Bio 215 Exam 1 + Amino Acids, Functional Groups, Carbohydrates, Protein Structure
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/393
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
394 Terms
1
New cards
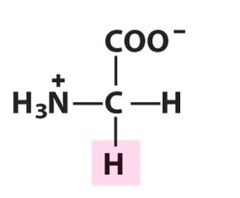
glycine
nonpolar
2
New cards
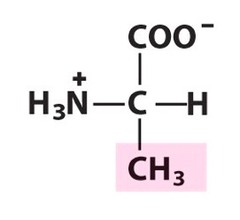
alanine
nonpolar
3
New cards
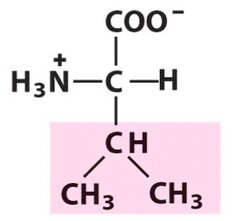
valine
nonpolar
4
New cards
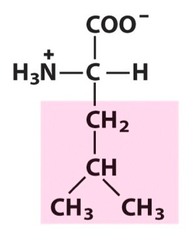
leucine
nonpolar
5
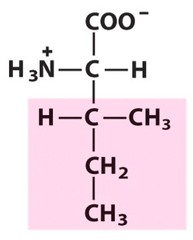
New cards
isoleucine
nonpolar
6
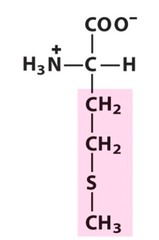
New cards
methionine
nonpolar
7
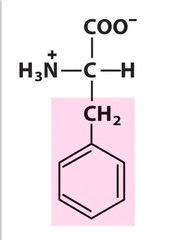
New cards
phenylalanine
nonpolar
8
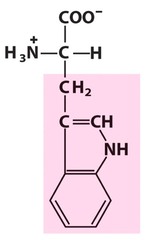
New cards
tryptophan
nonpolar
9
New cards
proline
nonpolar
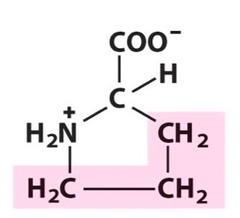
10
New cards
serine
uncharged polar
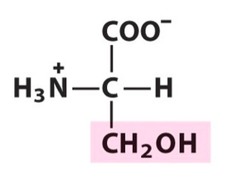
11
New cards
threonine
uncharged polar
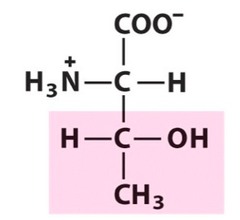
12
New cards
cysteine
uncharged polar
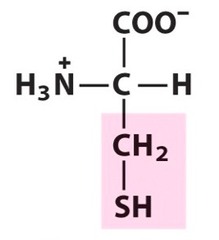
13
New cards
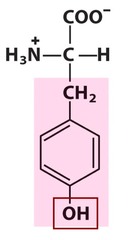
tyrosine
uncharged polar
14
New cards
asparagine
uncharged polar
15
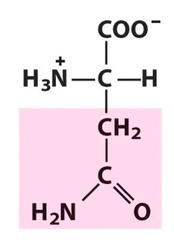
New cards
glutamine
uncharged polar
16
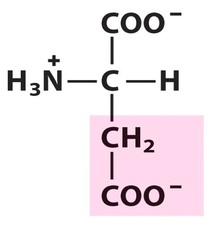
New cards
aspartate
negatively charged polar
17
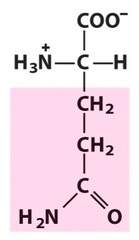
New cards
glutamate
negatively charged polar
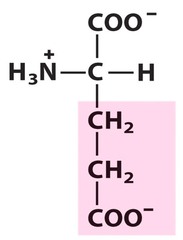
18
New cards
lysine
positively charged polar
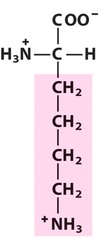
19
New cards
arginine
positively charged polar
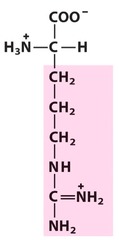
20
New cards
histidine
positively charged polar
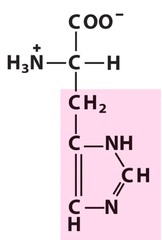
21
New cards
all characteristics of living things (there's 9)
organization
evolution of populations
DNA
reproduction
growth/development
response to environment
metabolism
homeostasis
contain one or more cells
evolution of populations
DNA
reproduction
growth/development
response to environment
metabolism
homeostasis
contain one or more cells
22
New cards
basic unit of life
smallest unit with capacity to live and reproduce, independently or part of a multi-cellular organism
smallest unit with capacity to live and reproduce, independently or part of a multi-cellular organism
cell
23
New cards
when were cells first observed
mid ______s
mid ______s
1600
24
New cards
who made the term "cell"
compartments in _______ slices
compartments in _______ slices
robert hooke, cork
25
New cards
who invented the first microscope
late ______s
late ______s
zacharias jansen, 1500
26
New cards
after 1665 there weren't many discoveries in cell biology
scientists were limited by
1. ___________ instruments
2. their way of _____________
scientists were limited by
1. ___________ instruments
2. their way of _____________
optical, thinking
27
New cards
optics improved in the ________s
the _____________ microscope was developed
the _____________ microscope was developed
1830 compound
28
New cards
who came up with the term "nucleus"
what year
what year
robert brown, 1831
29
New cards
robert hooke came up with what word
cell
30
New cards
robert brown came up with what word
nucleus
31
New cards
"cell theory" - what year
schleiden and schwann
schleiden and schwann
1838
32
New cards
EARLY cell theory breakdown
1. cell = unit of s___________, physiology, organization in living things
2. cell = both ___________ _________ and building __________
3. cells formed by free-_______________, like crystals
1. cell = unit of s___________, physiology, organization in living things
2. cell = both ___________ _________ and building __________
3. cells formed by free-_______________, like crystals
structure distinct entity block formation
33
New cards
who revised the early cell theory
virchow
34
New cards
REVISED cell theory breakdown
1. cell = unit of s___________, physiology, organization in living things
2. cell = both ____________________ and building __________
3. all cells come from ______________ cells
1. cell = unit of s___________, physiology, organization in living things
2. cell = both ____________________ and building __________
3. all cells come from ______________ cells
structure, distinct entity, block, preexisting
35
New cards
average human has ~________________ cells
30 trillion
36
New cards
current phylogenetic tree has _____ domains and name them
3, bacteria, archaea, eukarya
37
New cards
3 domain system
Bacteria = ________________
Archaea = ________________, many extremophiles
Eukarya = ________________ (including __________, plants, fungi, animals)
Bacteria = ________________
Archaea = ________________, many extremophiles
Eukarya = ________________ (including __________, plants, fungi, animals)
prokaryotes, prokaryotes, eukaryotes, protists
38
New cards
the phylogenetic tree was redrawn based on analysis of ________ sequences
BECAUSE it is a component of __________________ and these sequences change _________ over time
BECAUSE it is a component of __________________ and these sequences change _________ over time
rRNA, ribosomes, slowly
39
New cards
____________________ and archaea are more closely related to each other than to bacteria
eukaryotes
40
New cards
diverse groups/lineages of eukaryotic organisms
protists
41
New cards
(t/f) protists can be unicellular and multicellular
T
42
New cards
(t/f) viruses are considered living organisms
F
43
New cards
______ use host machinery to replicate. They are a complex of __________ and __________ acids (with RNA or DNA genome)
virus, protein, nucleic
44
New cards
what characteristics of life do viruses not exhibit?
metabolism, growth/development, homeostasis, contains one or more cells, can't reproduce on its own, response to environment
45
New cards
how do prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells differ?
prokaryotes don't have a nucleus and lack internal complexity
eukaryotes have a nucleus and extensive membrane bound organelles
eukaryotes have a nucleus and extensive membrane bound organelles
46
New cards
prokaryotes include which organisms?
a. bacteria
b. archaea
c. protists
d. all of the above
e. both a and b
a. bacteria
b. archaea
c. protists
d. all of the above
e. both a and b
e
47
New cards
average size of prokaryotes
____-____ ____ (units) diameter
____-____ ____ (units) diameter
1 5 um
48
New cards
average size of eukaryotes
____-____ ____ (units) diameter
____-____ ____ (units) diameter
10 100 um
49
New cards
basic structural features of all cells
1. surrounded by _______-based plasma membrane
2. ____________ machinery
3. ______ = hereditary information
4. ____________ = protein synthesizing machinery
1. surrounded by _______-based plasma membrane
2. ____________ machinery
3. ______ = hereditary information
4. ____________ = protein synthesizing machinery
lipid, metabolic, dna, ribosome
50
New cards
subcellular structures are best measured with the units
____ or ___
____ or ___
nanometers, angstroms
51
New cards
DNA helix diameter
____ nm
____ A
____ nm
____ A
2, 20
52
New cards
size of proteins is measured in
____
____
daltons
53
New cards
the smaller the surface area to volume ratio (it's worse), the ____________ the rates of chemical reactions
(bc problematic exchange of substance btw cell and environment)
(bc problematic exchange of substance btw cell and environment)
slower
54
New cards
(t/f) cells cope with the SA:V ratio problem by dividing
T
55
New cards
(t/f) cells deal with the SA:V ratio problem by stopping the cell growth cycle (like G0)
T
56
New cards
in G0, cells can become
1. ___________ (phase is reversible - can re-enter cell cycle)
2. terminally ________________ (non-reversible)
1. ___________ (phase is reversible - can re-enter cell cycle)
2. terminally ________________ (non-reversible)
quiescent, differentiated
57
New cards
brush border cells of intestinal epithelium
membrane folding
58
New cards
(t/f) membrane folding is not seen in prokaryotes
F
59
New cards
(t/f) membrane folding is limited to the plasma membrane in eukaryotes
F
60
New cards
(t/f) cells can cope w the SA:V ratio problem with active transport
T
61
New cards
transportation of 'cargo' by specialized carrier proteins
active transport
62
New cards
(t/f) the SA:V ratio problem is thought to be a driving force for the evolution of multicellularity
T
63
New cards
in prokaryotes
rigid protective layer of carbohydrate surrounding plasma membrane
rigid protective layer of carbohydrate surrounding plasma membrane
cell wall
64
New cards
process that separates subcellular components
"cell ___________________"
"cell ___________________"
fractionation
65
New cards
cell fractionation has ___ steps
1. cell ______ (broken open - chemical exposure)
2. _____________________ (subcellular stuff blended together - "cell soup")
3. _____________________ (centrifugal force differentially sediments the heterogenous mixture)
1. cell ______ (broken open - chemical exposure)
2. _____________________ (subcellular stuff blended together - "cell soup")
3. _____________________ (centrifugal force differentially sediments the heterogenous mixture)
3 lysis homogenization centrifugation
66
New cards
_________ = sediment at bottom after centrifugation
________________ = remaining liquid phase
________________ = remaining liquid phase
pellet, supernatant
67
New cards
in fractionation - centrifugation causes ______________ subcellular objects to form a pellet first
larger/denser
68
New cards
(t/f) hydroxyl groups deprotonate in an aqueous environment
F
69
New cards
(t/f) carboxylic acids deprotonate in aqueous solutions
T
70
New cards
measure of how fast a particle sediments when subjected to centrifugal force
sedimentation coefficient
71
New cards
(t/f) larger particles sediment faster and have higher S values
T
72
New cards
what contains the cytosol, organelles, subcellular structures
cytoplasm
73
New cards
How thick is the plasma membrane?
4-8 nm
74
New cards
fibrous network outside of the cell - made of various proteins and polysaccharides
extracellular matrix
75
New cards
functions of the ECM
___________/structure
adhesion/______________ to surrounding medium
___________/structure
adhesion/______________ to surrounding medium
support, anchorage
76
New cards
what makes up bacterial prokaryotic cell walls
peptidoglycan
77
New cards
Structure of peptidoglycan
polysaccharide chains made of N-acetylglucosamine and N-acetylmuramic acid cross-linked with peptides
78
New cards
technique to ID bacteria based on cell wall characteristics
also used for checking presence of bacteria in a sample
also used for checking presence of bacteria in a sample
gram stain
79
New cards
gram stain
- cells stained with _______ dye
- washed with ___________
- stained again with ___________ stain (color: _____)
- cells stained with _______ dye
- washed with ___________
- stained again with ___________ stain (color: _____)
purple, alcohol, counter, red
80
New cards
(t/f) thin cell walls give a gram positive stain
F
81
New cards
(t/f) gram stains focus on peptidoglycan
T
82
New cards
gram negative bacteria appears ______
red
83
New cards
(t/f) thick cell wall means purple color gets trapped in the cytoplasm and thin cell wall means purple can get easily alcohol-washed out
T
84
New cards
gram positive bacteria appear
purple
85
New cards
prokaryotic cell wall synthesis inhibitors
antibiotics that inhibit cell wall biosynthesis and compromise cell wall integrity
this makes bacteria susceptible to osmotic pressures and generally lyse
this makes bacteria susceptible to osmotic pressures and generally lyse
86
New cards
(t/f) the nuclear membrane is a double membrane
T
87
New cards
where are the ribosomal subunits made
nucleolus
88
New cards
short form for the complex of RNA and protein
(____ complex)
(____ complex)
RNP
89
New cards
ribosome sizes
prokaryotic = (size of small subunit)S + (size of large subunit)S = _____S
eukaryotic = (size of small subunit)S+ (size of large subunit)S = _____S
prokaryotic = (size of small subunit)S + (size of large subunit)S = _____S
eukaryotic = (size of small subunit)S+ (size of large subunit)S = _____S
30, 50, 70, 40, 60, 80
90
New cards
prokaryotic protein synthesis inhibitors
work by inhibiting ribosome activity
91
New cards
what accounts for half the membranes in an eukaryotic cell
ER
92
New cards
whose function is:
- lipid synthesis
- carbohydrate metabolism
- storing calcium
- detoxifying poison
- lipid synthesis
- carbohydrate metabolism
- storing calcium
- detoxifying poison
smooth er
93
New cards
a secreted protein would
a. go through the RER
b. go through the SER
a. go through the RER
b. go through the SER
a
94
New cards
what side of the golgi network is close to the ER
cis
95
New cards
what side of the golgi network is closer to the plasma membrane
trans
96
New cards
what adds a water molecule to a bond to break it
hydrolase
97
New cards
What does the endomembrane system include?
nuclear envelope, ER, golgi, lysosomes, vacuoles, plasma membrane, transport vesicles
98
New cards
process of organelle degradation that takes place inside the cell
used to remove old/damaged cell structures
used to remove old/damaged cell structures
autophagy
99
New cards
some _________________work by inhibiting cell wall _______________
(for bacteria and stuff)
(for bacteria and stuff)
antibiotics biosynthesis
100
New cards
(t/f) cells may have one or more vacuoles
t