(5) Antigens & Immunogens, Complement Activation
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
68 Terms
molecule that initiates an immune response
immunogen
molecule that binds to the product/mediators of an immune response, such as antibodies or T cell receptors
**can be a protein, carbohydrate, lipid, or other similar macromolecule
antigen
Are all immunogens antigens?
yes
Are all antigens immunogens?
no
What are 4 examples of molecules that make good immunogens?
large proteins, large glycoproteins, large polysaccharides, large nucleic acids
Do phospholipids, glycolipids, lipids in general, small carbohydrates, small polypeptides, and amino acids make good or bad immunogens?
bad
True or false: The charge on a protein has an influence on that protein's immunogenicity.
false
True or false: The shape of a protein has an influence on that protein's immunogenicity.
false
True or false: The size of a protein has an influence on that protein's immunogenicity.
true
(size is directly proportional to immunogenicity)
The bigger the protein, the better (stronger) or worse (weaker) it is as an immunogen?
better
The smaller the protein, the better (stronger) or worse (weaker) it is as an immunogen?
worse
antigens that are too small to provoke an immune responses; attach to carrier molecules to become conjugated so that they can elicit a response
haptens
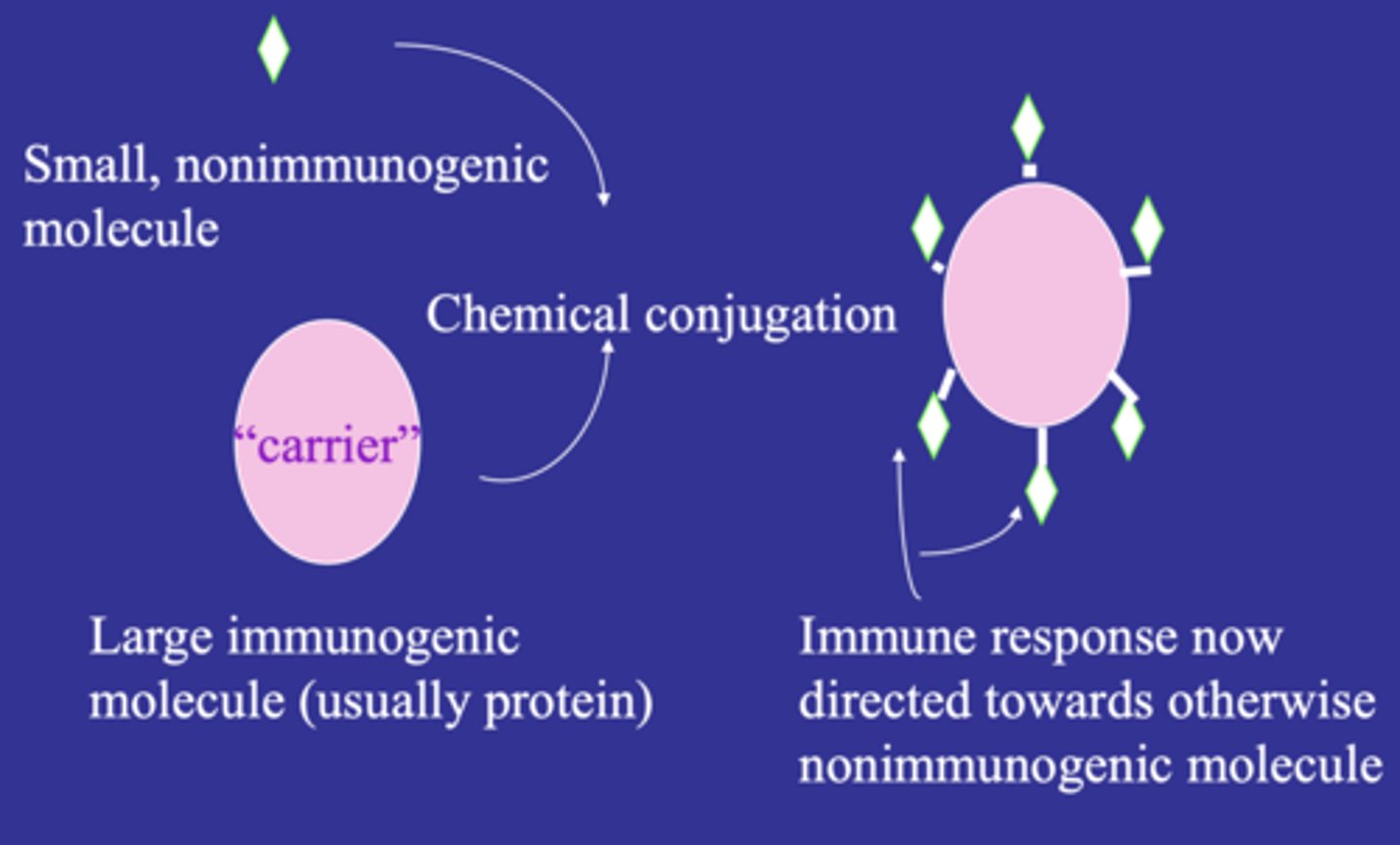
How can small, non-immunogenic molecules elicit an immune response?
conjugate with a large immunogenic molecule
antigenic determinant; certain region of an antigen molecule that binds to an antibody or TCR and stimulates an immune response
epitope
Epitopes are regions on the antigen that can bind to what two things?
antibody, TCR (via MHC)
True or false: An antigen can have multiple epitopes.
true
True or false: Epitopes are unique.
true
(think about it: antibodies have specificity for a certain epitope on an antigen - a certain epitope can't be recognized by all antibodies, only specific ones)
True or false: Most microorganisms have several antigens, which each can have multiple epitopes.
true
Immunogens are seen differently by B and T cells. What quality of an epitope do B cells recognize?
structure
(antibodies can't interact with it enough to recognize its full sequence - just binds to general structure)
Immunogens are seen differently by B and T cells. What quality of an epitope do T cells recognize?
linear sequence
(since antigen is chopped up by APCs and presented to T cells)
True or false: The complexity of a protein has an influence on that protein's immunogenicity.
true
(complexity is directly proportional to immunogenicity)
The more complex the protein, the better (stronger) or worse (weaker) it is as an immunogen?
better
The less complex the protein, the better (stronger) or worse (weaker) it is as an immunogen?
worse
In regards to epitopes, what classifies a molecule as a hapten? Why?
only one epitope, not complex enough to be immunogenic
(complexity is directly proportional to immunogenicity, and if an antigen only has one epitope, that's not very complex, so it is non-immunogenic, which is a hapten)
example of an immunogenic antigen with many identical epitopes
carbohydrate polymers
example of an immunogenic antigen with many different epitopes
(large) protein
Which 3 of the following are the strongest immunogens based on complexity?
A. amino acids
B. carbohydrates
C. lipids
D. complex proteins
E. haptens
F. simple peptides
G. steroids
B, D, F
Which 2 of the following are the weakest immunogens based on complexity?
A. amino acids
B. carbohydrates
C. lipids
D. complex proteins
E. haptens
F. simple peptides
G. steroids
A, E
Which has higher immunogenicity: lipids or steroids?
steroids
(more complex structure)
How does genetics play a role in determining immunogenicity?
some people are more responsive to an antigen than others
How is foreignness an important determinant of immunogenicity?
stronger immunogen is something that the body doesn't encounter regularly
How does persistence of an antigen determine immunogenicity?
if it is present for an abnormally long time, this gets the attention of the immune system
How does age determine immunogenicity?
immune system weakens with age, so older = less immunogenicity
How does nutritional status determine immunogenicity?
malnutrition weakens immune system = less immunogenicity
How does stress determine immunogenicity?
weakens immune system = less immunogenicity
How does overall health determine immunogenicity?
different health factors decrease immune response
Which of the following factors is most important in determining the immunogenicity of an antigen?
A. charge
B. shape
C. size
C
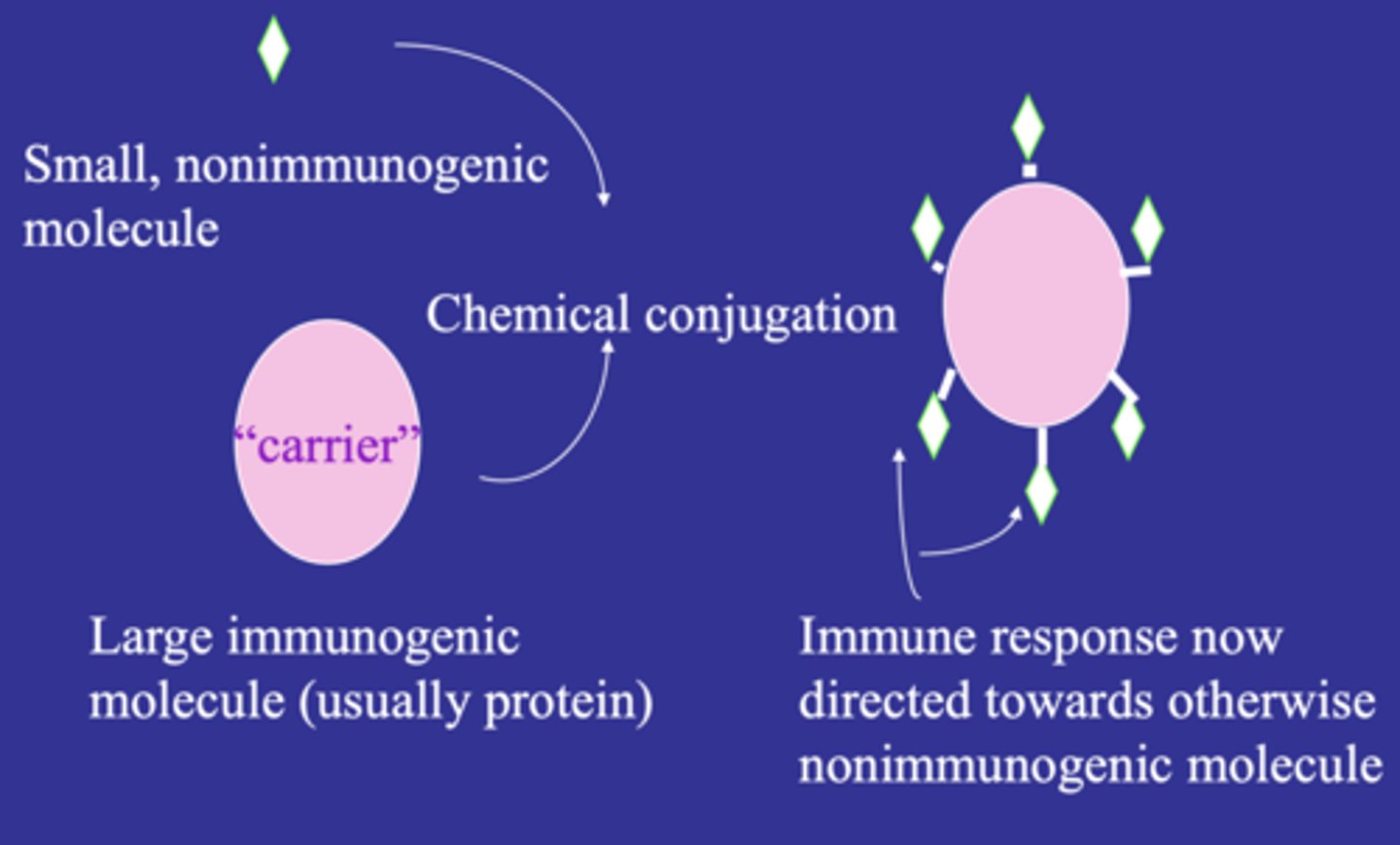
binding of an antibody to an epitope corresponding to an antigen that is different from the one the antibody was raised against
cross reactivity
close resemblance between foreign antigen and self antigen; exhibits immunological cross reactivity that may lead to autoimmune disorders
molecular mimicry
Many of the serum proteins that are a part of the complement cascade (10% of all serum proteins) are in what form? How are they activated?
inactive zymogens, cleaved into smaller molecules
Where are inactive complement proteins found?
blood
Where are complement proteins made?
liver
(also monocytes/macrophages)
refers to smaller subunits cleaved from unstable complement proteins that have biological activity (acts as a chemokine)
a
refers to larger subunits cleaved from unstable complement proteins that bind to membranes
b
Are opsonins examples of a or b subunits?
**prepare molecule for phagocytosis
b
Are cytokines examples of a or b subunits?
**lure in other leukocytes for the immune response
a
antibody or other substance that binds to foreign microorganisms or cells, making them more susceptible to phagocytosis
opsonin
enhancement of phagocytosis by coating an antigen with antibodies
tagging of particles and microorganisms for removal by immune system cells that have complement receptors
opsonization
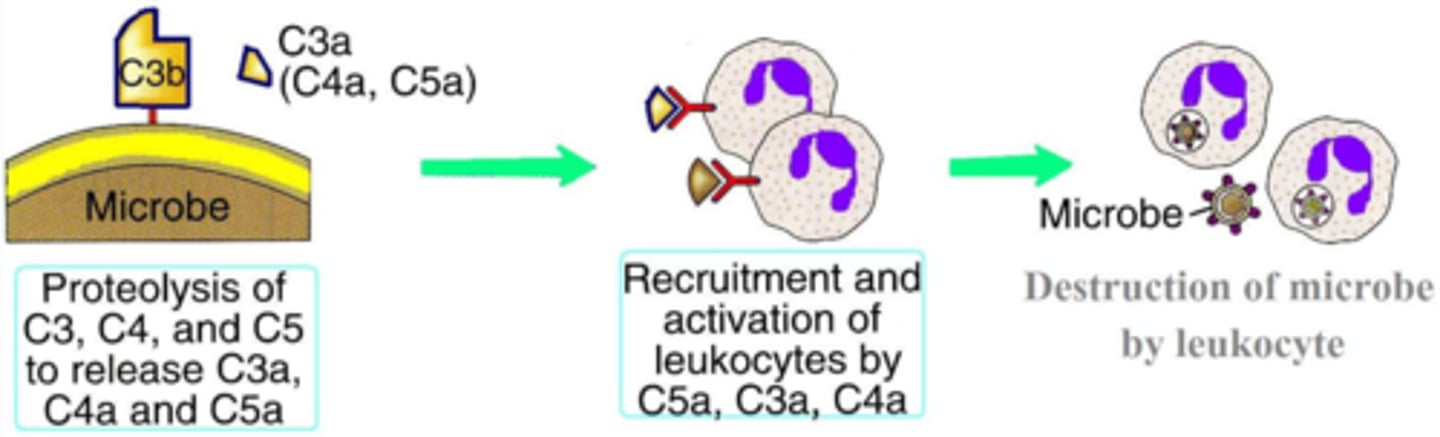
What does the complement cascade do to immune complexes? (Ag-Ab linked complexes)
removes from blood by tagging with complement b fragments
In the complement cascade, what is the protein C3 cleaved into?
C3a, C3b
When C3 is cleaved into C3a and C3b, which subunit binds microbes and antibody/antigen complexes? (acts as a strong opsonin)
C3b
When C3 is cleaved into C3a and C3b, which subunit acts as a chemoattractant?
C3a
Both C3b and C4b bind microbes and antibody/antigen complexes. Which one is stronger?
C3b
C3b receptor present on antibodies to bind to C3b (which has attached to microbes)
CR1
In addition to opsonization and phagocytosis, the complement cascade recruits and activates phagocytic and inflammatory cells to the site of complement activation. For example, it plays a role in the activation of what cells in order to promote inflammation?
mast cells
(promotes inflammation by releasing histamine)
complement subunits that directly stimulate mast cell release of histamine (general name + specific proteins)
anaphylatoxins; C5a, C3a, C4a
What is the strongest anaphylatoxin out of C3a, C5a, and C4a?
C5a
(C5a > C3a > C4a)
Which of the complement subunits functions as the strongest chemoattractant and activator of leukocytes?
C5a
(strongest anaphylatoxin; also C3a and C4a)
Which three complement subunits play a role in mast cell activation, chemoattraction, and general activation of leukocytes? (in order from strongest to weakest)
C5a, C3a, C4a
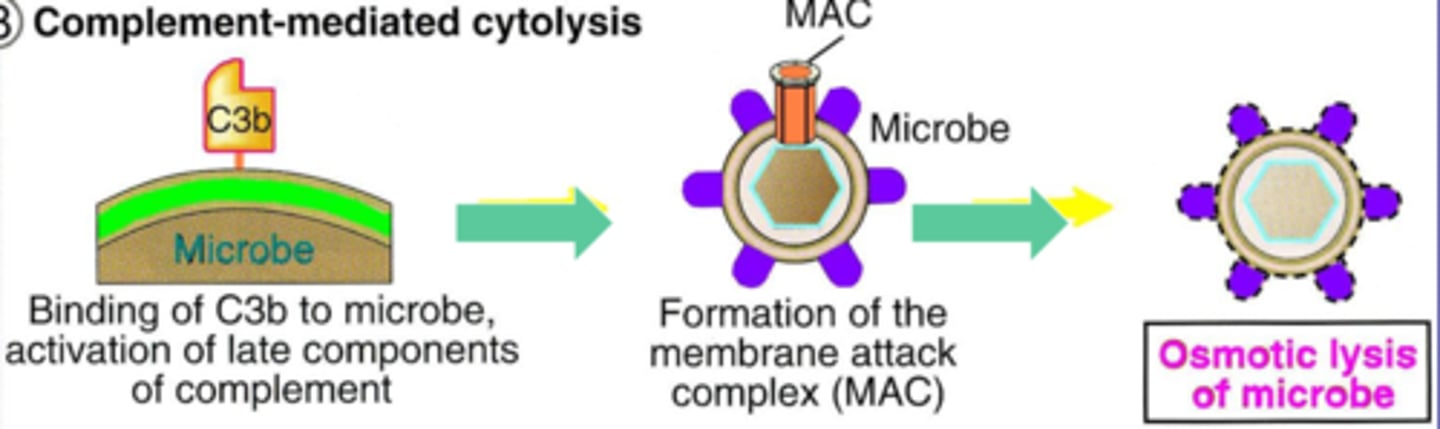
complex of terminal complement components that forms a pore in the membrane of the target cell, damaging the membrane and leading to cell lysis
membrane attack complex (MAC)
What is the ultimate goal of the complement system?
form MAC to lyse microbes
Which two complement subunits are responsible for regulation of vascular tone via vasodilation & edema?
C2a, C5a
The complement cascade functions to remove immune complexes. Specifically, what cells clear antigen-antibody complexes from plasma, especially if they are opsonized by C3b?
erythrocytes
The complement cascade functions to remove immune complexes. Specifically, what cells destroy them in the liver and spleen? (after erythrocytes have brought them there)
phagocytes
Which of the following is involved in opsonization?
A. C3b
B. MAC
C. C3a
D. C4a
A
Which of the following is NOT attributable to complement activity?
A. acting as opsonins
B. walling-off the inflamed area
C. serving as chemotaxins
D. stimulating the release of histamine
E. forming a membrane attack complex
B
A large, complex molecule that triggers a specific immune response against itself when it gains entry into the body is known as a(n)...
A. interferon
B. antigen
C. antibody
D. complement
E. opsonin
B
Opsonins...
A. enhance phagocytosis by linking the foreign cell to a phagocytic cell
B. include antibodies
C. include a certain complement protein
D. include antibodies and a certain complement protein
E. have all of the above characteristics
E