BICD 110 midterm 1
1/181
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
182 Terms
LECA
last eukaryote common ancestor
1.5-2 billion years ago
mechanistic cell biology
biochemistry, cell biology, molecular biology/genetics
golden age of cell bio as a prerequisite to understand disease
discovery of cells
problem of scale thru developing tech
electron microscope increased scale and resolution
Hooke
discovered plant cells
created compound microscope, 50x magnification into visible light (photons)
saw cells in cork micrograph drawing
Leeuwenhoek
discovered microorganisms (protists, bacteria), RB cells, cell theory
created single lens microscope, 200-300x magnification
saw mobile animacules in gum swabs
Schleiden
every part of plant is made up of cells
cells made from crystallization process
Schwann
plants and animals are composed of cells and their products
Virchow
all living organisms compared of one or more cells
cell is basic life unit
all cells arise from pre-existing cells
Brown and Flemming
using brown stains, they discovered nucleus, chromosomes, different stages of cell division
black reaction
staining in neurons allowed Golgi to find Golgi apparatus
modern light microscope
advanced optics, only limited by 100 nm resolution of light and advanced contrasting methods
DIC: differential interference contrast (destructive vs constructive interference of shifting light waves)
electron microscopy
superior resolution
much smaller wavelength than photons (2000 A) for high resolution
different types of electron microscopy
TEM, SEM, cryo-EM
TEM
transmission electron microscopy, shine electrons thru sample
thin samples: stained with heavy metals that refract electrons, metal binds to proteins and membranes
thick samples: fixed and dehydrated with heavy metals
SEM
scanning electron microscopy
surface of sample is metal shadowed
cryo-EM
cryogenic electron microscopy
unstained samples frozen, leads to non-crystalline ice
high sensitivity without metal, still measures direct e- interact
can also measure tomography of cells: 3D computer reconstructions
Palade
changed field of cell biology
thru his images of the cell that we’re still attempting to understand under mechanistic biology
different components of mechanistic cell bio?
biochemistry: modification, manufacture
cell bio: anatomy, behavior
molecular bio / genetics: inventory, hierarchy
identification and localization in organism of interest
some organisms (ex jellyfish) produce fluorescent proteins (FPs) that can be fused to gene of interest
prod recombinant fluorescent protein to be expressed in organism / cell line of interest
lower wavelength = more photon energy, purple on color spectrum
different strategies to deliver recombinant DNA to cells
transfection / transduction of cells results in expression of ectopical protein (out of place, ex: myosin w GFP)
over expression of protein (endogenous + exogenous protein ) (normal vs foreign to cell)
fluorescence microscopy
can visualize with GFPs where different compartments in a cell are spatially organized in their proteins
immunolabeling
use of antibodies to detect specific protein
generate antibodies to specific protein of interest: antibodies produced in response to infection
antibodies generated by injecting a model animal with antigen (interest) OR antibodies from a cell line (monoclonal antibodies) to be purified
immunolabeling process
immobilized antigen A of mouse
antigen injected in rabbit, produces primary antibody against antigen A, binds to protein of tissue
secondary antibodies, marker-coupled with GFP against rabbit antibodies, locates protein to amplify and visualize
brightens image to be visualized
parameters for immunolabeling
fixed with fixative such as formaldehyde or glutaraldehyde, to cross-link amino groups onto molecules. tissue embedded in paraffin for sectioning
permeabilized with non-ionic detergent to make plasma membrane permeable to reagents (ex: antibodies), dead tissue fixed in time
stained with marker (FPs) to covalently attach to specific antibodies with heavy metals (like gold) that create contrast. small fluorescent dyes can also bind to membranes or DNA
confocal microscopy to improve resolution
increases resolution by filtering out focus light
capture thinner focal plane using a pin hole
allows a larger imaged volume
4 key concepts of chemistry
molecular complementarity: mcs are 3D and interact in space / chemically, + - reactions
polymerization: from nucleotides to macromolecule DNA
chemical equilibrium: reversible reactions, dif temps, form / break bonds
energy: high energy bonds in ATP
energies of covalent bonds and noncovalent interactions
bond strength / energy is energy required to break / make bonds
covalent bonds are stronger and stable than noncovalent interactions (C=C > van den waals)
multiple noncovalent interactions combine to form strong associations
weaker when bond energy is close to thermal E, KB (van der waals, H bonds)
noncovalent interactions
additive to increase stability
binding disassociation constant Kd is a measure of affinity
conformational selectivity
induced fit: binding of one molecule changes conformation (3D structure) of other, increases molecular complementarity
Kd
low Kd means lower amount (concentration, M) for binding partner to form interaction
lower Kd = stronger interaction
hydrophobic effect
association depends on solvation, H2O
H2O is 70% of cell mass
driven by thermodynamics, increase entropy / disorder and decrease total surface area
macromolecules
chemical building blocks
universal building blocks polymerize / assemble to form essential macromolecules
goal is to understand how chemical properties give rise to macromolecule function
HOH present in all
lipids
amphipathic
hydrophilic head
hydrophobic fatty acyl tails
= makes phospholipid
proteins
monomers - amino acid
polymers - peptide bonds to form polypeptide
nucleic acids
nucleotides make nucleic acids with phosphodiester bonds
carbohydrates
monosaccharides and polysaccharides formed from glycosidic bonds
emergent properties of macromolecules
property that an individual subunit does not have, but arises from collective/complex system
RNA world theory
most ancient bio mc
starts from nucleotides to form a short to long oligomer pool
folding and emergence of ribozymes, catalytically active RNA
how to build a cell
step 1: creating a barrier
cell barrier functions
separates in and out (endogenous and exogenous)
interior biochemical environment can differ from the exterior
protection of endogenous macromolecules and processes from outside
allows to catalyze certain rxns that wouldn’t happen spontaneously
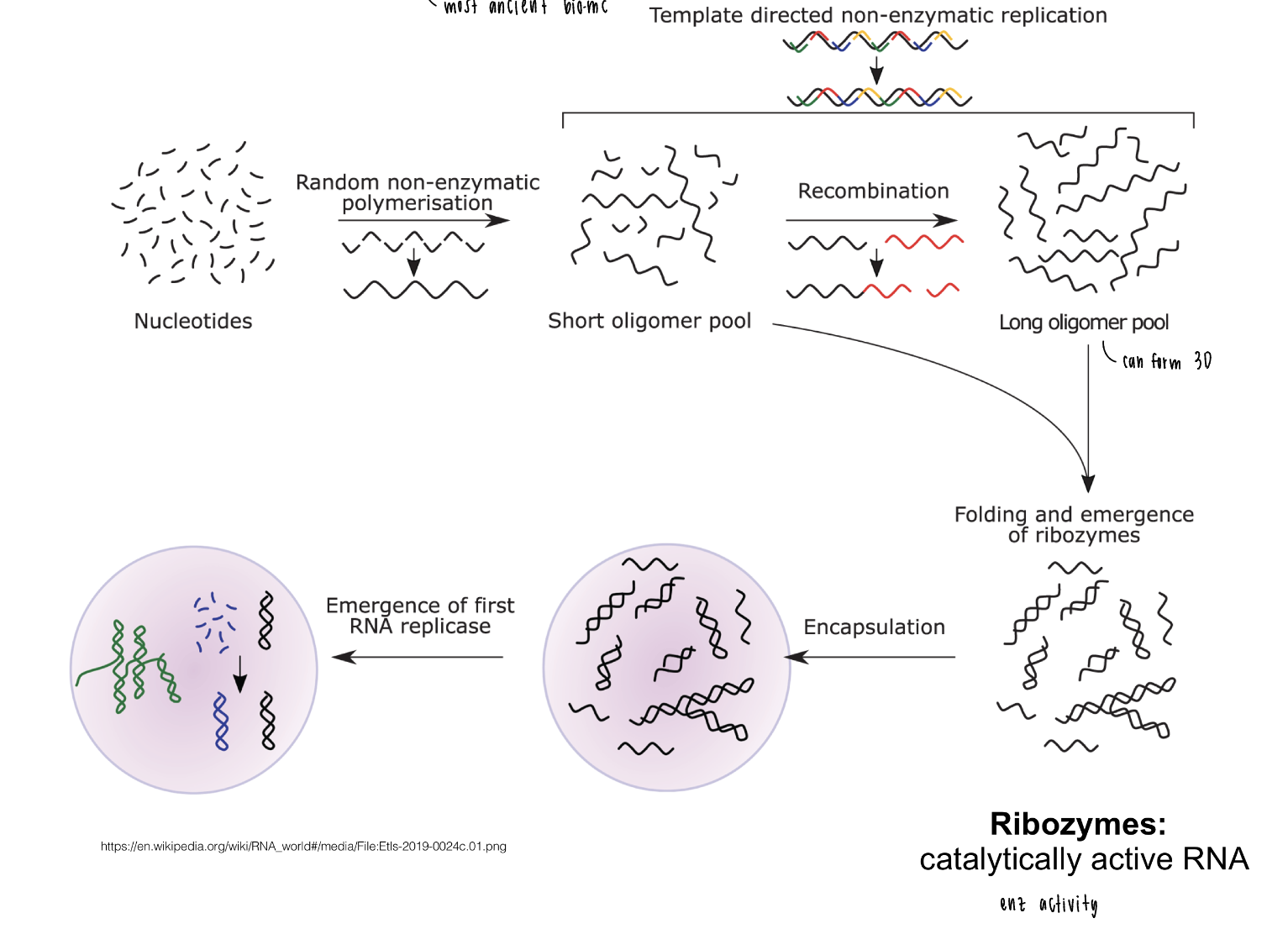
bilayer structure advantages
self assembly: driven by hydrophobic effect, 2 phospholipids tg
fluidity: lipids can move into bilayer plane
barrier is semi permeable
molecular shape of membranes
geometry matters
micelle: cone shape of molecule, packs into single layer
lipid bilayer: cylindrical, packs into bilayer
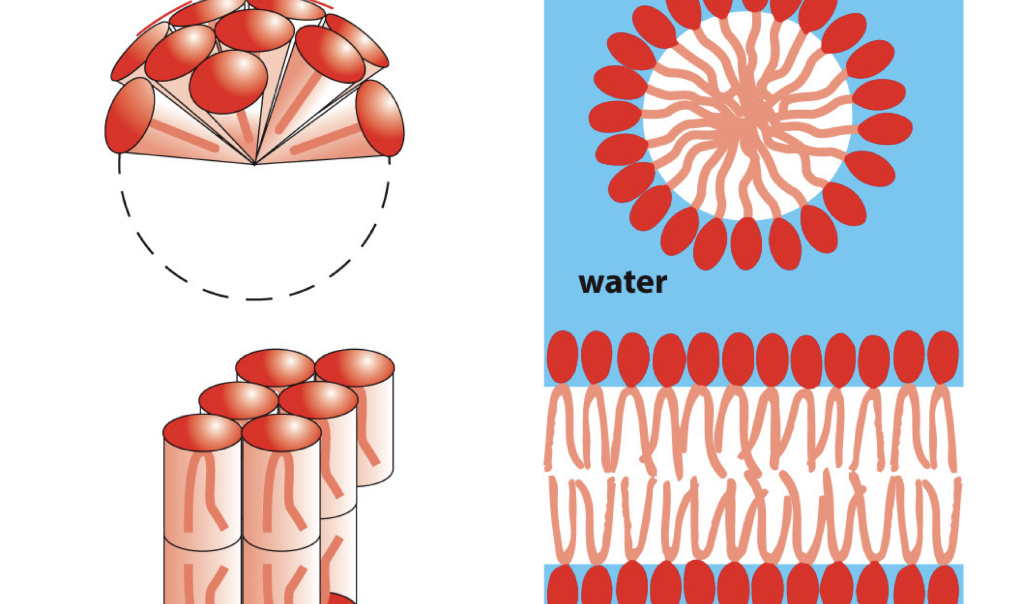
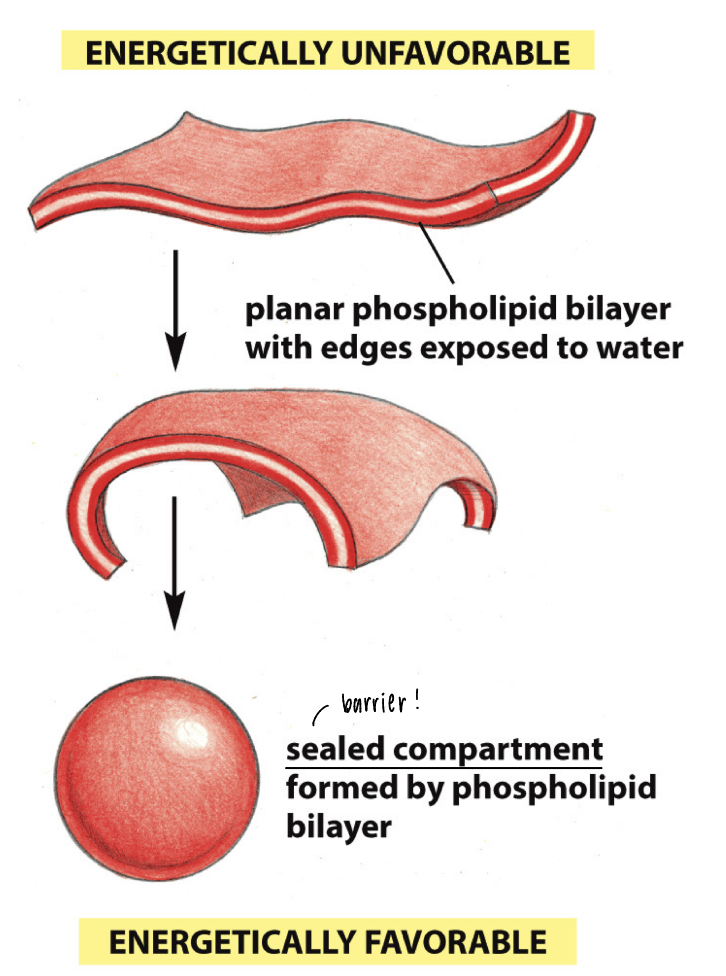
bilayer compartments
thermodynamically prone to form
energetically unfavorable: planar phospholipid bilayer has edges exposed to H2O
energetically favorable: sealed compartment of a barrier
bilayer fluidity
controlled by temperature
gel like to fluid like by adding heat
melting temperature Tm = temp at which 50% of lipids are fluid
fatty acid composition
control of bilayer fluidity
C=C bonds aren’t rotatable, cis bond (most naturally occurring) introduces rigid kink that prevents tight packing into bilayer
cis > trans via artificial desaturation processes can make trans fats
trans fats are unsaturated and more fluid, ways to modulate
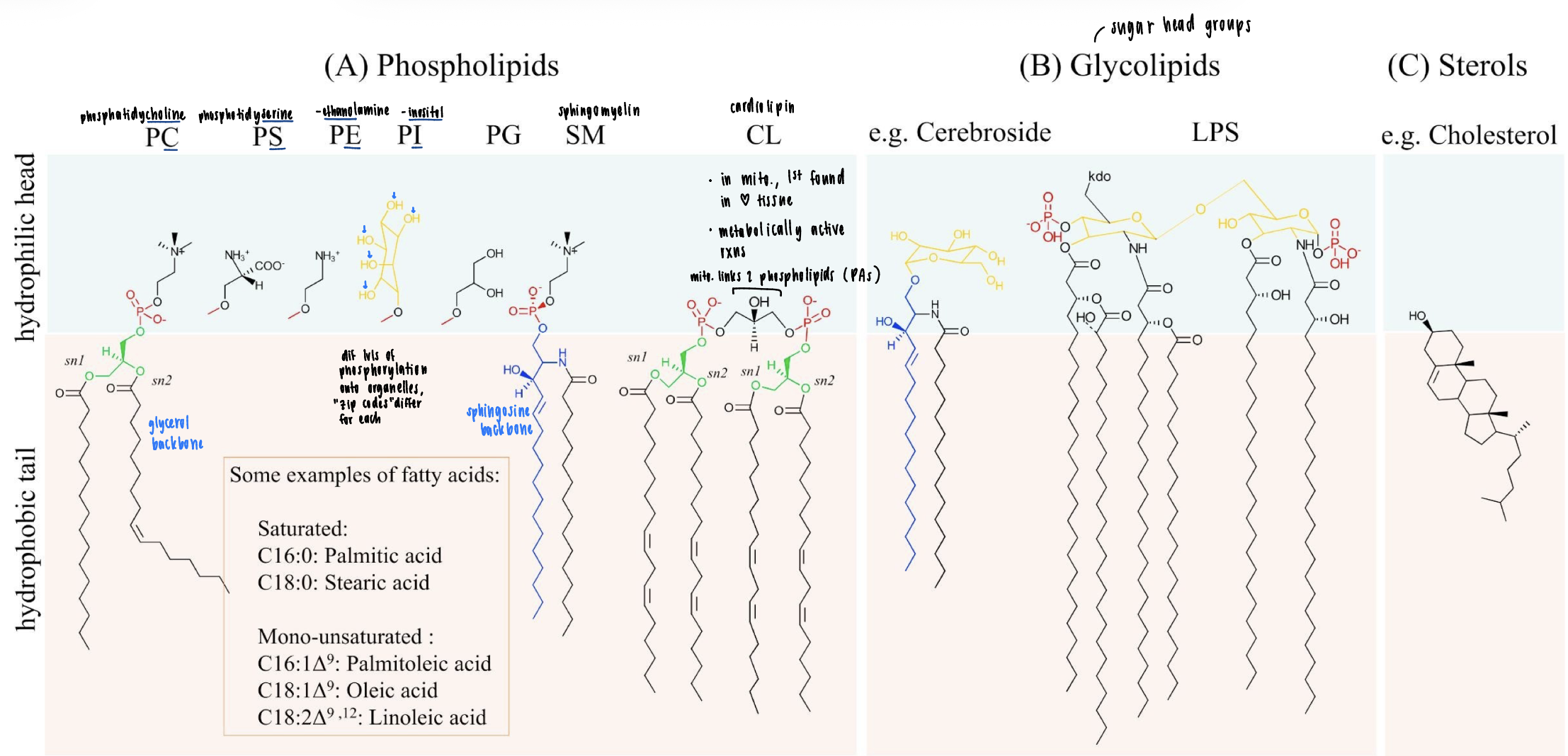
membrane lipid diversity
three groups: phosholipids (phospholipid head group), glycolipids (sugar heads), sterols (cholesterol
know the names and general features
homeoviscous adaptation
cells dynamically change their membrane lipid composition to control membrane fluidity
VdW forces btwn lipid tails determine fluidity
decreasing transition temp: unsaturated bonds (kinks), shorter acyl chains (less tail interaction)
increasing transition temp: saturated bonds (straight tails = packing), longer acyl chains (more VdW interactions)
cholesterol
special fluidity regulator
lowers membrane permeability (tight acyl chain packing)
adjusts membrane fluidity:
low temp - increase fluidity (prevents tight acyl chain packing, ex: decreasing butter solidifying)
high temp - decreases fluidity (rigid structure, ex: increase butter melting)
both are present at all temps, but dominating in dif temp ranges
polymers of amino acids
unbranched polymers: out of 20 AA, R side chains
side chains determine properties
polypeptide: linear polymer has free amino end and carboxyl end
protein function: derived from 3D structure, AA sequence and intramolecular noncovalent interactions
special amino acids
cysteine, glycine, proline
cysteine
can form disulfide bonds
-SH SH- to -S-S-
glycine
only has a proton as a side chain
allows for tight packing within polypeptide and facilitates interactions
proline
cyclized side chain
introduces kinks that can undergo cis-trans isomerization
phosphorylation of AA side chains
most abundant post-translational protein modification in eukaryotes
kinases catalyze transfer of phosphoryl group to AA side chain from ATP
reverse rxn: dephosphorylation, phosphatases
major eukaryotic phosphorylation sites: Ser, Thr, Tyr with an OH
prokaryote phosphorylation: on His, Glu, Asp
functions: enz regulation, protein-protein interactions, signaling networks, cell cycle
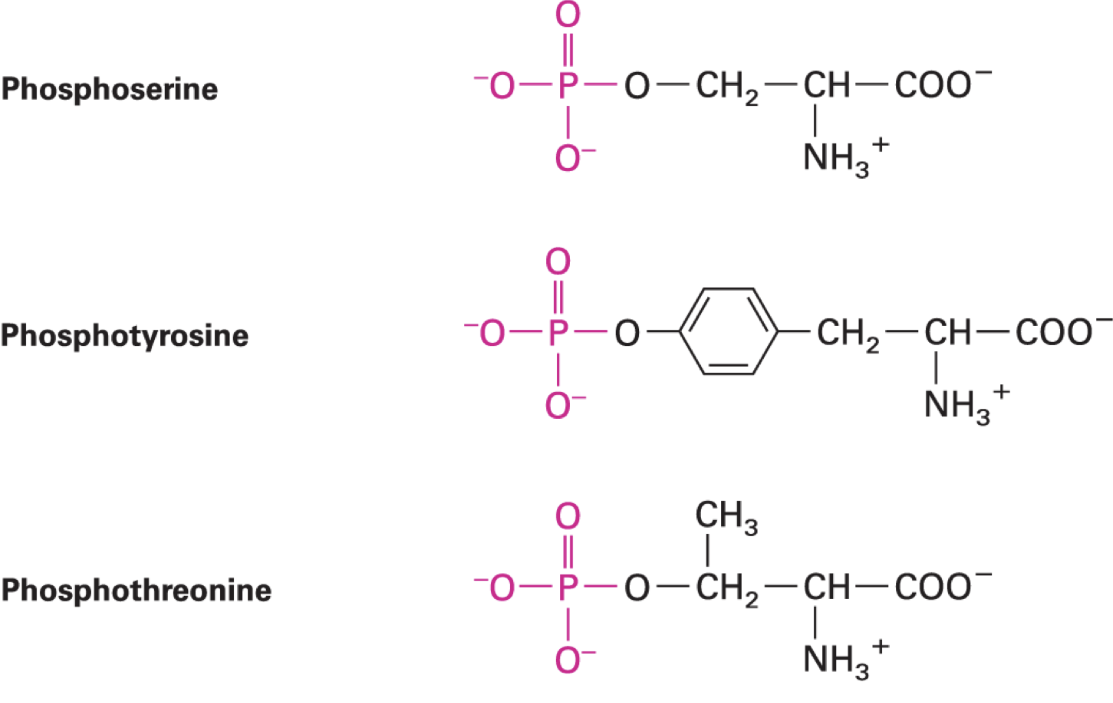
acetyl lysine
epigenetic control
cytoskeleton dynamics
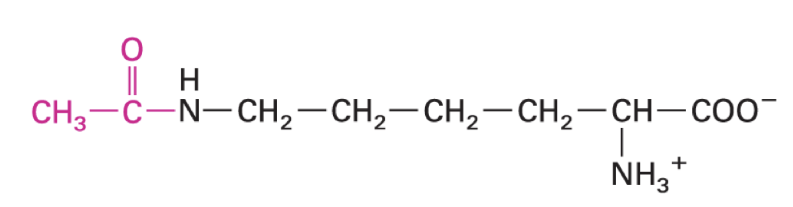
3-hydroxyproline
cross linking of collagens for stability
requires vitamin C
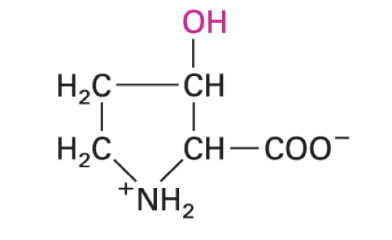
3-methylhistidine
molecular function largely unknown
urinary excretion index of muscle protein breakdown
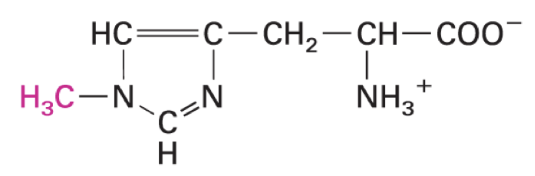
gamma-carboxylglutamate
high affinity binding of Ca ions
enriches in GLA domains like coagulation factors
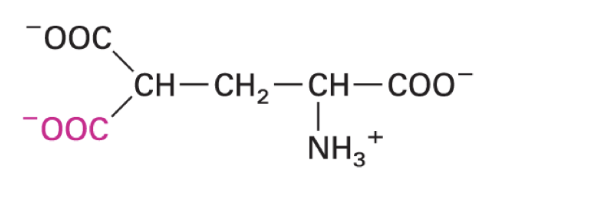
O-GlcNAc-threonine
placeholder for S/T phosphorylation sites
preference for intrinsically disordered domains with defects that impact cellular processes
proteins in human genome
20000 to 23000 protein encoding genes thru alternative splicing of mRNAs + post translational mods for distinct protein activities
protein hierarchical structure
primary: linear seq of AA linked by peptide bonds
secondary: local A helixes / beta sheets
tertiary: 3D peptide shape with a / B
quaternary: btwn multipeptide complexes
supramolecular complexes: very large, consisting of tens to hundreds of subunits
protein structure
protein seq specifies folding into secondary / tertiary structures that are functional units OR interact with other peptides to form quaternary units
intrinsically disordered proteins (w/o 3D structure) have conformational flexibilities for multiple functions
polypeptides with dissimilar seq can also fold into similar 3D-structures
homologous proteins evolved from a common ancestor
protein functions
structure: organizing genome, organelles, cytoplasm, protein, etc in 3D space
regulation: control protein activity
signaling: monitor enviro and transmit info
transport: move small mc and ions across membranes
enz activity
motors: generating force for movement, ex: myosin
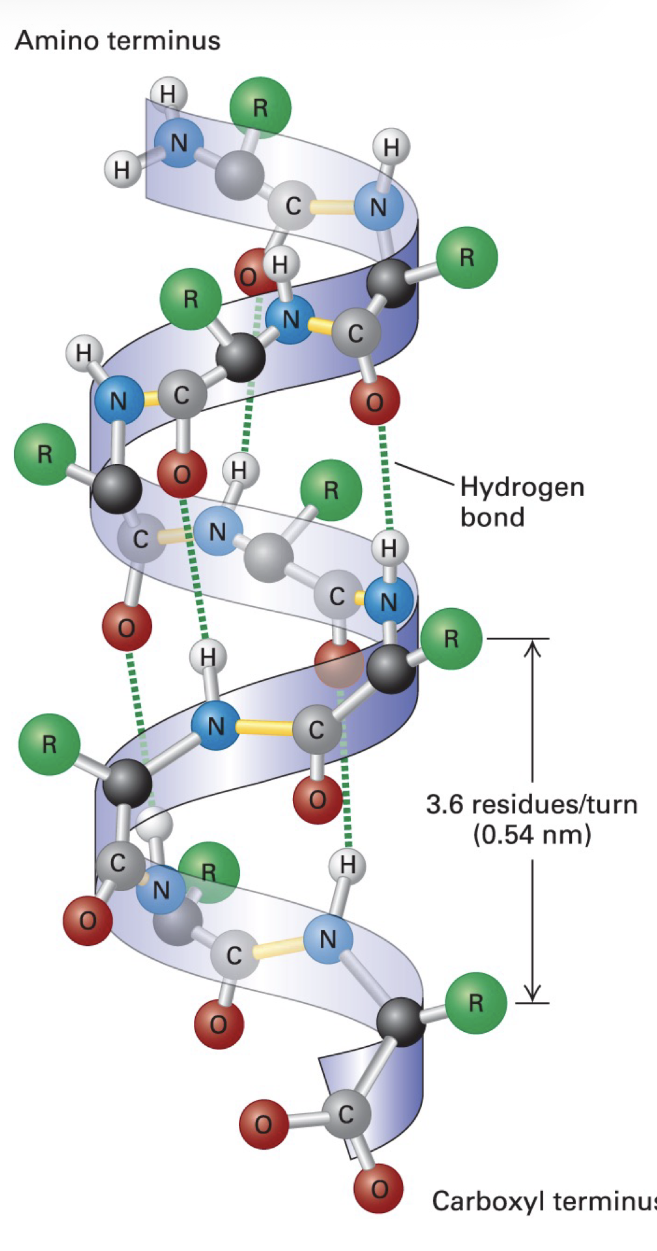
a-helix
secondary structure
stable arrangements of polypeptide chain (held together by backbone H bonds)
3.6 AA per turn
R groups project outward from surface of helix
prolines can’t participate in H bonding, excluded in helix
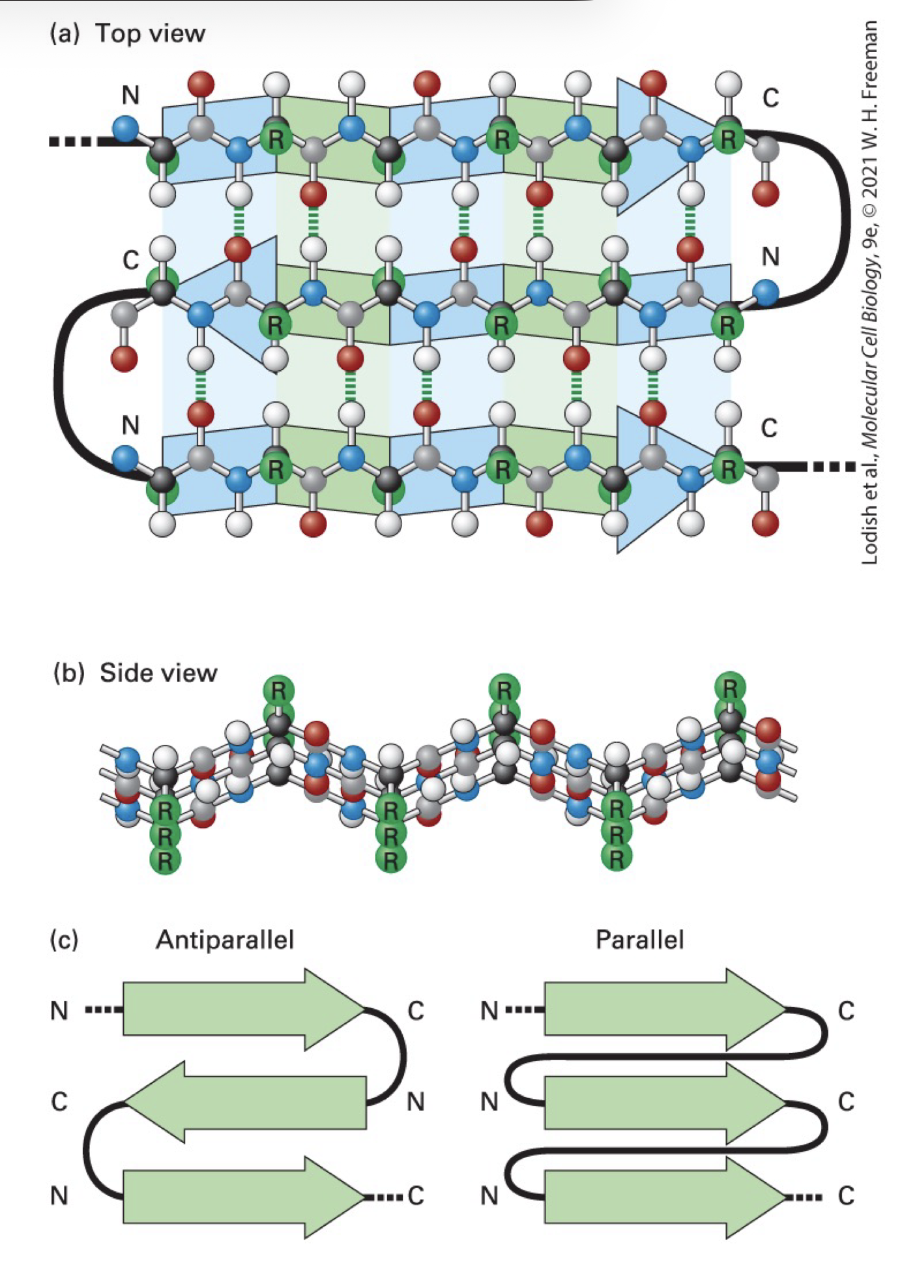
B-sheet
three stranded B sheet: antiparallel stands with connecting loops stabilized by H bonds btwn O and H atoms of AA on dif strands
a carbon bond angles prod pleated polypeptide backbone contour
alternative R groups project above and below plane of sheet
parallel B strand sheet: same N-to-C strand orientations with connecting loops
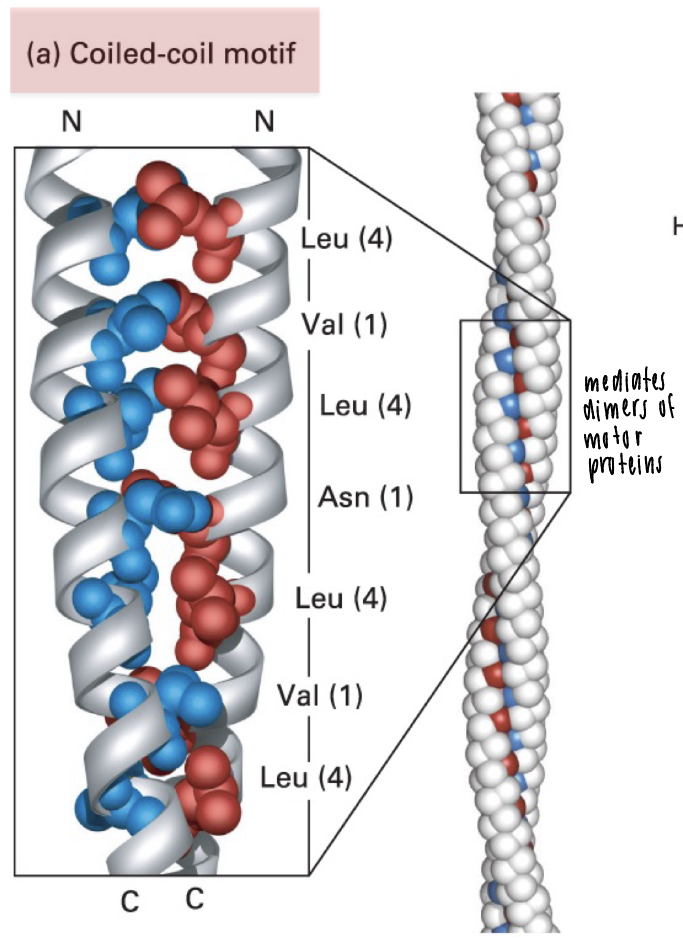
coiled-coil motif
two-a helices wound around each other
a-helix-heptad repeat seq with hydrophobic residue at positions 1 and 4
ex: motor proteins are mediated by coiled-coil formation to form stable dimers
oil drop model of protein folding
in tertiary structures
unfolded protein is folded to bury hydrophobic residues to the core
expose hydrophilic residues to surrounding aqueous environment
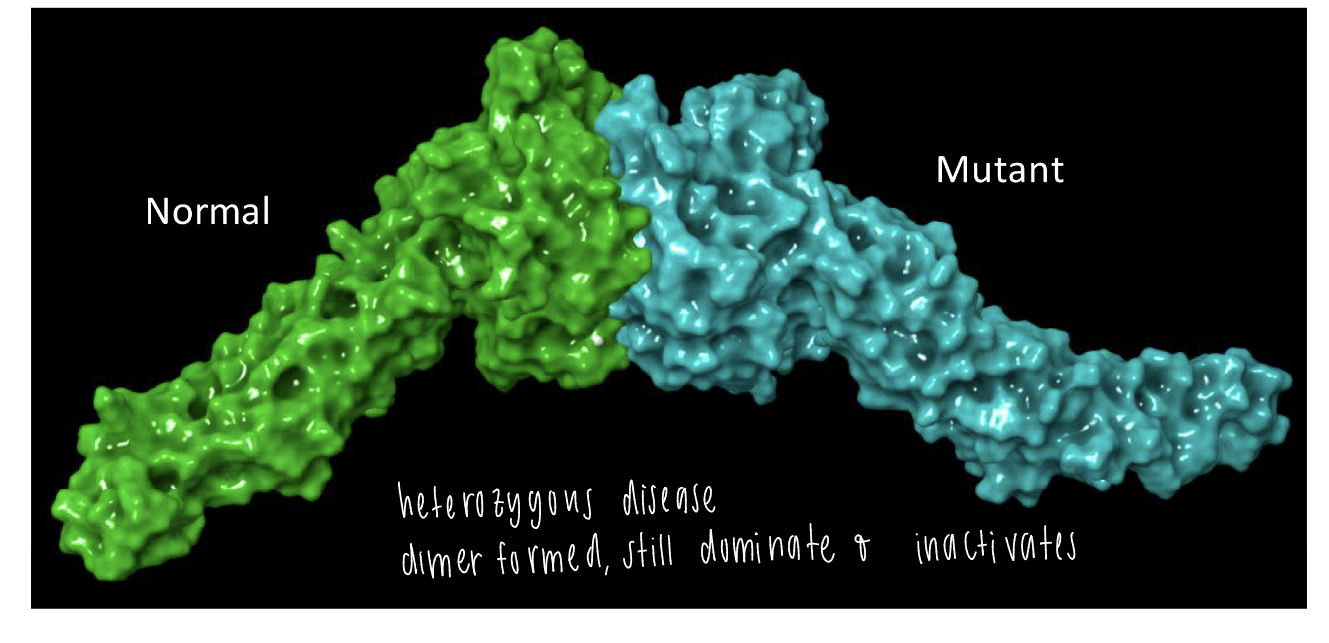
mitofusion 2
quaternary structure
heterozygous disease caused by a dimer formed btwn normal and mutant structure
mutant structure dominates and inactivates
complexity of eukaryotic cells
much larger than prokaryotic cells, “bag of bags”
eukaryotic cells have endomembrane system comprised of membrane-enclosed compartments (=organelles)
strong diversification of cell function, needed in a specific enviro
cytosol
matrix / fluid around organelles
cytoplasm
matrix including the organelles EXCEPT the nucleus
animal cell membrane compartments
ER (endoplasmic reticulum)
ER-Golgi intermediate compartment (ERGIC)
golgi apparatus
trans-golgi network (TGN)
plasma membrane (PM)
endo-lysosomal system
nucleus
mitochondria
lipid droplets (LD)
peroxisomes
animals vs plant cells
microvilli in animal cells increase SA for absorption of nutrients
cell wall (made of cellulose) maintains cell shape and protects against stress
vacuole (plant) maintains turgor osmotic pressure
chloroplasts for photosynthesis
plasmodesmata: for membrane transport, connect cytoplasms of adjacent plant cells
amount of lipid layers in membrane compartments
single bilayer: ER, ERGIC, golgi, TGN, PM, lysosomes, peroxisomes
two bilayers: mitochondria / chloroplasts, nucleus
monolayer: lipid droplets
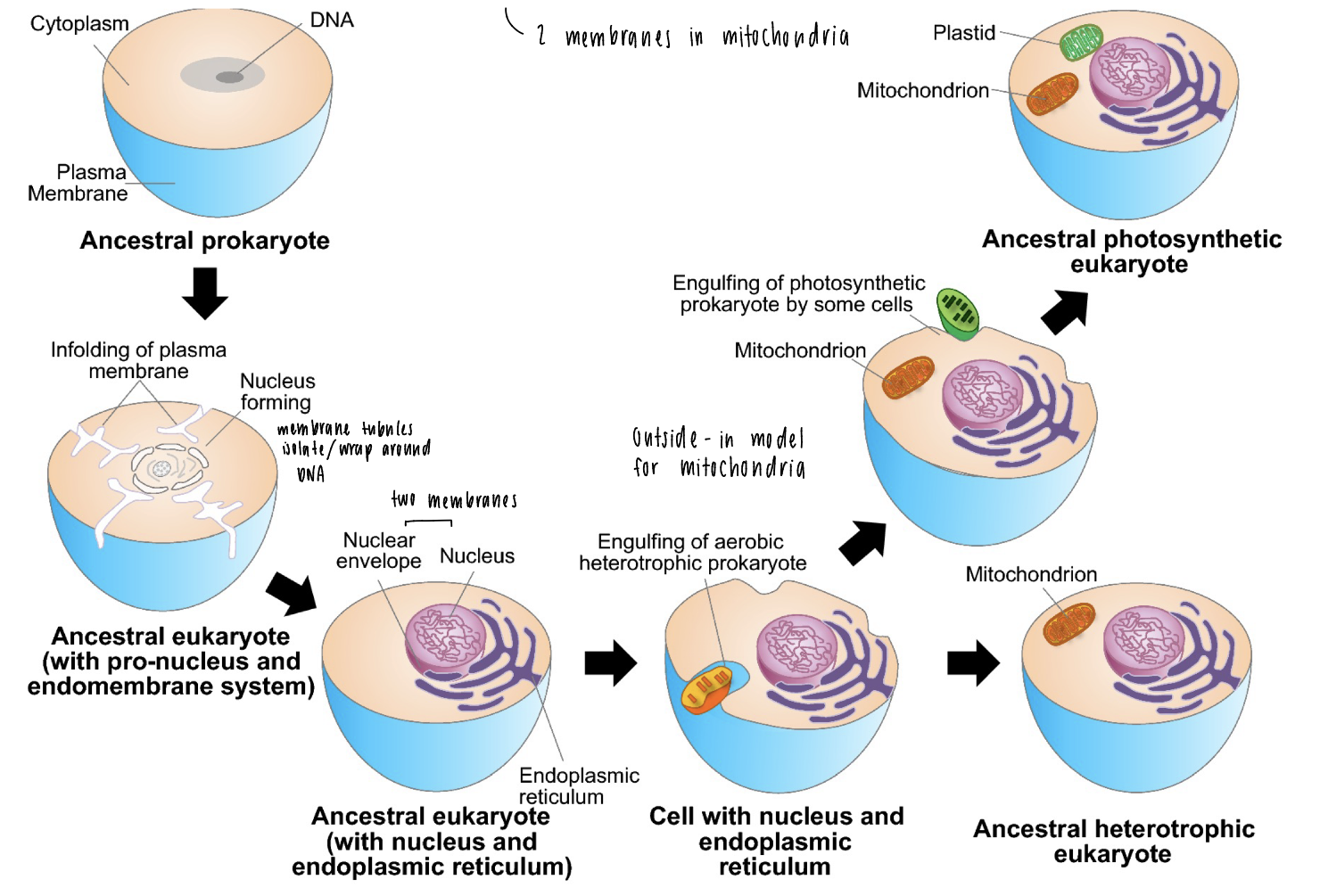
classical endosymbiosis
possible evolutionary scenario for origin of eukaryotic cells
ancestral prokaryote
membrane tubules isolate / wrap around DNA with a single membrane
nuclear envelope around DNA + nucleus makes two bilayers
“outside in” model for mitochondria, mitochondria engulfed by outer membrane = two membranes
inside-out evolutionary theory
different components are exchanges over time, fuse into each other for a gradual growth of membrane structures
lumen (including ER) is topologically equivalent to endomembrane
archaeal cells (ancient) have blebs that trap bacterial symbionts (like mitochondria)
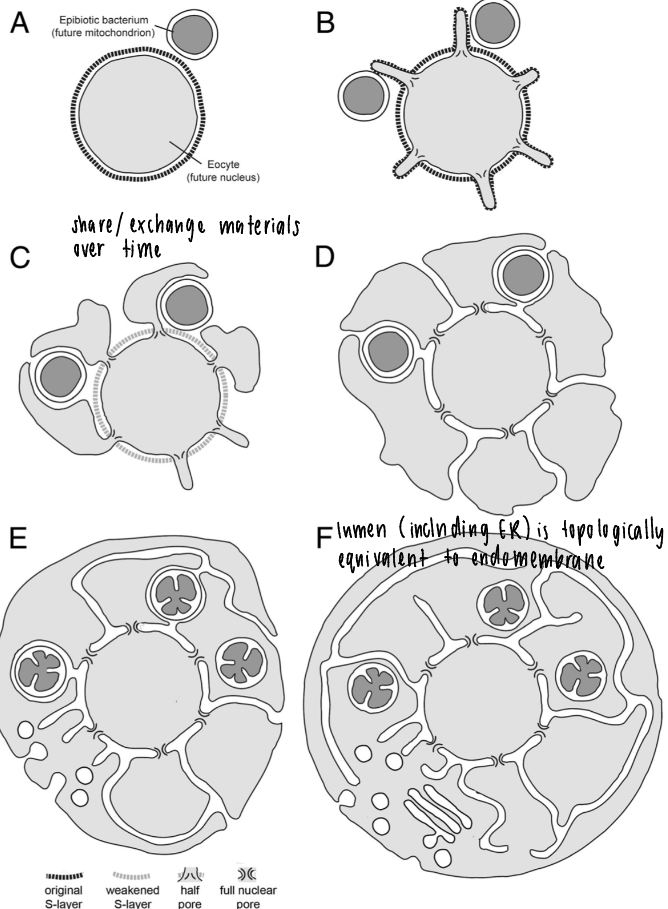
membrane donor to membrane acceptor compartment (inside-out theory)
single bilayer-enclosed organelles exchange contents
shapes: tubular, spherical, sheet-like
lumen (inside) is topologically identical to cell exterior (EC space) as part of a continuous, enclosed pathway separated from the cytoplasm
dynamic equilibrium: compartments are not static and depend on flux of material, specific seq of transport btwn compartments
organelle biogenesis and inheritance
stochastic and ordered inheritance
stochastic inheritance
every organelle comes from a parent organelle after random mixing / cell division
causes inheritance of dif compositions
in mitochondria, ER, golgi
ordered inheritance
occurs in chromosomes
nucleus
mitochondria dynamics
actin causes sorting during mitochondria division (fission - fusion)
actin waves (mixing) accelerates during mitosis, by comet tail formed during mitosis
can also be done during parasitic invasion, similar machinery utilized for actin
mixing NOT required for symmetrical inheritance of mitochondrial mass
purpose of actin wave
comet tails shuffle mitochondrial positions within cytoplasm
unmixed: less homogenous mixture of damaged vs healthy mitochondria to pass to daughter cells
want to pass down healthy mito to future generations
total cell membrane percentages
ER = highest lipid composition, includes rough and smooth
inner mitochondrial membrane is 2nd
80% of total cell membrane
individual organelles to total cell volume
mitochondria has higher vol than ER
cytosol has highest (50-60%)
space between membrane organelles
in cytosol, extremely crowded
debated of whether there’s enough space for 70% of our cells to contain H2O
endoplasmic reticulum
“mother” of all organelles, touches and interacts with 97%
rough: perinuclear region, near Golgi for protein processing
smooth: exterior of ER, tubules
ER regulation of mitochondrial fission
mitochondria constriction facilitated by ER prior to division (fission)
ER-mediated actin interactions at ER-organelle contact sites
*ER also controls fission of organelles other than mitochondria
ER regulation of mitochondrial fusion
mito/ER associated actin accumulates during fusion of mitochondria
rough ER function
ribosomes (black densities discovered by Pallade)
> 10 mil ribosomes bound to rER bc of high EC space
sheets have a stacked appearance that secrete high lvls of protein - secretory pathway
near nucleus and Golgi
protein folding and post-translational mods (N-glycans, S-S bonds)
protein quality control
why are so many ribosomes attached to the ER?
lumen of the ER is topologically equivalent to the EC space
if a protein is made that needs to go to EC space, it is co-translationally inserted into the ER lumen and anchored
smooth ER function
evenly distributed thru cytoplasm
tubular networks with 3-way junctions
responsible for lipid synthesis: steroid hormone synthesis (adrenal cortex, endocrine glands)
cellular detox center
calcium-ion storage (ex: control contraction of muscle cells)
ERGIC morphology
ER-golgi intermediate compartment
ER exit sites (ERES) > ERGIC > Golgi stack (cis, medial, trans)
ERGIC is an intermediate between exit and Golgi as a filter to proofread proteins
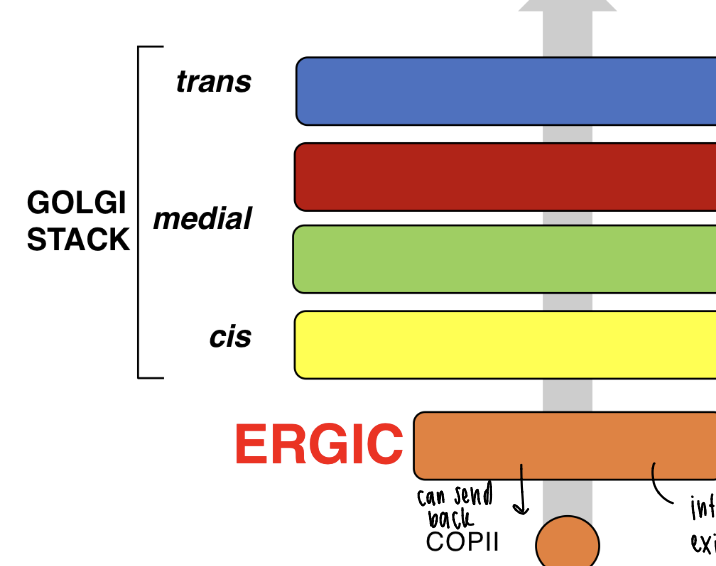
ERGIC function
vesicular tubular clusters (VTC) that are adjacent to ERES for export from ER
100-200 ERGICs/cell
COPI and COPII
only 50% of ERES are adjacent to Golgi membranes, but most ERES have ERGICs
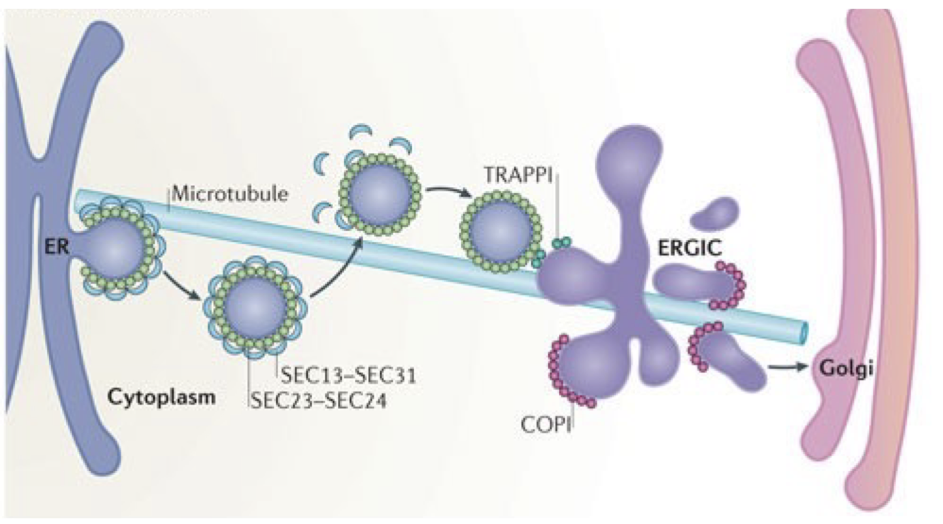
COPI
dependent for sorting of retrograde cargo from ERGIC
shipped back to ER
COPII
concentration / sorting of biosynthetic cargo
shipped toward Golgi
golgi apparatus morphology
cis face towards rER, trans face towards plasma membrane (PM)
present as ribbons in animals
golgi function
sorting hub (secretion out of cell, transport to other organelles)
enzymes are transmembrane proteins
lipid synthesis / transport
remodeling of N-glycans (tree-like) / adding O-glycans (linear)
lipidation of proteins as a post translational mod.
perinuclear region (adjacent to nucleus)
3-8 disc-like cisternae (diameter 1 um) stack to form ribbons of Golgi stack (100 stacks / cell) for distinct faces (cis medial trans) and stack polarity
stepwise mod of cargo
each cisternae has unique biochem comp / function
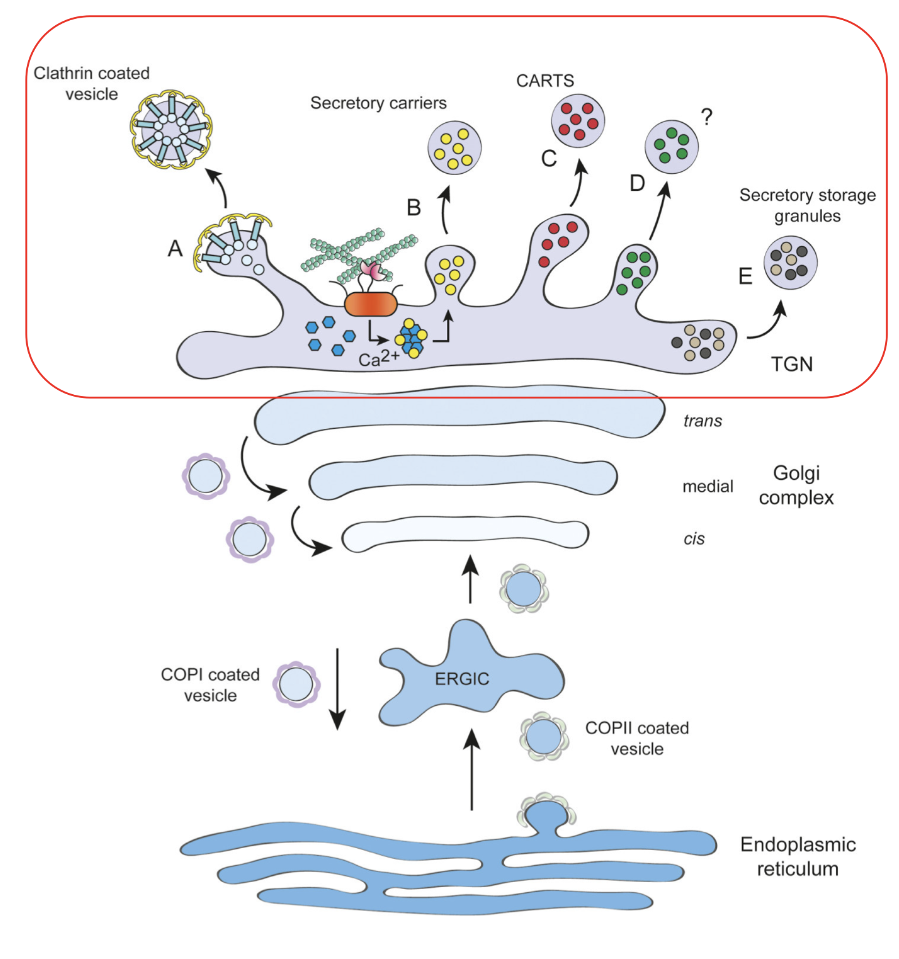
TGN function
trans-golgi network
sorting hub to receive cargo from endosomal system and golgi
transmembrane proteins + soluble lysosomal hydrolases, clathrin coated vesicles
large extracellular matrix proteins (ex: collagens)
protein complexes like dense core secretory granules
calcium-dependent sorting of sphingolipid-enriched carriers
plasma membrane morphology
membrane protrusions
most rigid membrane
contains transmembrane proteins (ex: glycoprotein facing EC fluid)
hydrophilic heads on the outside from lipid bilayer
filaments of cytoskeleton face cytoplasm
signal transduction thru proteins
plasma membrane function
physical barrier
selective permeability (impermeable to ions and polar mcs)
transport of solutes and macromolecules thru active transport and facilitated diffusion
endocytosis / phagocytosis / exocytosis
cell signaling
interactions w neighboring cells in tissues
fluid mosaic model: PM is a 2D liquid composed of discontinuous phospholipid bilayer with patches of embedded protein complexes (hence mosaic)
endo-lysosomal system morphology
endosomes can become lysosomes thru acidification, or can be recycled as multivesicular bodies
EML