2.5 joints
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
joints are also known as articulations
functions:
support & movement
structural categories of joints:
fibrous, cartilagenous, synovial
fibrous joints
-joined by ____
-mobile or immobile?
-examples: sutures, teeth to jaw
dense connective tissue, immobile: found in areas of body that require support rather than movement
cartilagenous joints
-joined by ____
-mobile or immobile?
-examples: pubic symphysis, intervertebral joints, ribs with costal cartilages
cartilage (hyaline or fibrocartilage), slightly mobile
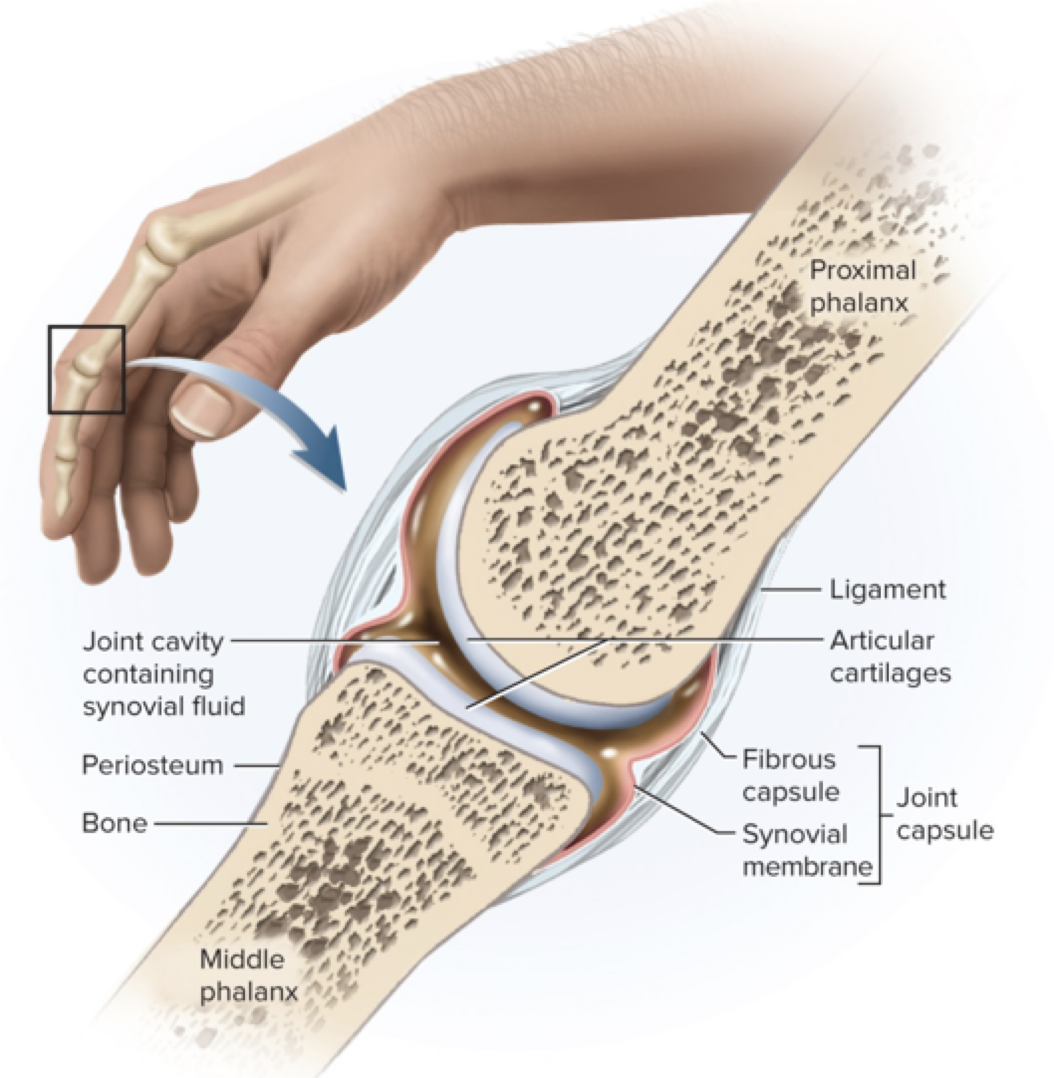
synovial joints
-joint cavities enclosed by ____ ____
-articular cartilage provides _____
-makes up most joints in the body
joint capsules, cushioning
synovial joint structure
-joint capsule made up of ____ & ____
-purpose of synovial fluid inside joint cavity:
-ligaments strengthen joints
fibrous layer, synovial layer, lubrication
flexion
decreasing the angle that the body makes
ex: flexing biceps or flexing leg (decrease posterior angle)
extension
increase angle that the body makes
ex: extending arm (from flexed position)
hyperextension
past neutral position
ex: hyperextension of hip means bringing leg behind
abduction
moving limb away from midline
ex: lifting arms up or raising legs to the side, fingers: spreading
adduction
moving limbs towards midline
fingers: keeping them together
hyperadduction
crossing limbs
opposition in fingers
touching thumb to pinky
medial/ internal rotation
rotating limbs towards body
lateral/ external rotation
rotating limb away from body
supination
rotation of elbow so that palms face anterior
pronation
rotating elbows so that palms face posterior
eversion
sole of feet facing laterally
inversion
sole of feet facing medially
planar flexion/ ankle extension
pointing feet
dorsiflexion/ ankle flexion
flexing ankle
range of motion: degrees in which the joint can move
determined by
-structure of ____ surfaces
-structure and tension of ligaments and joint capsules
-action of ___ and ___
articular, tendons, muscles
plane joint
-description
-type of movement
-ex: carpals, tarsals, vertebral articular process
flat articular surfaces slide past each other, multidirectional movement
hinge joint: description, type of motion, examples
convex end of bone articulates with c-shaped depression, allows for flexion & extension, elbow, interphalangeal joints, ankle
pivot joint: description, type of motion, examples
rounded portion of bone partially enclosed by ligament, allows for rotation, proximal radioulnar joint, atlantoaxial joint
ball and socket joint: description, type of motion, examples
round head of bone fits into corresponding depression, multidirectional movement, shoulder, hip
shoulder joint, aka glenohumeral joint: bones involved, type of joint, glenoid labrum: ___
glenoid fossa and head of humerus, ball and socket, deepens glenoid fossa
why is it so easy to dislocate the shoulder?
because of the ball and socket joint structure as well as the glenoid labrum, the shoulder is able to exhibit larger range of motion, but this also fails to protect against detachment
elbow: bones involved, type of joint, a feature about this joint
humerus, radius, ulna, hinge joints (humeroulnar joint and humuroradial joint) allow for flexion & extension, radioulnar joint creates pivot joint for rotation of wrist
hip: bones involved, type of joint, a feature about this joint
acetabulum and femur, ball and socket, ligamentum teres (carries arteries to head of femur)
difference between shoulder and hip joints
shoulder joints are more prone to dislocation because of its glenoid labrum, but hip joints are rarely dislocated because it’s tightly bound by ligaments and doesn’t exhibit wide range of motion
knee
-medial & lateral ___ ____ are on either side of the tibia to prevent ____ __
-cruciate ligaments: crossed ligaments
-anterior cruciate ligaments help to prevent ___
-posterior cruciate ligaments help to prevent ____
collateral ligament, lateral displacement, hyperextension, posterior displacement of tibia
ankle: bones involved, type of joint, a feature about this joint
tibia, fibula, talus, hinge joint composed from talotibial joint and talofibular joint, intertarsal joints/ plane joints allow for inversion & eversion
The lateral and medial ____________ stabilize and cushion the knee.
cruciate ligaments
epicondyles
menisci
epiphyses
menisci
When climbing the stairs, __________ at the knee and hip joints lifts or pushes your whole body weight up onto each step.
abduction
extension
flexion
adduction
extension involves increasing the angle that the body makes. when the body extends from the flexion movement, that's what pushes the body weight up onto each step. this activates the glutes and quads.
The articulation of the tibia, fibula, and talus at the ankle produces flexion and extension as well as inversion and eversion.
True
False
false