SLP ANAPHY - Unit 6
1/64
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Respiratory System
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
65 Terms
Respiration
this is the exchange of gases between the atmosphere, blood, and cells
Ventilation
the process of breathing air in and out of the lungs (inhaling and exhaling)
Gas Exchange
the process of moving oxygen and removing carbon dioxide between the alveoli and capillaries
Pulmonary ventilation (breathing)
External (pulmonary) respiration
Internal (tissue) respiration
the 3 processes of supplying oxygen:
Pulmonary ventilation (breathing)
this is the exchange of gases that occurs within the alveoli of the lungs through inhaling and exhaling
TRUE
TRUE or FALSE: inhalation permits oxygen to enter the lungs and exhalation removes carbon dioxide from the lungs
External (pulmonary) respiration
this is the exchange of gases between the alveoli of the lungs and capillaries, where they lose carbon dioxide and gain oxygen
Internal (tissue) respiration
this is the exchange of gases between the blood and systemic capillaries and tissue cells, where tissues lose carbon dioxide and gain oxygen
Hemoglobin
this is the protein in the blood where oxygen binds to for transport in the bloodstream
Alveoli
this is where gas exchange in the lungs during pulmonary ventilation occurs
Alveoli and Capillaries
this is where gas exchange during external respiration occurs
Capillaries and Tissue Cells
this is where gas exchange during internal respiration occurs
Structurally and Functionally
the respiratory structures can be categorized into two:
Nose
Nasal Cavity
Pharynx
Associated Structures
structural parts of the upper respiratory system:
Larynx
Trachea
Bronchi
Lungs
structural parts of the lower respiratory system:
Conduction Zone
Respiratory Zone
the components of the respiratory system can be divided by their function into:
Conducting Zone
this zone is a series of interconnecting cavities and tubes both out and in of the lungs
Nose
Nasal Cavity
Pharynx
Larynx
Trachea
Bronchi and Bronchioles
Terminal Bronchioles
these are the parts of the conducting zone:
Respiratory Zone
this zone is composed of tubes and tissues within the lungs where gas exchange occurs
Respiratory Bronchioles
Alveolar Ducts
Alveolar Sacs
Alveoli
these are the parts of the respiratory zone:
TRUE
TRUE or FALSE: the conducting zone filters water and moistens the air and conducts it to the lungs, while the respiratory zone is the main site where gas exchange occurs
External Nose
the external entryway of the respiratory system
Nasal Cavity
this is the internal part of the nose; the large space in the interior aspect of the skull and is superior to the oral cavity
Cartilage and Skin and lined with Mucous Membrane
what is the external framework of the nose composed of?
TRUE
TRUE or FALSE: the nose is the visible external portion, and the nasal cavity is the internal portion of the skull
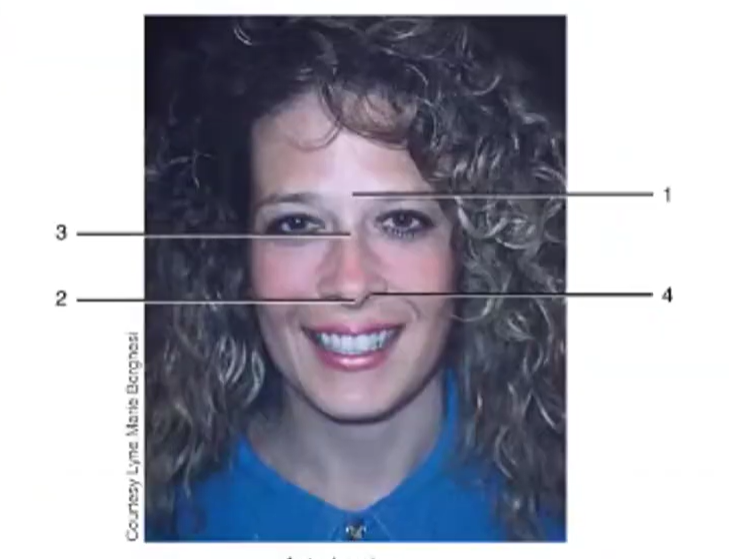
Root
Apex
Bridge
Nares
surface anatomy of the nose:
Pharynx
is a funnel-shaped tube that starts at the nasal pharynx and extends to the cricoid cartilage
Pharynx
this is a passageway for air and food, providing a resonating chamber for speech sounds, and houses the tonsils
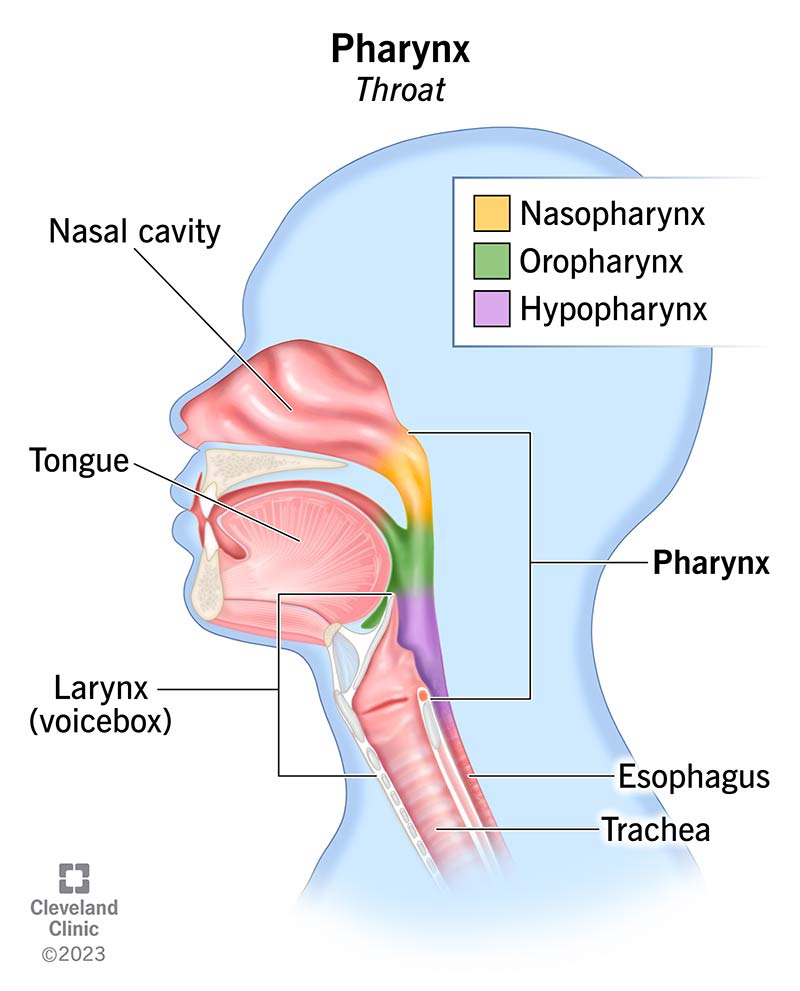
Nasopharynx - at the nasal cavity
Oropharynx - back of the mouth
Laryngopharynx - in the larynx area
the three anatomical regions of the pharynx
Larynx (Voice box)
this is a passageway that connects the pharynx and trachea which houses the vocal cords
9 pairs (3 single, 3 paired)
how many pairs of cartilages does the larynx have?
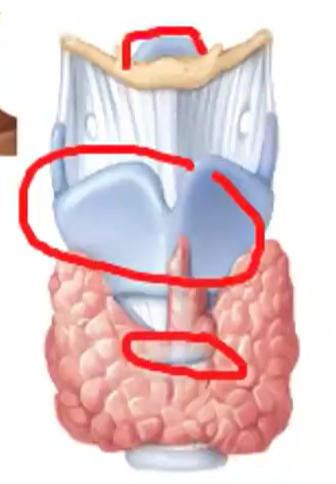
Thyroid Cartilage - the Adam’s Apple
Epiglottis - a leaf-shaped flap of cartilage, unattached and free to move like a trap door, that covers the larynx to prevent food from entering
Cricoid Cartilage - a ring of hyaline cartilage and the landmark for making an emergency airway called a tracheostomy
cartilage of the larynx that occur singly:
Arytenoid Cartilages - influence changes in position and tension in the vocal cords, because they are the point of attachment of the different muscles for speech
Corniculate Cartilages - pieces of elastic cartilage that are located at the apex of each arytenoid cartilage
Cuneiform Cartilages - club-shaped cartilage anterior to the corniculate cartilages that support the vocal cords
cartilage of the larynx that occur in pairs:
Laryngeal Vestibule
portion of the cavity of the larynx above the laryngeal vestibule
Infraglottic Cavity
portion of the cavity pf the larynx below the vocal folds
Vestibular Folds - superior pair
Rima Vestibuli - space between
Vocal Folds - inferior pair
Rima Glottidis - space between
mucous membrane folds and spaces:
Intrinsic Muscles - attach cartilage with each other
Extrinsic Muscles - attach cartilage to other structures outside the throat
the muscles that move the larynx:
Phonation
the action of contracting and relaxing the muscles varies the tension in the vocal folds and the air passing through the larynx, which vibrates the vocal folds, producing sound by setting up sound waves in the column of air in the pharynx, nose, and mouth
TRUE
TRUE or FALSE: the variation in the pitch of the sound is related to the tension of the vocal folds
TRUE
TRUE or FALSE: the greater the pressure of air, the louder the sound
TRUE
TRUE or FALSE: the higher the pitch, the longer the vocal folds stretch, and the louder the volume, the greater the tension of the vocal folds
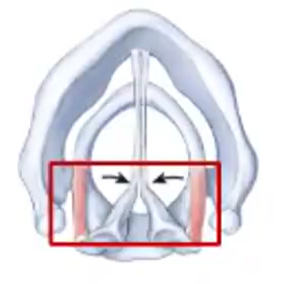
Lateral Cricoarytenoid Muscle
when contracted, this muscle pulls the vocal folds together (adduction), closing the rima glottidis
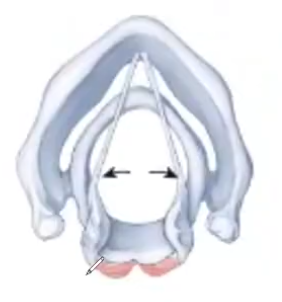
Posterior Cricoarytenoid Muscle
when contracted, this muscle pulls the vocal folds apart (abduction)
Trachea (Windpipe)
a tubular passageway for air, located anterior to the esophagus, that extends to the thoracic vertebrae, and divides into right and left primary bronchi
Hyaline Cartilage Rings
the trachea is covered with ___ which allows it to expand when breathing
Bronchi
at the superior border of the 5th thoracic vertebrae, they enter the lungs to allow gas exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide
TRUE
TRUE or FALSE: the right main bronchus is more vertical. shorter, and wider, and is more likely for food to be aspirated in the right main bronchus
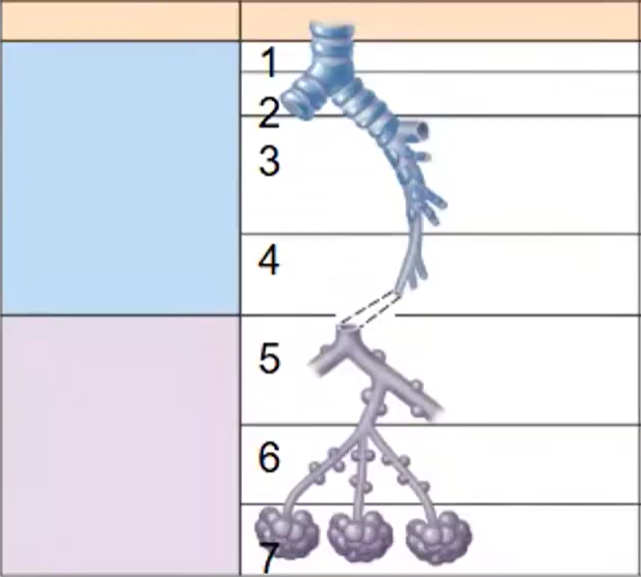
Trachea → Main Bronchi → Lobar and Segmental Bronchi → Terminal Bronchioles → Respiratory Bronchioles → Alveolar Ducts → Alveolar Sacs
airway branching (conduction zone and respiratory zone):
Carina
the internal ridge that divides the primary bronchi
Lungs
paired organs in the thoracic cavity, and are separated by the heart and the mediastinum and other organs
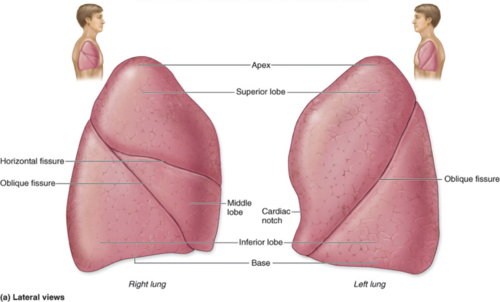
Apex - superior part of the lung
Base - inferior part of the lung
the lungs are divided into two parts:
TRUE
TRUE or FALSE: when inhaling, the lungs expand, and during exhalation, the lungs contract
Pleural Membrane
the lungs are enclosed and protected by a ___
Parietal Pleura - external pleura that covers the lungs
Visceral Pleura - internal pleura that covers the internal surface of the thoracic cavity
these compose the pleural membrane, and reduce friction during lung movement, protecting the lungs
Fissures
Lobes
FILL IN THE BLANKS: ___ divide the lungs into ___
Right, 3
Left, 2
FILL IN THE BLANKS: the ___ lungs has ___ lobes, while the ___ lung has ___ lobes
Oblique Fissure
this is a diagonal fissure divides the lungs into lobes
Horizontal Fissure
this fissure divides the right lung into 3 lobes
Alveoli (Alveolus)
site where gas exchange occurs - this is where diffusion of oxygen into the bloodstream and diffusion of carbon dioxide outside of the bloodstream
Pulmonary Arteries (deoxygenated blood) and Bronchial Arteries (oxygenated blood)
blood vessels which supply blood to the lungs
Pulmonary Arteries
these are the only arteries that carry deoxygenated blood; these arteries carry blood to the lungs to be oxygenated, which flow to the pulmonary veins, and are drained in the left atrium of the heart
Bronchial Arteries
these arteries perfuse into the bronchi and bronchioles of the lungs, supplying oxygenated blood to the lungs
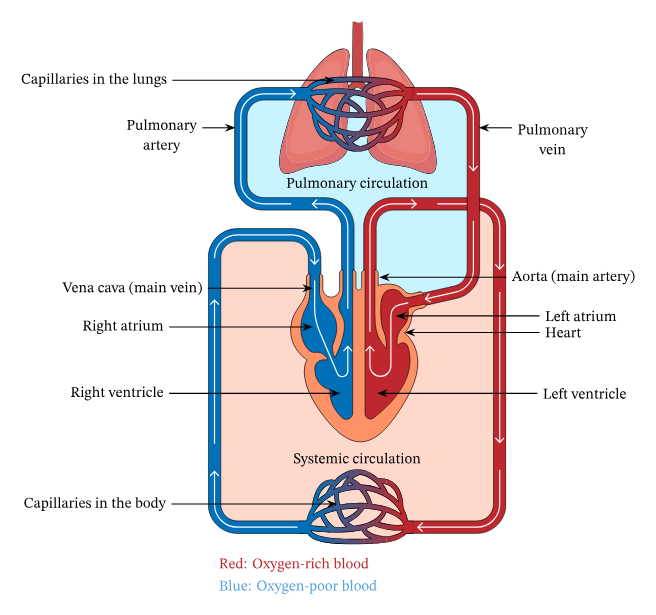
Pulmonary Arteries (Pulmonary Circulation) → Lungs → Pulmonary Veins (Systemic Circulation) → Heart (Left Atrium)
pulmonary and systemic circulation (blood flow from the lungs to the heart):
Ventilation-Perfusion Coupling
perfusion (blood flow) to the lungs matches the extent of ventilation (airflow) of the alveoli in the area
Pulmonary Ventilation (Breathing)
this is the flow of air into and out of the lungs; airflows between the atmosphere and the alveoli of the lungs because of alternating pressure differences created by contraction and relaxation of respiratory muscles