Bio exam 6-9
1/118
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
119 Terms
If monomers are joined in a reaction it is called: |
|---|
anabolic
Free energy is released in: |
|---|
catabolic reactions
|
|---|
false
Entropy or conversion of energy to an unstable state, is part of the: |
|---|
2nd law of thermodynamic
Enzyme action may be inhibited by all of the following EXCEPT: |
|---|
presence of cofactors
All energy enters the earth's biosphere from the:
sun
Metabolism refers to only catabolic reactions of a cell or organism.
false
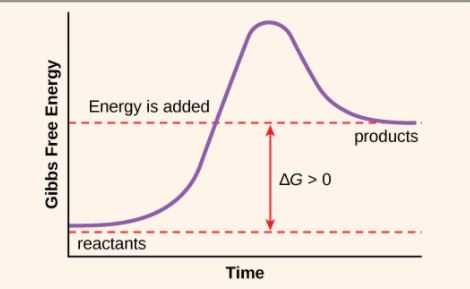
endergonic
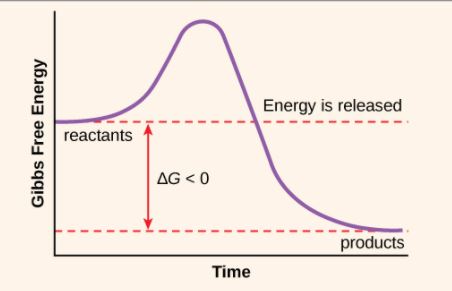
exergonic
Breaking bonds in which part of the ATP molecule provide energy for reactions in the cell?
phosphate group
An allosteric INHIBITOR does which of the following?
Binds to the active site and blocks it from binding substrate
Most enzymes are proteins.
true
Plants store energy via photosynthesis in the bonds of:
glucose
Which of the following statements about endergonic and exergonic reactions is false?
Endergonic reactions take place slowly and exergonic reactions take place quickly
Photosynthesis is a catabolic pathway.
false
In cellular respiration the energy in the bonds of glucose is transferred to:
bonds of phosphates in ATP
When a molecule is oxidized it
lose electrons
The majority of ATP is produced by which set of reactions?
oxidative phosphorylation
All of the following occurs in mitochondria EXCEPT:
glycolysis
Glycolysis can occur in anaerobic conditions as long as _________ is regenerated using fermentation.
NAD+
Which wavelength of light is best for photosynthesis? |
|---|
blue
All of the following are photosynthetic pigments EXCEPT:
melanin
Which of the following occurs in membranes of the thylakoids? |
|---|
light dependant reactions
Which component uses ATP, NADPH & CO2 to build glucose? |
|---|
Calvin Cycle, Light Independent Reactions or Dark Reactions
In which of the following is H2O split to generate H+ and oxygen? |
|---|
Photosystem II
Chemiosmosis involves
movement of hydrogen ions across a mitochondrial membrane
The energy currency used by cells is
ATP
A reducing chemical reaction
adds an electron to the substrate in the form of a H atom
Which pathway receives electrons from NADH?
ETC
At the end of glycolysis, a small amount of ATP is made.
true
What is the source of electrons for the chloroplast electron transport chain?
water
What two main products result from photosynthesis?
sugars/carbohydrates and oxygen
Which statement about thylakoids in eukaryotes is NOT correct?
Thylakoids exist as a maze of folded membranes
Which molecule must enter the Calvin cycle continually for the light-independent reactions to take place?
CO2
The photosynthesis equation is the reverse of cellular respiration.
true
Cells that produce signals that act on neighboring cells are called:
paracrine
Signal molecules that can go directly through the cell membrane to find their receptors inside are called: |
|---|
hydrophobic
The passing of a signal from the outside to the inside of the cell across the cell membrane is called: |
|---|
signal transduction
All of the following are cell surface receptors EXCEPT: |
|---|
steroid intracellular
Another name for Apoptosis |
|---|
programmed cell death
Neurotransmitter released and binding on adjacent neurons. |
paracrine signaling
The secretion of hormones by the pituitary gland into the bloodstream.
endocrine signaling
The release and binding of IL-1 ligand on the same monocyte
autocrine signaling
Coordination of contraction in connected cardiac muscle cells.
direct signaling across gap junctions
Which type of molecule acts as a signaling molecule in yeasts?
mating factor
All of the following are considered second messengers except:
tyrosine kinase
Why are ion channels necessary to transport ions into or out of a cell?
Ions are charged particles and cannot diffuse through the hydrophobic interior of the membrane
Apoptosis can occur in a cell when the cell is:
damaged, no longer needed, infected by a virus
Endocrine signals are transmitted more slowly than paracrine signals.
true
Cell signaling can result in:
increased cell metabolism, cell growth, cell death
metabolic pathway
series of biochemical reactions that converts one or more substrates into a final product
Gibb’s free energy
amount of energy available to do work
Activation energy
energy required for reaction to happen
1st law of thermodynamics
all energy in universe is constant, energy cannot be created or destroyed
2nd law of thermodynamics
the transfer of energy is not completely efficient
with each reaction some energy is lost
ATP composition
adenosine backbone and 3 phosphate groups
sodium-potassium pump
energy from ATP hydrolysis used to move 3 sodium ions out and 2 potassium ions in
enzymes
protein catalysts that speed up reactions
enzyme regulation
helps control cell environment to meet specific needs
temp or pH
competitive enzyme inhibition
inhibitor has similar shape to substrate and competes for active site
noncompetitive enzyme inhibition
bind to enzyme at different location slowing down reaction rate
allosteric inhibitors
modify active site of enzyme so that substrate binding is reduced or prevented
allosteric activators
modify active site of enzyme that substrate binding is increased
enzyme cofactors
one or more required for enzyme function
feedback inhibition
end product of pathway inhibits upstream step
redox reaction
electrons transferred from one molecule to another
reducing agent
donate electron in redox reaction
oxidizing agent
accept electron in redox reaction
phosphorylation
adding a phosphate group to a molecule
hydrolysis of ATP
ADP+Pi
90% of ATP is produced by
chemiosmosis
cellular respiration reaction
C6H12O6 + 6 O2 → 6 CO2 + 6 H2O + ~36 ATP
Metabolic pathways involved with cellular respiration
glycolysis, oxidative phosphorylation, citric acid cycle, oxidation of pyruvate
glycolysis(in)
1 glucose, 2 NAD+, 2 ATP, 4 ADP
glycolysis(out)
2 pyruvate, 2 NADH, 4 ATP, 2 ADP
glycolysis
occurs in cytoplasm
10 enzymatic reactions
anaerobic
oxidation of pyruvate
if oxygen is present —> 2 pyruvate enter mitochondria —> converted to Acetyl CoA
beginning of citric acid cycle
citric acid cycle
occurs in mitochondrial matrix
citrate oxidized —> 3 NADH + 1 FADH2 made and CO2 released —> 1 GTP/ATP produced
—> oxaloacetate
citric acid cycle (out per glucose)
4 ATP, 6 CO2, 10 NADH, 2 FADH2
oxidative phosphorylation(structure)
ETC and chemiosmosis
oxidative phosphorylation(ETC)
electrons from NADH and FADH2 moved to O2 —> redox reactions+energy released —> proton gradient
oxidative phosphorylation(chemiosmosis)
uses kinetic energy from protons in gradient to create ATP(~36)
which process creates the most ATP
oxidative phosphorylation
lactic acid fermentation
occurs in muscle cells when O2 is limited
pyruvate + NADH ←→ lactate + NAD+
metabolism without O2
fermentation regenerates NAD+ so glycolysis can continue
alcohol fermentation
anaerobic yeast species
catalyzed by pyruvate decarboxylase —> alcohol dehydrogenase
autotrophs
self-feeding organisms
photoautotrophs
use sunlight to make food
plants, algae, cyanobacteria
chemoautotrophs
capture energy from inorganic chemicals
thermophilic bacteria
heterotrophs
rely on autotrophs for energy, heterotrophs eat other heterotrophs for energy
photosynthesis equation
6 CO2 + 6 H2O —> C6H12O6 + 6 O2
metabolic pathways of photosynthesis
light dependent reaction
calvin cycle
light reaction
converts light energy to chemical energy
occurs in thylakoid membrane of chloroplasts
calvin cycle
uses ATP and NADPH to make sugar
occurs in stroma of chloroplasts
chloroplast structure
double membrane, stroma, grana(stacks of thylakoids), lumen(inside thylakoid)
main pigments of thylakoid membrane
chlorophyll a, chlorophyll b, B-carotene
thylakoid membrane components
Photosystem I and II, ETC molecules, NADP reductase, ATP synthase
Photosystem II
1st system
absorbs light energy and uses it to transport electrons from H2O to the ETC, producing O2 as a byproduct
Photosystem I
2nd system
uses light energy to transport electrons to NADP+, forming NADPH
stages of calvin cycle
fixation, reduction, regeneration