Legitimacy, Separation of Powers and Rule of Law
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
What are the key parts of Dicey’s formulation of the rule of law?
Legal certainty - Rely on clear laws enacted properly; no arbitrary exercise of power.
Personal liberty - Citizens detained and punished only if break law.
Due process - Fair procedures.
Equality before the law - Treat all citizens, public officials alike.
Courts - Protectors of individual liberty.
What are the factors considered under Bingham’s conceptualisation of the rule of law?
Law must be accessible, intelligible, clear and predictable.
Questions of legal right and liability resolved by law not discretion.
Laws apply equally. Except where objective differences justify differentiations.
Law protect human rights.
Provide means resolve civil disputes. Without cost or delay.
Public officials exercise powers reasonably + good faith. Do not exceed powers.
Adjudicative procedures must be fair.
State comply international law obligations.
How did A v Secretary of State illustrate application of the rule of law?
[Right to liberty]
Anti-Terrorism Act 2001; indefinite detention without trial. Only foreign national not British citizens.
Breach Art 5, 14 ECHR. Discriminate on nationality.
Indefinite detention without trial infringe rule of law.
How did R v Secretary of State (Home Department) illustrate application of the rule of law?
[Right to fair hearing]
Convicted murderer. Mandatory life sentence. Judge set ‘tariff’ (i.e. minimum no. years served for probation).
Minister use Act to increase tariff.
Held - ECHR declaration of incompatibility. Rule of law stipulate courts punish offenders not public officials.
How did R (UNISON) v Lord Chancellor illustrate application of the rule of law?
[Access to justice]
Employment Tribunal law introduce fees order; previously not required.
Held - Fees were unlawful. Impeded access to justice.
Fees unlawful if render futile / irrational bring claim.
May be lawful if everyone can afford, account for full / partial remission.
How did M v Home Office illustrate application of the rule of law?
M (asylum seeker). Subject to deportation order. Applied judicial review.
HC judge request delay to deportation. Interim order delay.
Minister ignored it. Believe acted legally. Crown immune from contempt proceedings.
Held - Crown not immune. Public officials equally accountable.
Are there limits to the court upholding the rule of law?
[R v Director of Serious Fraud Office]
Director of SFO halted investigation into company trading in Saudi Arabia.
Ministers advised him British lives at stake; counter-terrorism initiatives.
Held (HOL) - Valid. Breach rule of law. But lives of citizens outweigh important bribery investigation.
True or False: There is a formal separation of powers within the UK constitution.
False.
Why? Because unwritten constitution, un-codified.
Partial separation exists. Informal system checks and balances.
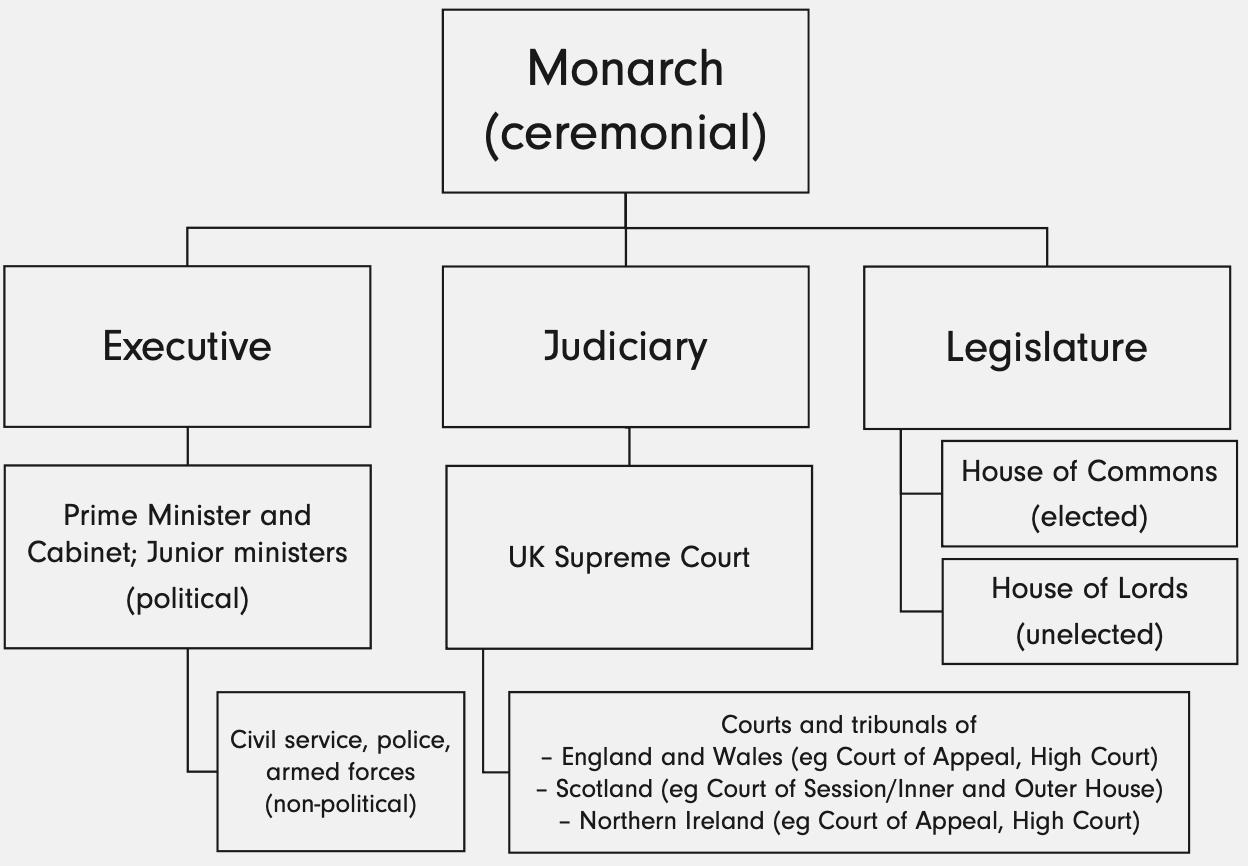
Who makes up the executive branch of the state?
Monarch, PM, government ministers, civil service, members of police and armed forces.
Who makes up the judicial branch of the state?
Monarch, all legally qualified judges, magistrates.
How does the House of Commons Disqualification Act 1975 ensure limited separation of powers between the executive and legislature?
Disqualifies civil servants, armed forces, police from being MPs.
Limit of 95 government ministers sit in Commons.
What are ‘Henry VIII’ powers within certain Acts of Parliament?
Powers to enable Government to amend / repeal primary legislation via delegated legislation.
Example - Retained EU Law (Reform and Revocation) Act 2023
What is the ‘Salisbury Convetion’?
HoL won’t reject bill forming major part government manifesto.
What are ‘standing orders’ within the House of Commons?
Allow for emergency debates; Speaker decides if necessary.
Allocate time to official Opposition.
Government bills debated at 2nd reading.
What is the purpose of ‘General Committees’?
Referred to public bill committee of MPs post debate.
Review clauses; make necessary amendments.
Discuss specific areas: Scottish Grand Committee, Welsh Grand Committee etc.
What is the purpose of ‘Select Committees‘?
Examine ‘expenditure, administration and policy’ departments.
Staffed entirely by back-benchers.
Gov has majority on them.
Power to question ministers including PM.
What is ‘individual ministerial responsibility’?
Political convention. Minister resigns if:
Personal conduct issue.
Conflict of interest public duties and private interests.
Proper administration of departments.
Example - Priti Patel unauthorised meetings with Israeli officials, BJ ‘Partygate’ affair.
What is the ‘collective cabinet responsibility’?
Cabinet collectively responsible to Parliament for Gov’s actions as a whole.
Gov must retain confidence of HoC.
Convention = Minister resigns if speak out against Gov.
PM can suspend convention (e.g. Brexit referendum).
Example - Robin Cook on Iraq War 2003.
Are the royal prerogatives open to scrutiny by Parliament?
No.
Concern national security, defence, deployment armed forces.
Courts deem ‘non-justiciable’ issues.
Convention seek Parliament approval before deployment of military. Recognised in Cabinet Manual. But no requirement if emergency.
How has the ‘Constitutional Reform and Governance Act 2010’ limited the Government’s prerogative of treaty ratification?
HoC can hold vote to prevent Gov ratifying treaty.
HoL can do likewise, but only prompt Gov to provide explanatory note for ratification.
How is judicial independence secured from the executive?
Appointments - Made by Judicial Appointments Commission. Impartial; free from political control.
Tenure - Secure job terms. Senior judges only removable via HoC and HoL vote. Can’t dismiss on basis Gov disagrees decision.
Salary - Decided by independent body (Senior Salaries Review Board). Funded by ‘Consolidated Fund’ (i.e. permanent reserve).
Immunity Civil Action - Protected from suits re judicial actions (i.e. errors).
Constitutional Conventions - Executive does not criticise judicial decisions. Judges don’t engage political activity.
Sub-judice Rule - Parliament refrains discussing matters being heard by courts.
Contempt of court - Prevents ministers commenting on cases outside of Parliament.
What is the role of the Lord Chief Justice?
Responsible for training, guidance and deployment of judges.
Represents views of judiciary to Parliament.
Lord Chancellor no longer has this role. But still a member of cabinet.
What is the procedure for appointing judges?
PM advise Monarch on filling vacancy: Lord Chief Justice, Master of Rolls, Lord Justices of Appeal, President Family Division, KB’s Division, HC judges. Lord Chancellor consult LCJ before informing PM. LCJ consult JAC to hold selection process.
SC appointments made by Monarch on advisement by PM. In turn, receives recommendation from LC. Recommendations sourced from ‘selection commission’ staffed by senior judges.
How does the judiciary hold the executive to account?
Process of judicial review.
Ensure executive does not exceed / abuse prerogative powers.
Does not assess merits but legality of decision.
What powers do the courts have with regard to the extent of the royal prerogatives (RPs)?
Courts decide:
If RPs exist or not;
New RPs cannot be created;
Existing RPs scope cannot be widened.
BBC v Johns - BBC claimed Crown had RP regulate broadcasting (i.e. BBC’s Royal Charter). Claim entitlement rely Crown exemption income tax. Rejected. Could not widen scope of existing RP.
What powers do the courts have with regard to the exercise of the RPs?
[Blackburn v AG]
More limited.
B argue Gov unlawfully surrender Parliament sovereignty via Treaty of Rome.
Held - No power to review exercise. Once RP exists, it exists.
Are there RPs where the courts can review its exercise?
[CSSU v Minister for Civil Service]
Stipulated executive’s RPs or statutory powers not automatically immune to judicial review.
Except where ‘non-justiciable’:
Making international treaties
Control of armed forces
Defence of realm
Dissolution of Parliament
Prerogative of mercy
Granting public honours.
Why? Areas of ‘high politics’. Courts lack knowledge / expertise; seek avoid political implications.
What procedures are in place to keep the legislature and judiciary separate?
House of Commons (Disqualification) Act 1975 - Judicial office holders cannot be MPs.
Convention MPs won’t criticise judges.
Sub-judice rule (as above)
Bill of Rights 1689 - Freedom of speech within Parliament. Courts cannot censure MPs because privileged.
Can Parliament overturn a judicial decision?
[Burmha Oil v Lord Advocate]
Yes.
HoL awarded compensation to BO for losses during WW2.
Parliament passed War Damages Act 1965. No further compensation payable.