Unit 3 Exam
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/134
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 4:29 PM on 11/7/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
135 Terms
1
New cards
Radiometric Dating
a method for determining the absolute age of rocks and fossils, based on the half-life of radioactive isotopes
2
New cards
Half-Life
the time required for 50% of a radioactive isotope to decay
3
New cards
Stromatolites
layered rocks that form when certain prokaryotes bind thin films of sediment together
4
New cards
Endosymbiosis
a symbiotic relationship where one organism lives inside the other
(Ex: a prokaryote cell engulfed a small cell that would evolve into an organelle found in all eukaryotes)
(Ex: a prokaryote cell engulfed a small cell that would evolve into an organelle found in all eukaryotes)
5
New cards
Serial Endosymbiosis
a theory that supposes that mitochondria evolved before plastids through a sequence of endosymbiotic events
6
New cards
Cambrian Explosion
the time (in geological history) when most of the major groups of animals first appear in the fossil record
(called "explosion" because the relatively short time for this diversity to appear)
(called "explosion" because the relatively short time for this diversity to appear)
7
New cards
Prior to the Cambrian explosion, all large animals were ___________ __________ and appear to have been grazers, filter feeders, and scavengers. The explosion changed all of this.
soft-bodied
8
New cards
Plate Tectonics
a theory that the continents are part of great plates of Earth's crust that essentially float on the hot, underlying portion of the mantle
9
New cards
Continental Drift
movements in the mantle cause the plates to move over time (very slowly)
(promotes/causes Allopatric speciation)
(promotes/causes Allopatric speciation)
10
New cards
Pangaea
the supercontinent that formed near the end of the Palezonic era, when plate movements brought all the landmasses on Earth together
(drove some species to extinction and allowed others to thrive)
(drove some species to extinction and allowed others to thrive)
11
New cards
Mass Extinction
a large number of species become extinct worldwide (result of global environmental changes)
12
New cards
Permian Mass Extinction
(claimed about 96% of marine animal species) Volcanism and lava resulted in extreme amounts of Co2 and warming, which led to ocean acidification
13
New cards
Cretaceous Mass Extinction
occured 65 million years ago, killing 78% of all species (including dinosoars). Caused by an asteroid hitting the Earth.
(the large amounts of sediment in the atmosphere blocked the sun and caused a long period of global freeze)
(the large amounts of sediment in the atmosphere blocked the sun and caused a long period of global freeze)
14
New cards
Adaptive Radiation
periods of evolutionary changes in which groups of organisms form many new species whose adaptations allow them to fill different ecological roles, or niches, in their communities.
Ex: Darwins finches of the Galapagos Islands
Ex: Darwins finches of the Galapagos Islands
15
New cards
Exaptation
a trait or structure of a taxonomic group that takes on a function that never previously existed (derived by evolution)
Ex: the use of feathers for mating displays or flight (feathers originally evolved to keep warm)
Ex: the use of feathers for mating displays or flight (feathers originally evolved to keep warm)
16
New cards
How many mass extinctions have been documented over the past 500 million years?
5 mass extinctions have been documented
17
New cards
Evolution works by ________________ with existing structures
Evolution works by "tinkering" with existing structures
18
New cards
Phylogeny
the evolutionary history of a species of group of related species
19
New cards
Systematics
a discipline focused on classifying organisms and determining their evolutionary relationship
20
New cards
To avoid confusion when communicating about their research, biologists refer to organisms by __________ ____________ names.
Latin Scientific
21
New cards
Binomial
(latinized format for naming species) consisting of the genes and specific epithet
Ex: Apis mellifera (Honey Bee)
Ex: Apis mellifera (Honey Bee)
22
New cards
Genus
a taxonomic category above the species level (the first word of a binomial)
Ex: Apis mellifera --> [Apis]
Ex: Apis mellifera --> [Apis]
23
New cards
Linnaean System
living organisms are classified into groups depending on their structure and characteristics
24
New cards
Taxon
the named group at any level of the hierarchy
Ex: for a leopard, 'Panthera' is a taxon at the genus level and Mammalia is at the class level
Ex: for a leopard, 'Panthera' is a taxon at the genus level and Mammalia is at the class level
25
New cards
Phylogenetic Tree
a branching diagram that represents the evolutionary history of a group of organisms
26
New cards
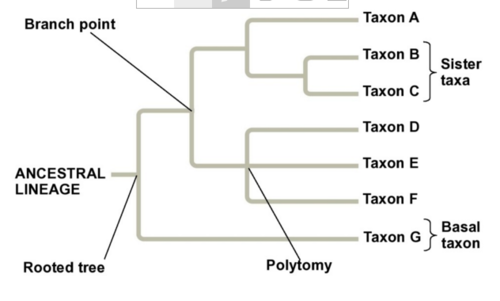
Branch Point
represents a common ancestor of the two evolutionary lineages diverging from it
27
New cards
Evolutionary Lineage
a sequence of ancestral organisms leading to a particular descendent taxon
28
New cards
Sister Taxa
groups of organisms that share an immediate common ancestor that is not shared by any other group
Ex: chimps and humans
Ex: chimps and humans
29
New cards
Rooted
means that a branch point within the tree represents the most recent common ancestor of all taxa in the tree
30
New cards
Basal Taxon
a lineage that diverges from all other members of its group early in the history of the group
31
New cards
Homologies
similarity in characteristics resulting from a shared ancestry
32
New cards
Analogy
similarity between two species that is due to convergent evolution (rather than common ancestor)
occurs when similar environmental pressures and natural selection produce similar adaptations from different evolutionary lineages
occurs when similar environmental pressures and natural selection produce similar adaptations from different evolutionary lineages
33
New cards
Cladistics
an approach to systematics in which organisms are placed into groups called clades based primarily on common descent
34
New cards
groups that include an ancestral species and all of its descendants
A group of species that includes an ancestral species and all its descendants
Ex: Mammalia, Aves (birds), angiosperms, insects
Ex: Mammalia, Aves (birds), angiosperms, insects
35
New cards
Monophyletic
taxa that consists of a common ancestor and all of its descendents
36
New cards
Paraphyletic
taxa that consists of a common ancestor and some but not all of its descendents
37
New cards
Polyphyletic
taxa that includes distantly related organisms but does not include their most recent common ancestor
38
New cards
Shared Ancestral Character
a character that originated in an ancestor of the taxon
Ex: hair is a character shared by all mammals but not found in their ancestors
Ex: hair is a character shared by all mammals but not found in their ancestors
39
New cards
Shared Derived Character
an evolutionary novelty that is unique to a particular clade
(a character in a species that has changed since the species descended from its past ancestors)
(a character in a species that has changed since the species descended from its past ancestors)
40
New cards
Outgroup
a species or group of species from an evolutionary lineage that is closely related to but not part of the species being studied
Ex: outgroup -> Gibbons (20 species of apes)
Ex: outgroup -> Gibbons (20 species of apes)
41
New cards
Ingroup
a species or group of species whose evolutionary relationships are examined in a given analysis
Ex: ingroup -> Great Apes
Ex: ingroup -> Great Apes
42
New cards
In phylogenetic trees, the length of branches do not indicate the degree of __________________ _____________ in each lineage.
Evolutionary Lineage
(instead proportional to the times at which each particular event occurred)
(instead proportional to the times at which each particular event occurred)
43
New cards
Maximum Possibility
one should first investigate the simplest explanation that is consistent with the facts
44
New cards
Maximum Likelihood
when considering multiple phylogenetic hypotheses, evaluates that the choosen evolutionary model will have generated the observed sequences
45
New cards
What are the 5 biological kingdoms?
Monera (prokaryotes)
Protista (mostly unicellular organisms)
Plantae
Fungi
Animalia
Protista (mostly unicellular organisms)
Plantae
Fungi
Animalia
46
New cards
Horizontal Gene Transfer
when genes are transfered from one genome to another (such as exchange of transposable elements)
Ex: when a host and its endosymbiont become a single organisms
Ex: when a host and its endosymbiont become a single organisms
47
New cards
Eukaryotes can acquire genes by _______________ ____________ ________ from prokaryotes.
Horizontal Gene Transfer
48
New cards
Yeast
unicellular fungi that live in damp places and can reproduce by budding (eukaryotic and asexual)
49
New cards
Hyphae
one of many connected filaments that collectively make up the mycellium of fungus
50
New cards
Chitin
a strong but flexible polysaccharide (chitin-rich walls can enhance feeding my absorbtion)
51
New cards
Septa
one of the cross walls that divide a fungal hyphae into cells
52
New cards
Coenocytic Fungi
a fungus that lacks septa and whose body is made of cytoplasmic mass
53
New cards
Mycelium
mass of hyphae
54
New cards
Members of domain _________ have a nucleus and other membrane bound organelles
Eukarya
55
New cards
What are the two main types of body structure?
single cells (yeasts) and multicellular filaments
56
New cards
Mycorrhizae
a mutualism between fungi and plant roots
57
New cards
Ectomycorrhizal
a symbiotic fungus that forms hyphae over plant roots
58
New cards
Arbuscules
specialized branching hyphae that penetrate plant cells for extraction or exchange of nutrients
(parasitic and mutalistic fungi)
(parasitic and mutalistic fungi)
59
New cards
What are the 4 types of fungi?
free-living, parasitic, mutualistic, and carnivorous
60
New cards
Spores are ___________
haploid
61
New cards
Spores can survive poor environmental conditions through _____________
Dormancy
62
New cards
Asexual reproduction is entirely ___________ ; uses mitosis
haploid
63
New cards
Molds
a fungus that grows as a filamentous fungi that produce spores by mitosis
64
New cards
Yeast are single celled and reproduce through ______________
budding
65
New cards
Cryptomycetes
unicellular fungi that have flaggelated spores
66
New cards
Microsporidan
unicellular parasites of protists and animals
(have a small genome and lack flagella)
(have a small genome and lack flagella)
67
New cards
Chytrids
mostly aquatic fungi with flagellated zoospores
(mostly unicellular; some form colonies with hyphae)
(mostly unicellular; some form colonies with hyphae)
68
New cards
Zoopagomycetes
multicellular parasites or commensal symbionts of animals
(includes a fungus that attacks insects and turns them into "zombies")
(includes a fungus that attacks insects and turns them into "zombies")
69
New cards
Mucoromycetes
Black Bread Mold (fast growing mold)
(contain arbuscular forming groups) - important in lichens and mycorrhizal networks of plants
(contain arbuscular forming groups) - important in lichens and mycorrhizal networks of plants
70
New cards
Ascomycetes
commonly called sac fungus
(have a symbiotic relationship with cynobacteria and other plants)
(have a symbiotic relationship with cynobacteria and other plants)
71
New cards
Basidomycetes
"Club Fungi" - includes most familiar fungi such as rust, mushrooms, and shelf fungi.
(only sexual reproduction)
(only sexual reproduction)
72
New cards
Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungus
a symbiont fungus whose hyphae grow through plant roots and into the root cell
73
New cards
Spores
in Fungi, a haploid cell, produced sexually or asexually that produces mycellium after germination
(produced in the sporophyte by meiosis)
(produced in the sporophyte by meiosis)
74
New cards
Plasmogamy
fusion of cytoplasm of cells (cells from 2 individuals)
75
New cards
Karyogamy
fusion of haploid nuclei contributed by two parents
76
New cards
Heterokaryon
A fungal mycelium that contains two or more haploid nuclei per cell.
77
New cards
Dikaryotic
a fungal mycellium with two haploid nuclei per cell (one from each parent)
78
New cards
The sexual processes of karyogamy and meiosis "generate extensive ______________ ______________"
Genetic Variation
79
New cards
Deuteromycete
traditional classification for a fungus with no known sexual stage
80
New cards
Sporopollenin
a durable polymer that prevents exposed zygotes from drying out
81
New cards
Cuticle
a covering for a plant made of wax and other polymers which provides protection
82
New cards
What does a Cuticle help do?
helps as waterproofing and prevents extensive water loss (desiccation)
83
New cards
Stomata
the small openings on the undersides of most leaves that allows gas exchange in and out of the plant
84
New cards
Vascular Tissue
cells joined into tubes that transport water and nutrients throughout the body
85
New cards
Liverworts, mosses, and hornworts don't have ____________ tissue
vascular
86
New cards
Bryophyte
an informal name for a moss, liverwort, or any non-vascular plant that lives on land
87
New cards
Lycophytes
club mosses and their relatives
88
New cards
Monilophytes
ferns and their relatives
89
New cards
Gymnosperms
a vascular plant that bears naked seeds
90
New cards
Angiosperms
A flowering plant which forms seeds inside a protective chamber called an ovary.
91
New cards
Microphylls
a small (spine shape leaf) supported by a singular strand of vascular tissue (found only in lycophytes)
92
New cards
Megaphylls
leaves with highly branches vascular system
93
New cards
What are the two types of vascular tissue?
xylem and phloem
94
New cards
Xylem
conducts the water and minerals
95
New cards
Phloem
cells arranged into tubes that distribute sugars, amino acids, and other organic products
96
New cards
Homospores
Plants that produce one type of spore
97
New cards
Heterospores
a plant species that has 2 types of spores
(microspores and megaspores)
(microspores and megaspores)
98
New cards
Megaspore
spores that develop into female gametophytes
99
New cards
Microspore
smaller spores that develop into male gametophytes
100
New cards
Integument
layer of sporophyte tissue that envelops and protects an ovule of a seed plant
Gymnosperms - one integument
Angiosperms - two integuments
Gymnosperms - one integument
Angiosperms - two integuments