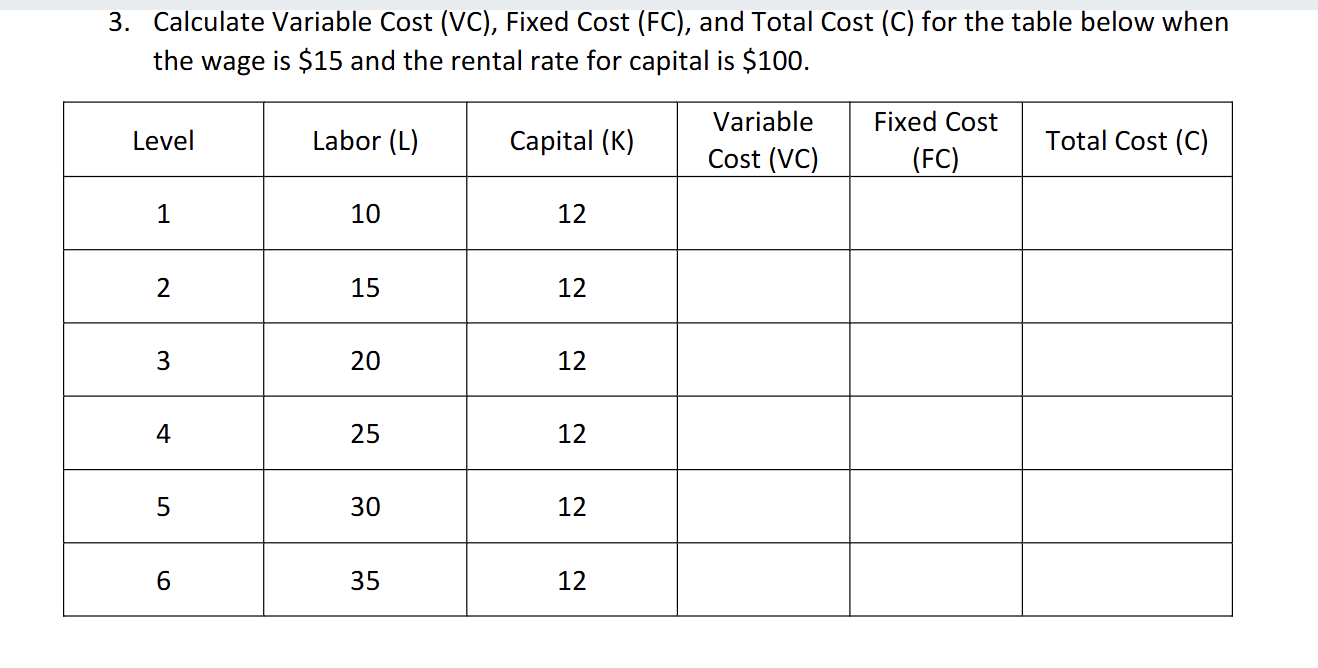
How would you find Fixed Cost
it would be capital X the rental rate so 10 X 12 and fixed is constant so the entire row would be 1200
How would you find total cost
Variable cost + fixed costs = the total cost
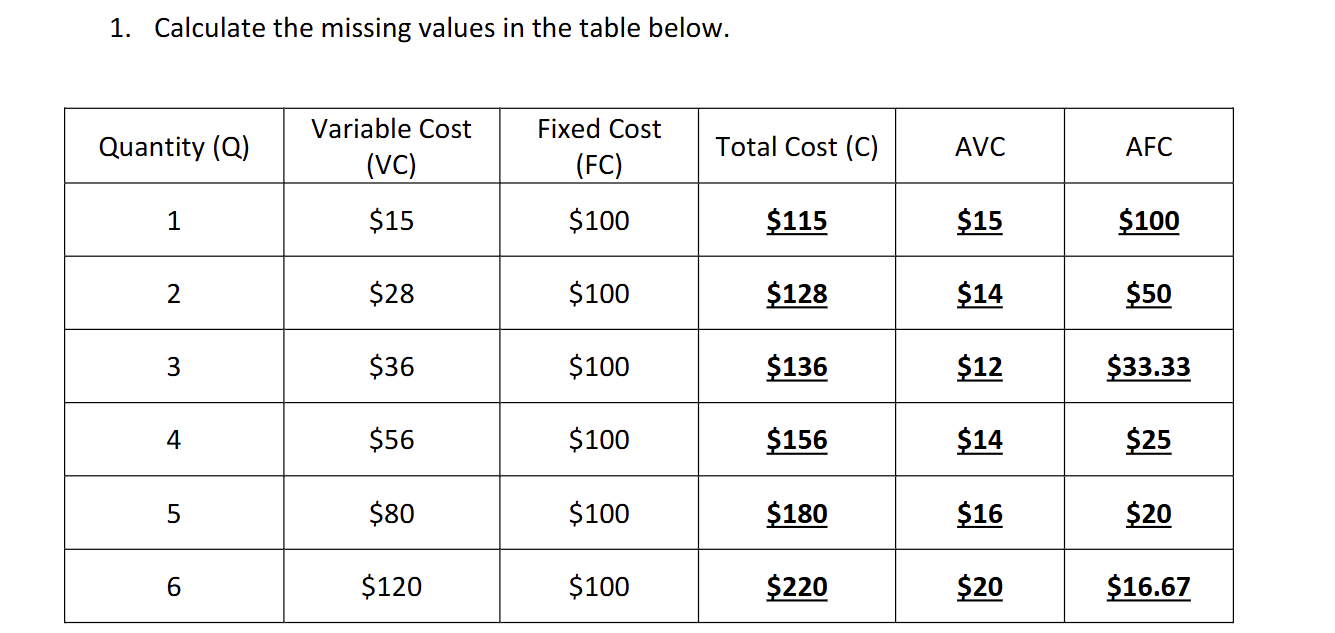
how would you find AFC and AVC
AFC would be fixed cost/quantity 100/1
AVC would be Variable cost/quantity 15/1
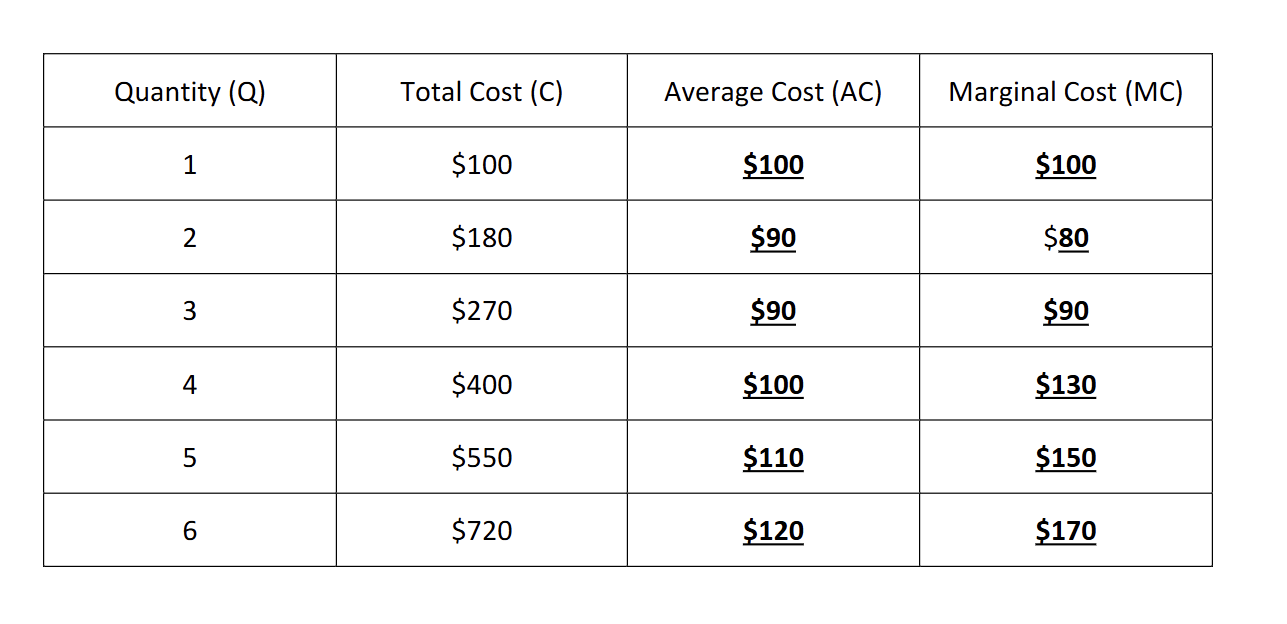
how to find average cost in a graph like this
Total Cost/Quantity
How would you find Marginal Cost
Difference in C(cost)
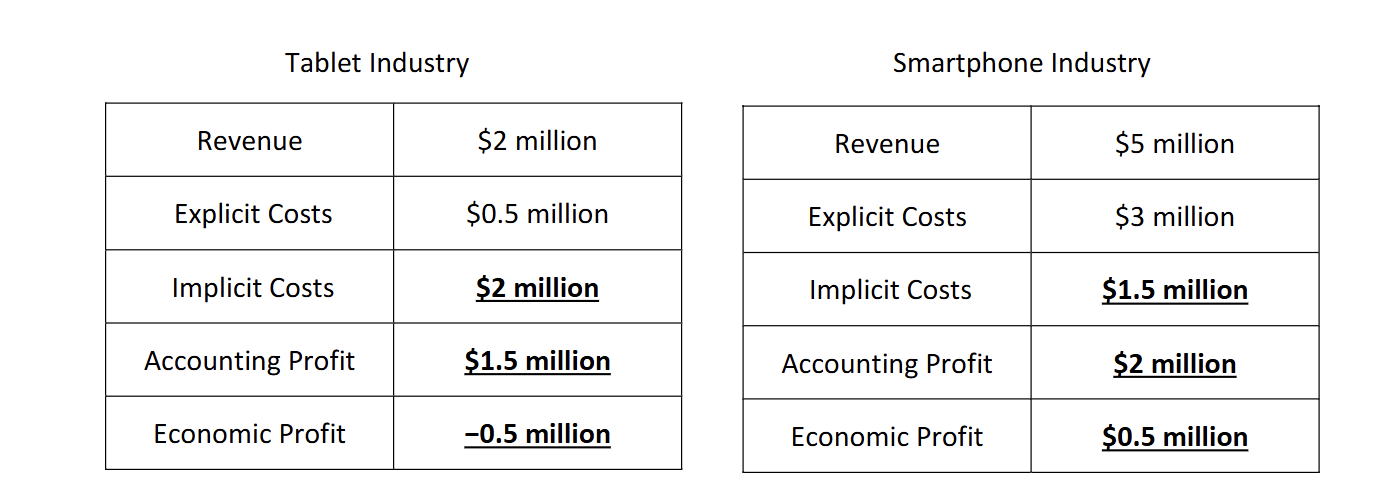
How would you find Accounting profit
Subtract total explicit costs from total revenues.
Examples of Explicit Costs
wages paid to workers,
money used to purchase machines and
equipment, rent paid for buildings
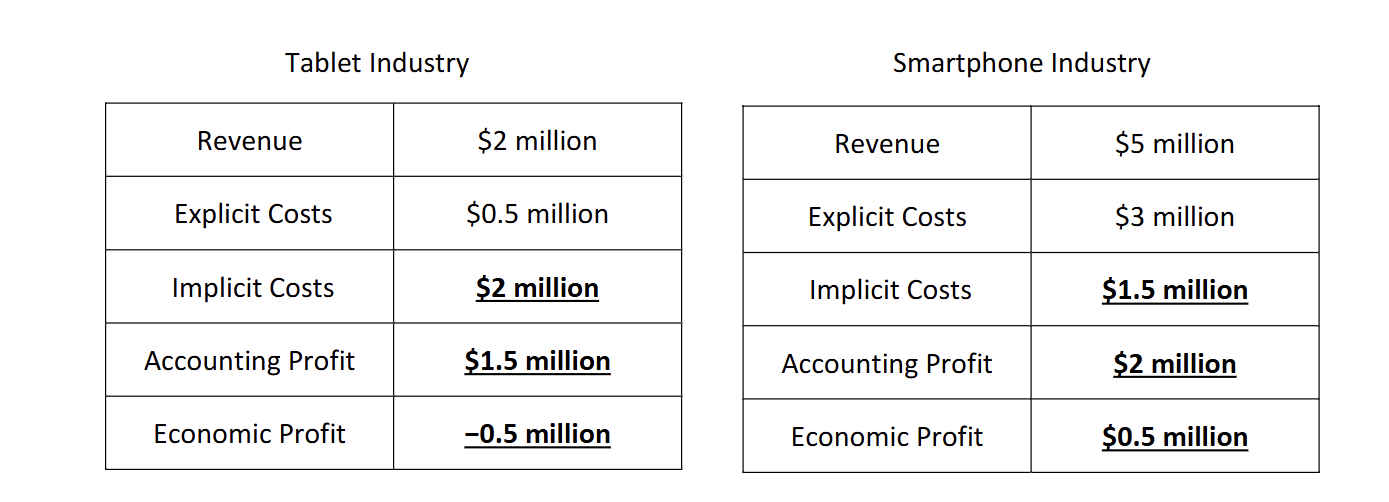
How would you find the implicit costs
it would be the Opportunity costs of accounting profit s
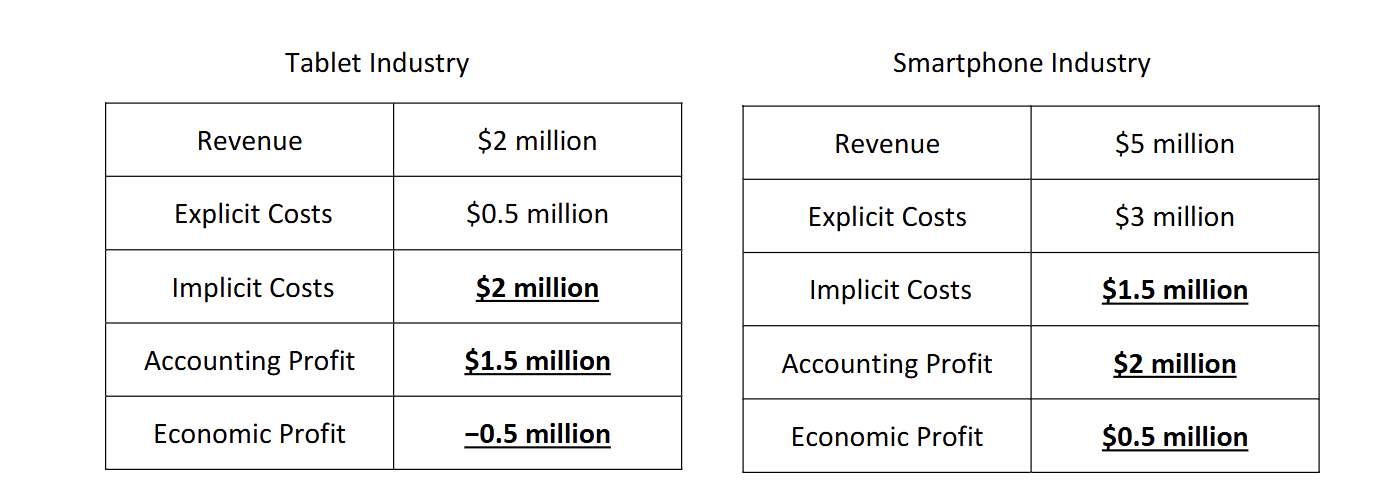
How to find economic profit
implicit costs - accounting profit
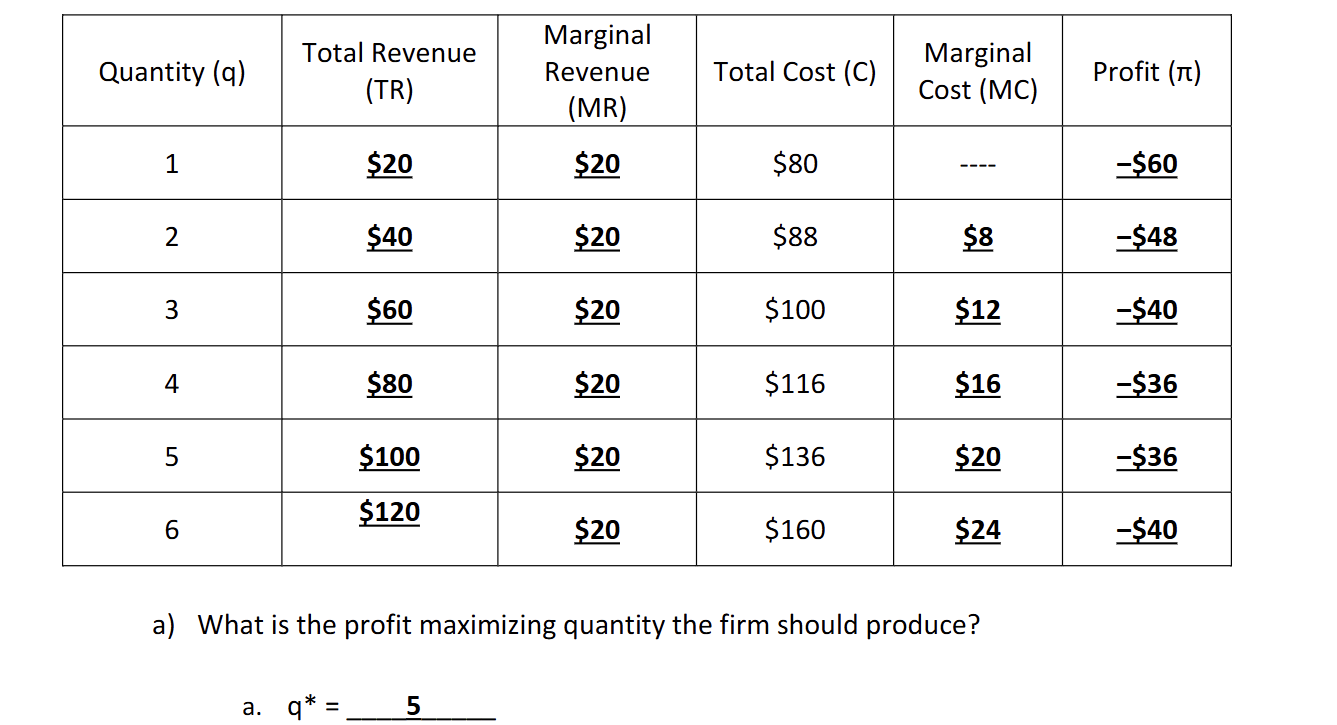
How would you find profit maximizing quantity
Where the marginal Revenue = Marginal Cost
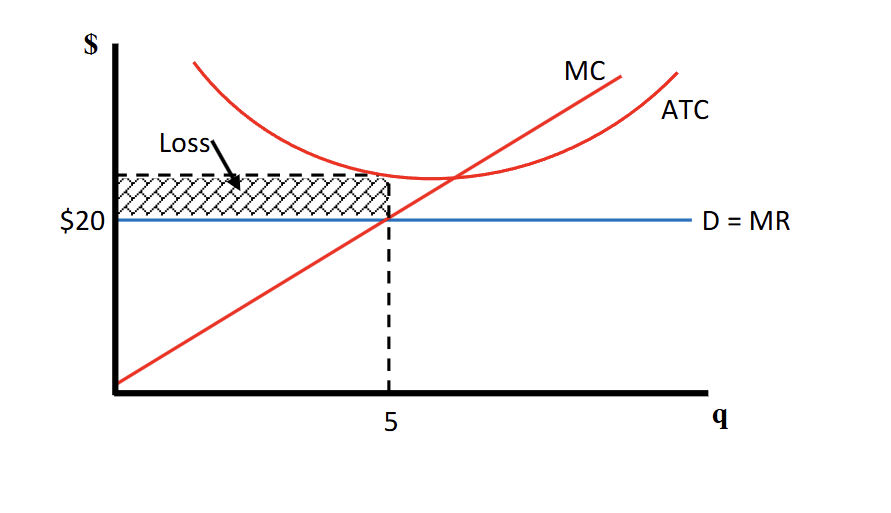
What does a firms economic loss on a graph look like
If MR = 20 and PMQ = 5 the loss would be whats over the MR line
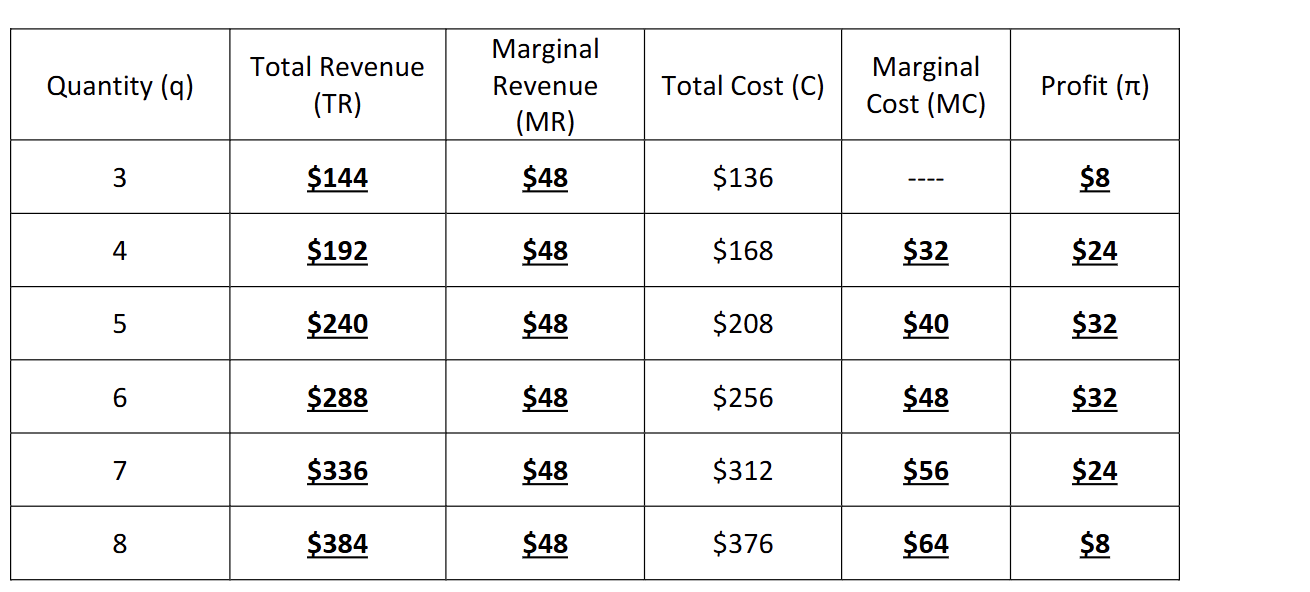
how to find profit in this perfectly competitive market
Total Revenue - Total cost
how do you know if firms will enter or exit the industry in the long run
if the profit is negative they will exit, if it is positive they will enter
what is the economic profit in the long run if the profit is positive
0 because perfect competition will drive it there
what is the economic profit in the long run if the profit is negative
0 also
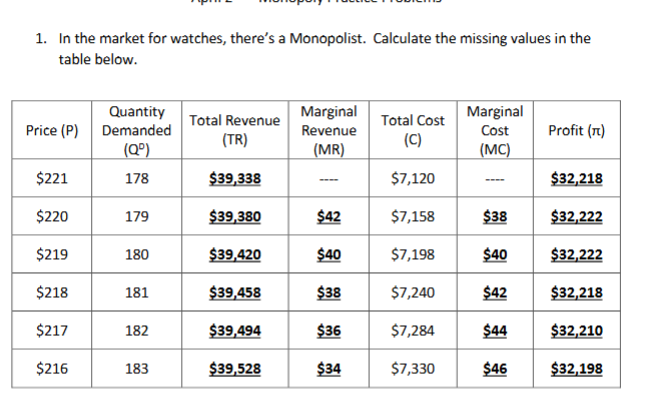
How would you find MR in a monopolist table
Difference in TR
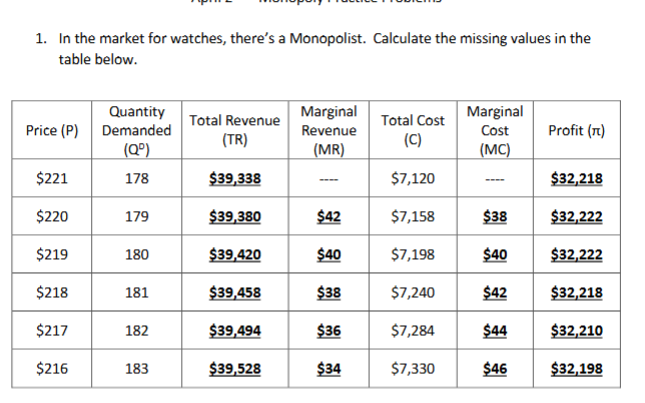
How would you find TR in a monopolist table
Price X Qd
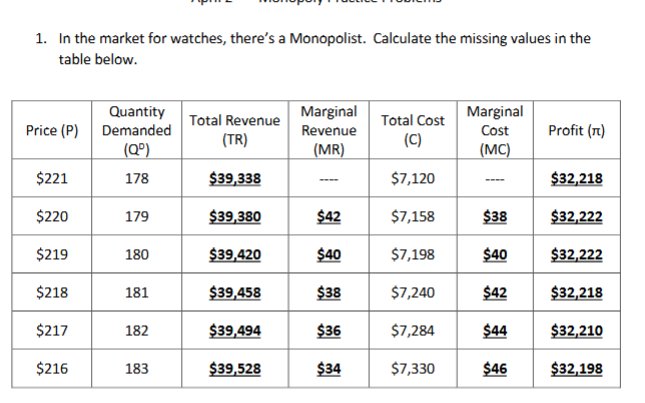
How would you find MC in a monopolist table
Difference in total cost
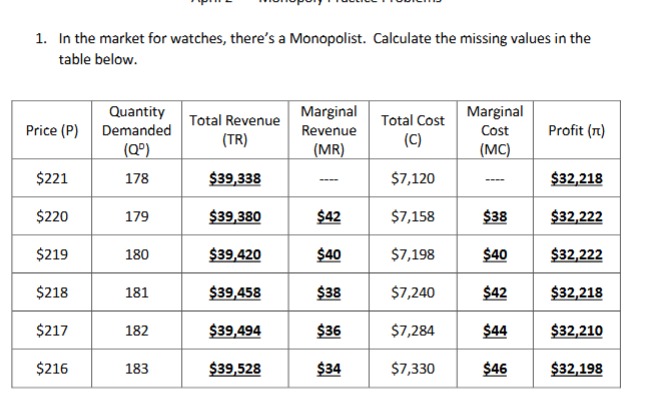
How would you find profit in a monopolist table
Total revenue minus total cost.
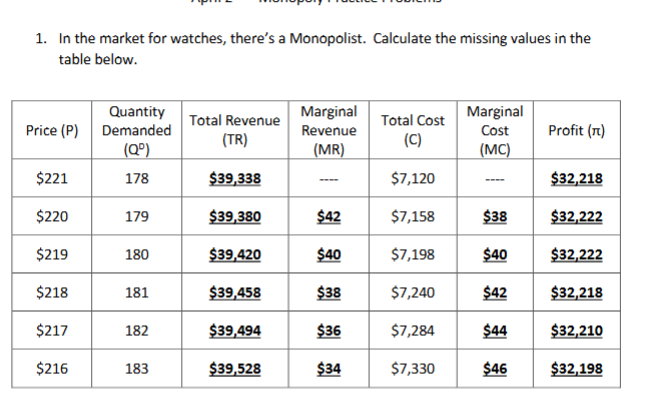
What is the profit maximizing quantity the Monopolist will produce?
where marginal revenue = marginal cost (is also the price the monopolist will charge and profit)
if the government imposes a per unit tax on something what would that look like on a graph
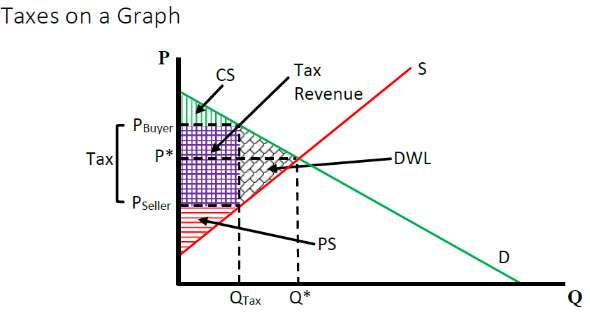
If demand is relatively more inelastic than supply, what is the economic incidence of a tax
Buyers will bear more burden of the tax
If supply is relatively more inelastic than Demand, what is the economic incidence of a tax
Sellers bear more of the burden
Statutory Incidence
who legally pays the tax while Economic Incidence refers to who actually bears the burden of the tax.
If demand or supply is perfectly inelastic, what is the deadweight loss associated with a tax?
There is no deadweight loss because the quantity sold remains constant regardless of the tax.
According to the Benefit Principle, who is it fair to tax?
Those who benefit from government services
If the government imposes a tax of $50 on everyone regardless of income, is the tax
proportional, progressive, or regressive?
Regressive
Progressive tax
The tax takes a larger percentage from higher-income earners than from lower-income earners.
regressive
The tax takes a smaller percentage from higher-income earners than from lower-income earners.
Are sales taxes and Social Security taxes proportional, progressive, or regressive?
Regressive
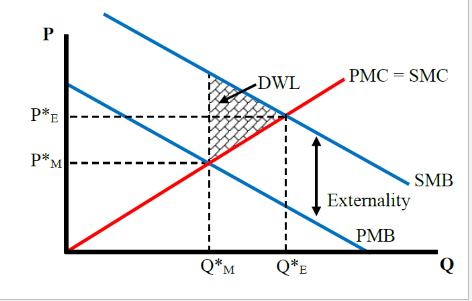
Does the flu shot have a positive externality or a negative externality?
A positive externality, as it reduces the likelihood of flu spread in the community.
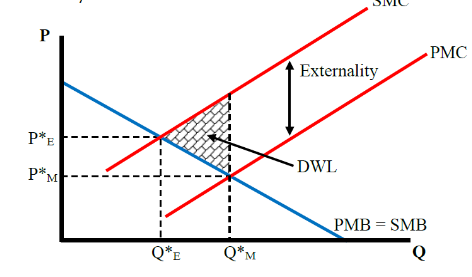
what is a negative externality
A negative externality occurs when a third party is adversely affected by an economic transaction or decision, leading to costs not reflected in the market price. Examples include pollution, where a factory's emissions impact local residents' health.
What does a negative externality look like
What does a postive externality look like
What are the 2 conditions needed to apply the Coase Theorem?
Clearly defined property rights and low transaction costs.
If my consumption of a unit of a good prevents you from consuming the same unit at
the same time, then the good has what property?
Rivalry
What type of good is rival in consumption, but non-excludable?
A common resource.
If the good is non-excludable, what problem does this create?
The free-rider problem, where individuals benefit from resources or services without paying for them, leading to under-provision.
If the good is non-rival in consumption, what policy could the government implement to
encourage higher levels of consumption?
gov subsidies or price reductions
Using your knowledge of economics, you estimate that the demand for aluminum is elastic. If you decide you want to increase your total revenue, should you lower your price of aluminum or increase your price of aluminum?
You should lower your price of aluminum, as an elastic demand means that lower prices will lead to a proportionally larger increase in quantity demanded, thereby increasing total revenue.
The government needs money to pay for the costs of public education. The government
is considering using a tax to raise the required revenue. Under the Efficiency Principle,
who would pay the tax?
The tax should be designed to minimize deadweight loss
What type of good is non-rival in consumption, but excludable?
A club good, or artificial scarce good.
If a good is non-excludable, what problem does this create?
People will free ride on the consumption of the good
The price elasticity of demand for diamond earrings is −1.1. If a diamond jewelry store wants to increase the revenue it gets from selling diamond earrings, what should it do?
Decrease its price of diamond earrings to increase the quantity sold, since the demand is elastic.
Marginal cost is also
The slope of the total cost curve
What is the definition of Diseconomies of Scale?
The situation in which long-run average cost increases as the quantity produced increases
What is Derived Demand?
The demand for inputs that results from the demand for consumer goods
Which of the following is not an assumption of the Perfect Competition model?
Goods are differentiated
perfect competition model
An economic model where numerous small firms compete against each other, selling identical products, with no single firm controlling the market price.
In a market with a monopoly, what is the relationship between the demand curve and the marginal revenue curve?
The demand curve is downward sloping, while the marginal revenue curve lies below the demand curve and also slopes downward. This reflects that the monopolist must lower the price to increase output, causing marginal revenue to decrease faster than price.
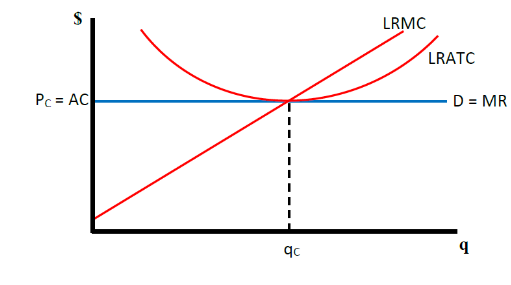
what does a Perfect Competition in the Long-Run graph look like
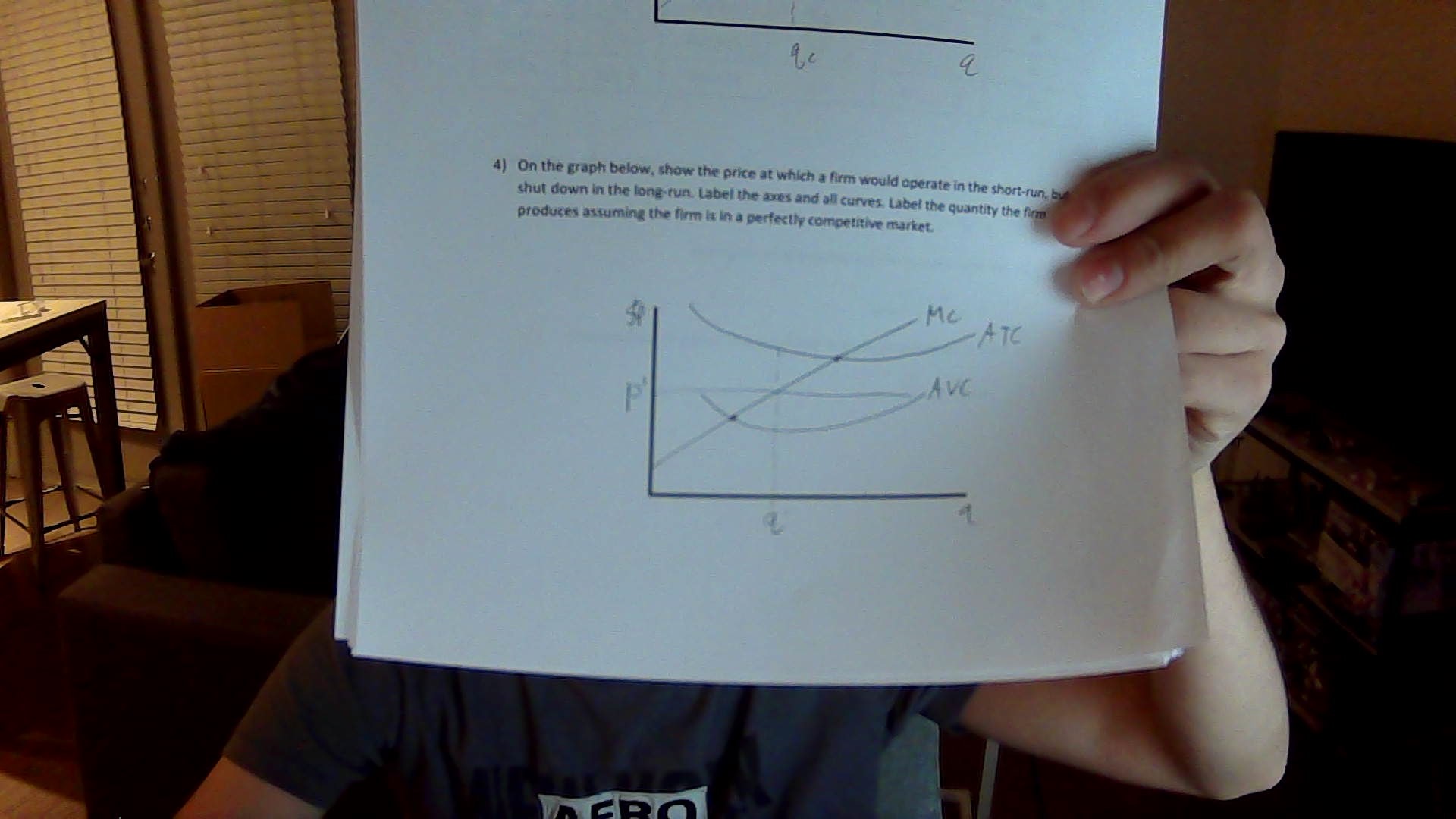
show the price at which a firm would operate in the short-run, but
shut down in the long-run graph
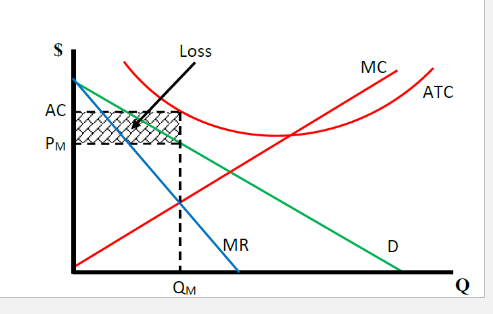
What does a monopoly making economic losses in the short run look like
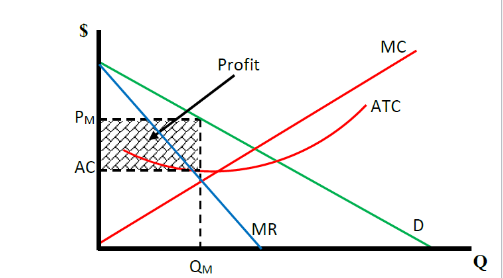
What does a monopoly making economic profit in the short run look like
Public Ownership
the government owns and manages the business
Regulation
the company is privately owned, but the government creates rules to control the price the firm charges and quantity the firm produces
Under a monopoly, the demand curve would be
downward sloping since its the same as he market curve and the monopolist faces the entire market demand.
what is economic profit
total revenue minus explicit and implicit costs
The government needs money to pay for construction and maintenance of roads and bridges. The government is considering using a tax to raise the required revenue under the benefit principle, who would pay the tax?
the people who use and benefit from the roads and bridges the most should pay the tax.
how does the substitution effect impact the supply of labor?
when wages increase, the op cost of leisure increases so people will supply more hours of labor because they choose to work more hours instead of enjoying leisure time.
what is the substitution effect
The substitution effect refers to the change in quantity demanded of a good or service as consumers replace it with cheaper alternatives when its price changes.
Marginal revenue is also
the slope of the total revenue curve
what is the condition under which the firm will shut down production immediately?
when price is less than average variable cost. This means the firm cannot cover its variable costs and will incur fewer losses by stopping production.
what does the Law of Diminishing Marginal Returns state?
the marginal product of an input will decrease as more of the input is used holding all other inputs constant This principle illustrates that adding additional units of a resource while keeping others constant will eventually yield lower additional output.
what are the properties of a public good?
A public good is a non river in consumption and non excludable which means that one person's consumption does not reduce its availability to others, and no one can be effectively excluded from using it.
how is market price determined in the long run perfectly competitive equilibrium
the market price is determined by average total cost at the minimum point of the average total cost curve, where firms earn normal profits, resulting in no incentive for entry or exit in the market.
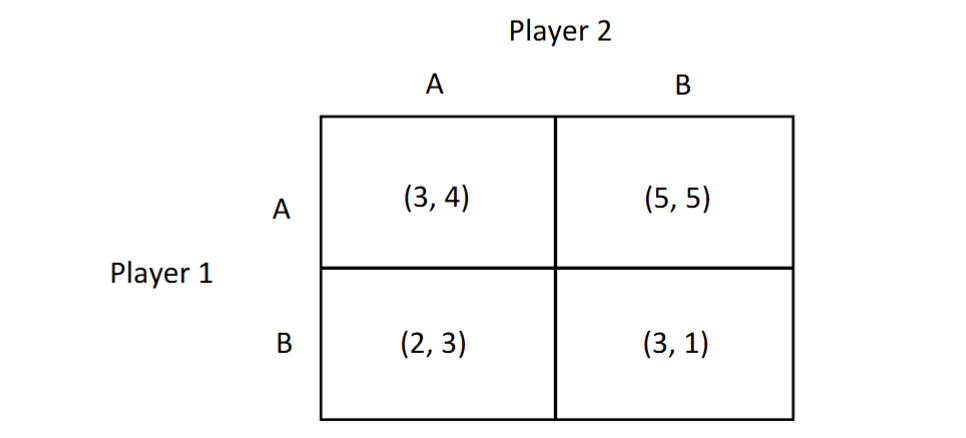
if player 1 plays A what is player 2s best response
it would be B because 5 is bigger than 4
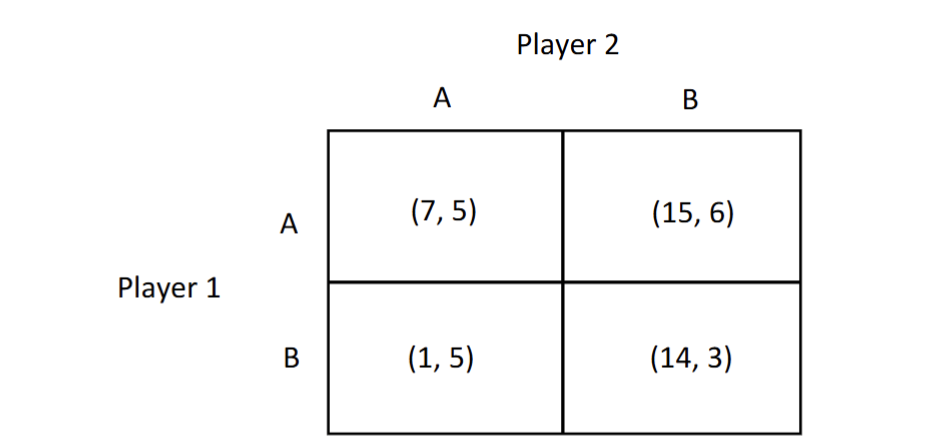
does player 1 have a dominant strategy?
Yes if he plays A, he will win on both A and B for P2
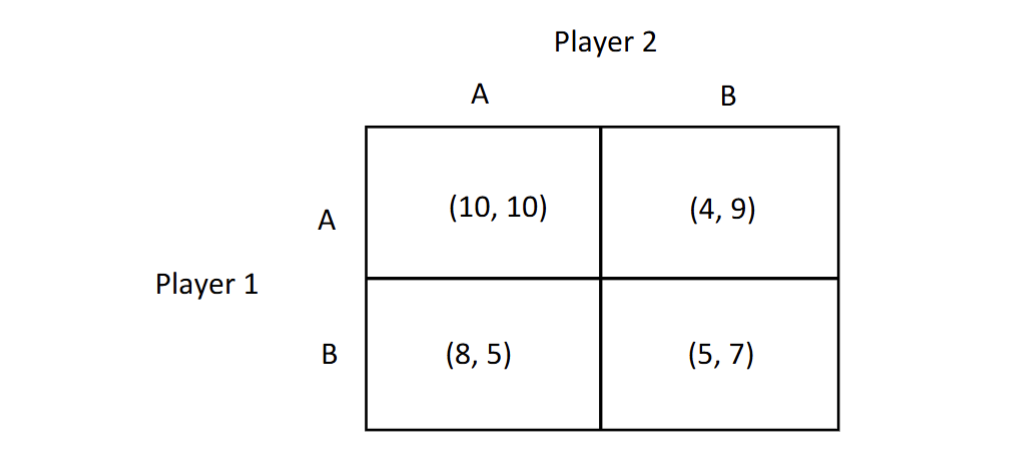
What would be the Nash equilibrium in this graph
The Nash equilibrium occurs where each player's strategy is optimal given the strategy of the other player, so 10/10, 5/7