Unit 3 Biochemistry
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/102
Last updated 12:26 AM on 12/6/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
103 Terms
1
New cards
describe an organic compound
a chemical compound produced by/occur naturally in organisms, all include carbon
2
New cards
name organic compounds
breast milk, ear wax
3
New cards
list elements that are commonly found in organic compounds
CHONPS; carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, phosphorus, sulfer
4
New cards
describe a hydrocarbon
a simple chain of hydrogen with carbon
5
New cards
list some hydrocarbons
methane (CH4), ethane (C2H6), propane (C3H8), butane (C4H10)
6
New cards
describe a substituted hydrocarbon
hydrocarbon with 1 or more hydrogen replaced with a "functional group"
7
New cards
list some substituted hydrocarbons
ethyl alcohol (C2H5OH), acetic acid/vinegar (CH3COOH), adenosine triphosphate
8
New cards
what is a "functional group"
a substituent that determines the chemical behavior of the compound
9
New cards
name some functional groups
hydroxyl (-OH), carboxyl (-COOH), phosphate (-PO4)
10
New cards
describe the effect of functional groups on hydrocarbon structure and function
functional groups can affect the bonds that hold macromolecules together, as well as affect its polarities; this changes the function of the hydrocarbons
11
New cards
define organic macromolecules
large, complex substituted organic molecules with specific roles in organisms
12
New cards
compare polymer to monomer
monomers are single unit building blocks of larger molecules whereas a polymer is a long chain of monomers, large molecules
13
New cards
describe the general characteristics/function of carbohydrates
composed of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen; used primarily as sources of energy (some function as structural compounds)
14
New cards
name and identify monosaccharides
simplest carbohydrates, monomers; single-ringed, also called sugars/names end in -ose
15
New cards
name and identify disaccharides
double-ringed sugar, form through dehydration synthesis - 2 monosaccharides stuck together
16
New cards
name and identify oligosaccharides
carbohydrates composed of few (2-10) monosaccharide units
17
New cards
name and identify polysaccharides
more than 2 monosaccharides stuck together in chains, complex carbohydrates/polymers
18
New cards
identify a diagram of the structure of glucose
C6H12O6
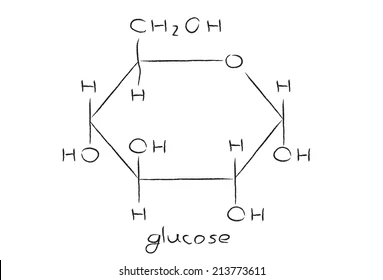
19
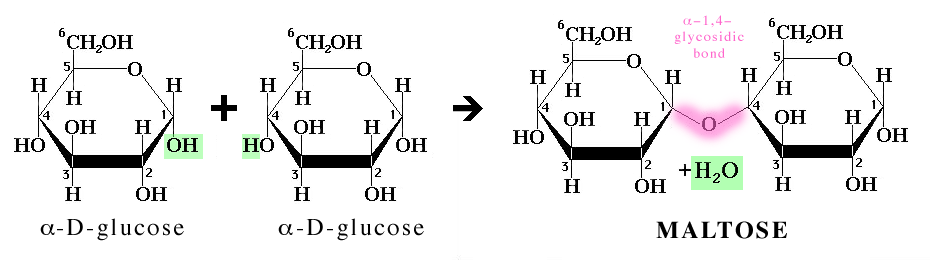
New cards
be able to diagram the formation of disaccharide through dehydration synthesis bonding
20
New cards
describe the breakdown of a disaccharide through hydrolysis
breaking of a bond between monomers by adding water
21
New cards
describe what is meant by an isomer
two molecules that share the same molecular formula but different structural formulas
22
New cards
name a pair of isomers
glucose and fructose
23
New cards
compare the structure, source, and function of 4 polysaccharides discussed in class (1)
starch: molecule made of long chains of sugar molecules (C6H10O5) in which plants store excess sugar in roots, stems, and leaves, plant source
24
New cards
compare the structure, source, and function of 4 polysaccharides discussed in class (2)
cellulose: touch structural polysaccharide ((C6H10O5)n) found in plant cell walls that is relatively waterproof and hard to digest, plant source
25
New cards
compare the structure, source, and function of 4 polysaccharides discussed in class (3)
glycogen: molecules used by animals to store excess sugar in the liver (4-6 hr supply), animal starch, highly branched, animal source (C24H42O21)
26
New cards
compare the structure, source, and function of 4 polysaccharides discussed in class (4)
chitin: tough structural polysaccharide found in the exoskeleton of insects, spiders, and crustaceans, and cell walls of fungi, animal source (C8H13O5N)n
27
New cards
identify reactants of a chemical reaction shown as a chemical equation
substances to the left of a chemical equation, present at the start of the reaction
28
New cards
identify products of a chemical reaction shown a a chemical equation
substances to the right of the chemical equation, result of reaction
29
New cards
describe what is meant by the law of conservation of matter
that the amount of matter stays the same, even when the matter changes form
30
New cards
describe what is meant by the law of conservation of energy
that the amount of energy is neither created nor destroyed (measure through joules)
31
New cards
explain how chemical reactions uphold the law of conservation of matter and energy
the amount of matter and energy in a chemical reaction cannot be created or destroyed; mass and energy of the product is the same as the reactants
32
New cards
explain why a chemical reaction must be balanced
it allows us to predict the amount of reactants needed and amount of products formed in order to abide by the rules of the laws
33
New cards
draw/analyze reaction coordinates to identify energy contained in reactants/products of a chemical reaction
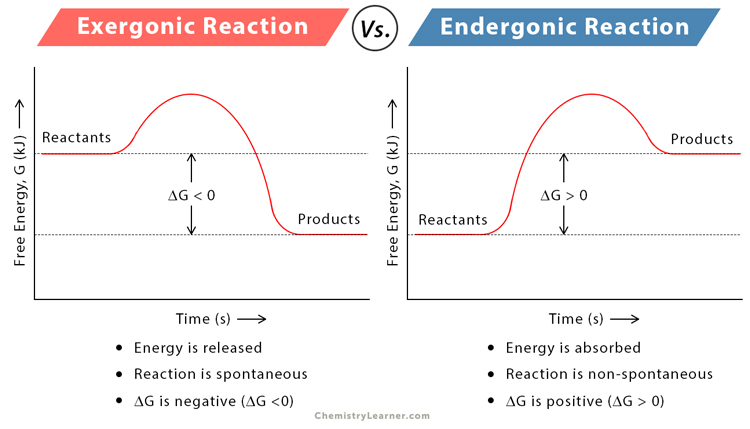
34
New cards
identify role of organic catalysts (enzymes) in lowering activation energy needed to promote a chemical reaction
catalysts decrease the amount of energy required by speeding up chemical reactions without being destroyed itself
35
New cards
identify the role of an enzyme on a reaction coordinate
lowers the free energy of activation of a reaction so the reactants can transition and form products
36
New cards
compare exergonic vs endergonic reactions
both require an input of activation energy and use enzymes to lower the energy needed to complete the reaction
37
New cards
exergonic reactions
energy in reactants are greater than energy in products, release surplus energy as heat and light
38
New cards
endergonic reactions
products hold more energy than reactants provide, energy is absorbed from environment and look dark and cold
39
New cards
identify examples of each and recognize each from reaction coordinates
exergonic - photosynthesis, endergonic - aerobic cellular respiration
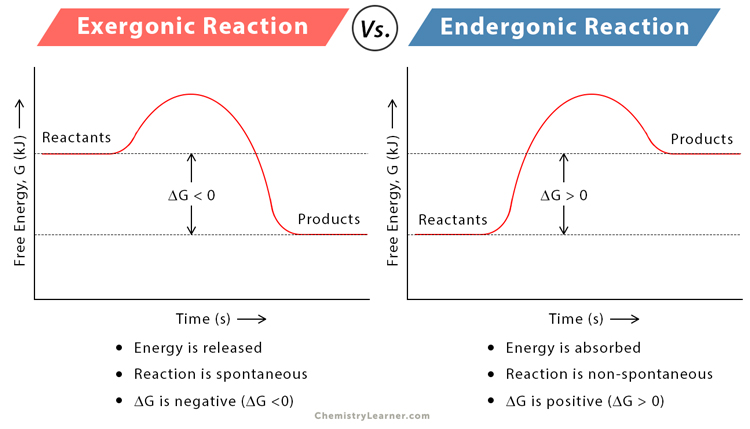
40
New cards
describe the general characteristics/function of proteins
contain CHONS, found in hair, nails, skin, muscle, feathers, include hormones, antibodies, and crustaceans (cell walls of fungi)
41
New cards
diagram the general structure of an amino acid, understand how "r" represents replacement groups that can form 20 amino acids
replacement groups differ between each specific amino acid
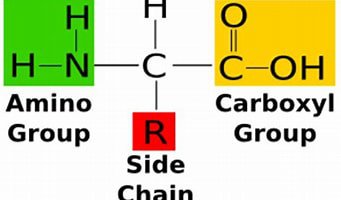
42
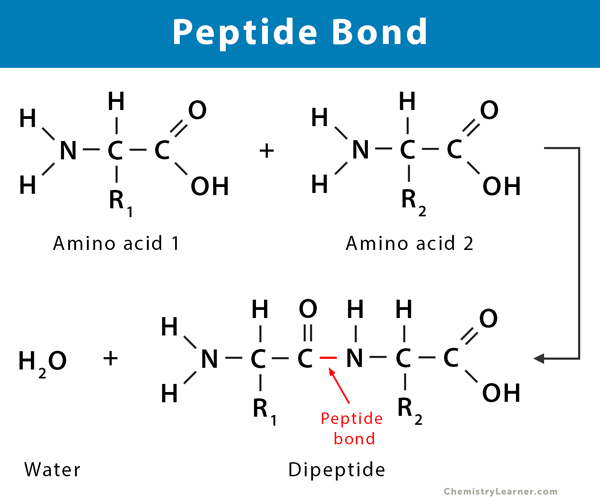
New cards
be able to diagram the formation of a dipeptide by forming a peptide bond
43
New cards
describe the breakdown of a dipeptide through hydrolysis
breaking of a peptide bond by adding water
44
New cards
fibrous proteins
structural function, long, straight chains, located in nails, skin, muscles
45
New cards
globular proteins
function as chemical reactions, are chains folded into 3d shape (glob like), located in hormones, antibodies, enzymes
46
New cards
examples of fibrous proteins
collagen, keratin
47
New cards
examples of globular proteins
hemoglobin
48
New cards
describe the role of enzymes in organisms
organic catalysts that react only with a specific substance that matches its unique 3d shape to release products
49
New cards
describe how enzymes are affected by denaturation
normal shape gets changed, no longer matches shape of the substrate; caused by changes in pH and high temperatures
50
New cards
identify various enzymes and their substrates
amylase and starch, lactase and lactose, catalase and hydrogen peroxide
51
New cards
describe the lock and key theory pertaining to enzyme function
the substrate acts as the key and the enzyme as the lock, active site is the key hole; substrate fits with the enzyme to complete reactions and release products
52
New cards
draw a correctly labeled diagram representing enzyme, substrate, enzyme substrate complex, active site, products
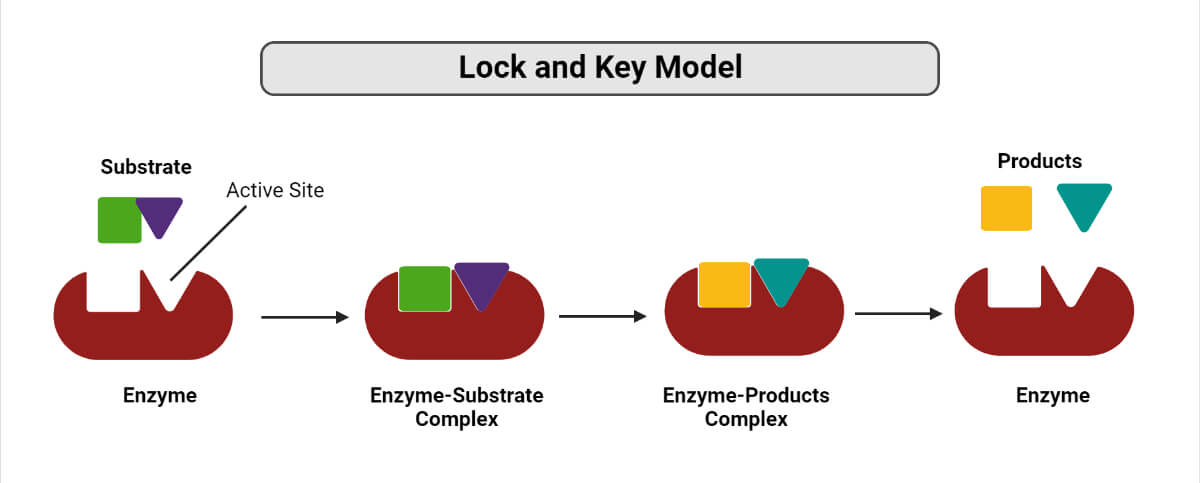
53
New cards
describe the general characteristics/function of lipids in organisms
contain carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, insoluble in water, reserve energy in animals; includes triglycerides (fats and oils), waxes, and steroids
54
New cards
name and describe the monomers of a triglyceride
3 fatty acids + 1 glycerol
55
New cards
diagram the formation of a triglyceride
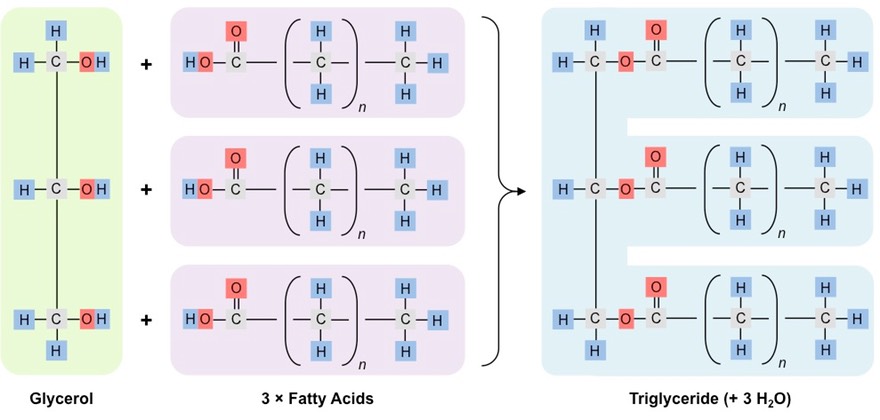
56
New cards
other lipids; waxes
structural lipid, not a triglyceride; beeswax, ear wax (cutin)
57
New cards
other lipids; steroids
4 fused rings of carbon to which many different groups of elements are attached; cholesterol, testosterone
58
New cards
other lipids; phospholipids
special type of triglyceride found within cell membranes (50%), both polar and nonpolar
59
New cards
types of triglycerides; fats
saturated with hydrogen, solid, no double bonds, less healthy (hydrophobic), animal source
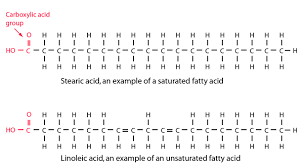
60
New cards
types of triglycerides; oils
unsaturated; not as much hydrogen, liquid, many double bonds, more healthy, plant source
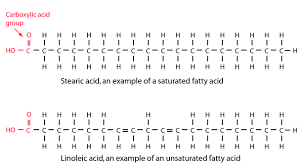
61
New cards
describe the nature and function of phospholipids
acts as a barrier to protect the cell against environmental viruses; makes up 50% of cell membrane
62
New cards
diagram the simplified structure of a phospholipid
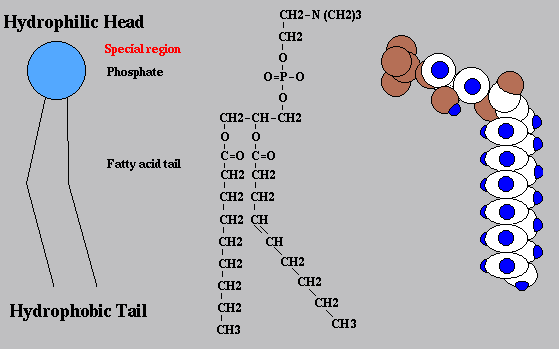
63
New cards
identify polar/nonpolar ends
polar, hydrophilic head, nonpolar, hydrophobic tail
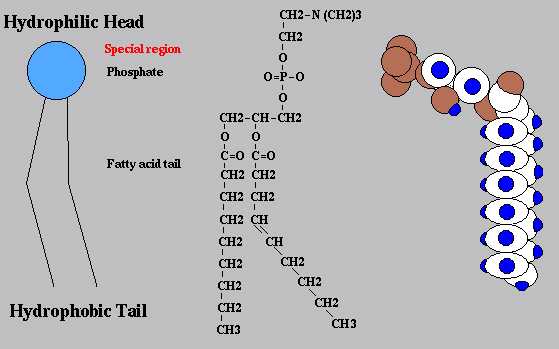
64
New cards
describe how phospholipids form cell membranes
phospholipids will arrange themselves in a pattern where the hydrophilic heads face the water and the tails don't to form cell membranes
65
New cards
describe the role of dna in cells
gets copied during cell division, stores the genetic code; determines protein structure, found in the nucleus
66
New cards
describe the role of rna in cells
temporary copy of genetic code, directly used in protein synthesis, found in nucleus, ribosome, cytoplasm of cell
67
New cards
diagram the structure of dna polymers
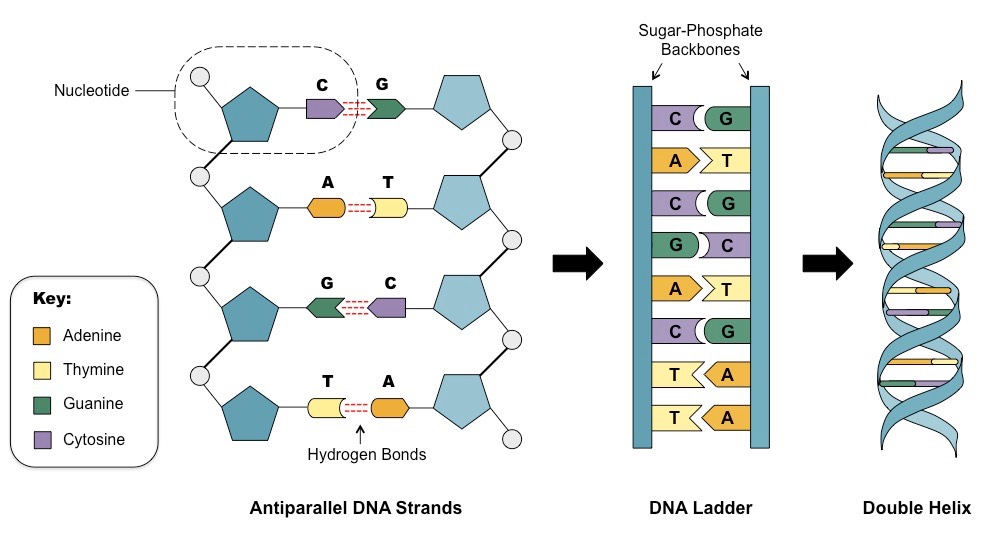
68
New cards
diagram the structure of rna polymers
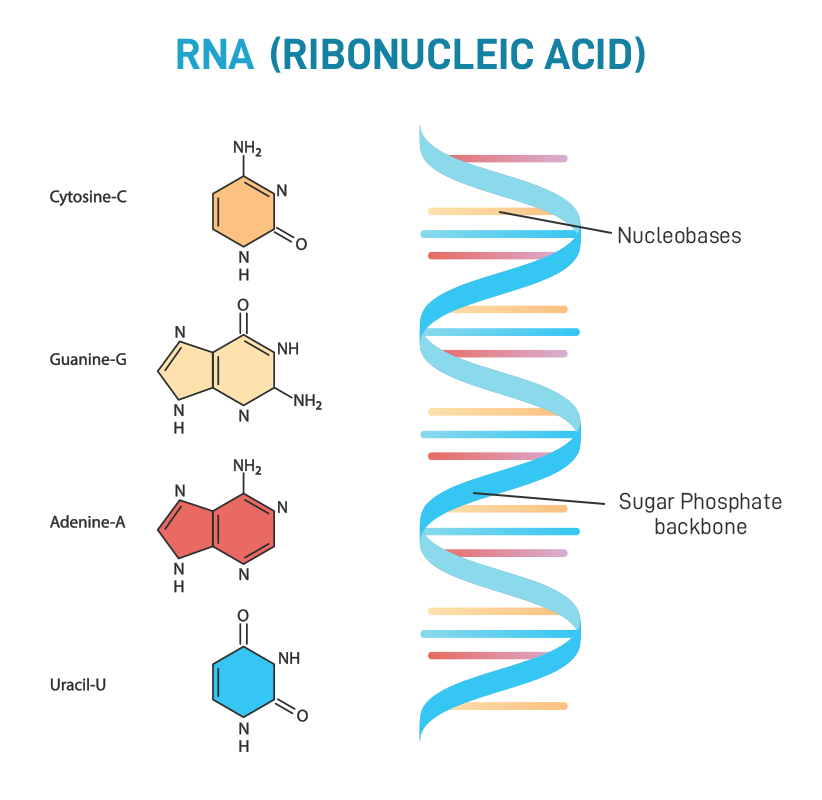
69
New cards
diagram and describe a nucleotide
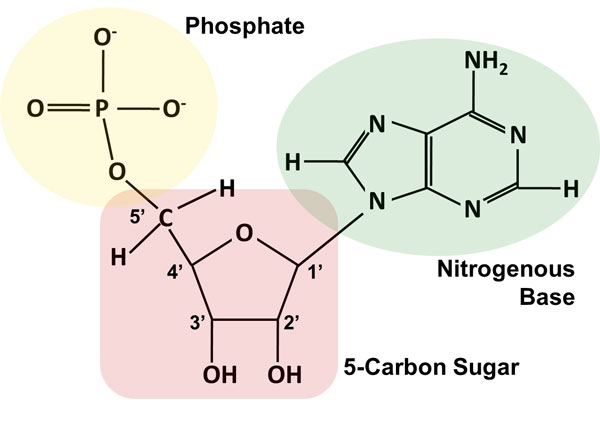
70
New cards
dna nucleotides
contains deoxyribose sugar, may contain thymine, guanine, cytosine, adenine bases
71
New cards
rna nucleotides
contains ribose sugar; has extra oxygen, may contain uracil, guanine, cytosine, adenine bases
72
New cards
dna base pairing rules
cytosine and guanine, thymine and adenine
73
New cards
rna base pairing rules
uracil and adenine, cytosine and guanine
74
New cards
polar molecules
a molecule with two oppositely charged regions
75
New cards
nonpolar molecules
a molecule with the same charged regions
76
New cards
hydrophobic substances
"water-fearing"; non-polar substances, do not dissolve in water easily
77
New cards
hydrophilic substances
"water-loving"; polar substances, dissolve easily in water
78
New cards
examples of polar, hydrophilic molecules/substances
alcohole
79
New cards
examples of nonpolar, hydrophobic molecules/substances
lipids like oil
80
New cards
diagram and describe the formation of hydrogen bonds in water
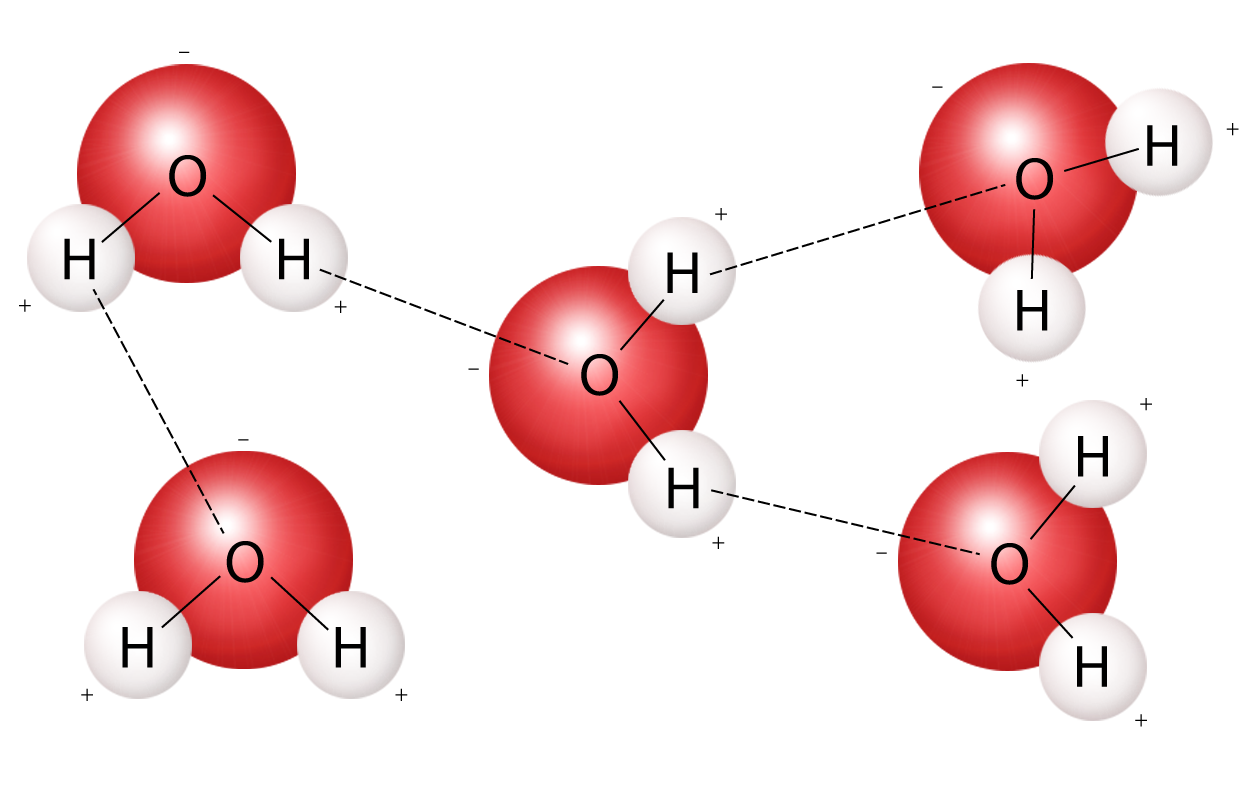
81
New cards
adhesion
attractive forces between two different substances
82
New cards
cohesion
attractive forces between two like things
83
New cards
capillary action
when water can defy gravity; especially through narrow spaces
84
New cards
meniscus
a curve in the surface of water when touching a different material
85
New cards
specific heat
the ability for water to be able to absorb heat and transfer it
86
New cards
density of ice
the ability for ice to float because it is less dense than water, unlike most solids
87
New cards
universal solvent
the ability for water to be able to dissolve more substances than any other liquid on earth
88
New cards
how does adhesion and cohesion promote life on earth
these forces transport water from the roots to the leaves in plants
89
New cards
how does capillary action promote life on earth
when water is being transported through plants, the defying of gravity allows it to flow up through its roots and leaves
90
New cards
how does specific heat promote life on earth
water is able to absorb heat and transfer it to stabilize living conditions
91
New cards
how does the density of ice promote life on earth
to act as a blanket for the water underneath the ice, but also allow living organisms in the water to stay alive
92
New cards
how does the universal solvent promote life on earth
it holds the ability to be able to carry and transport chemicals, minerals, and nutrients essential to living organisms everywhere
93
New cards
aqueous solutions
solution in which something is dissolved in water (solvent)
94
New cards
solute
part of the solution that is dissolved in the water
95
New cards
solvent
liquid dissolving the solute
96
New cards
properties of acid solutions
form hydrogen (H) ions when mixed with water, have a low pH (stronger acid)
97
New cards
properties of base solutions
form hydroxide (OH) ions when mixed with water, have a high pH (stronger base)
98
New cards
be able to draw and label the pH scale with common substances on the scale
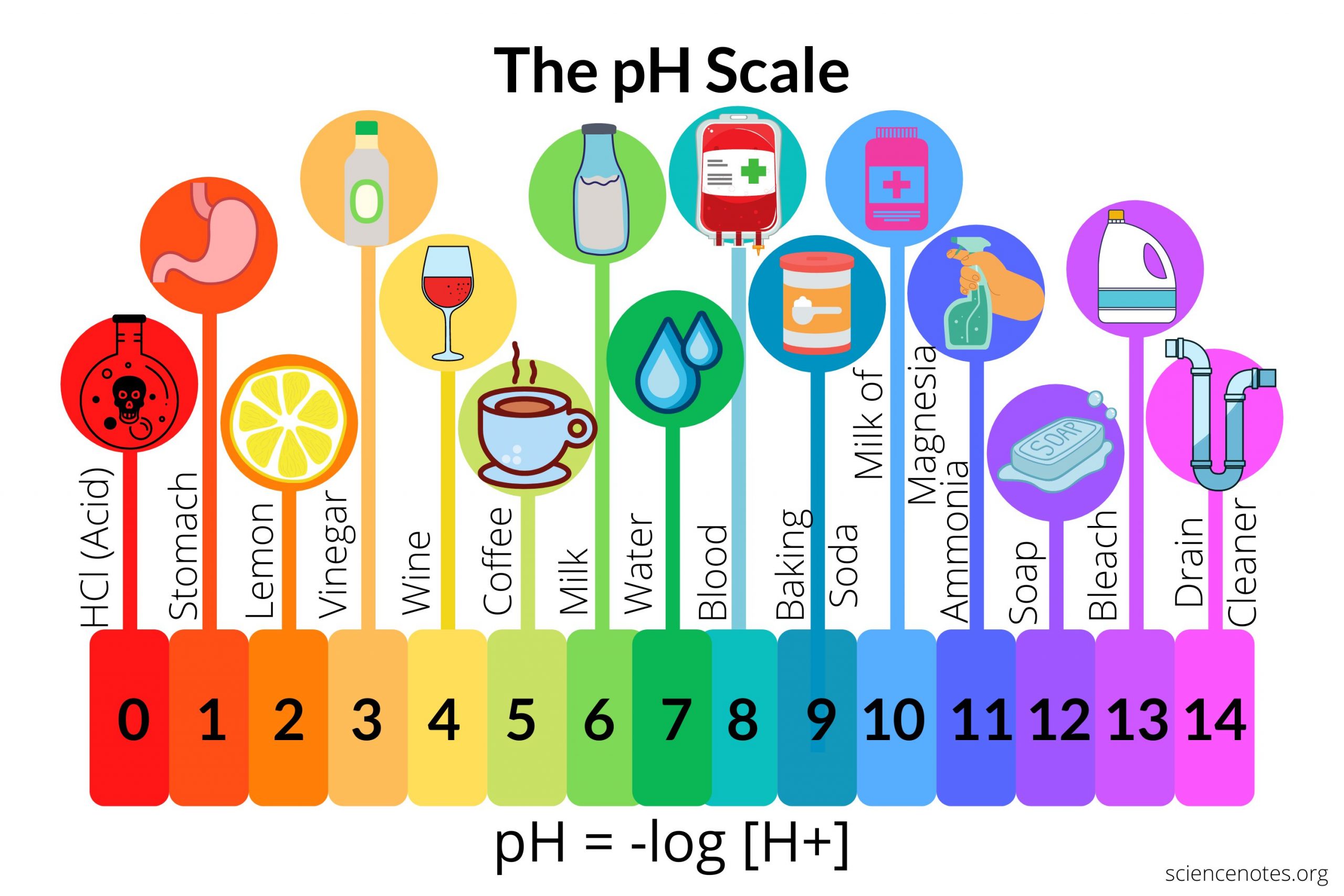
99
New cards
describe the role of a buffer and neutralization in organisms
a chemical that purposely neutralizes an acid or base; when acids and bases react to form harmless salt and water
100
New cards
explain the proper use of litmus
changes the color of the paper to blue or red; blue means basic, red means acidic