GCSE Pearson Edexcel Separate Science Chemistry: Ionic and Covalent Structures
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
Simple covalent molecules
Molecules that contain only a few atoms held together by covalent bonds
Giant covalent structures
Contain many atoms held together by covalent bonds and arranged as a regular lattice
Intermolecular forces
The forces between molecules
Intramolecular forces
The forces inside a molecule, holding the atoms together
Polymer
A structure made of very large molecules, arranged in repeating patterns eg. plastics
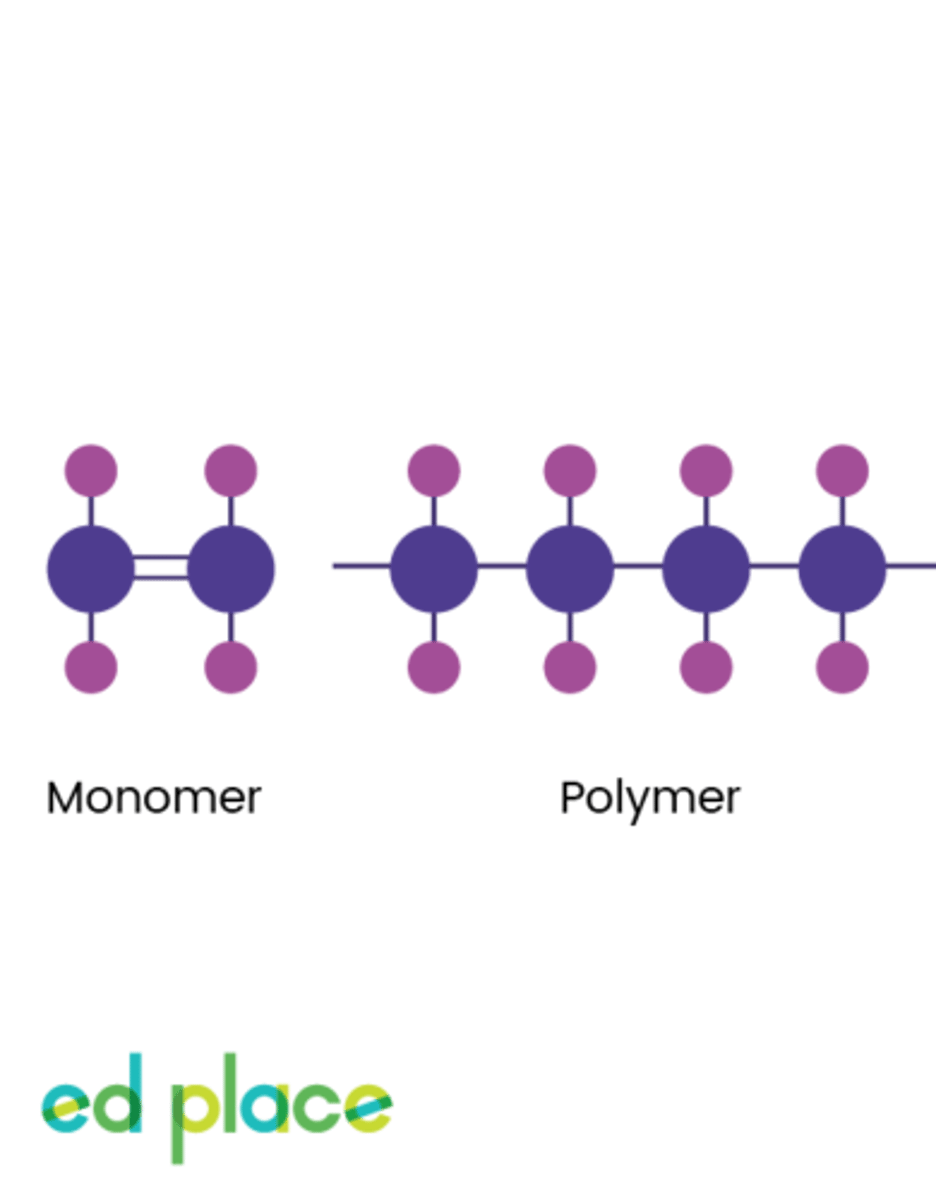
Monomer
A molecule that can be bonded to other identical molecules to form a polymer
Natural polymers
Polymers that occur in nature eg. DNA, proteins and cellulose
Addition polymers
Polymers that are formed from simple linking of monomers
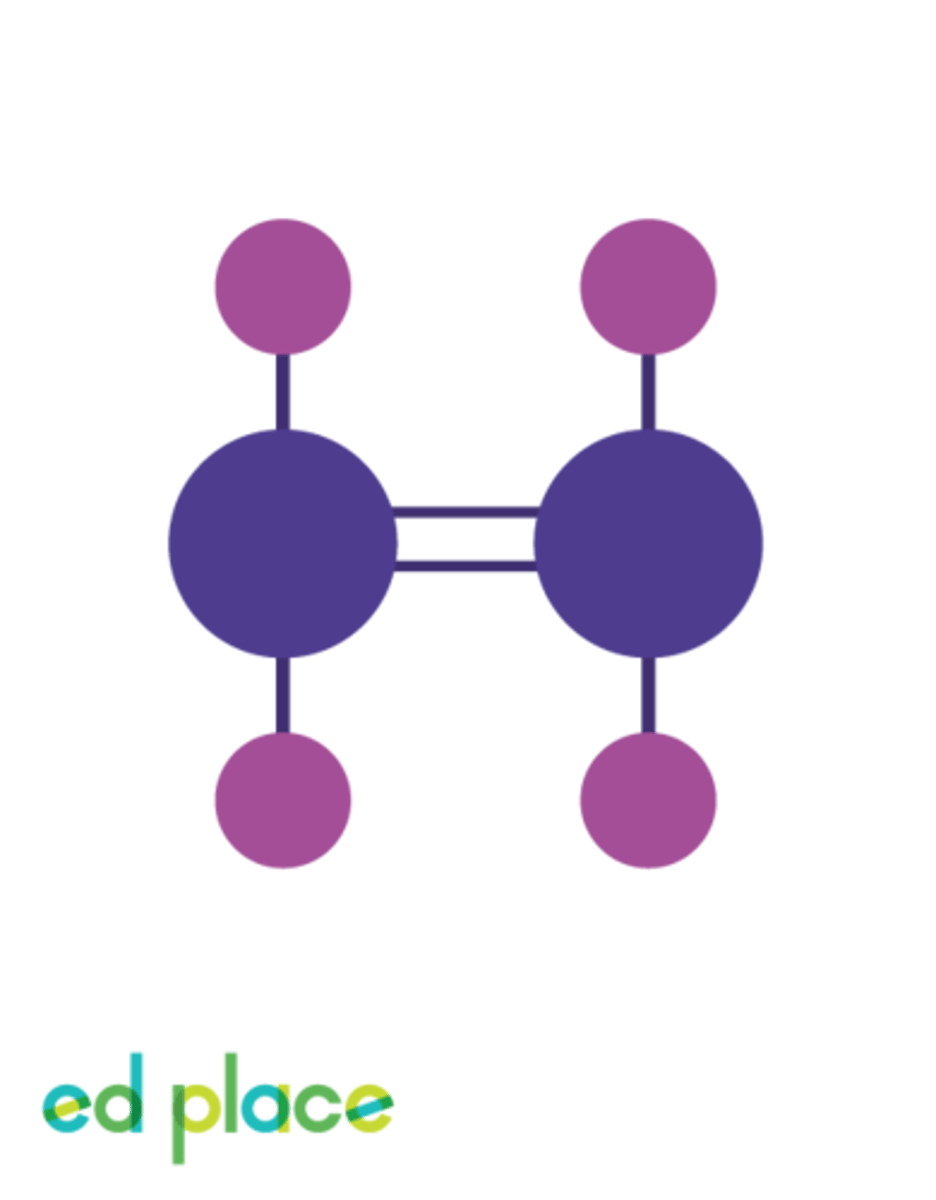
Displayed formula
A chemical formula showing all the bonds in the molecules as individual lines
Polymerisation
The reaction of monomer molecules to form long polymer chains
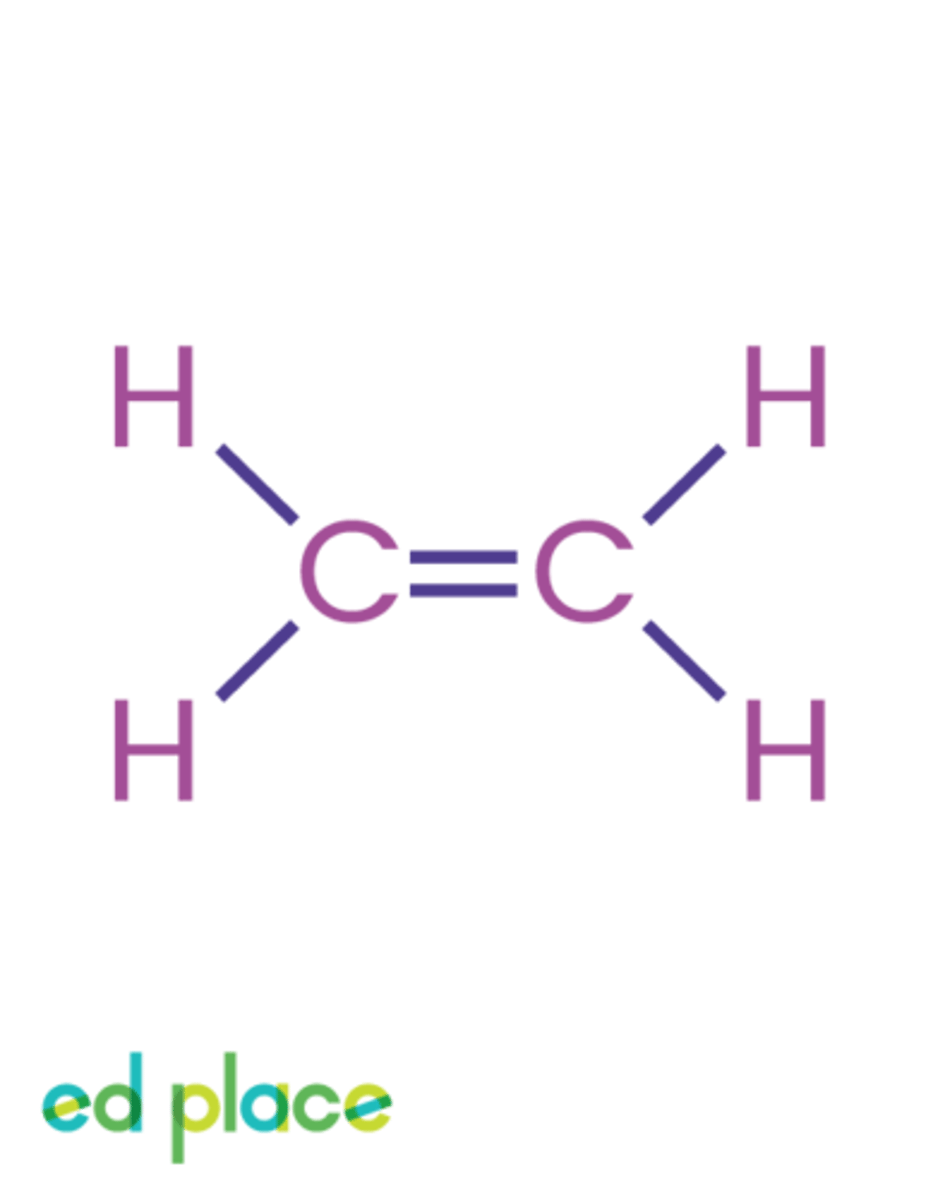
Alkene
A compound containing only carbon and hydrogen that contains a carbon-carbon double bond
Graphene
A form of carbon consisting of a single layer of atoms
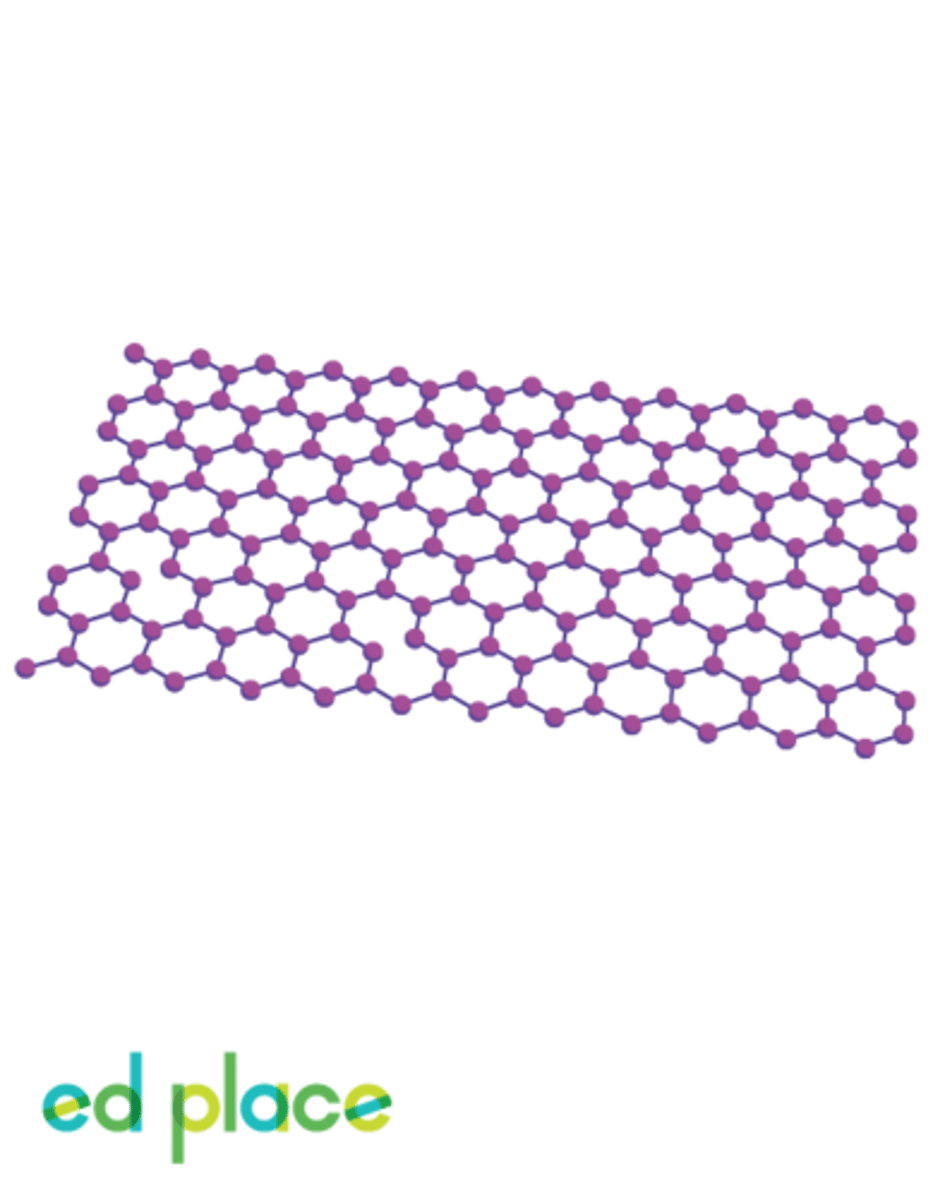
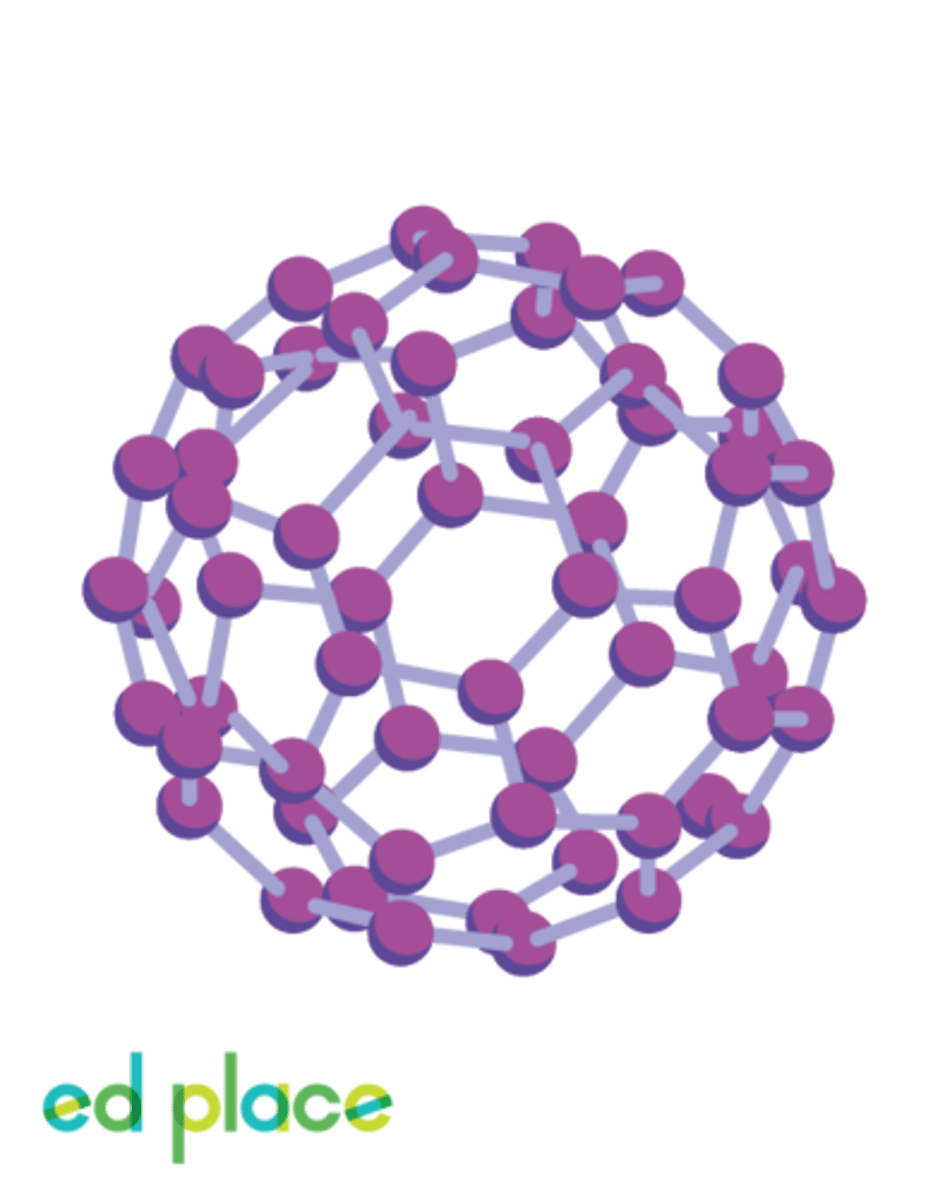
Fullerenes
A form of carbon with fused rings making a partially closed mesh
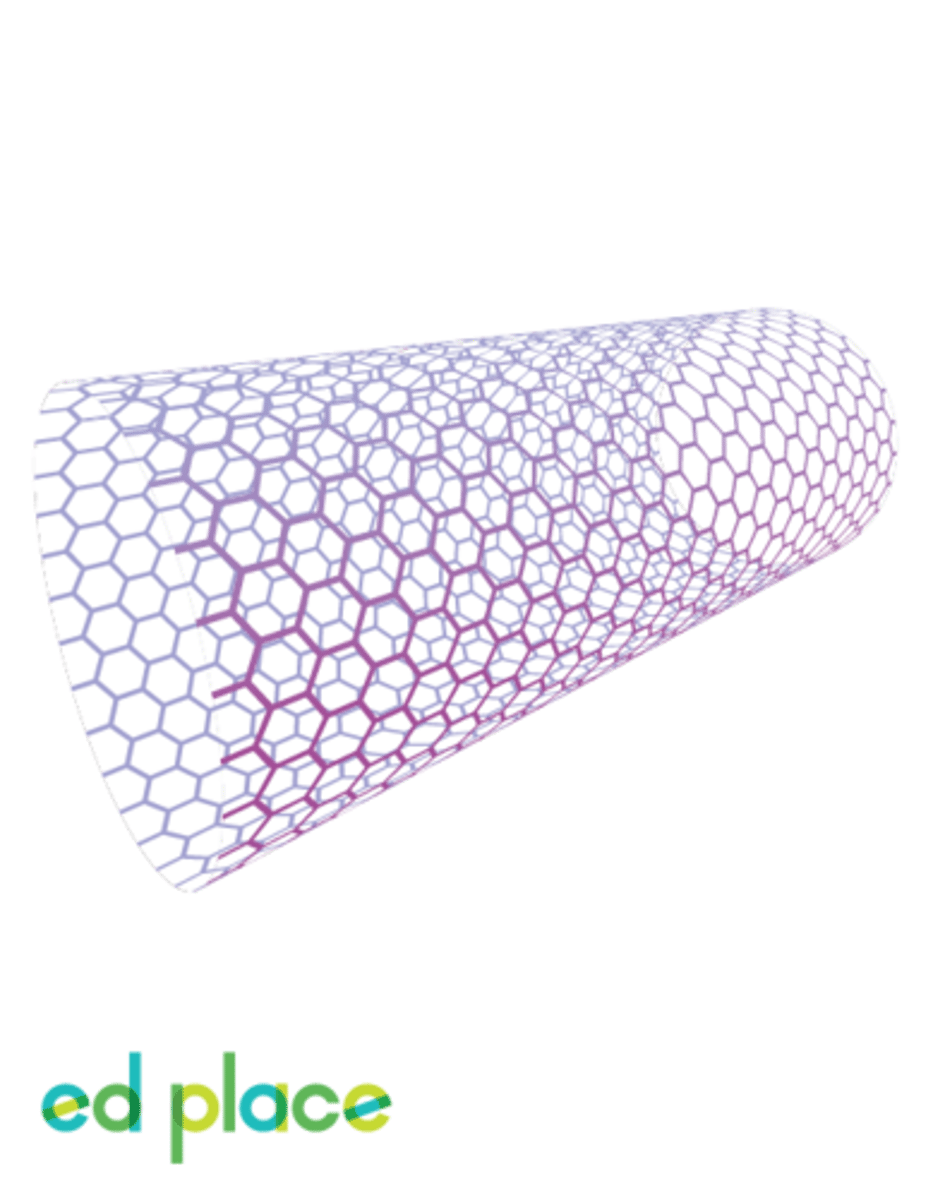
Nanotubes
Tube-shaped molecules made up of carbon atoms
Conductor
A material that allows the flow of electrical charge through it
Insulator
A material that does not allow the flow of electrical charge through it
Catalyst
A substance that speeds up a chemical reaction but is not used up by it
Biodegradable
Description of a substance that can be decomposed by bacteria or other living organisms
Delocalised
Description of an electron that is not fixed to a particular atom but is free to move about
Anisotropic
Description of a material that has different values when measured in different directions e.g graphite