Biology paper 1
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/14
Last updated 3:21 PM on 1/20/26
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
1
New cards
\
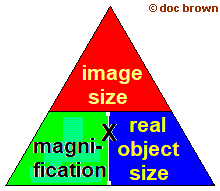
calculating size of an object
2
New cards
Animal cell structures
* Nucleus
* Cytoplasm
* Cell Membrane
* Mitochondria
* Ribosomes
* Cytoplasm
* Cell Membrane
* Mitochondria
* Ribosomes
3
New cards
Plant cell structures
* Cell membranes
* Ribosomes
* (Cellulose) Cell Wall
* Mitochondria
* Cytoplasm
* Permanent Vacuole
* Chloroplasts
* Nucleus
* Ribosomes
* (Cellulose) Cell Wall
* Mitochondria
* Cytoplasm
* Permanent Vacuole
* Chloroplasts
* Nucleus
4
New cards
Eukaryotic Cells
Examples of eukaryotic cells - Animal cells, Plant cells
\
They all have a cell membrane, cytoplasm and genetic material/ DNA (enclosed in a nucleus)
\
They all have a cell membrane, cytoplasm and genetic material/ DNA (enclosed in a nucleus)
5
New cards
Prokaryotic Cells
Examples of prokaryotic cells - Bacteria cells
\
Prokaryotes are single-celled living organisms which have cytoplasm, cell wall, cell membrane, slime capsule, plasmids, flagella and genetic material (not enclosed in a nucleus)
\
Prokaryotes are single-celled living organisms which have cytoplasm, cell wall, cell membrane, slime capsule, plasmids, flagella and genetic material (not enclosed in a nucleus)
6
New cards
Specialisation in Animal cells
As the organism develops, the cells differentiate to form specialised cells, acquiring different sub-cellular structures to carry out different functions.
Cells can be specialised to function within a tissue, an organ,
Examples; nerve cells, muscle cells, sperm cells
Cells can be specialised to function within a tissue, an organ,
Examples; nerve cells, muscle cells, sperm cells
7
New cards
Specialisation in Plant cells
Plants also have specialised cells with adaptations for the roles carried out within the plant
E.g. Root hair cells, Photosynthetic cells, Xylem cells, Phloem cells
E.g. Root hair cells, Photosynthetic cells, Xylem cells, Phloem cells
8
New cards
Root Hair Cell Adaptations
* They greatly increase the surface area available for water to move into the cell
* They have a large permeant vacuole that speeds up the movement of water by osmosis from the soil across the root hair cell
* They have many mitochondria that transfer the energy needed for the active transport of mineral ions into the root hair cells
* They have a large permeant vacuole that speeds up the movement of water by osmosis from the soil across the root hair cell
* They have many mitochondria that transfer the energy needed for the active transport of mineral ions into the root hair cells
9
New cards
Photosynthetic Cell Adaptations
* They contain chloroplasts which contain chlorophyll which trap the sunlight needed for photosynthesis
* They are usually positioned in continuous layers in the leaves and outer layers of the stem of a plant so they absorb as much sunlight as possible
* They have a large permanent vacuole that helps keep the cells ridged due to osmosis, many rigid cells together form photosynthetic tissue to support the stem and they keep the leaf spread out to be able to capture as much sunlight as possible
* They are usually positioned in continuous layers in the leaves and outer layers of the stem of a plant so they absorb as much sunlight as possible
* They have a large permanent vacuole that helps keep the cells ridged due to osmosis, many rigid cells together form photosynthetic tissue to support the stem and they keep the leaf spread out to be able to capture as much sunlight as possible
10
New cards
Xylem Cell Adaptations
* Xylem cells are alive when they are first formed but lignin builds up spirals in the cell walls, the cells die and form long hollow tubes that allow water and mineral ions to move easily through them from one end of the plant to the other
* The spirals and rings of lignin in xylem cells make them very strong and help them to withstand the pressure of water moving up the plant
* The spirals and rings of lignin in xylem cells make them very strong and help them to withstand the pressure of water moving up the plant
11
New cards
Phloem cell adaptations
* The cell walls between cells break down to form special sieve plates, allowing water carrying dissolved food to move freely up and down the tubes to where it is needed
* Phloem cells lose a lot of their internal structures but are supported by companion cells which keep them alive, with the mitochondria of companion cells transferring energy needed to move dissolved food up and down the plant in phloem
* Phloem cells lose a lot of their internal structures but are supported by companion cells which keep them alive, with the mitochondria of companion cells transferring energy needed to move dissolved food up and down the plant in phloem
12
New cards
Diffusion
The spreading out of particles in any substance, in solution of a gas, resulting in a net movement from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration on the concentration gradient
13
New cards
Diffusion in living organisms
In living organisms dissolved substances such as glucose and urea, and gases such as oxygen and carbon dioxide move in and out of cells
14
New cards
Osmosis
allows the movement of substances
15
New cards