AP Micro U1
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
Scarcity
There is a finite quantity of goods and resources
Economics
Study of scarcity and choice
Resource
Anything that can be used to produce a good
Good
Item that must be used to receive a benefit
Service
Someone or something does an action for you for your benefit
Factors of Production
Land, labor, capital, entrepreneurship
Economy
System for coordination societies productive and consumptive activities
Trade
Exchange of goods and services
Market economy
Producers decide production specifics
Traditional Economy
Simple trade between families and tribes
Command economy
Industry is publicly owned, and central authority makes production and consumption decisions
Mixed economies
Market-based systems with limited government oversight
Incentives
Rewards/ punishments that motivate choice
Property rights
Establish ownership, give trade rights
Opportunity Cost
Value of the next-best decision given up when you make a decision
Marginal analysis
Study of costs and benefits of doing a little more/ a little less
Trade-off
When you give up one thing to get another
Marginal Benefit/ cost
The loss/gain from doing something once more
Microeconomics
Study of how individuals, households, and firms make decisions and how those decisions interact
Macroeconomics
Concerned with the behavior of the economy as a whole
Positive Economics
Branch of economic analysis that describes how the government actually works
Normative economics
Makes prescriptions about the way the economy should work
Production Possibilities Curve/ Fronteir
Shows trade offs facing an economy that produces two goods
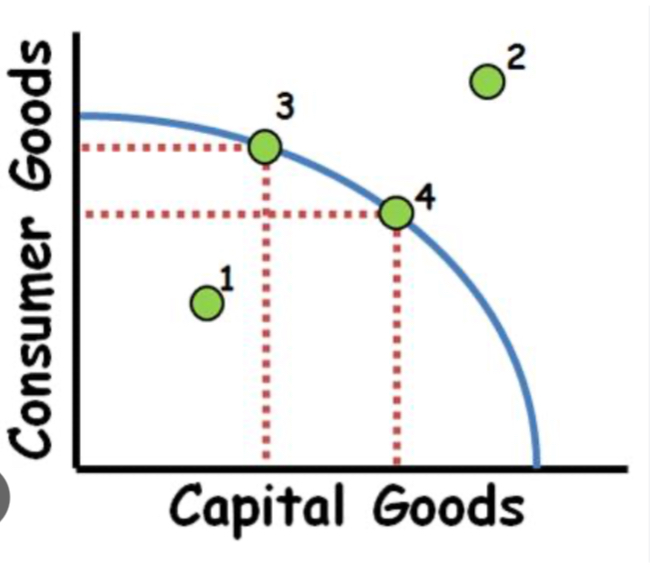
Inefficient
Point 1
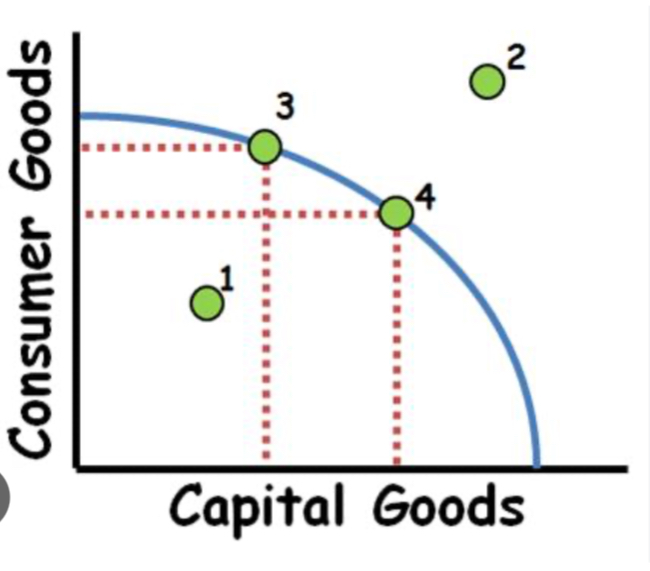
Efficient and feasible
Points 3 and 4
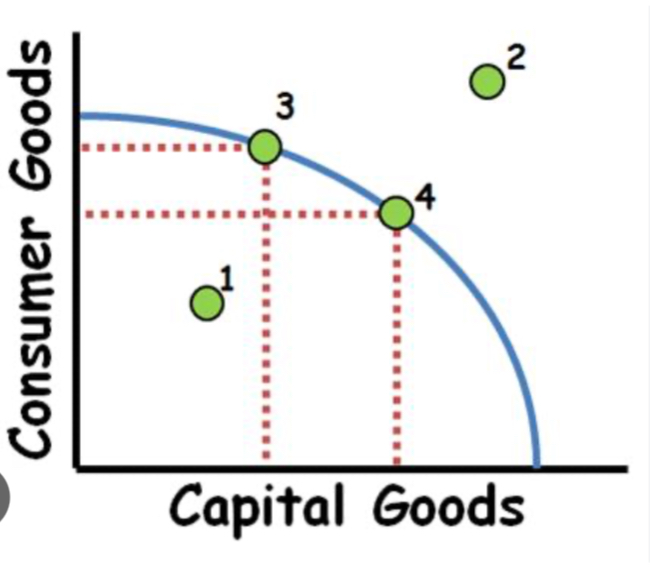
Impossible
Point 2
Economy is efficient
No mutually beneficial transaction goes unexploited
Economy achieves productive efficiency
It produces on PPC
Economy achieves allocative efficiency
It produces on PPC and consumers are as well off as possible
Graph shifts in/out
Production possibilities expand/ decrease
PPC growth sources
Technology, increase in available resources
Gains from trade
People can get more from trade than if they were self sufficient
Specialization
Each person specializing at the tasks they are good at performing
Competitive advantage
Producer faces lowest opportunity cost of producing
Absolute advantage
Producer can make more than others with a given amount of time/resource
Terms of trade
Rate at which one good can be exchanged for another
Trade is efficient if
A good is obtained for less than the opportunity cost of producing it
Output method
Opportunity Cost of 1A = B/A of B (constant time)
Input method
Opportunity Cost of 1A =A/B of B (change in time)