Veterinary Parasitology CH4 P2 - Nematodes of Ruminants and Other Animals
1/20
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Part 2 of study material for Chapter 4 of Diagnostic Parasitology for Veterinary Technicians. For class BIO225 at MWCC.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
Gongylonema pulchrum
Esophageal worm of ruminants
Found: Worldwide
Affects: Sheep, goats, cattle (more rarely pigs and horses)
Adult worms live in esophagus, embeds in mucosal lining
Ingestion of intermediate host is the dung beetle or cockroach
"Worms with bumps" - zigzag shape
Eggs seen on fecal flotation

Trichostrongylus sp, Haemonchus sp.
"Hair round" (Trichostrongylus), "Blood spear" (Haemonchus)
Often most common nematode in ruminants
Cattle, sheep, goats
Adults found in abomasum, sm. & lg. intestine
Cause of infection: Ingestion of infective larvae
Trichostrongylus is zoonotic, Haemonchus is not
Eggs are morulated and too similar to differentiate genus in a fecal
Feed on blood of host
Treated with fenfendazole, levamisole and ivermectin

Bottle jaw in sheep
Infection with Haemonchus may overwhelm a host's ability to replace proteins and blood lost. This results in decreased intravascular oncotic pressure resulting in edema. The gathering of edema in the submandibular area is termed 'bottle jaw'.

Strongyloides papillosus
Threadworm
Found: Worldwide
Cause of infection: Ingestion of larvae or penetration of skin (between hooves); migrate to lungs, coughed up and swallowed
Parthenogenetic larvae have a rhabitiform esophagus
Stage 3 larvae can be free-living or infective
Can pass in colostrum
Prepatent period: 5-7 days
Constant reinfection from pasture living - can reduce reinfection by rotation pasture with nonruminant animals (horses, mules, donkeys)
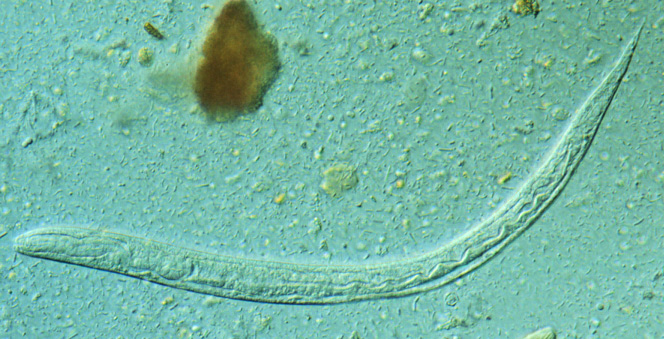
Trichuris ovis
Whipworms - "Hair tail"
Found: Worldwide
Cause of infection: Ingestion of infective ova
Adults in cecum and colon
Unembryonated eggs with bipolar plugs
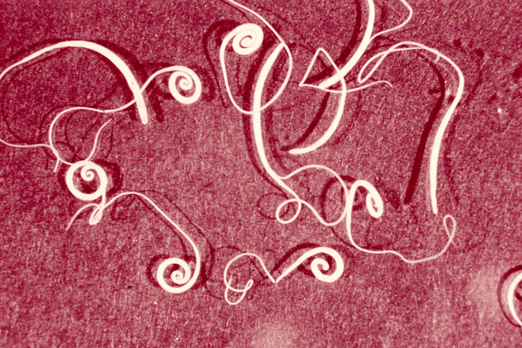
Elaeophora schneideri
Arterial sheep worm - "Bearing oil"
Found: In Western and Southwestern United States
Only domestic host is sheep
Carried by infected horse flies
Adults in common carotid, can cause obstructions
Microfilariae only found in skin capillaries in face, can cause dermatitis
Prepatent period: 4.5 months or longer
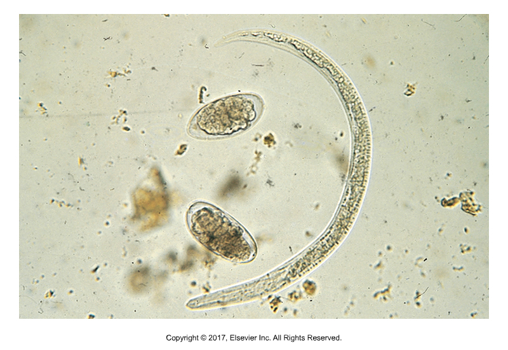
Dictyocaulus sp.
Ruminant lungworm - "Netlike stalk"
Found: Worldwide
Cause of infection: Ingestion of infective larvae
Adults live in bronchi, females lay eggs in lungs, coughed up, swallowed and hatch in intestine, larvae mature in environment to infective stage
Ingested larvae migrate to lymphatics, then to the heart, then to the lungs where they mature
Coughing is most common symptom
Eggs can be found in sputum
Larvae can be found in fecals
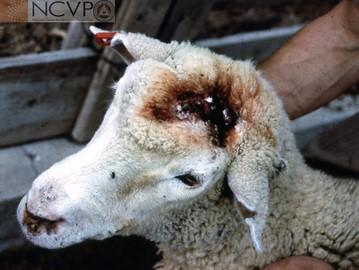
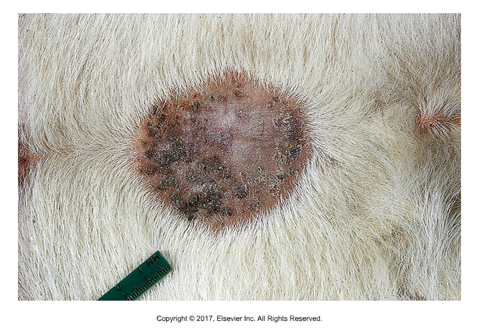
Stephanofilaria stilesi
"Crown thread"
Found: In United States
Transmitted by the horn fly Haematobia irritans
Cause dermatitis along ventral midline, near umbilicus
Starts as small red papillae, then larger areas of pruritus and alopecia with a thick, moist crust
Adults and microfilariae can be found in skin scrapings
Must be careful not to confuse skin microfiliariae with Rhabditis strongyloides which is present in almost all domesticated animals and can also cause dermatitis
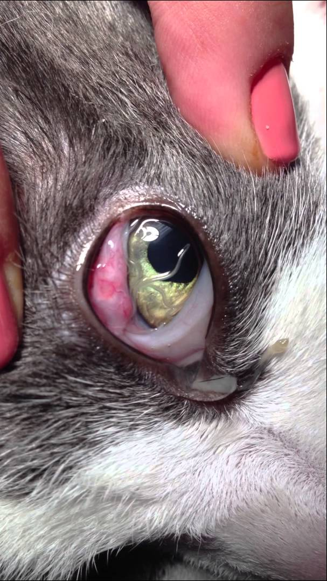
Thelazia sp.
Transmitted by the intermediate host, the face fly (Musca autumnalis)
Adults found in conjunctiva and tear duct
Tears can have eggs or first stage larvae
Setaria cervi
Carried by female mosquito
Adults are large and white and found at necropsy or during surgery free inside the peritoneal cavity
Microfilariae can be found in peripheral blood smears

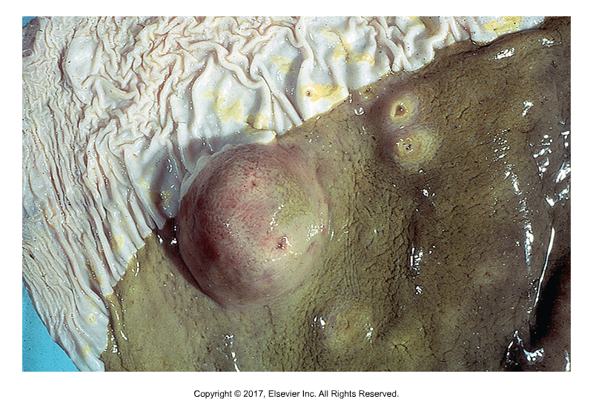
Habronema sp. Draschia sp.
Horse stomach worm
Found: Worldwide
Passed by flies (Muscidae family) which is intermediate host
Symptoms: Gastritis, diarrhea, nodules in stomach; can also cause skin involvement "summer sores"
Elongated, thin shelled, larvated eggs found in fecals
Eggs or larvae ingested by flies
Cause of infection: Horse accidentally ingests fly with infective larvae inside
Fly control and pasture rotation can limit infections
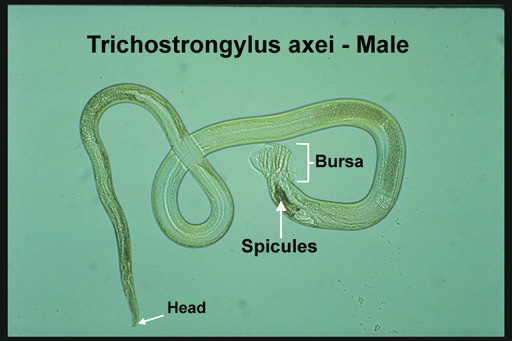
Trichostrongylus axei
Feed on blood in horse stomach
Ingestion of infected soil
Can also infect cattle, sheep and pig
Strongyle egg found in fecal float
Pasture management, treatment and pickup of feces can limit infections
Parascaris equorum
Found: Worldwide
Small intestine of horse, mainly foals
Cause of infection: Ingestion of ova
Larvae migrate to liver through hepatic portal vein, then travel to lungs, coughed up and swallowed
Largest of equine nematodes, can grow to 50cm
Adults have distinctive lips
Light infections can be asymptomatic, heavy infections can cause unthriftiness, colic, potbelly, depression and cough

Strongylus vulgaris, Strongylus equinus
Found: Worldwide
Cause of infection: Ingestion of larvae
Adults live in large intestine
Large strongyles — most pathogenic
Strongyle egg
Eggs pass into environment and develop into larvae on blades of grass
Larvae migrate through mesenteric arteries to the liver, molt into next stage, migrate back to large intestine and mature in mucosal lining
Symptoms: Colic, weight loss, fever, lethargy, loss of appetite
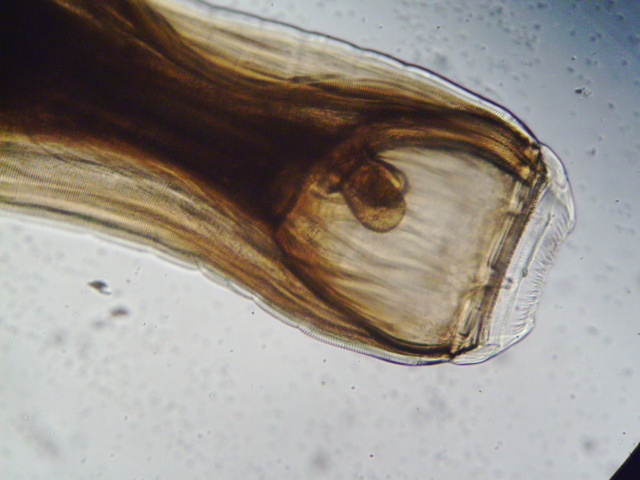
Oxyuris equi
Horse pinworm
Found: Worldwide
Adults in cecum, colon, rectum
Adult females exit anus, lay eggs with sticky, irritating gel that causes pruritus
Horses will swish tails constantly, rub their rumps and have broken tails hairs
Prepatent period: 4-5 months
Eggs can rub off on fencing or feeders and infect same host or new animals
Eggs have single operculum with flat end, often larvated
Eggs can be found on fecal scraping or scotch tape test; rare to find eggs on fecal flotation
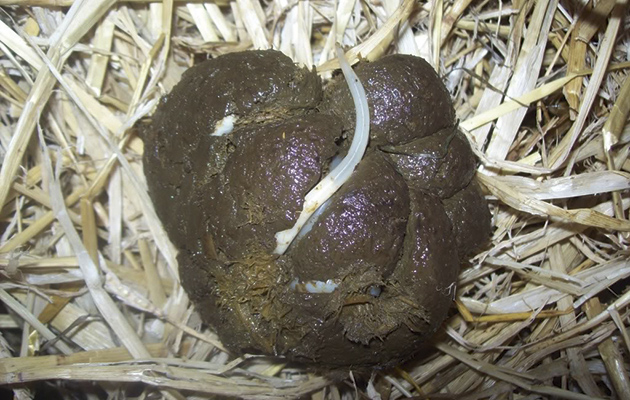

Habronema sp., Draschia sp
Stomach worm
Adults are only found in the stomach, but larvae are deposited by house flies (Musca domestica) onto the skin and can cause cutaneous habronemiasis or "summer sores"
Often go away over the winter untreated
Most often found on legs, withers and male genitals

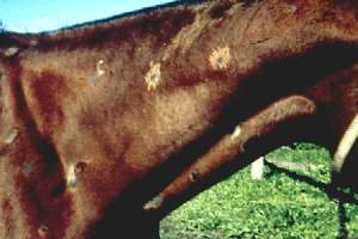
Onchocerca cervicalis
"Tumor tail"
Carried by the intermediate host, the biting midge ("No see-ums")
Adults are in ligamentum nuchae
Microfilariae are in dermis
Symptoms: Itching, alopecia, patchiness along head, neck and ventral midline
Microfilariae in skin scraping is not diagnostic as 90% of animals are infected
Diagnostic is by punch biopsy placed in saline on slide- can see vigorously swimming microfilariae
In rare cases, can cause opthalmia and blindness
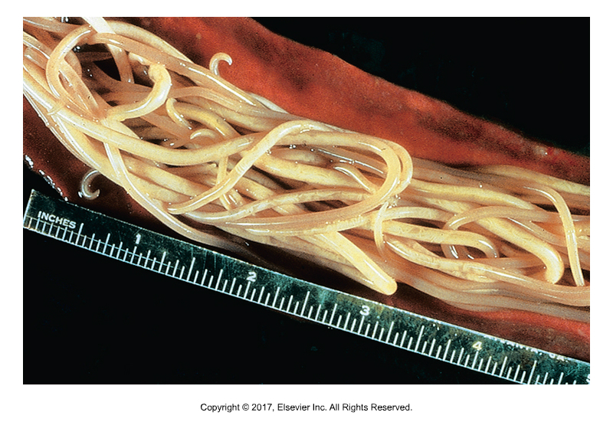
Ascaris suum
Found: Worldwide
Cause of infection: Ingestion of infective ova
Not zoonotic
5mm wide and 41 cm long
Adults can be passed in feces, can cause bowel obstruction
Eggs passed in feces and hatch in environment as infective larvae
Larvae hatch and migrate to liver, molt, migrate through blood to lungs, coughed up and swallowed.
Adults mature in small intestine
Symptoms: Reduced weight, unthriftiness, respiratory symptoms in pigs
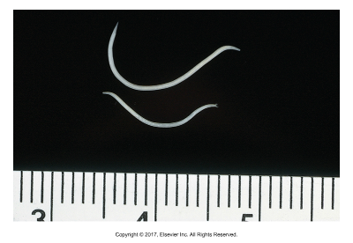
Oesophagostomum dentatum
"Esophagus mouth"
Found: Worldwide
Nodular worm of pigs
Large intestine
Larval form causes nodules to form in the large intestine, can cause obstruction
Prepatent period: 50 days
Strongyle type egg
Symptoms: Anorexia, diarrhea, weight loss
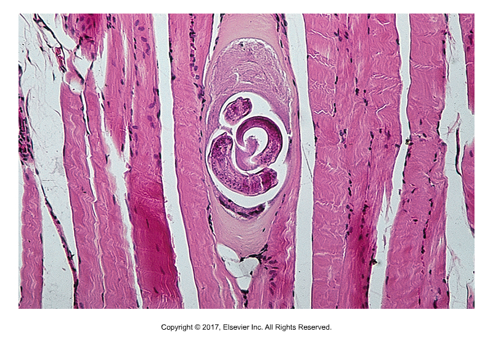
Trichinella spiralis
"Small hair"
Pigs are intermediate AND definitive host
Adults in small intestine
Found: Worldwide (except for Australia and Denmark)
Cause of infection: Ingestion of contaminated, undercooked pork
Zoonotic
Female 4mm long, male is smaller
Larvated egg
Domestic animals often asymptomatic
Larvae encyst in skeletal muscle
Diagnosed by muscle biopsy
Metastrongylus elongates
Found: Worldwide
Earthworm is intermediate host
Cause of infection: Ingestion of earthworm
Adults in bronchi and bronchioles
Prepatent period: 24 days
Heavy eggs, must be flotation solution with SG >1.25 or by sedimentation
Symptoms: Cough, slow growth, unthriftiness