Cardiac Physiology: Heart Health in Ageing
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
What is the leading cause of mortality in the elderly?
Cardiovascular disease (CVD), accounting for approximately 40% of all deaths.
What percentage of heart failure deaths occur in individuals aged 65 and older?
About 88% of heart failure deaths.
What are the intrinsic factors contributing to ageing-related heart problems?
Cumulative lifetime impacts of repeated insults and injuries, such as myocardial infarctions and hypertension, leading to maladaptive myocardial remodeling and heart failure.
What insights have animal models provided regarding cardiac aging?
Genome-wide transcriptome analyses have revealed specific transcriptional alterations in pathways related to stress response, mitochondrial function, fatty acid metabolism, contractility, hypertrophy, inflammation, and extracellular matrix production.
How does the performance of the ageing heart change under stress?
The ageing heart shows impaired function and symptoms of heart failure, including exercise intolerance and dyspnea.
How does exercise performance differ between older and younger adults?
The heart performs less effectively during peak physical exercise in older adults (ages 60-80) compared to younger adults (ages 20-30).
What role does the autonomic nervous system (ANS) play in heart response to exercise?
The ANS regulates heart response to acute exercise by increasing sympathetic tone and decreasing parasympathetic tone, leading to increased heart rate and contractility.
What changes occur in the autonomic nervous system as the heart ages?
Responsiveness to autonomic stimuli diminishes due to sympathetic dysregulation, β-adrenergic receptor desensitization, and increased circulating noradrenaline levels.
What effect can exercise training have on the ageing heart?
Exercise training can reverse desensitization to adrenergic stimuli, improving exercise capacity, contractility, and diastolic filling rates.
What happens to exercise-induced changes in the ageing heart when β1-receptors are antagonized?
The observed effects of exercise training on the ageing heart are blocked, indicating mediation through direct modulation of β-AR signaling.
What is stress cardiomyopathy, also known as Takotsubo cardiomyopathy?
A condition that mimics a heart attack, triggered by sudden emotional stress, characterized by symptoms like dyspnea and chest pain.
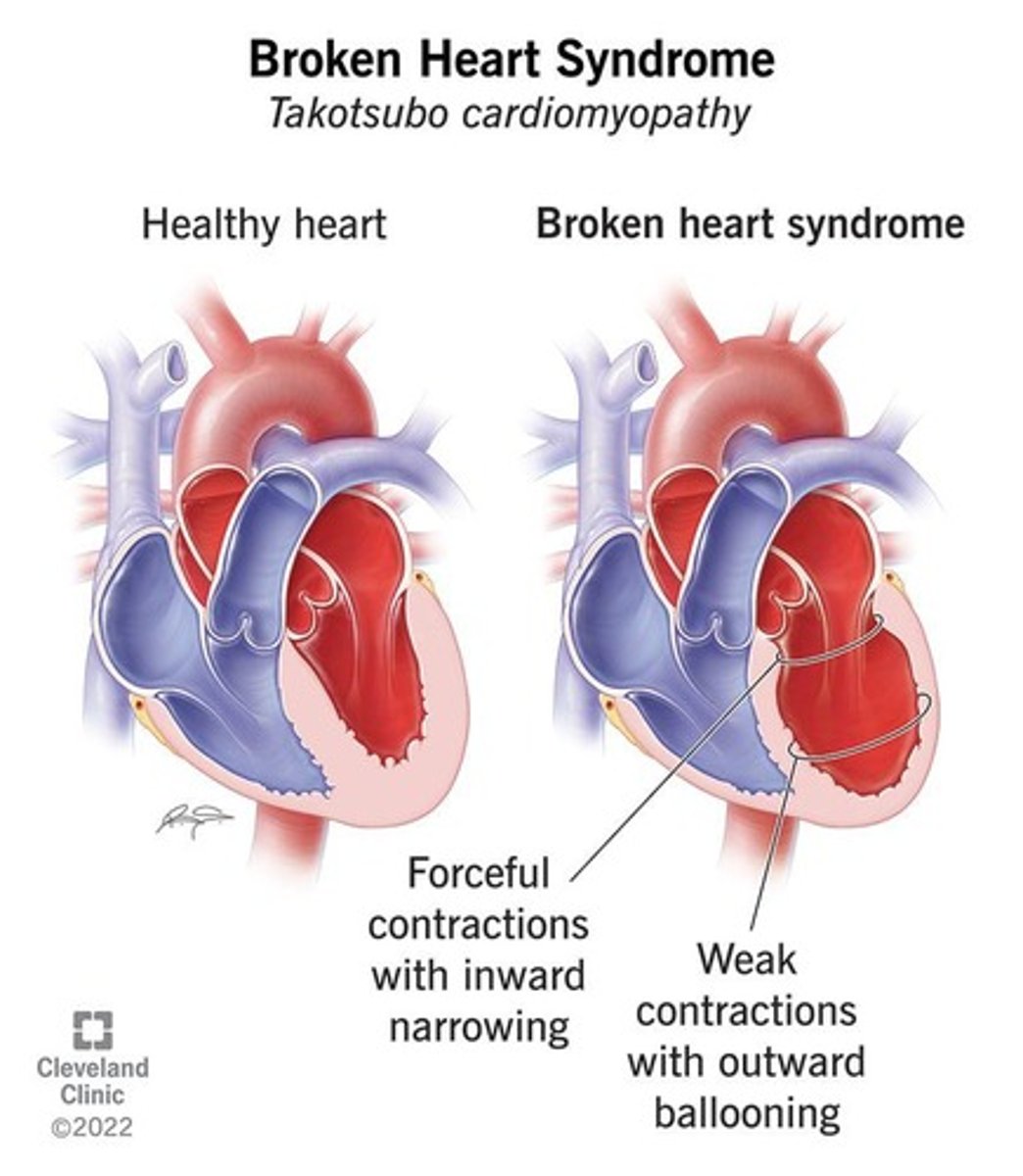
What are the primary symptoms of stress cardiomyopathy?
Symptoms include dyspnea, chest pain, arrhythmia, transient left ventricular apical ballooning, ST elevation, and increased enzyme/biomarkers.
Who is most affected by stress cardiomyopathy?
Typically affects females aged 50 and older, often with a history of psychiatric or neurological disorders.
What is the mortality rate associated with stress cardiomyopathy?
The mortality rate is very low, as is the recurrence of the condition.
What demographic is projected to account for nearly 20% of the population by 2030?
Adults over the age of 65.
What is the fastest growing demographic group in society?
Individuals aged 85 years and older, estimated to increase by more than 230% by 2050.
What physiological changes occur in the heart due to ageing?
Impaired inotropic and chronotropic responses to adrenergic stimulation due to greater β-AR occupancy and desensitization.

How does the heart's noradrenaline level change with age?
Heart noradrenaline levels increase with age due to decreased reuptake and increased tissue spillover.
What is the impact of acute exercise on heart rate and contractility?
Acute exercise leads to increased heart rate and contractility due to heightened sympathetic tone.
What are the molecular phenotypes of cardiac aging?
They include transcriptional changes related to stress response, mitochondrial function, and inflammation, mirroring changes in the failing heart.
What is the relationship between exercise and the ageing autonomic nervous system?
The ageing autonomic nervous system shows diminished responsiveness, impacting heart performance during exercise.
What is the significance of β-adrenergic receptor desensitization in older adults?
It leads to blunted intracellular calcium responses, impairing heart function during stress.