Biomolecules
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
What is water made up of?
Water is the substance in which all metabolic reactions take place in cells and in which all substances are transported around the body
Water is composed of atoms of hydrogen and oxygen
One atom of oxygen combines with two atoms of hydrogen by sharing electrons; this is covalent bonding
How do water molecules have a dipole nature?
The sharing of the electrons is uneven between the oxygen and hydrogen atoms
The oxygen atom attracts the electrons more strongly than the hydrogen atoms, resulting in a weak negatively charged region on the oxygen atom (δ-) and a weak positively charged region on the hydrogen atoms (δ+)
This separation of charge due to the electrons in the covalent bonds being unevenly shared is called a dipole
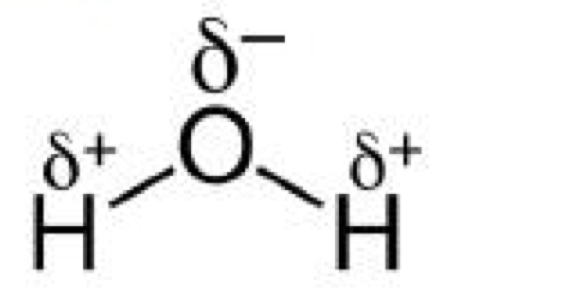
How is water a polar molecule?
As a water molecule has one end that is positively charged and one end that is negatively charged
why do water molecules flow past each other in a liquid state?
Hydrogen bonds form between the positive and negatively charged regions of water molecules as a result of the polar nature of water
Hydrogen bonds are weak when they are few in number, so they are constantly breaking and reforming; this means that water molecules flow past each other in a liquid state
What is cohesion and adhesion?
Cohesion is the attraction of water molecules to each other ( hydrogen bonds between water molecules )
Adhesion is the attraction of water molecules to molecules of a different substance( hydrogen bonds between water and other molecules )
How does water’s solvent properties make it good at transporting substances?
As water is a polar molecule many ions, e.g. sodium and chloride ions, and covalently bonded polar substances, e.g. glucose, will dissolve in it
Water molecules surround charged particles; the positive parts of water are attracted to negatively charged particles and the negative parts of water are attracted to positively charged particles
The surrounded molecules break apart e.g. sodium chloride molecules break into sodium ions and chloride ions
The ions surrounded by water molecules have dissolved
This allows chemical reactions to occur within cells as the dissolved solutes are more chemically reactive when they are free to move about
Metabolites ( a molecule that takes part in a metabolic reaction ) can be transported efficiently in a dissolved state
What elements do carbohydrates contain?
Carbon (C), hydrogen (H), and oxygen (O).
Why is carbon important in organic compounds?
Carbon can form covalent bonds with many elements (including C, H, O, N, S), making compounds stable and able to form chains or rings.
What kinds of structures can carbon form in molecules?
Straight chains, branched chains, or rings.
What is a monomer and a polymer?
A monomer is a small single subunit; many monomers join via polymerisation to form a polymer.
What are the three main types of carbohydrates?
Monosaccharides, disaccharides, and polysaccharides
What are Monosaccharides?
the monomers of carbohydrate; they can join together to make carbohydrate polymers
Monosaccharides are simple carbohydrates
Monosaccharides are sugars
What are the four monosaccharides you need to know?
α ( alpha ) - Glucose , β (beta) - Glucose,
Fructose , Galactose
glucose is a hexose sugar
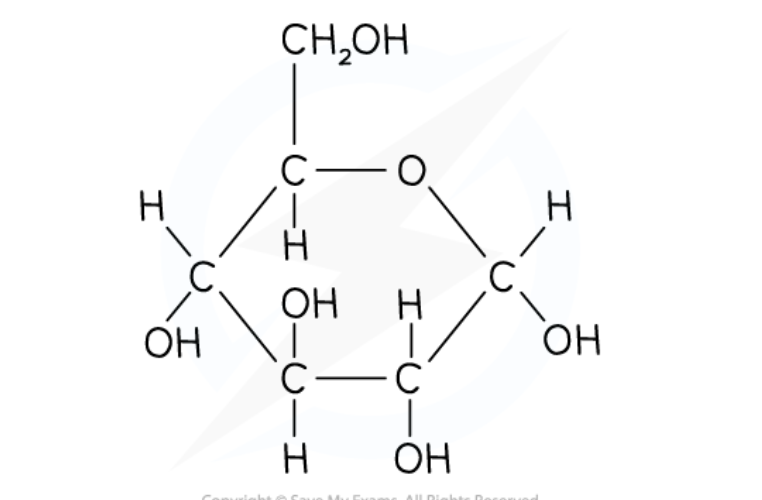
What is the structure and role of alpha glucose?
The main substrate for respiration ( the main molecule that is used (broken down) in cellular respiration to release energy.)
the form is which carbohydrate is transported in mammalian blood
forms the polysaccharides starch and glycogen
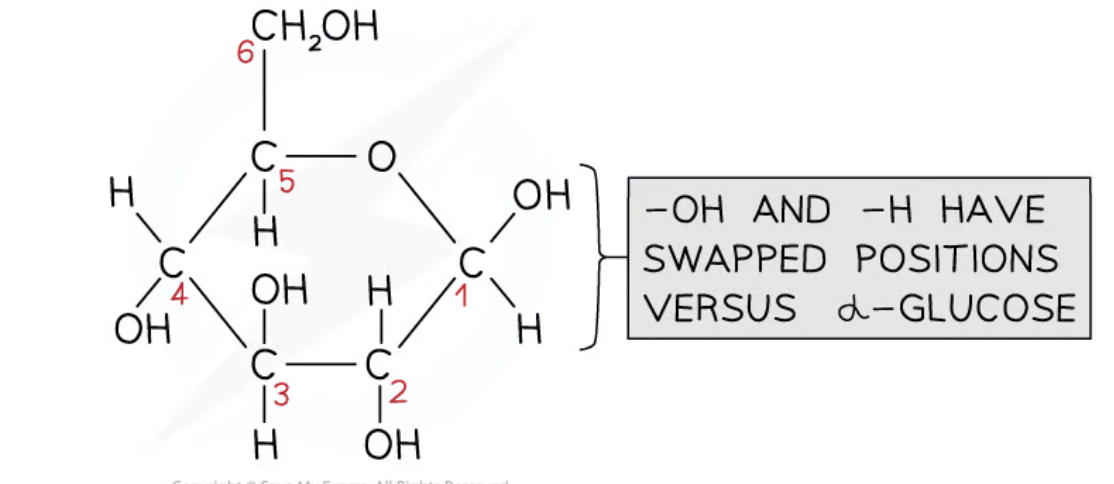
What is the structure and role of beta glucose?
Forms the polysaccharide cellulose
What is the role of Fructose?
found in nectar and many fruits, it is sweeter than glucose, helps attracts animals for fruit dispersal , with glucose forms disaccharide sucrose
What is the role of galactose?
With glucose, form disaccharide lactose
What is the function of Monosaccharides?
The main function of monosaccharides is to store energy within their bonds
When the bonds are broken during respiration, energy is released
The structure of glucose is related to its function as the main energy store for animals and plants
It is soluble so can be transported easily
It has many covalent bonds which store energy
Monosaccharides can combine through condensation reactions to form larger carbohydrates
Some monosaccharides are used to form long, structural fibers, which can be used as cellular support in some cell types
What are Disaccharides?
A type of carbohydrates formed when 2 monosaccharides join together via condensation reactions
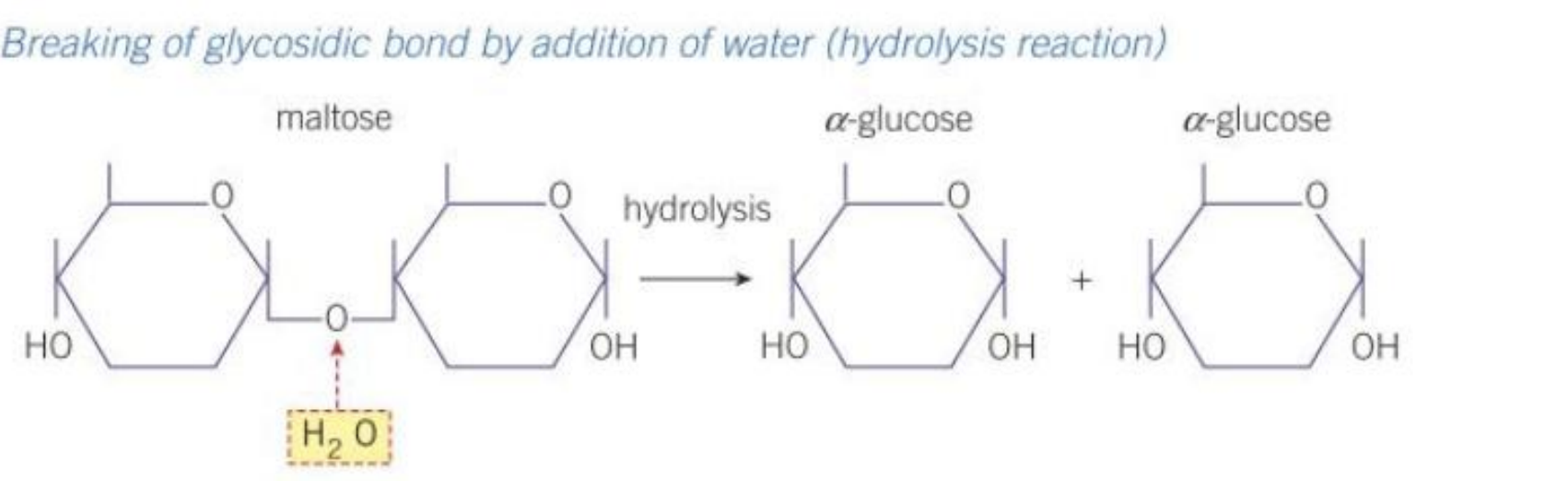
What are Condensation and Hydrolysis reactions?
Condensation reaction: the joining together of molecules through the removal of water
Hydrolysis reaction: the splitting of molecules through the addition of water
What are the three disaccharides you need to know?
Maltose:
glucose + glucose —> maltose+ water
Lactose:
glucose + galactose —> lactose + water
Sucrose:
glucose + fructose —> sucrose + water
—> joined by a glycosidic bond
Draw out the condensation reaction that forms maltose
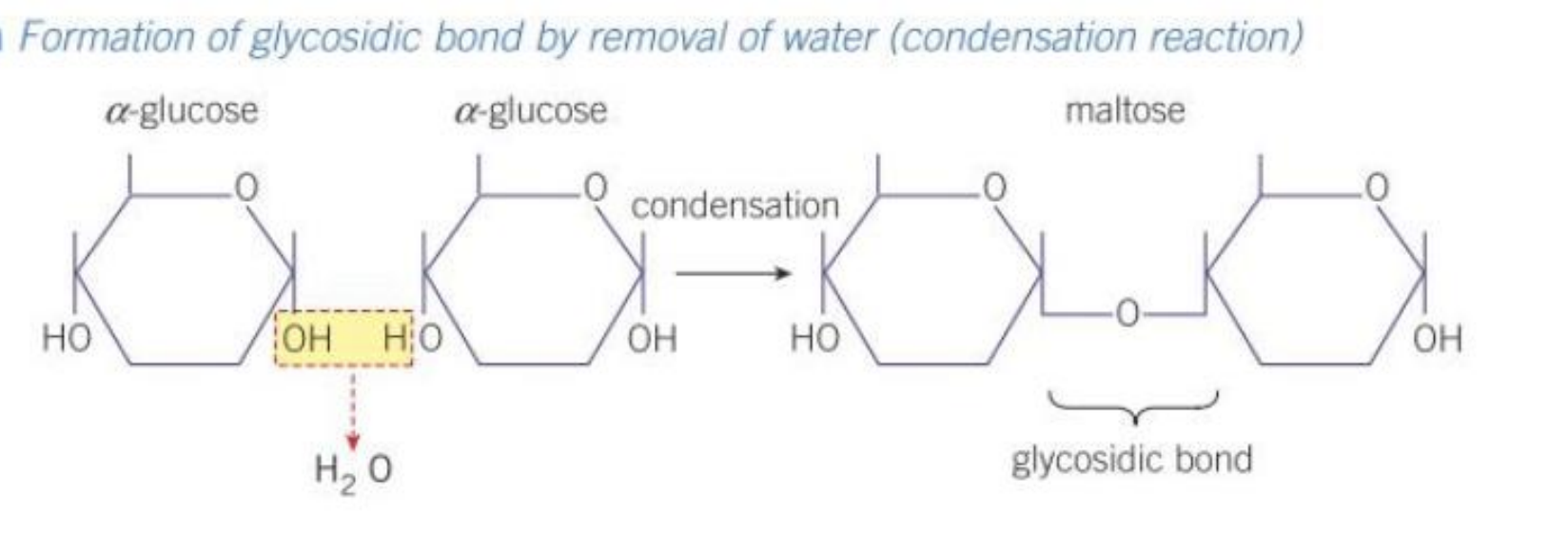
Draw out the hydrolysis reaction that separates maltose
What is the function of disaccharides?
to provide the body with a quick-release source of energy
Disaccharides are made up of two sugar molecules so they're easily broken down by enzymes in the digestive system into their respective monosaccharides and then absorbed into the bloodstream
Due to the presence of a large number of hydroxyl groups, disaccharides are easily soluble in water
These hydroxyl groups form hydrogen bonds with the water molecules when dissolved in aqueous solutions
Just like monosaccharides they are sweet in taste
Sucrose, also known as table sugar, is an example
What are polysaccharides?
are carbohydrate polymers, repeated chains of many monosaccharides joined by glycosidic bonds in a condensation reaction
what are the three polymers you need to know?
Starch, Glycogen , Cellulose
Name the two polymers starch is made up of
Amylose and Amylopectin
Name the Monomers that make up starch, Cellulose and Glycogen
Starch: Alpha glucose
Cellulose: Beta glucose
Glycogen: Alpha glucose
What are the bonds between monomers in amylose and amylopectin?
1-4 glycosidic bonds in amylose
1-4 and 1- 6 glycosidic bonds in amylopectin
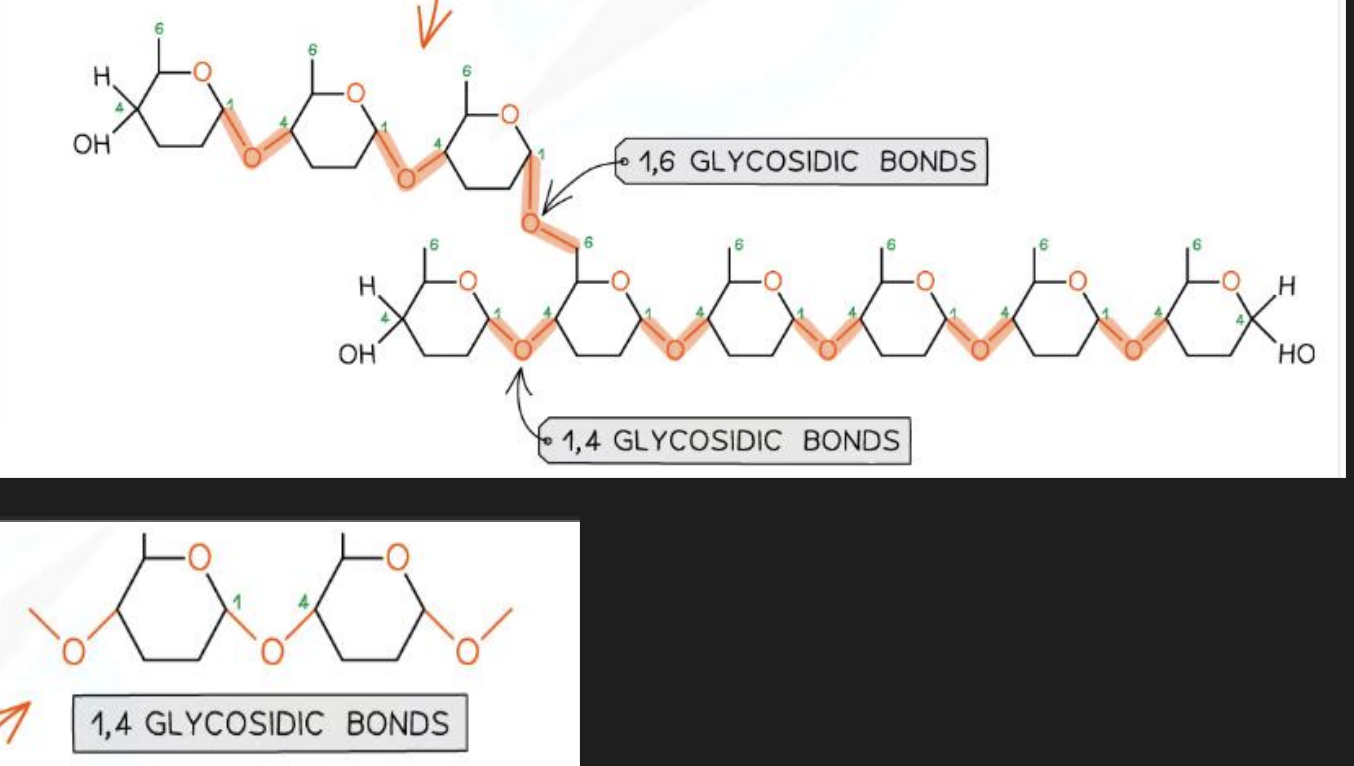
What are the bonds between monomers in cellulose?
1-4 glycosidic bonds
What are the bonds between monomers in glycogen?
1-4 and 1-6 glycosidic bonds
what is the function of Starch
Store of glucose as an energy reserve
What is the function of Cellulose?
Structural strength —> make up cell wall
what is the function of glycogen?
Store of glucose
Where are these polysaccharides located?
Cellulose: In plants , cell wall
Starch: Stored as granules in plastids ( double-membrane-bound organelles found in plant and algal cells ) —> in plants
Glycogen: animals, mainly in muscle and lever cells
Explain the structure of Starch
made of two polymers:
Amylose: an unbranched, long chain that coils into a helix
Amylopectin: a branched molecule
Explain the structure of cellulose
-polymer forms long straight chain
-chains are held in parallel by many hydrogen bonds to form fibrils
-Microfibrils: strong threads made of long cellulose chains joined together by hydrogen bonds forming cross linkages
Explain the structure of Glycogen
A highly branched molecule
has more 1-6 bonds than starch
Explain how the structure of starch leads to its function
helix can compact to fit a lot of glucose in a small space
branched structures increases surface area for rapid hydrolysis back to glucose, which is released rapidly
large and Insoluble →doesn't diffuse easily out of cells, won’t affect water potential, so won't affect osmosis
Amylopectin is more soluble than amylose
Explain. how the structure of cellulose leads to its function
Many hydrogen bonds provide collective strength
insoluble → won’t affect water potential
Explain how the structure of Glycogen leads to its function
Branched structure increases surface area for rapid hydrolysis back to glucose
insoluble → won’t affect water potential
What is the glycosidic bond?
When two hydroxyl (OH) groups on different monosaccharides interact to form a strong covalent bond called a glycosidic bond
one water molecule is always released
broken when water is added ( hydrolysis)