Scarcity, Energy Security and Climate Change
1/17
Earn XP
Description and Tags
week 8
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
what is scarcity?
situation which something is not easy to get(short supply)
what is energy?
power derived from the utilization of physical or chemical resources(oxford dictionary)
the ability to do work(physics term)
list 5 mains forms of energy.
-heat energy
chemical
electromagnetic
nuclear
mechanical
explain heat energy
-internal motions of the atom, because moving particle produce heat
-can be produced by friction
-can causes changes in temperature and phase of any form of matter
explain chemical energy
-energy that stored in the bond of atoms & molecules
-when bonds are broken, energy released
explain electromagnetic energy
-power lines carry this into your home in the form of electricity
explain nuclear energy
-the nucleus of an atom is the source of nuclear energy
explain mechanical energy
-the energy acquired, when work is done to an object
-when we kick a football, we give mechanical energy to the football to make it move
Energy Security
energy security is an uninterrupted availability of energy sources at an affordable price (defines by IEA)
explain 4As of energy security
-AVAILABILITY
-ACCESSIBILITY
-AFFORDABILITY
-ACCEPTABILITY
List all of the greenhouse gas (GHG) based on Kyoto Protocol 1992
-carbon dioxide
-methane
-nitrous oxide
-hydroflourocarbons
-perfluorocarbons
-sulfur hexafluoride
Sources of GHG?
CO2 - fossil fuel use in transportation, building heating and cooling, manufacturing industries, open burning, bushfire
CH4 - deforestation reduces offset agriculture, natural gas distribution, waste landfills, wetlands
N 2 O - fertilizer, biomass gasification, transportation
Halo -C, water vapors, CO, NO 2 - human activities
What is the effect of GHG?
-increment of 1.19 celcius global temperature
-united nations paris agreement set a target of limiting warming to 1.5 celcius
-united nations global climate change conference set a target of zero carbon emission by 2050
Hoe does climate change affect human health?
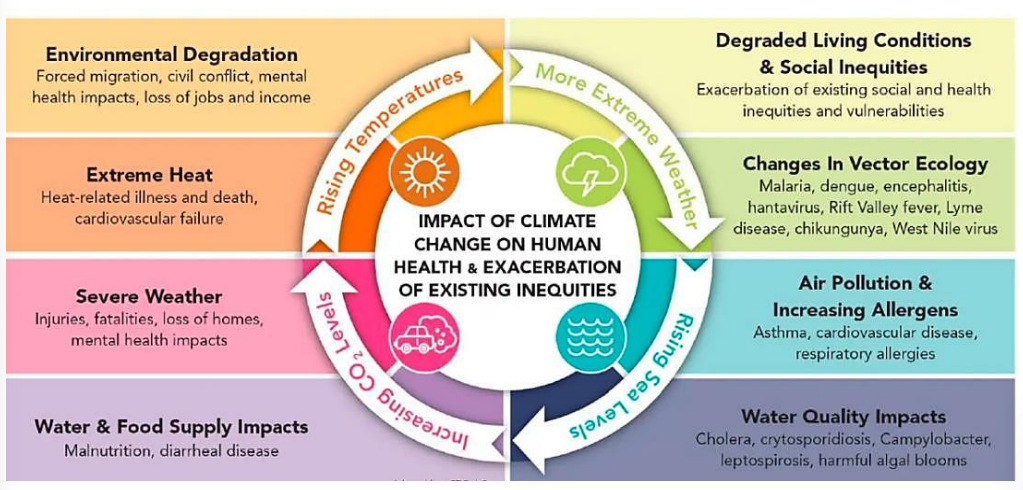
Kyoto Protocol
-aimed to reduce the emission of gasses that contribute to global warming
-this protocol operationalizes the united nations framework convention on climate change by comitting industrialed countries and economies in transition to limit and reduce greenhouse gases GHG emissions in accordance with agreed individual targets
what is Carbon footprints?
-footprint means area of interest
-Carbon footprint is defined as annual emission of carbon dioxide due to personal, community ,organization ,event or product that is used in daily life
-unit , gCO2 or kgCO2 or tCO2
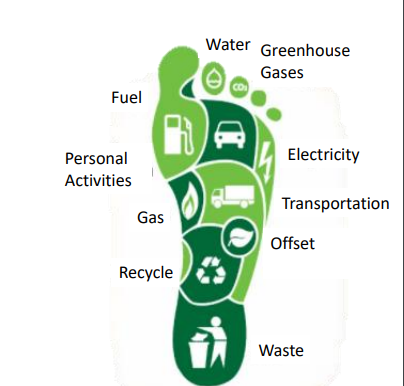
1 kgCO2 is emitted when?

Calculation of carbon footprint for electrical appliances
Power of 1 electrical appliance (kW) x efficiency (decimal point) x duration of usage in 1 day (hour) x 39 g CO2 / 50 kWh
