Chapter 10 Power and Influence in the Workplace
1/43
Earn XP
Description and Tags
OBHR
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
what is the meaning of power?
Power referes to the capacity of a perosn, team or organization to influence others
what can having power do? (3)
potential to change attitudes and behaviour( not actual attempt to change)
targets perception that powerholder controls a valued resource
required a minimum level of trust by both parties
power involves unequal dependence
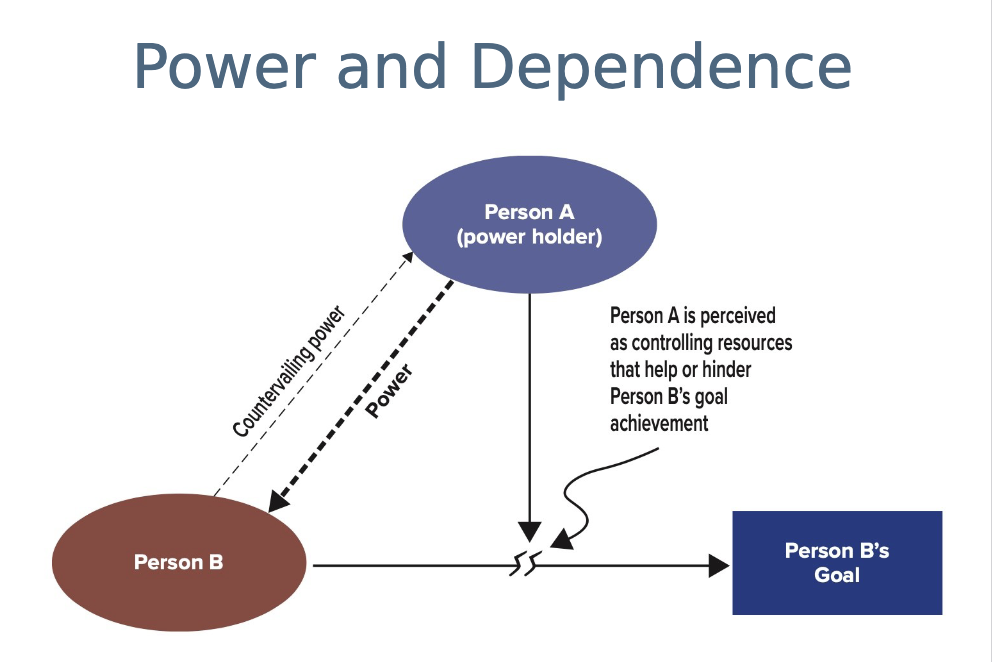
Explain the power and dependence diagram
Person A (Power Holder) controls resources that help or hinder Person B’s goals.
Person B depends on Person A for goal achievement.
The more Person A controls what B needs, the more power A has.
Countervailing power: Person B can also influence or resist Person A’s power
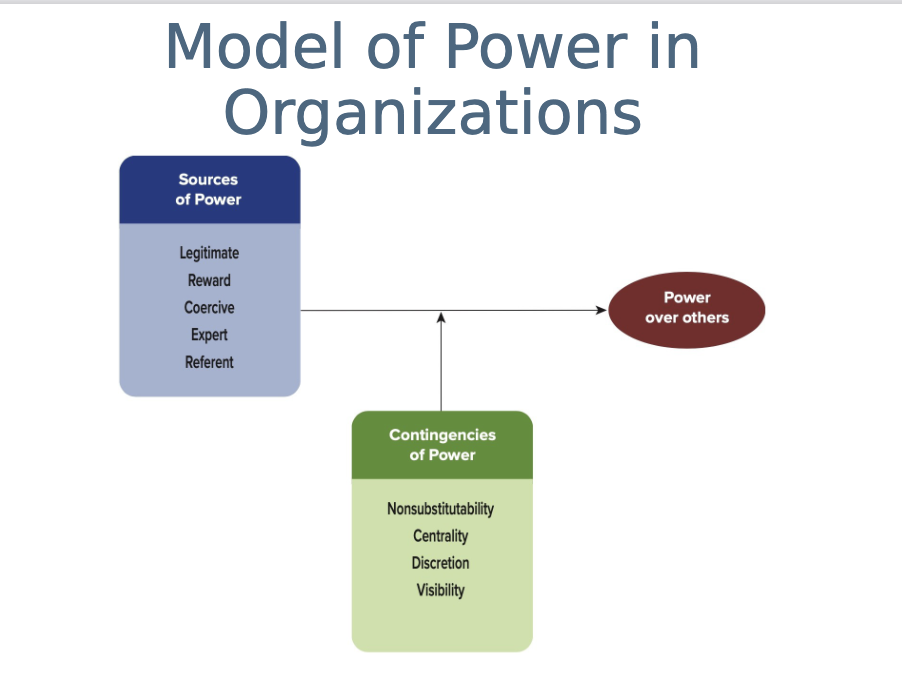
in the context of the model what are sources of power in an organization?
sources of power in organizations include…
Legitimate power – based on position or authority.
Reward power – ability to give rewards (e.g., bonuses, promotions).
Coercive power – ability to punish or withhold rewards.
Expert power – power from skills or knowledge.
Referent power – power from respect or admiration.
Different sources = different ways people gain influence.
What factors strengthen or weaken someone’s power inother words contingencies of power?
some contingencies of power include…
Nonsubstitutability – no one else can do what you do.
Centrality – how important your role is to others’ success.
Discretion – freedom to make decisions independently.
Visibility – how much others notice your work or influence.
what is legitimate power?
legitimate power is an agreement that people in specific roles can request behaviours from others.
in legitimate power what are zone of indifferences?
zone of indifference is the…
domain of behaviours that power holders can ask of others( in other words how much you can ask of others until they wont do it)
however there are several factors that influence size of the zone indifferences
in the context of legitimate power, what is norm or reciprocity?
norm of reciprocity is the obligation to reciprocate favors
how does information control be used as a form of legitimate power?
to start off “IC” is the right to control information that others value
info control generates power through gatekeeping and framing
What is expert power?
“EP” the capacity to influence others by possessing knowledge or skills that they value
in the context of expert power, what are ways organizations can cope with uncertainty
organizations’s can operate better in predicatble environments
people gain power by using their expertise to…
prevent, forecast and absorb environmental changes
What is reward power?
“RP” is wher you control rewards valued y others ,remove negative snactions
what is coercive power?
“CP” is the ability to apply punishment like force you to do something
what is referent power?
“RfP” is the capacity to influence others though idetification with and respect for the power holder — associated with charisma
why is deference to power a problem?
its a problem because following with minimal evaluation the guidance of people who are charistmatic or calm to have legitimate or expert power.,
What is nonsubstitutability in power? (contingencies of power)
Power increases when your skills or resources cannot be replaced easily.
The more unique or hard-to-find what you offer is, the more power you have.
How can you increase nonsubstitutability?
Control access to the resource (make it harder for others to get).
Differentiate your resource or skill (make it special or unique).
How does developing a personal brand increase power?
A strong personal brand highlights your unique and valuable abilities.
It makes you nonsubstitutable because others see you as one of a kind.
What is centrality (contingencies of power)
centrality refers to the…
Power grows when others depend on you to get their work done.
The more people you affect — and the faster they feel your impact — the more central you are.
What is visibility in power? (contingency of power)
Power increases when others know you control valuable resources.
Social interactions and symbols of power (e.g., office location, recognition) make your influence more visible.
What is discretion in power? ( contingencies of power)
Power increases with freedom to make your own decisions.
Strict rules or policies reduce discretion — and therefore, power.
How can low nonsubstitutability weaken power?
If others can easily replace your skills or resources, your power drops.
When many people can do the same job, you lose uniqueness.
How can low centrality weaken power?
If few people depend on you, or your work has little impact, your power is limited.
Slow or indirect effects on others make your role seem less important.
How can low visibility weaken power?
If people don’t see or know what you contribute, they can’t value your influence.
Working behind the scenes or lacking recognition reduces power.
How can low discretion weaken power?
If rules, policies, or managers tightly control your actions, you have little freedom.
No ability to make decisions = no real influence.
although beneficial, power can have its consequences, explain Type A: Feeling empowered
People feel independent and free from others’ control.
Leads to higher motivation, job satisfaction, and performance.
HOWEVER can cause overconfidence, less mindful thinking, more stereotyping, and lower empathy or accuracy when judging others.
although beneficial, power can have its consequences, explain Type B: Power over others
Comes from legitimate, reward, and coercive power sources.
Creates a sense of duty or responsibility toward others.
HOWEVER leads to more mindful, careful thinking, less stereotyping, and more empathy for how one’s actions affect others.
What are social networks in organizations? (2)
They’re connections between people through interdependence.
People join networks to bond, follow social norms, and gain resources.
What is social capital? (2)
It’s the knowledge, opportunities, and resources shared through your network.
Built on mutual support, trust, and coordination.
What power resources do social networks provide? (3)
Information (Expert Power) – Access to knowledge others don’t have.
Visibility – Being known and recognized.
Referent Power – Gained through trust and respect in relationships.
What are strong ties in social networks? (2)
Close, frequent relationships (friends, teammates).
Offer resources quickly and in large amounts, but they’re less unique.
Strong ties = fast help, but similar ideas.
What are weak ties in social networks? (2)
Loose connections or acquaintances.
Offer unique and new information, but less often.
Weak ties = slow help, but fresh ideas.
What happens when you have many ties?
More ties = more access to resources.
Technology helps maintain more ties, but there’s still a limit to how many you can manage well.
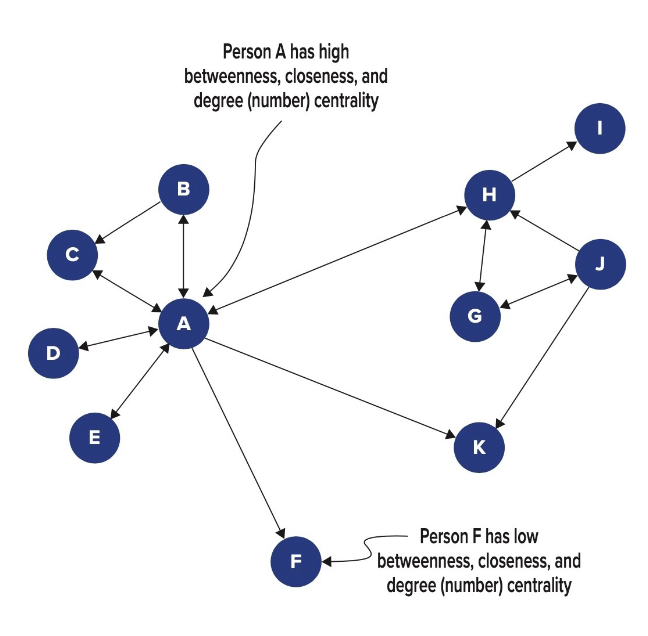
What is social network centrality?
It’s how important or influential a person is within a social network.
The more central you are, the more power you have.
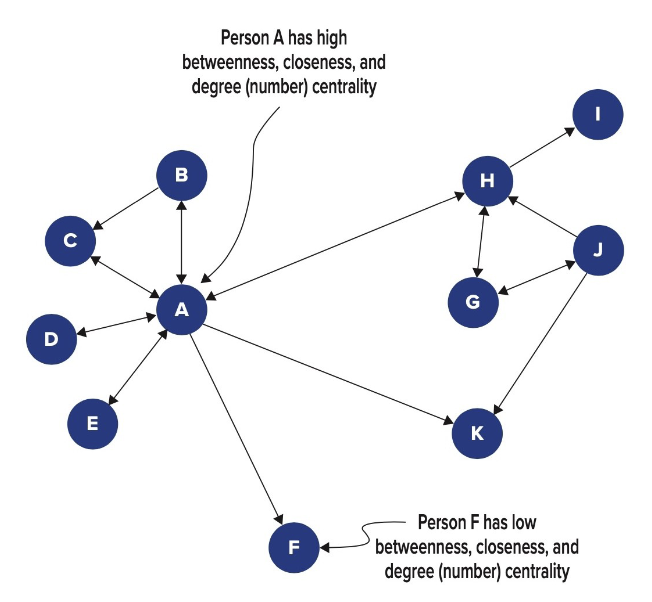
What are the 3 factors of social network centrality?
Betweenness – You act as a bridge connecting others.
→ You control information flow.Degree Centrality – You have many direct connections.
→ You’re well-connected and visible.Closeness – You have strong, quick access to others.
→ You can reach anyone efficiently.
Bridge + Popular + Connected Fast = Central Power
What does it mean to influence others?
it refers to any behaviour that attempts to alter another persons attiudes or behaviour
What does influencing others rely on?
It uses one or more power bases (like expert, referent, reward power)
and depends on power contingencies (the situation).
Why is influencing others important at work?
It’s Important for coordination and leadership—helps people work together and follow direction.
What are the two main types of influence tactics?
Hard tactics – Forceful, using pressure or authority.
Soft tactics – Persuasive, using logic, relationships, or charm.
Hard tactics: explain what Silent authority
When people change their behaviour just because of the power holder’s request or presence.
👀 Example: You follow your manager’s rule even without being told directly.
💪 Based on legitimate power (authority).
Hard tactics: What is assertiveness in influence?
Using vocal authority — reminding, checking, or pressuring others to comply.
⚡ Example: A supervisor repeatedly tells you to meet a deadline.
💥 Based on legitimate and coercive power.
Hard tactics:
Hard tactics:
Hard tactics: