exercise 30 KTTK: Methyl Red and Voges-Proskauer tests (micro. lab)
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
Methyl Red and Voges-Proskauer (MR-VP) broth is
combination medium
what the MR-VP broth is used for
used for both Methyl Red and Voges-Proskauer tests
what the methyl red (MR) test is designed to detect and how it is set up
organisms capable of mixed acid fermentation producing acids and products such as
• Lactate
• Succinate
• Formate, which becomes
• H2
• CO2
• Ethanol
• Acetate
what is added to perform the methyl red test
pH indicator methyl red [dye] and ethanol
Products overcome phosphate buffer to lower pH below 4.2 seen by
adding pH indicator methyl red
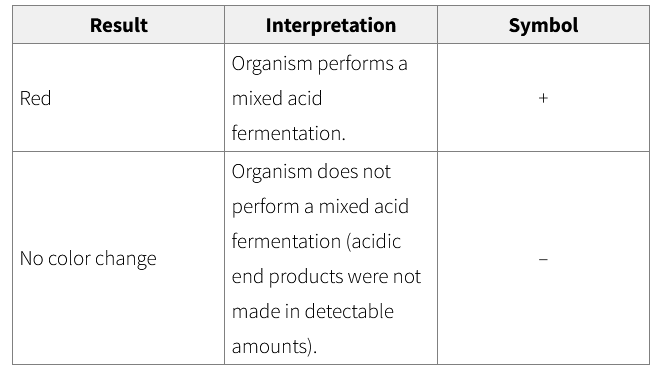
below pH 4.2
turns red indicating a positive result
at pH 6.2 and above
turns yellow indicating a negative result
between pH 4.2 to 6.2
will turn shades of orange which also indicate negative result
Voges-Proskauer test is designed to identify
organisms that ferment glucose and produce products with neutral pH
• Acetoin
• 2,3-butanediol
Procedural Diagram for the Methyl Red and Voges-Proskauer Tests
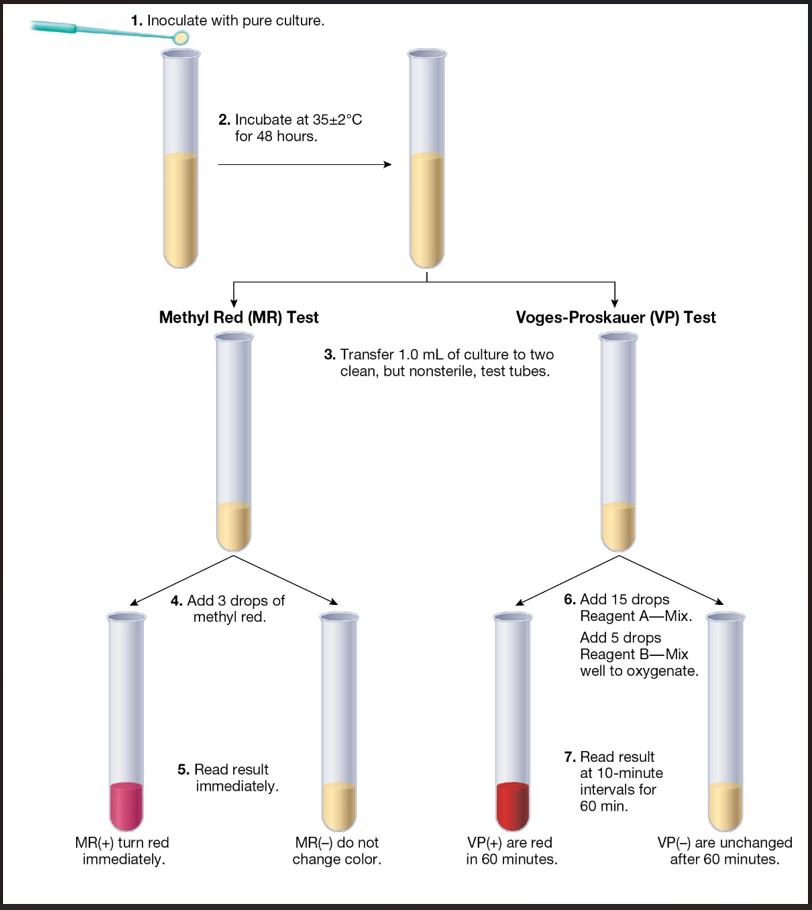
Voges-Proskauer positive organisms can
produce many of products that methyl red positive organisms can, but turn to producing above products in acid environment
what is added to perform the Voges-Proskauer test
VP reagents
VP reagent A: α-naphthol
VP reagent B: Potassium hydroxide (KOH)
oxidizes acetoin to
diacetyl
Diacetyl reacts with guanidine to
produce red color
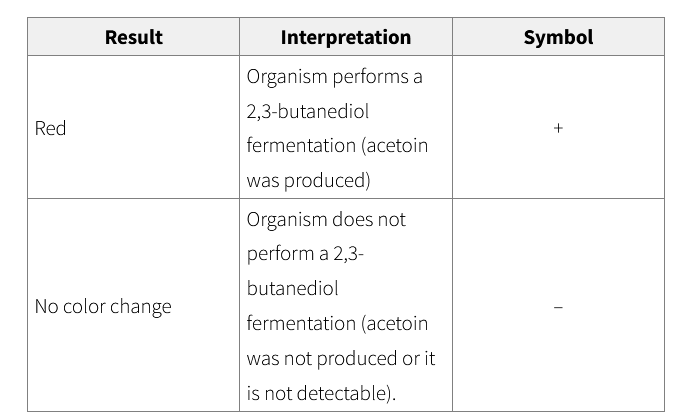
Red color change indicates
positive VP test
Weak positive test may
change to pink color
No color change or copper color
indicates negative VP test
(application) methyl red Voges-Proskauer broth is used
• Components of IMViC battery of tests (Indole, Methyl red, Voges-Proskauer, and Citrate) used to distinguish between Enterobacteriaceae family members and differentiate them from other Gram-negative rods
• Escherichia, Shigella, and Salmonella species are methyl red positive whereas Enterobacter, Serratia, and Erwinia species are Voges-Proskauer positive
Methyl Red Test Results and Interpretations
Voges-Proskauer Test Results and Interpretation
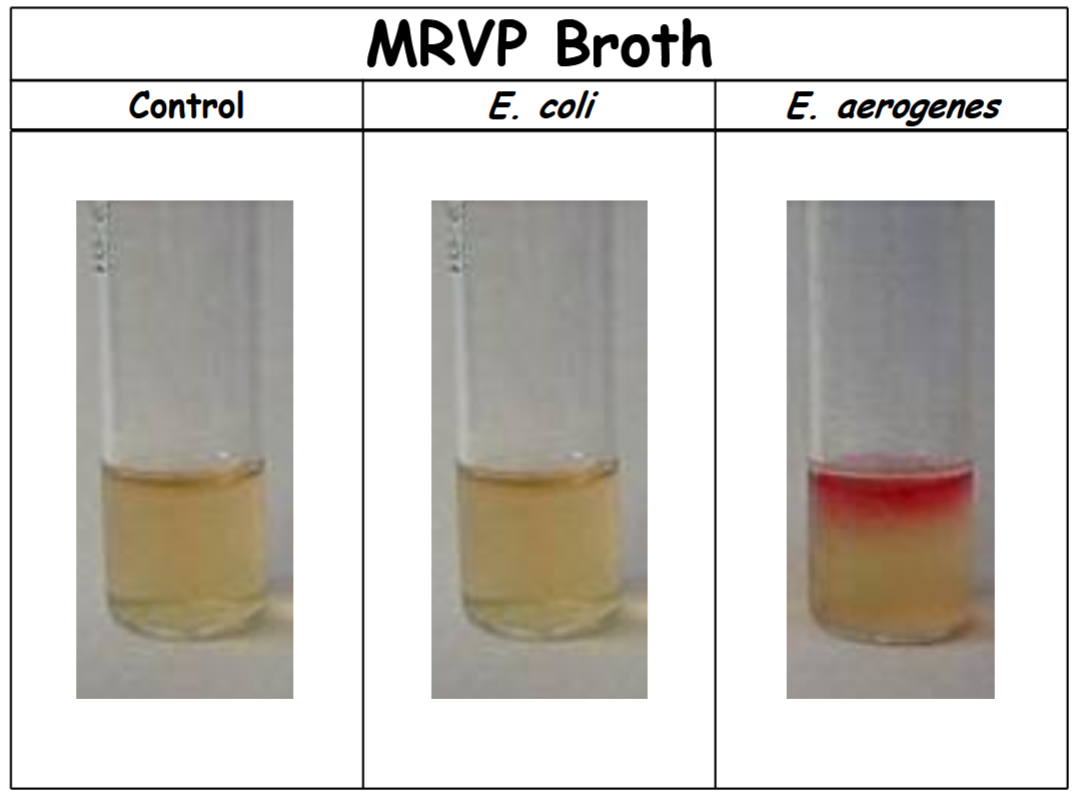
Voges-Proskauer Test – Results #1
control: no color change (-). Organism does not perform a 2,3-butanediol fermentation (acetoin was not produced or not detectable)
E. coli: no color change (-). Organism does not perform a 2,3-butanediol fermentation (acetoin was not produced or not detectable).
E. aerogenes: red (+). Organism performs a 2,3-butanediol fermentation (acetoin was produced)
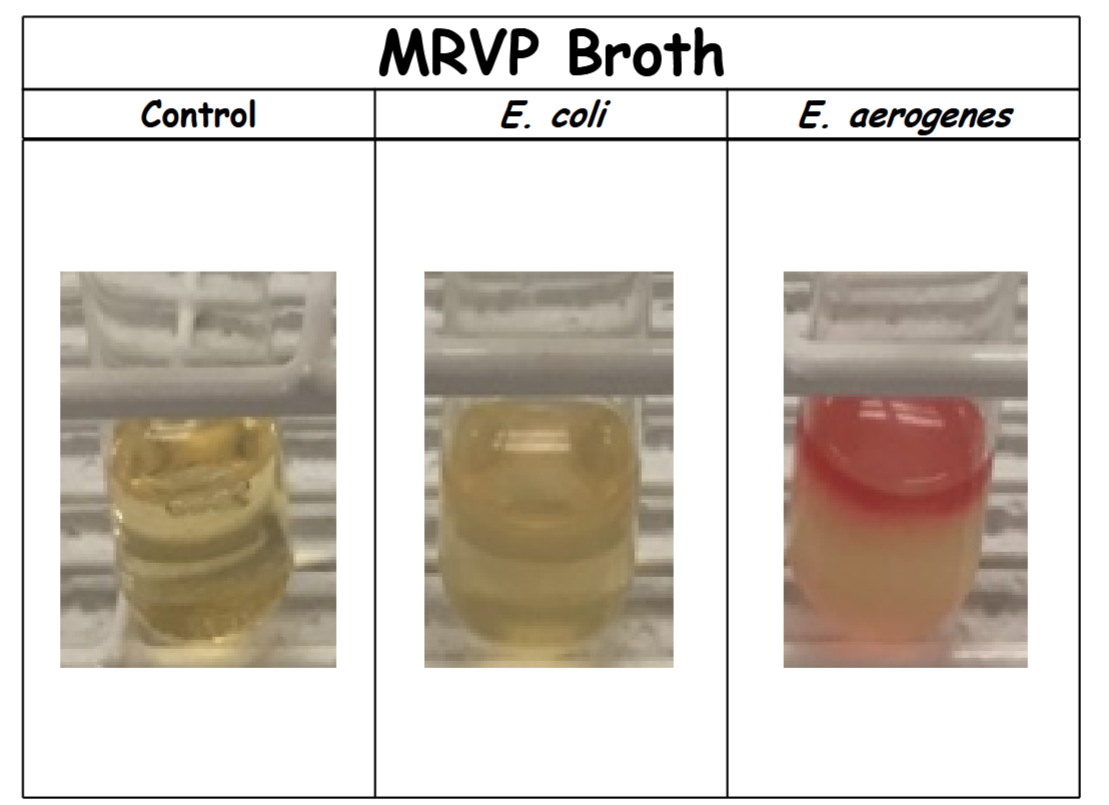
Voges-Proskauer Test – Results #2
control: no color change (-). Organism does not perform a 2,3-butanediol fermentation (acetoin was not produced or not detectable).
E. coli: no color change (-). Organism does not perform a 2,3-butanediol fermentation (acetoin was not produced or not detectable).
E. aerogenes: red (+). Organism performs a 2,3-butanediol fermentation (acetoin was produced)
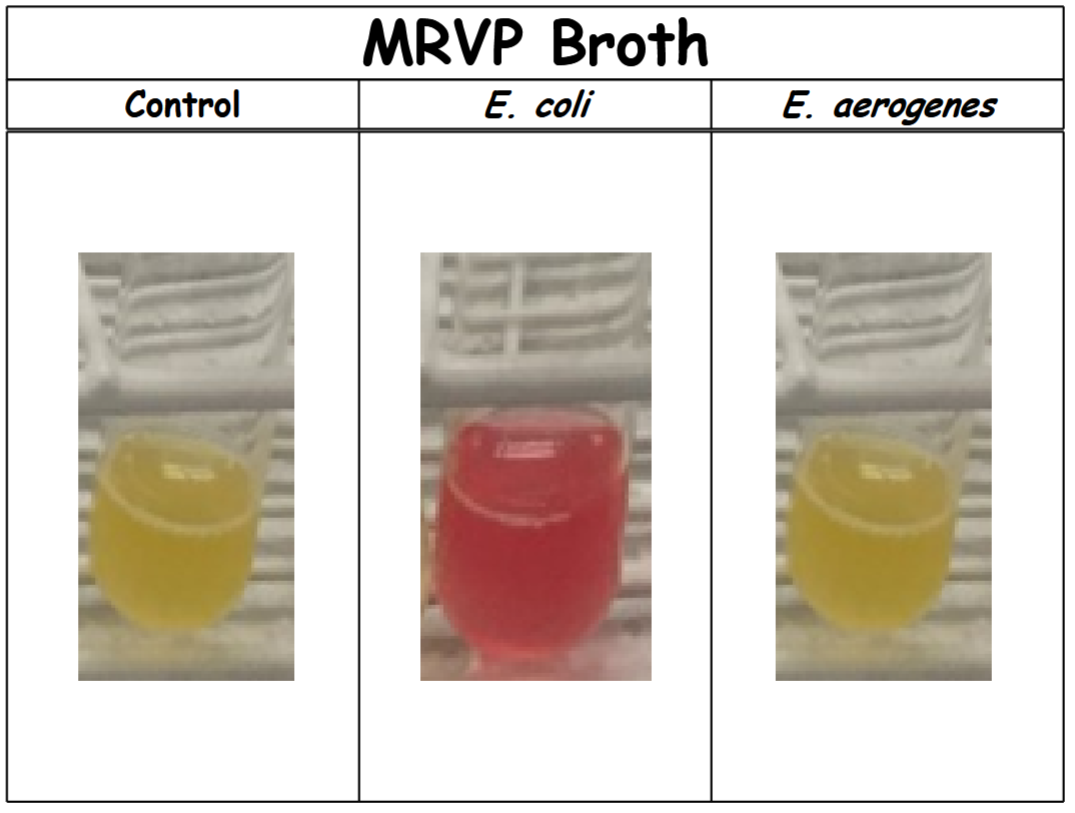
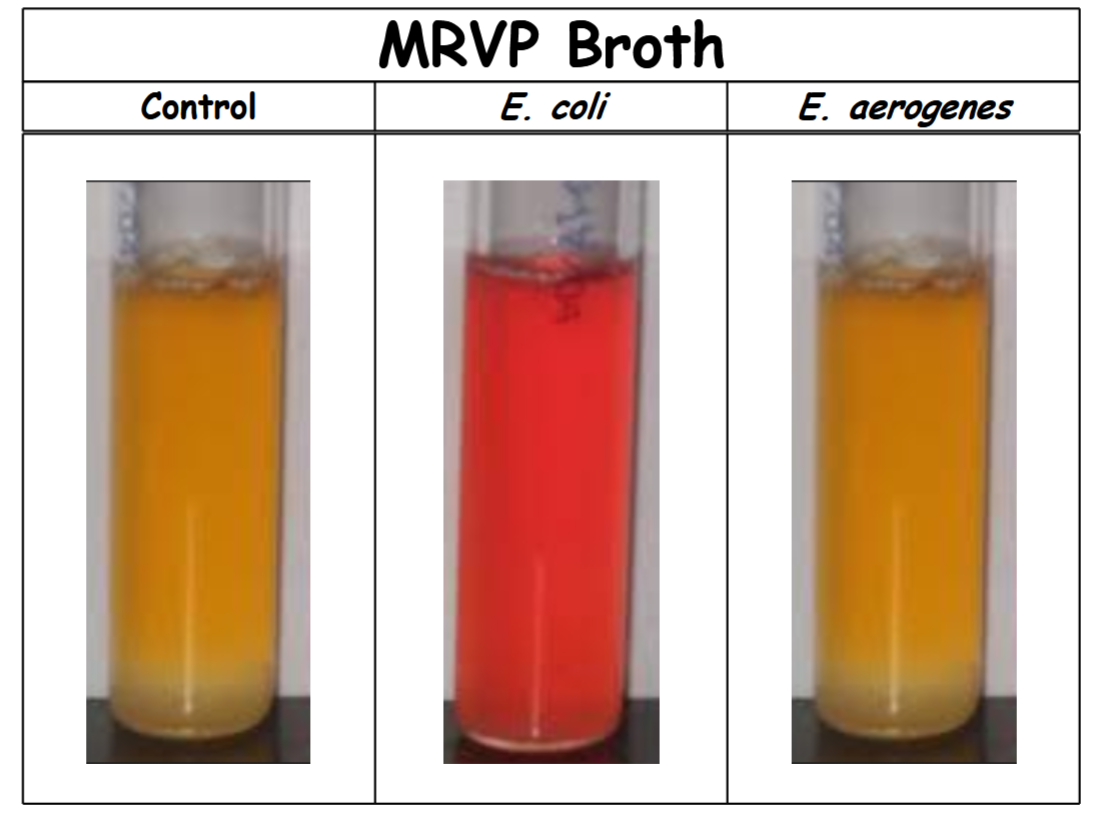
Methyl Red Test – Results #1
control: no color change (-). Organism does not perform a mixed acid fermentation (acidic end products were not made in detectable amounts).
E. coli: red (+). Organism performs a mixed acid fermentation.
E. aerogenes: no color change (-). Organism does not perform a mixed acid fermentation (acidic end products were not made in detectable amounts).
Methyl Red Test – Results #2
control: no color change (-). Organism does not perform a mixed acid fermentation (acidic end products were not made in detectable amounts).
E. coli: red (+). Organism performs a mixed acid fermentation.
E. aerogenes: no color change (-). Organism does not perform a mixed acid fermentation (acidic end products were not made in detectable amounts).