Genetics and Human Development Overview
1/94
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
95 Terms
Genetics
study of the mechanism of heredity
Mendel
Proposed basic principles of genetics in mid-1800s by studying inherited characteristics that were either all or none.
Human Genome Project
Determined human DNA sequence, which can aid in genetic research and genetic screening.
Diploid number
46 chromosomes in all cells except gametes.
Homologous chromosomes
23 pairs of chromosomes, including 1 pair of sex chromosomes that determine genetic sex (XX= female, XY=male).
Karyotype
Diploid chromosomal complement displayed in homologous pairs.
Genome
genetic (DNA) makeup; two sets of genetic instructions (maternal and paternal).
Gene pairs (alleles)
Genes that occur at the same locus (location) on homologous chromosomes.
Homozygous
Alleles are the same for a single trait (DNA sequence is same on both homologous chromosomes).
Heterozygous
Alleles are different for a single trait (DNA sequence is different on one homologous chromosome than other).
Dominance
One allele masks (suppresses) expression of its recessive partner.
Dominant allele
Is denoted by a capital letter.
Recessive allele
Is denoted by the same letter in lower case.
Dominant trait
Is expressed even if the other allele codes for a recessive trait (ex: JJ or Jj will result in double-jointed thumbs). Designated as J ; tight thumb ligaments is recessive trait DESIGNATED as j.
Recessive trait
Is expressed only if both alleles are recessive.
Fertilization
The process where a sperm cell from a male unites with an egg cell (oocyte) from a female to form a zygote.
Zygote possibilities
Independent assortment and random fertilization together result in ~72 trillion zygote possibilities.
Sperm Reaches the Egg
Millions of sperm are released during ejaculation, but only a few hundred reach the egg in the fallopian tube.
Sperm Penetration
The sperm must break through the egg's protective outer layer (zona pellucida).
Fusion of Sperm & Egg
The sperm's nucleus fuses with the egg's nucleus, combining genetic material from both parents.
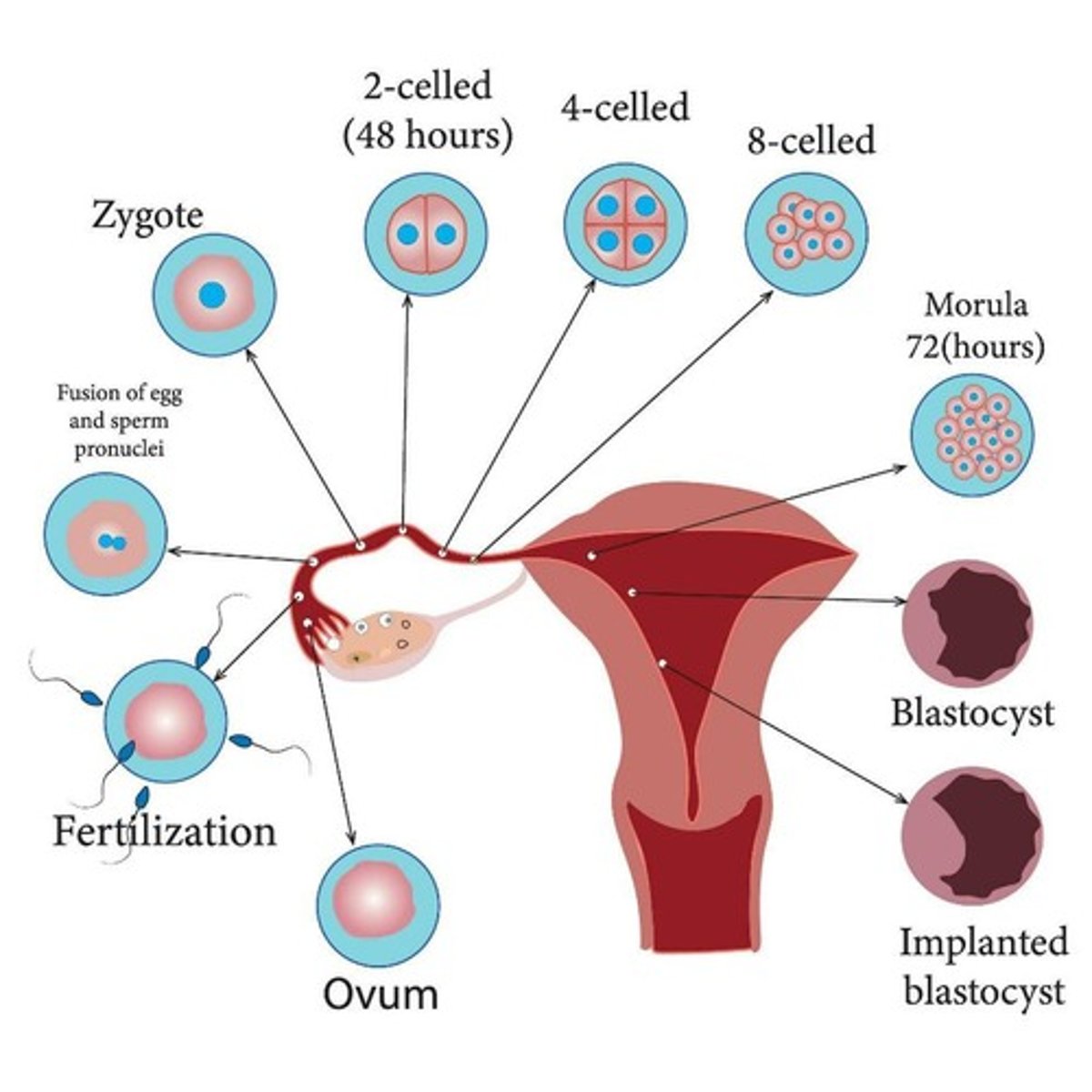
Formation of Zygote
The fertilized egg (now called a zygote) starts dividing into more cells and travels to the uterus.
Blastocyst
Around day 4 or 5, the embryo, which consists of ~100 cells, is now referred to as a _____________.
Implantation
Begins 6-7 days after ovulation when trophoblast cells adhere to the site with proper receptors and chemical signals.
Inflammatory-like response
Occurs in endometrium as uterine blood vessels become more permeable and leaky; inflammatory cells invade the area.
Erosion of endometrium
As endometrium is eroded, the blastocyst burrows into the lining, surrounded by a pool of leaked blood.
Endometrial cells
Cells that cover and seal off the implanted blastocyst.
Implantation failure
Occurs when the uterus becomes nonreceptive again. About two-thirds of all zygotes formed fail to implant by end of first week or spontaneously abort. An estimated 30% of implanted embryos later miscarry because of genetic defects of embryo, uterine malformation, or unknown problems.
Implantation completion
Usually completed by day 12 after ovulation (Day 26 of menstrual cycle).
Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG)
Hormone secreted by trophoblast cells and later chorion that prompts corpus luteum to continue secretion of progesterone and estrogen.
hCG levels
Rise until the end of month 2 and decline as the placenta begins to secrete progesterone and estrogen.
Placentation
Formation of placenta, a temporary organ that originates from both embryonic and maternal tissues.
Chorionic villi
Fingerlike projections developed from the chorion that are invaded by new blood vessels extending to the embryo.
Placenta functionality
Fully formed and functional by the end of month 3, providing nutritive, respiratory, excretory, and endocrine functions.
Embryonic placental barriers
Include membranes of chorionic villi and endothelium of embryonic capillaries.
Gastrulation
Occurs during week 3 when the embryonic disc transforms into a 3-layered embryo with ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm.
Organogenesis
Formation of body organs and systems set in motion by gastrulation.
Embryo length at week 8
Approximately 22 m (1 inch) long from crown (head) to rump (bottom) with all organ systems recognizable.
Heart development
The heart begins to beat by 3.5 weeks with two vessels forming the heart fused and bent into an 'S' shape.
Fetal period
Weeks 9-38, characterized by rapid growth of body structures established in the embryo.
Fetus growth
Grows to 360 mm (14 inches) and 3.2 kg (7 lbs +) during the fetal period.
Germinal Stage
Weeks 1-2, where the fertilized egg divides and implants in the uterus.
Embryonic Stage
Weeks 3-8, where major organs and structures form, and the baby starts looking like a tiny human.
Fetal Stage
Weeks 9-birth, where the baby grows larger, organs mature, and by birth, the baby is fully formed.
Genes
Segments of DNA that contain the 'recipe' or blueprints for the synthesis of proteins.
Gene expression
Can be controlled by other genes.
Punnett Square
A simple diagram used to predict the possible genetic outcomes of offspring based on the genes (alleles) inherited from parents.
Alleles
Each parent has two alleles for a trait, one from each of their parents, with one allele passed down to the child.
Punnett Square
Shows all possible combinations of alleles in offspring.
Eye Color Bb
Example of an eye having dominant (B = Brown) and recessive (b = Blue) trait. If both parents are Bb (carriers of blue eyes but have brown eyes).
Genotype
Genetic makeup of a person for a trait.
Phenotype
Physical expression of genotype.
Independent Assortment
Alleles of two different traits on different chromosomes are distributed independently.
Crossover
Process where homologous chromosomes exchange gene segments, increasing genetic diversity.
Random Fertilization
Single egg fertilized by a single sperm in a random manner.
Zygote
Result of fertilization, leading to massive amounts of possibilities due to independent assortment and random fertilization.
Genetic Variability
Unique combinations of genes in each gamete leading to diversity.
Multiple Genes
Most traits are controlled by multiple genes, not just one.
Dominant Alleles
Show their traits even if only one copy is present.
Recessive Alleles
Only show their traits if both copies are the same.
Albinism
Condition resulting from two recessive genes (aa) leading to lack of pigmentation.
Normal Pigmentation: Albinism Example
Result of having at least one dominant gene (AA or Aa). Normal pigmentation (but carries the albinism gene).
Recessive Inheritance
Some recessive genes can lead to normal traits, while dominant genes can cause disorders.
Achondroplasia
A type of dwarfism that is a dominant trait.
Cystic Fibrosis
A genetic disorder passed down as a recessive trait.
Tay-Sachs Disease: Genetic Disorder Passed Down
An example genetic disorder passed down as a recessive trait. Most genetic disorders are passed down as recessive traits, meaning you need two copies of the gene to have the condition.
Examples: Albinism, cystic fibrosis, and Tay-Sachs disease.
Seed Shape
Example trait with alleles Round (R) or Wrinkled (r).
Seed Color
Example trait with alleles Yellow (Y) or Green (y).
Gametes
Sperm and eggs that result from independent assortment and crossing over.
Trait Combinations
Possible combinations of traits in offspring due to independent assortment.
Genetic Disorders
Most are passed down as recessive traits requiring two copies of the gene.
Albinism
A genetic condition characterized by a lack of pigment in the skin, hair, and eyes.
Cystic fibrosis
A genetic disorder that affects the respiratory and digestive systems due to thick mucus production.
Tay-Sachs disease
A fatal genetic disorder that results in the destruction of nerve cells in the brain and spinal cord.
Carriers (Heterozygotes)
Individuals with one normal and one recessive gene who do not have the disorder but can pass it to their children.
Dominant traits
Traits that require only one copy of the gene to be expressed, such as widow's peaks, freckles, dimples, and rolling your tongue.
Dominant disorders
Genetic conditions that are rare because they often cause early death before being passed to the next generation.
Huntington's disease
A genetic disorder that typically appears around age 40, with a 50% chance of being inherited by children if a parent has it.
Incomplete Dominance
A genetic situation where a person inherits one normal and one mutated gene, resulting in a blend of both traits. Happens when neither allele is fully dominant over the other.
Sickle cell disease
A genetic disorder characterized by the production of sickle-shaped hemoglobin, leading to various health complications.
SS (Normal)
Genotype that produces normal hemoglobin.
Ss (Carrier - Sickle Cell Trait)
Genotype that produces both normal and sickle-shaped hemoglobin, possibly with mild symptoms.
ss (Sickle Cell Disease)
Genotype that produces only sickle-shaped hemoglobin, which can lead to severe symptoms.
Sex-linked traits
Traits controlled by genes located on the X chromosome.
X chromosome
A chromosome that carries over 1,400 genes.
Y chromosome
A chromosome that carries about 200 genes.
Males (XY)
Individuals with one X chromosome, where any recessive gene on the X is fully expressed.
Females (XX)
Individuals who must inherit two copies of a recessive gene to show an X-linked disorder.
Genetic screening
A process that provides information to prospective parents about the risk of passing genetic conditions to their children.
PKU (Phenylketonuria) and Congenital hip dysplasia
Genetic disorder that can be managed if detected early.
Congenital hip dysplasia
A condition that can affect a child's health and can be managed if detected early.
Pedigree Analysis
A method used by genetic counselors to collect medical history from several generations to trace genetic traits.
Blood Tests & DNA Analysis
Methods used to screen for carriers of genetic disorders and detect hidden recessive genes.
Recurrent miscarriages
A condition that may prompt couples to consider genetic testing.
In-vitro fertilization with genetic screening
A reproductive option that allows for better medical care and treatment planning.
Genetic risks
The potential for individuals to pass genetic disorders to their offspring.