Psychology Exam 2 Review
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/123
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 7:57 PM on 3/13/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
124 Terms
1
New cards
Sensation
Detecting enviromental stimuli
2
New cards
Perception
Interpreting sensory information
3
New cards
Transduction
Translating the sensory information into a neural signal
4
New cards
Sensory Adaptation
When something is unimportant, old stimuli, or not urgent you tune it out
5
New cards
Selective Attention
The purposeful act of paying attention to one thing over another
6
New cards
Frequency/Closeness of Waves (Vision)
Generates the color of what we see
7
New cards
Height/Peaks of Waves (Vision)
Generates the brightness of what we see
8
New cards
Percent of Brain Dedicated to Vision
50% of Cerebral Cortex
9
New cards
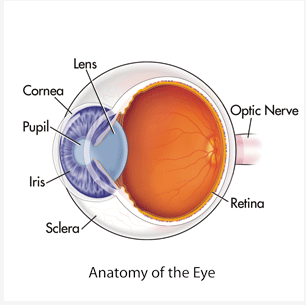
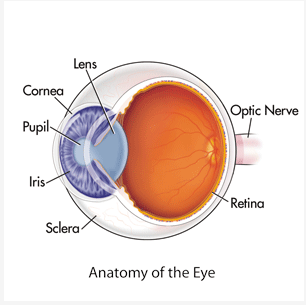
Cornea
* Outer-Most Layer
* First Part of Eye that Bends the Light
* Protects the Eye from Debri
* First Part of Eye that Bends the Light
* Protects the Eye from Debri
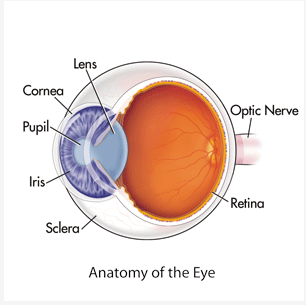
10
New cards
Pupil
* Center of the eye (literal black hole)
* Allows Light to Enter the Depths of the Eye
* Allows Light to Enter the Depths of the Eye
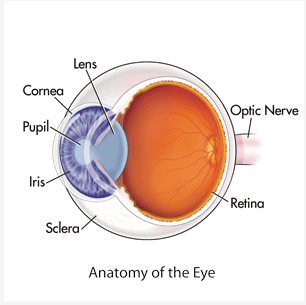
11
New cards
Iris
* A Muscle that can Relax, Constrict, and Constract
* Controls Size of Pupil // Light Allowed into the Eye
* Substances can also Control Constriction and Constraction
* Controls Size of Pupil // Light Allowed into the Eye
* Substances can also Control Constriction and Constraction
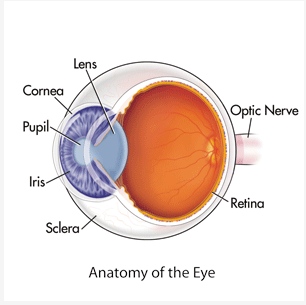
12
New cards
Lens
* Adjusts the Bending of the Light
* Makes the Image Sharper or Less Sharp
* Makes the Image Sharper or Less Sharp
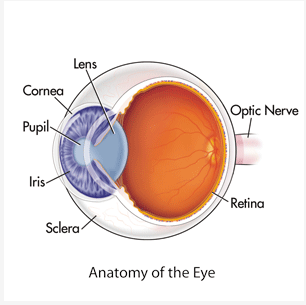
13
New cards
Retina
* All Light Information is Directed into the Retina
* Neurons that Translate Light to Neuron Signals
* Neurons that Translate Light to Neuron Signals
14
New cards
Forea
* Middle of the Retina
* Perception of Fine Details
* Perception of Fine Details
15
New cards
Rods
* Sensitive to Light
* Needs very Little Light to Send Signals
* Located on the Edge of the Retina
* Only percieves in Black and White
* Needs very Little Light to Send Signals
* Located on the Edge of the Retina
* Only percieves in Black and White
16
New cards
Cones
* Needs a Lot of Light Information
* Located in Center of the Retina
* Used in Fine Details of an Image
* Percieves Color of the Light
* Located in Center of the Retina
* Used in Fine Details of an Image
* Percieves Color of the Light
17
New cards
Optic Chiasm
The Crossing of Optic Nerves to Opposite Sides of the Brain
18
New cards
Optic Tract
The Optic Nerve has Fully Crossed to the other Hemisphere
19
New cards
Visual Pathways
* 90% of Optic Tract Axons end in the Thalamus
* Sent to Amygdala to Access Danger
* Sent to Occipital Lobe: Visual Cortex
* 10% of Optic Tract Axons end in the Hypothalamus
* Controls the release of Melatonin based off Light Information
* Sent to Amygdala to Access Danger
* Sent to Occipital Lobe: Visual Cortex
* 10% of Optic Tract Axons end in the Hypothalamus
* Controls the release of Melatonin based off Light Information
20
New cards
Trichromacy Theory
* Eye has 3 Cones
* Long Wavelengths (Red)
* Medium Wavelengths (Green)
* Short Wavelengths (Blue)
* Long Wavelengths (Red)
* Medium Wavelengths (Green)
* Short Wavelengths (Blue)
21
New cards
Trichromacy Theory for Colorblindness
* Missing of 1 out of the 3 Cones leads to Colorblindness
* Missing anymore than 1 Cone leads to White, Grey, and Black Vision
* Missing anymore than 1 Cone leads to White, Grey, and Black Vision
22
New cards
Opponent Process Theory
* Our Occipital Lobe has Opposing Channels for Color
* When One Channel is Active the others are Not
* When One Channel is Active the others are Not
23
New cards
Opponent Process Theory Channels
* Red-Green Channel
* Blue-Yellow Channel
* Black-White Channel
* Blue-Yellow Channel
* Black-White Channel
24
New cards
Color Vision
* Two Theories
* Trichromacy Theory
* Opponent Process Theory
* Trichromacy Theory
* Opponent Process Theory
25
New cards
Trichromacy Theory v.s Opponent Process Theory
* Trichromacy Theory explains Color Processing at Retinal Level
* Opponent Process Theory explains Color Processing at Thalamus or Cortical Level
* Opponent Process Theory explains Color Processing at Thalamus or Cortical Level
26
New cards
Feature Detector Cell (Object Recognition)
Cells that specifically activate when seeing specific objects or shapes
27
New cards
Problem: Feature Detector Cell
Not every object is the same and there are so many things, create too many cells
28
New cards
Gestalt Psychology (Object Recognition)
Takes in the whole thing and tries to break it down into patterns
29
New cards
Figure and Ground
What is the Important Part of the Oject and what is the Background
30
New cards
Proximity
The Organization of Objects by the Closeness to Each Other
31
New cards
Similarity
The Organization of Objects by the Similarity of Objects to Each Other
32
New cards
Continuity
The Organization of Objects based on the Creating of a Smooth Line
33
New cards
Closure
The Organization of Objects by the Unbroken Angles and Gaps in the Objects
34
New cards
Simplicity
The Use of other Principles to come up with Simplist Solution for an Object or Image
35
New cards
Monocular Cues
Information or Clues from One Eye Only
\
* Texture
* Size Comparison
\
* Texture
* Size Comparison
36
New cards
Binocular Cues
Comparing of Information from One Eye to the Other
\
* Retinal Disparity
* Depth Determination
\
* Retinal Disparity
* Depth Determination
37
New cards
Nearsightedness
Elongated Eyeball, Lens Focuses image in Front of the Retina
38
New cards
Farsightedness
Short Eyeball, Lens Focuses image Behind the Retina
39
New cards
Astigmatism
Surface of Cornea is Uneven, Leads to Distorted Image
40
New cards
Height/Peaks of Waves (Audition)
Determines Loudness of the Sound
41
New cards
Frequency/Closeness of Waves (Audition)
Determines Pitch of the Sound
42
New cards
High Pitch
Wave Length is Closer Together
43
New cards
Low Pitch
Wave Length is Farther Apart
44
New cards
Pinna (Outer Ear)
Outer-most part of the ear that Funnels Sound Waves into Ear
45
New cards
Ear Canal (Outer Ear)
A Hole in the ear that Carries Sound Deeper into the ear
46
New cards
Ear Drum (Outer Ear)
Seperates Outer Ear from Middle Ear, Waves of Sound Turn into Vibrations
\
* also known as Tympanic Membrane
\
* also known as Tympanic Membrane
47
New cards
Oscicles (Middle Ear)
Carries Vibrations Deeper into the ear
\
Made of:
* Hammer
* Anvil
* Stimup
\
Made of:
* Hammer
* Anvil
* Stimup
48
New cards
Oval Window (Inner Ear)
Seperates Middle Ear and Inner Ear
49
New cards
Cochlea (Inner Ear)
Filled with Fluid that Vibrates with Input
\
* Cochlea Duct has Basiler Membrane
\
* Cochlea Duct has Basiler Membrane
50
New cards
Basiler Membrane (Inner Ear)
Turns Vibrations into Neuron Signals
\
* Movement of Organ of Corti causes Transduction
\
* Movement of Organ of Corti causes Transduction
51
New cards
Audition Pathway after Ear
* Auditory Nerve
* Brain Stem
* Thalamus
* Temporal Lobe
* Brain Stem
* Thalamus
* Temporal Lobe
52
New cards
Ultrasound
Above 20,000 Hz
53
New cards
Infrasound
Below 20 Hz
54
New cards
Humans Can Hear
Between 20 to 20,000 Hz
55
New cards
Pitch Perception
Most Sounds are not a Pure Pitch, but Several Tones
56
New cards
Center of Cochlea
Lower Pitched Sounds are Percieved
57
New cards
Near the End of Cochlea
Higher Pitched Sounds are Percieved
58
New cards
Minimum and Maximum of Sound
160 dB is the Max, Higher will Burst Ear Drum
\
0 dB is the Minimum, Lower will NOT be Percieved
\
0 dB is the Minimum, Lower will NOT be Percieved
59
New cards
Gate Control Theory
Limited Amount of Processing of a Certain Amount of Information from One Part of the Body
60
New cards
Olfactory Receptors
Transduce Chemical Signals
\
Need to be Replaced every 4-6 weeks because of Chemical Response
\
Need to be Replaced every 4-6 weeks because of Chemical Response
61
New cards
Pathway of Olfaction
Olfactory Receptors → Olfactory Nerve → Olfactory Bulbs → Olfactory Cortex and the Amygdala
\
* Only One to Skip Thalamus
\
* Only One to Skip Thalamus
62
New cards
Taste Receptors
Located on Tongue on Papillae
\
Replaced Every 4-6 weeks or On Demand (burned tongue)
\
Replaced Every 4-6 weeks or On Demand (burned tongue)
63
New cards
Papillae
Each Papillae has 1-100 Taste Buds
64
New cards
Taste Buds
Each Taste Bud has 50-150 Receptors
65
New cards
Pathway of Gustation
Medulla → Thalamus → Somatosensory Cortex and Orbitofrontal Cortex
66
New cards
Drive Theory
Motivation Drives Internal Homeostasi
67
New cards
Drive Activation
When Moving Away from Set Goal (Tension and Arousal)
68
New cards
Drive Reducation
When Goal is Addressed (Relief and Reward)
69
New cards
Incentive Theory
Reward that Pulls Behavior in a Particular Direction
70
New cards
Rewards (Incentive Theory)
* Intrinsic: Internal Reward (Pride)
\
* Extrinsic: External Reward (Money)
\
* Extrinsic: External Reward (Money)
71
New cards
Testosterone
* High Testosterone = Anger and Aggression
* Low Testosterone = Depression and Sadness
\
* Levels Fluctuate Often
* Enviromental Triggers (Superbowl)
* Low Testosterone = Depression and Sadness
\
* Levels Fluctuate Often
* Enviromental Triggers (Superbowl)
72
New cards
Estrogen
* High Estrogen = Ovulation
* Low Estrogen = Menapause
\
* Levels Fluctuate Less Often
* Montly Fluctuation
* Low Estrogen = Menapause
\
* Levels Fluctuate Less Often
* Montly Fluctuation
73
New cards
Cues for Hunger
* Stomach Contraction
* Low Blood Sugar/Insulin
* Leptin Levels
* Low Blood Sugar/Insulin
* Leptin Levels
74
New cards
Leptin
Hormones produced by Fat Cells
\
Hypothalamus Monitors Leptin Levels and Adjust Metabolism Based off it
\
Hypothalamus Monitors Leptin Levels and Adjust Metabolism Based off it
75
New cards
Cues for Satiety
* Hormone CCK Increases in Digestive System
* Reduction of Ghrelin in Blood
* Takes 20 Minutes for Full Response to Occur after Eating
* Reduction of Ghrelin in Blood
* Takes 20 Minutes for Full Response to Occur after Eating
76
New cards
BMI
BMI Treats All Weight the Same
\
* Muscle Weight v.s Fat Weight not Assumed
* Sexes Weighted the Same
* Age is Not Addressed
\
* Muscle Weight v.s Fat Weight not Assumed
* Sexes Weighted the Same
* Age is Not Addressed
77
New cards
Body Fat Percentage
Takes into Account Sex and Age, however Takes a Lot of Information to Calculate
78
New cards
Lifestyle and Genes
Lifestyle
* Fast Food Consumption
* Automation of Jobs
\
Genes
* Carry More Weight
* Rate of Metabolism
* Ideal Body Weight
\
Both Genes and Lifestyle Influence Weight
* Fast Food Consumption
* Automation of Jobs
\
Genes
* Carry More Weight
* Rate of Metabolism
* Ideal Body Weight
\
Both Genes and Lifestyle Influence Weight
79
New cards
Ideal Weight Loss
Gradual Weight Loss to Aviod Leptin Reaction (Slowed Metabolism)
80
New cards
Physiological Needs (Maslow’s Needs)
* Most important and Least Gratisfying
\
Food, Water, and Shelter
\
Food, Water, and Shelter
81
New cards
Saftey (Maslow’s Needs)
Weather, Predators, Coldness/Hotness
82
New cards
Belongingness (Maslow’s Needs)
Relationships
83
New cards
Esteem (Maslow’s Needs)
Respect Ourselves and Feel Respected by Others
84
New cards
Self Actualization
The Last Layer of the Pyrimad
\
Met Your Full Potential
\
Met Your Full Potential
85
New cards
Yerkes-Dodson Law
Perfect or Right Amount of Emotion/Arousal to Perform a Certain Level of Task
86
New cards
Voluntary Emotion Expression
Controlled by Cerebral Cortex
87
New cards
Spontaneous Emotion Expression
Controlled by Subcortical Structures (ex. Amgydala)
88
New cards
Darwin Believed
Emotions were Shaped by Evolution
\
* Social Smile
* Universal Human Emotion
\
* Social Smile
* Universal Human Emotion
89
New cards
Display Rules
Norm that Specifies When, Where, How a Person Expresses Emotion
\
* U.S. v.s Japan
\
* U.S. v.s Japan
90
New cards
Gender Norms
Socially Acceptable Emotion in One Gender over Another
91
New cards
James-Lange Theory
Physical Sensation Results in Specific Conscious Feeling
\
* “I’m crying so I must be sad”
* Problem: Too Simple
\
* “I’m crying so I must be sad”
* Problem: Too Simple
92
New cards
Cannon-Bard Theory
Simultaneous and Independent assessment of Physical Sensations and Subjective Feelings
\
* Physically feel oen sensation and have subjective experience of another
* Problem: Independent Assessment
\
* Physically feel oen sensation and have subjective experience of another
* Problem: Independent Assessment
93
New cards
Schacter-Singer Theory
Physical Sensation Evaluation First, then take into Account Subjective Feelings
94
New cards
SAME Theory
Physical Responses Vary in Intensity and Specificity
\
Specificity Levels Determines Level of Processing
* Dissappiontment (less Specific. more Processing)
* Disgust (more Specific, less Processing)
\
Specificity Levels Determines Level of Processing
* Dissappiontment (less Specific. more Processing)
* Disgust (more Specific, less Processing)
95
New cards
Classical Conditioning
Neutral Simulus paired with One Which Generates a Response
\
* Pavlov
* Bell (Neutral)
* Food (Salvation)
\
* Pavlov
* Bell (Neutral)
* Food (Salvation)
96
New cards
Contiguity
Things Occur Close Togther
\
* Unconditioned Stimuli and Conditioned Stimuli
\
* Unconditioned Stimuli and Conditioned Stimuli
97
New cards
Contingency
Always Occuring Together
98
New cards
Extinction
Unconditioned Stimuli and Conditioned Stimuli are no Longer Paired
99
New cards
Spontaneous Recovery
Reapperance of Conditioned Response after Period of Rest
100
New cards
Generalization
Conditioned Response to not only the Conditioned Stimuli but Similar Objects to the Conditioned Stimuli