Astigmatism
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
Astigmatism
Defined as a refractive condition. It is the difference in refractive power between the two principal meridians of the eye
Power meridian
meridian of greatest optical power
Axis meridian
meridian of least optical power
Refractive Power (Dioptres)
Radius of Curvature (mm)
2 Meridian descriptions
Meridional differences in:
curvature and/or flattening rates of
cornea
crystalline lens
refractive index of optical components
Shape of posterior pole
Astigmatism Causes
Structural
Corneal
Lenticular
Other internal astigmatism
Total
Classification of Astitgmatism
spherical
Cornea is seldom _____
Corneal
astigmatism implies anterior
posterior
True corneal astigmatism must include
10-14%
True corneal astigmatism must include posterior
posterior neutralizes ____% of anterior astigmatism
optical
Corneal astigmatism = _____ description
anatomical
Corneal toricity = ________ description
Internal Astigmatism
In _____ Astigmatism, the posterior pole (retina) may be:
toric in shape
tilted
decentred
toric in shape
tilted
decentred
In Internal Astigmatism, the posterior pole (retina) may be:
?
?
?
Corneal astigmatism
Lenticular astigmatism
Other internal astigmatism
Total astigmatism is the combination of
Regular Astigmatism
Principal meridians, 90o apart
Irregular Astigmatism
principal meridians not 90o apart
more than 2 principal meridians
no principal meridians
often acquired (i.e. secondary to)
trauma
disease
Regular
with-the-rule
against-the-rule
oblique
Irregular
Astigmatism Types
According to axis orientation (minus Cyl form)
With-the-Rule Astigmatism
Ocular astigmatism in which the refractive power of the vertical (or near vertical) meridian is the greatest
Correcting minus cylinder axis 0-30o, 150-180o
In WTR Astigmatism, the correcting minus cylinder axis are ___ & ___
Against-the-Rule Astigmatism
Ocular astigmatism in which the refractive power of the horizontal (or near horizontal) meridian is the greatest
Correcting minus cylinder axis 60-120o
In ATR Astigmatism, the correcting minus cylinder axis is ___
Oblique Astigmatism
Astigmatism in which the two principal meridians lie somewhere between the axes defining either WTR or ATR astigmatism
Correcting minus cylinder axis 31-59o, 121-149o
In OBL Astigmatism, the correcting minus cylinder axis are ___ & ___
ASTIGMATISM REFRACTIVE CYLINDER
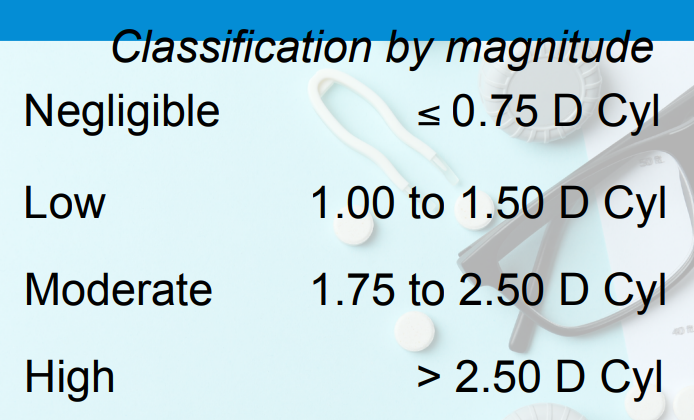
Classification by magnitude
?
?
?
?
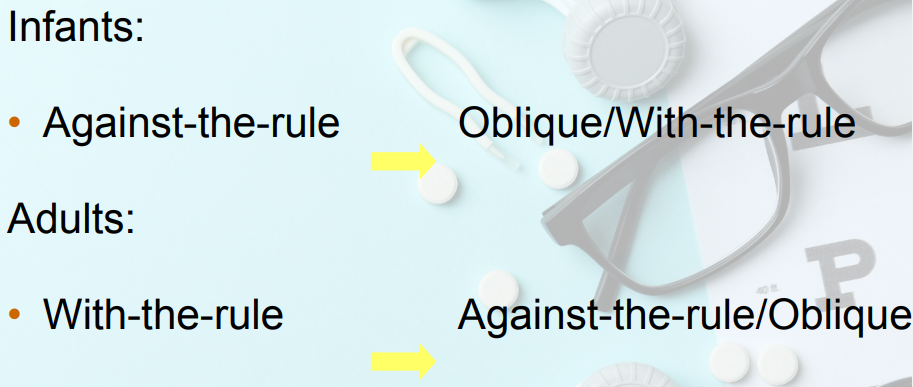
Astigmatism Incidence Shift with Age
Infants
___ → ___
Adults
___ → ___

Astigmatism Components
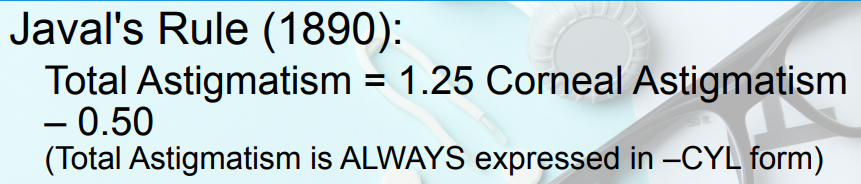
DETERMINING THE OCULAR ASTIGMATISM FROM THE CORNEAL ASTIGMATISM
Javal’s Rule (1890)

DETERMINING THE OCULAR ASTIGMATISM FROM THE CORNEAL ASTIGMATISM
Grosvenor et al. (1988)
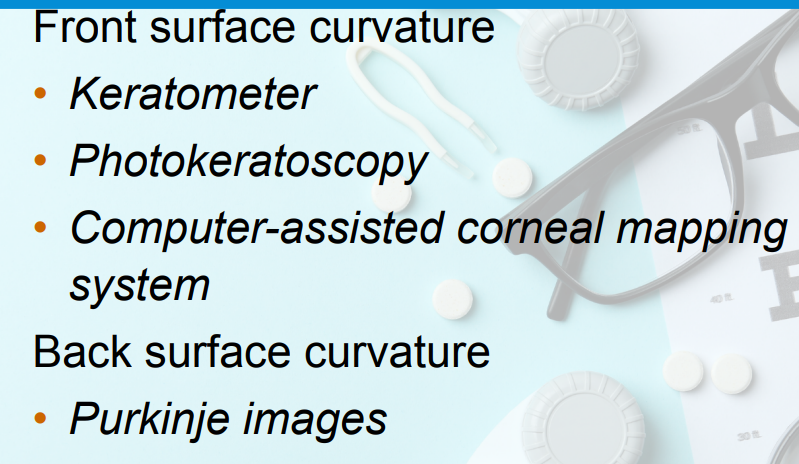
MEASUREMENT OF ASTIGMATISM
Front surface curvature
?
?
?
Back Surface Curvature
?