Anatomy and Physiology Muscular System
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
Functions of Muscular System
Produce movement
locomotion of the whole body, facial expressions, circulation of blood, passage of food, etc.
Maintains posture
working against gravity to keep us upright
Stabilizes joints
reinforces the connection of bones
Generates heat
cellular respiration causes heat energy, allowing constant body temperature
Characteristics of muscular tissue
Excitability (the ability to respond to a stimulus from a motor neuron to a hormone)
Contractibility (the ability to shorten when stimulated)
Extensibility (the ability to lengthen or stretch, even past their original shape)
Elasticity (the ability to recoil or bounce back to the original shape and length after being stretched)
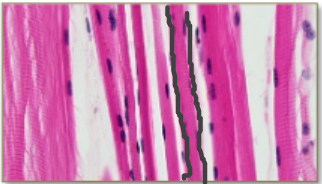
Skeletal Muscle
Cylindrical
Striated (stripes)
Multinucleated
Voluntarily contracted
Contracts slowly or very quickly
Connected to bones
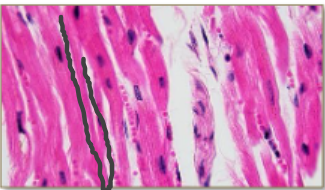
Cardiac Muscle
Branched
Striated
Uninucleated
Involuntarily contracted
Mostly slow and steady contractions except during short periods of activity
Found in heart muscle
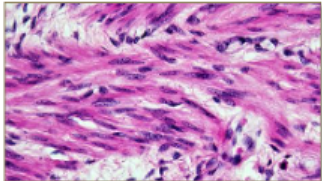
Smooth Muscle
Uniform layers
Nonstriated
Uninucleated
Involuntary contractions
Slow contractions, long periods of time (for digestion, etc)
Found in walls of internal organs (stomach)
Skeletal Muscle Basics
Attach to bones and skin of face
Voluntary
Organ of muscular system
Skeletal Muscle Composition
Skeletal muscle tissue
Nervous tissue
Blood
Connective tissue
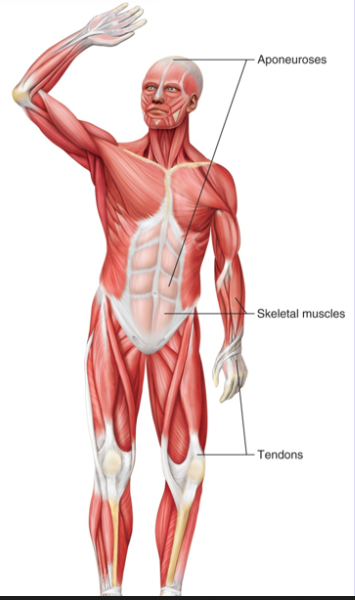
Coverings on Skeletal Muscle
Fascia (a type of dense connective tissue that may project beyond the ends of its muscle fibers, which form tendons)
Tendons (connect muscle to bone)
Aponeurosis (type of fascia)
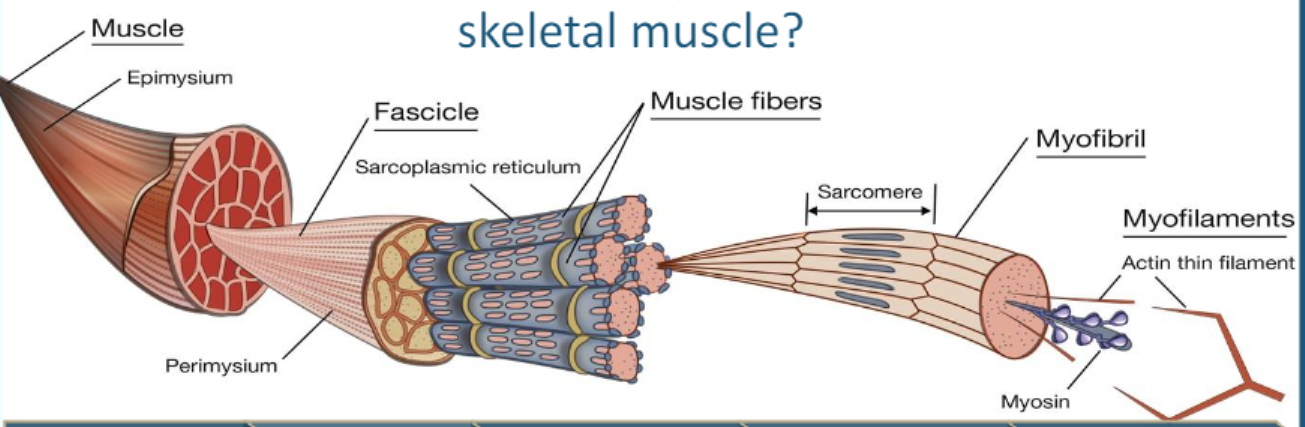
Microscopic Structure of Muscle Order (least complex —> most complex)
Myofilament —> Myofibril —> Muscle Fiber —> Fascicle —> Muscle
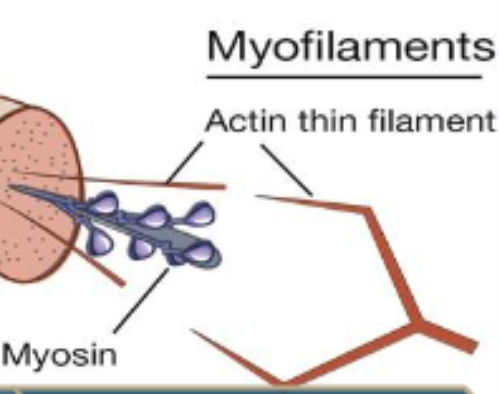
Myofilaments
2 types
Actin (thin) and myosin (thick)
Make up sliding filament theory
Responsible for contracting activity of muscle fiber
Located intracellularly
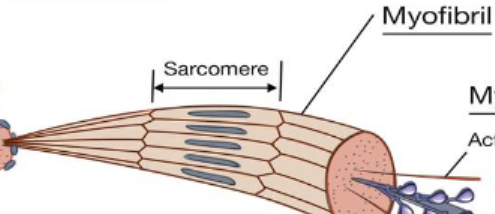
Myofibril
Thread-like organelles of the muscle fibers
Structured in long, striated units called sarcomeres
Located intracellularly
Overlapping parallel groups of thick and thin filaments in a repeating pattern; the underlying basis for the striation pattern
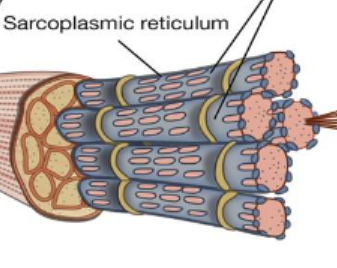
Muscle Fiber
Long, thin muscle cells
Each cell is covered by endomysium
Sarcoplasmic reticulum supplies Ca2+ ions to disable tropomyosin/troponin complex
A single muscle cell, multinucleated and may be many centimeters long
Within a muscle, surrounded by a layer of connective tissue called endomysium
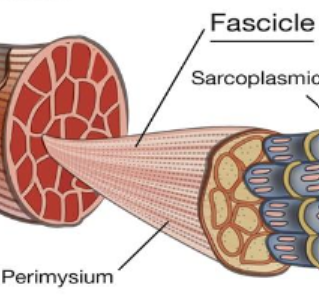
Fascicle
Bundles within muscles
Within a muscle, surrounded by a layer of connective tissue called perimysium
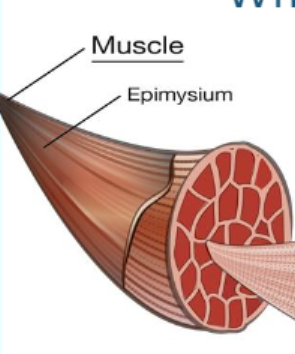
Muscle
Skeletal Muscle is attached to bone by tendons and is made of many bundles of muscle fibers
Surrounded by a layer of connective tissue called epimysium and in some cases an additional layer called muscle fascia
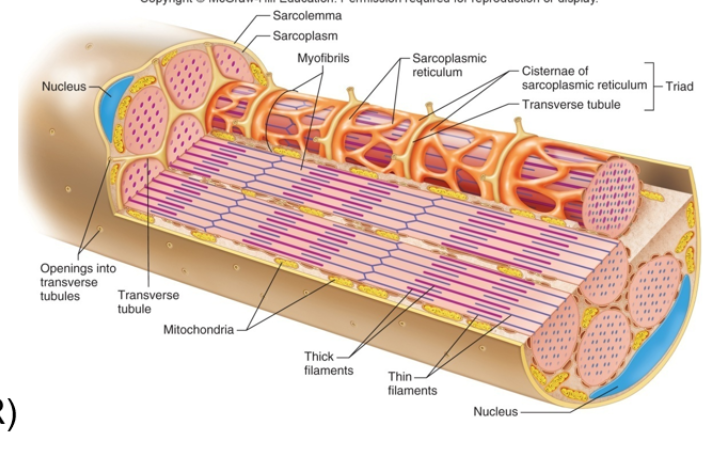
Skeletal Muscle Fibers Characteristics
Also called muscle cell
Multinucleated
Sarcolemma (the muscle cell membrane)
Sarcoplasm (muscle cell cytoplasm)
Has many myofibrils (contain thin actin and thick myosin)
Has sarcomeres (the muscle unit of contraction and relaxation)
Has the sarcoplasmic reticulum (storage of calcium ions and plays a role in relaxation and contraction)
Has the Transverse (T) Tubule (extension of skeletal and cardiac cell membranes)
Striation Pattern
Developed by arrangements of myofilaments in myofibrils
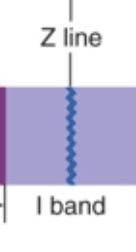
I Band
Light bands
Contain Actin
Held together by direct attachments to structures called Z lines (center of I bands)
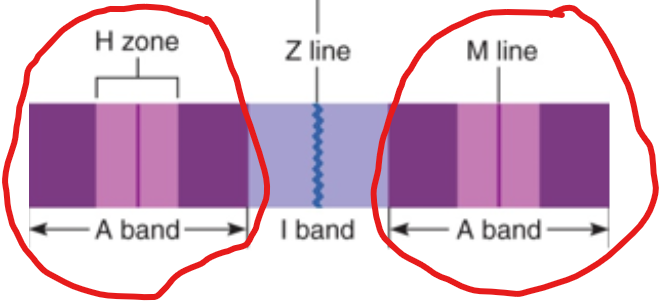
A band
Dark band
Composed of thick myosin filaments overlapping thin actin filaments
Contains an H zone consisting of only myosin filaments
The thickened part is called the M line that consists of proteins that help hold myosin in place.
Myosin filaments are also held in place by the Z lines and are attached to them by a large protein called titin (connectin).
Protection of Muscle Fibers
Epimysium (covers the whole muscle) —> Perimysium (covers a fascicle) —> Endomysium (covers an individual muscle fiber)
Having these membranes allow them to slide without bursting during contractions.
Myasthenia Gravis (MG)
Autoimmune disorder
Antibodies attack acetylcholine receptors on skeletal muscle fibers (specifically motor end plates = a chemical synapse between the terminal part of the motor neuron and the target muscle) in neuromuscular junctions
1/3 ACh receptors
Widespread muscle weakness and fatigue
Use drugs that inhibit acetylcholinesterase
Immunosuppressant Drugs
Administer antibodies that inhibit harmful ones
Plasma exchange