AP Human Geography Final Study (Unit 4-7)
1/71
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
72 Terms
Nation vs State
Nation = group of people with a shared characteristic. State= a territory with settlement and sovereign gov.
Nation-State vs Multi-National State vs Multi-State Nation vs Stateless Nation
Nation-State = state with dominantly one nation (Japan)
Multi-National State = State with multiple nations (USA)
Multi-State Nation = Nation that located in many states (Muslims)
Stateless Nation = Nation that doesn’t have a central state (Kurd)
Definition of Self Determination
belief by a group of people that a government can be sovereign and can be stable
Autonomous Region vs Semi- Autonomous Region
Autonomous Region = a region within a state that has large amount of ability to govern itself
Semi- Autonomous Region = a region with a state that has some amount of ability to govern itself.
Shatterbelt and Demilitarized Zone Defintions
A shatter belt is a region that in between two conflicting areas ; dividing two or more states or areas.
A Demilitarized Zone is area between states or areas that a border is set for agreement and treaties. (Korea Borders)
Colonialism and Neocolonialism Definitions
Colonialism- a practice of conquering areas and exerting political control over the settlement
Neocolonialism - a practice of using influence to other nations and states
Colonialism vs Imperialism
Colonialism - a practice of conquering areas and exerting political control over the settlement
Imperialism- exerting force over other nations to gain political power without making settlement and colonies.
Definitions of Boundaries : Relic , Antecedent , Subsequent, Consequent , Superimposed, and Geometric
Relic Boundary - a boundary that no longer exist
Antecedent boundary - boundaries set before human settlement
Subsequent boundary = boundary set based on different cultures
Consequent boundary = boundary set to accommodate different groups
Superimposed boundary = boundary that were forced upon by external force
Geometric boundary = boundary that are straight lines that go along the lines of latitude
How does Superimposed boundaries demonstrate ethnocentrism.
Superimposed boundaries set aside people cultural value and make decision based on only their liking. (Berlin Conference)
Chokepoints Definition
a narrow passage way that has to be passed to get from one area to another.
Steps of making a boundary.
Define - A boundary is agreed upon and set
Delimited - Marking the boundary on a map and physically marking it
Demarcated - The process of marking a boundary (border walls)
Boundary Disputes : Definitional , Locational , Operational
Definitional Border Disputes - A boundary dispute that happens over misinterpreting boundary documents.
Locational Border Disputes - A dispute over the location of the boundary and ownership of land (Mississippi River change)
Operational Border Dispute - A dispute about how the border should be ran (Kashmir)
Allocational Border Disputes - A dispute that happen what is within boundaries such as resources.
What the purpose of UNCLOS?
Set of legal sea borders each varying distance from state’s borders and having their own special regulations and laws.
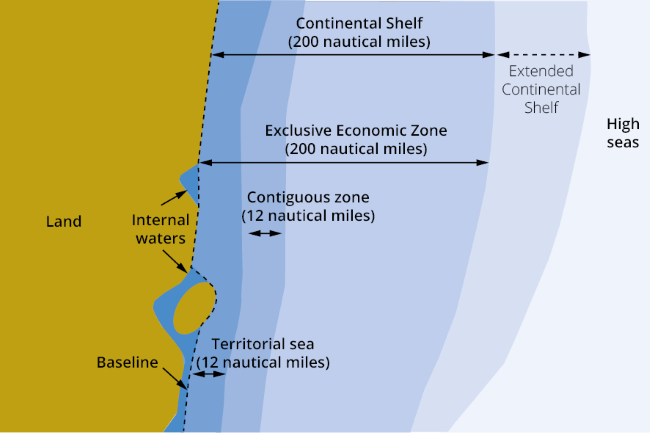
What are the regulations for Economic Export Zones (EEZs) and Territorial Waters?
Economic Export Zones (EEZs) - area of water that is under a state’s control to extract and exploit usually used for natural resources. (extends to 200 nautical miles)
Territorial Waters - Water that is fully under a state’s control
What is gerrymandering?
Gerrymandering - After a census, voting districts get redistricted unfairly to give advantage to one side.
Cracking vs Packing in Gerrymandering
Cracking - spread like-minding voters equally across all districts
Packing - clustering like-minding voters into one or few districts.
What do the two types of states : Federal and Unitary mean?
Unitary State = a state that governing in one area
Federal State = devolute their power to multiple areas in their state
Why do countries join Supranational Organizations?
States join supranational in order to have advantage in their economic, political , social and much more aspect of their state and to build a stronger sense of global community.
Centrifugal vs Centripetal Forces
Centrifugal Forces- factors that divide a country or area
Centripetal Forces - factors that unite a country or area.
Intensive vs Extensive Farming Practices.
Intensive Farming Practices - Practices that use more capital, less land resulting in higher yield and profit
Extensive Farming Practices - Practices that use less capital, more land resulting in lower yield and profit relative to intensive.
What is the relationship between type of farming practices and distance from market.
Intensive Farming Practices are located closer to the market because they need less land, have higher transportation costs, and often contain permissible. Extensive require more land so they are situated in land further the market and do not contain permissible.
Subsistence vs Commercial Farming
Subsistence Farming - Farming with the goal of sustaining one self or a family and to sell extra. (More common in LDCs)
Commercial Farming - Farming for the goal of profit and to scale up business requiring more mechanical.
Define Plantation, Mixed Crop and Livestock, and Market Gardening (intensive practices)
Plantation - Intensive farming of one or more plants usually cash crops to make the most profit
Mixed Crop and Livestock - Agricultural practice that grows crops and raise livestock. Farmer grow crops like corn or soybeans to feed the livestock.
Market Gardening - Production of flowers, vegetables,or flower as cash crops sold directly to local customers.
What is the difference between Market Gardening and Plantation?
Plantation is usually owned by wealthy individuals or company and are done on larger estates.
Market Gardening on the other hand, grows crops by local market or farmers and uses less land.
Define Shifting Cultivation / Slash and Burn Agriculture , Nomadic Herding , and Ranching (Extensive Farming)
Shifting Cultivation - clearing a lot of land usually by burning for agricultural purposes, farm there, and move to another plot of land after the soil fertility decreases
Nomadic Herding - seasonal moving along routes to regions with grazing land and water resources with their livestock. done in arid climate.
Ranching - farming where livestock have huge amount of land to graze upon. Commonly done for commercial purposes.
List and Define the 3 settlement patterns
Clustered- settlement where home are packed together
Dispersed- settlement where home are more space out
Linear- settlement that are along a river, road, train, and etc...
List and Define the 3 survey methods
Long lots - Individual parallel parcels that have access to resources like transportation or rivers.
Metes and Bounds - A system that uses physical features of geography and distances to make a boundary around a land.
Township & range - uses longitude and latitude to make a grid like system.
List and Define the Agricultural Revolutions.
1st Agricultural Revolution = first finding of agriculture where humans discovered planting, hunting, grazing.
2nd Agricultural Revolution = alongside the industrial revolution increase food production caused by the increase in technology.
Green Revolution = increase in chemical fertilizers that help increase food prod.
Value Added Crops Definitions
producing a different more valuable variant of a crop like wheat turning to flour.
Organic Farming Definition
a type of farming that attempts to get rid of environmental consequences of chemical fertilizer and grow food more naturally.
Define Free Trade Policies
policy or decision by non or governmental organization to give fair pay to farmers around the world.
What happens with the role of women in agriculture as the country develops
Women are usually are given less roles in agriculture but they get more roles as a country develops. They are still the majority of farmers in developing countries.
What idea is demonstrated in the bid rent theory? (Unit 5)
Bid- Rent Theory shows the relationship with land prices and zones of agriculture. The closer a zone is to the cbd (market) the higher the land price.
What idea is demonstrated in Von-Thunen Model
Von- Thunen Model shows the spatial layout of zones of agriculture based on their urgency to transport and land size needed.
What is the correlation with Bid-Rent and Von-Thunen Model?
The Bid Rent shows the distance away from market and the price for land decrease further you go this in shows in Von Thunen as extensive farming which uses more land is furthest away since they use land less intensively meaning less price.
Site vs Situation Factors
Site factor - description of place based on characteristic of its location (Tall building in New York)
Situation factor - description of place based on connections between different places (Business in London near a port)
Mega city vs Meta City
Megacity - a settlement over 10 million people
Metacity - a settlement over 20 million people
Boomburbs vs Exurbs vs Edge cities
Boomburbs - suburban that is urbanizing but still retains their suburban feel
Exurb - an settlement outside suburbs with connections to metro areas.
Edge Cities - Urban areas located at the outskirts with their own economic focus and usually connected to major roads.
What is purpose of edge cities?
A regional area for business activity for the suburban population
What does the Gravity Model state?
The Gravity Model states that the larger or more prominent a city is the more interaction they will get from other cities.
What does the Central Place Theory state?
Central Place Theory states that larger settlements have larger range and better services than smaller settlements.
Range vs Threshold
Range is the amount of distance that people are willing to go for a service
Threshold is the minimum amount of people required to sustain a service
Range and Threshold in Central Place Theory
Higher level of settlement contain more large service meaning they have the most range and threshold
Primate City vs Rank-Size Rule
Primate City Rule indicates that in an given area the largest settlement is two times the population of the 2nd largest.
Rank-Size Rule says that the nth population rank of city is 1/nth of the largest settlement.
What the cause of Primate City and Rank- Size Rule?
The Primate City will cause the development to be more concentrated on the largest settlement causing an uneven settlement.
Rank-Size Rule has more equal pattern so the development wouldn’t be as uneven as Primate Cities.
What relationship is shown in bid-rent theory?
the relationship between zones of city and land cost
What type of building are made depending on the place in the bid rent theory?
This shows that zones near cbd are going to build vertically to deal with high land cost and lower land cost will move more outwards (single family homes) creating sprawl
Relationship of distance from cbd and service provided
The farther away a zone is from the CBD the less services like public transportation will be provided
Define Urban Sustaining Practices : New Urbanism, Greenbelt, Urban Growth Boundaries, and SMART Growth.
New Urbanism = Urban policies that create more walkability to reduce urban sprawl and make life in the city much more efficient and easier.
Greenbelt = Areas where homes and business aren’t allowed to be built on.
Urban Growth Boundary = A regional boundary to restrict urban sprawl.
Smart growth = a type of new urbanism policies that tries to protect the environment and people’s health.
What are reason that people are against urbanizing?
Urban practices often damage the environment. People want to maintain the environment so that we don't suffer for future generations.
People feel urbanism will make a place lose its sense of place by becoming a more economical place.
Define these segregation practices : Redlining and Blockbusting
Redlining - discriminatory act to deny loans to minorities to buy a house
Blockbusting - real estate agents convince white people to sell houses for low prices and mark up the price when minorities come.
Definition of Gentrification
Gentrification - poorer urban areas get renewed by wealthier people or organization.
Positive and Negative effects of Gentrification
Positives of Gentrification = increase in jobs, improved house, more business
Negatives of Gentrification = pushes old residents out as they cannot handle the rising price.
Greyfields vs Brownfields
Greyfields - previously retail or commercial shopping sites that suffered or abandoned due to lack of investment or outclassed by competitions
Brownfields - An area that has been abandoned due to pollution or contamination from previous occupants.
List and Explain the 5 sectors of economy
Primary Sector - sector of jobs that extract material
Secondary Sector - sector of jobs that manufacture goods
Tertiary Sector - sector of jobs that provide services
Quantaray Sector - sector of jobs that analyze data and info.
Quinary Sector - sector of jobs that make higher level decision
Relationship of dominant sectors as a country develops.
As a country develops it provides less jobs in the primary or secondary sector as technology and machinery have taken up those jobs and there isn’t a need for manual labor.
Offshoring
A process of moving business to area with cheaper labor
What is presented in Dependency Theory?
MDCs will take advantage of LDCs for their cheap labor exchange for high- profit goods.
What is negative effect of LDCs according to the Dependency Theory?
If any semi / periphery countries fall short on exporting their economy will fall but for core they will go to another country for those materials making it harder for LDCs to get on the same level as core countries.
Define these Zones : Special Economic Zones, Export Process Zones , Break-of-Bulk Point, and Free-Trade Zones
Special Economic Zone = Areas where laws are different from the rest of the country for business and trade purposes.
Export Process Zone = areas that promote economic growth by giving incentives to foreign companies.
Break-of-Bulk Point = an area where transports are assembled and packaged to be transported
Free Trade Zones = areas where goods can be made and shipped with no fees.
Multiplier Effect
to earn more from output than inputs
Define these business practices : Just-in-Time Delivery, Agglomeration, Growth Pole, and Neoliberal Policies.
Just in Time Delivery - companies receive parts and shipment moments before they need it
Agglomeration - Cluster of similar industries to reduce company cost
Growth Poles - An area in a region that stimulates economic growth and is connected to industries.
Neoliberal policies = policies that seek to promote free trade agreement between countries attempting to make a more globalized economy
Define the grosses: GDP, GNI, GNI and GDP per capita
Gross Domestic Product = the total value of good/services made in an country
Gross National Product = value of good/services made only by country’s citizens (domestically and abroad)
Gross National income per capita = The average amount of income per country citizen (including from other countries)
GDP per capita = the average amount of income per country citizen (only within country’s border)
Define HDI and GII
Gender Inequality Index - measurement of a country's gender equality. If opportunities are given to both genders or more to one gender. Less inequality the higher the development
Human Development Index (HDI) - measurement of every person’s standard of living with multiple factors like literacy rate , life expectancy , health care, etc.. in a country
Microfinance Definition
providing microloans to individual or small businesses in semi or periphery countries.
What is the purpose of microloans
Minorities are often given microloans by society members to help a individual or small buisness financially
Commodity Dependence Definition
A country's economy being heavily relying of only one commodity. If that commodity falls their economy will be damaged.
Commodity Chain Definition
a linked system of processes that gather resources,convert them to goods, and transport and sell the product.
Define Post Fordist and Fordist Production
Fordist production - form of mass production in which worker is assigned to one task to perform repeatedly
Post-fordist production - growth of new production methods defined by flexible productions and fragmenting markets into individual segments
What happens at each stage of the Rostow Model?
Stage 1 Tradition Society - job are mostly subsistence agriculture and majority are in primary sector
Stage 2 Precondition for Takeoff - More developed countries ask for raw materials creating more jobs in secondary but still most in primary.
Stage 3 - Urbanization occurs, more job opportunity, and more in secondary sector
Stage 4 Drive to Maturity - global trade occurs, more specialization, and become more independent from global trade partners.
Stage 5 Age of Mass Consumption - More in tertiary sector, economy highly developed, and services and goods not only for need but also wants.
Universalizing and Ethnic Religion
Universalizing Religion - Religion that seek to gain more followers (Islam)
Ethnic Religion - Religion that stay more reserved and majority of their people stay within one area or region (Hinduism)