Immunology Lecture 14 secondary lymphoid tissues
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
67 Terms
What does the secondary lymphoid tissue include?
Spleen, Lymph nodes, MALT, tonsils and adenoids, peyers patch
What cells are involved in adaptive activation?
- dendritic cells show antigen to T cells
- follicular dendritic cells show antigen to B cells
What does the primary lymphoid tissue have?
bone marrow and thymus
Areas where lymphocytes encounter antigens, become activated, undergo clonal expansion, and differentiate into effector cells
secondary lymphoid organs
how are the lymph nodes, spleen and the MALT connected to each other?
via the blood and lymphatic circulatory systems
stromal cells
Cells that provide structure or support for parenchymal cells
(are packed with lymphocytes, macrophages, and dendritic cells)
True or False:
the lymph node has a capsule around it
True (are encapsulated tissues)
The_____ provides ideal microenvironments for encounters between antigens and lymphocytes
lymph node
Entering the lymph node is called what? What is it called when existing?
afferent lymphatics is entering, efferent lymphatics is existing
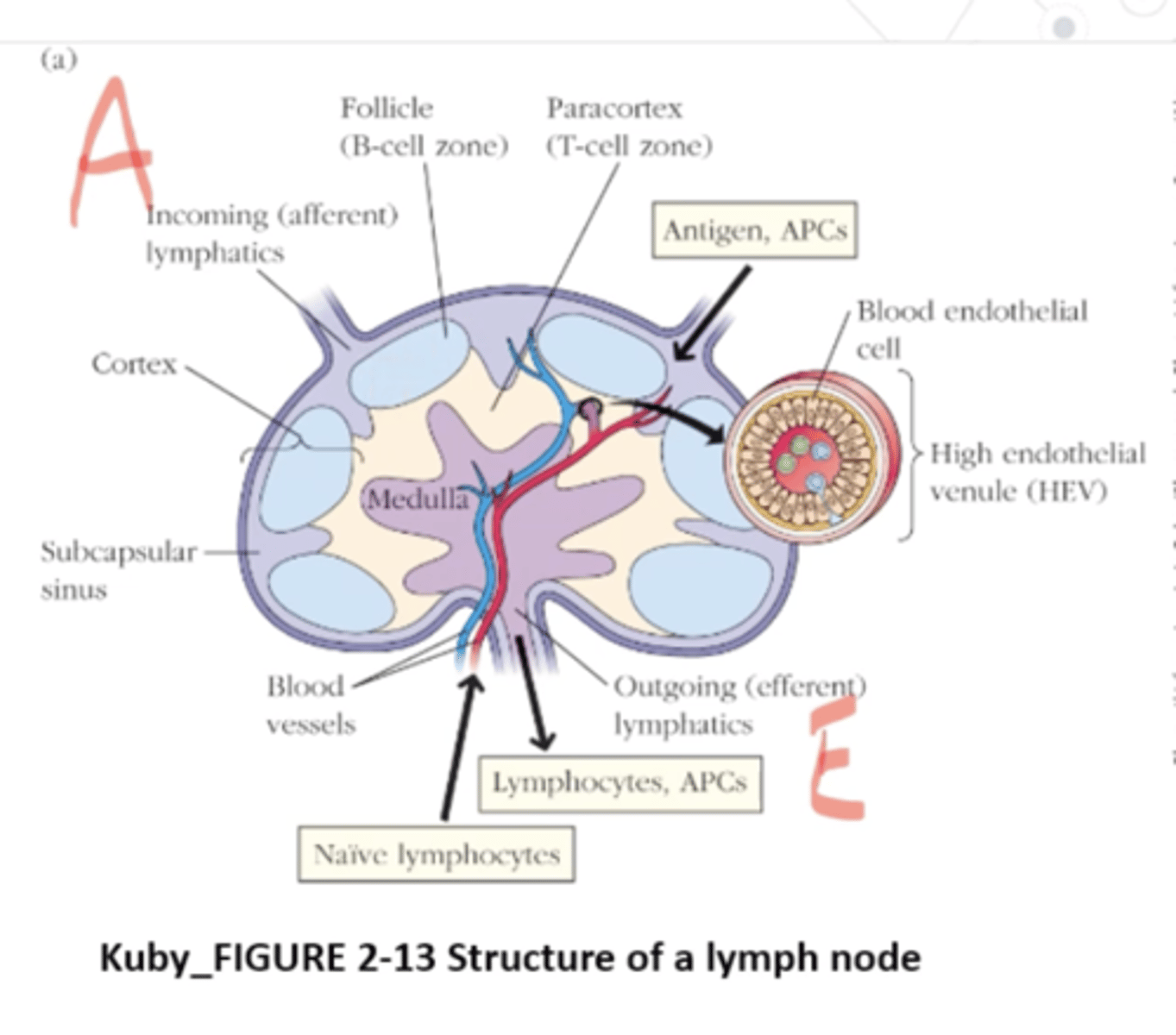
What happens when naive T cells enter the lymph node?
they browse MHC-peptide Ag complexes on surfaces of APCs in the paracortex, the lymph node's T-cell zone
What do the APCs do after the naive T cell enters the lymph node?
APCs position themselves on a network of fibers that arise from stromal cells call fibroblastic reticular cells
What does the fibroblastic reticular cell conduit system (FRRCC) do?
guides the T cell movements via associated adhesion molecules and chemokines
Which of the following is the main site of activation of the adaptive immune response?
A. secondary lymphoid tissue
B. mucosal surfaces
C. Thymus
D. blood
A
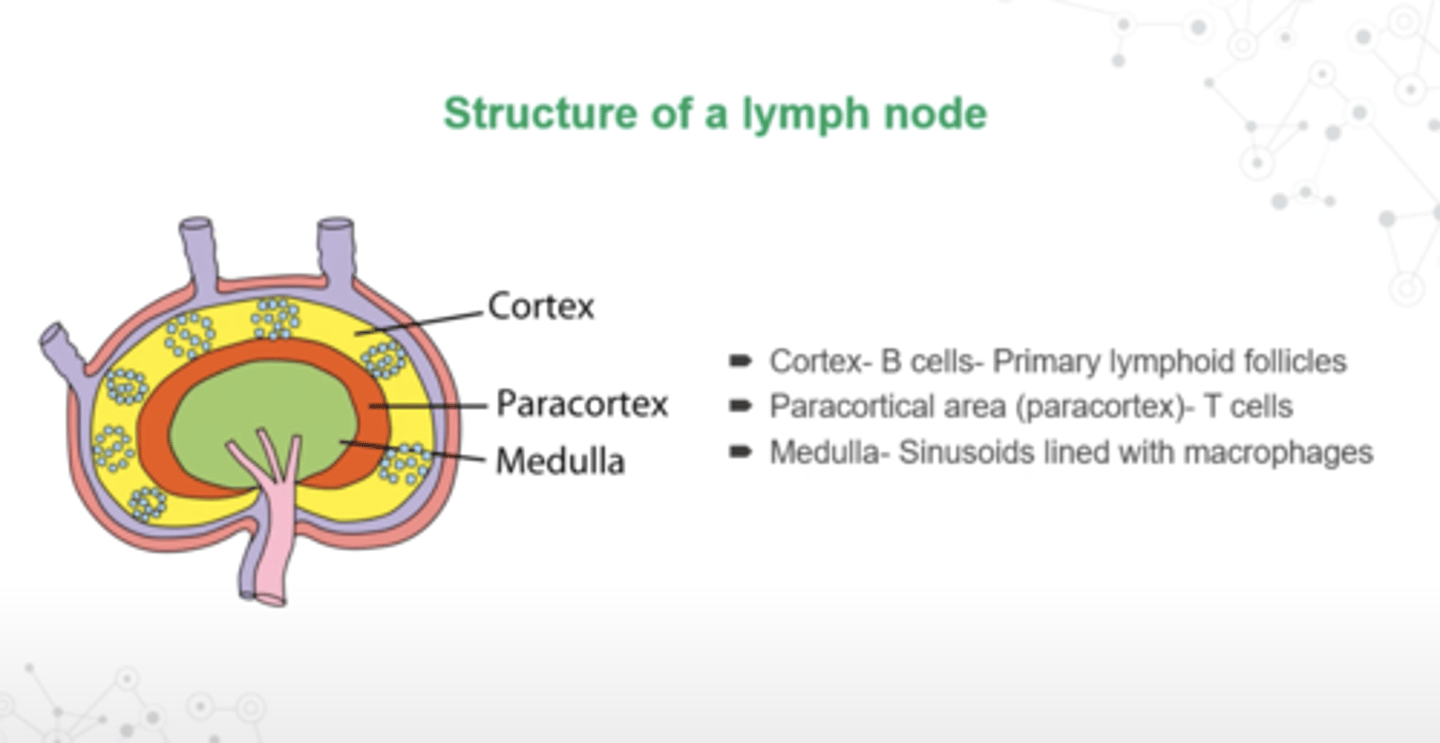
What is the structure of a lymphnode?
- Cortex: B cells- primary lymphoid follicles
- Paracortical area (paracortex): T cells
- Medulla: sinusoids lined with macrophages
True or False:
Stromal cells will express adhesion molecules that are different depending on the area of the lymph node that they find themselves
True
True or False:
stromal cells are going to have different molecules that are either going to be expressed with interactions of either B cells or T cells
True
Lymphocytes and other cells of the immune response can enter lymph node either via _________ or via the __________
1. lymphatics
2. blood circulation
What is the outside of the lymph node surrounded by?
collagenous capsule
What is Trabeculae penetrate?
the inside of the lymph node from this capsule
underlying capsule is the
subcapsular sinus
The inner part of the lymph node is the
medulla
What is medullary sinus?
where cells and fluid from the medulla can drain into
What happens when lymphocytes become activated within the lymph node?
they organize themselves into follicles
What do B-lymphocytes produce?
follicles within the outer part of the lymph node the cortex
The ______ constitutes the B-cell zone of the lymph node
cortex
Within the cortex, the B cells will form in structures called
germinal centers that develop in response to antigenic stimulation
After cells are activated, where can they exit from?
they exit the lymph node by using the efferent lymphatic vessel
Which is the largest lymphoid organ?
spleen
What is the function of the spleen?
- Site of lymphocyte proliferation and immune surveillance and response
- Cleanses blood of aged blood cells and platelets; macrophages remove debris
How is the spleen nourished??
by splenic artery and vein, which enter and exit at the hilum
True or False:
The spleen filters the blood
True
Damages RBCs get caught and disposed of by the ______
spleen
This organ filters out bacteria. People without this organ have increased susceptibility to infections. A site for reserves of blood, platelets and monocytes. What is this organ?
spleen
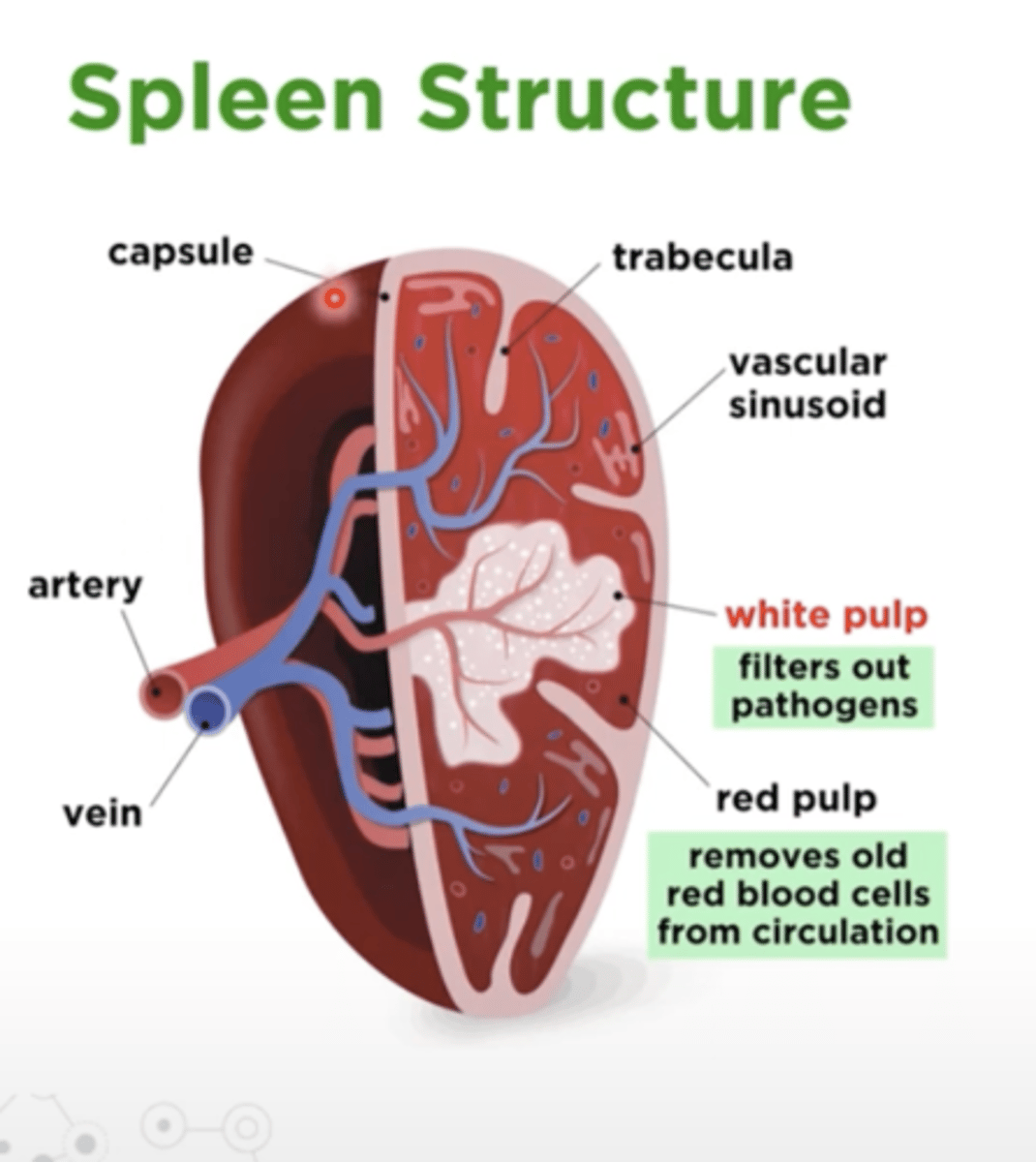
1. What does the white pulp in the spleen do?
2. What does the red pulp do?
1. filters out pathogens
2. removes old red blood cells from circulation
True or False:
Your ribs protects your spleen
False
True or False:
The spleen organizes the immune response against blood borne pathogens
True
What is the first line of defense against blood-borne pathogens?
the spleen
In the spleen, red blood cells are compartmentalized in the
red pulp
In the spleen, white blood cells are segregated in the
white pulp
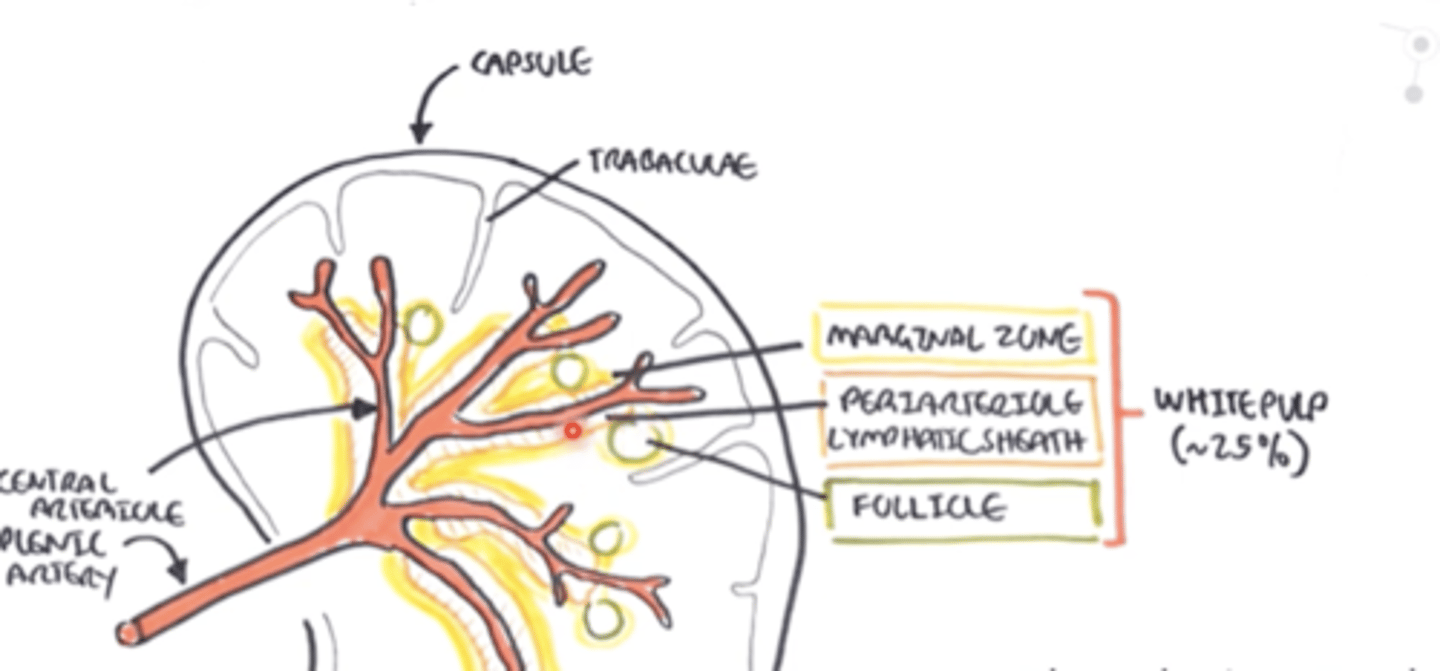
What borders the white pulp?
a specialized region of macrophages and B cells known as the marginal zone
periarteriolar lymphoid sheath (PALS) is in the
white pulp
What does the Trabecular artery feed into?
the white pulp
In the spleen, there's a central arteriole and a follicular arteriole, by which lymphocytes can enter the ________ from the blood circulation.
white pulp
What is another reason why the spleen is important?
for sequestration of platelets and maintenance of platelet level in the blood circulation
Trabecular artery goes through
the central arteriole and then branches out to the Follicular arteriole
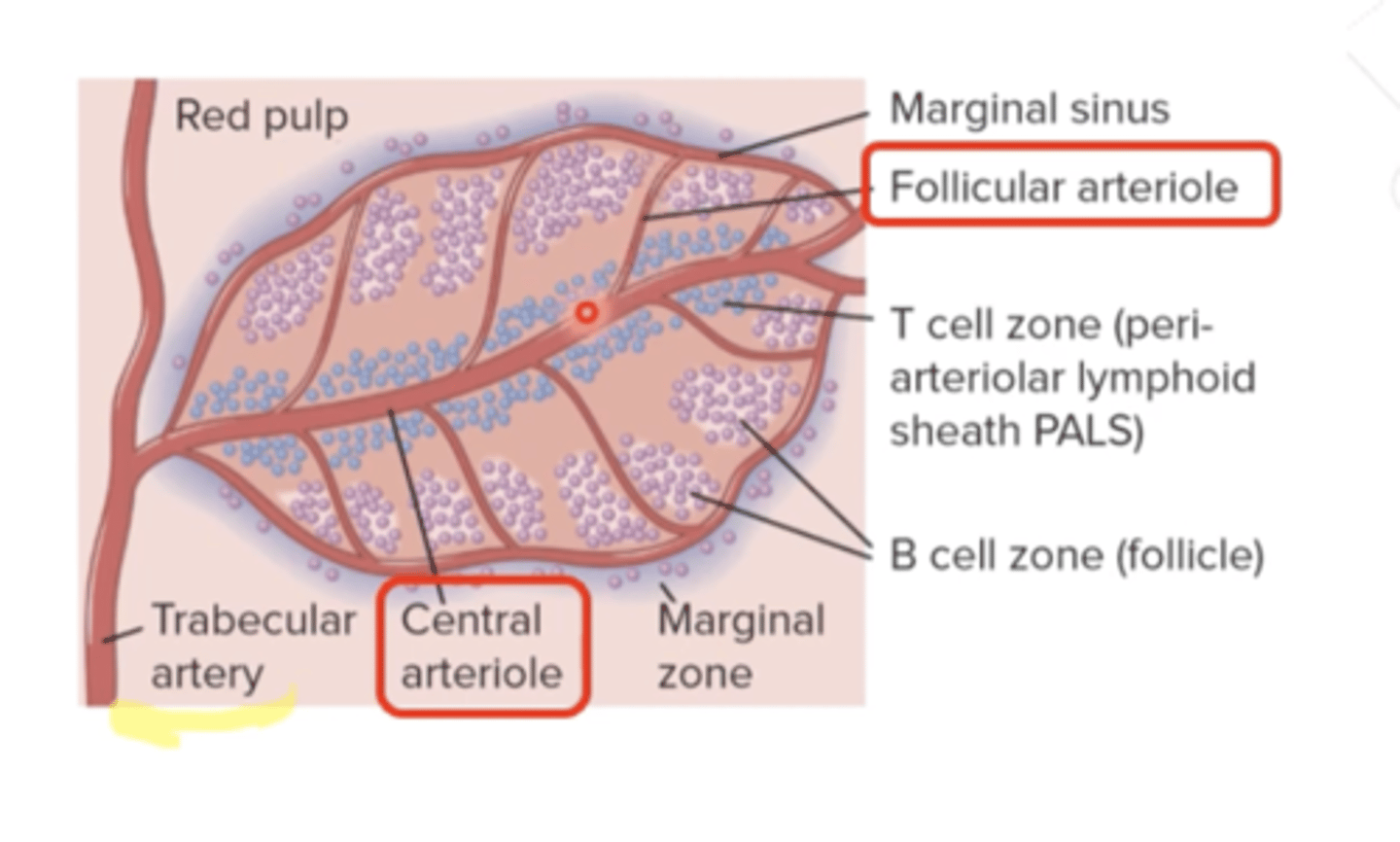
What are the central arteriole and the follicular arteriole surrounded by?
white pulp
What does the periateriole lymphatic sheath have?
T cells and macrophages
The splenic artery branches into arterioles and those into end-capillaries, which are open-ended. What does it mean by open-ended?
it allows for blood to spill out into the splenic tissue
In the white pulp, what is the T cell zone?
it's the periarteriolar lymphoid sheath or PALS
What is the outer area of the white pulp?
marginal zone
What do the B-cells do in the white pulp?
organize themselves into follicles (with germinal centers), just like the lymph node
The PALS region of the spleen is most heavily populated by_______
T cells
Venous sinuses
collect the blood and that blood goes into collecting veins
Between the arteries and the veins, there are the cords, what is there many of?
macropahges
The cords and the venous sinuses make-up the
red pulp (75% of spleen)
1. In the White pulp, DCs come from blood and present ___ to ____ at the lymphatic sheath.
2. The activated _____ go to the _______ and activate B cells
1. Ags to T cells
2. T cells go to the follicle
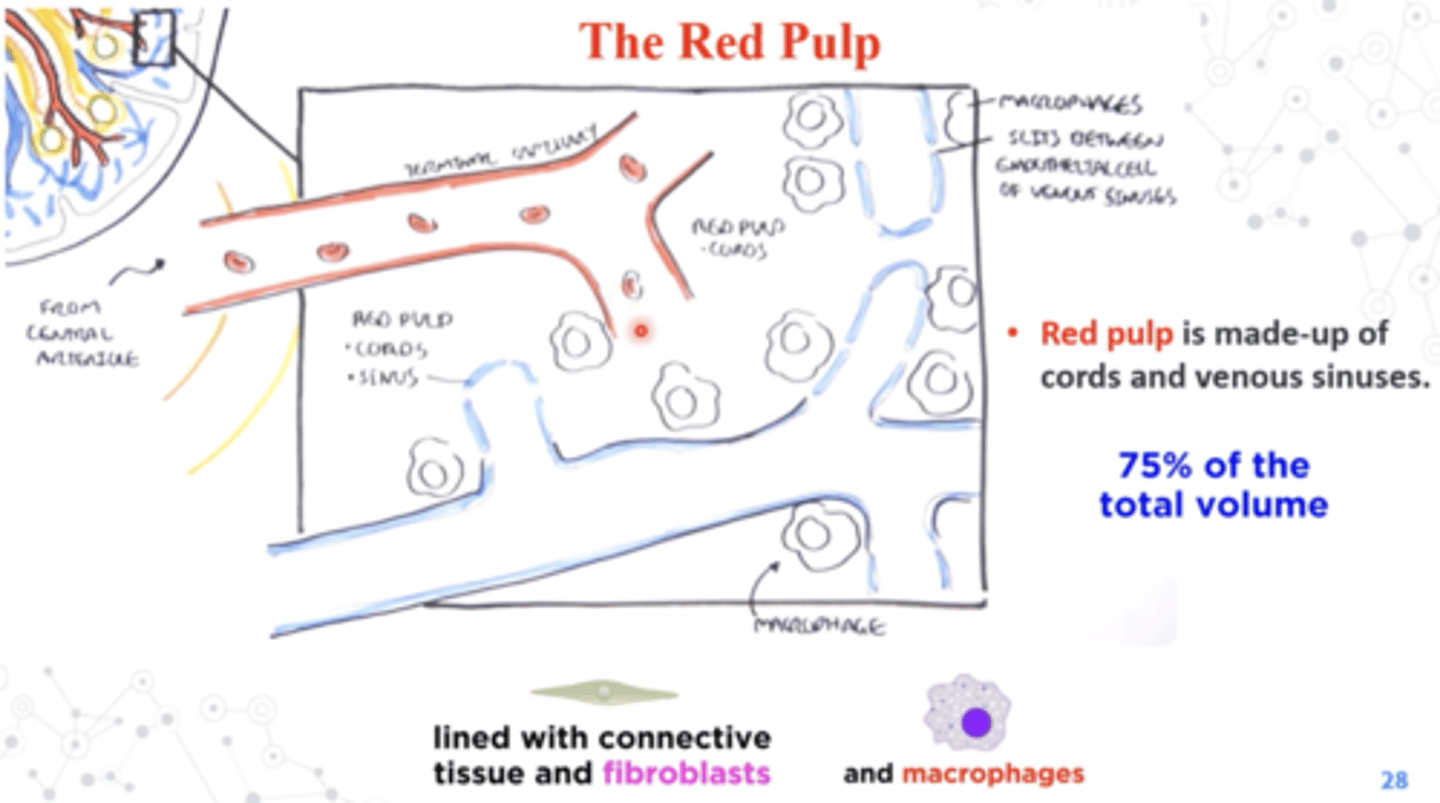
What happens when blood enters open circulation?
hint: this happens in the red pulp
Old and damaged RBC can be eaten by macrophages
In order to re-enter circulation a RBC....
hint: we're talking about red pulp
must be flexible enough to fit through the interendothelial slit
True or False:
Old and damaged RBCs are able to pass through the interendothelial slit
False, they get eaten by macrophages
Viruses and other blood-borne pathogens can also be captured by macrophages and be presented at the
white pulp
Name the Mucosa-Associated Lymphoid tissues (MALT)
- NALT (your nose)
- BALT (lungs)
- GALT (gut)
pharyngeal tonsils
in the throat
Palatine tonsils
on the palate
Lingual tonsils
on the back of the tongue
includes a network of follicles and lymphoid microenvironments associated with the intestines
GALT
Peyer's patch is located w
wall of the small intestine
What is peyer's patch associated with?
With M cells, which sample Ags in the gut and pass them to the underlying dendritic cells and macrophages