PerDev 1st Qtr Areas of Personal Development
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
Areas of Personal Development
Physiological
the physical change in the body as well as the sense and changes in skills related to movement
Social
inborn capacity to relate to others
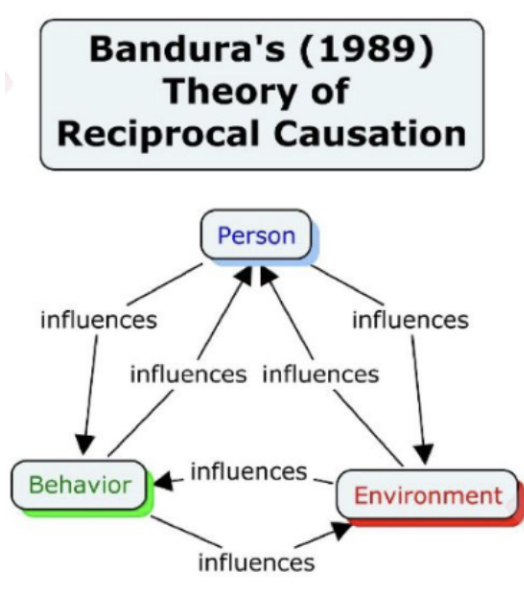
Albert Bandura’s theory of Human Agency
the capacity of humans to exercise control over their own lives as the essence of humanness
- Self-efficacy is the belief that one can succeed in what one wants to do
Emotional
has to do with the feelings that you experience
Emotion
a physiological experience (state of awareness) that gives you information about the world; a response that generates biochemical reactions in our bodies
Feelings
your conscious awareness of the emotion itself; a reaction to emotions; are subjevctive in nature
Cognitive
refers to a person’s intellectual abilities as shown in his/her thoughts, attitudes, beliefs and values
Attitude
a relatively enduring organization of beliefs, feelings, and behavioral tendencies towards socially significant objects, groups, events or symbols
3 components
affective, behavioral, cognitive
Behaviorism: B/F/ Skinner’s Operant Conditioning Theory
a person is the sum of total behaviours that were rewarded by his/her environment and hence were developed through repetition and reinforcement
Modeling
the people that one looks up to can influence his/her identity, beliefs, and values
Spiritual
defined as deiscovering oneself beyond the ego. It is known as the soul, spirit, or the inner essence that is often taken for granted
Values
subjective judgments that people make about the importance of certain things or issues; what one considers as essential to his or her self.; principles or standards; ideas or goals
Virtues
qualities, which typically reflect what one prizes and are universally considered to be good and desirable; lived values, values in action, which are achieved on a dependably regular basis
Values and virtues
the guiding principles that a person lives by; help shape a person’s belief, forming a system that can be used as a guide to determine what is right and wrong and what is true and false
Belief system
a moral code by which one sets standards, that serve as a guide throughout one’s life
Physiological (physical) and mental development
Puberty
Adolescence
Growth hormones
Metacognitive thinking
Emotional development
Emotional intelligence - the ability to recognize and control as well as to manage one’s emotions so as to enhance relationships with others
Emotional identification and regulation
Empathy - to read and understand other
Emotional development
one’s ability to cope with and manage emotions and ahve positive relationships
Mental development
the ability to think clearly and make good decisions, cope with stress and manage emotions
Cognitive development
related to mental function which also deals with logic; the process of cognition does influence mental health
Mental development
related to one’s emotions, the mind, and the intellectual process
Karen Horney’s Socio-Cultural View of Knowing Oneself (social)
Early childhood experiences are largely influenced responsibly for the formation of one’s personality
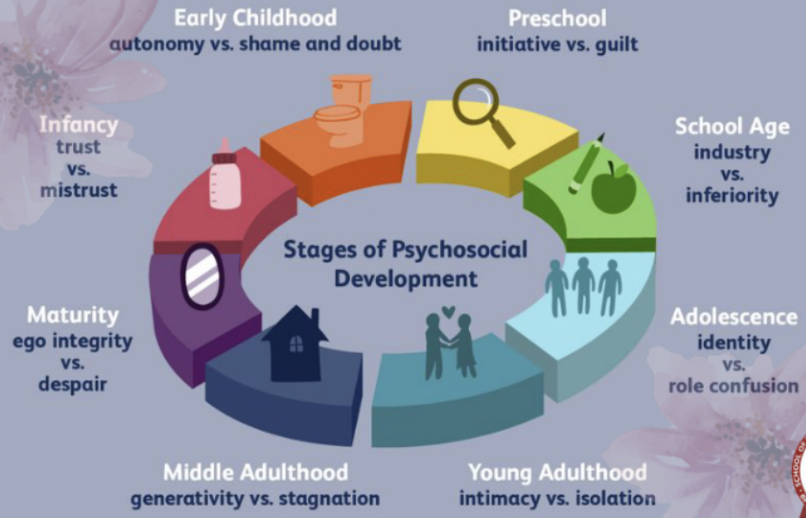
Erik Erikson (social)
Personality develops throughout the life cycle and stretches from infancy to old age
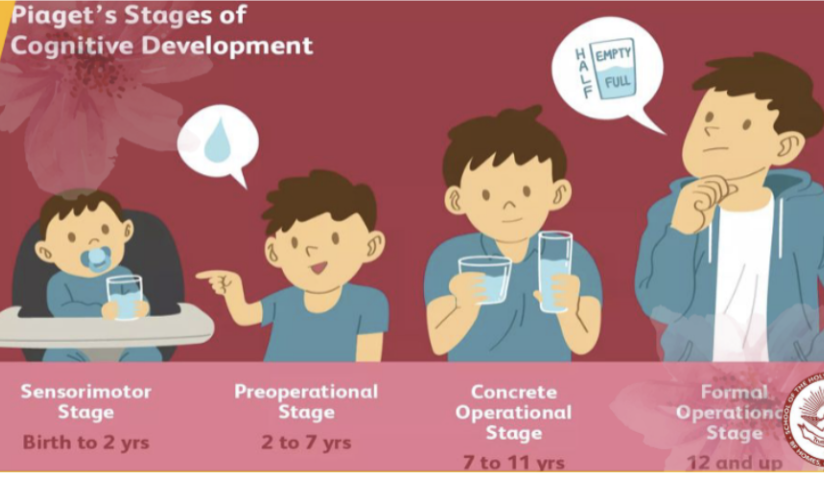
Jean Piaget’s theory (cognitive)
Sensorimotor stage
Pre-operational stage
Concrete operational stage
Formal operational stage
Teens reach the last stage of cognitive development and therefore have increased mental capacity in terms of hypothesizing, logical, and abstract thinking
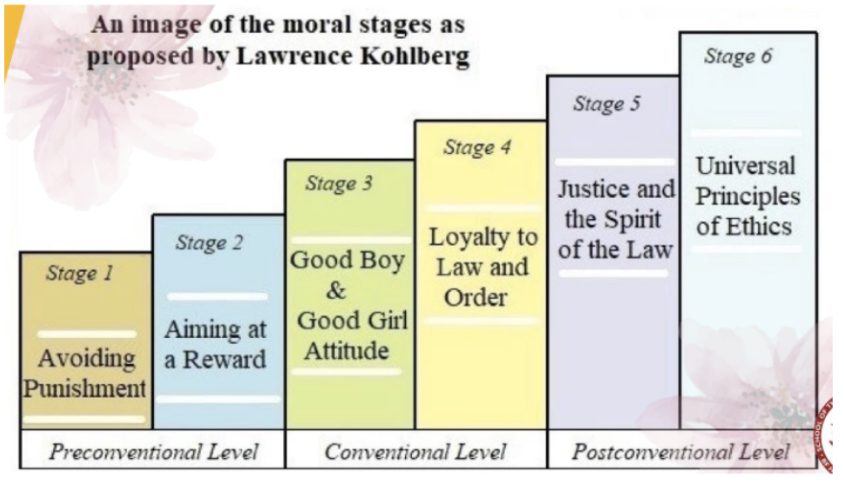
Lawrence Kohlberg’s theory (moral)
6 stages grouped into 3 levels:
Pre-conventional
Conventional
post -conventional
Start from being centered on the needs and wants to considering and negotiating, to a concern for the common good and universal principles, sometimes at the cost of being self-beneficial
St. Teresa of Avila (spiritual)
“INTRERIOR CASTLE”
Persons mature in holiness, as they grow deeper in knowledge & love for their Creator
Those who practice faith actively are resilient in the face of adversities
Those who believe in a higher being have a deeper sense of hope and purpose
3 ways of the Interior life or 3 stages of the spiritual life
Purgative stgae
Illuminative stage
Unitive stage
Sigmund Freud
Psychoanalytic theory
Mind has 3 level of awareness:
Conscious
Subconscious or preconscious
Unconscious
3 Provinces of the mind
Id (instinct)
Ego (relaity)
Superego (morality)
Slip of the tongue: Freudian slip
Alfred Adler
Inferiority complex (his own childhood experiences)
Striving for superiority vs striving for success
Malaadjustments
Carl Jung
Psychospiritual dimension of self
Personal unconscious and collective unconscious
Individuation or self-realization
Achetypes:
Persona/Shadow
Anima/Animus
Great mother/Wise old man
Hero/Self