Foveal Specializations, Phototransduction, Spectral Sensitivity - Neurophysiology and Perception Spring 2026
1/166
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
167 Terms
the concave shape of the fovea
What is the foveal reflex d/t?
they are pushed to the side
What happens to the inner retinal elements in the fovea?
concave mirror
The foveal pit acts as a _____, reflecting light back to the ophthalmoscope light
We do not want light (photons) to be scattered/deflected or absorbed. This will maximize VA.
Why is it important that there the inner retinal components are pushed to the side in the area of the fovea?
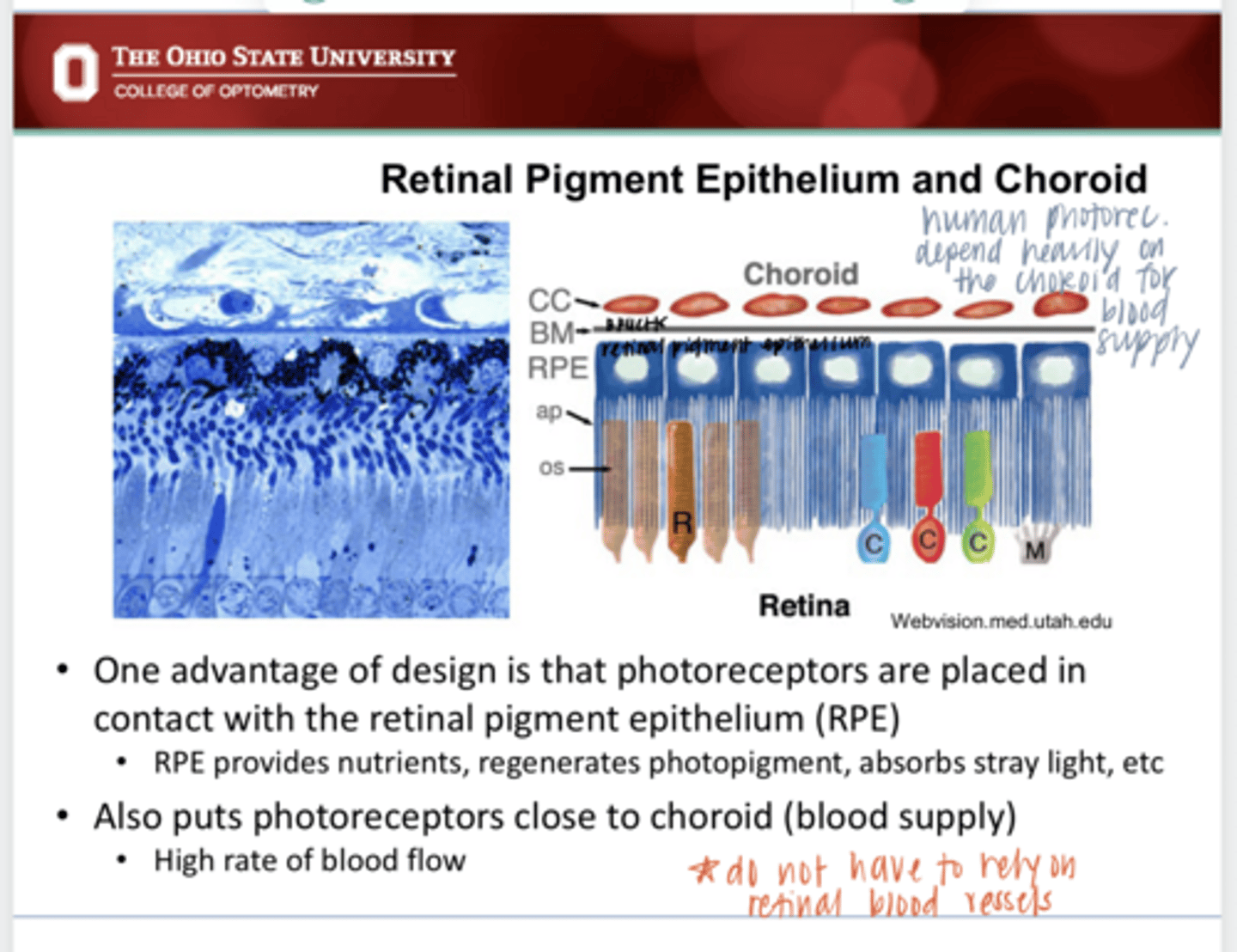
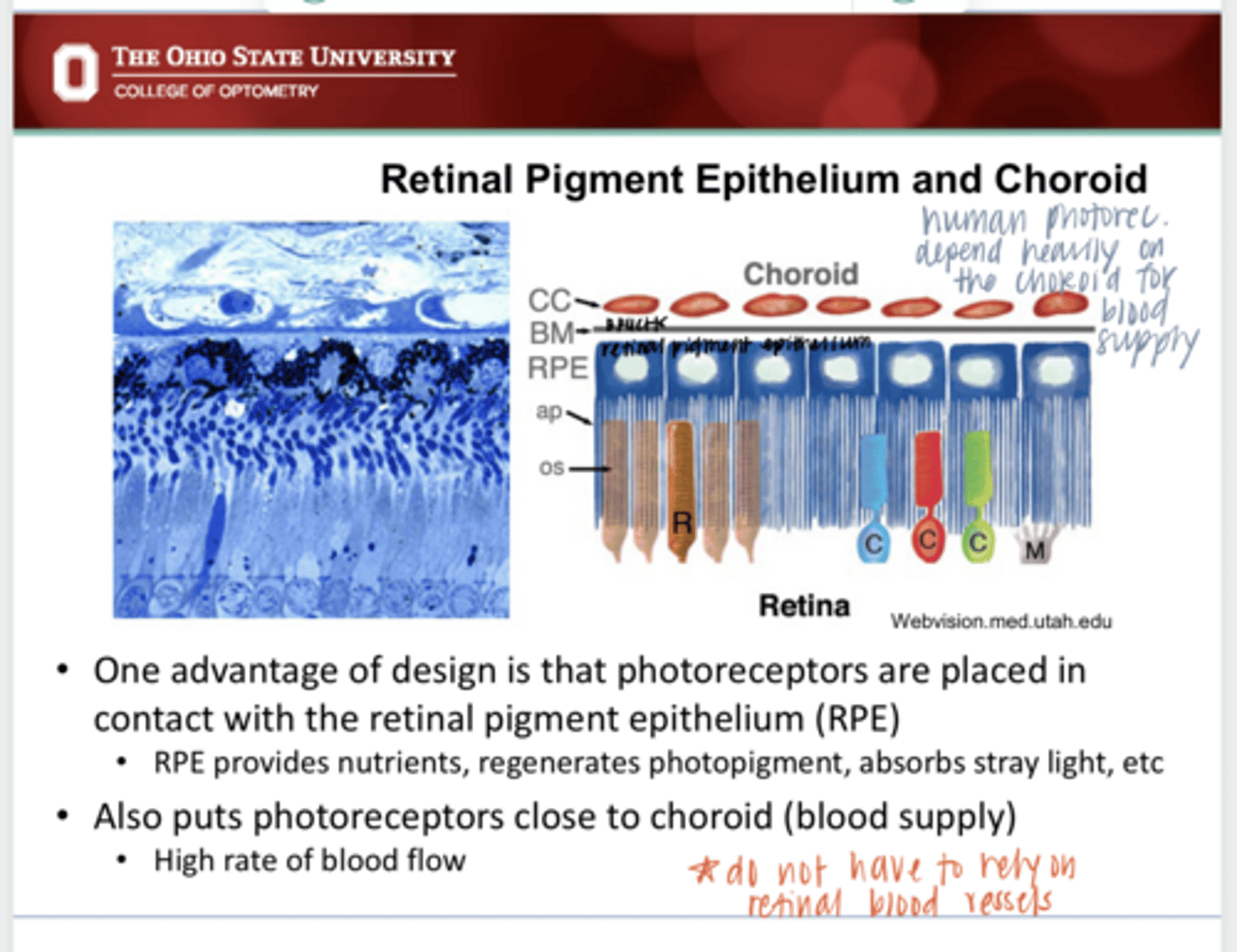
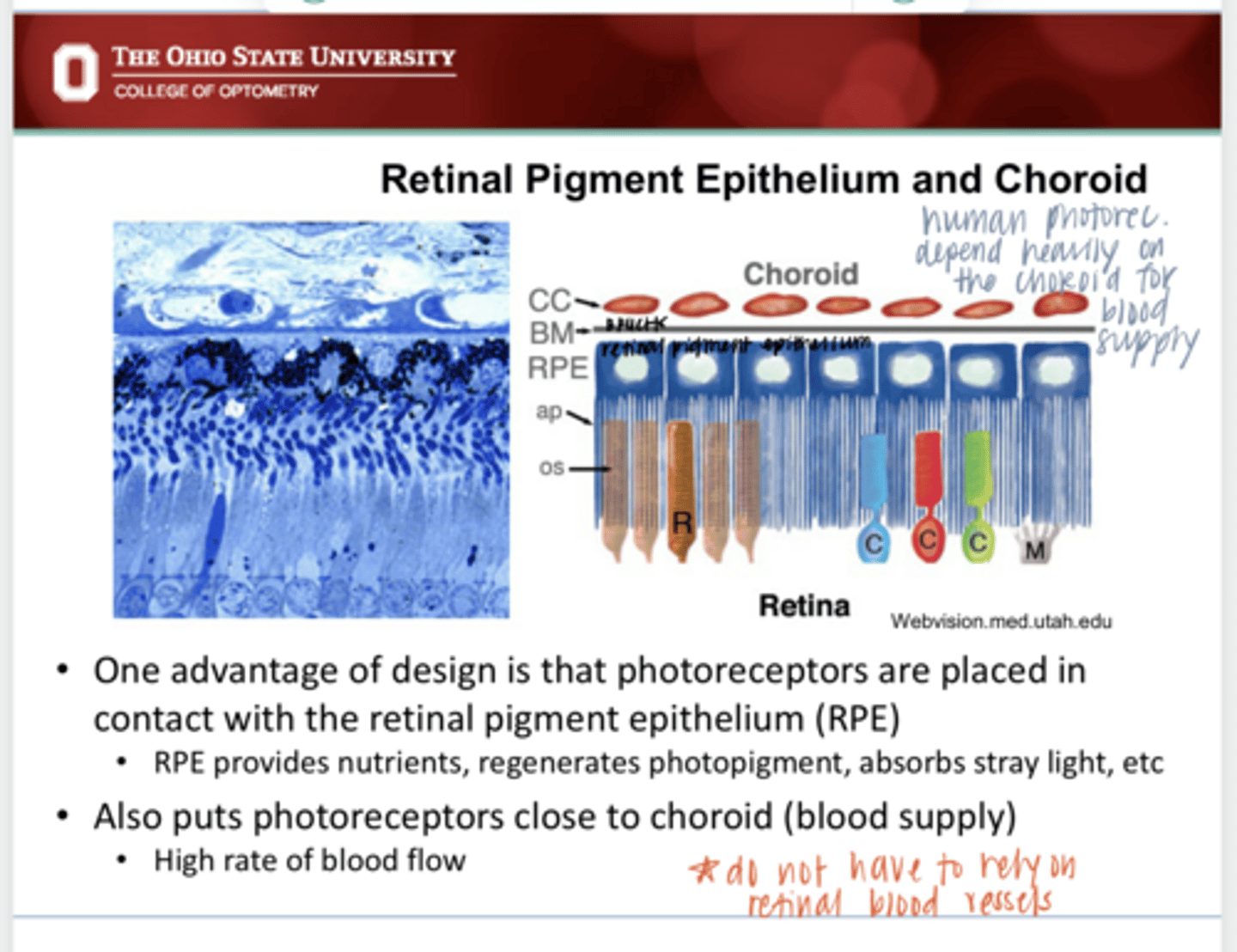
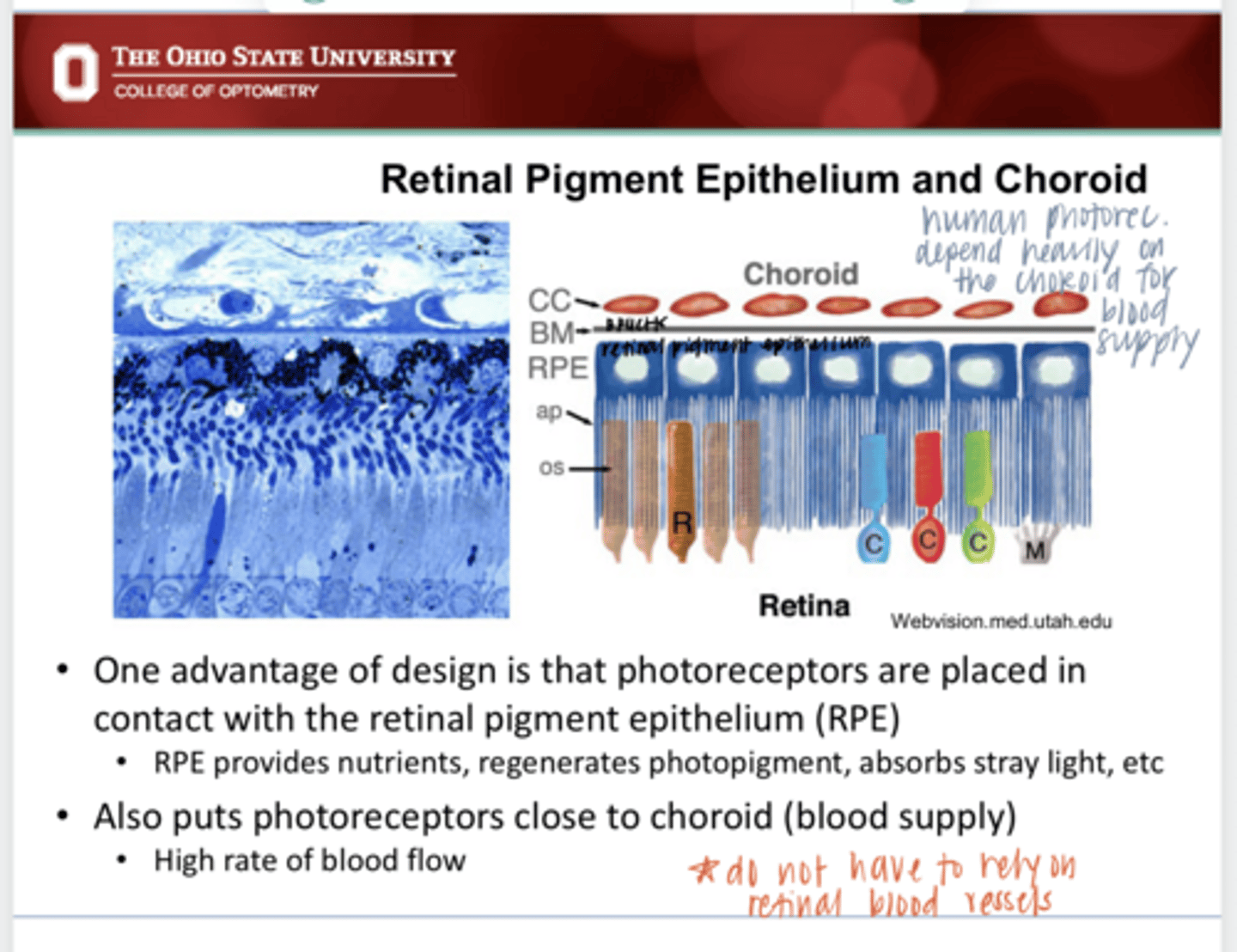
Photoreceptors are placed in contact with the RPE which provides butrients, regenerated photopigment and absorbs stray light. Photoreceptors are also in close contact with the choroid (blood supply) which provides a high rate of flow.
What is the advantage of "backwards" designed retina in a human?
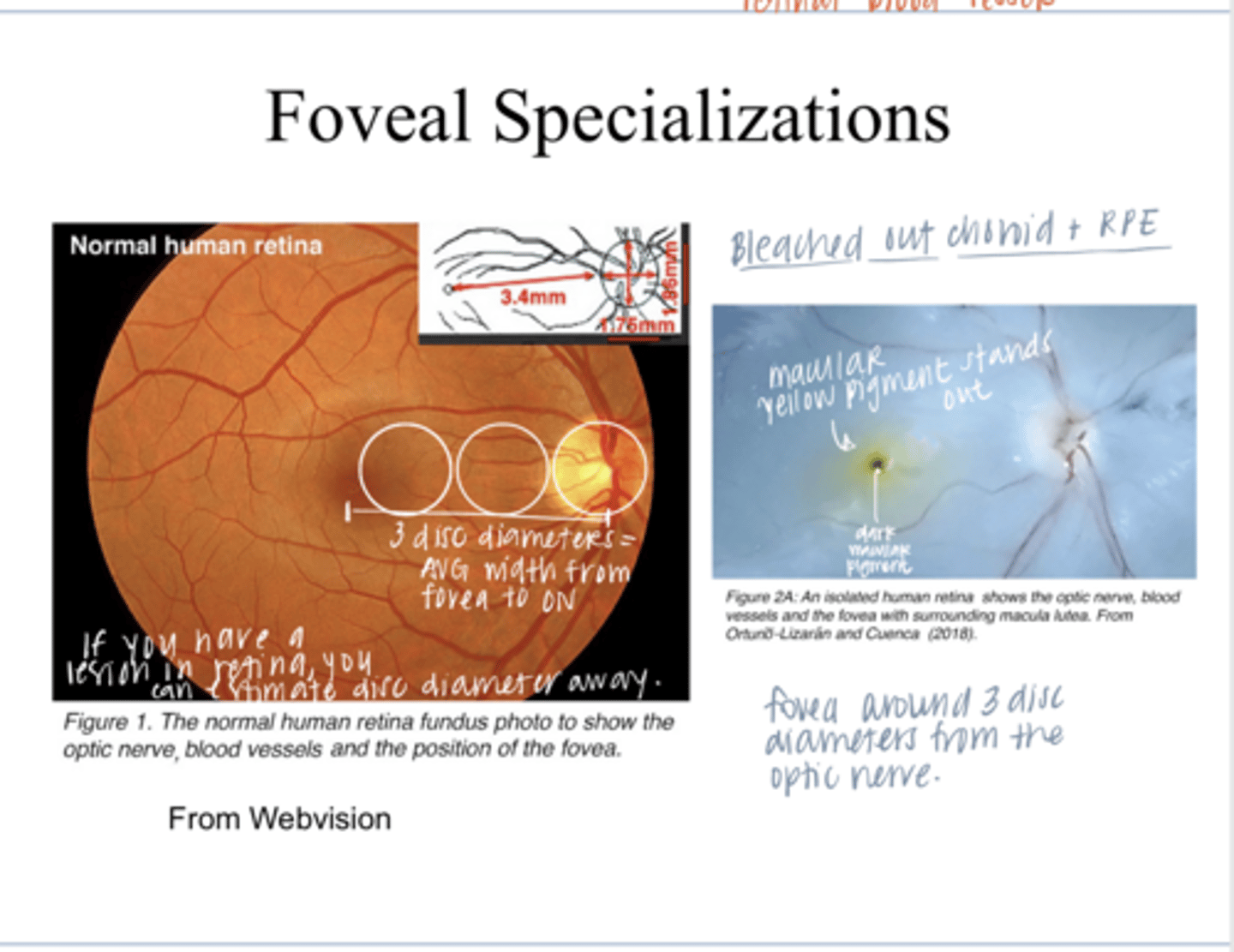
3 disc diameters
What is the avg # of disc diameters between the fovea and the optic nerve head?
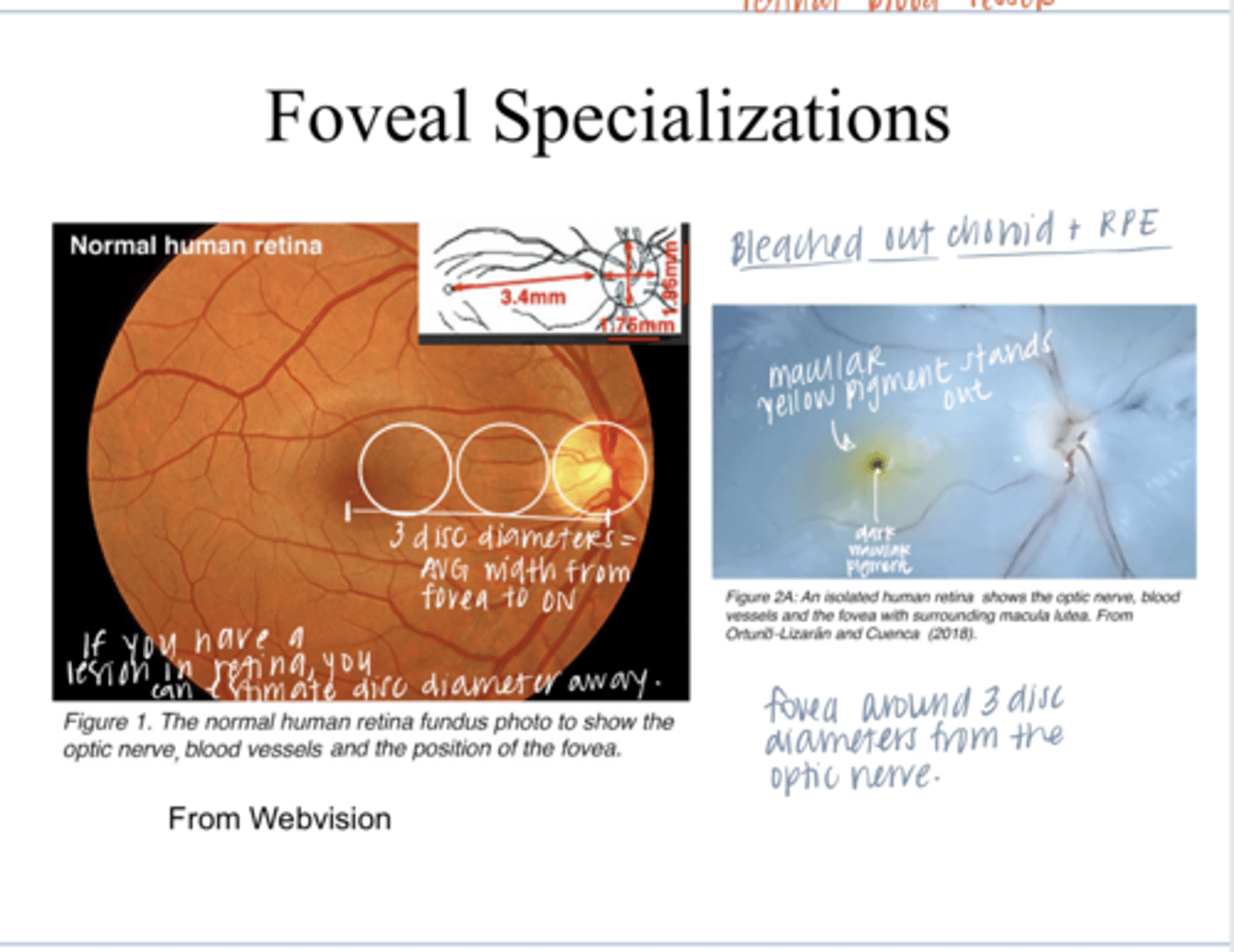
Photo of Macular Pigment in a Bleached out Retina
Photo of Macular Pigment in a Bleached out Retina
fovea
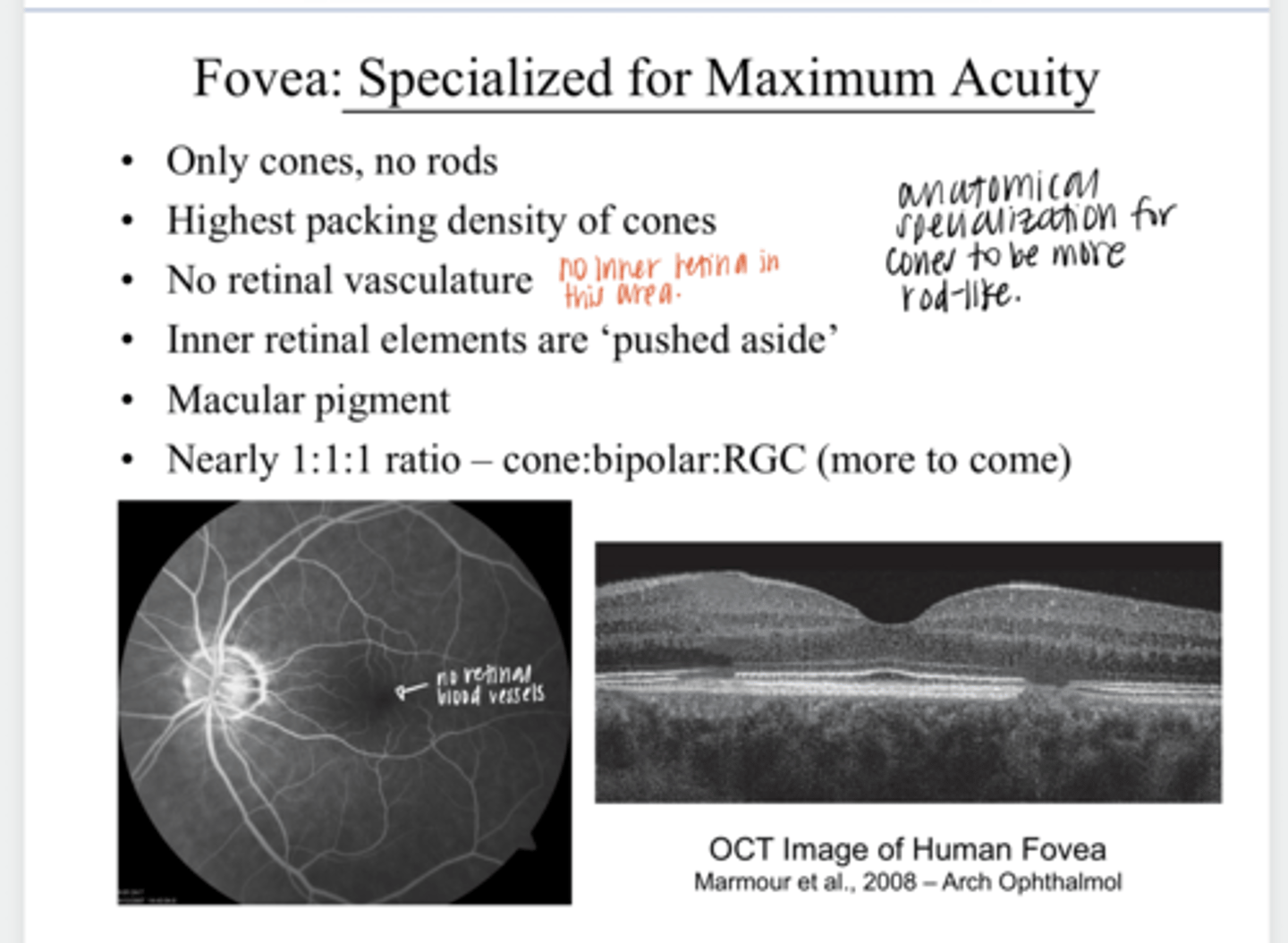
The ___ is specialized for maximum acuity
cones
There are only (cones/rods) at the fovea
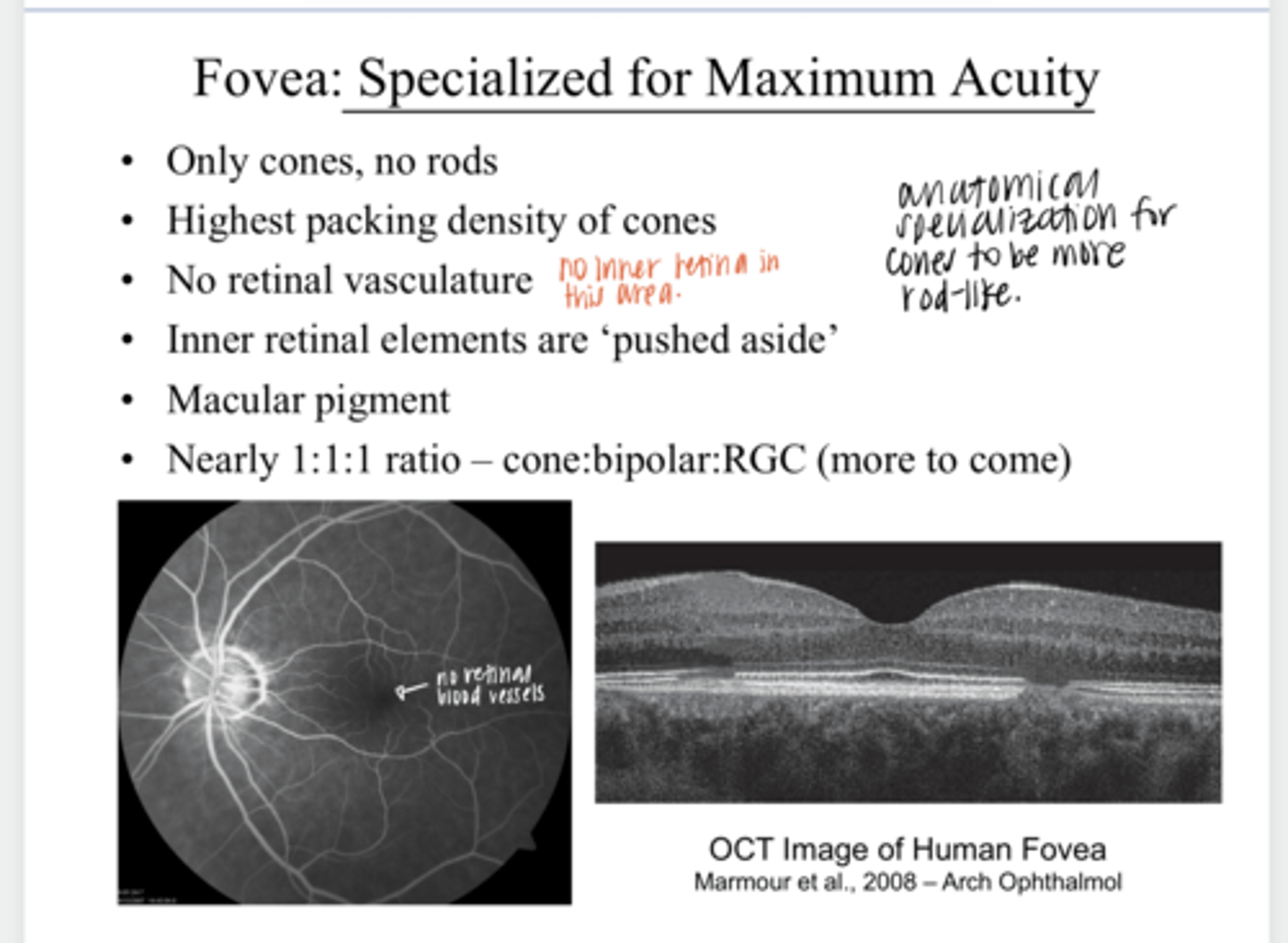
at the fovea
Where is the highest packing density of cones present?
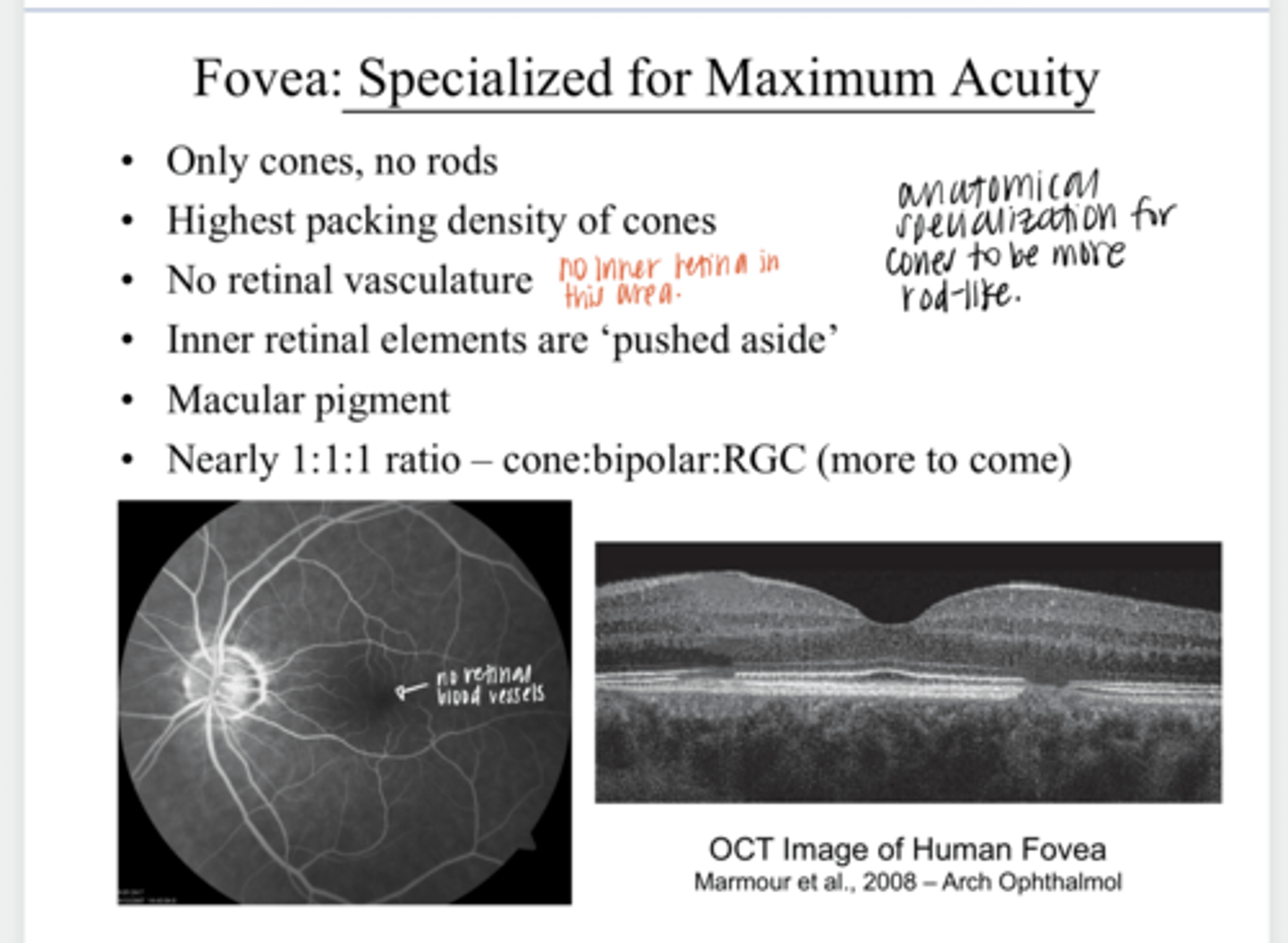
no
Is there any retinal vasculature present at the fovea?
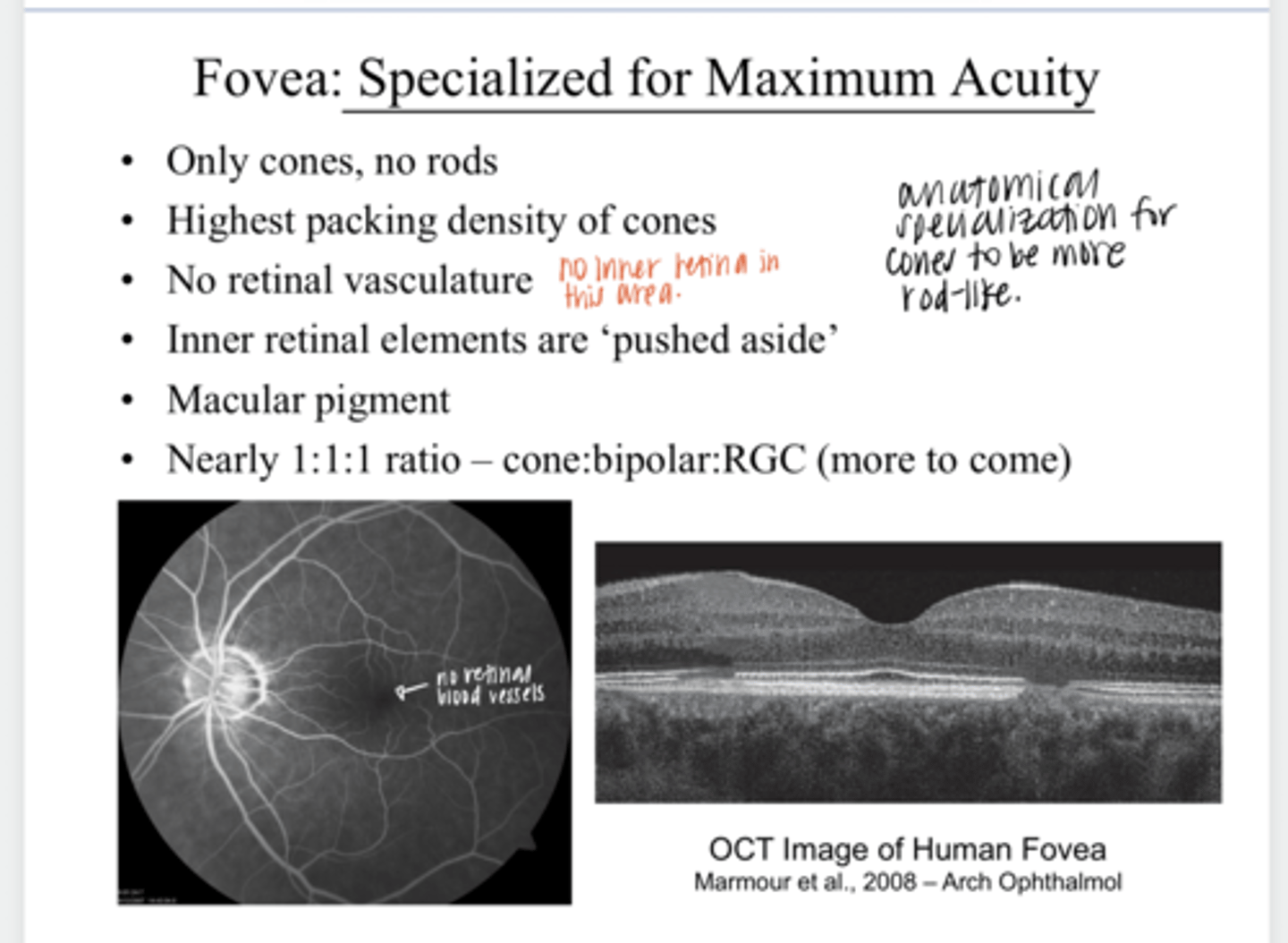
they are pushed aside
What happens to the inner retinal elements at the fovea?
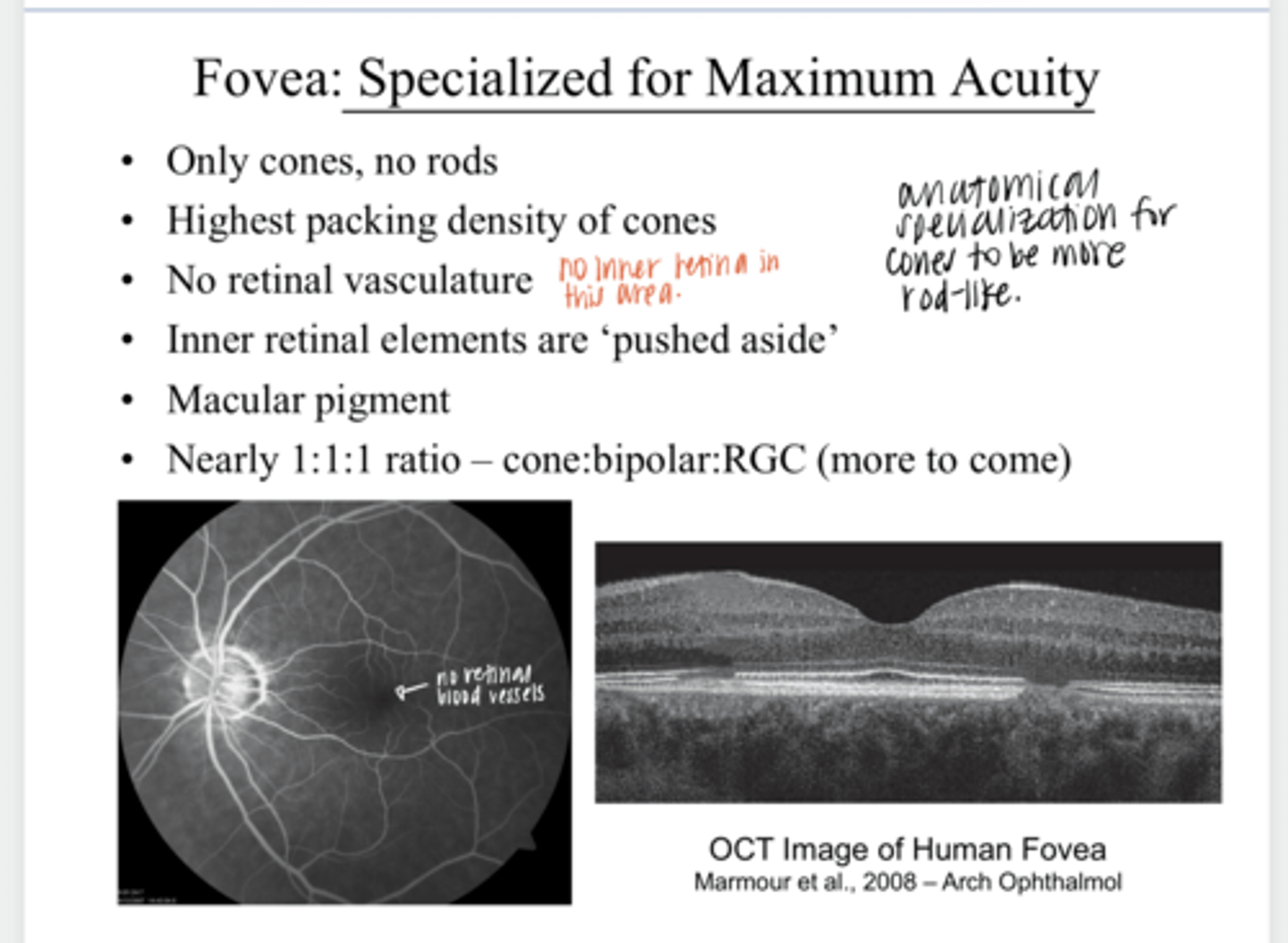
macular pigment
What is present in the fovea?
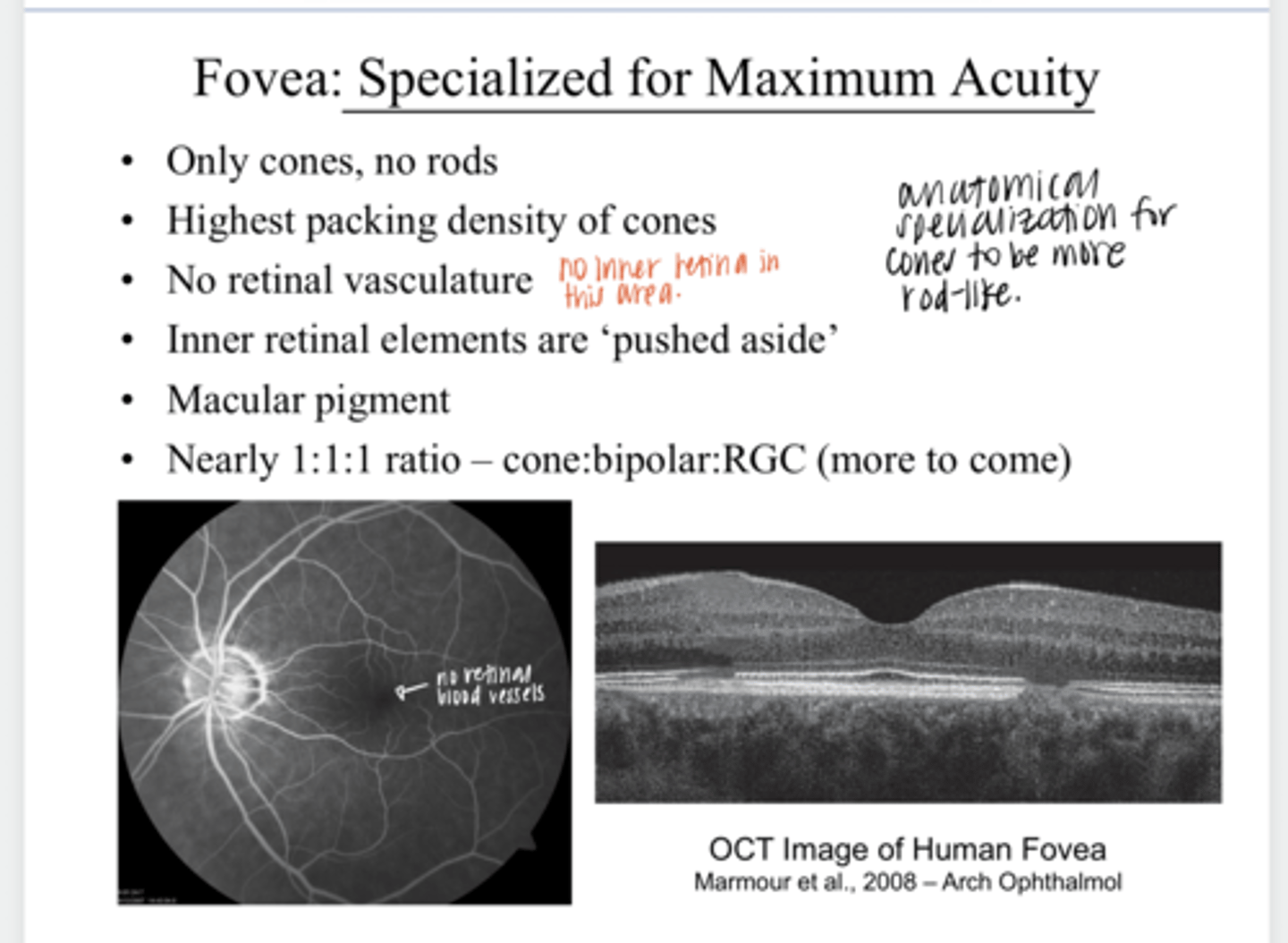
1:1:1
There is a ______ ratio of cones:bipolar cells:ganglion cells
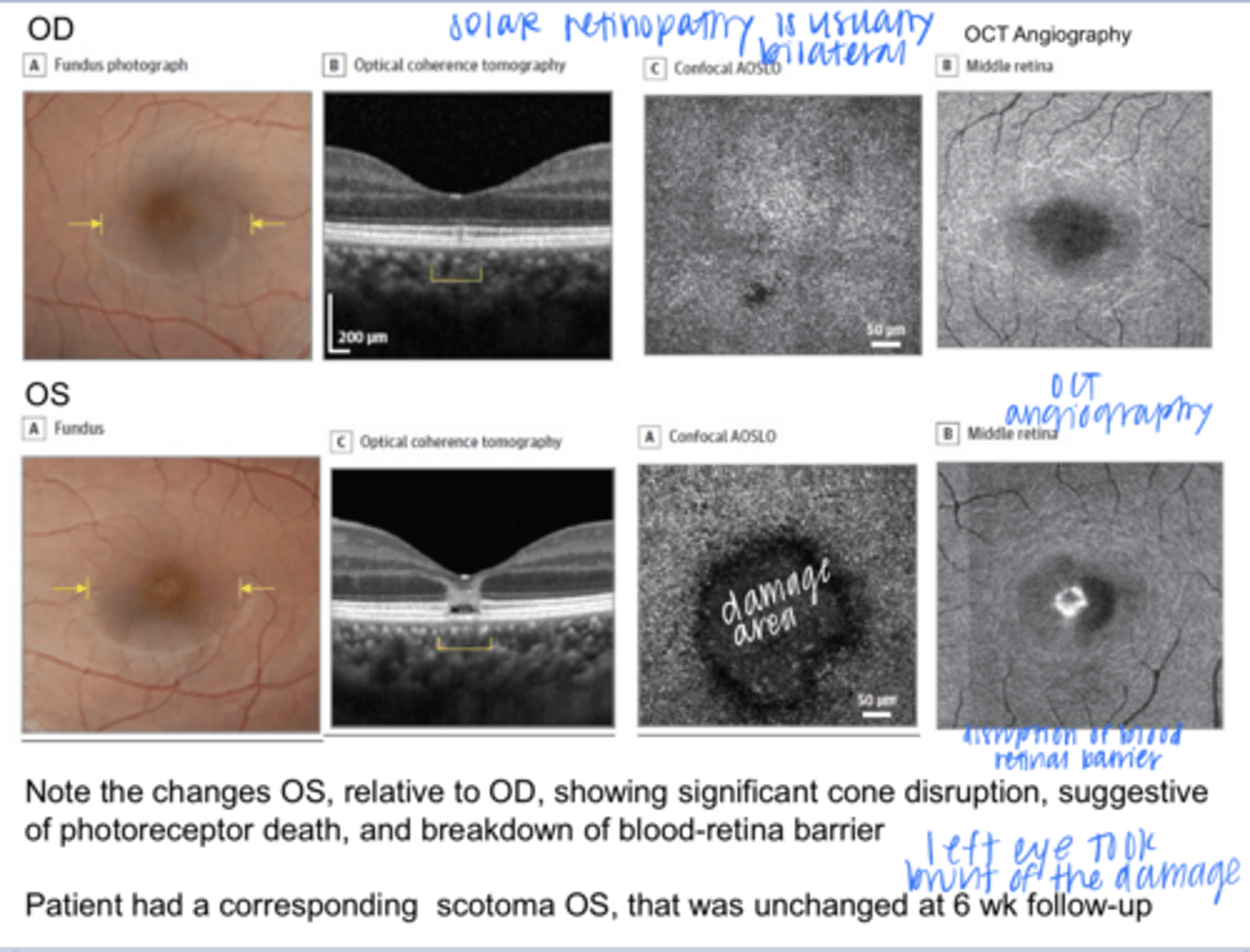
Significant cone disruption, suggestive of photoreceptor death. Breakdown of the blood-retina barrier. Patient had a corresponding scotoma OS -- unchanged at 6wk F/U.
Woman in 20s presents 3 days after Aug 21 2-17 solar eclipse with blurred vision and metamorphopsia OS. Reports she stared at the rim for about 6s with no protection, before looking again with glasses for 20s. VA was 20/20 OD and 20/25 OS.
OCT images are attached.
What is being shown in the OS?
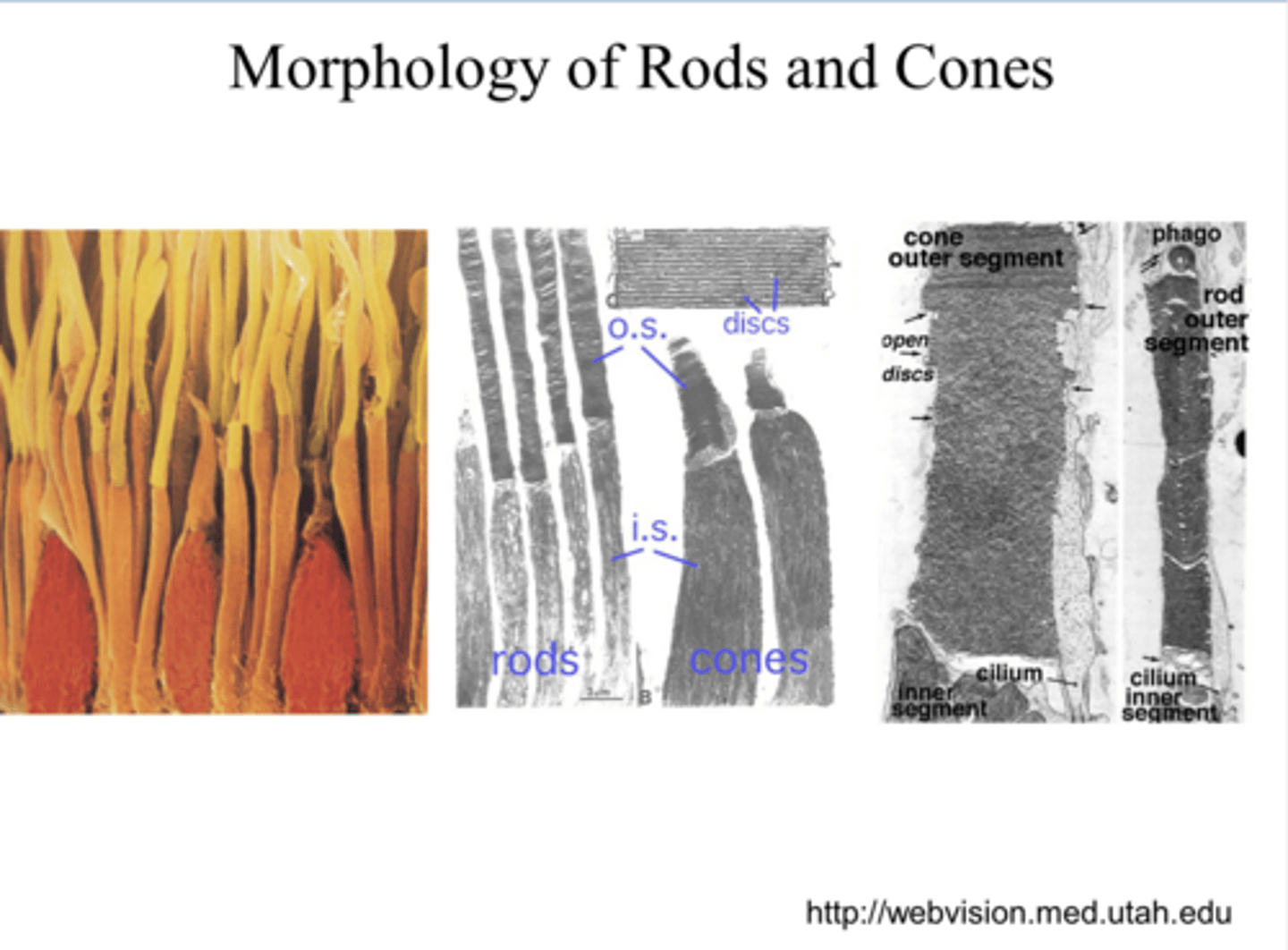
in the outer segment of the rods and cones
Where does photo-transduction take place in the retina?
visual photopigment
What do the discs of the photoreceptors house?
molecules that have a net charge
What are ions?
current (I)
the net movement of charges (ions)
voltage (V)
the difference in electrical charge across space
the difference in electrical charge (voltage) that exists across the plasma membrane
In neurons, what is the membrane potential?
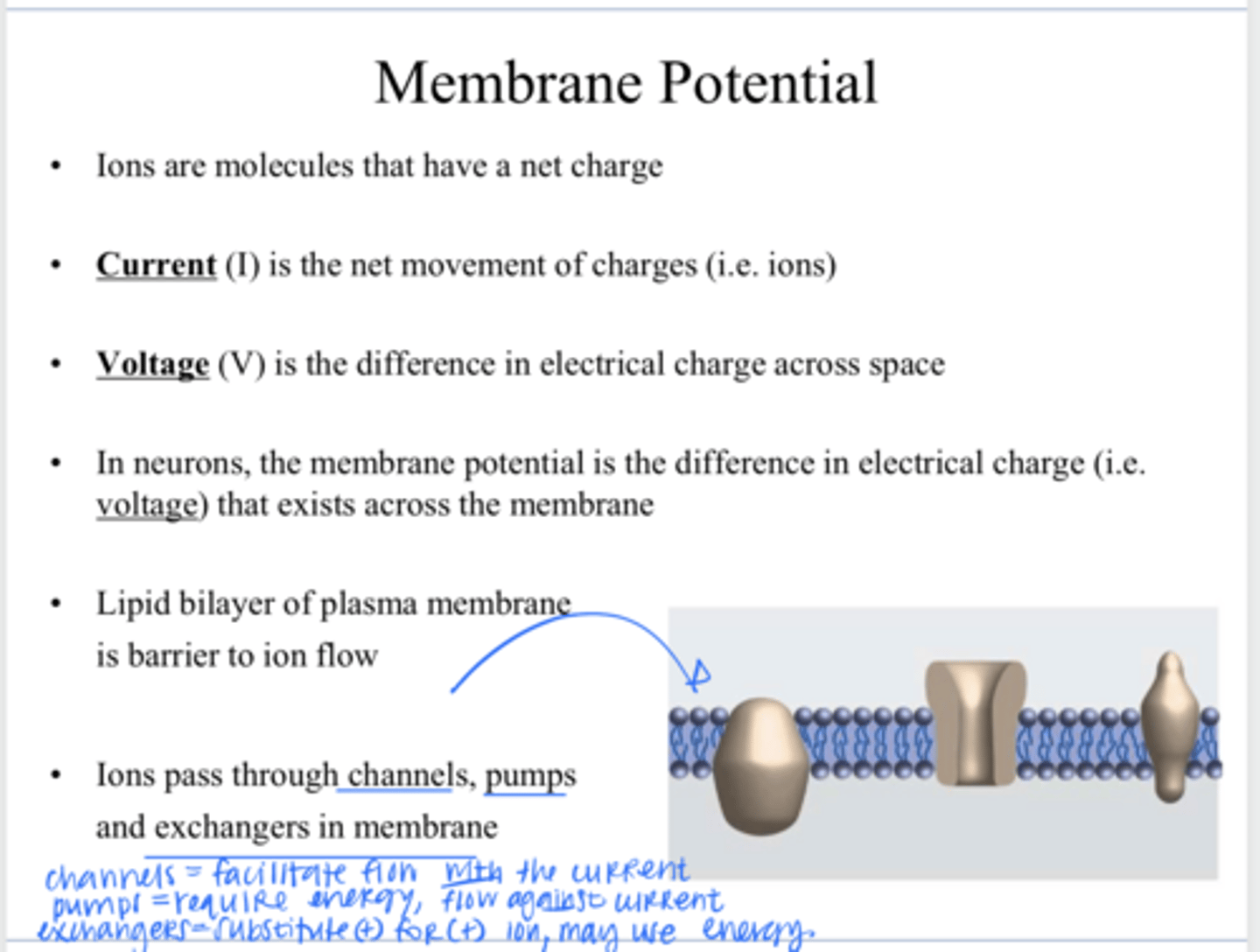
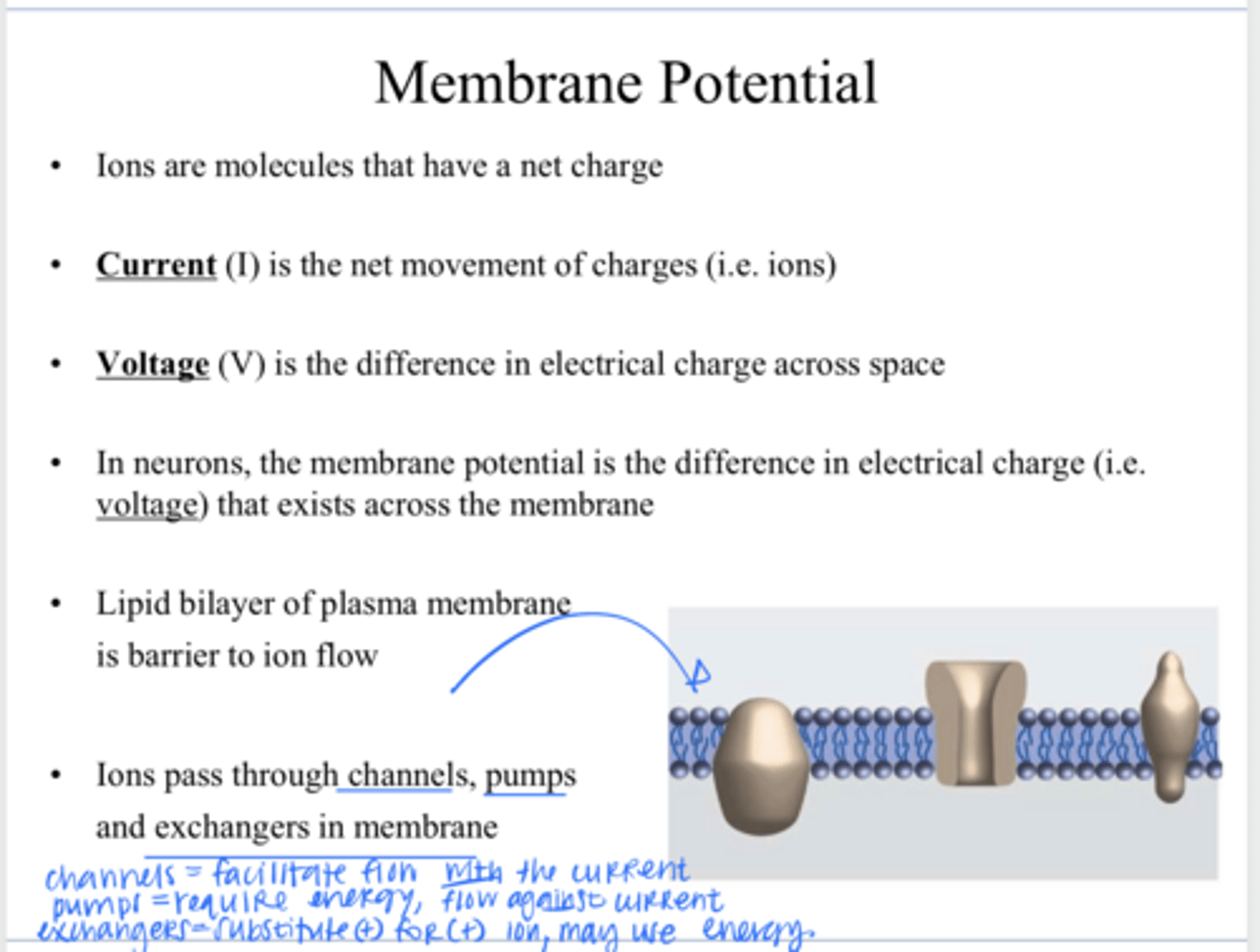
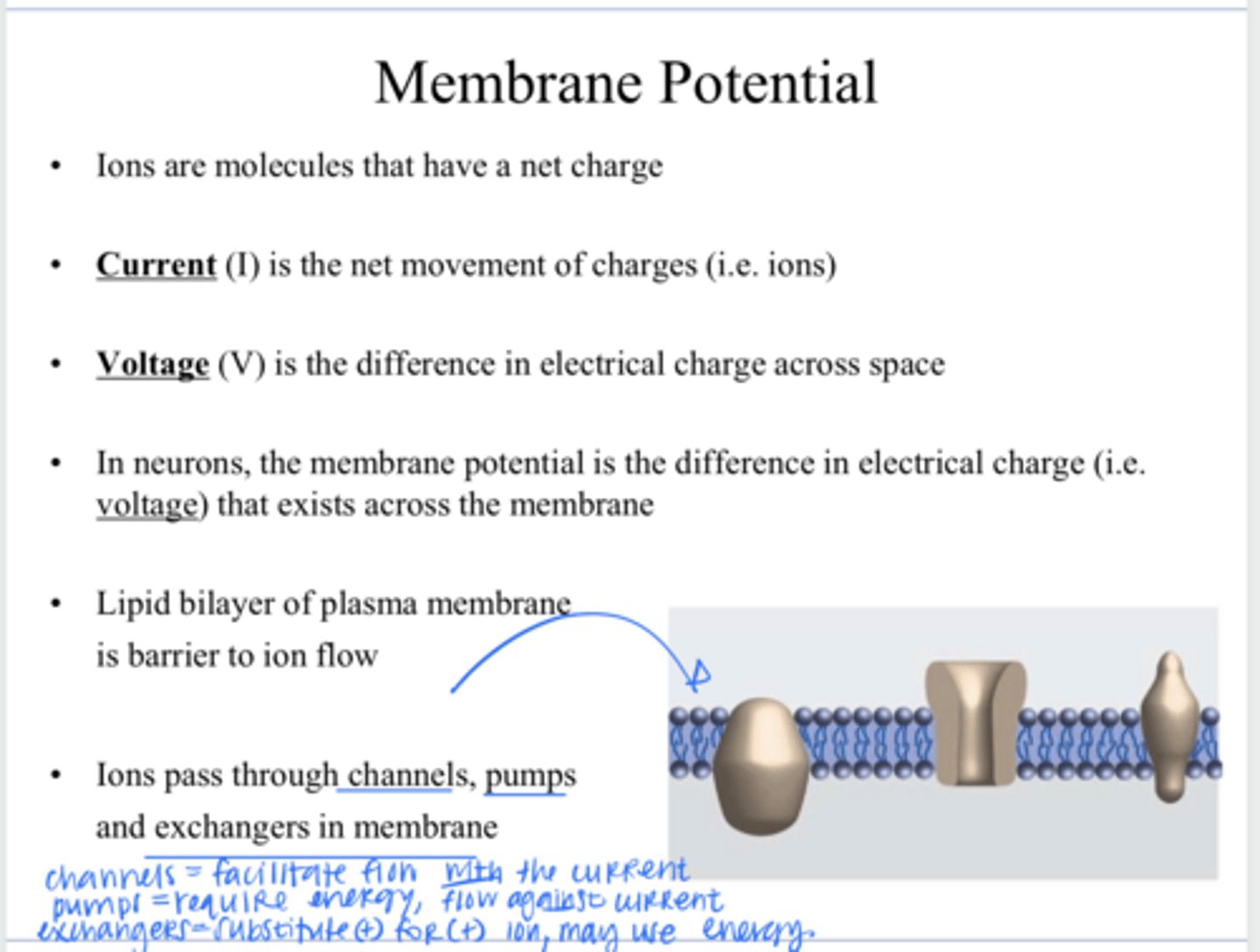
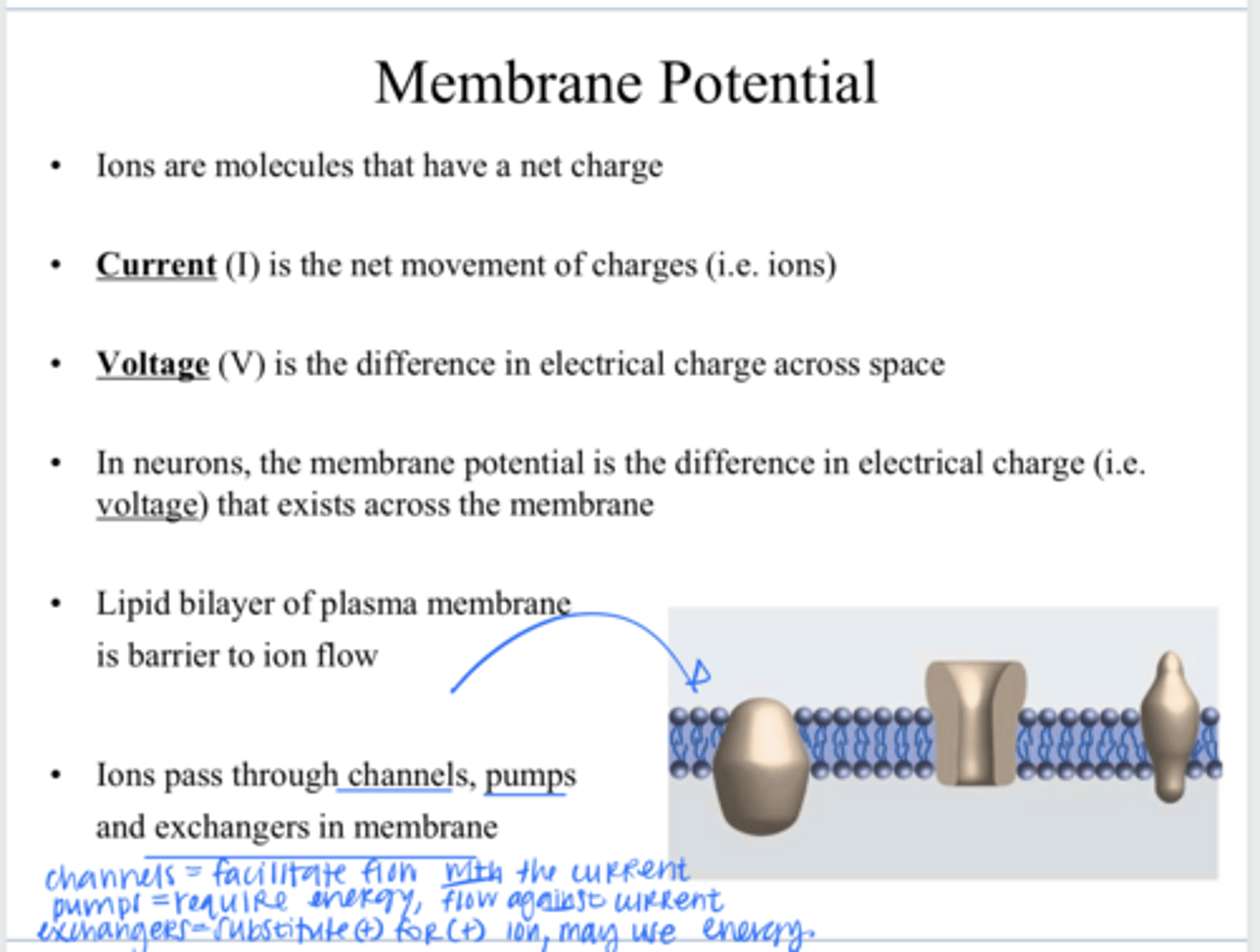
lipid bilayer
What is a barrier to ion flow across a plasma membrane?
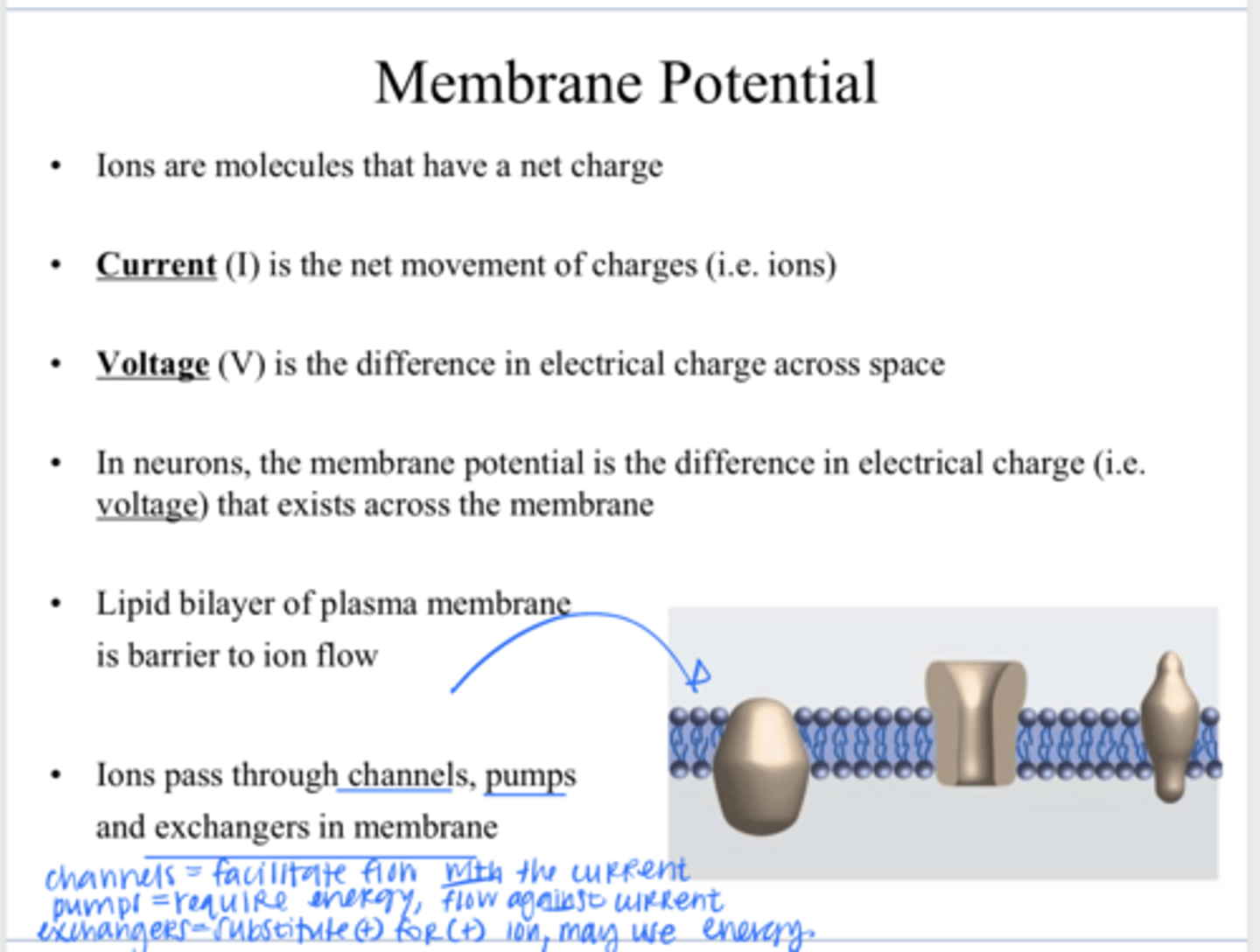
through channels, pumps, and exchangers in the membrane
How to ions pass through a plasma membrane?
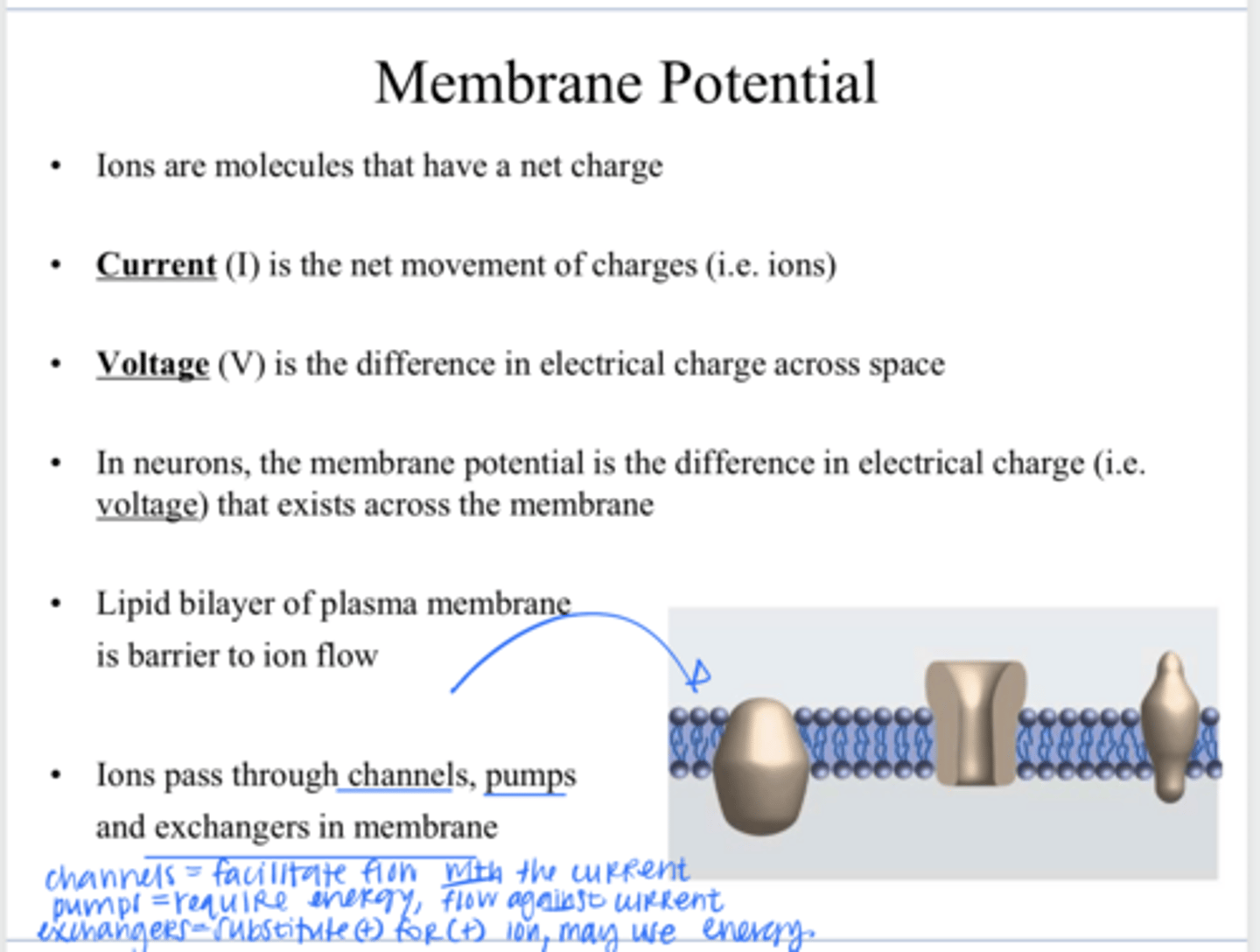
allowing specific ions (like Na+, K+, Ca2+) and small polar molecules to pass through lipid bilayer primarily via passive transport down their concentration/electrical gradient
What is the function of a plasma membrane channel?
an active transport protein in cell membranes that uses energy (usually from ATP) to move ions or molecules against their concentration gradient
What is the function of a plasma membrane pump?
a protein in cell membranes that moves ions or molecules across, swapping one substance for another (usually + molecule for another + molecule)
What is the function of a plasma membrane exchanger?
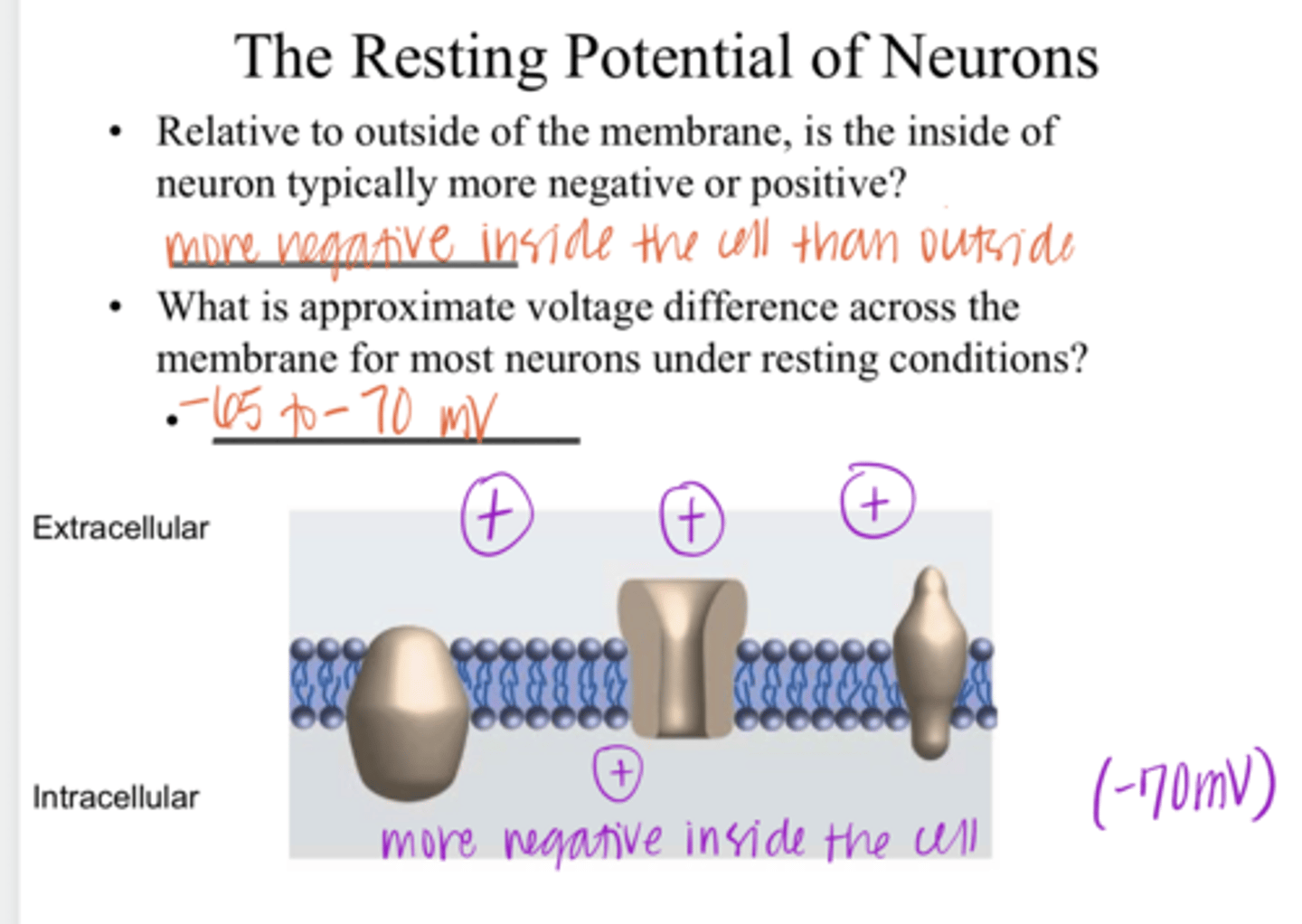
Inside of the neuron is typically more negative (resting = -70mV)
Relative to outside of the membrane, is the inside of the neuron typically more negative or positive?
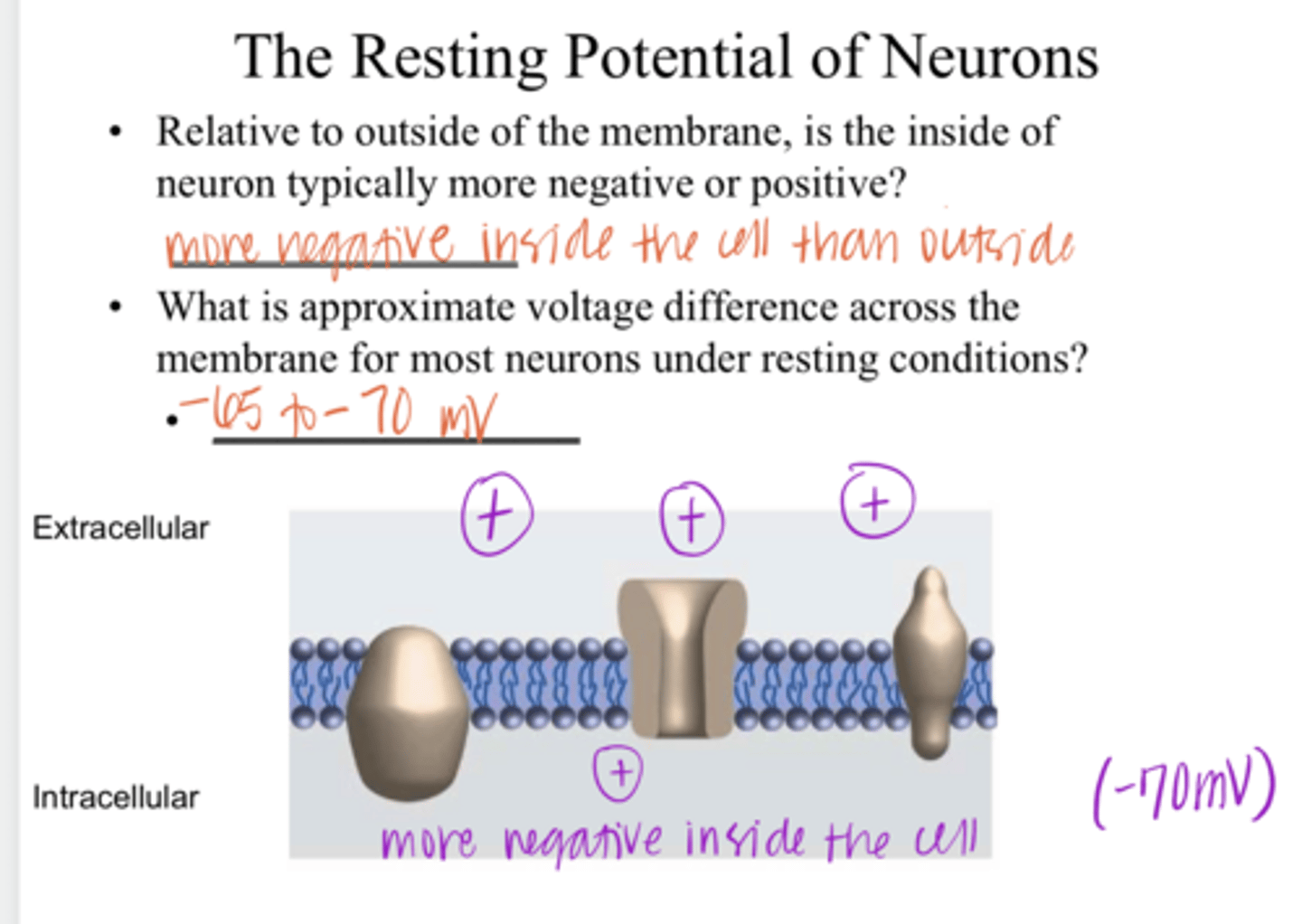
-65 to -70mV
What is the approximate voltage difference across the membrane for most neurons under RESTING conditions?
1) large organic molecules (proteins, DNA) are negatively charged and are trapped inside the cel
2) Na+/K+ ATPase pumps 3 Na+ out of the cell and 2 K+ into the cell. (more positive on the outside of the cell)
What are 2 reasons in which the resting membrane potential of neurons is negative?
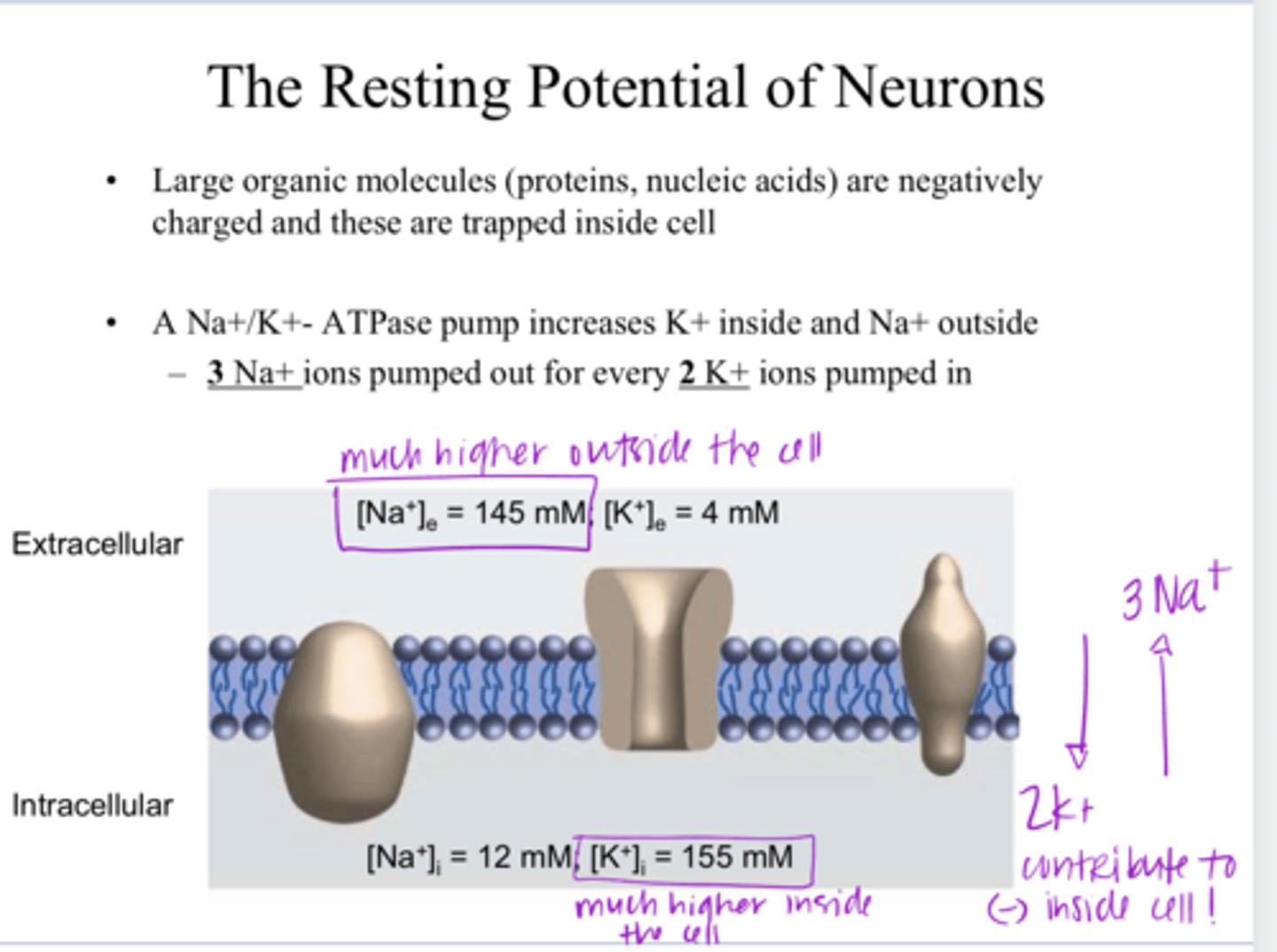
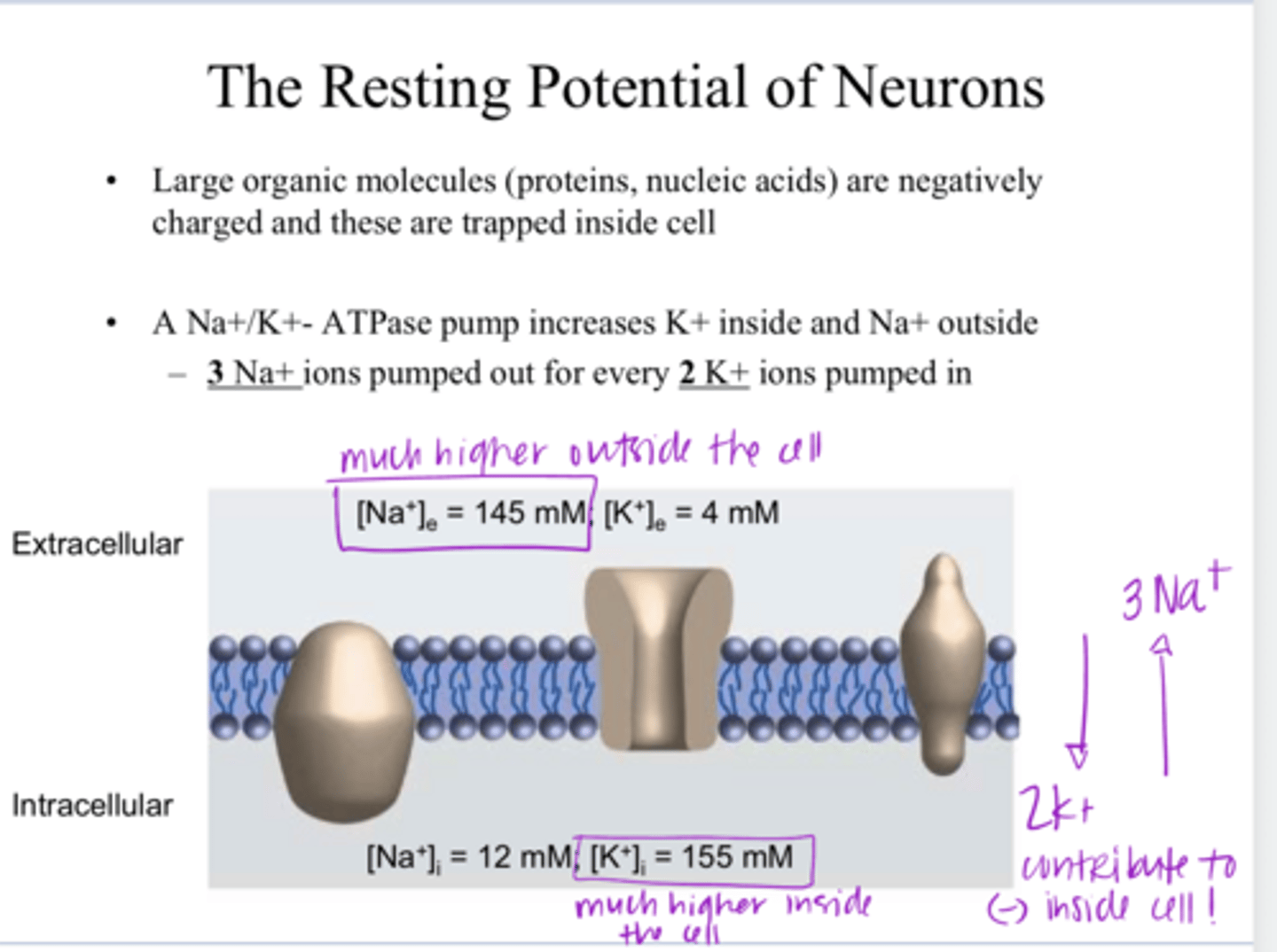
higher on the outside of the cell
** Na+/K+ ATPase pumps 3 Na+ out of the cell and 2 K+ into the cell.
Is the conc of Na+ higher on the outside or inside the cell?
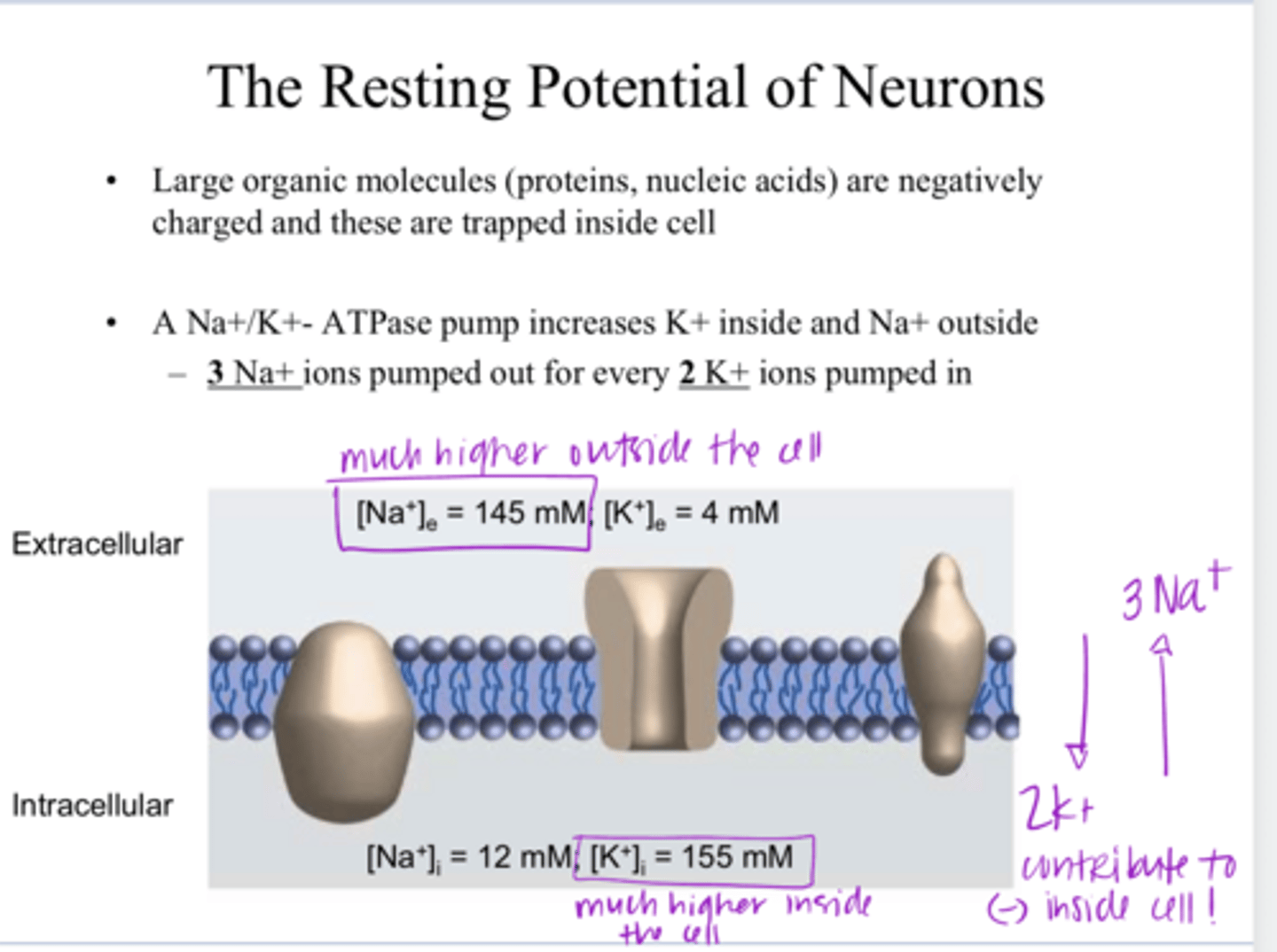
higher on the inside of the cell
** Na+/K+ ATPase pumps 3 Na+ out of the cell and 2 K+ into the cell.
Is the conc of K+ higher on the outside or inside the cell?
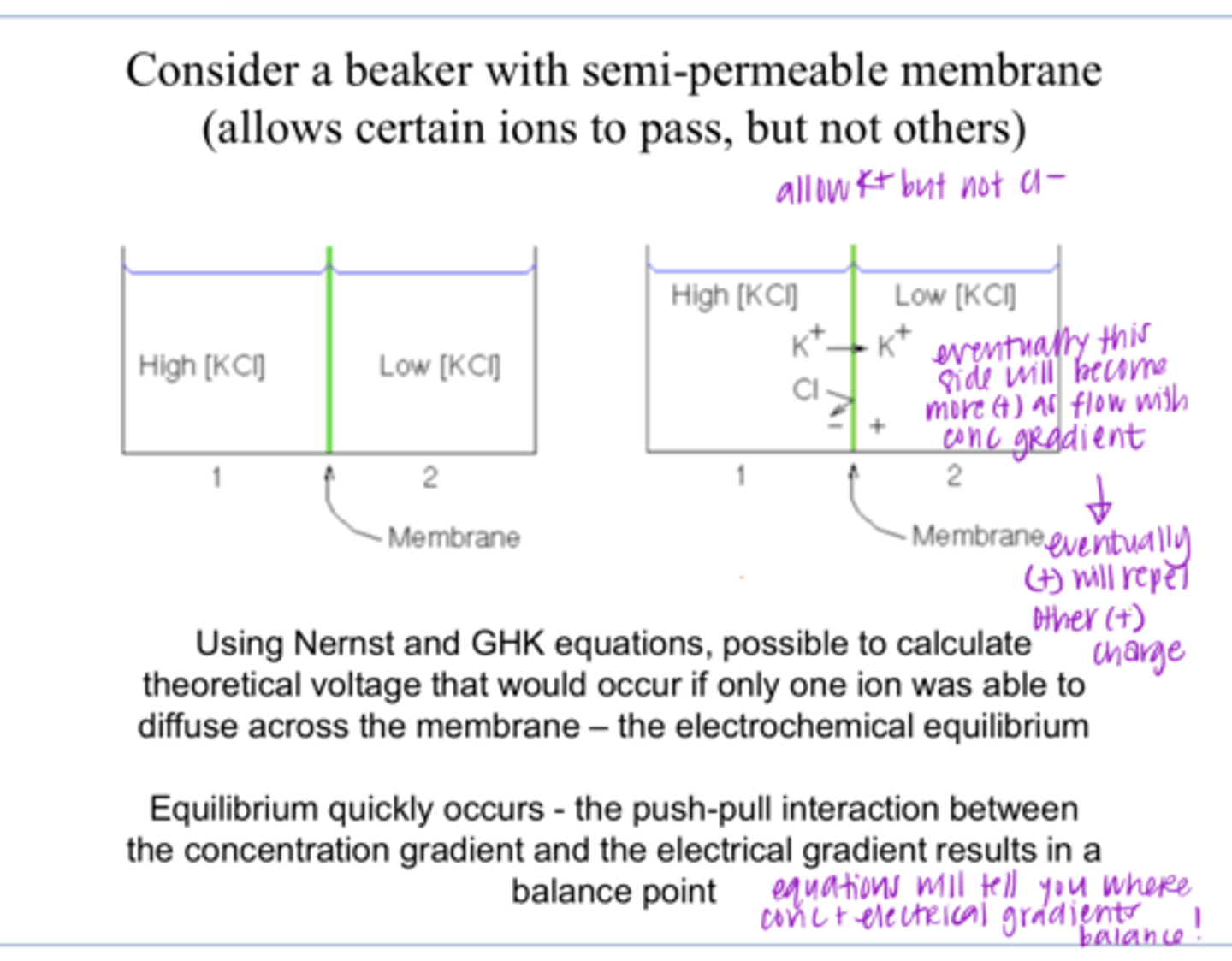
Nernst and Goldman-Hodgkin-Katz Equations
The resting ionic gradient that exists across the plasma membrane are governed by what equation?
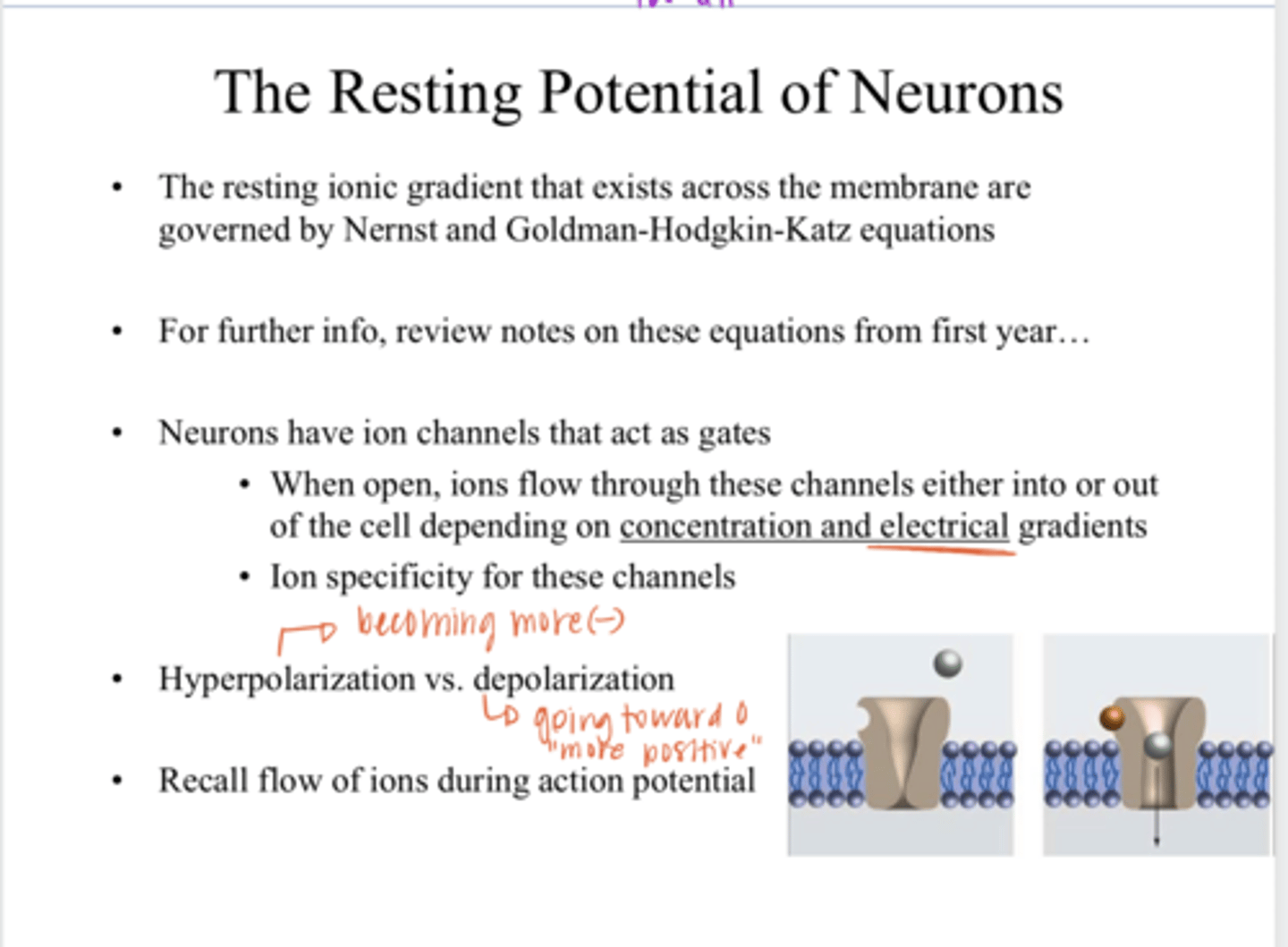
gates
Neurons have ion channels that act as ____
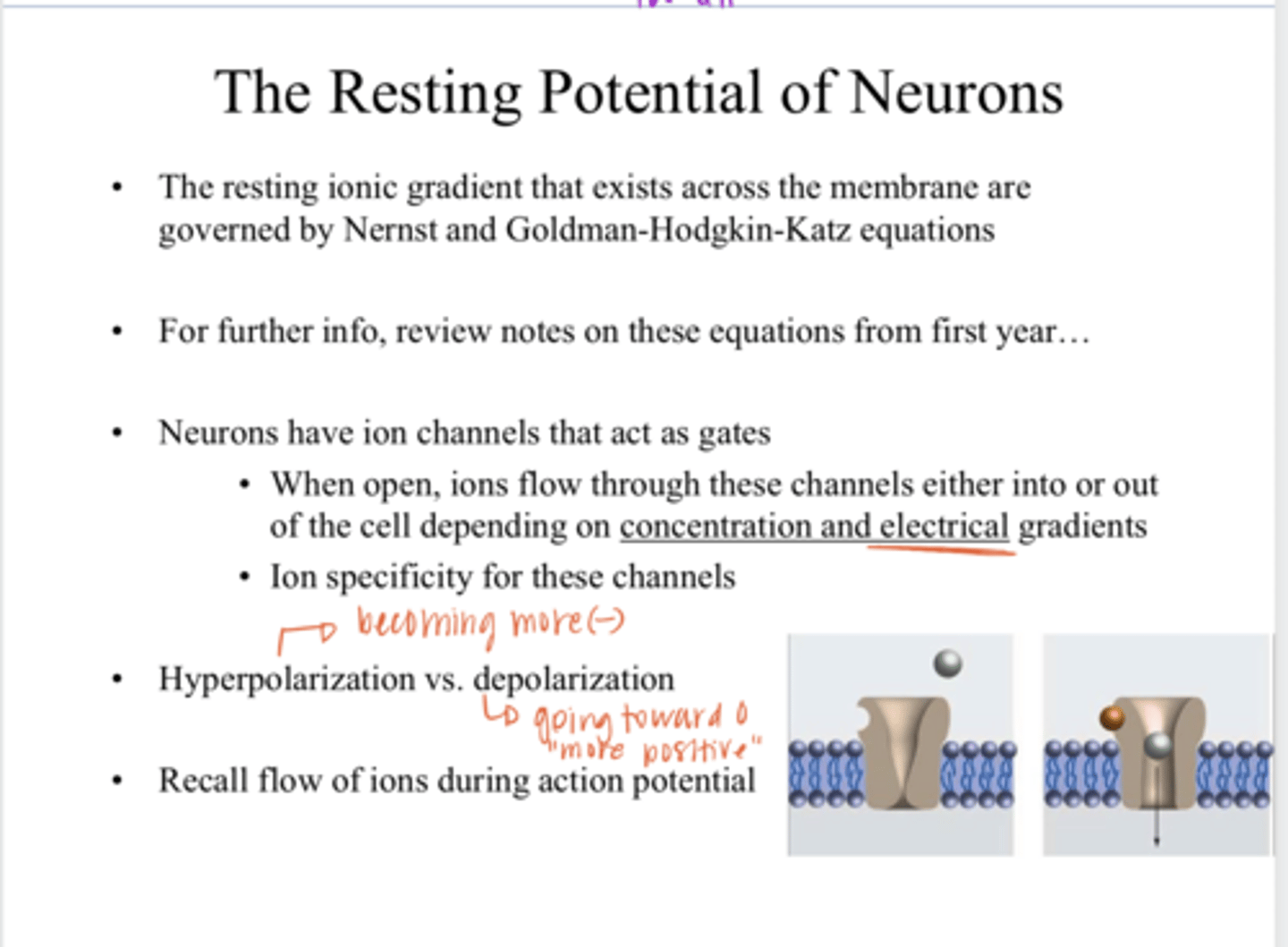
depending on conc and electrical gradients
Ions will flow in/out of a cell through channels depending on what?
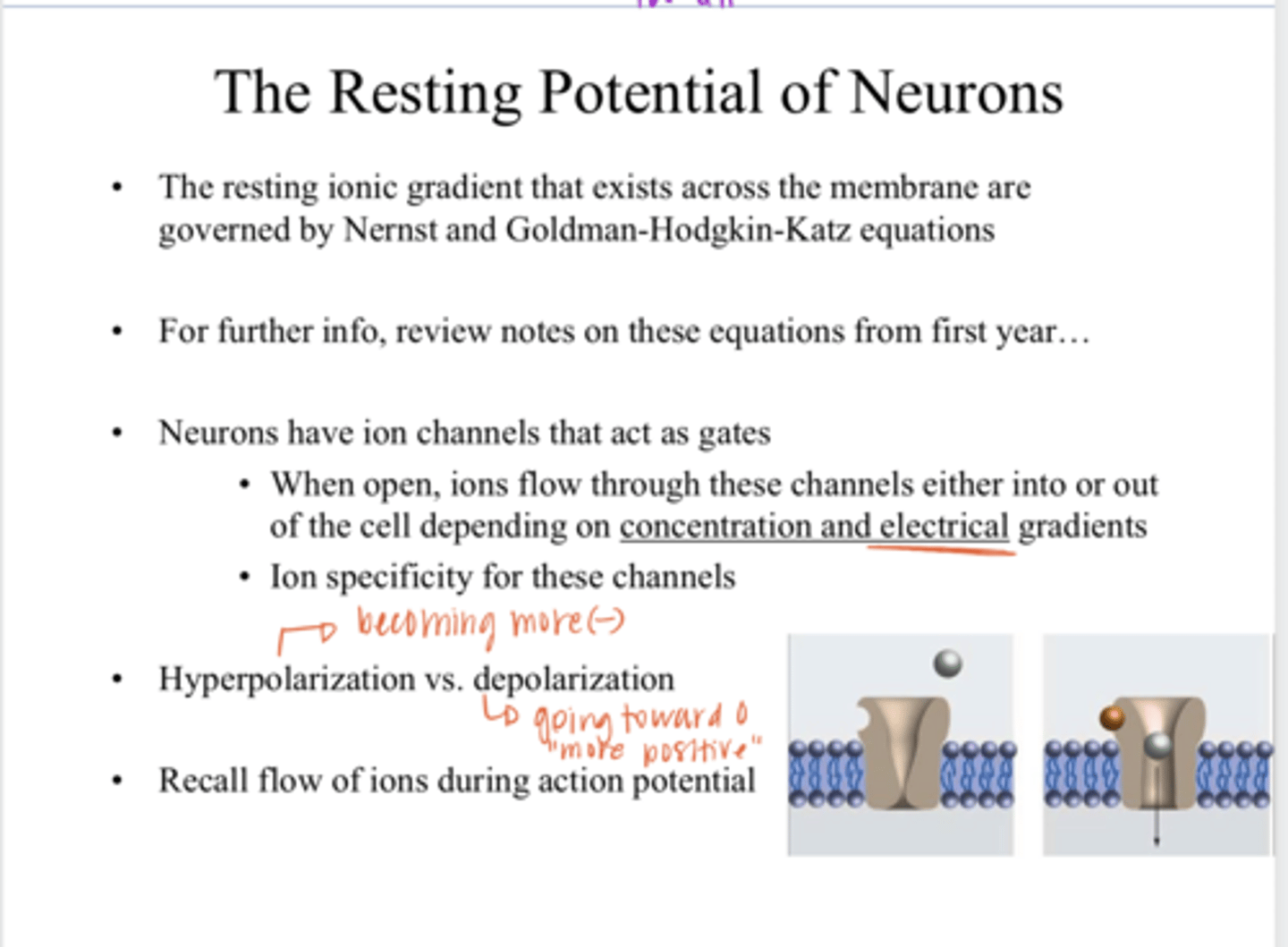
Hyperpolarization of a Neuron
the internal charge of a neuron becomes more negative than its resting potential
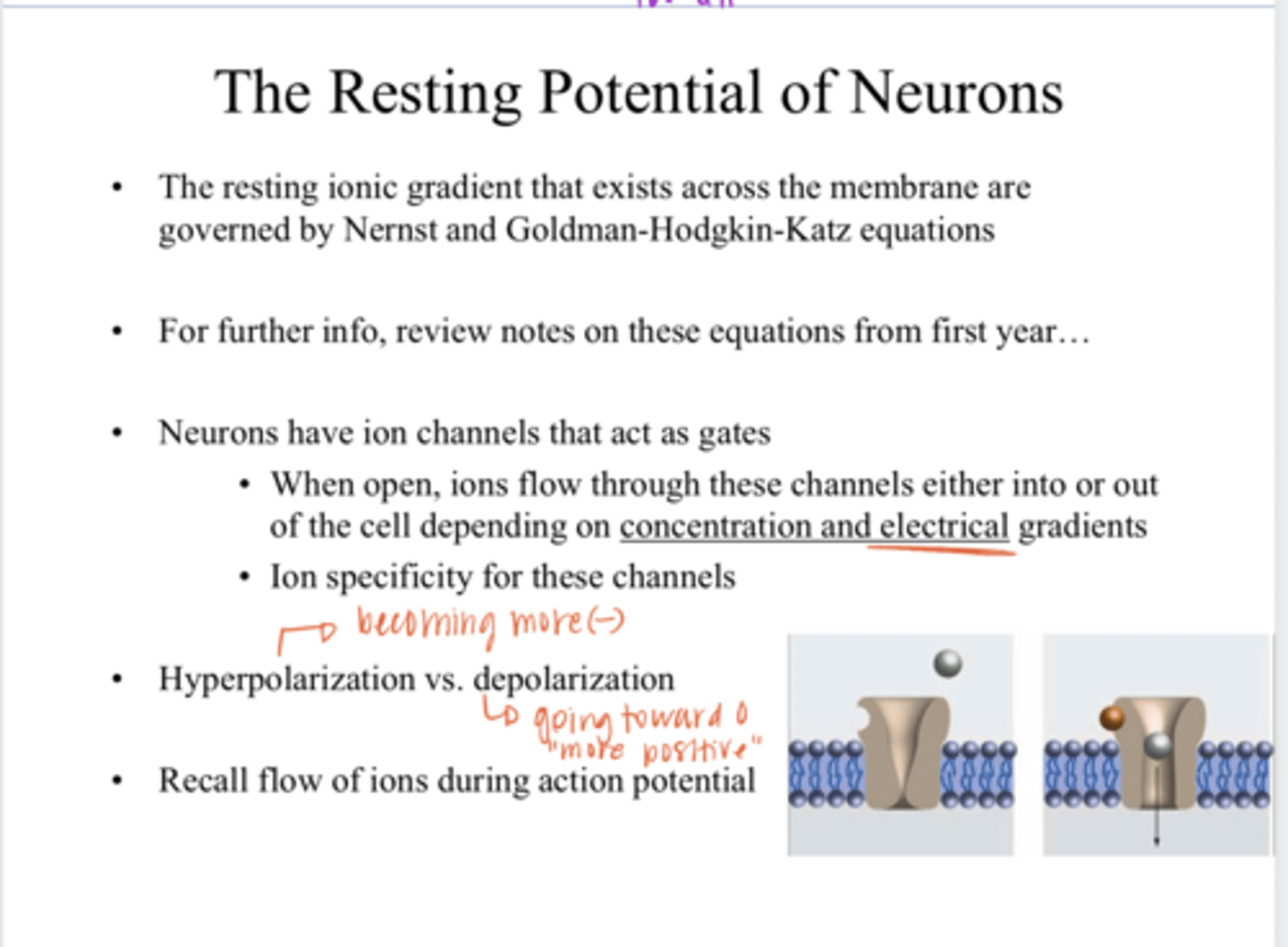
Depolarization of a Neuron
the internal charge of a neuron becomes less negative (more positive) than its resting potential, going towards a 0 charge
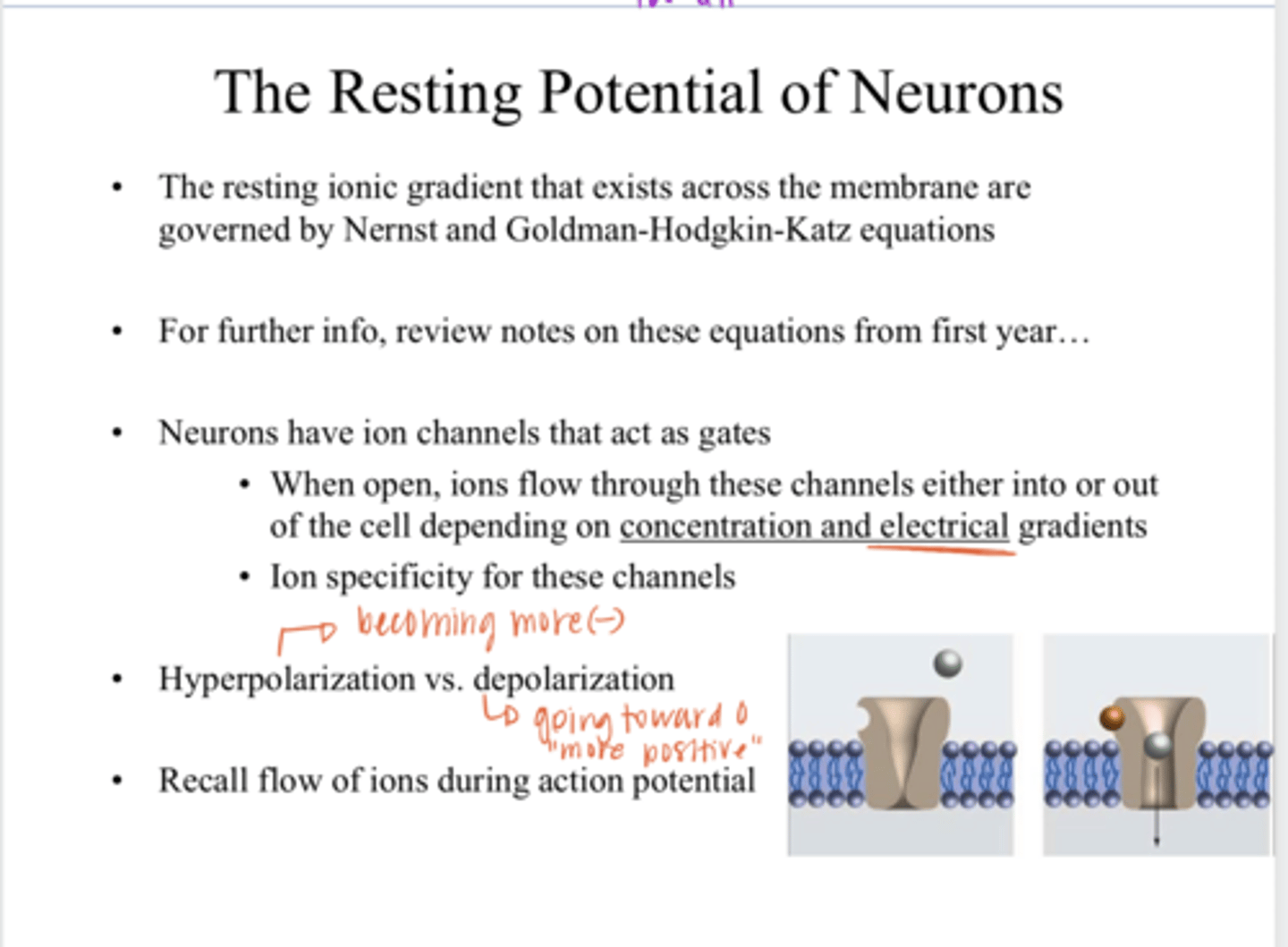
equilibrium
the push-pull interaction between the concentration gradient and the electrical gradient results in a balance point
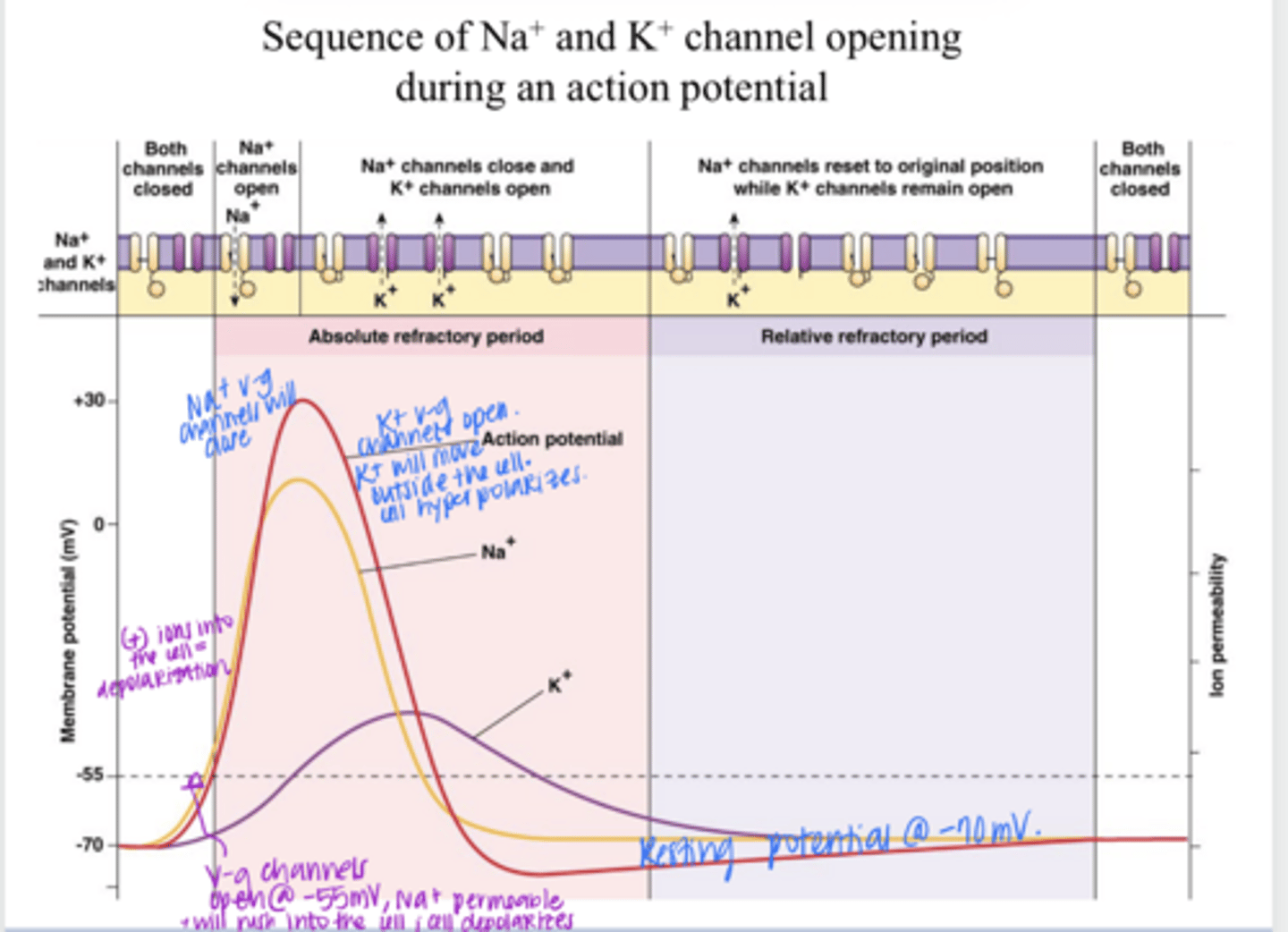
Typical CNS Sequence of Na+ and K+ Channel Opening During AP Pic
Typical CNS Sequence of Na+ and K+ Channel Opening During AP Pic
retinal ganglion cells -- detection of the action potential of these cells
The first recordings of electrical activity were obtained from what cells?
true
True or False:
It took a long time before first recordings of photoreceptors were achieved
less negative (about -40mV in PR compared to -70mV in other neurons)
Tomita's intracellular recordings indicated that the resting membrane potential of photoreceptors in the dark was less ________ than that of a regular neuron
yes -- and similar across the animal kingdom
Do rods and cones have similar resting membrane potentials?
hyperpolarize (become more negative)
Cones _____ in response to light
no -- this is unlike other CNS neurons
Are rods and cones capable of firing action potentials?
graded
Rather than the all or nothing feature of action potential, the light responses of rods/cones are _____
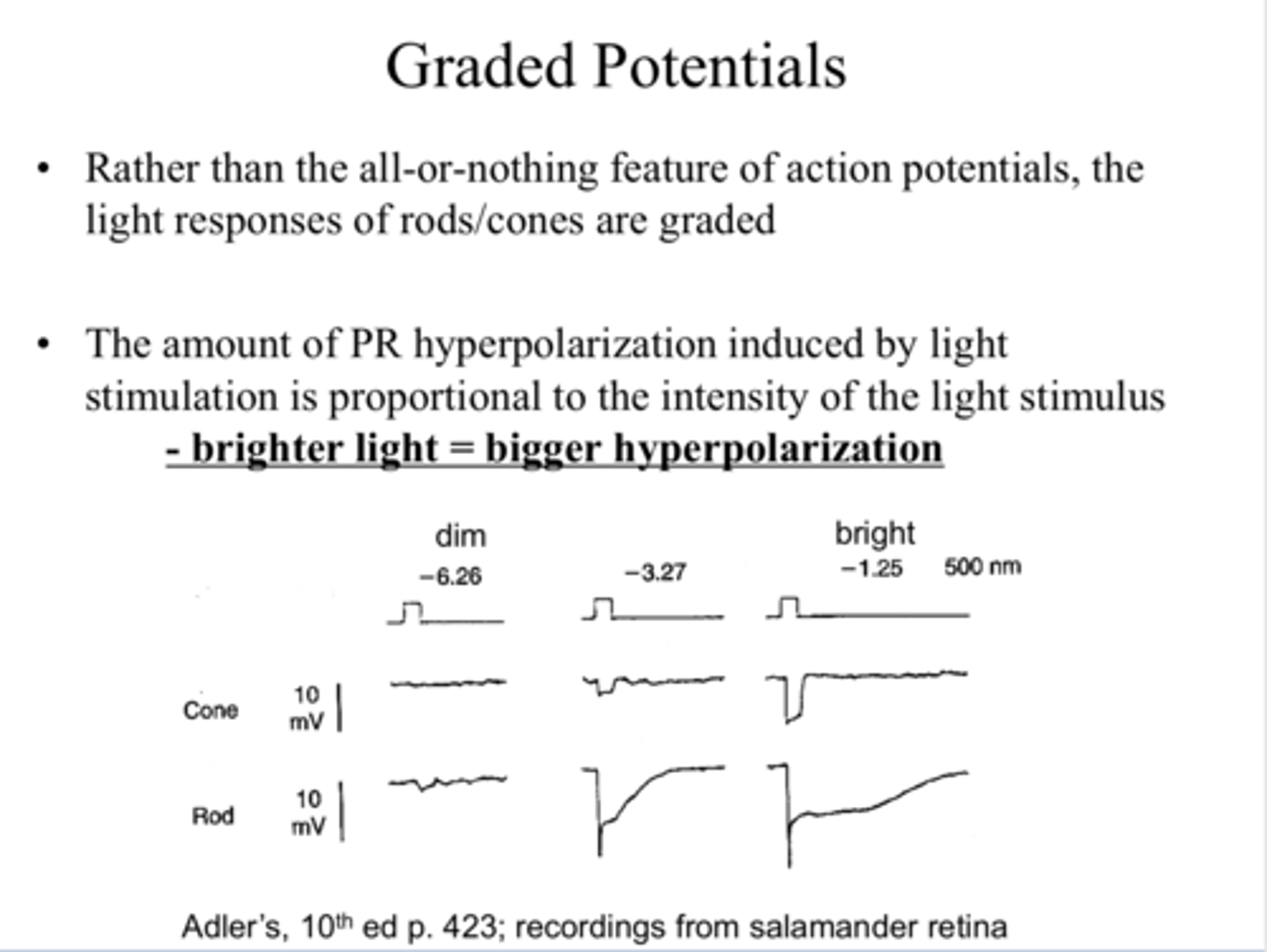
proportional
**brighter light == bigger hyperpolaization
The amount of PR hyperpolarization induced by light stimulation is (proportional/ inverse) to the intensity of the light stimulus
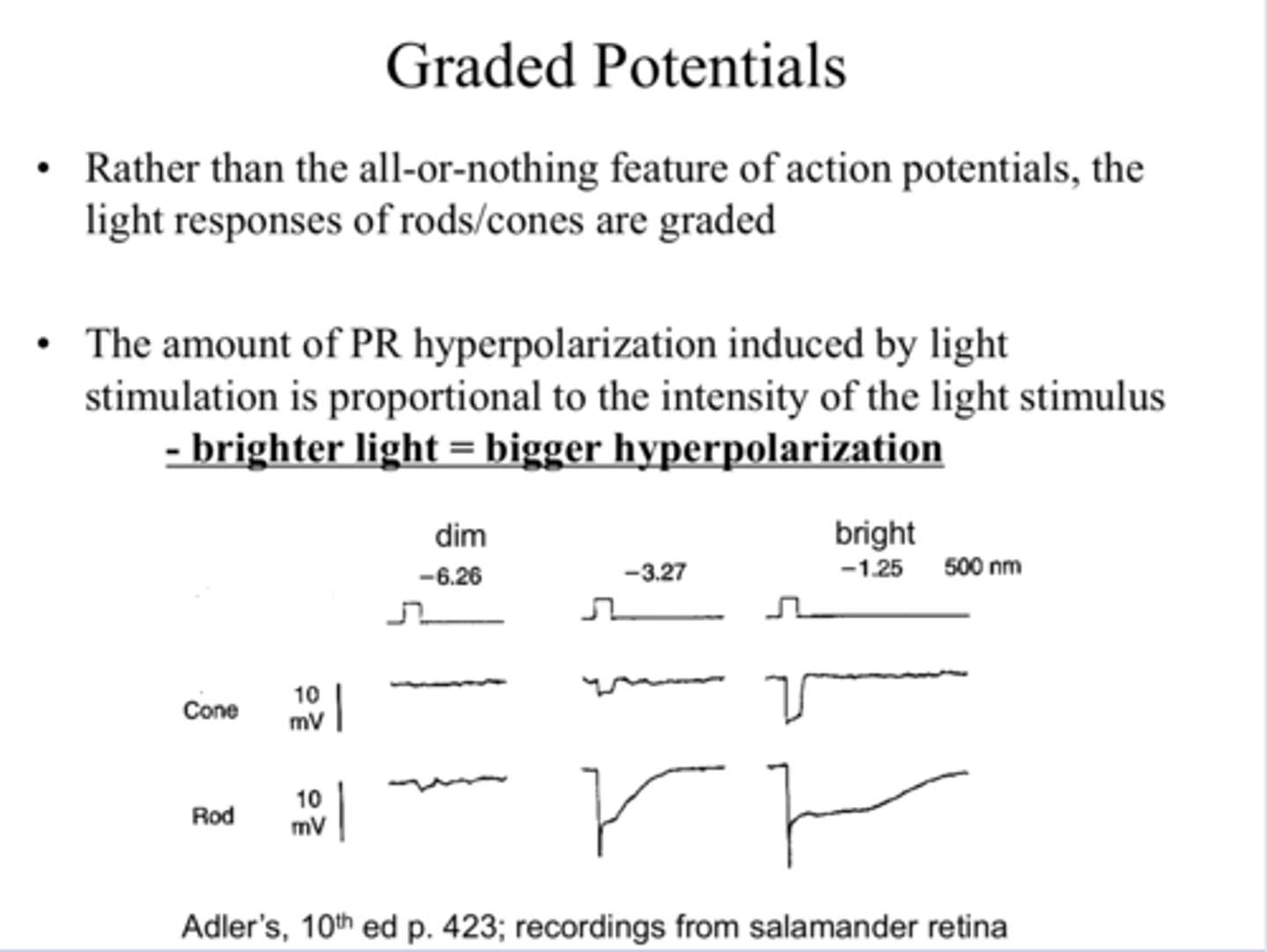
-65mV
The maximum light response is a hyperpolarization to about _____ from resting potential of -40mV
1) Open channels that are only permeable to Cl- ions (move - ions into the cell)
2) Close channels that allow (-) ions out of the cell
3) Close channels that allow (+) ions into the cell
4) Open channels that allow (+) out of the cell
What are some possible explanations for the hyperpolarizing light responses of photoreceptors?
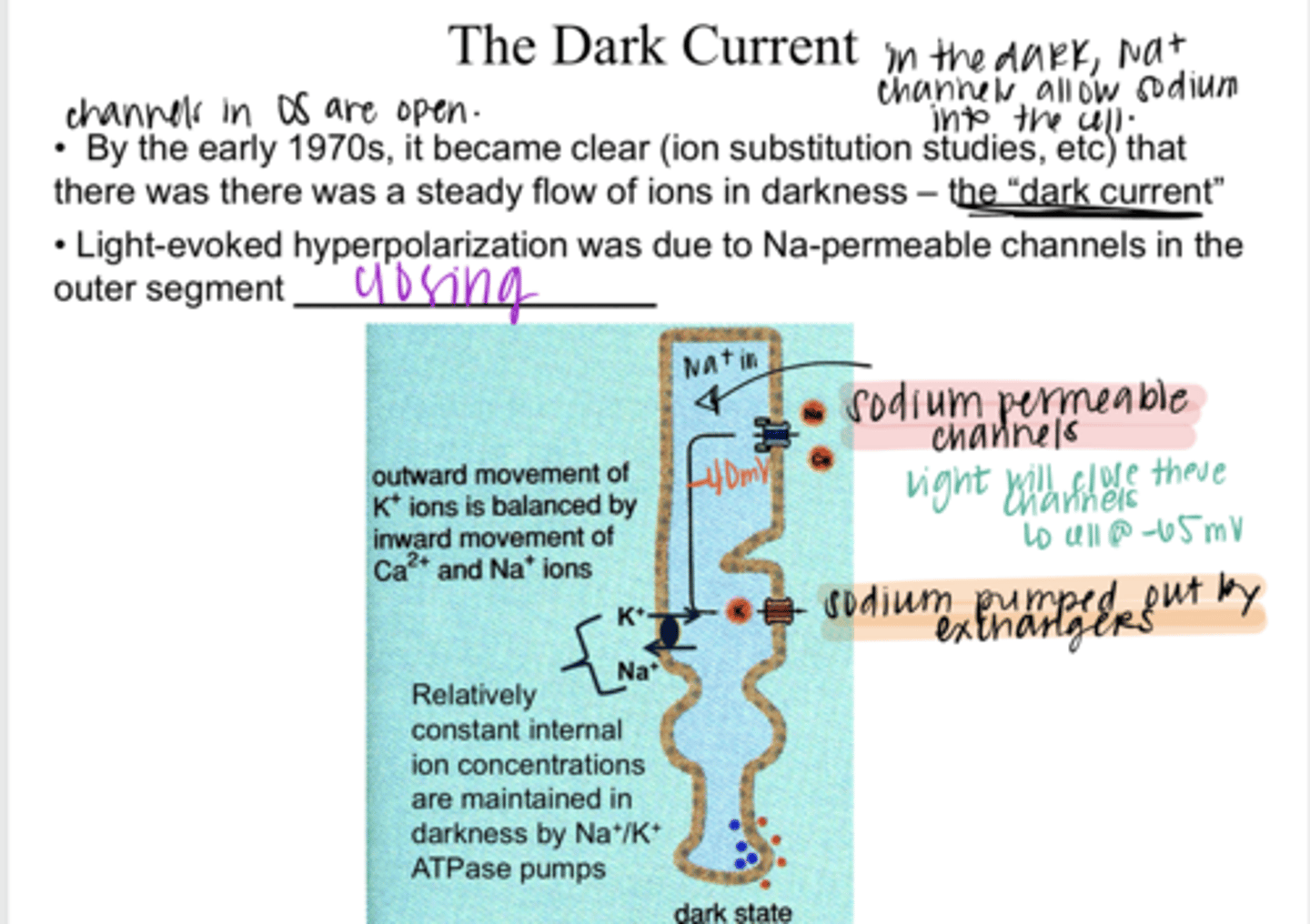
steady flow of ions in darkness INTO the photoreceptor from Na+ permeable channels in the outer segment. Cell will sit at -40mV in darkness d/t more positive Na+ in the cell.
What is the "dark current" referring to regarding photoreceptors?
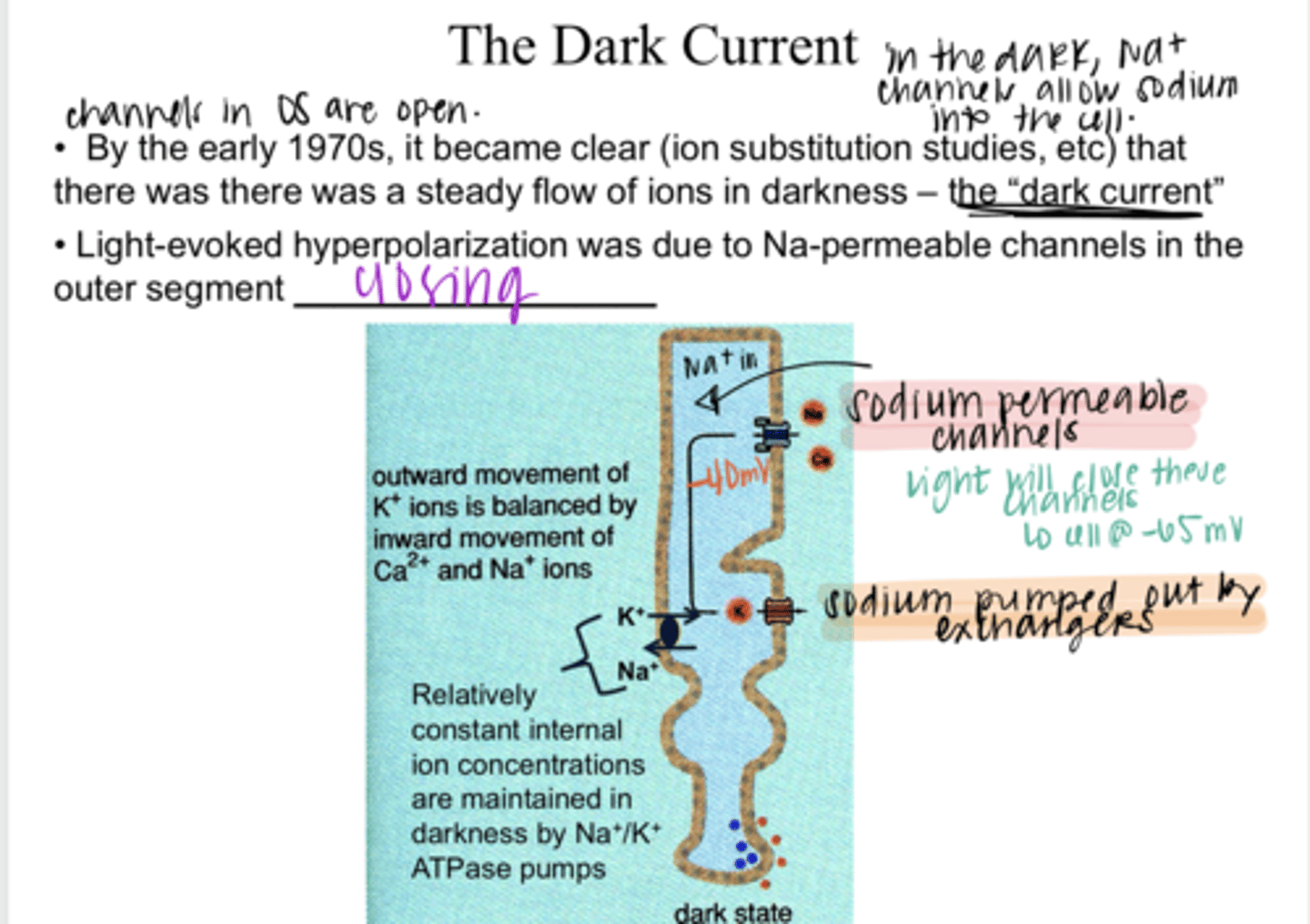
closing
Light-evoked hyperpolariztion is d/t Na+ permeable channels in the outer segment ______
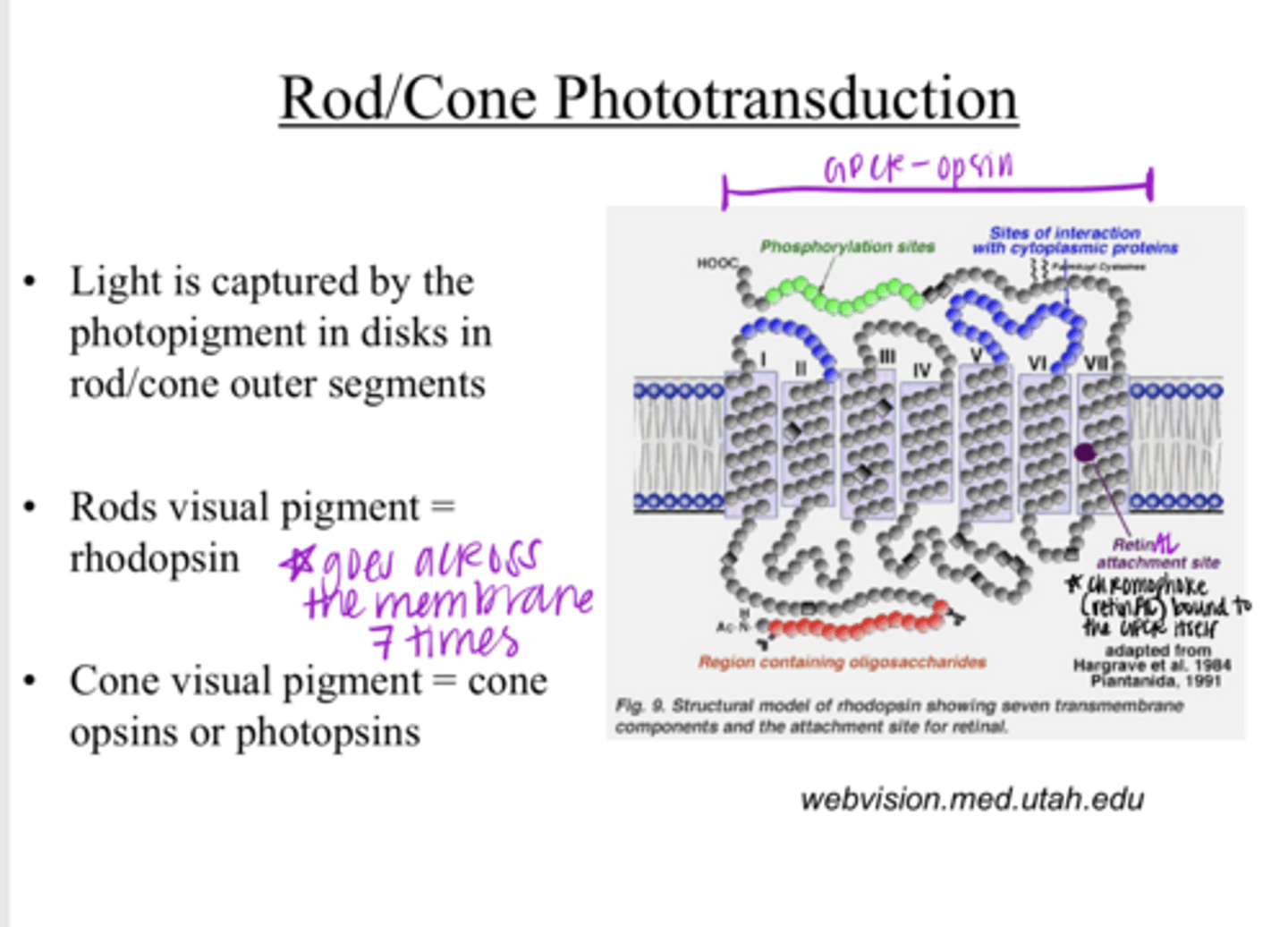
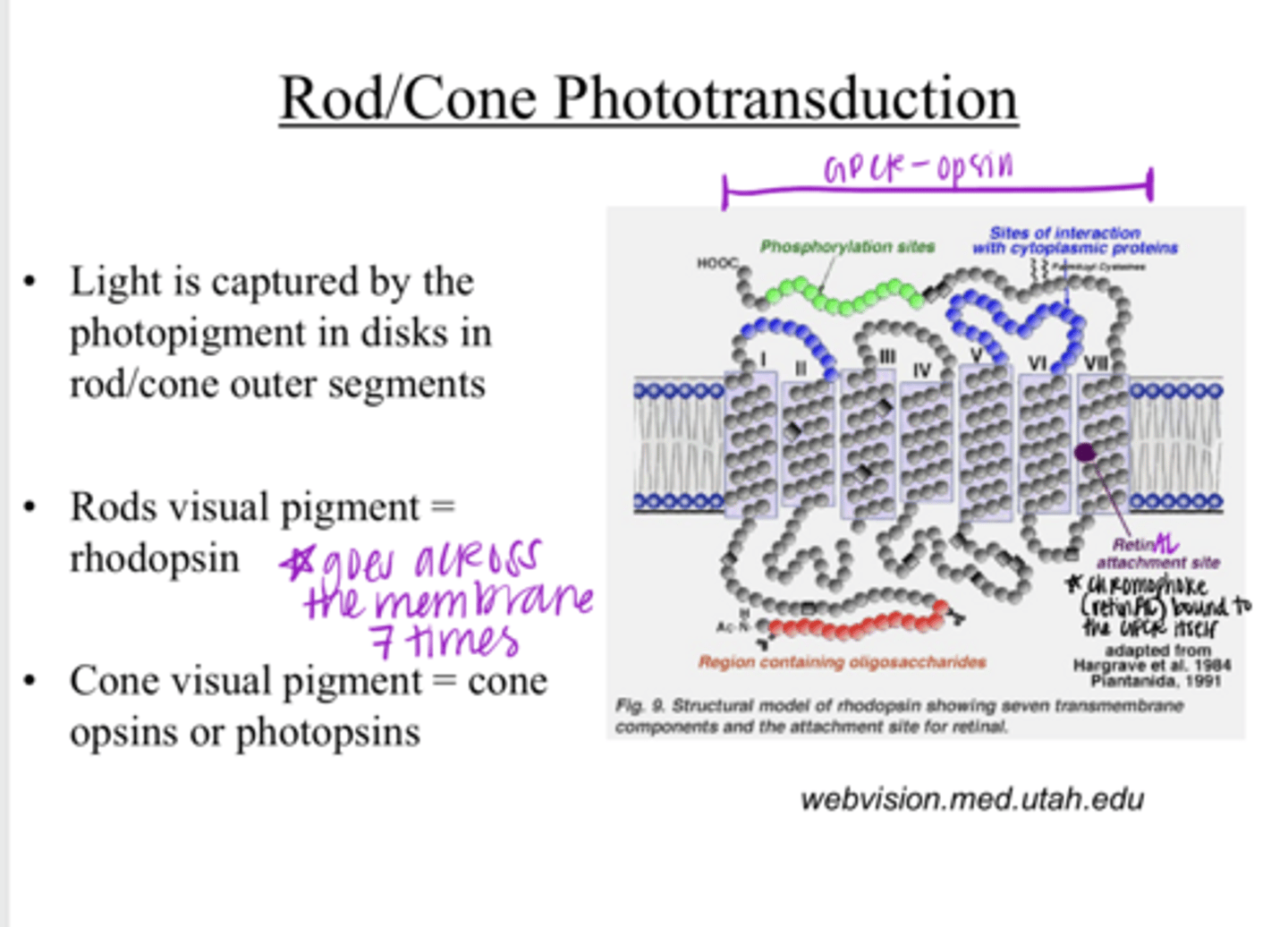
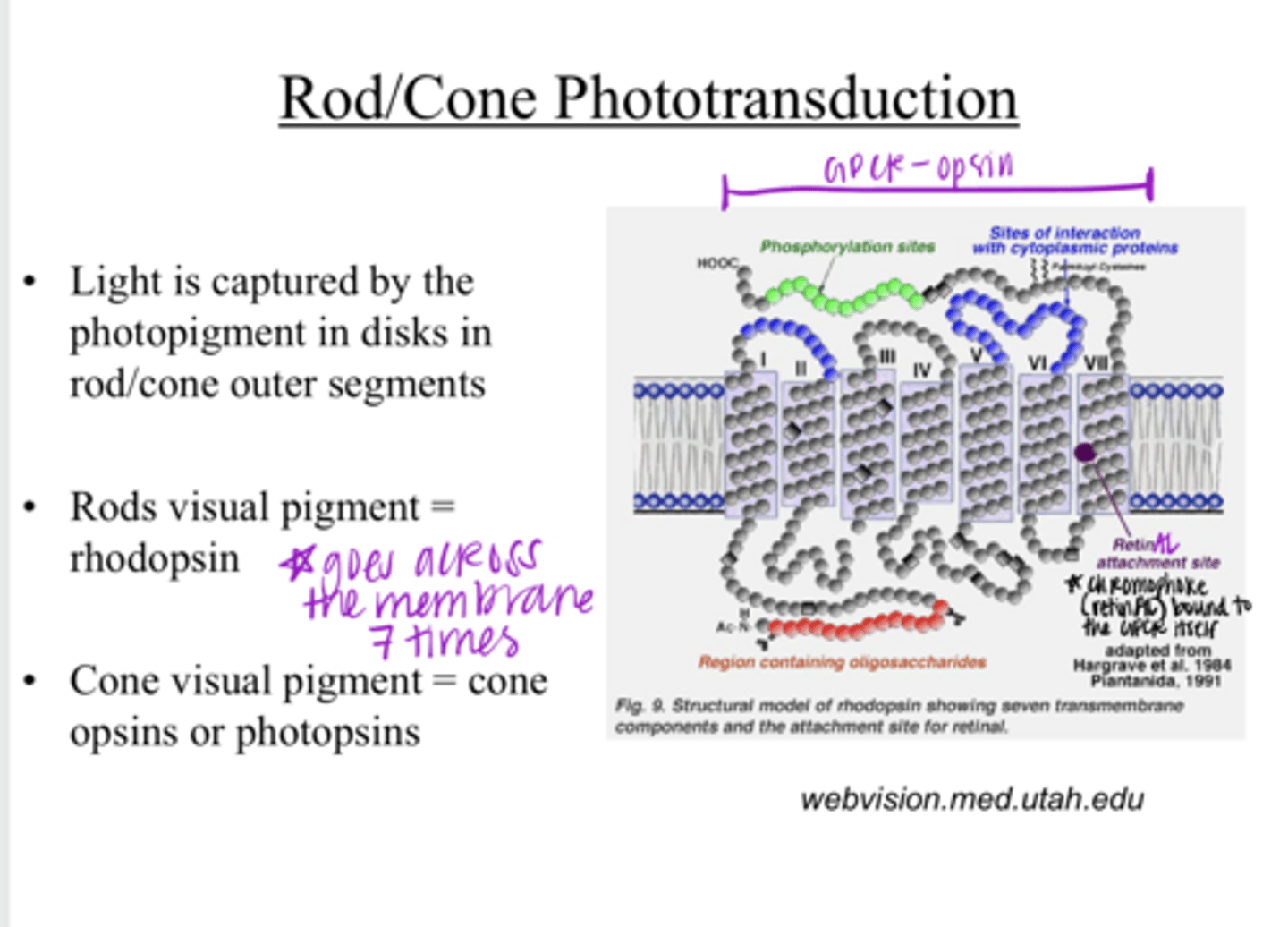
Light is captured by the photopigment in disks in the rod/cone outer segments
Light is captured by what? Where?
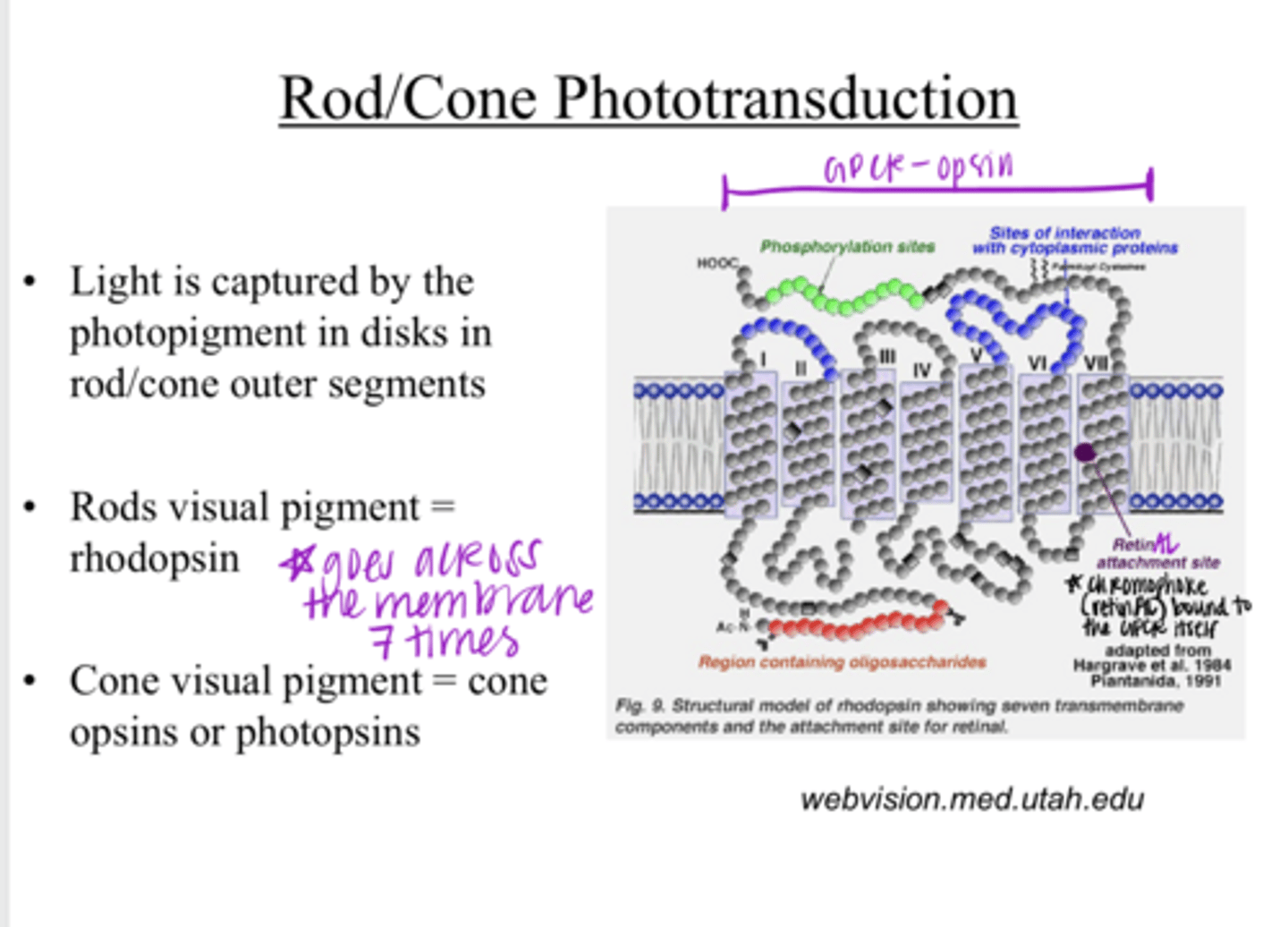
rhodopsin
What is the visual pigment of rods?
cone opsins or photopsins
What is the visual pigment of cones?
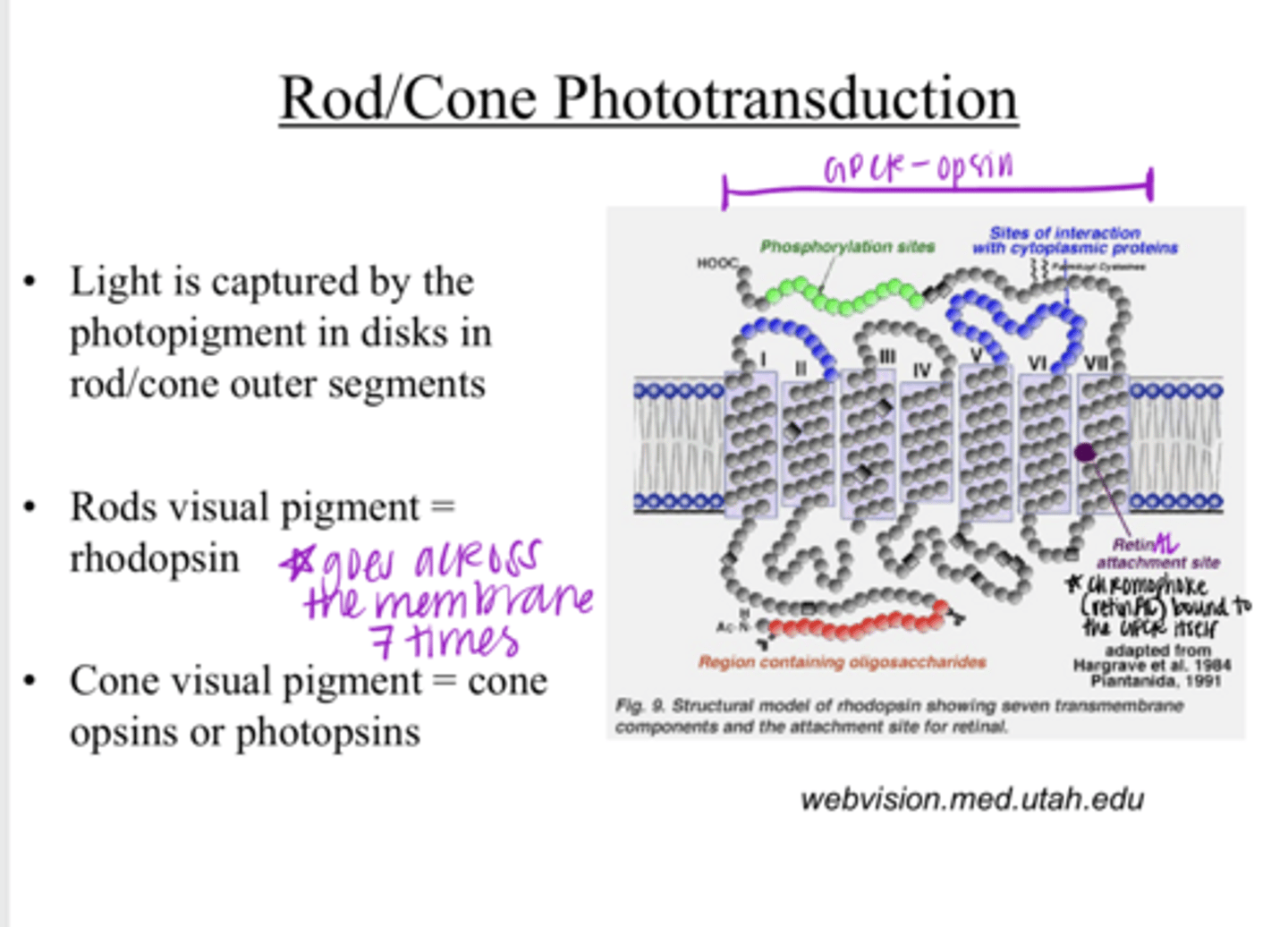
1) opsin protein
2) a chromophore retinAL
The visual pigment consists of what 2 components?
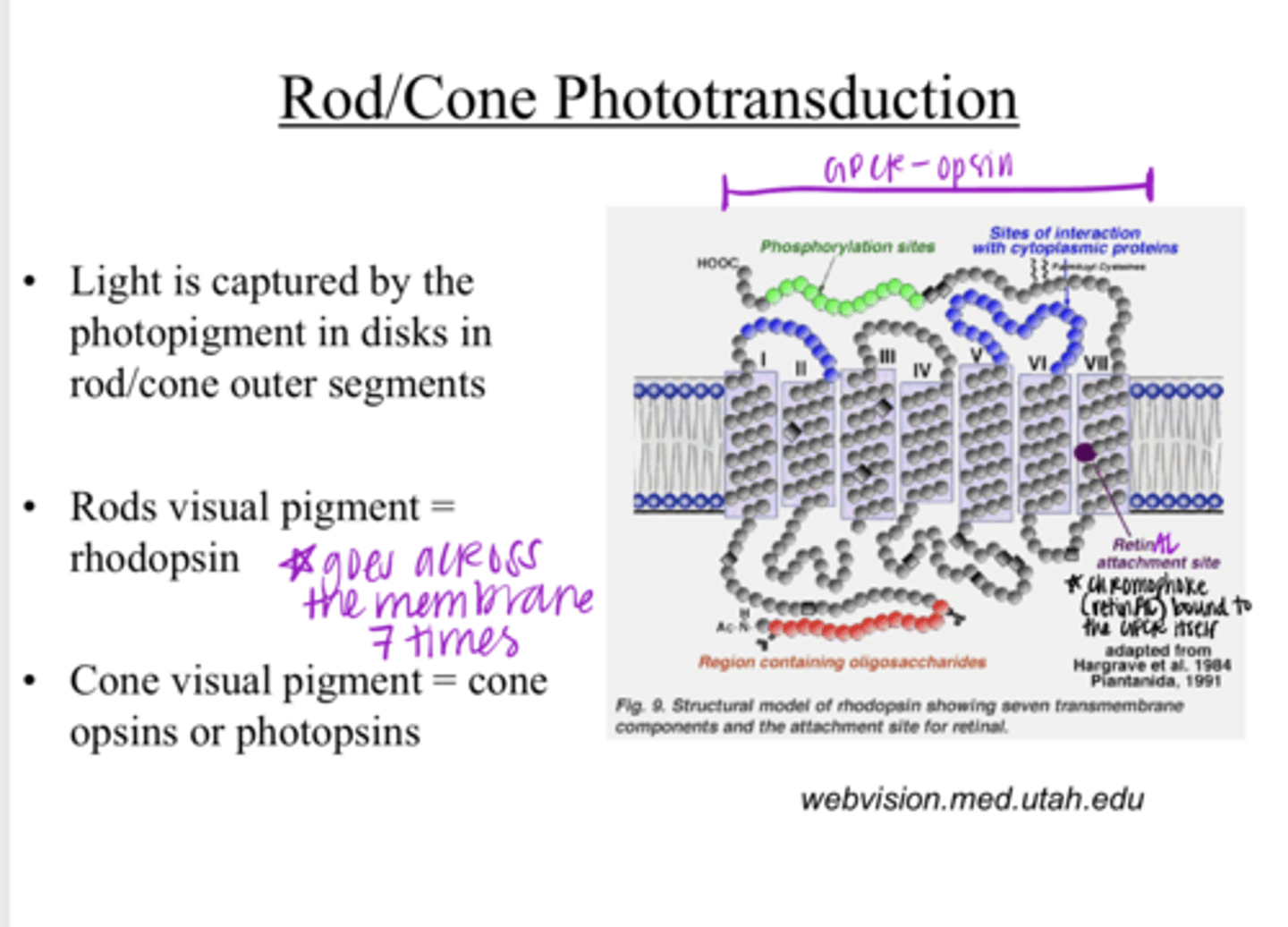
a 7-transmembrane domain receptor (GPCR)
What is the opsin protein of a visual pigment?
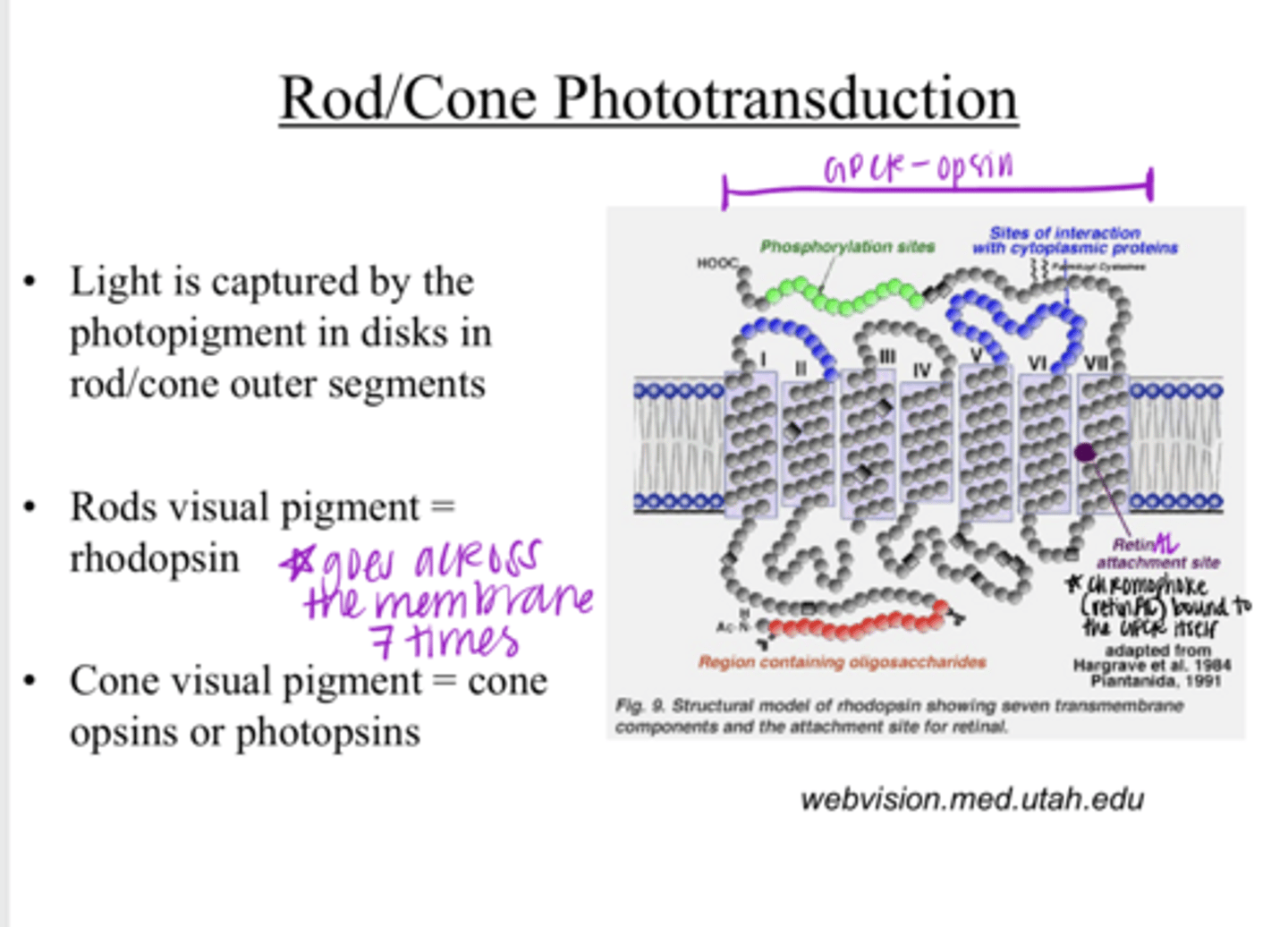
Vit A
What is the chromophore retinAL a derivative of?
true
True or False:
The retinAL is the same for all cones and rods
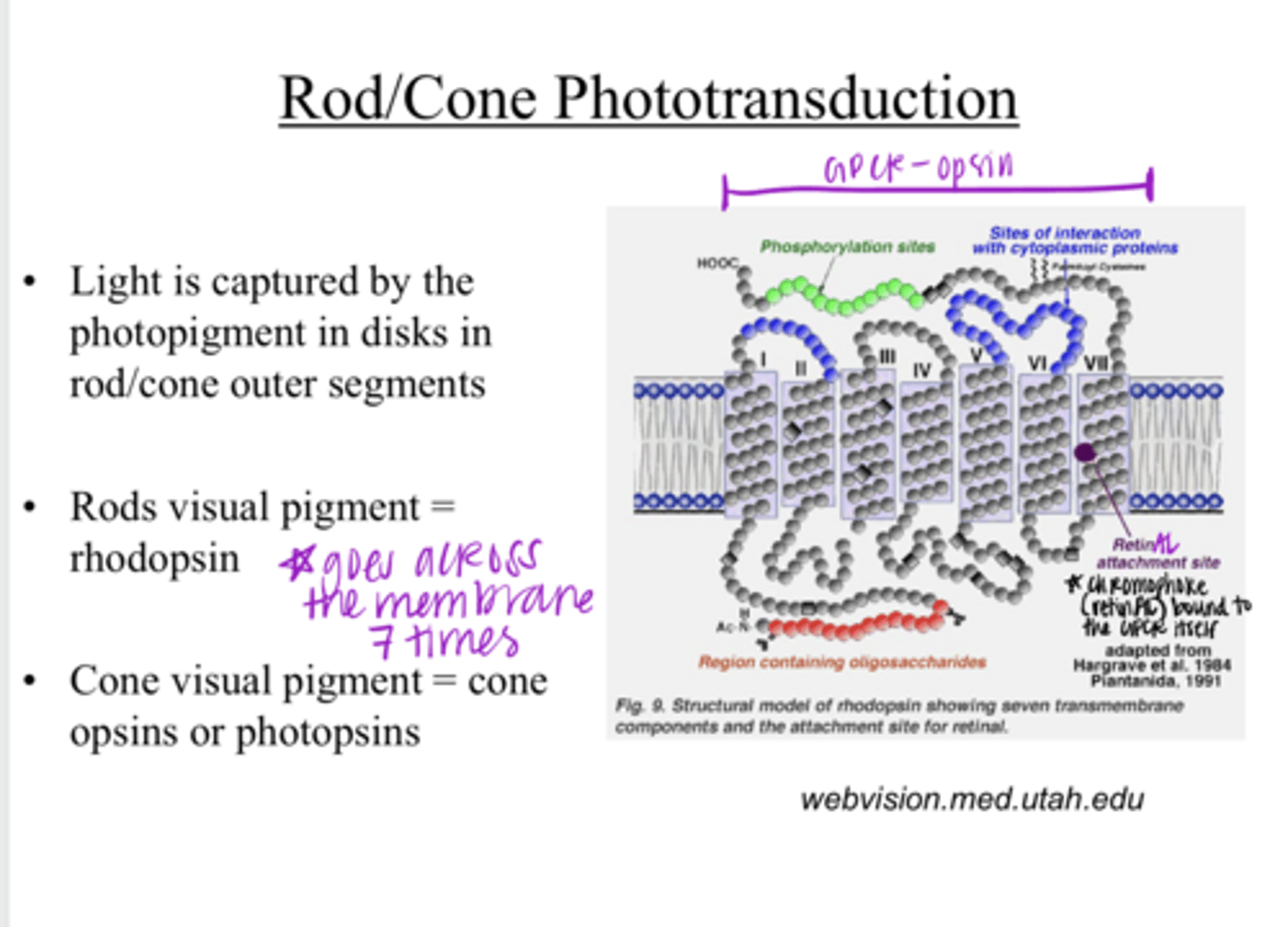
G coupled protein receptor
Opsins are part of a _____ family
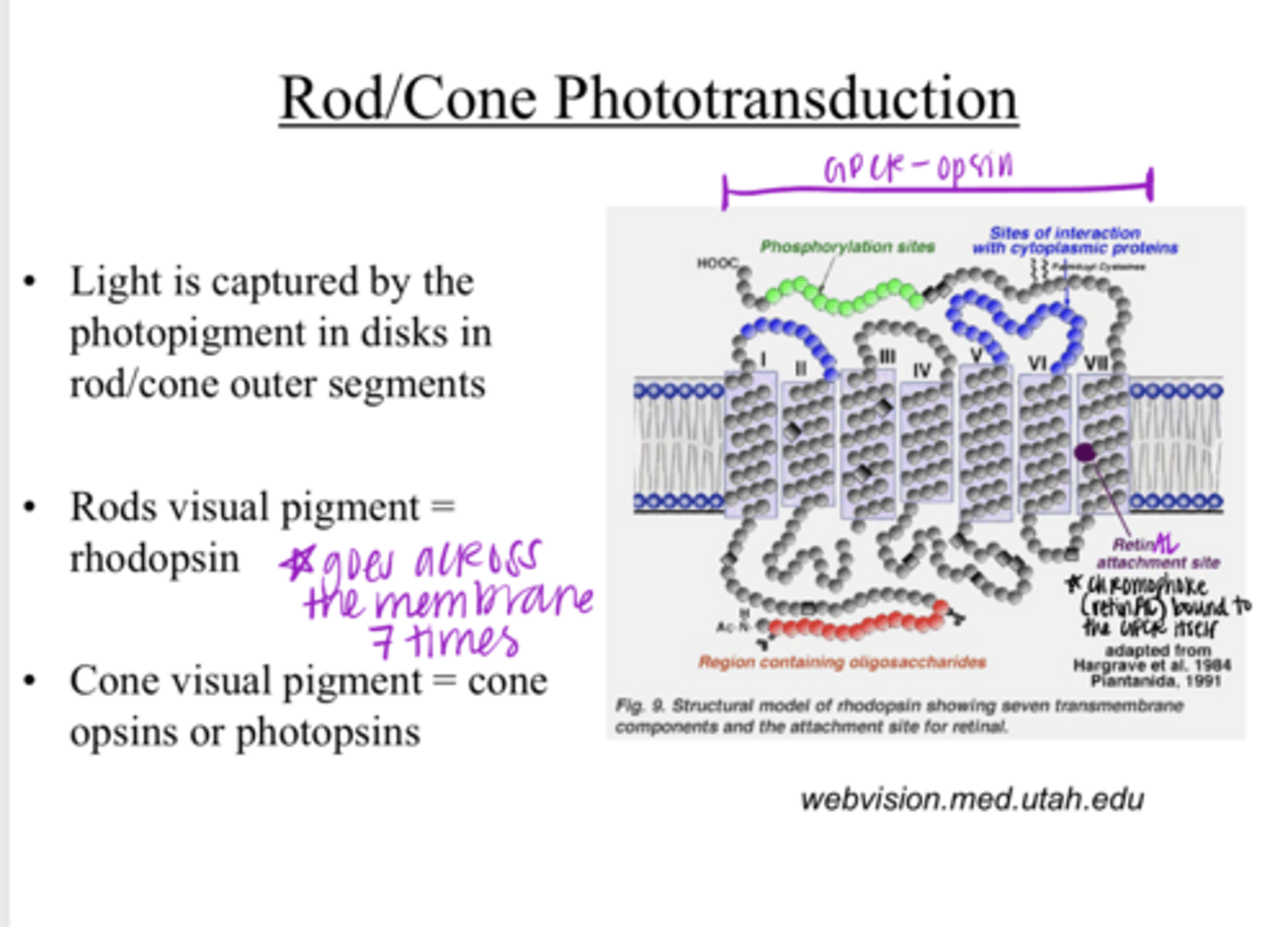
a conformational change
Unlike other receptors that are stimulated by a chemical, the chromophore (ligand) for the opsin (retinAL) is bound to the protein and undergoes what with stimulation by light?
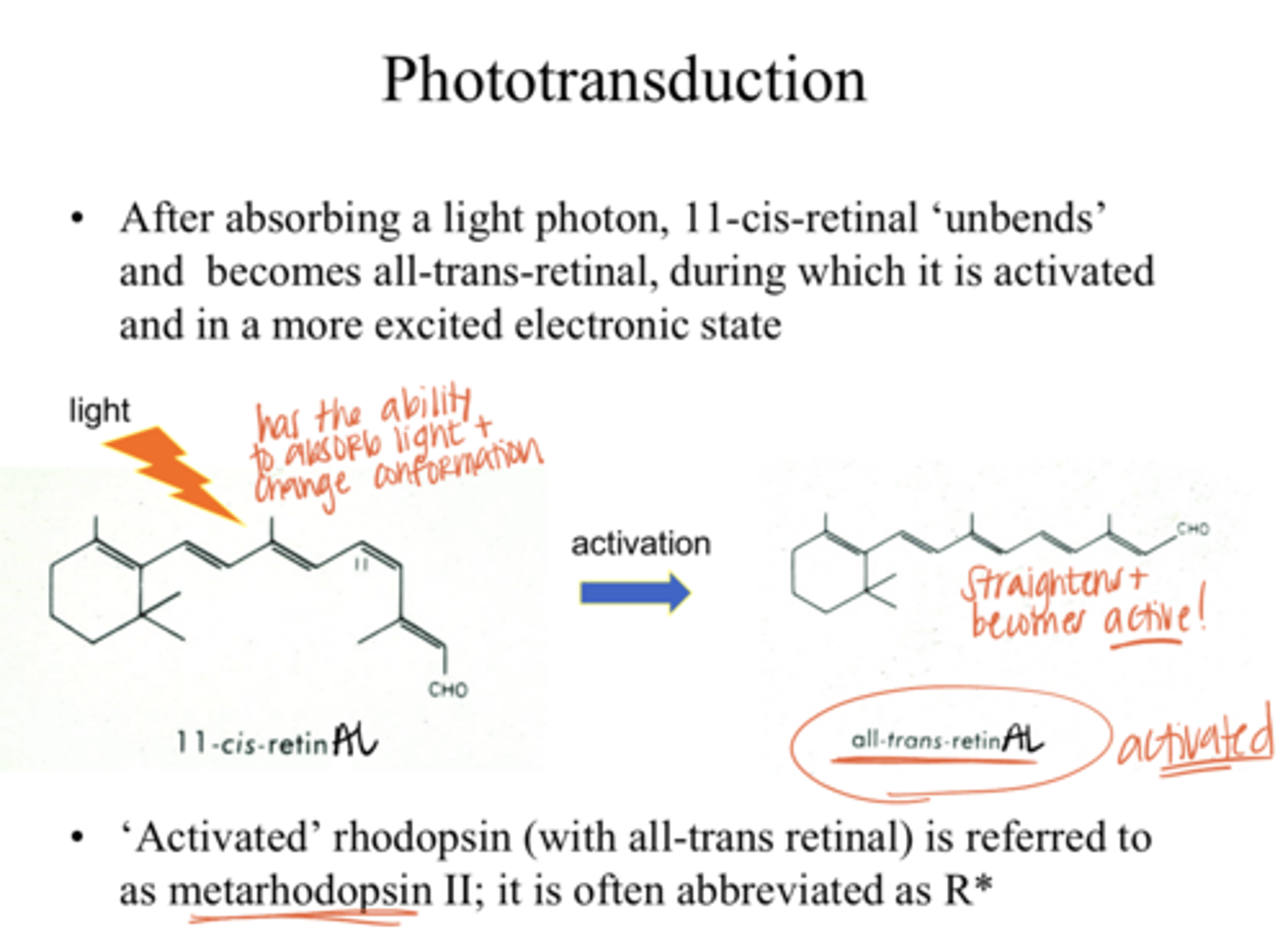
"unbends" and becomes all-trans-retinAL (more active state)
After absorbing a light photon, 11-cis-retinAL does what?
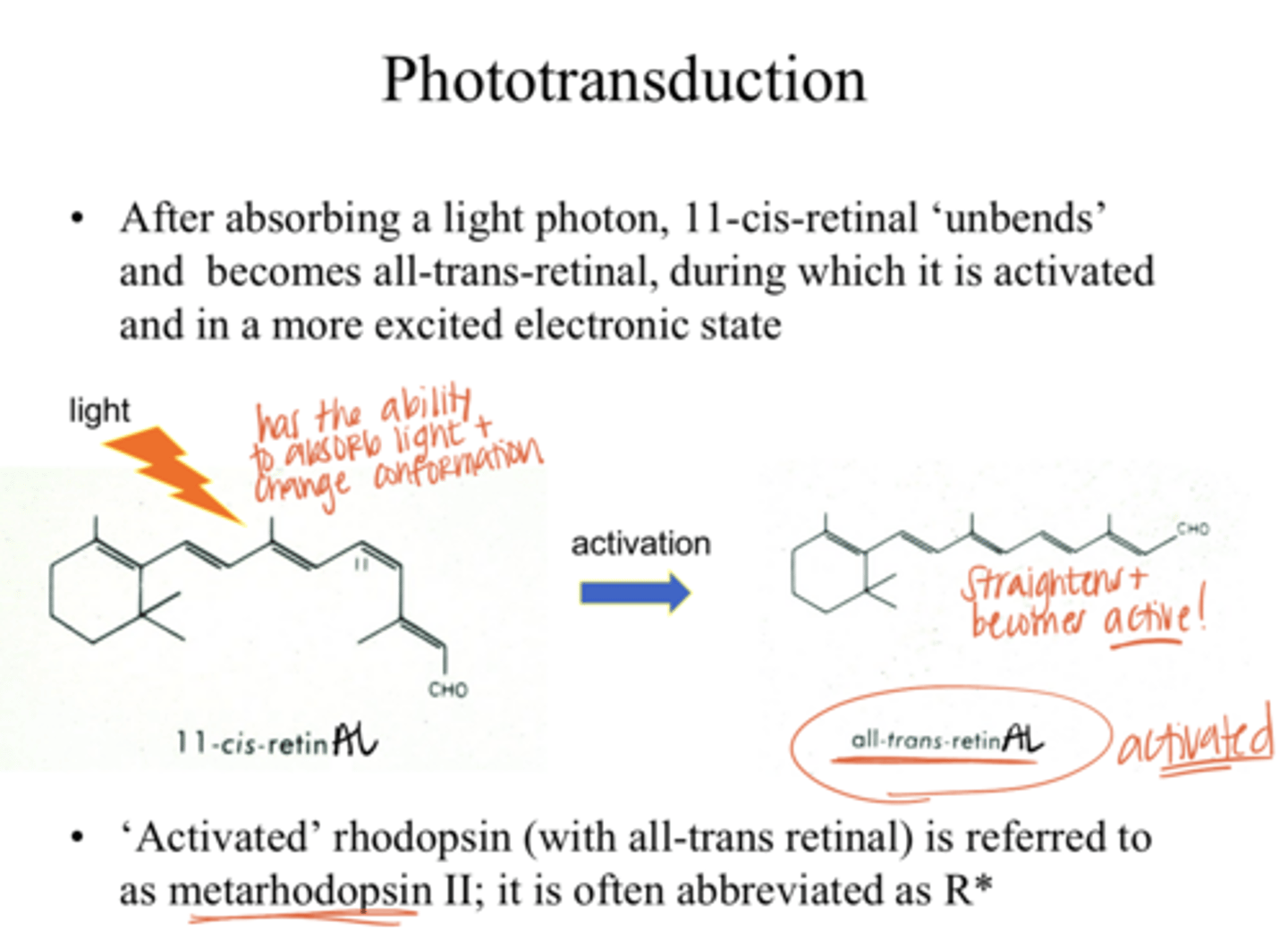
all-trans retinAL
Which is in a more excited electronic state?
11-cis retinAL OR all-trans retinAL
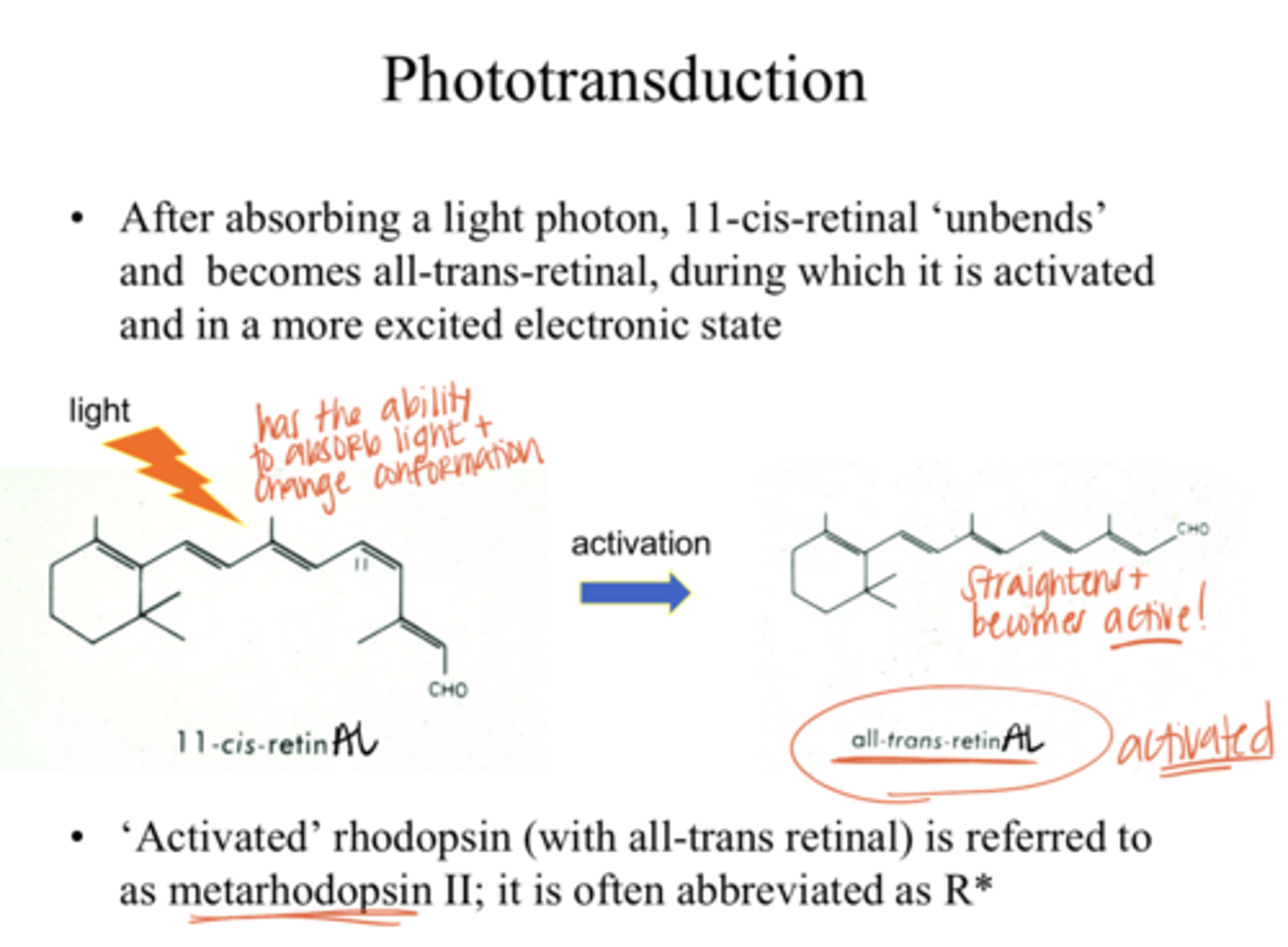
R*
"activated" rhodopsin is abbreviated as what?
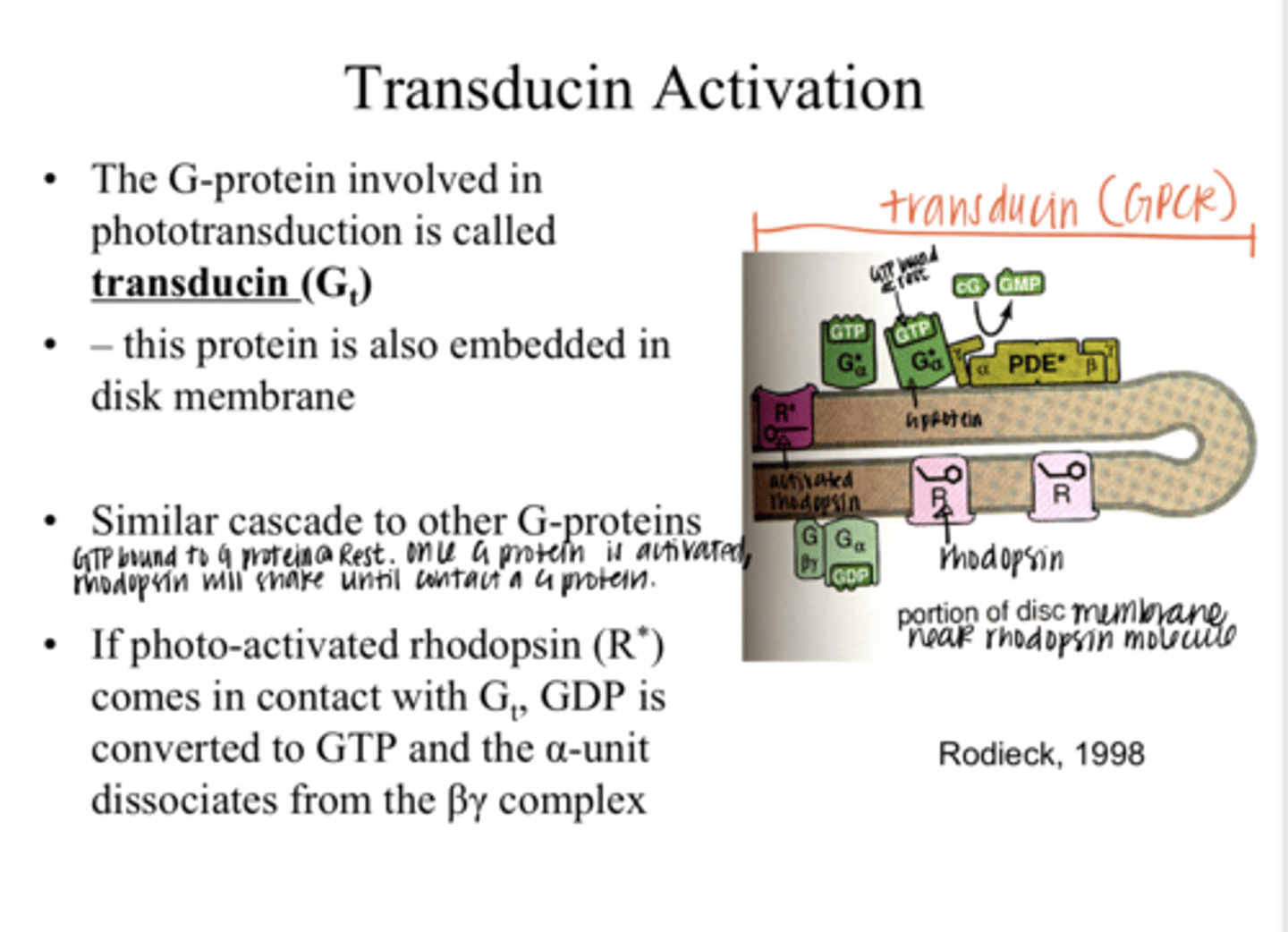
transducin (Gt)
The G protein that is involved in phototransduction is called what?
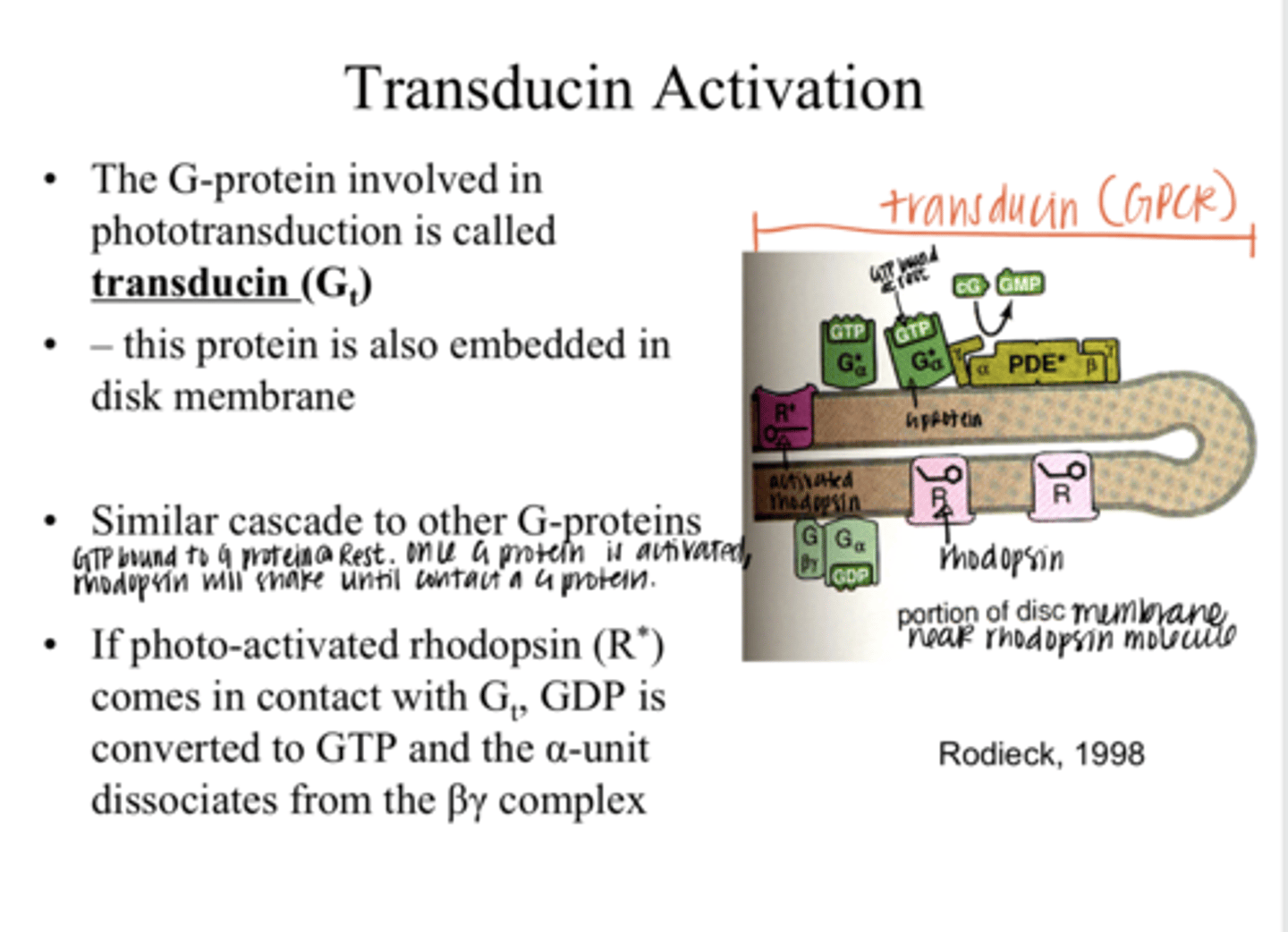
into the disc membrane
Where is transducin (Gt) embedded?
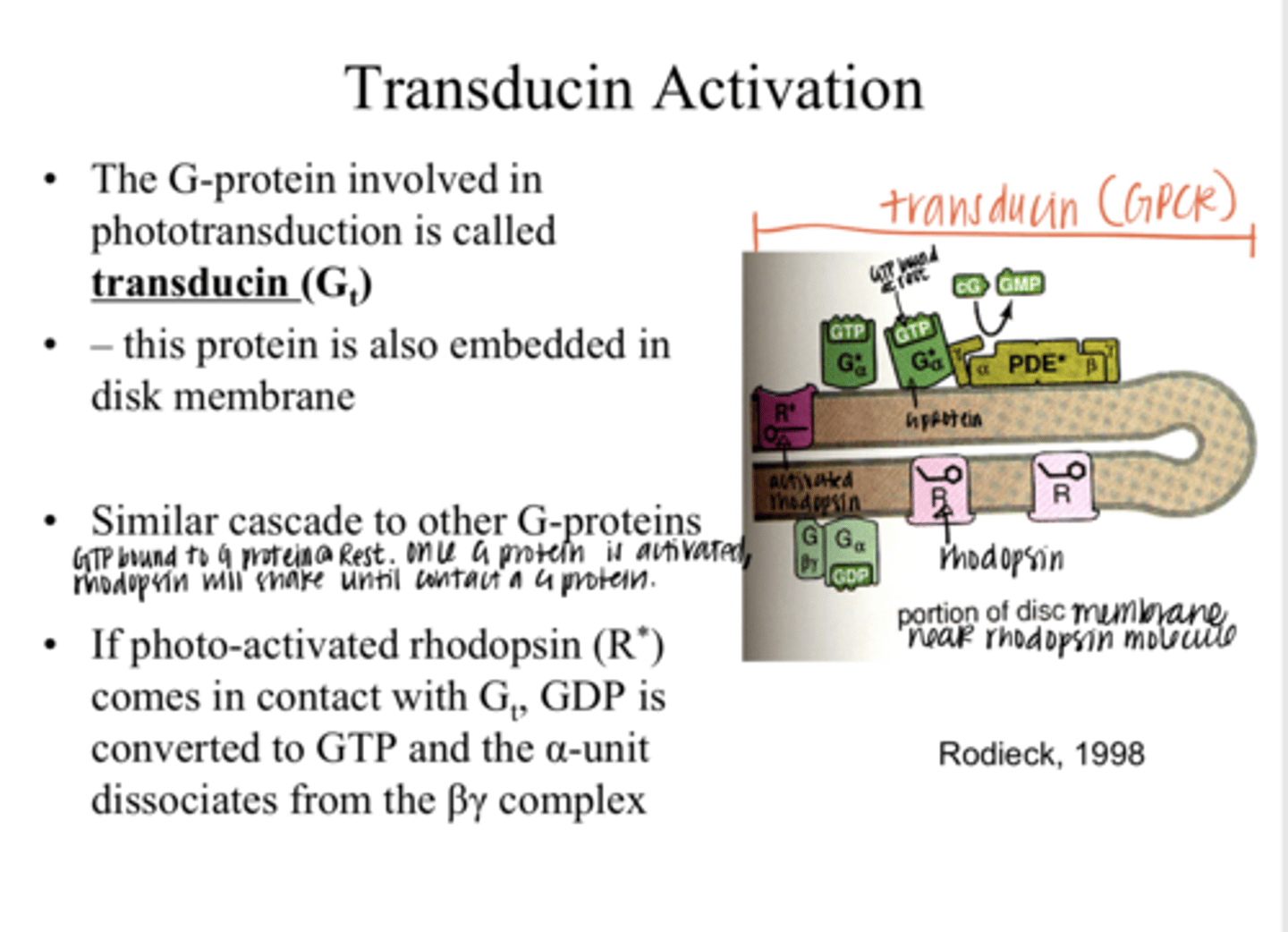
true
True or False:
Transducin (Gt) has a similar cascade to other G proteins
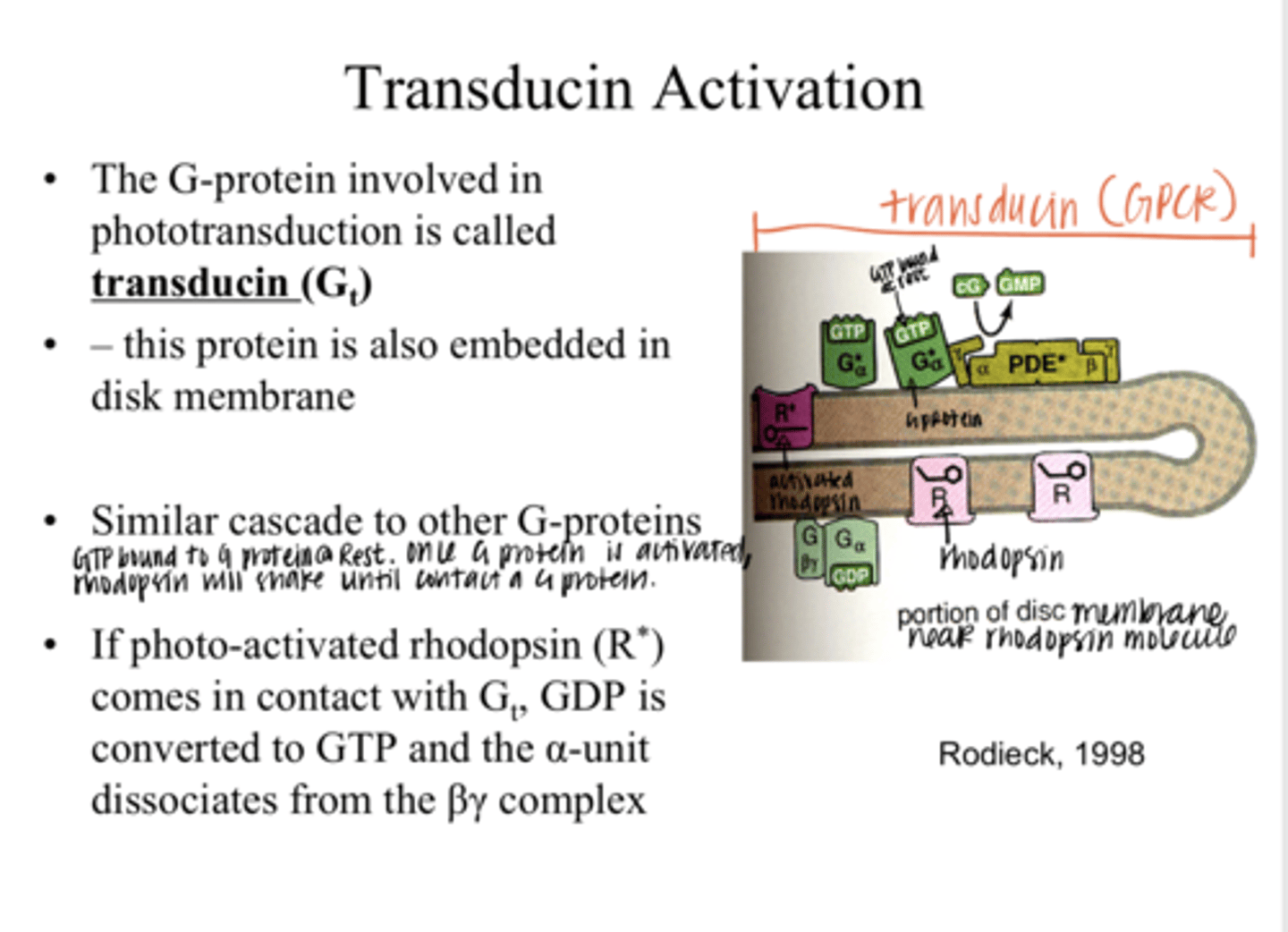
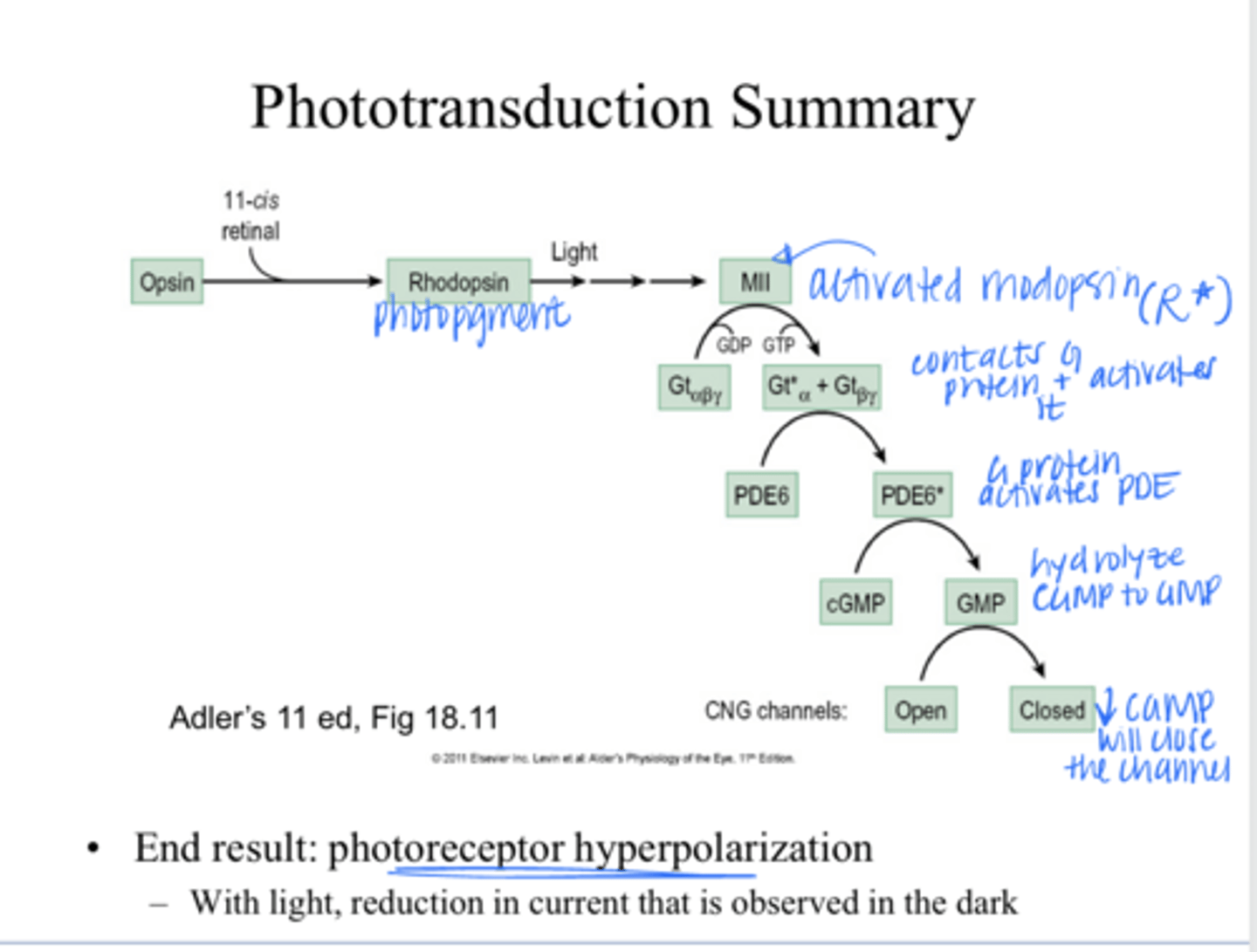
GDP is converted to GTP and the α-unit dissociates from the βγ complex
If photo-activated rhodopsin (R*) comes in contact with a transducin (Gt) molecule, what happens?
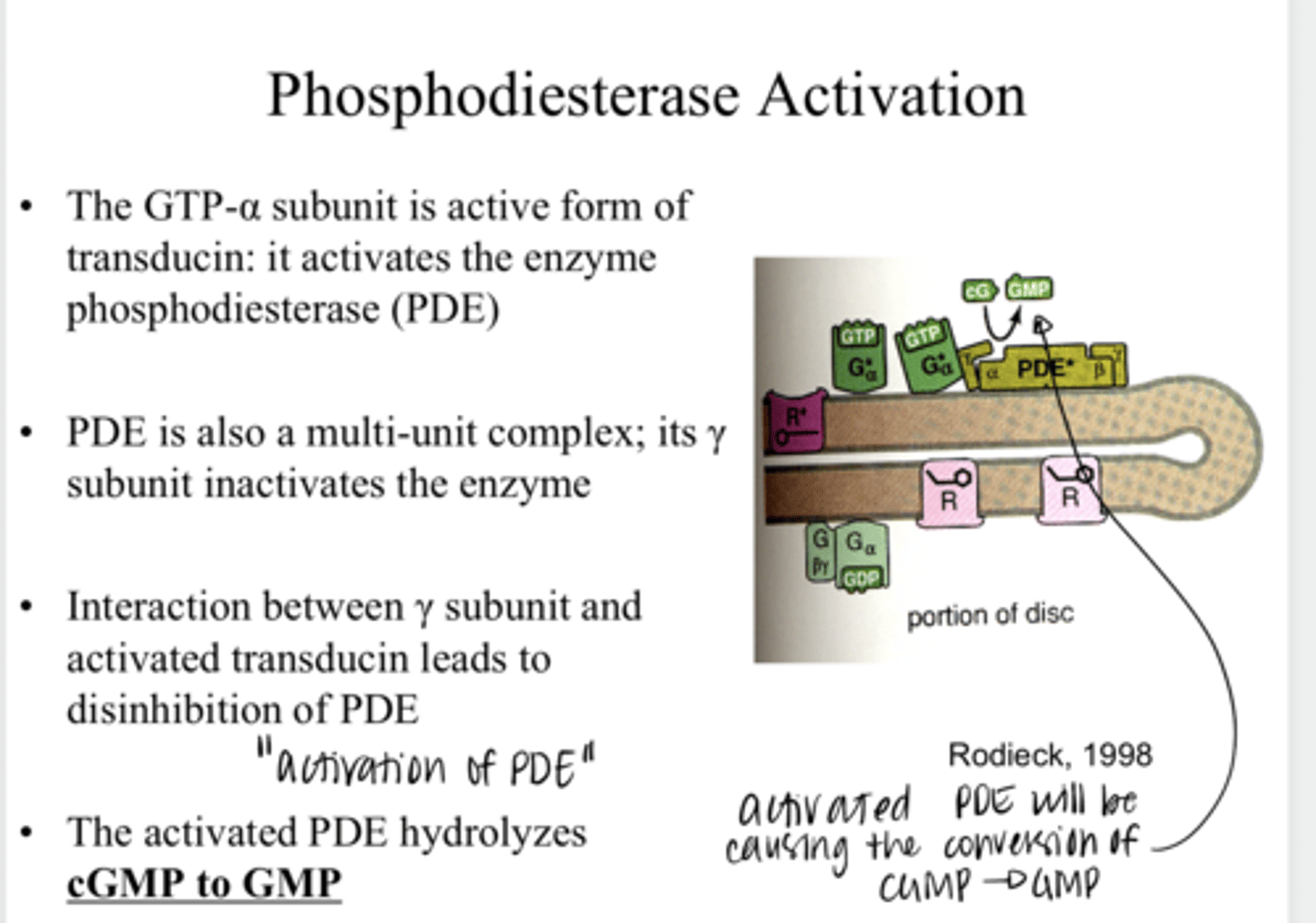
The GTP-α subunit is active; it activates the enzyme phosphodiesterase (PDE)
After GDP is converted to GTP and the α-unit dissociates from the βγ complex, what happens?
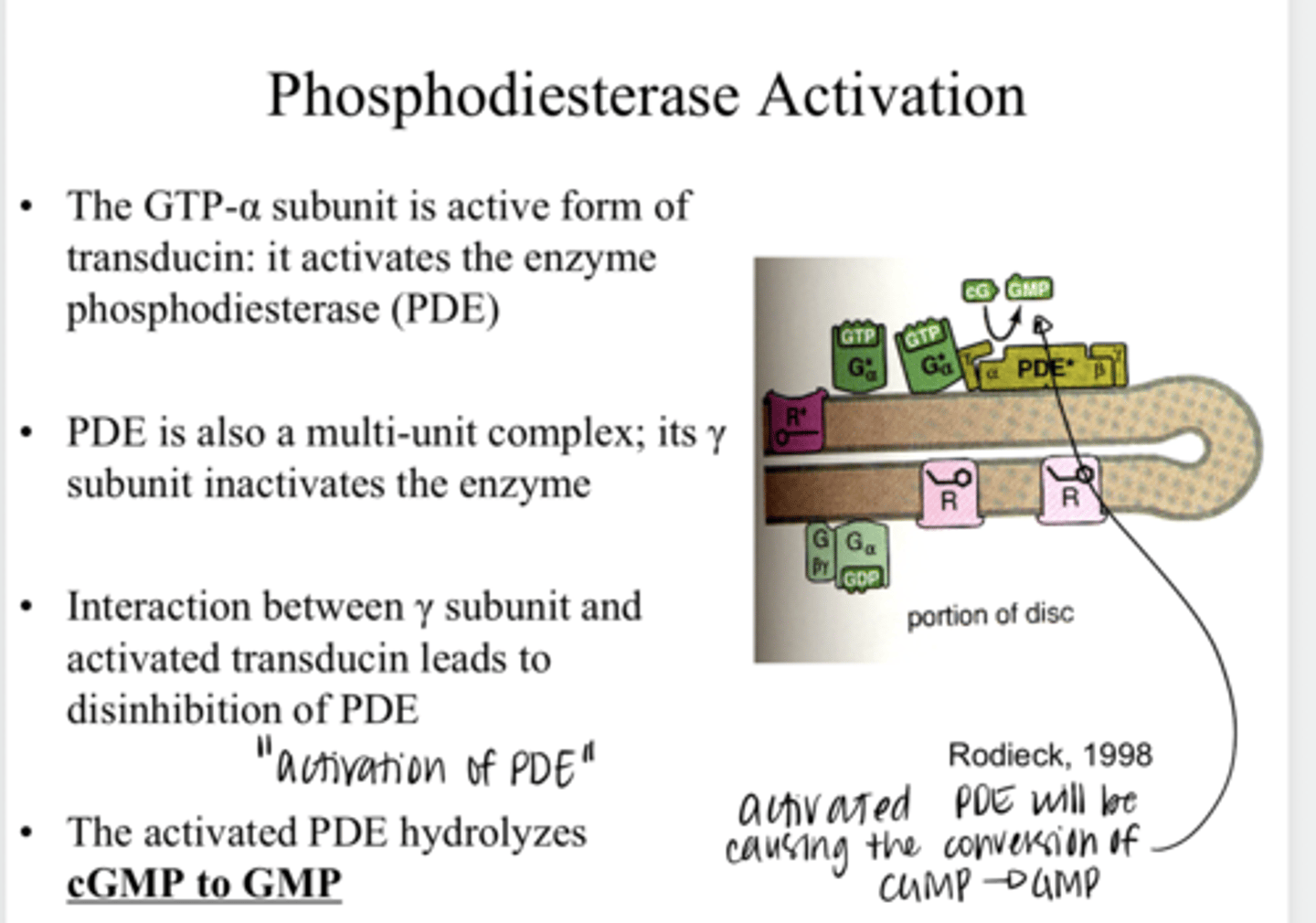
will hydrolyze cGMP to GMP
What is the function of PDE in the phototransduction cascade?
-There are cGMP gated channels in the outer segment, the presence of intracellular cGMP keeps these channels open (Na+ flow into the cell)
-cGMP gated channels are OPEN with lights OFF (in the dark)
How does the activation of PDE lead to the hyperpolarizing light responses of the rods and cones?
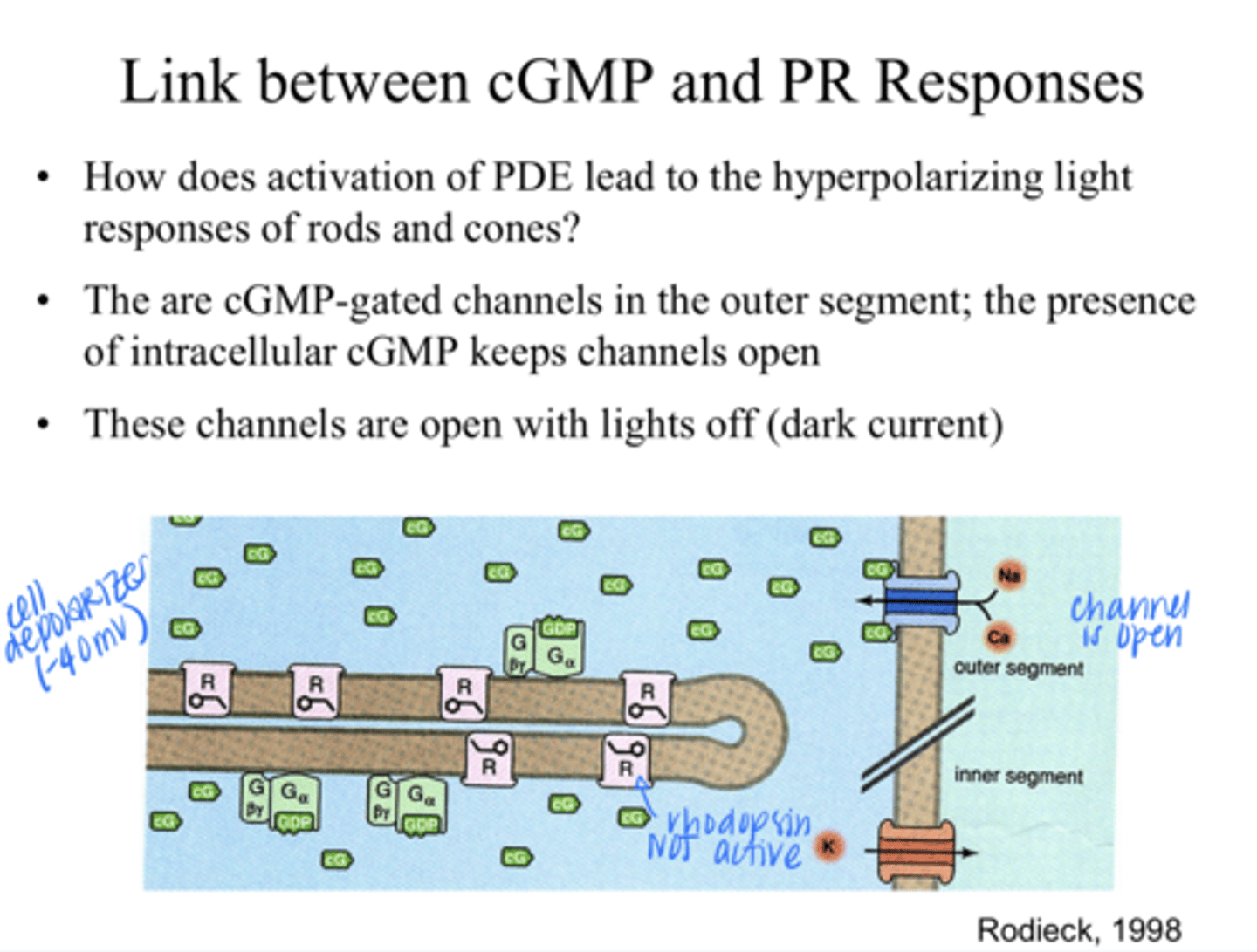
Decrease in internal cGMP levels. Without cGMP present, the cGMP-gated channels in the outer segment close
With light stimulation & activation of PDE, what happens to the internal cGMP levels and thus the channels?
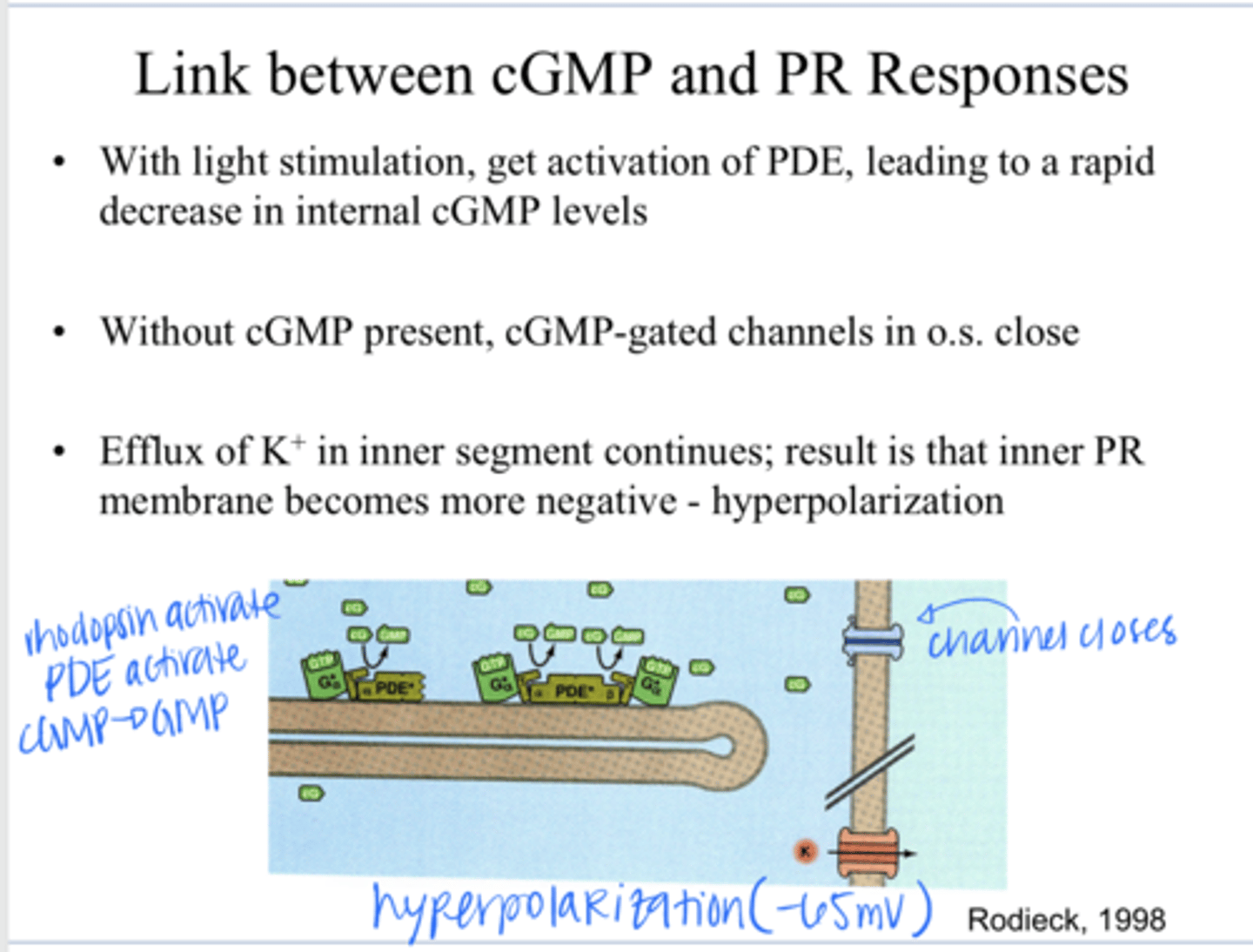
the efflux of K+ continues in the inner segment, the inner photoreceptor membrane becomes more negative (hyperpolarization)
When the cGMP-gated channels in the outer segment close, how does the cell hyperpolarize?
true
True or False:
Rods and Cones have a number of features that make them somewhat unusual compared to other CNS neurons ?
1) photopigment that captures light
2) more depolarized resting membrane potential in the dark (-40mV)
3) use graded potentials instead of action potentials
What are the differences in rods/cones that are different than other CNS neurons?
they hyperpolarize
In response to light, what happens to rods and cones?
yes
Is 11-cis-retinAL the same in both rods and cones?
no
Is the opsin protein the same for rods and cones?
1 -- rhodopsin
In humans, how many types of opsin are in rods?
3
In humans, how many types of cone opsins are there?
S = short wavelength; M = medium wavelength; L = long wavelength
What are the 3 cone opsins?
in the inner segment of the PR
Where is opsin made?
transferred to the O.S. of the PR
Where is opsin transferred after it is made?
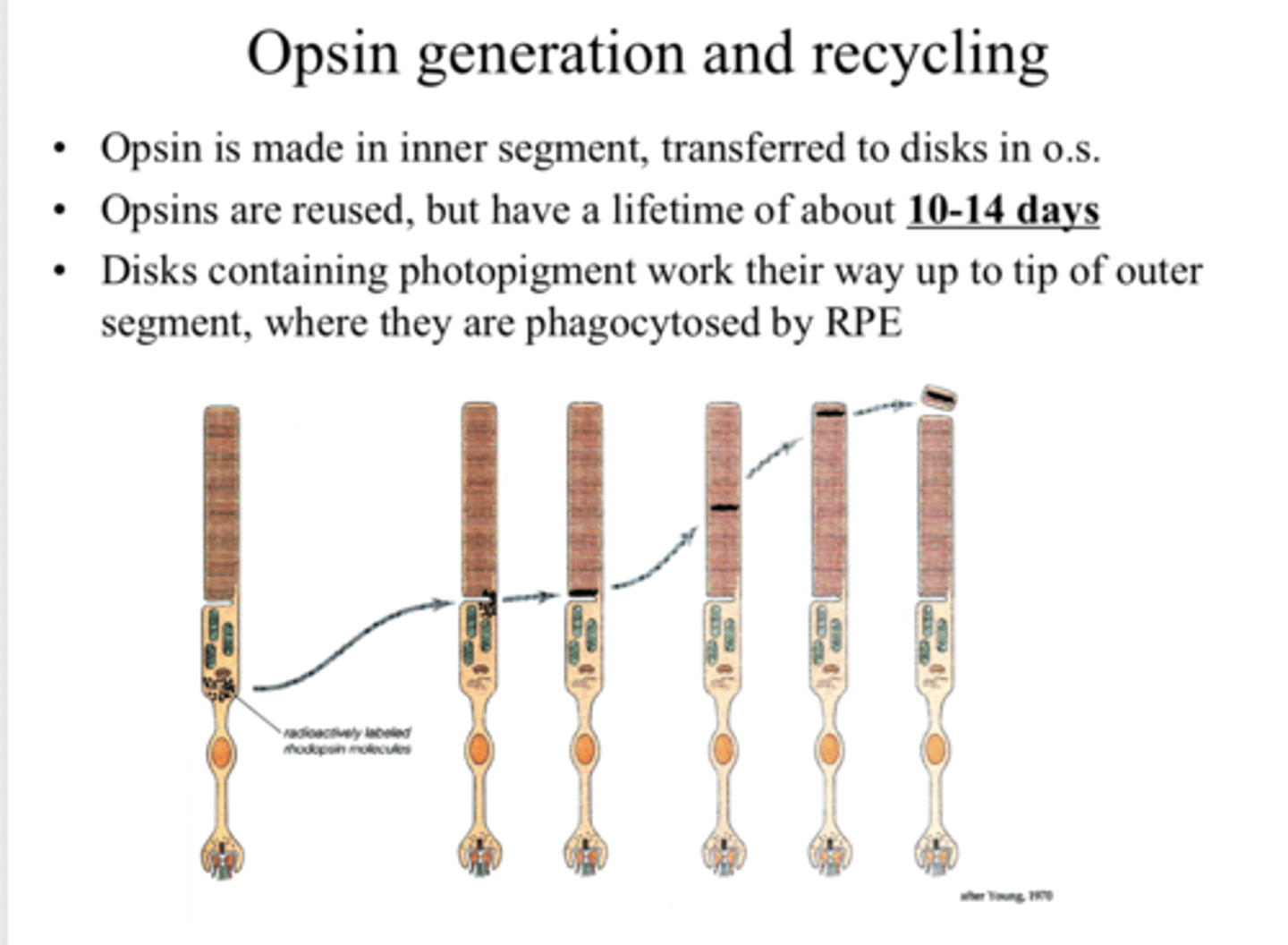
yes
Are opsins reused?
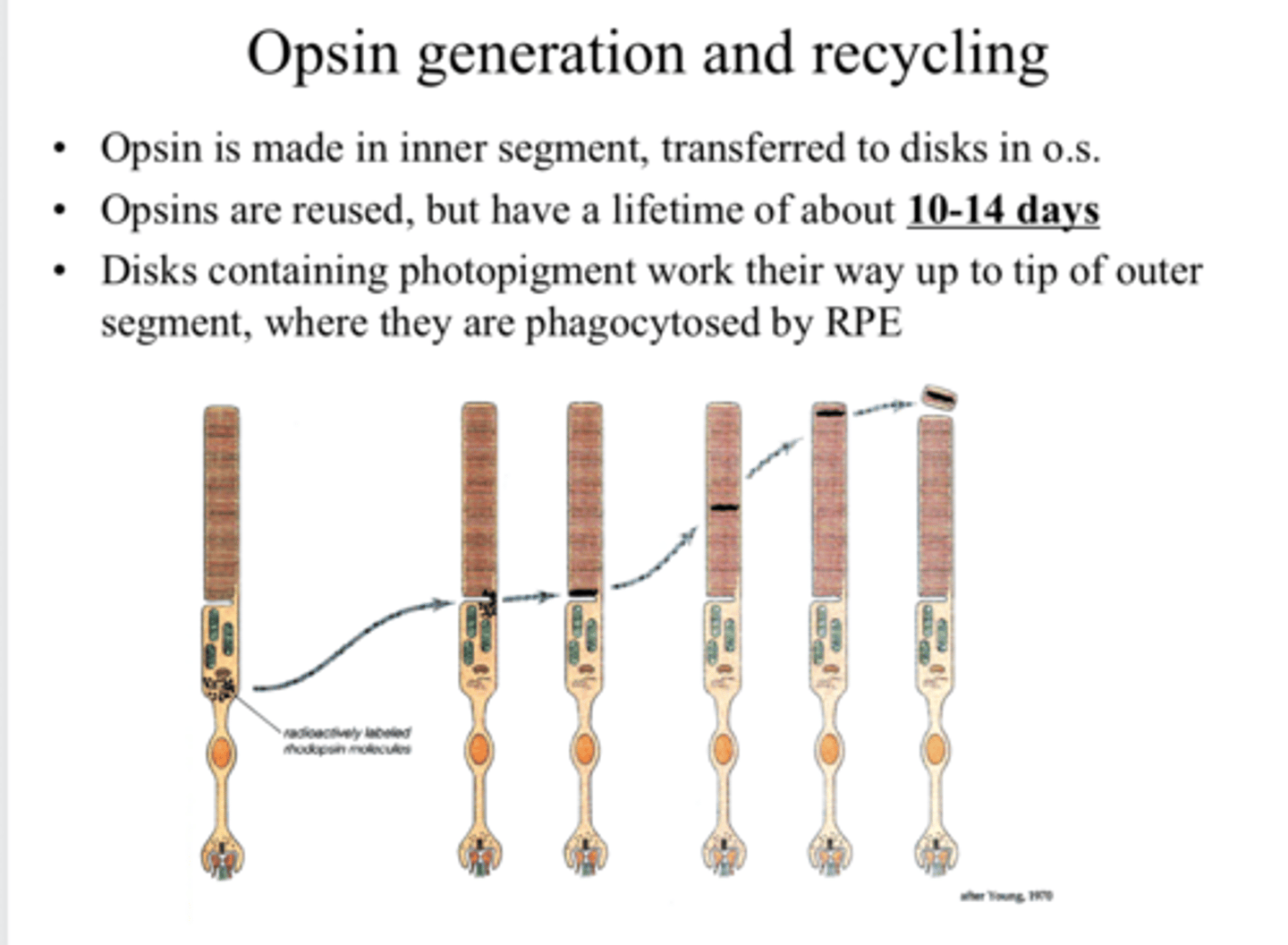
10-14 days
What is the lifetime of an opsin?
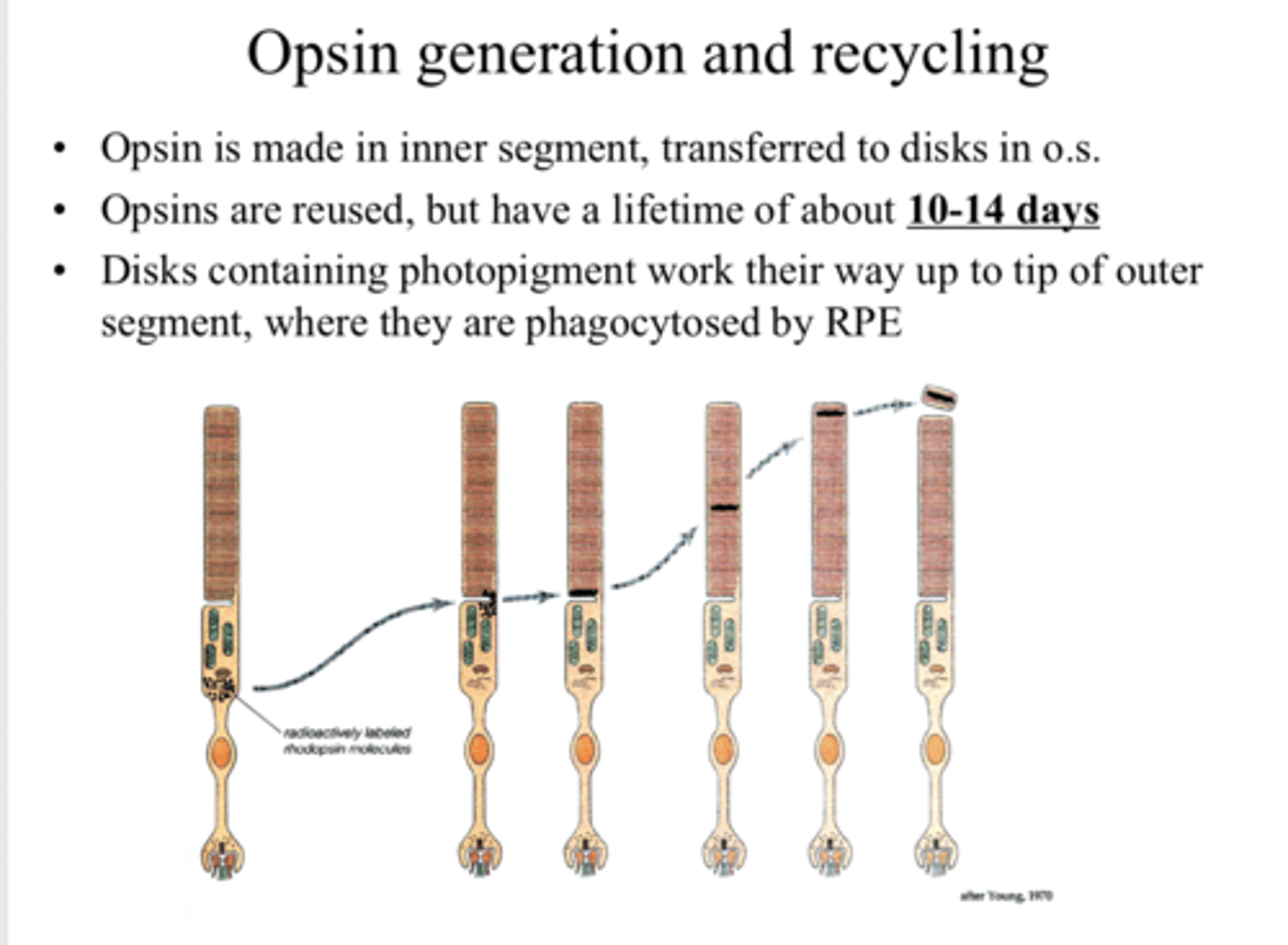
where the disks are phagocytosed by the RPE
Disks containing photopigment work their way up to the tip of the outer segment, where what happens?
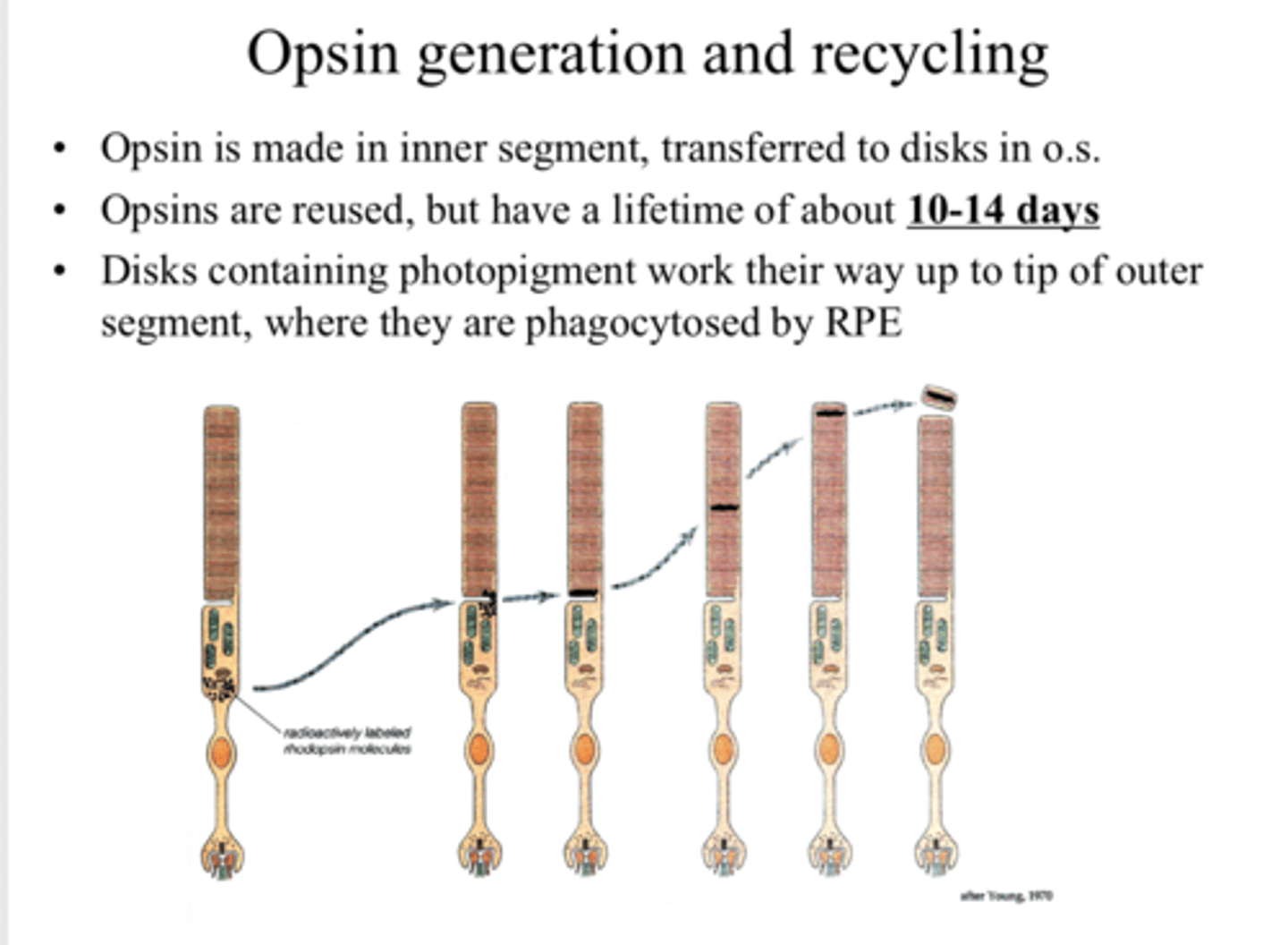
near the top of the outer segment
Where will the older photopigment be located?
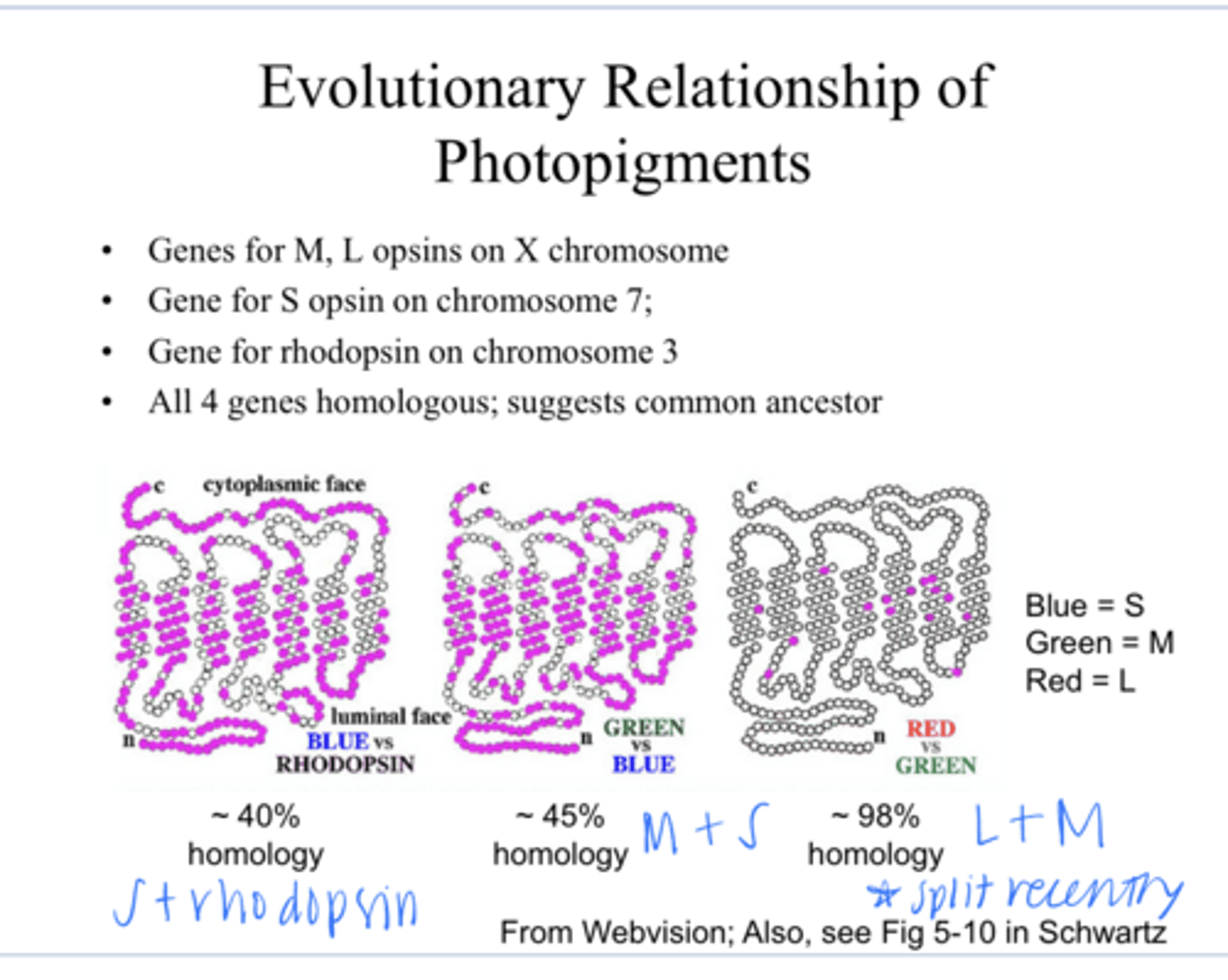
on the X chromosome -- why a lot of color vision defects are sex-linked
Where are the genes for the M and L opsins?
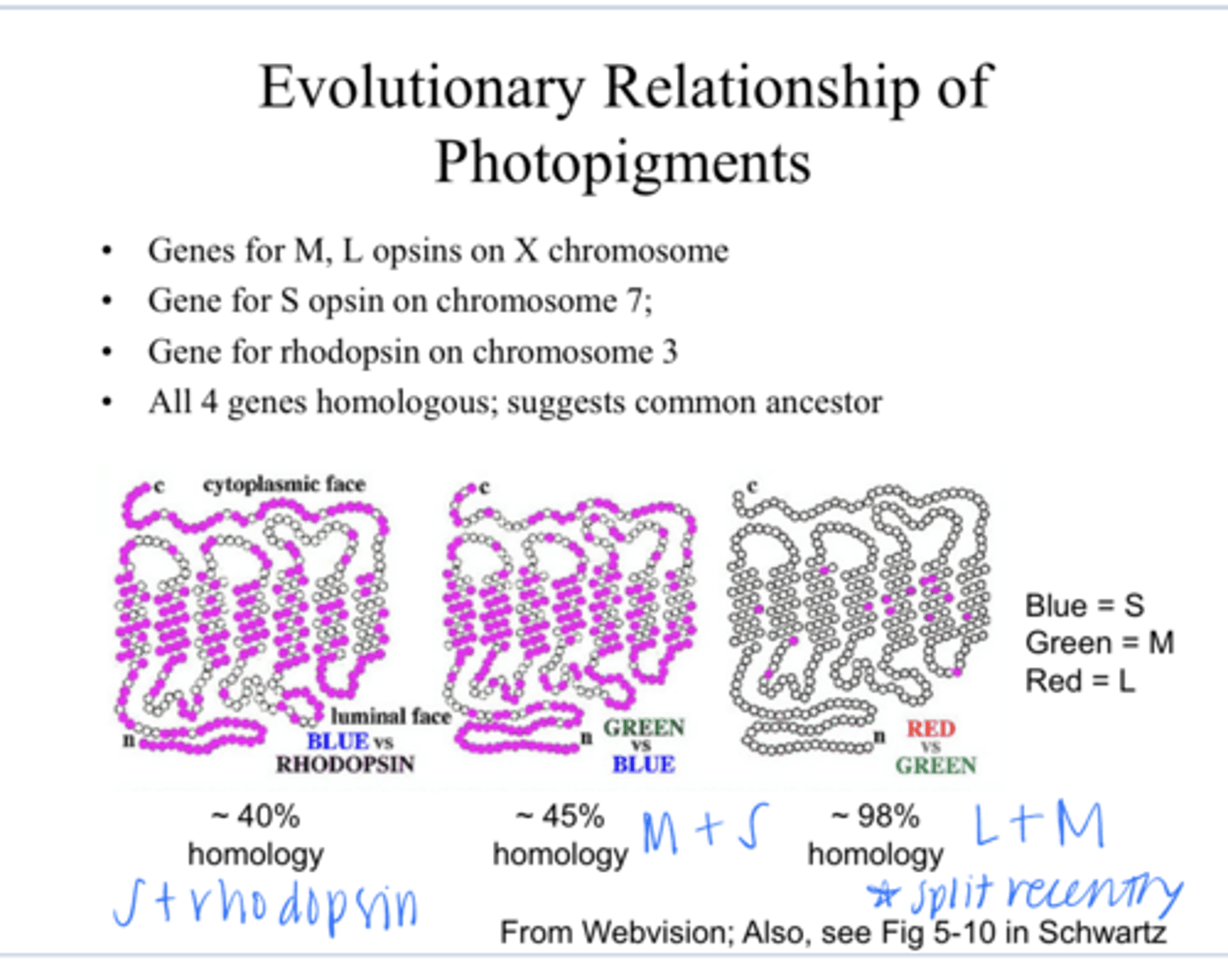
on chromosome 7
Where are the gene for the S opsins?
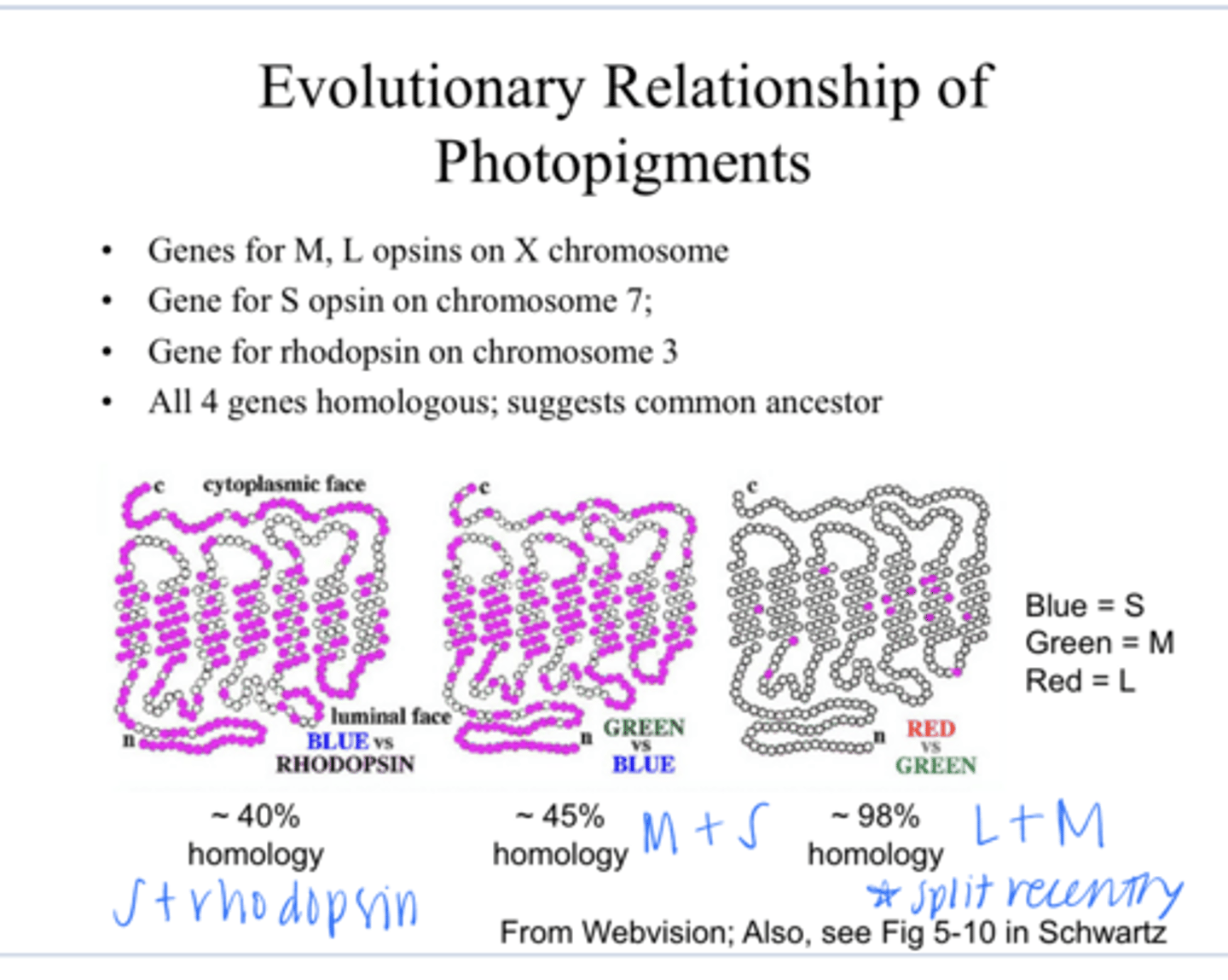
on chromosome 3
Where is the gene for rhodopsin?
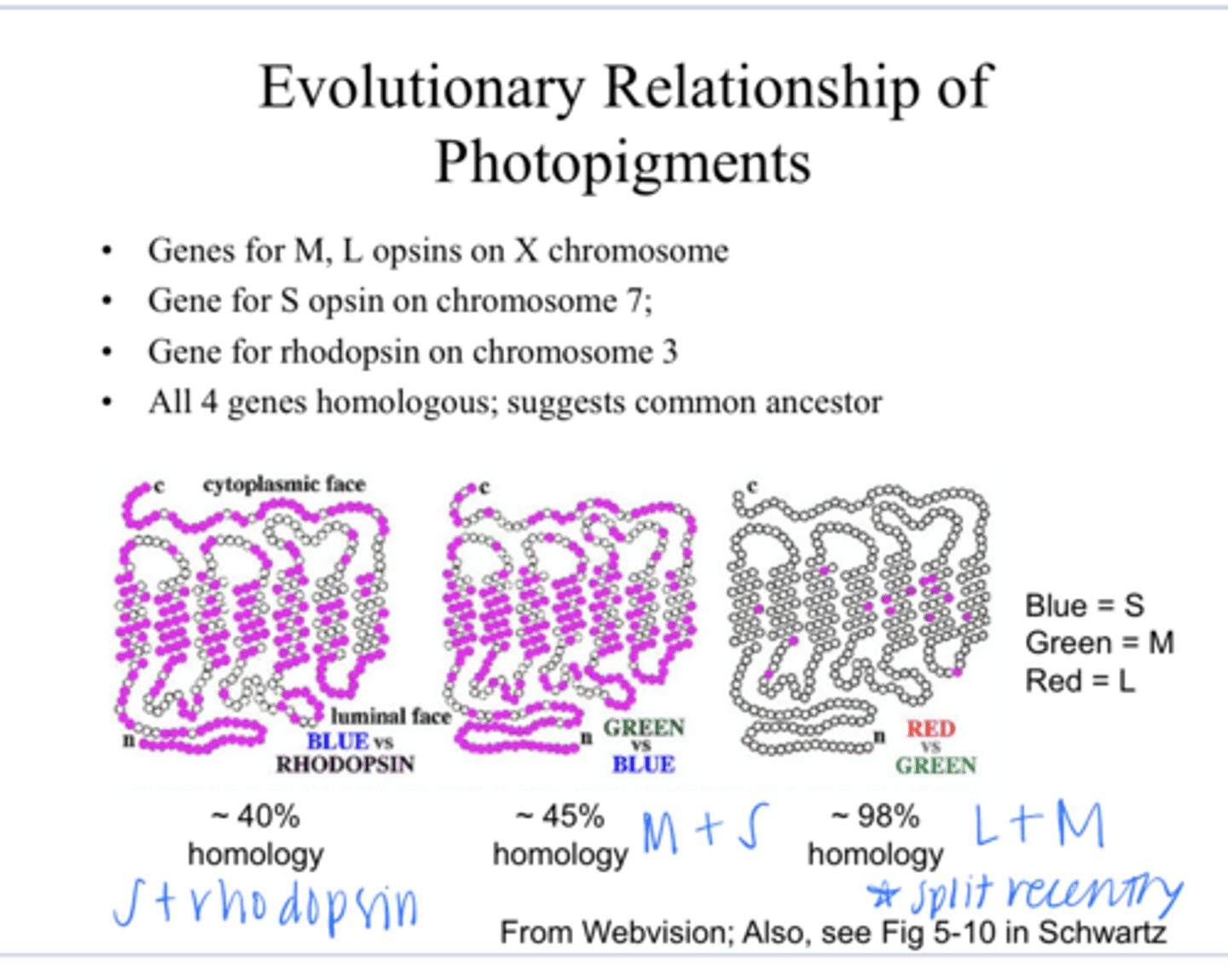
yes -- suggest there is a common ancestor
Are all 4 genes homologous for the S,M,L and rhodopsin?
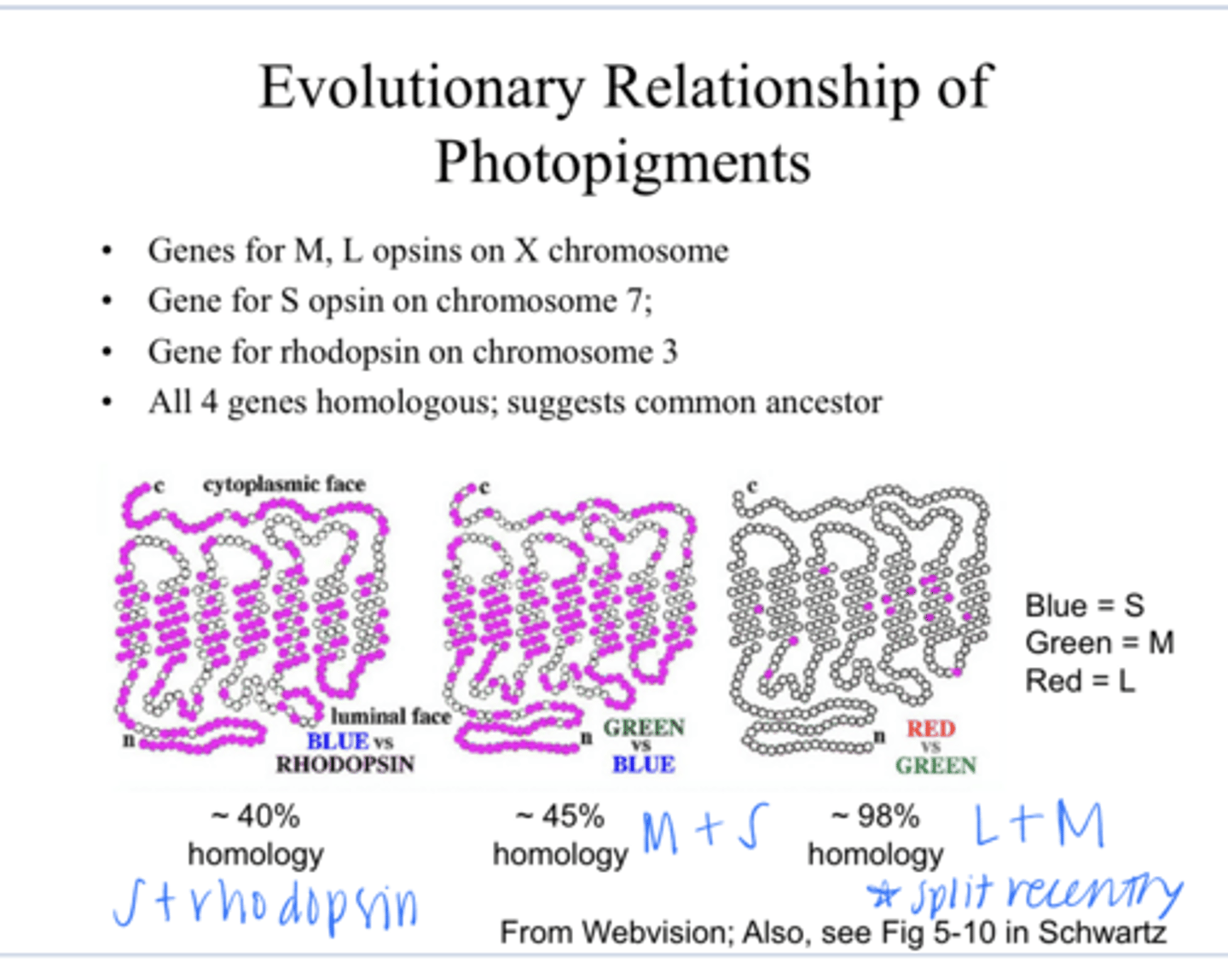
L and M
The close homology between _____ genes suggests that the evolutionary split between these 2 occurred recently
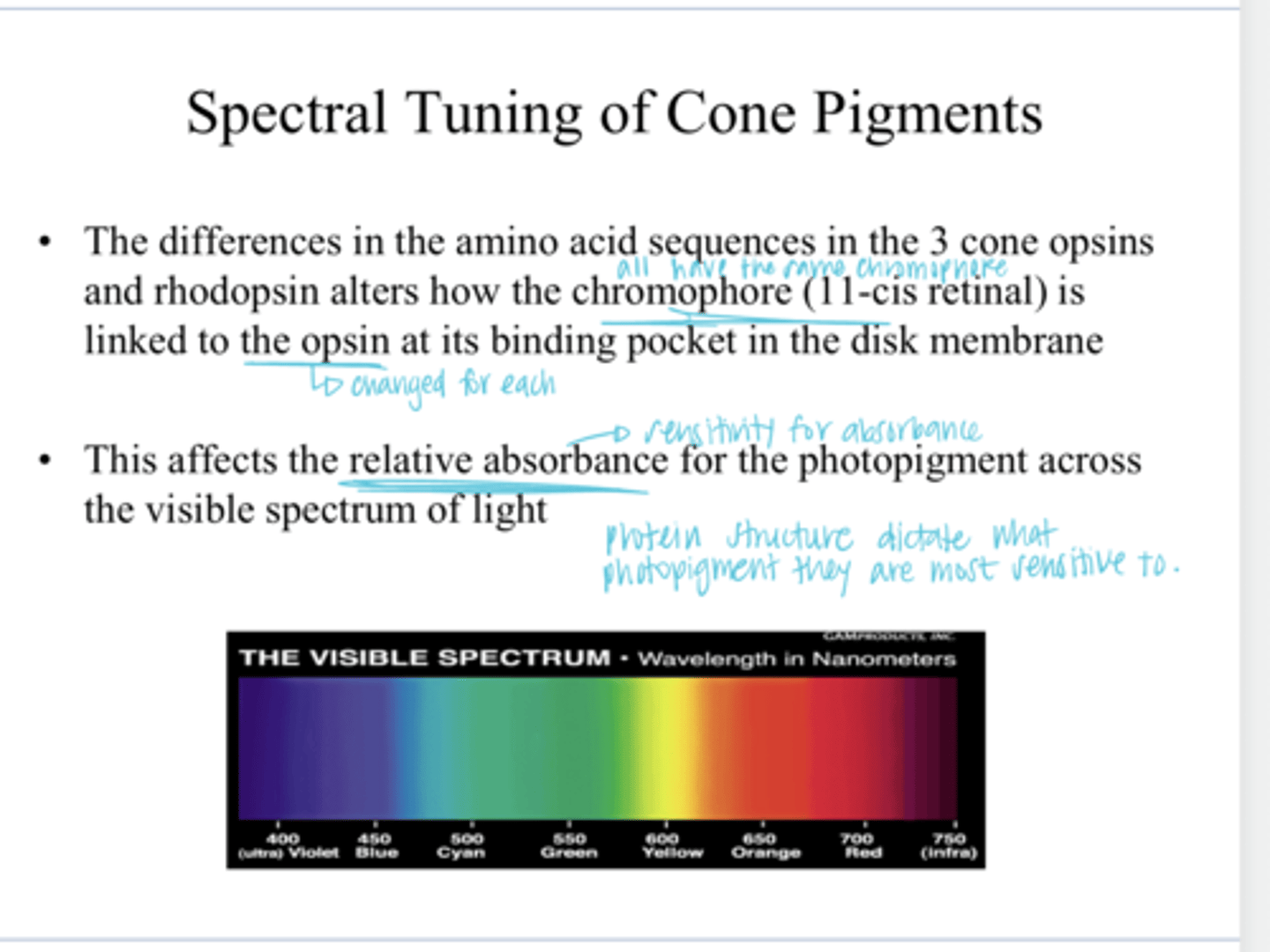
how the chromophore (11-cis retinaAL) is linked to the opsin binding pocket in the disc membrane
The differences in the amino acid sequences in the 3 cone opsins and rhodopsins alters what?
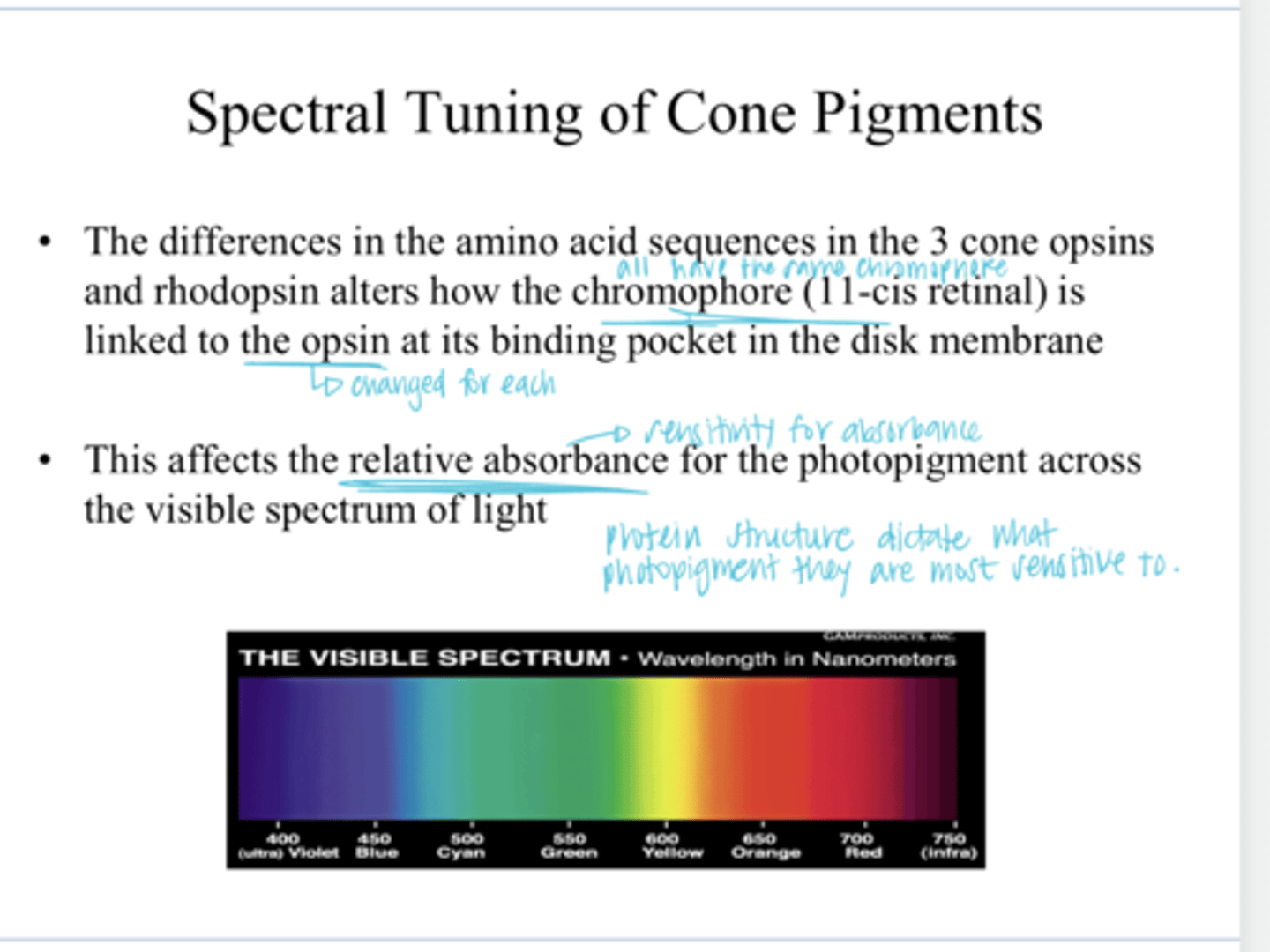
the relative absorbance (sensitivity) for a specific photopigment across the visible spectrum of light
How the chromophore (11-cis retinaAL) is linked to the opsin binding pocket in the disc membrane affects what?
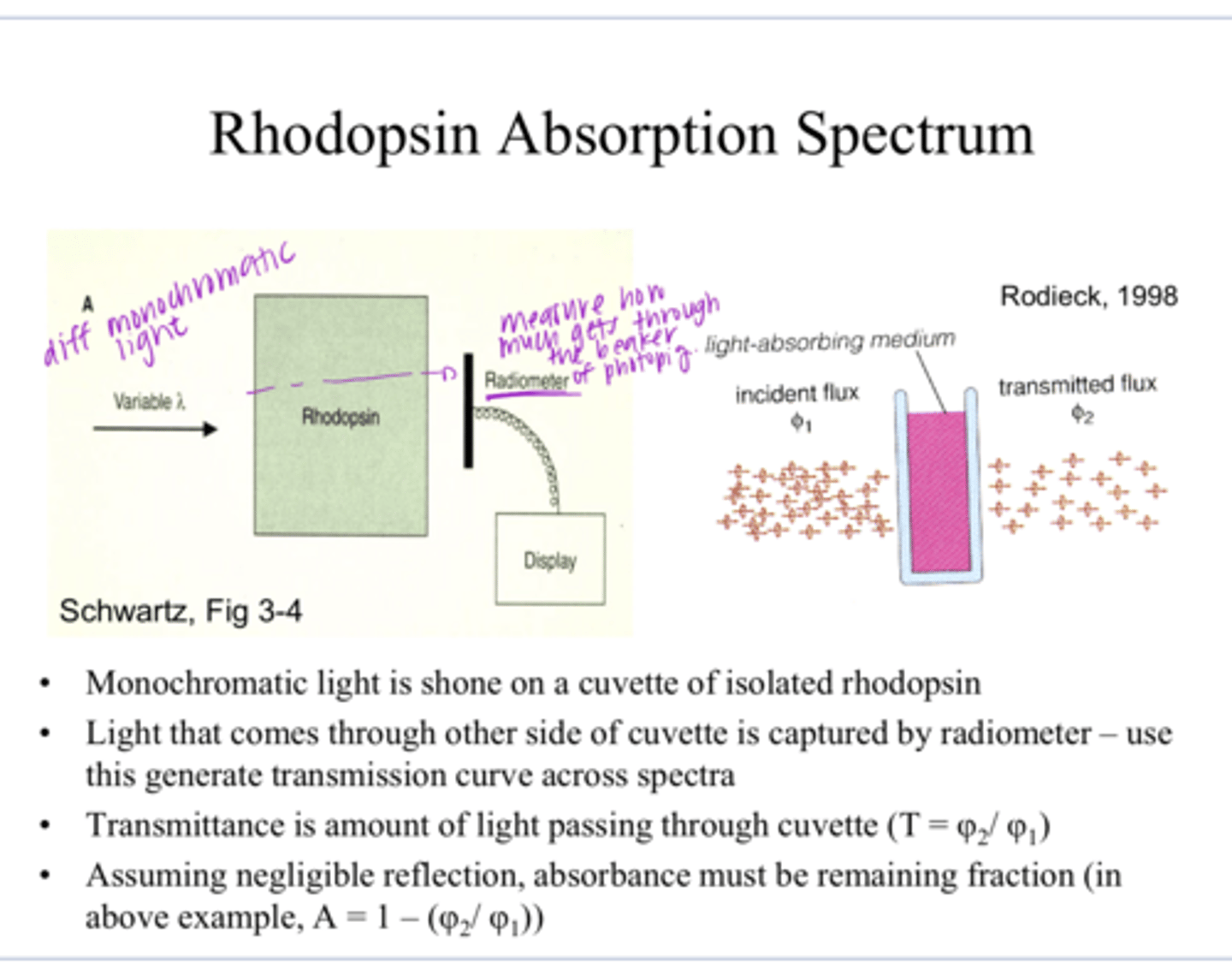
1) Monochromatic light is shone on a cuvette of isolated rhodopsin
2) Light that comes through the other side of the cuvette is captured by a radiometer -- use this to generate a transmission curve across a specta of light
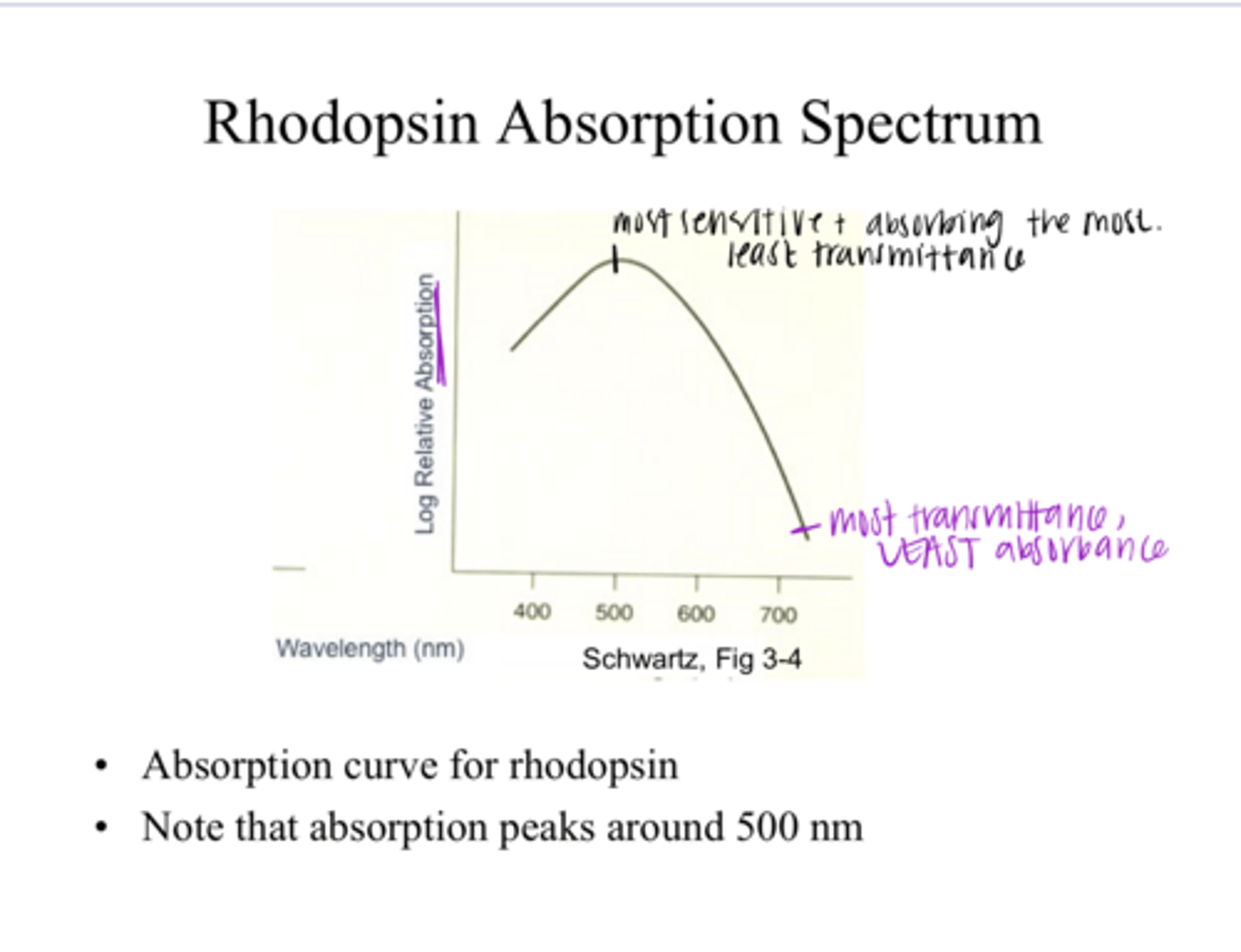
How is the rhodopsin absorption spectrum measured?
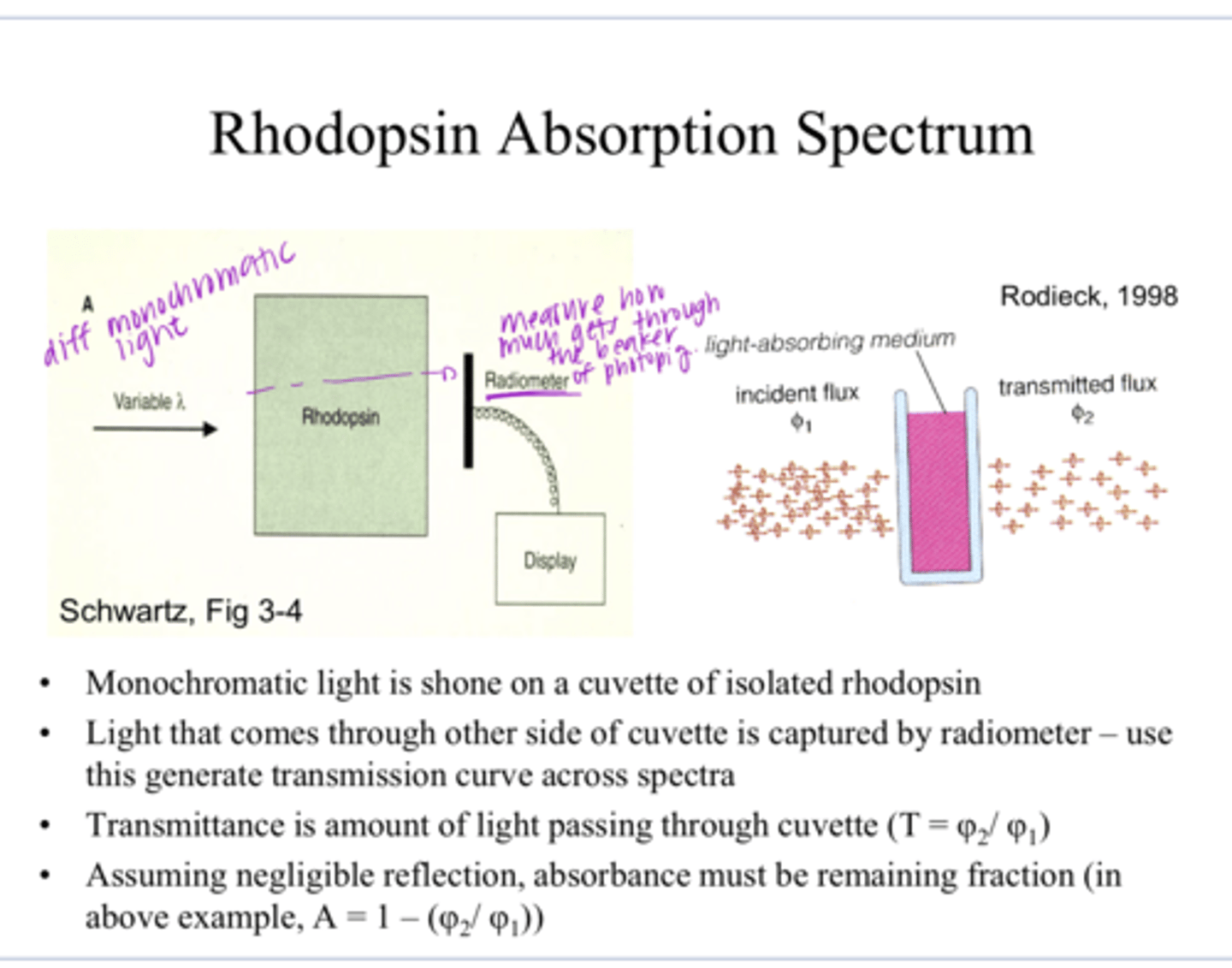
the amount of light that is allowed to pass through
What is the transmittance of a pigment?
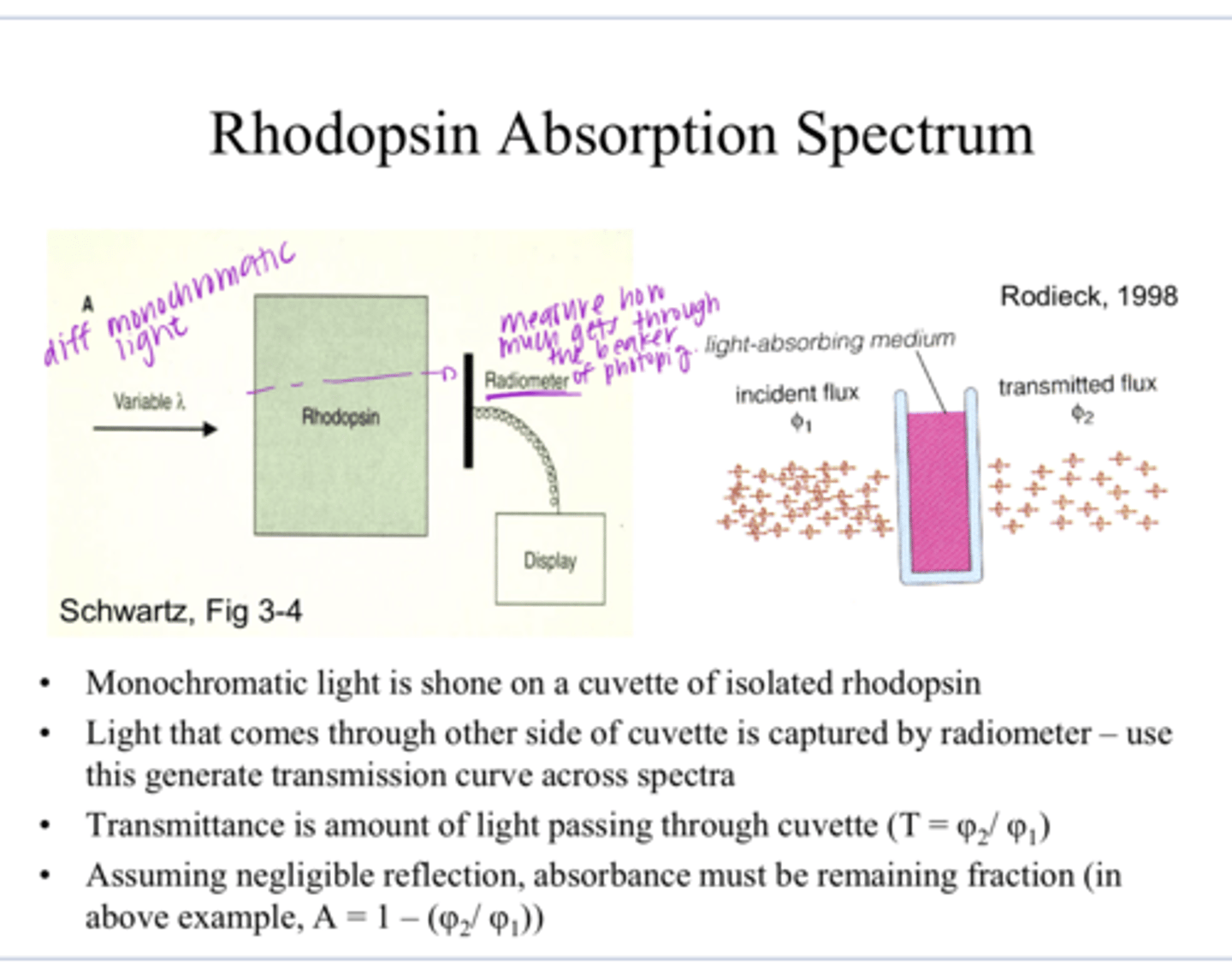
Absorbance is all the light that is not transmitted through
A = 1 - T
What is the absorbance of a pigment?
Rhodopsin Absorption Spectrum Example Pic
Rhodopsin Absorption Spectrum Example Pic
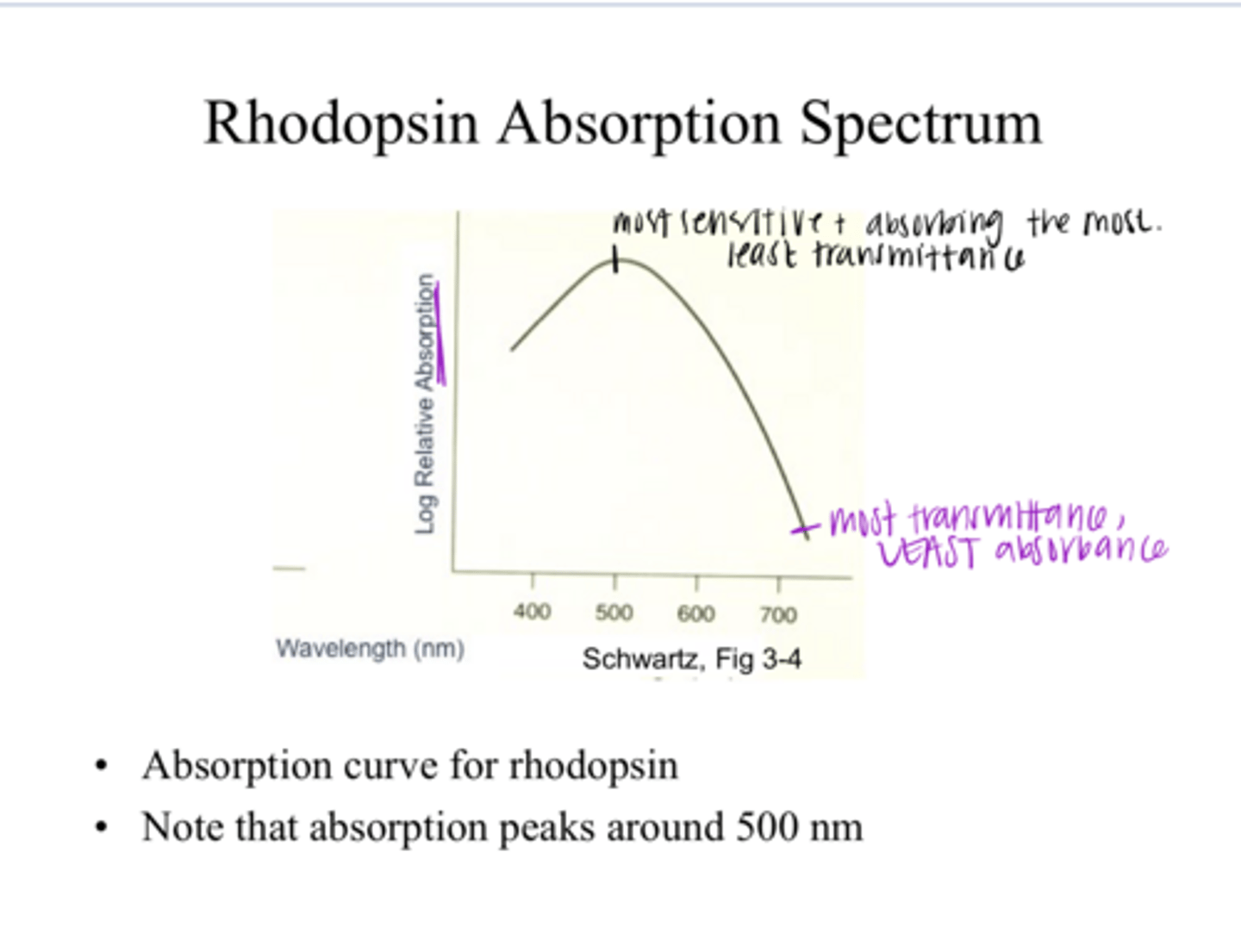
500nm
What is the peak absorption in this rhodopsin absorption spectrum? SEE PIC
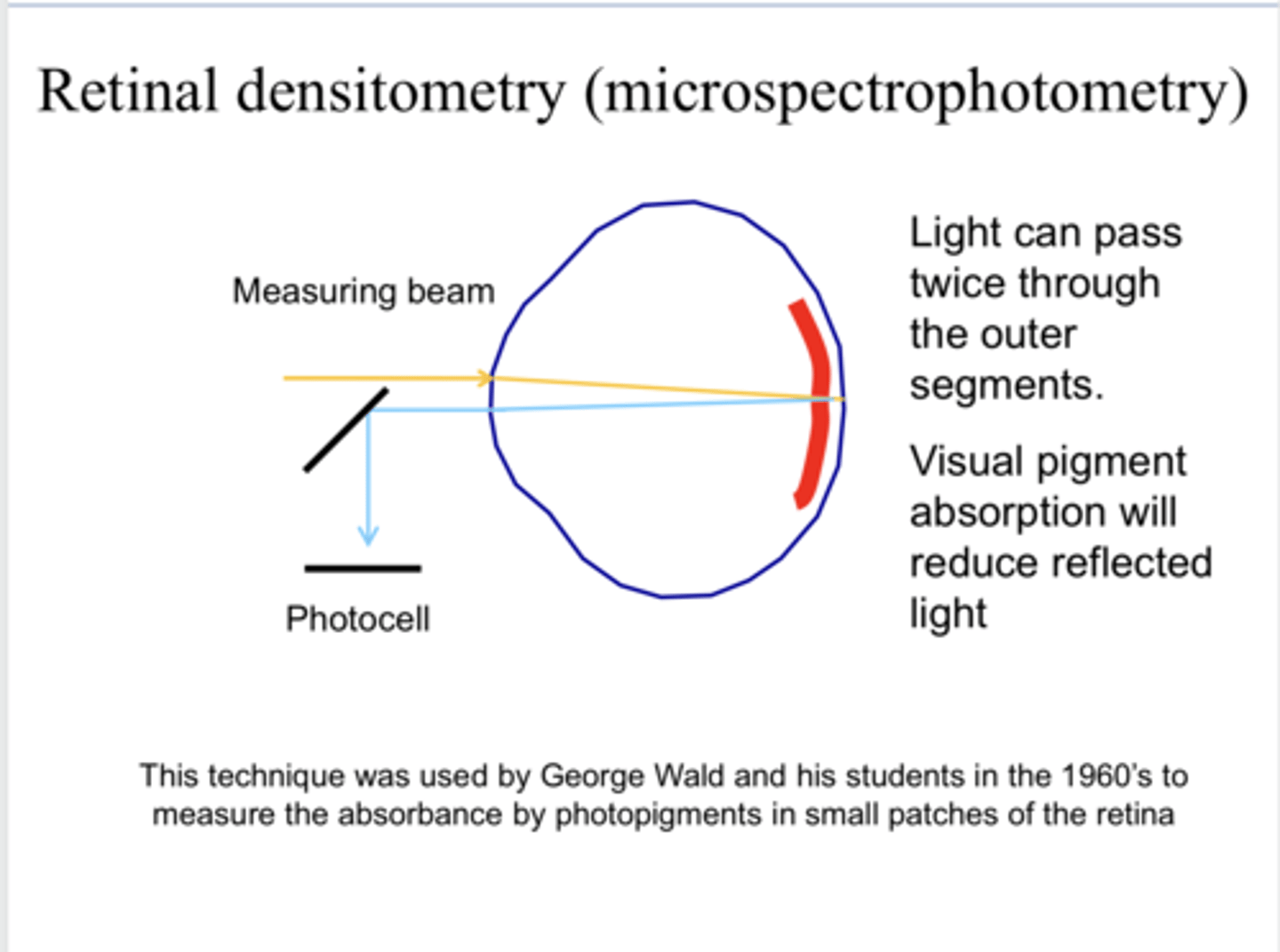
1) Flash in very small amount of light into the eye
2) Measure about of light that bounced back out of the eye (reflected)
LESS bounce back = MORE absorbance
How is retinal densitometry performed?
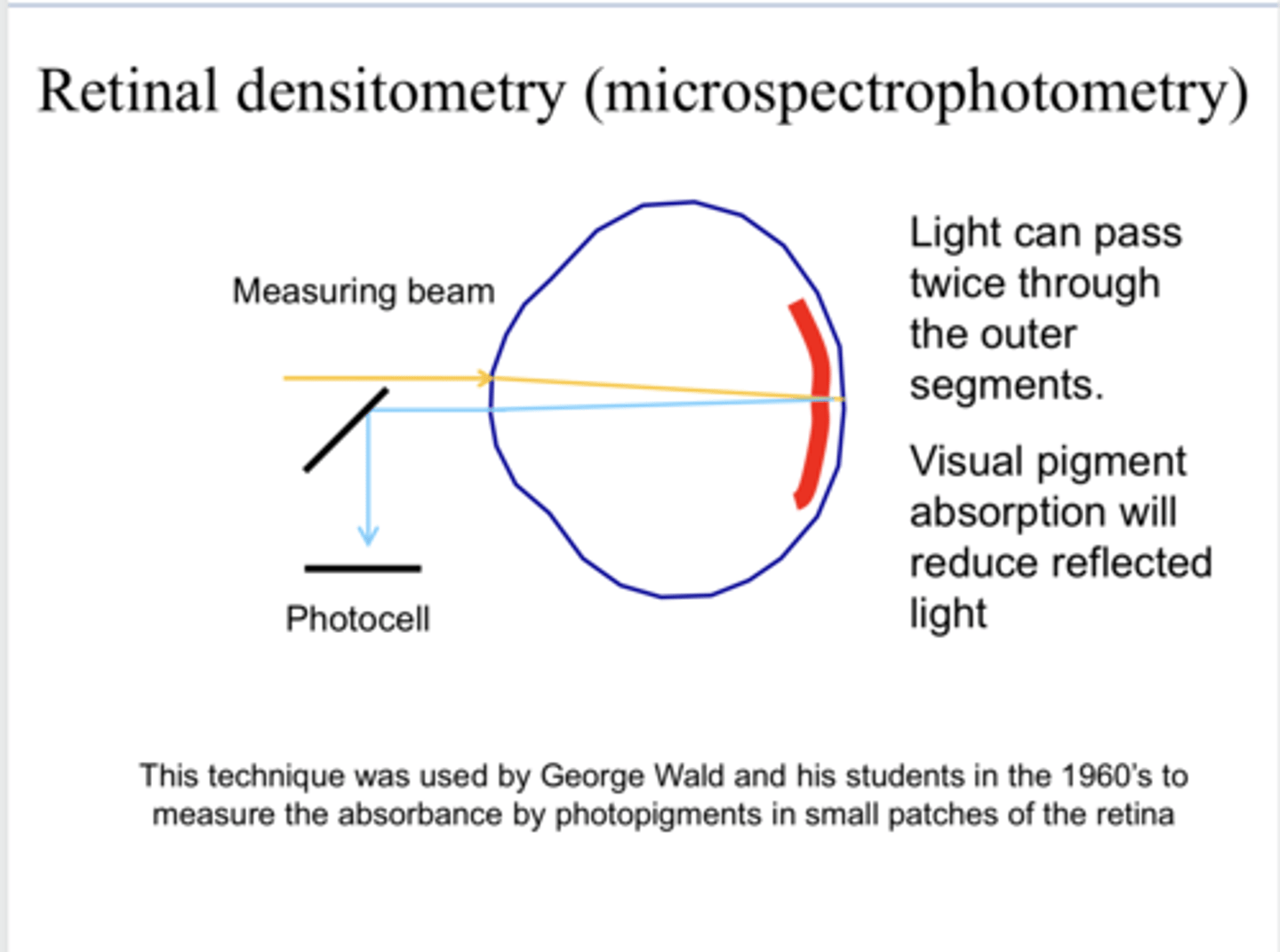
2x through the outer segment of the photoreceptors
With retinal densitometry, how many times can the light incident on the retina pass through the outer segment of the photoreceptors before leaving the eye via reflection?
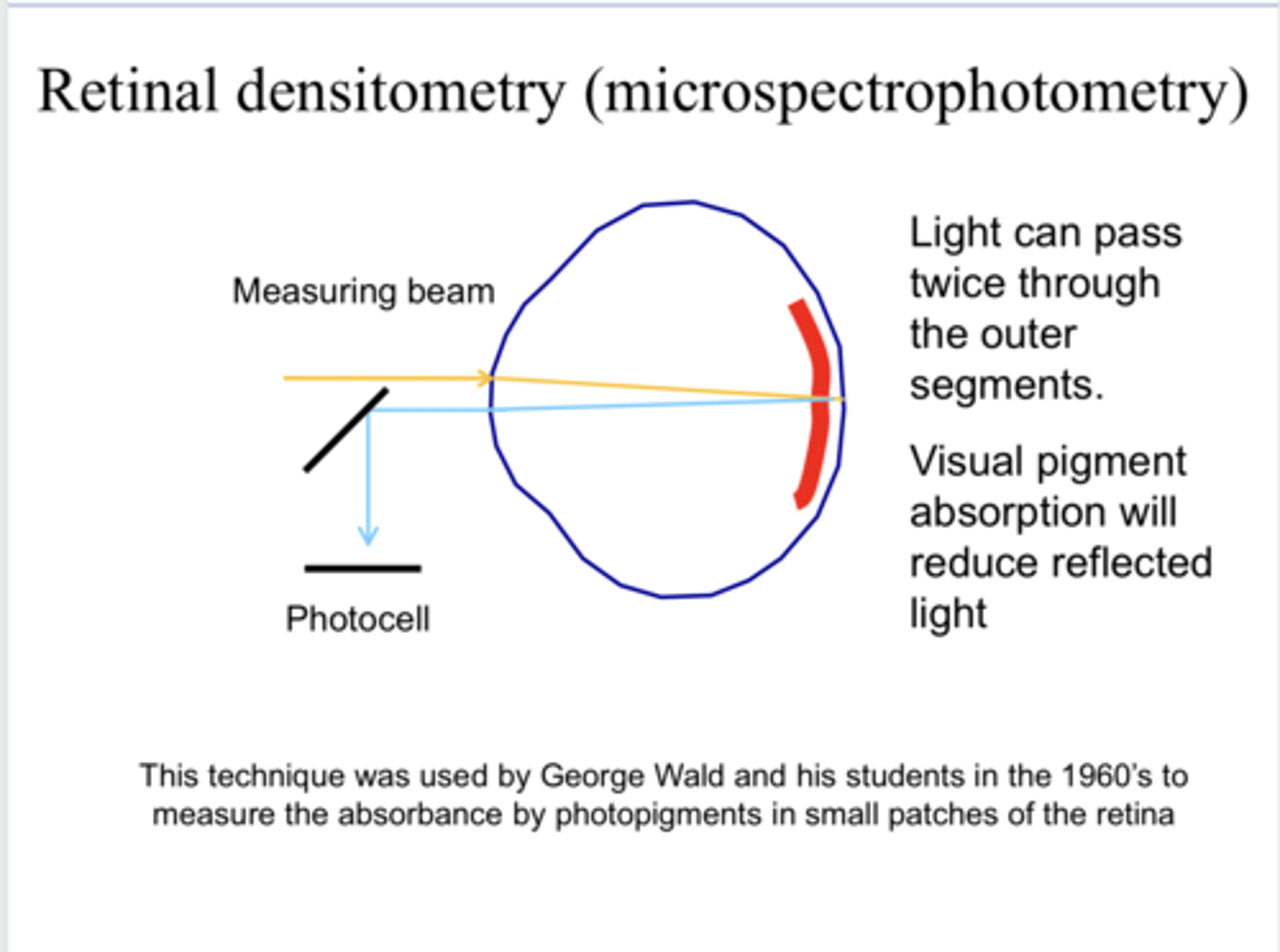
reduce
With retinal densitometry, visual pigment absorption will _____ reflected light