4. Behavioral Immune System
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
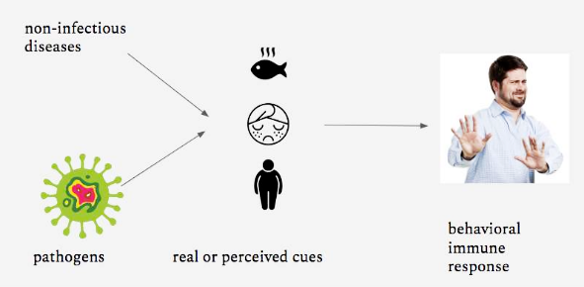
Behavioral immune system definition
Psychological system to avoid pathogens.
Parasite threat uniqueness
Persistent, invisible, and internally harmful.
Functional invisibility
Parasites cannot be easily detected.
Hurt-from-within threat
Pathogens damage the body internally.
Immunological cost
Physiological immunity is energetically costly.
Proactive defense
Avoidance prevents immune activation.
Disgust function
Avoid infection and contamination.
Fear function
Avoid external physical threats.
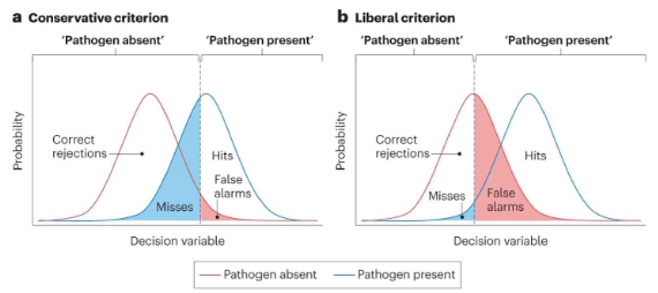
Smoke Detector Principle
Overreacting is less costly than underreacting.
Functional Flexibility Principle
Response adjusts to vulnerability context.
COVID coughing reactions
Increased moral judgment under disease threat.
Disease and dating
Avoidance reduces social and mating behavior.
Disease and xenophobia
Ingroup preference increases under pathogen threat.
Collectivism link
High pathogen prevalence correlates with collectivism.
Health-attractiveness link
Attractiveness used as proxy for health.
Why parasites are a unique threat
They are persistent, invisible, and harm the body from within
Hurt-from-within threats
Pathogens that damage the body internally
Hurt-from-without threats
Predators and physical dangers causing external harm
Why immune responses are costly
They consume energy and impair normal functioning
Fear vs disgust
Fear avoids external threats, disgust avoids infection
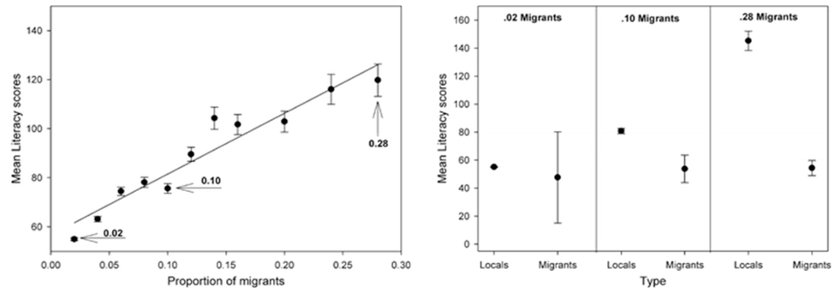
Ecological fallacy / Simpson’s paradox
Aggregate-level effects can reverse at the individual level
Parasite-Stress Theory of Sociality
High pathogen prevalence leads to more collectivism, conformity, and xenophobia
Tight Cultures
Strict norms, low tolerance for deviance.
Loose cultures
Flexible norms, higher tolerance.

Galton’s Problem
Cultures may share traits because they are neighbors or related (not independent)