home assignments and jeopardy and overview slides unit 2
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
100 Terms
A patient has fluid in the pleural cavity due to infections. Where is the fluid accumulating when the patient stands up?
A. Costodiaphragmatic recess
b. Costomediastinal recess
C. Right lower lobe
d. Left lower lobe
Costodiaphragmatic Recess
What's the relationship of the left pulmonary artery to the primary bronchi?
a.Anterior
b. Posterior
C. Superior
d. Inferior
Superior
Which cardiac chamber forms the base of the heart mainly?
a.Right atrium
b.Right ventricle
c. Left atrium
d. Left ventricle
Left Atrium
Where to auscultate mitral valve
Left 5th intercostal space along the midclavicular line
Which of the following conducting sequences in the heart is correct?
a. AV node, SA node, bundle branches, bundle of His
b. SA node, bundle of His, AV node, bundle branches
c. SA node, AV node, bundle of His, bundle branches
d. AV node, bundle of His, SA node, bundle branches
C. SA node, AV node, bundle of His, bundle branches
Blood from which of the following arteries supports 1st and 2nd intercostal structures?
A. Thyrocervical trunk
b. Thoracoacromial artery
c. Costocervical trunk
d. Superior thoracic artery
Costocervical trunk
Which of the following blood vessels provide oxygen and nutrients to the lungs?
a.Pulmonary artery
b.Pulmonary vein
c.Bronchial artery
d.Bronchial vein
Bronchial artery
At which vertebral level does the esophagus course through the diaphragm?
a. T8
b. T10
C. T12
d. L2
B. T10
Which thoracic vertebrae have only full costal facets on their vertebral bodies?
A. T1 and T9
b. T2 and T10
C.T9 and T10
D. T10 and T11
D. T10 and T11
Which rib articulates with the xiphosternal joint?
a. Rib 2
b. Rib 5
c Rib 7
d. Rib 9
C. Rib 7
A patient complains of numbness/tingling around nipple line. Which dermatome is compromised?
a. T2
b.T4
C. T6
d. T8
B. T4
19. Where to put the chest tube during pneumothorax?
a. Superior border of the 4th or 5th ribs
b. Superior border of the 5th or 6th ribs
c. Inferior border of the 4th or 5th ribs
d. Inferior border of the 5th or 6th ribs
B. Superior border of the 5th or 6th ribs
Which muscles are primary inspiratory muscles?
A. External intercostals and membranous internal intercostals
b. Internal intercostals and membranous internal intercostals
C.External intercostals and innermost intercostals
d. Internal intercostals and inner most intercostals
A. External intercostals and membranous internal intercostals
Where can you find the thoracic duct?
A. Between the esophagus and the trachea
B. Between the esophagus and the azygos vein
C.Between the sympathetic trunk and the azygos vein
d. Between the sympathetic trunk and the esophagus
B. Between the esophagus and the azygos vein
Which unique cardiac muscle can be found in the atria?
a. Trabeculae carneae
b. Papillary muscle
C. Pectinate muscle
D. Chordae tendineae
C. Pectinate muscles
Which vessels containing the blood with high concentration of oxygen?
a. Pulmonary artery and aorta
b. Pulmonary vein and aorta
c. Pulmonary artery and bronchial artery
d. Carotid artery and brachiocephalic vein
B. Pulmonary vein and aorta
What is the fibrous capsule of the heart innervated by
Phrenic nerve c3-C5
Where do anterior cardiac veins directly drain to
Right atrium
When does the heart get its blood supply
When ventricles relax; diastolic
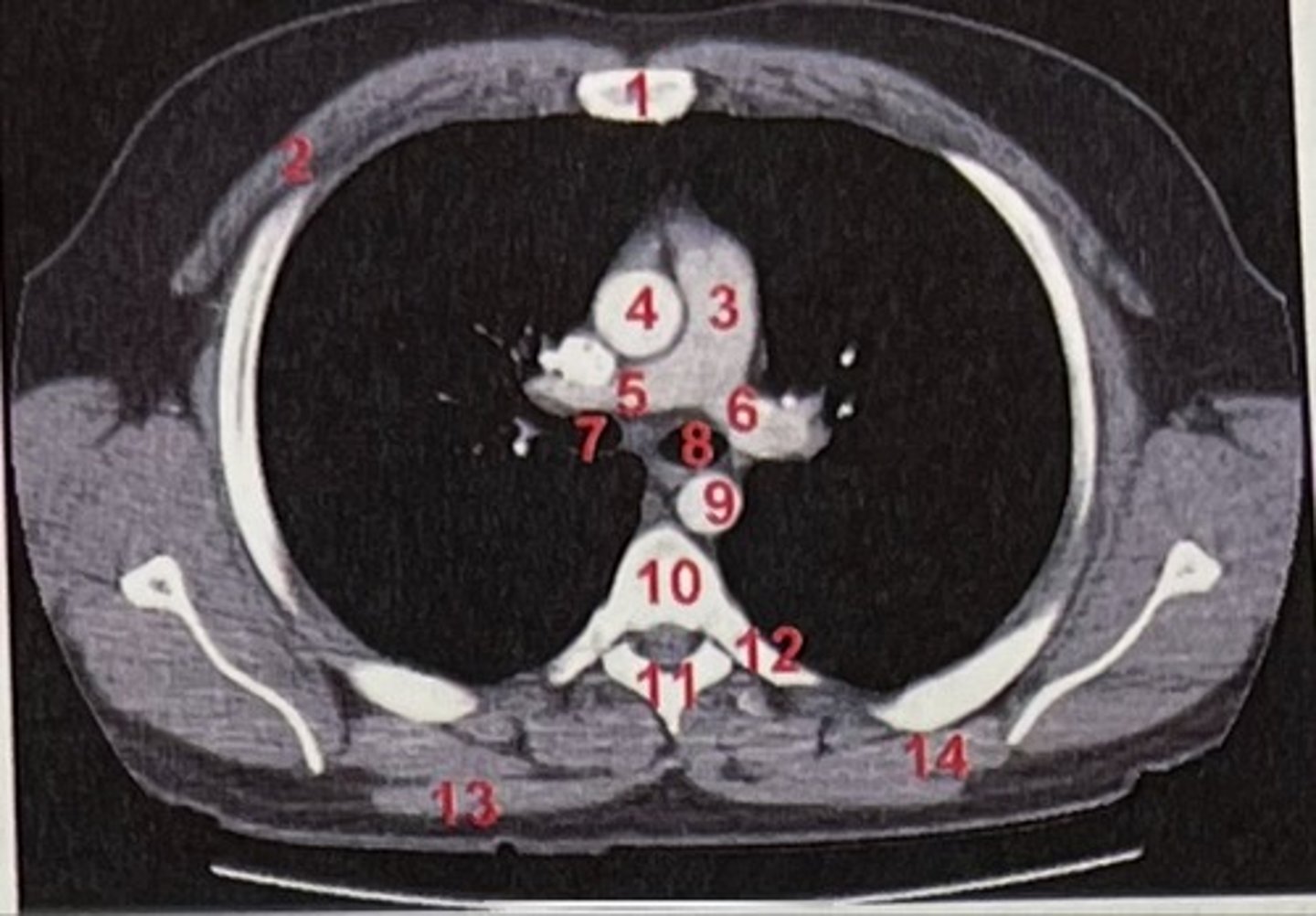
Sternum
What is 1
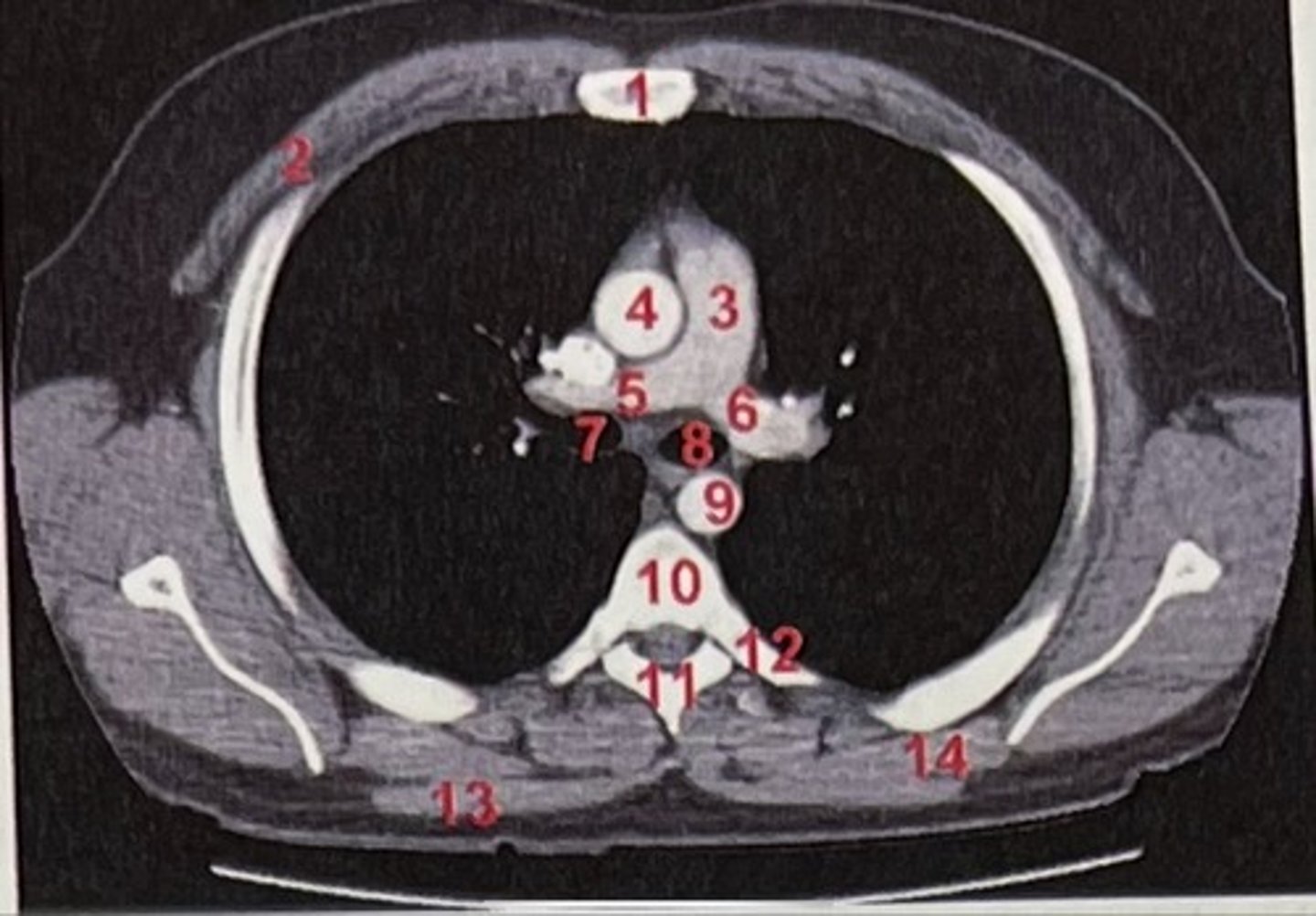
pectoralis major
What is 2
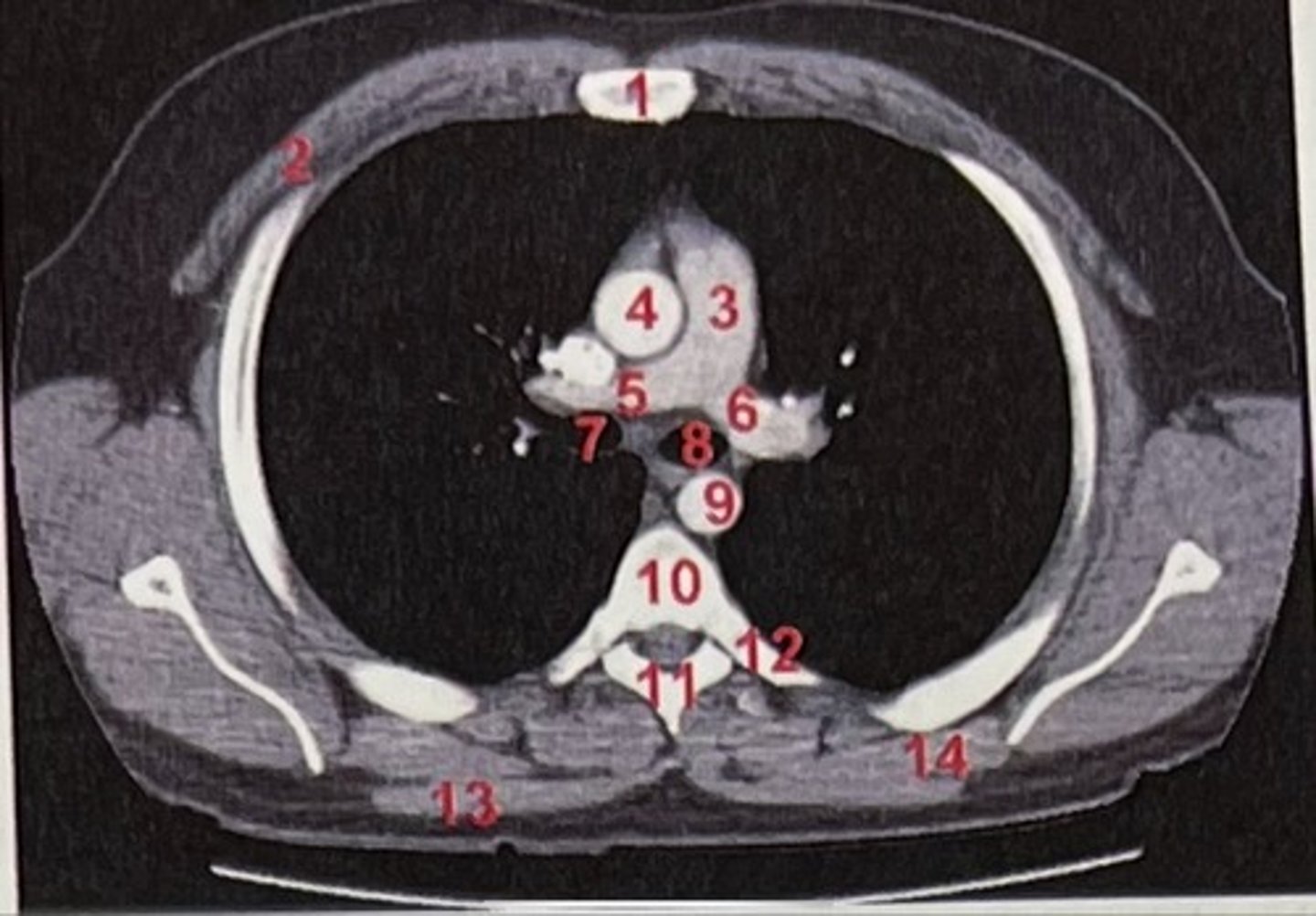
Pulmonary trunk
What is 3
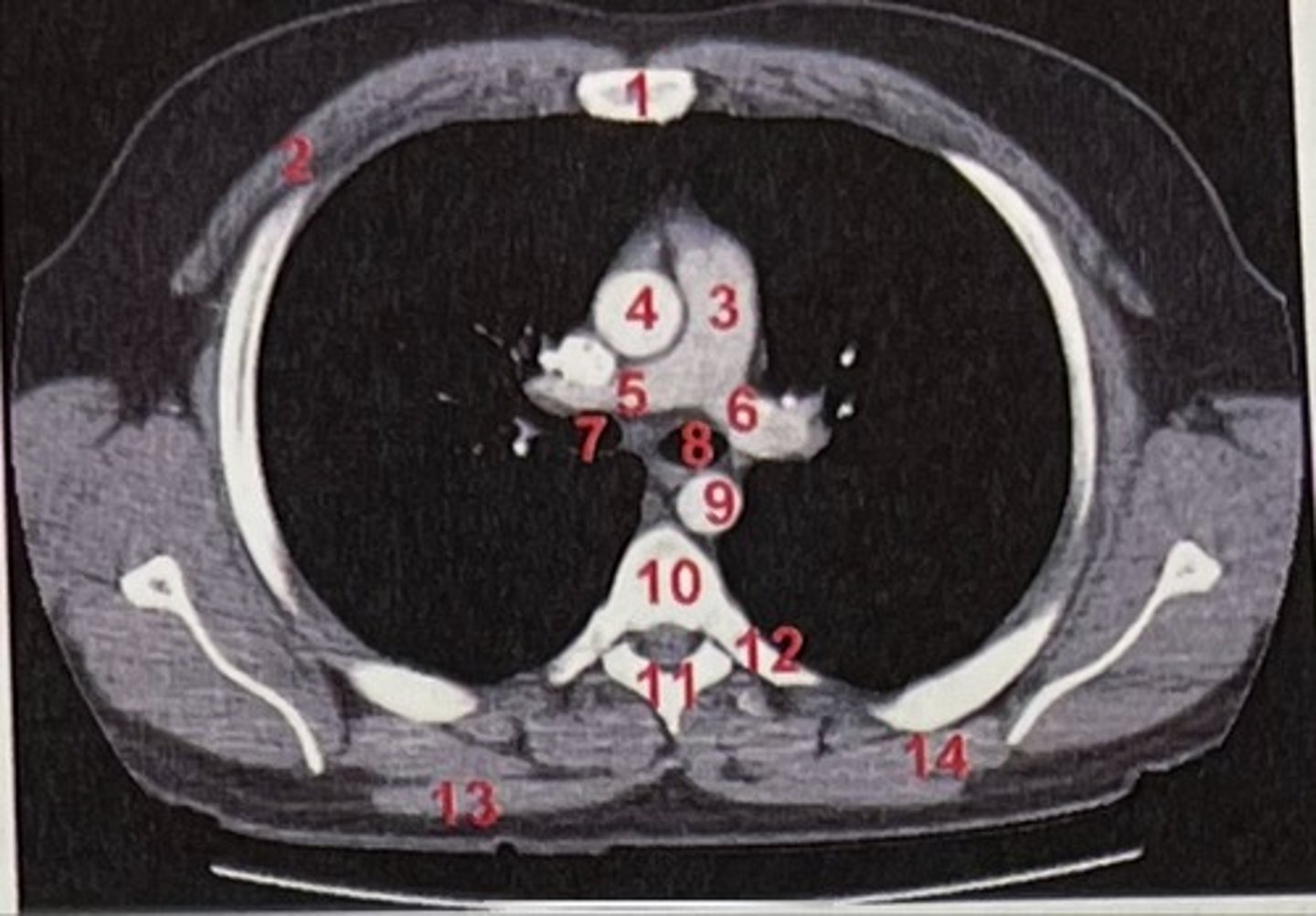
Right and left pulmonary arteries
What is 5 and 6
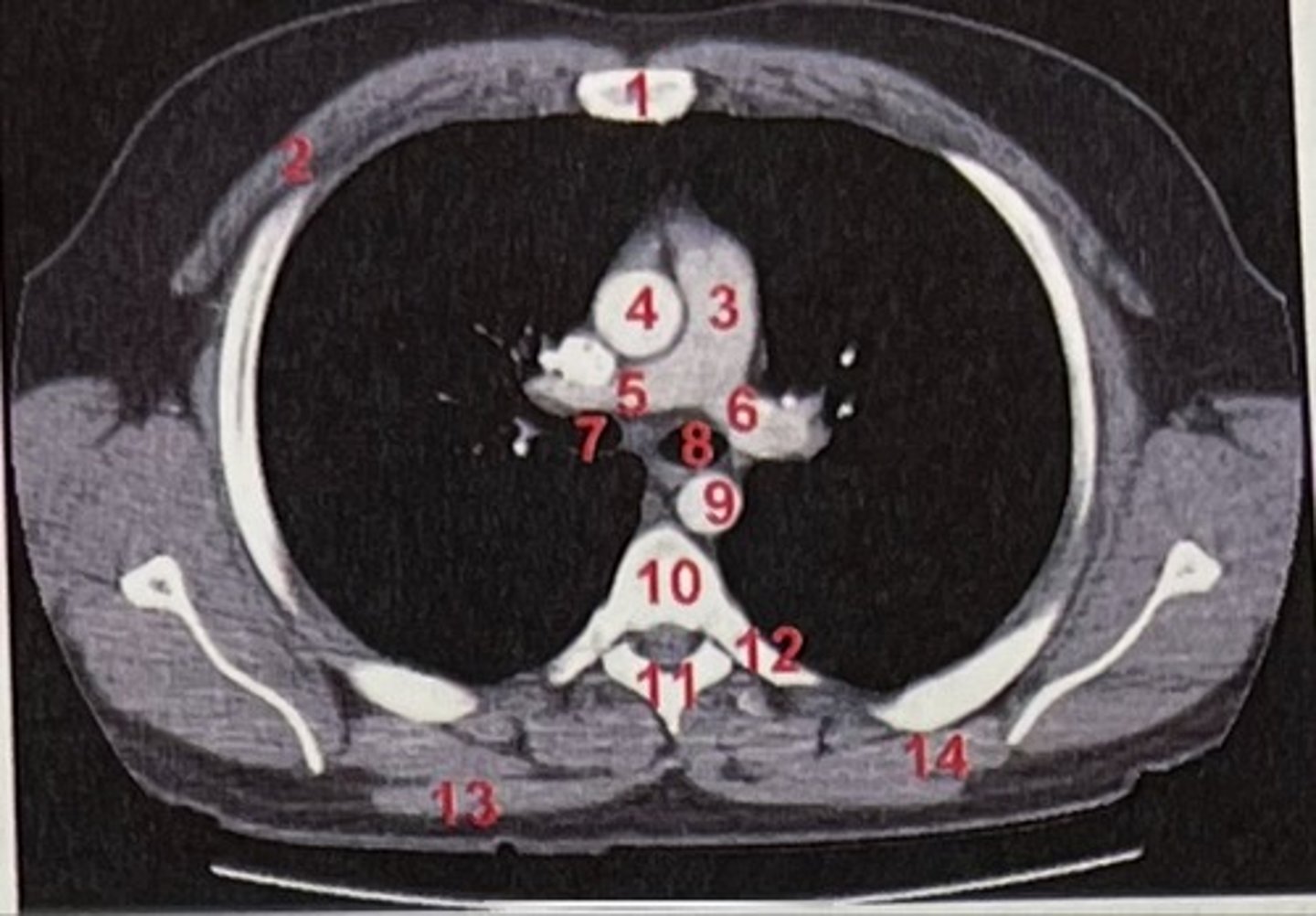
Ascending aorta
What is 4
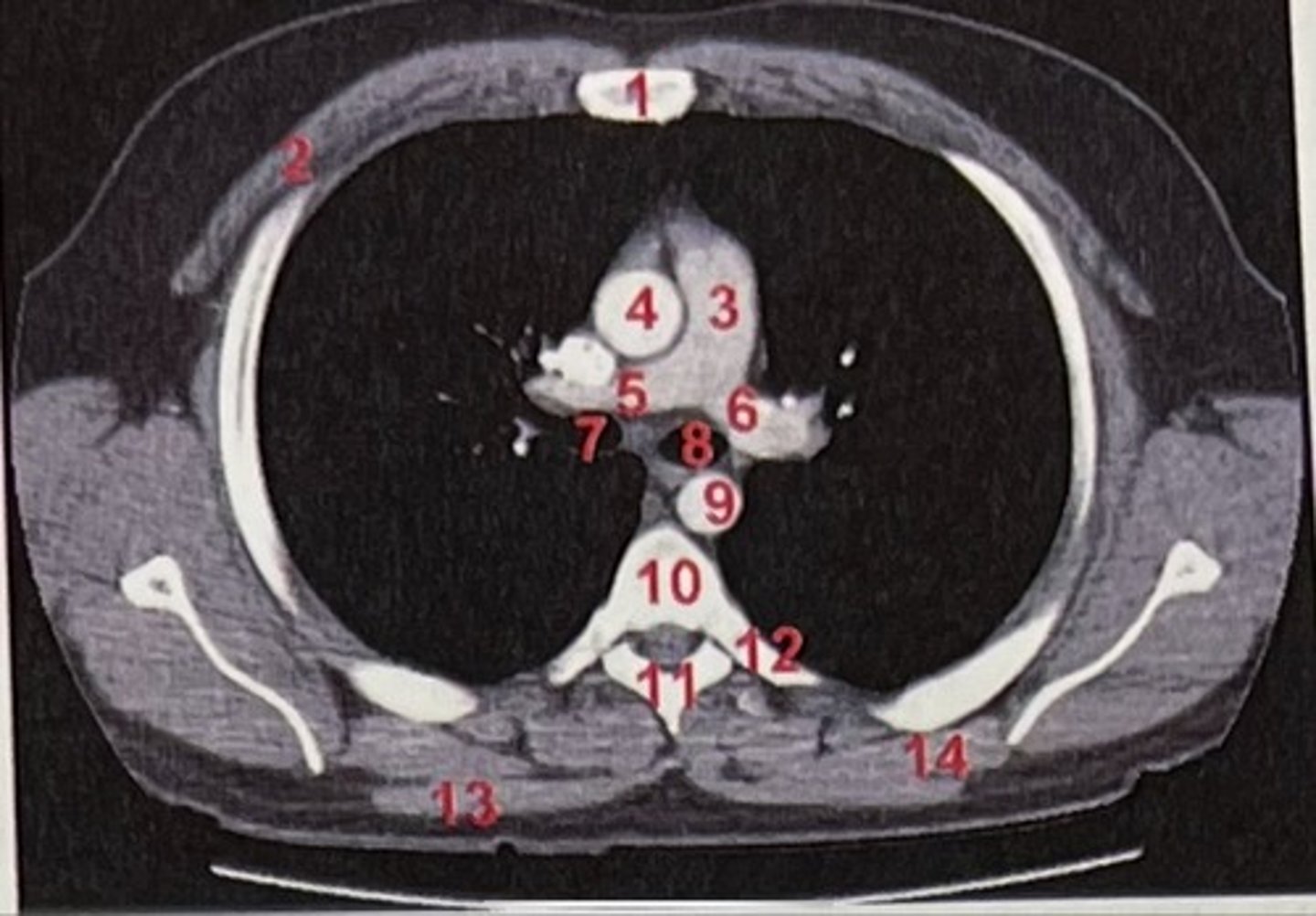
right primary bronchus, left primary bronchus
What is 7 and 8
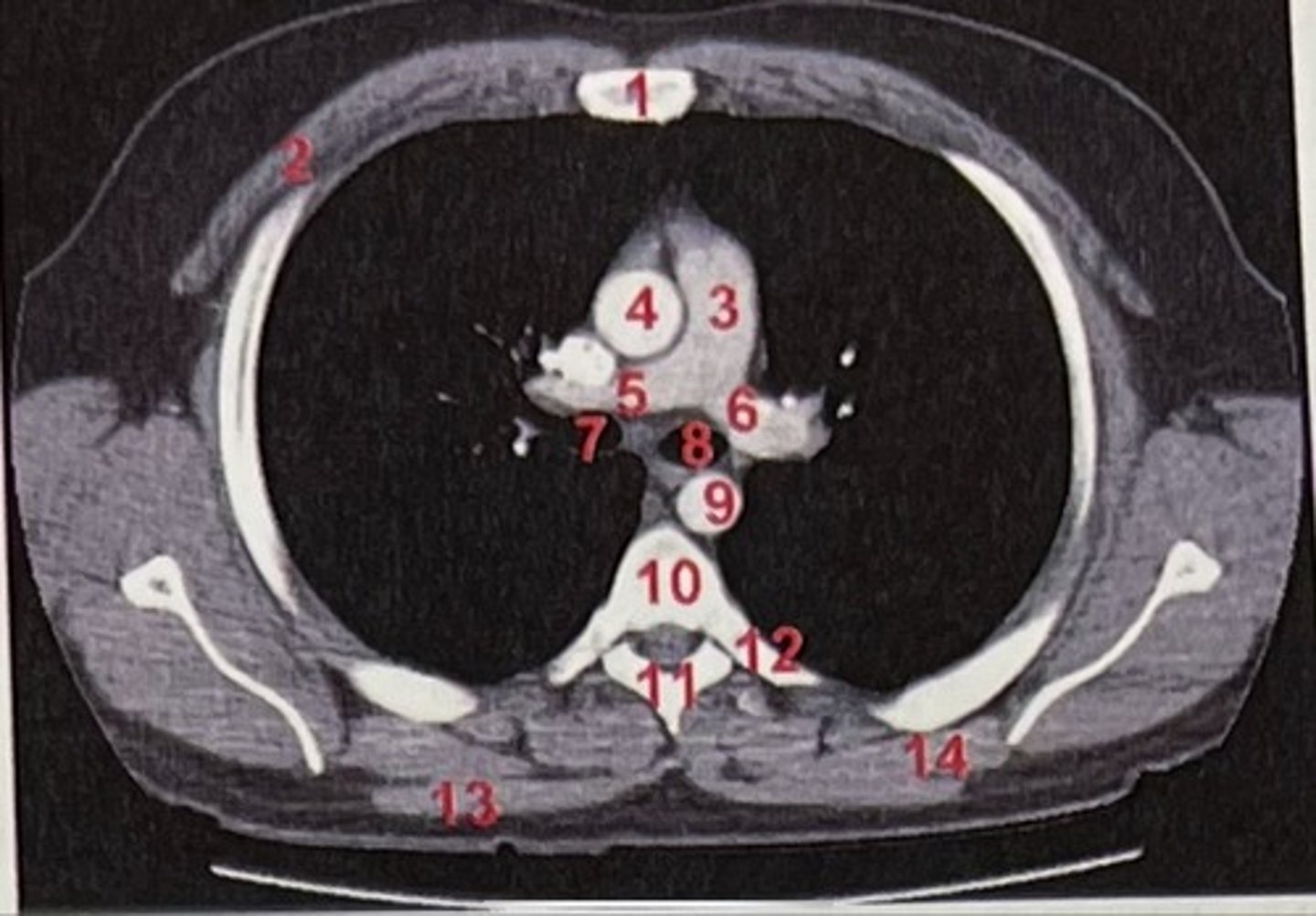
Descending aorta
What is 9
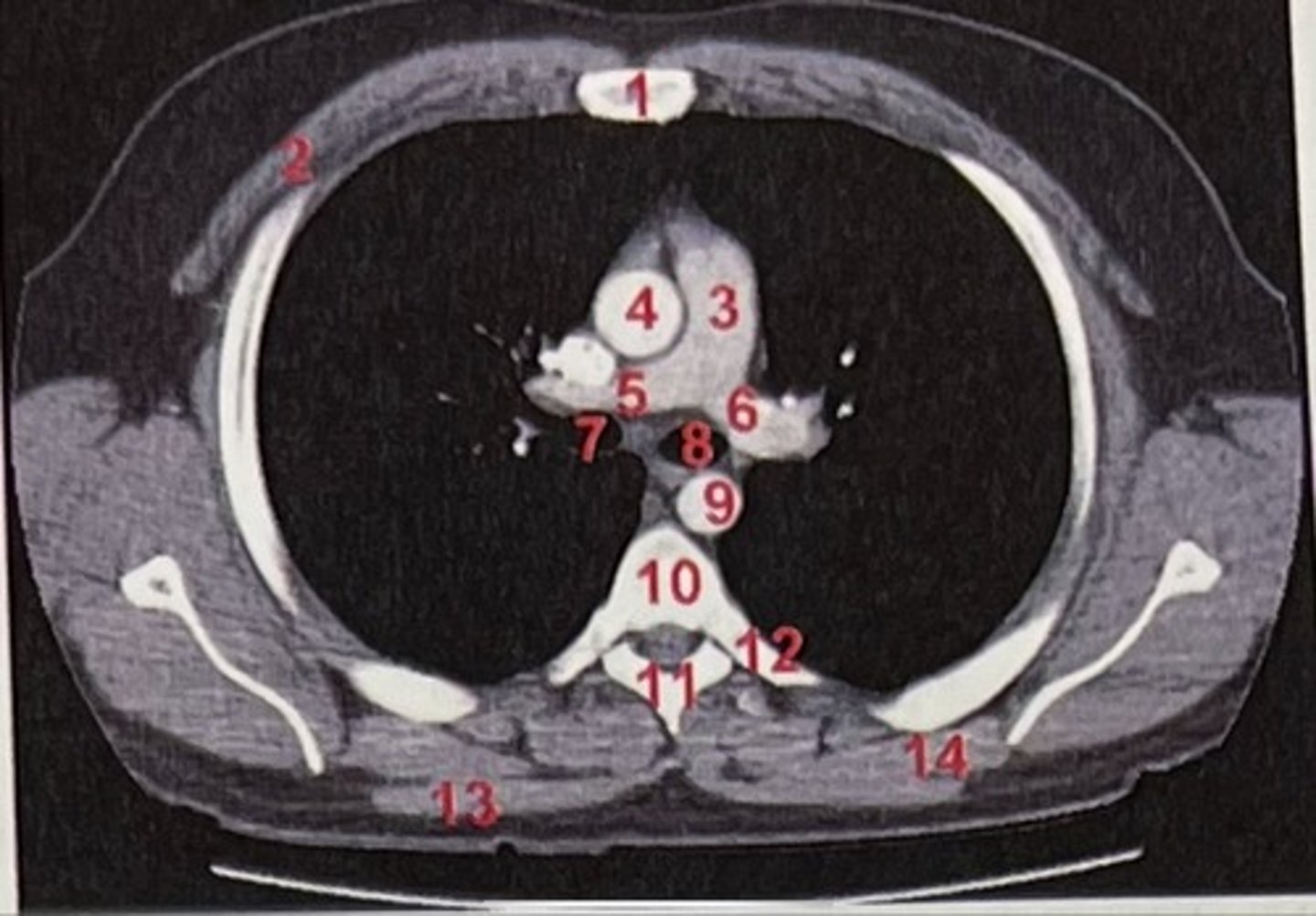
Rhomboid major
What is 14
pubic symphysis
What is 1
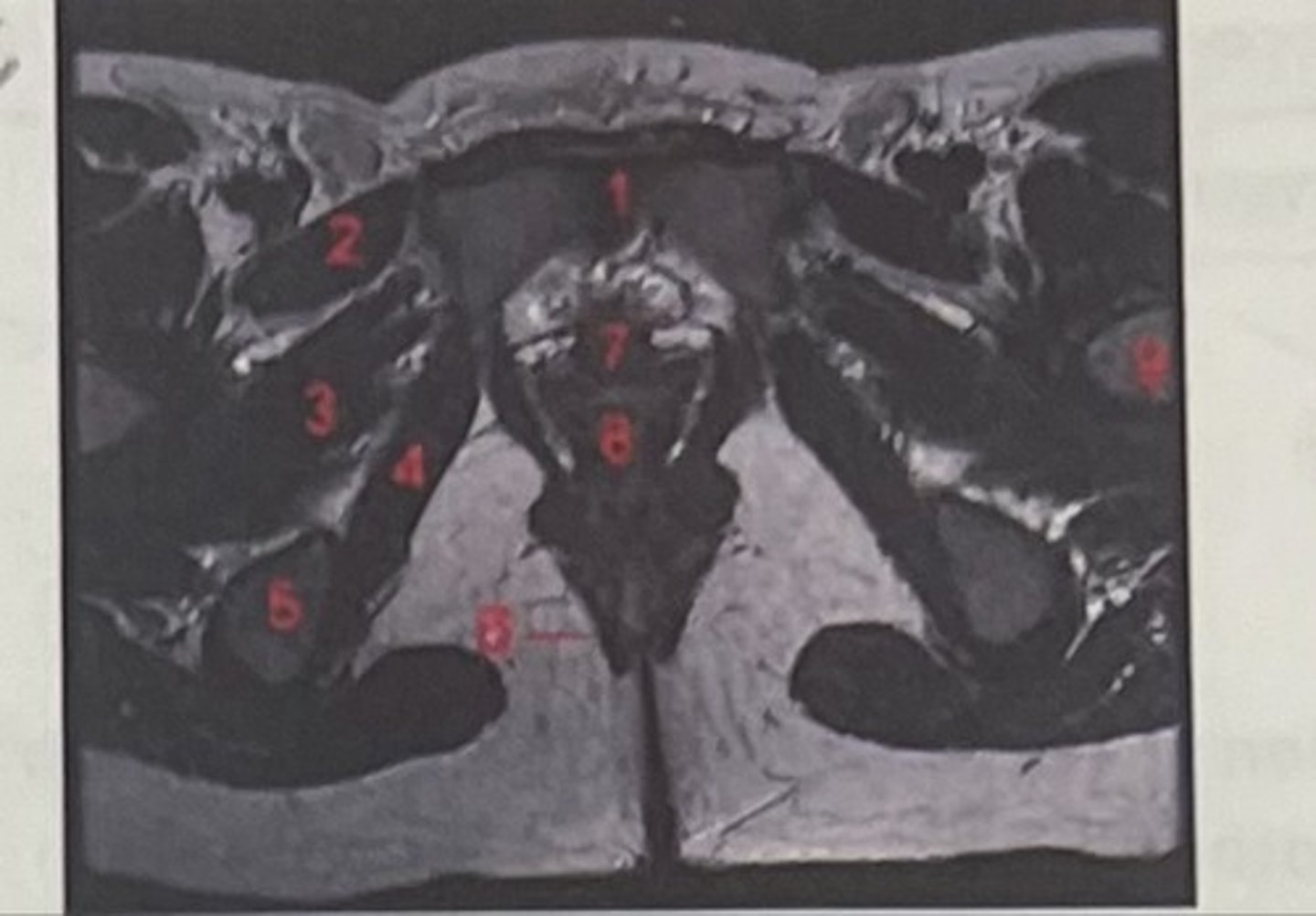
Pectineus
What is 2
Obturator externus
What is 3
obturator internus
What is 4
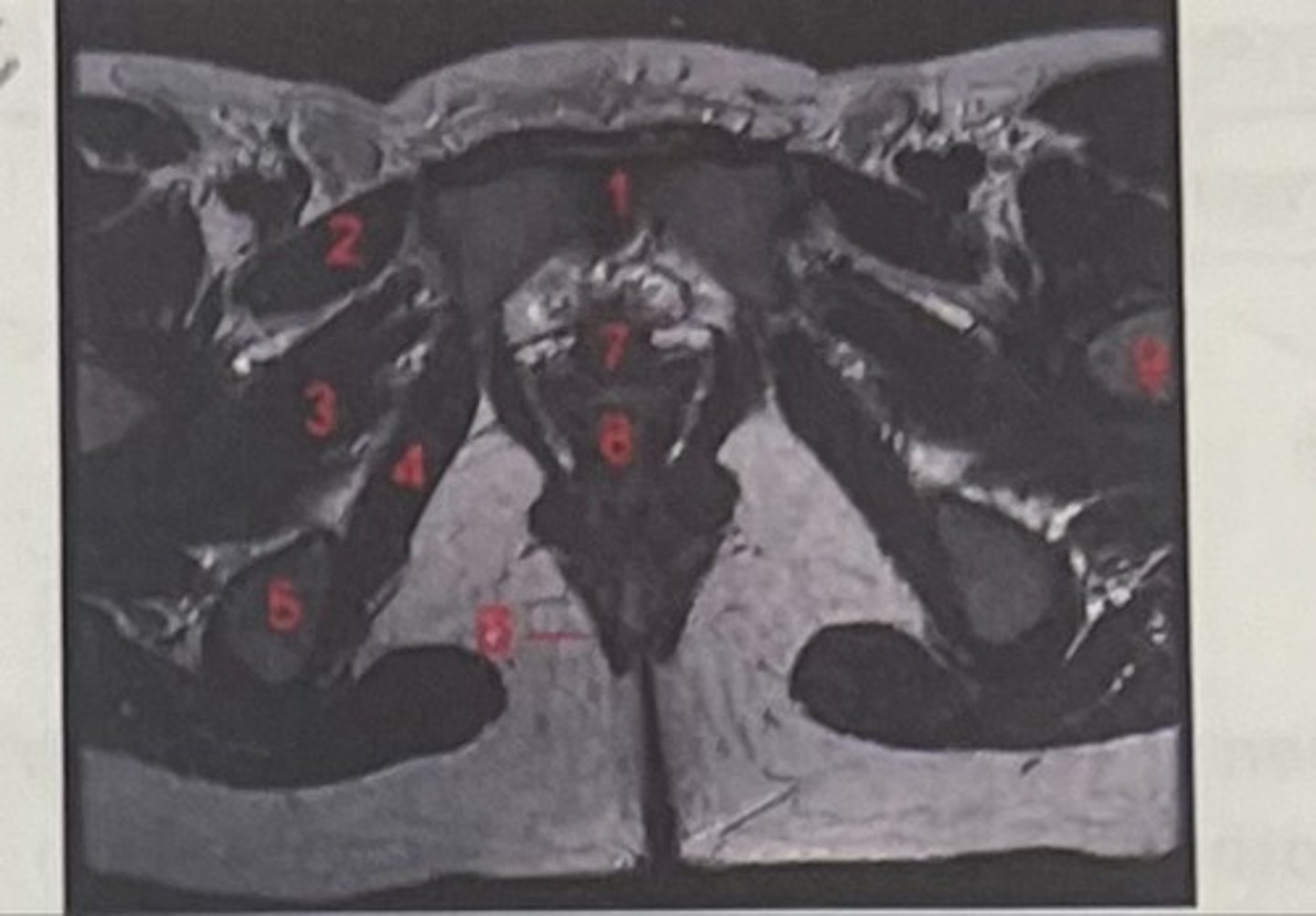
ischial tuberosity
What is 5
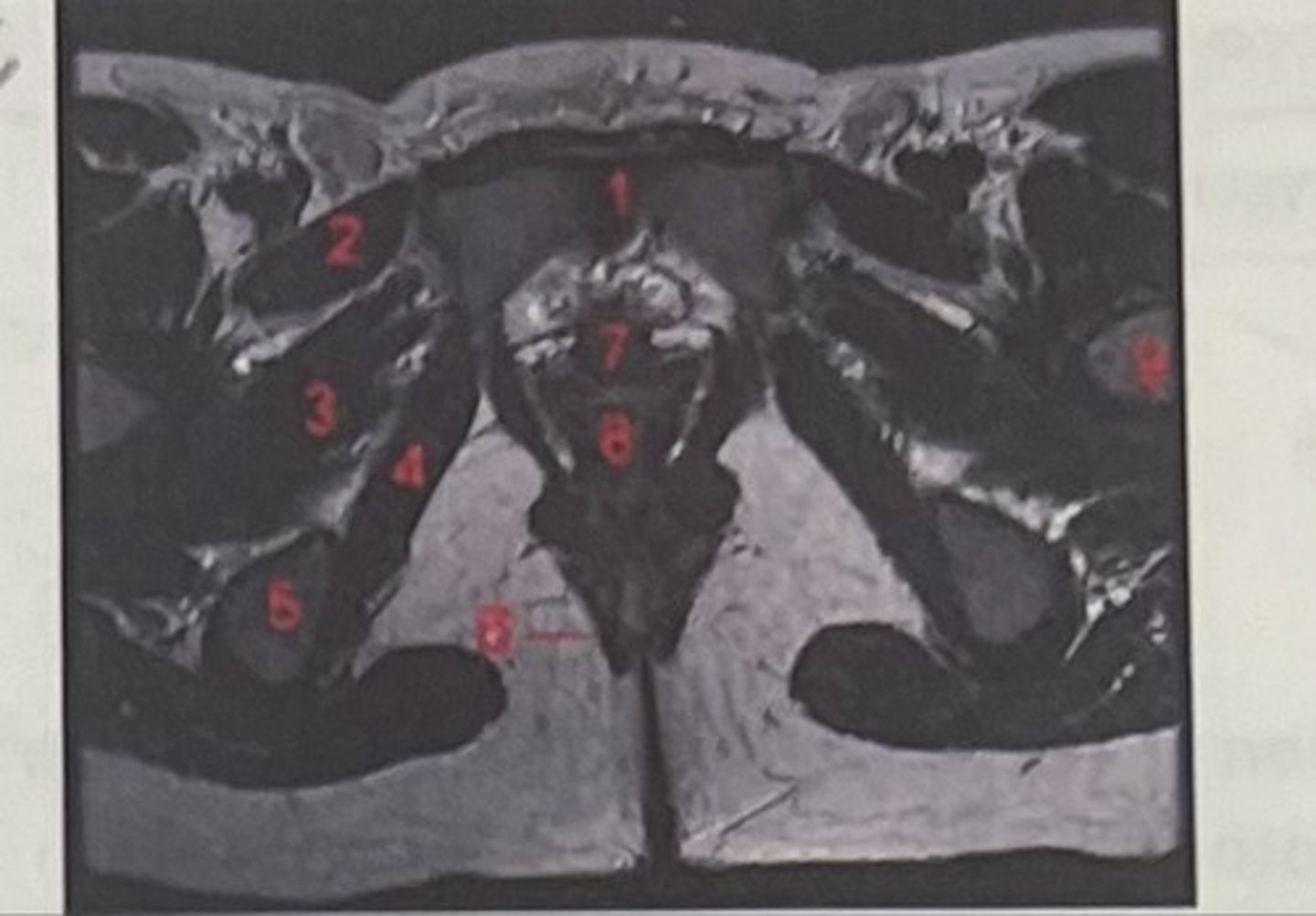
external spincter
What is 6
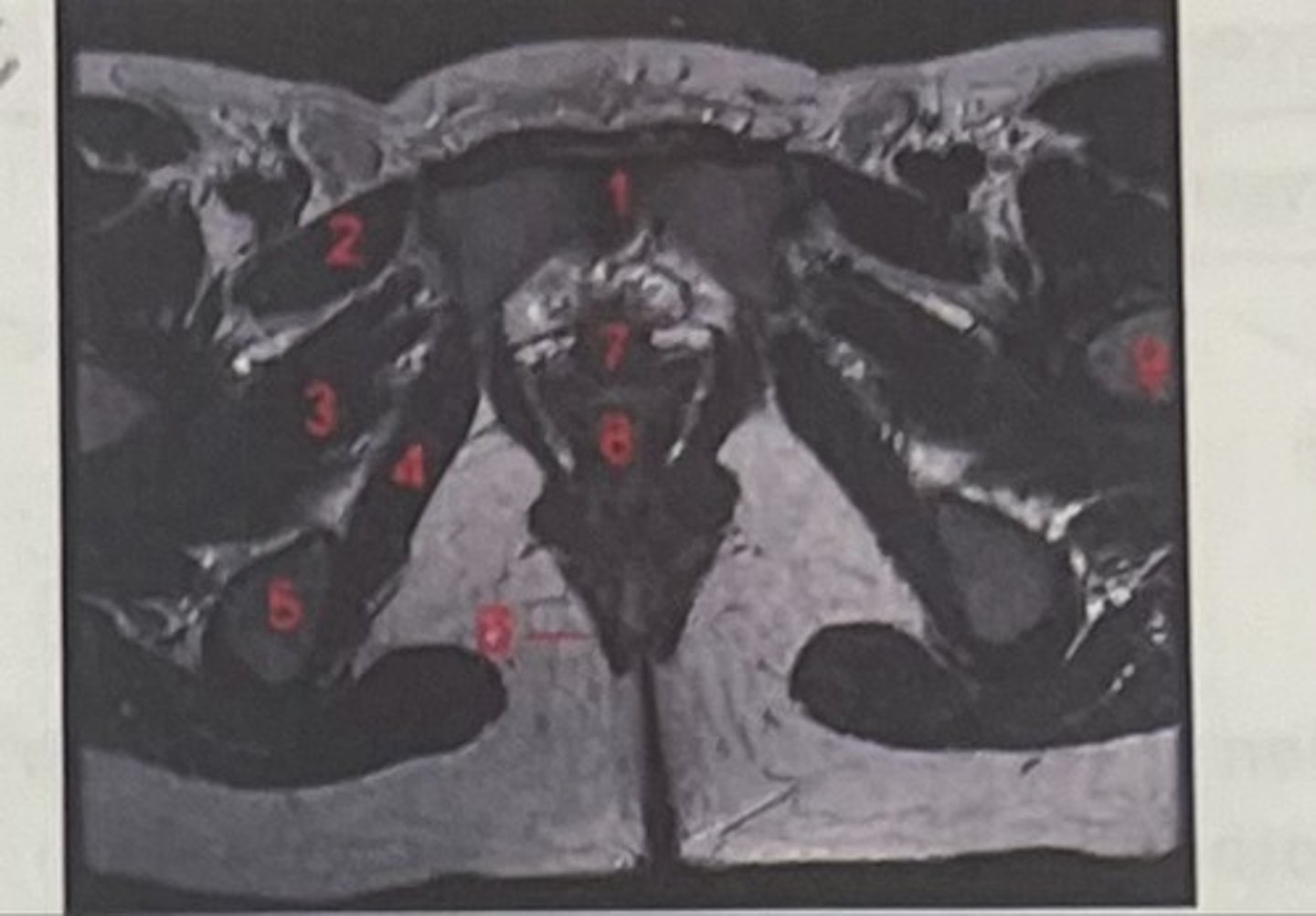
Urethra
What is 7
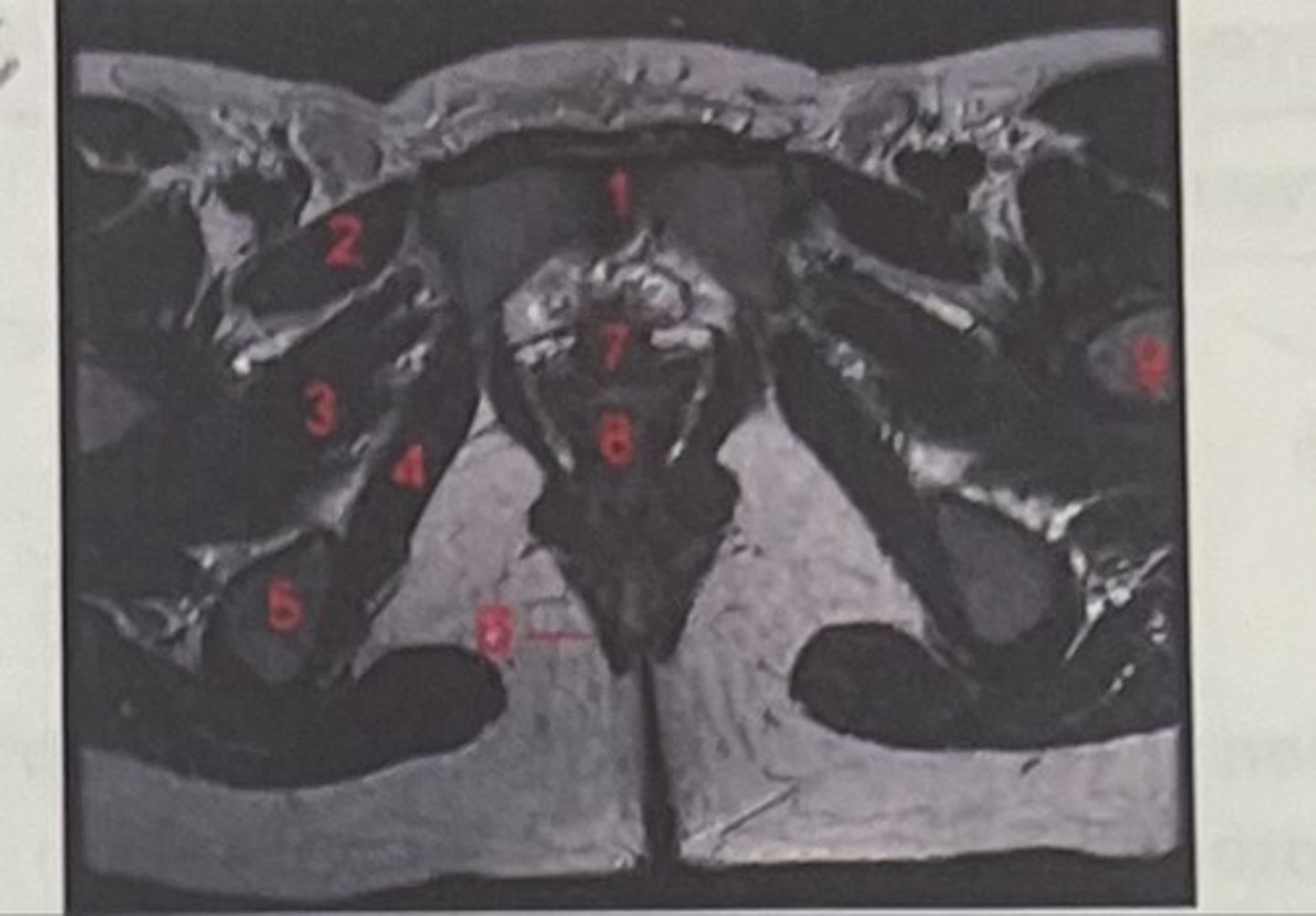
Vagina
What is 8
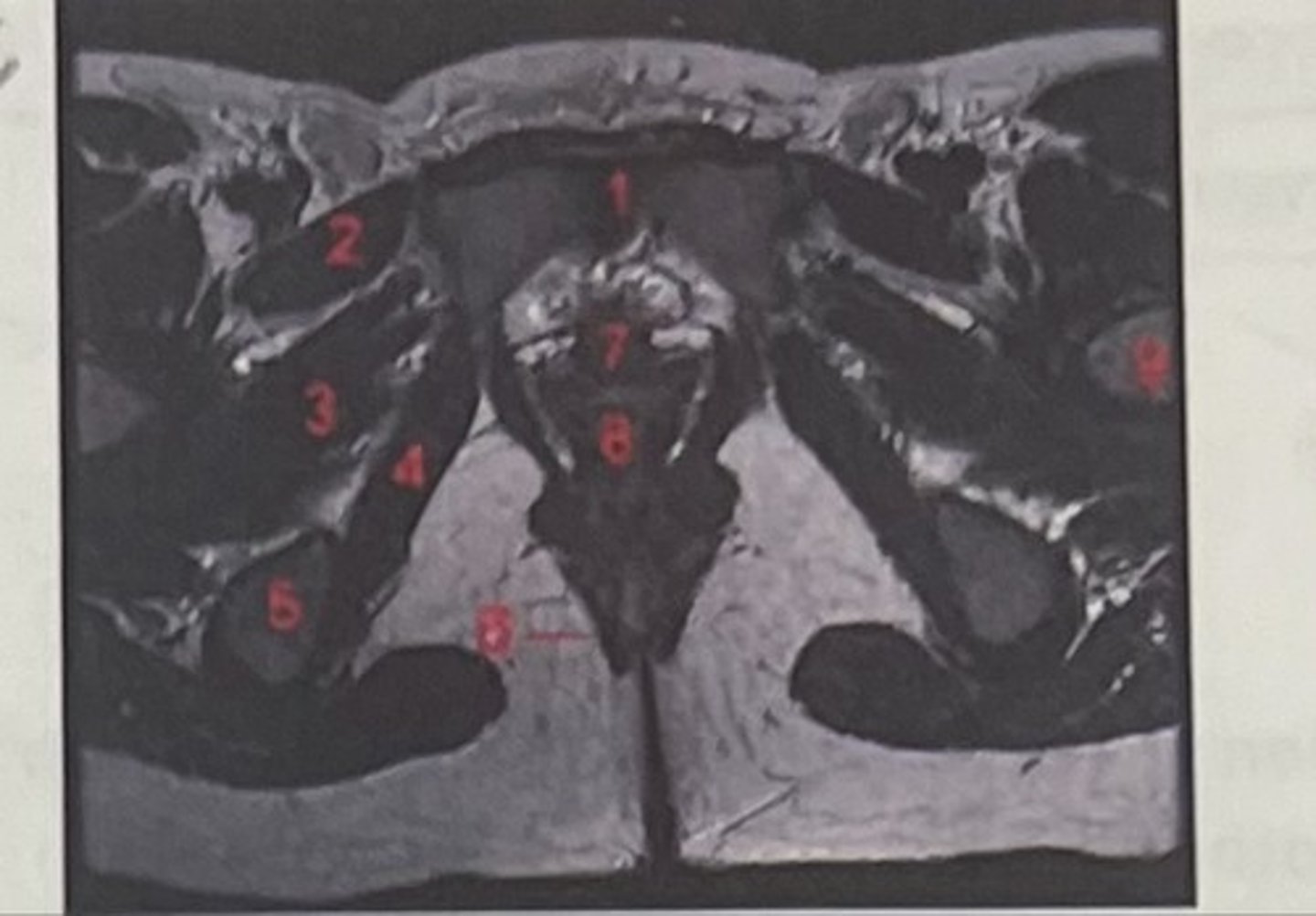
Femoral nerve
What is 9
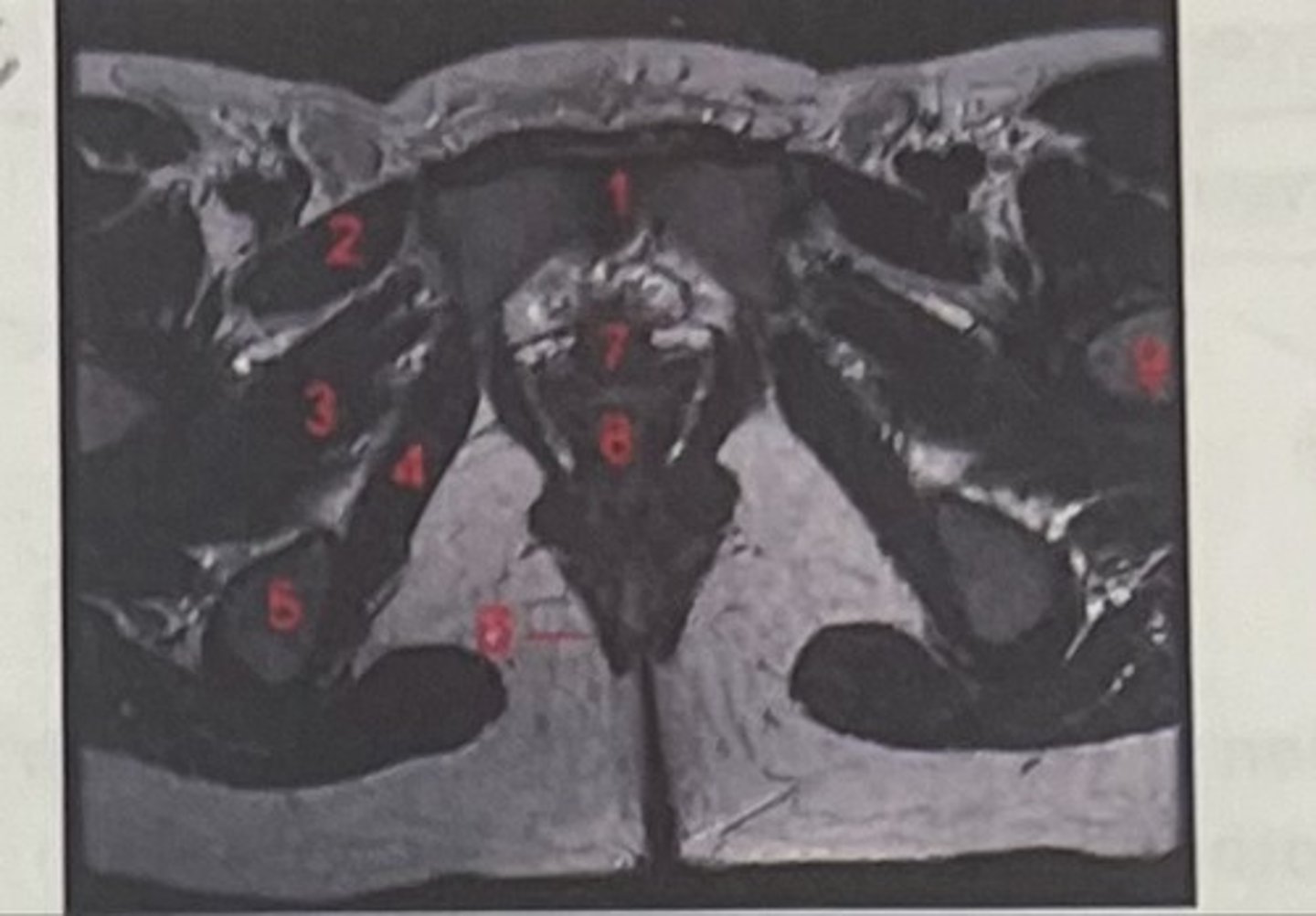
Left lung
What is 1
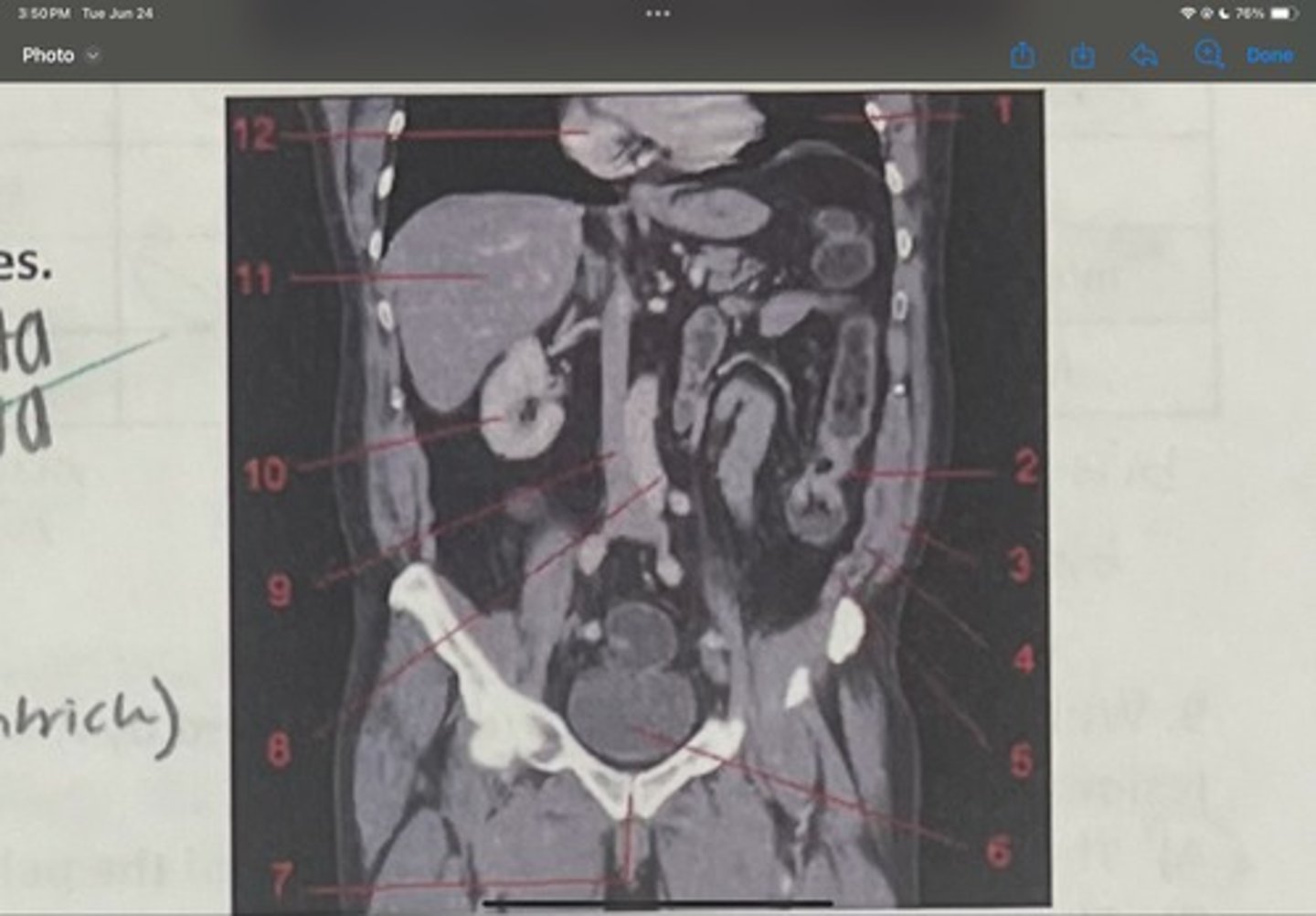
Descending colon
What is 2
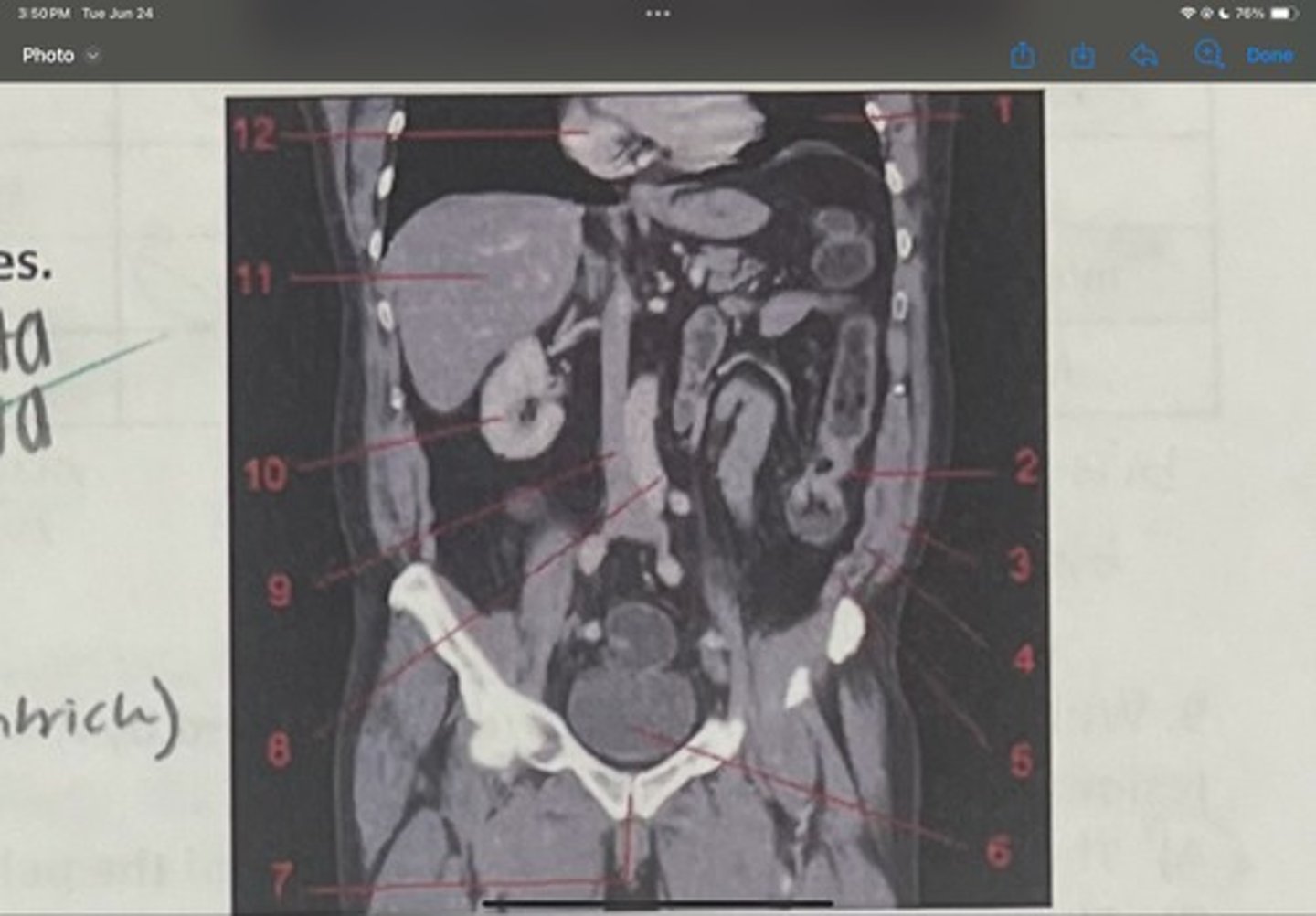
External oblique
What is 3
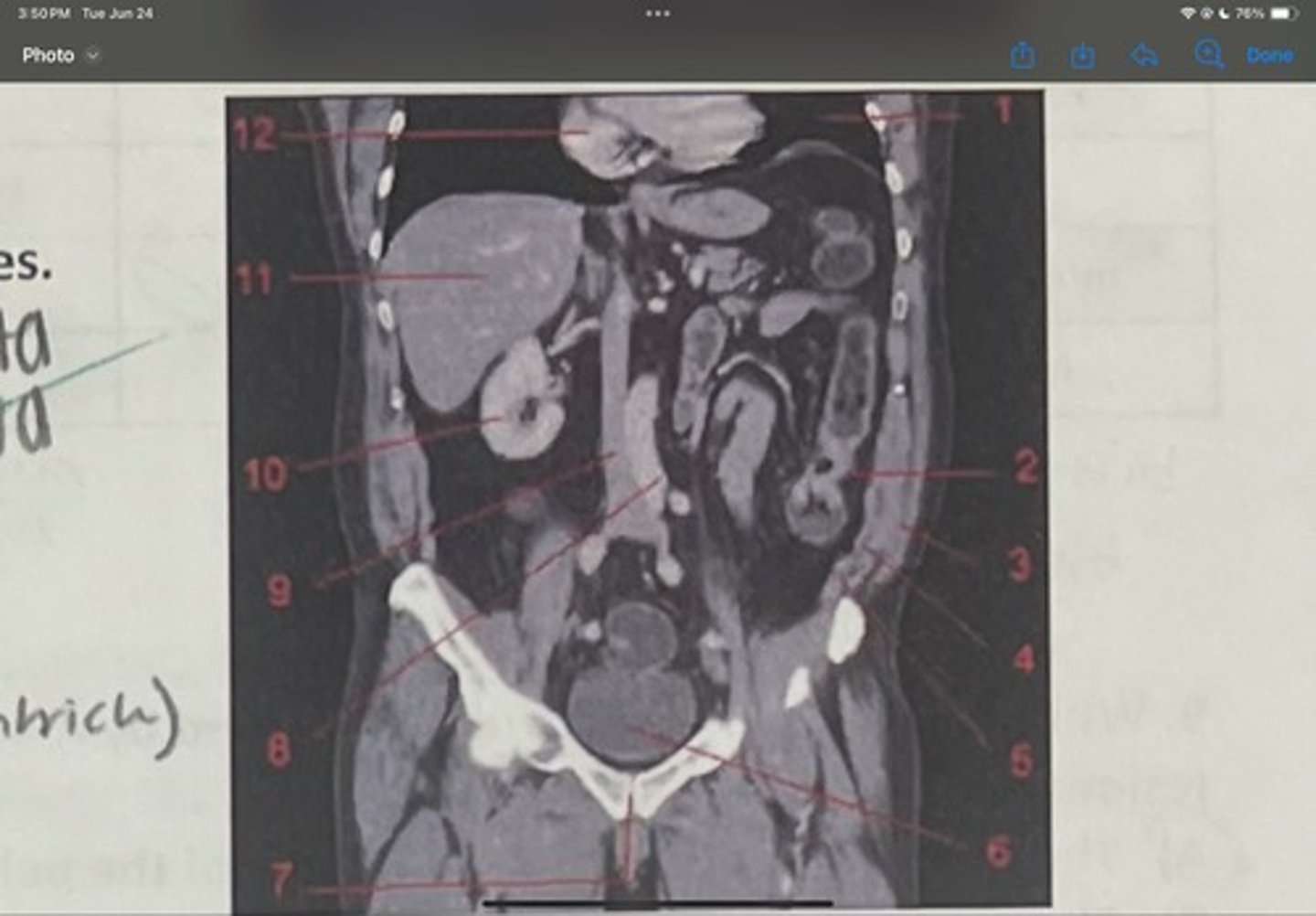
Internal obliques
What is 4
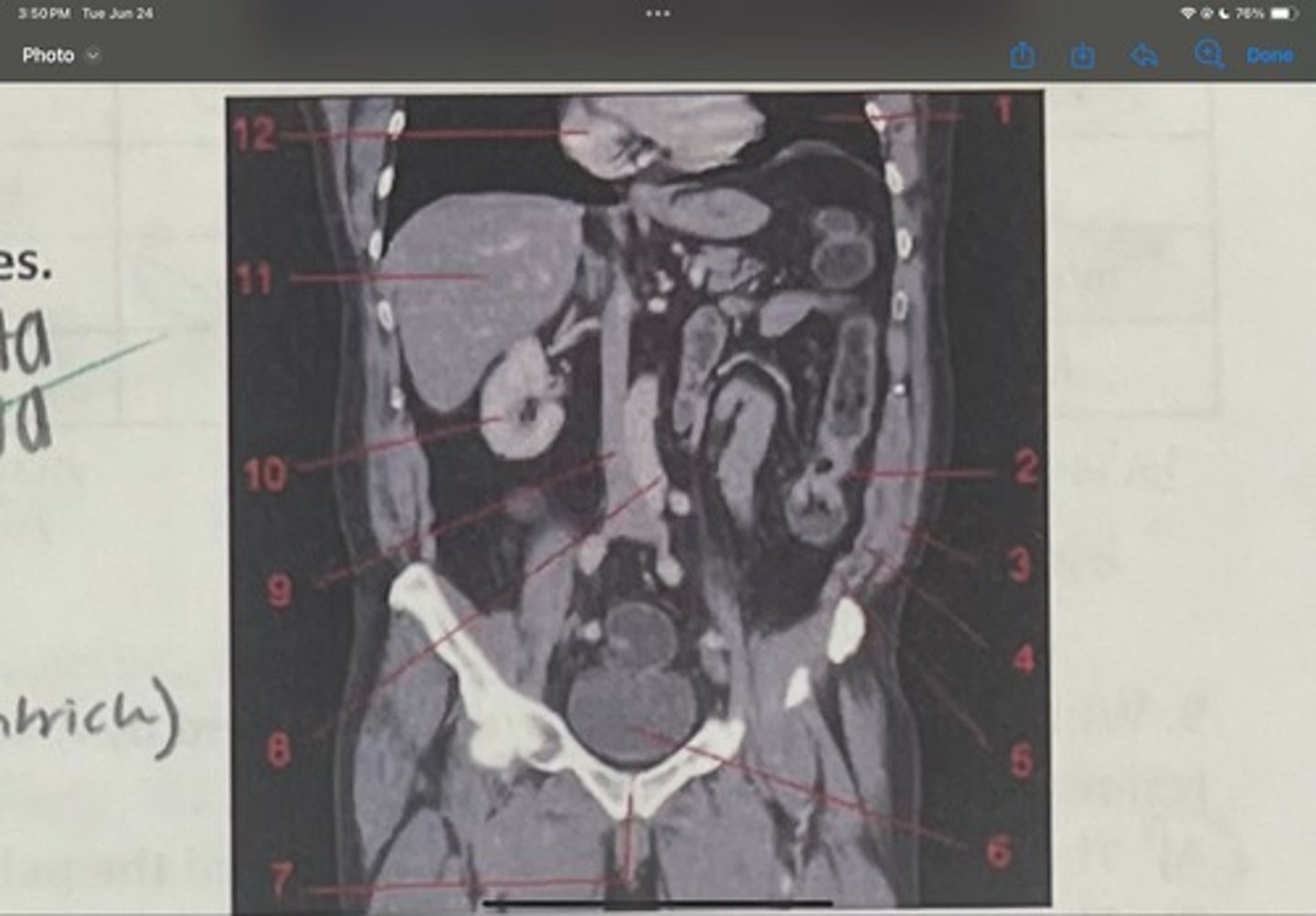
Transversus abdominis
What is 5
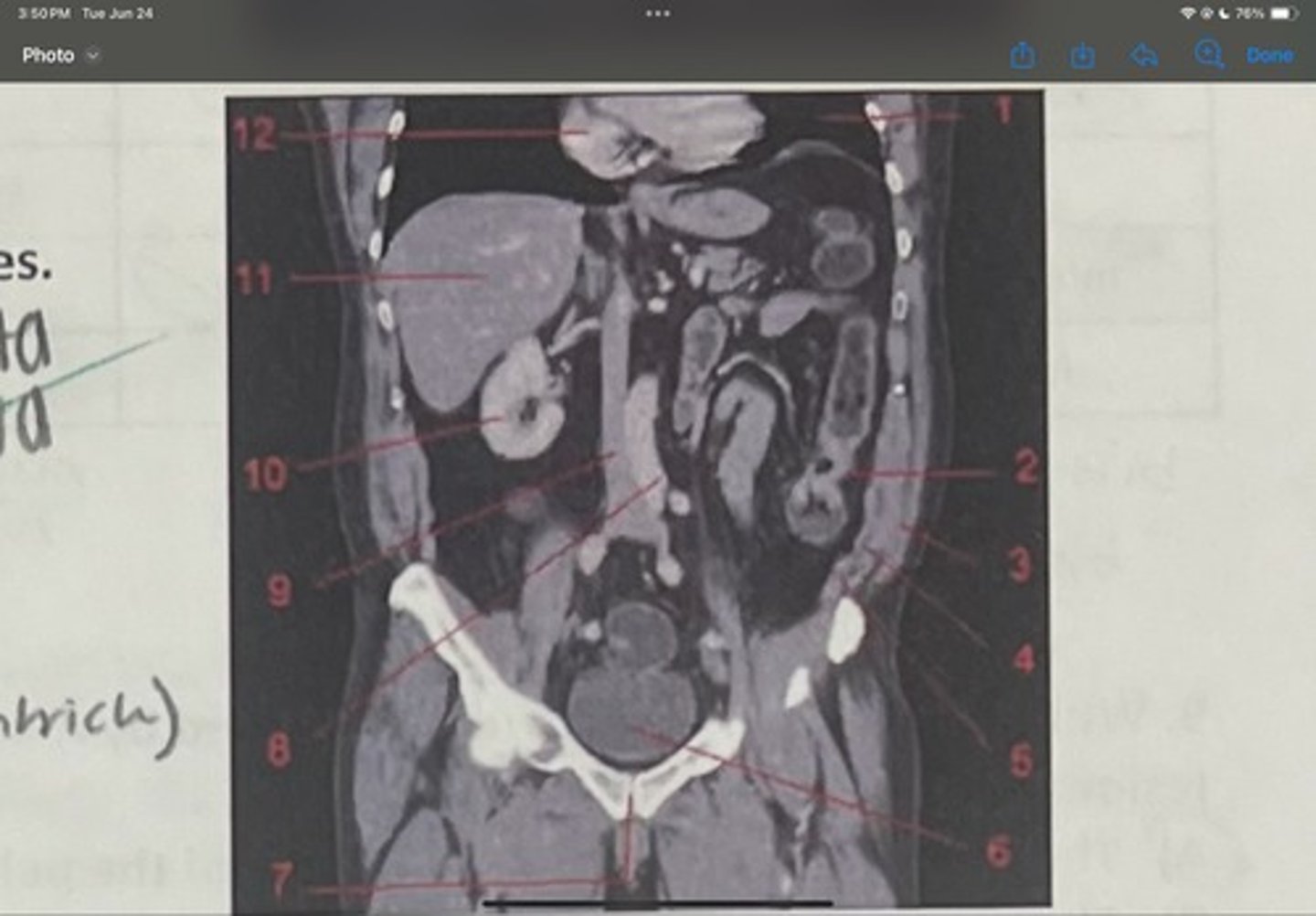
Bladder
What is 6
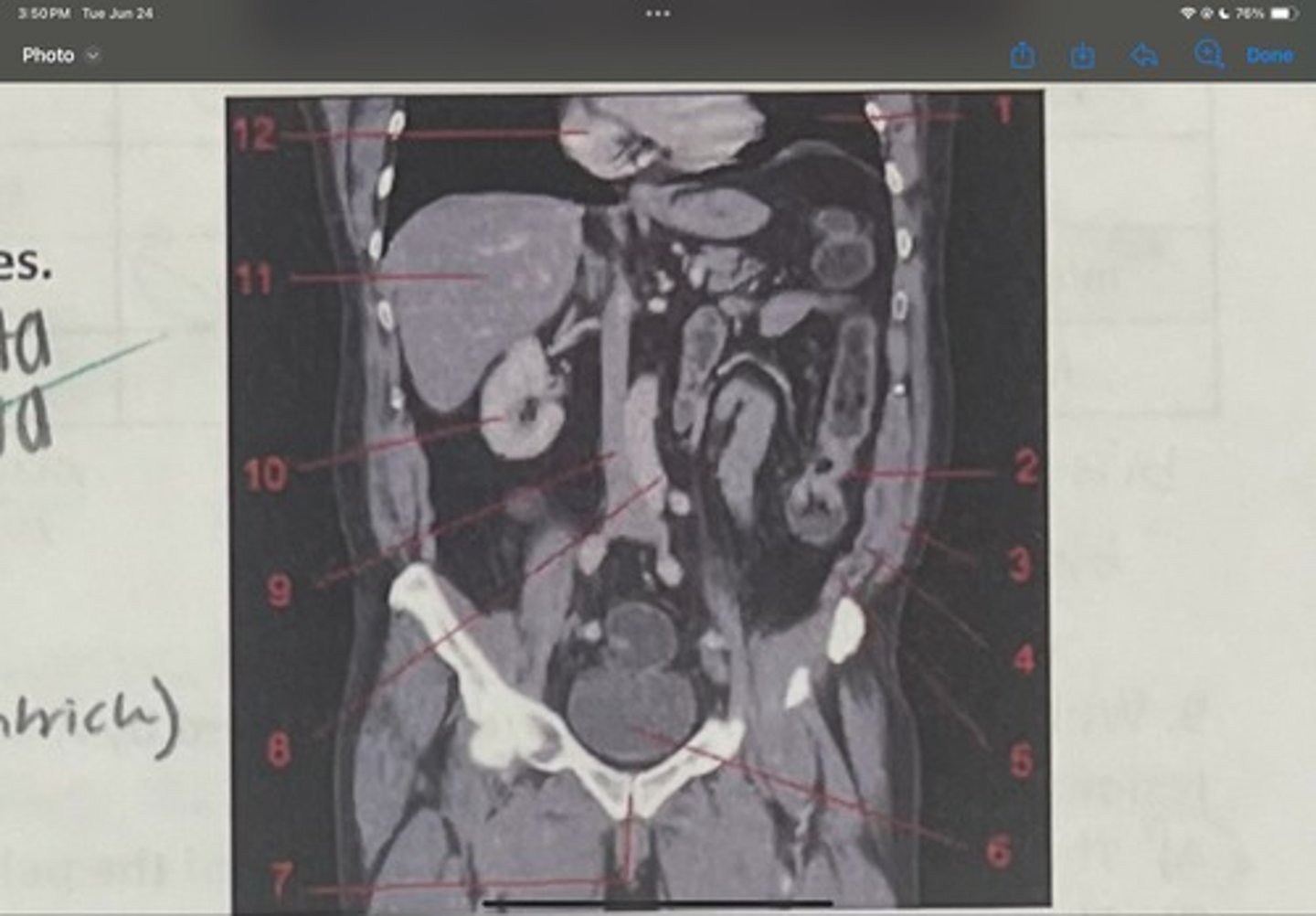
Pubic sysmphysis
What is 7
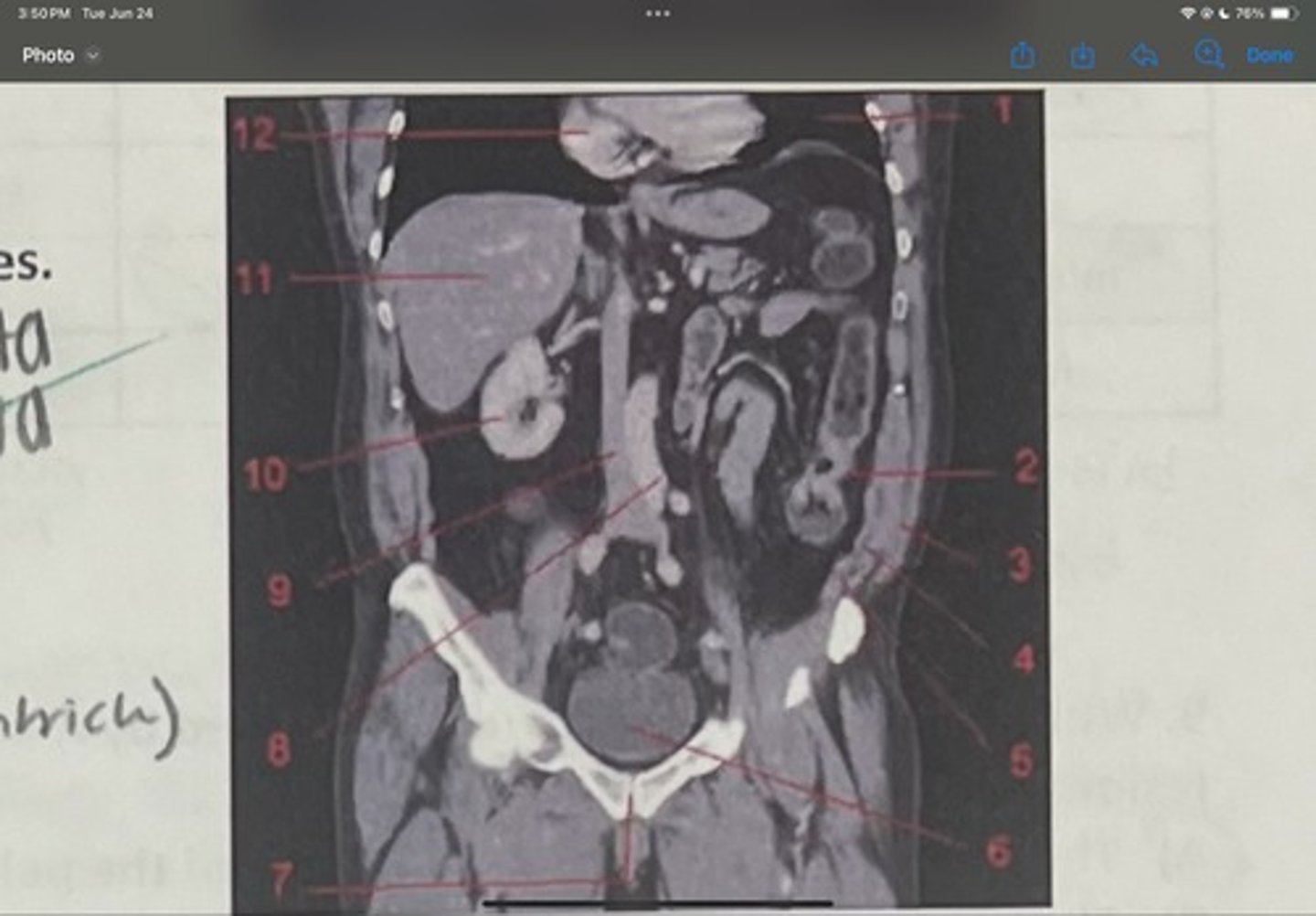
Abdominal aorta
What is 8
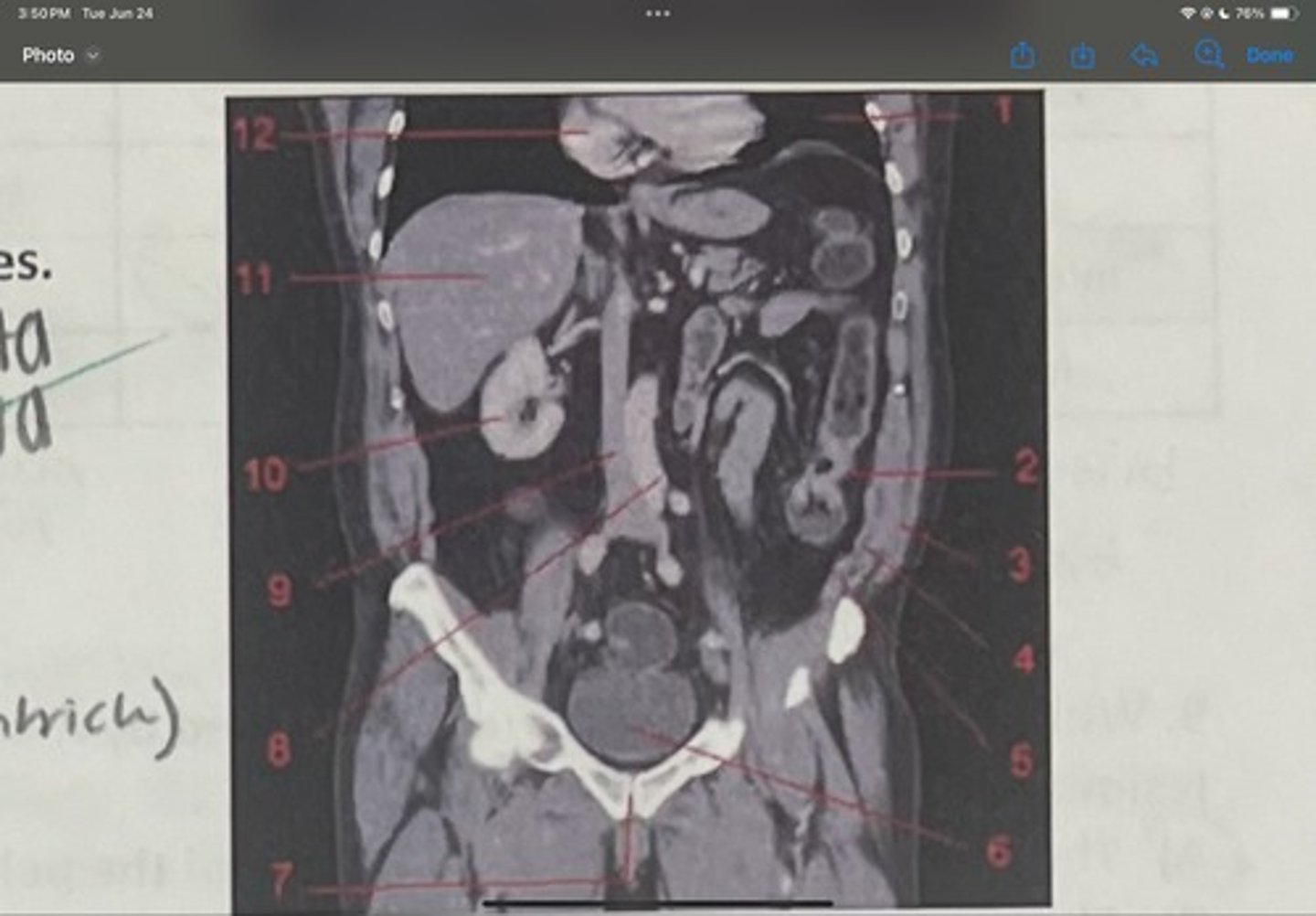
Inferior vena cava
What is 9
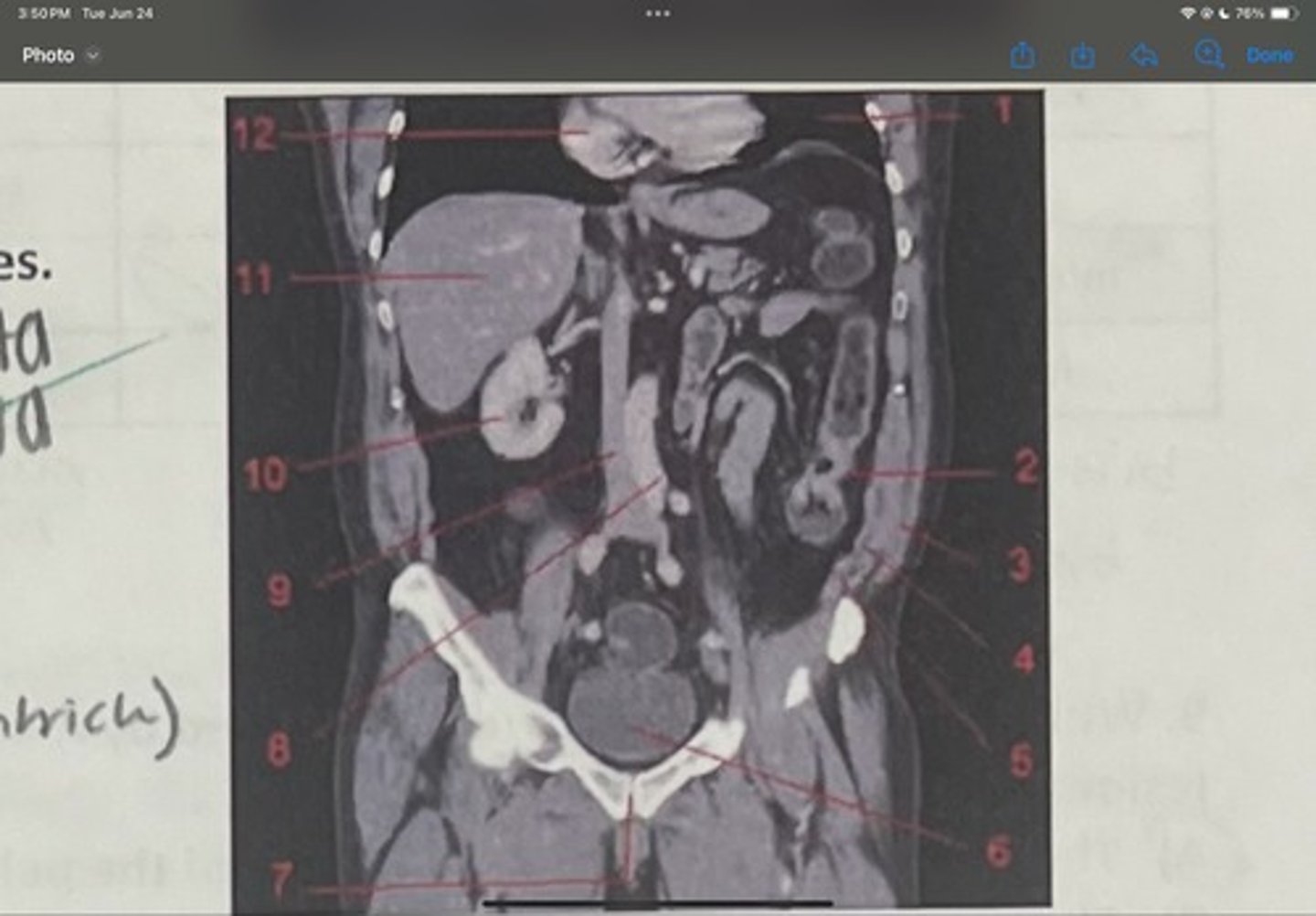
Right kidney
What is 10
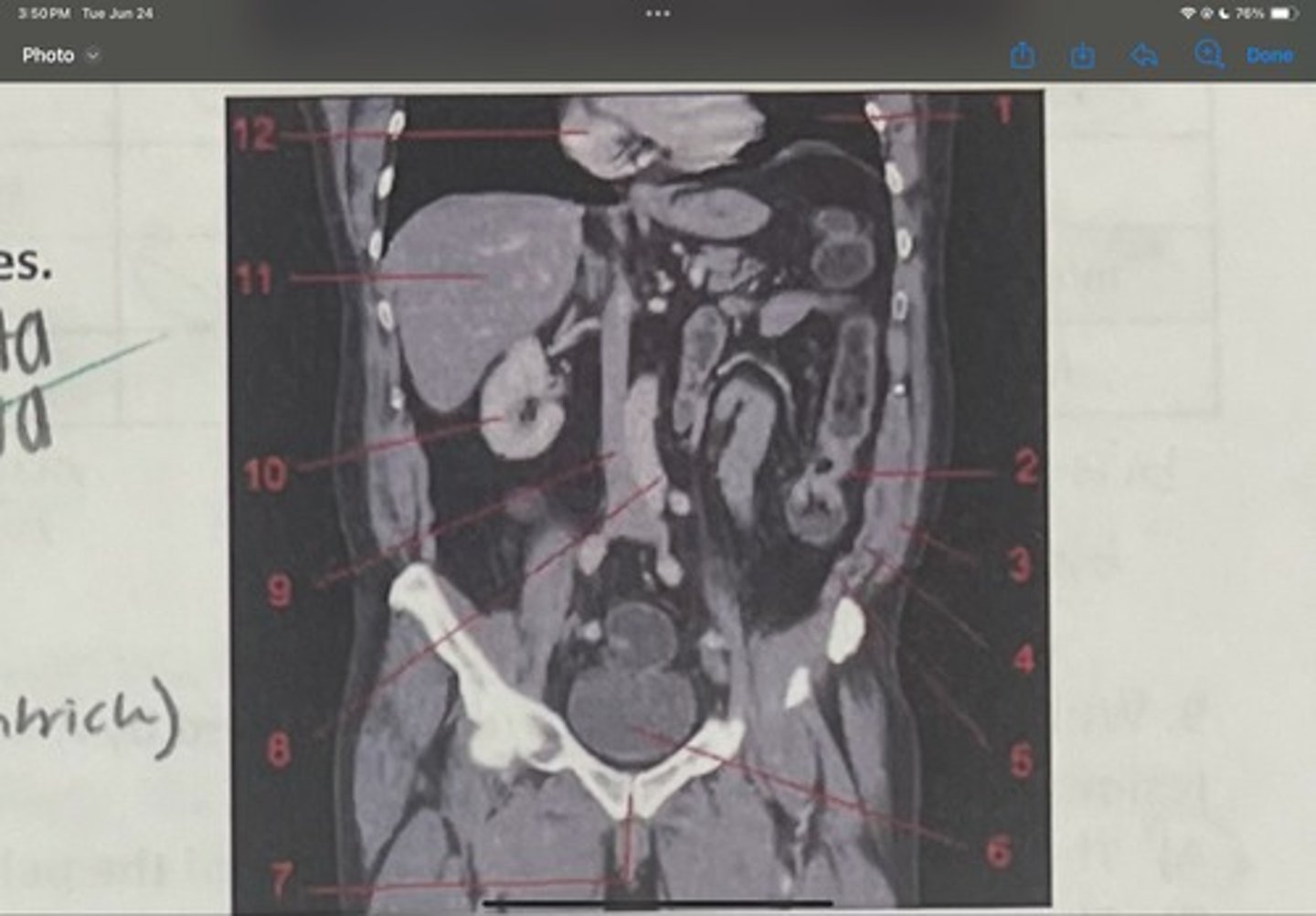
Liver
What is 11
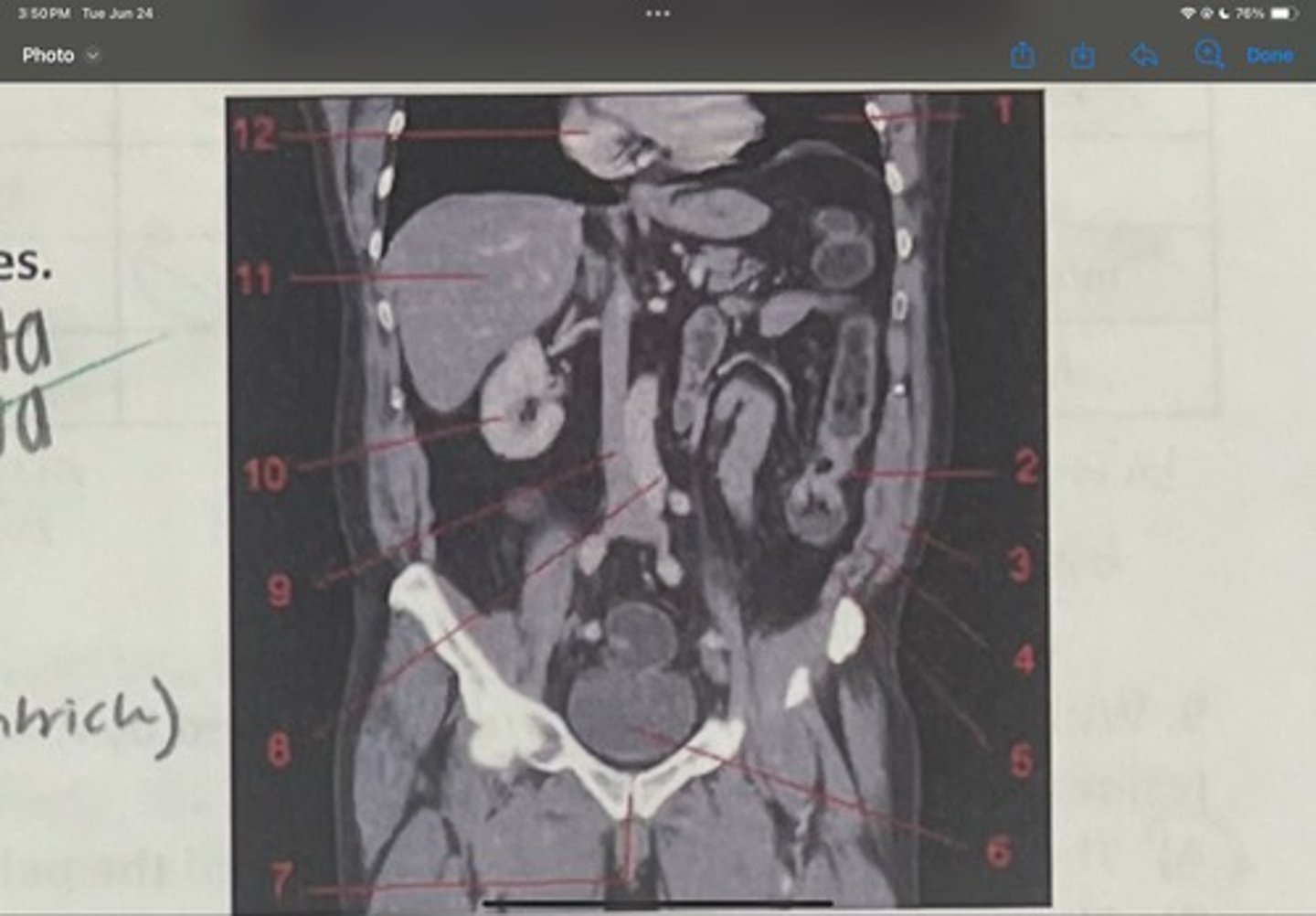
Heart (right ventricle)
What is 12
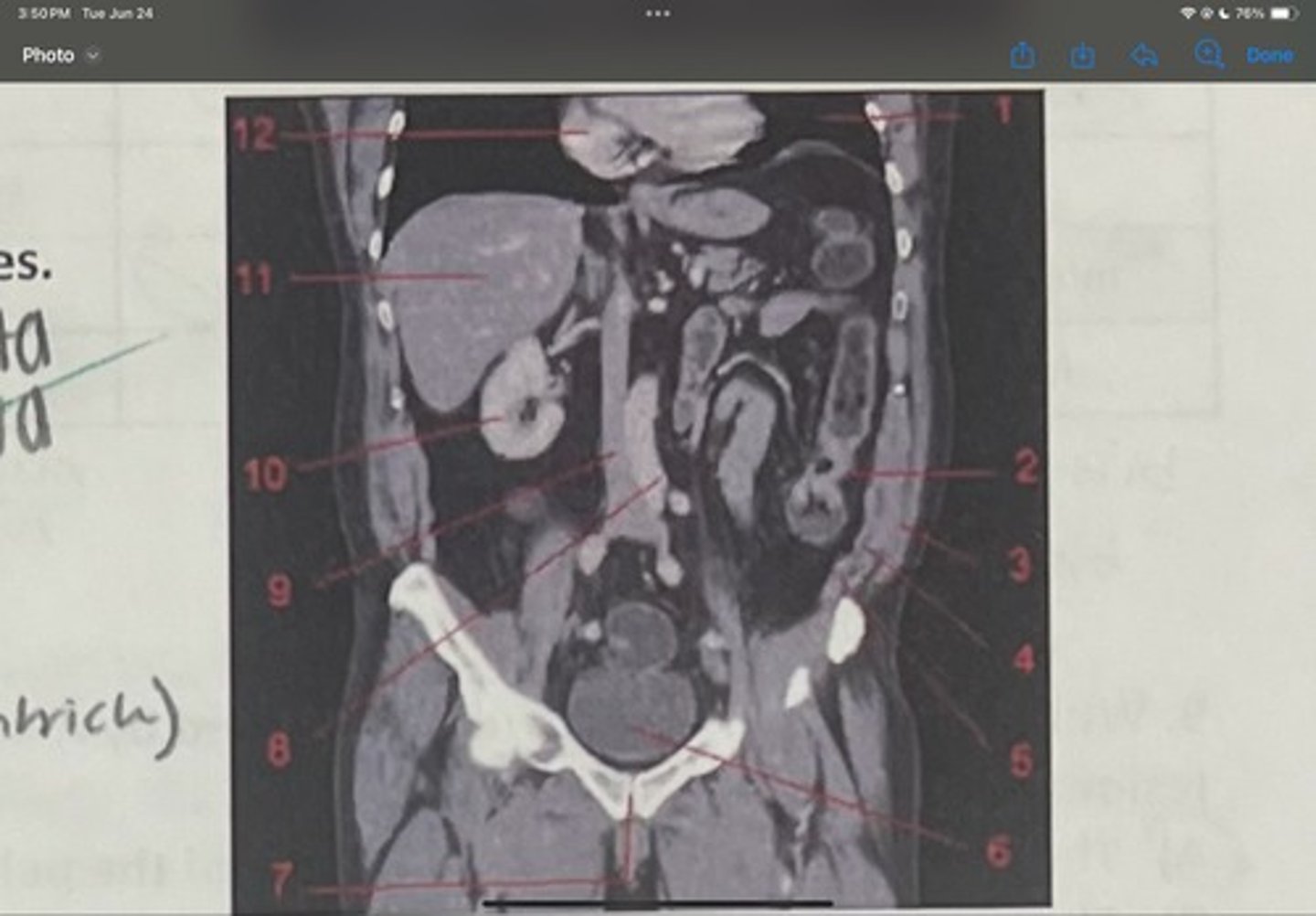
Subcostal nerve (T12)
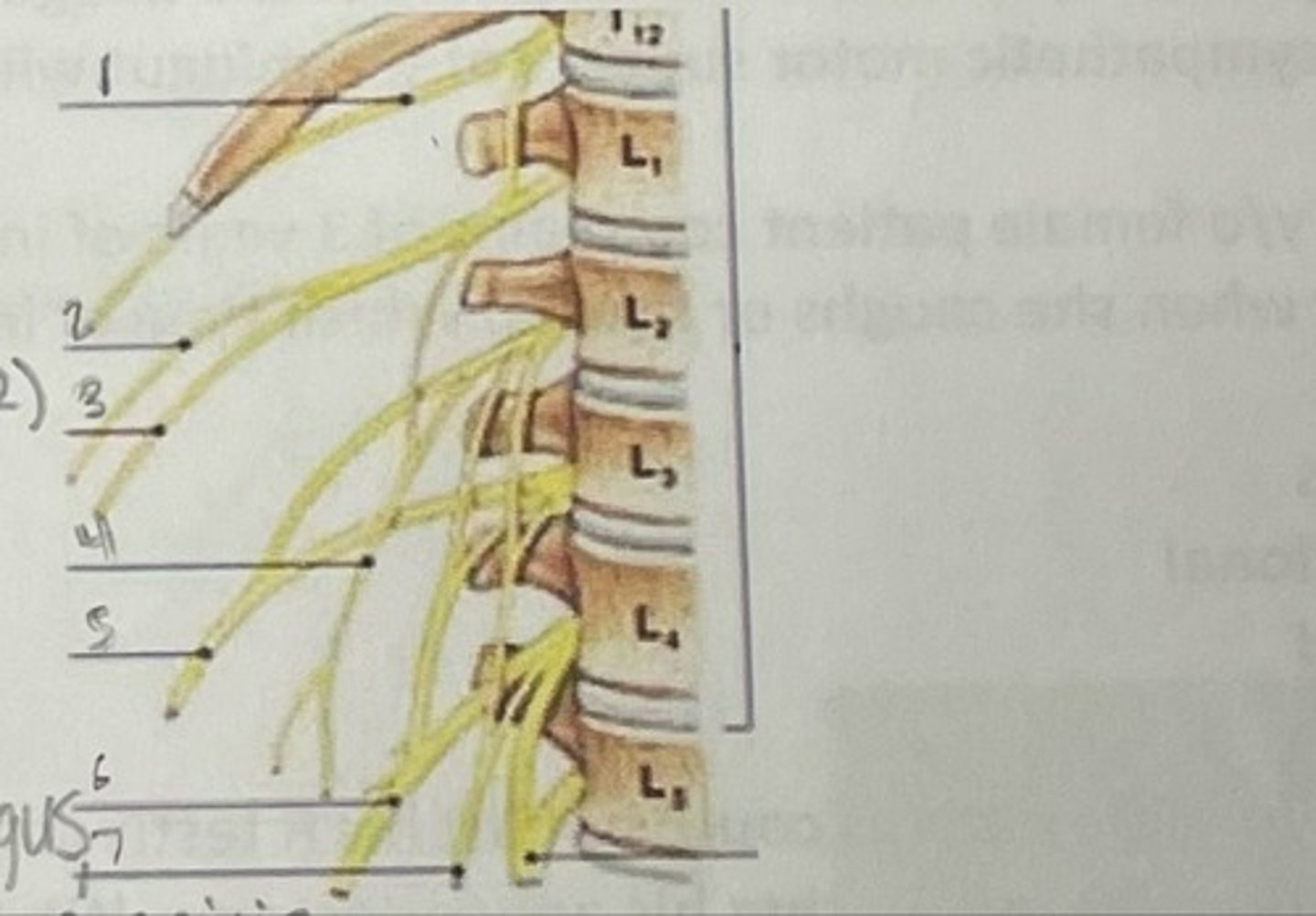
What is 1
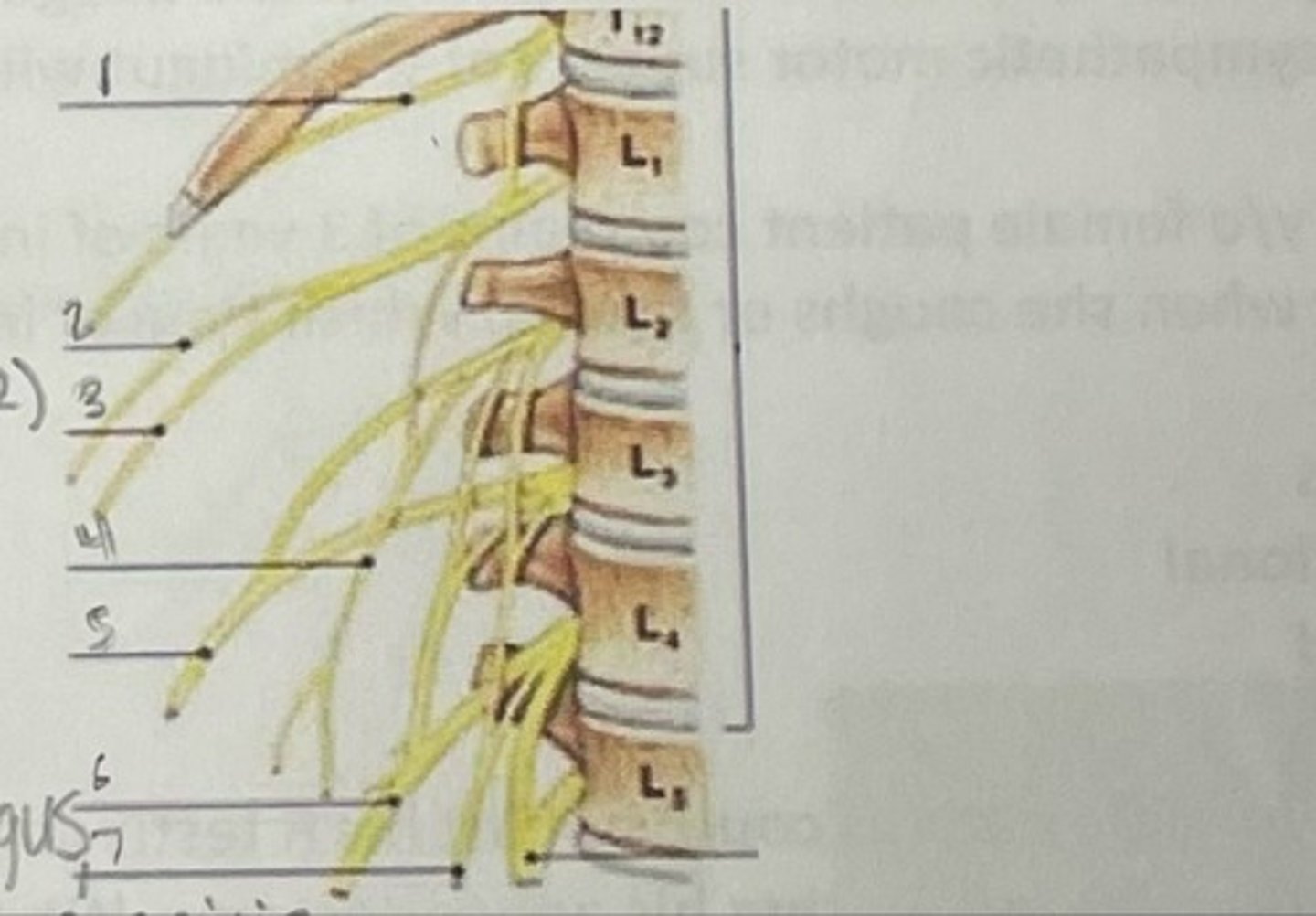
Illiohypogastric nerve (T12/L1)
What is 2
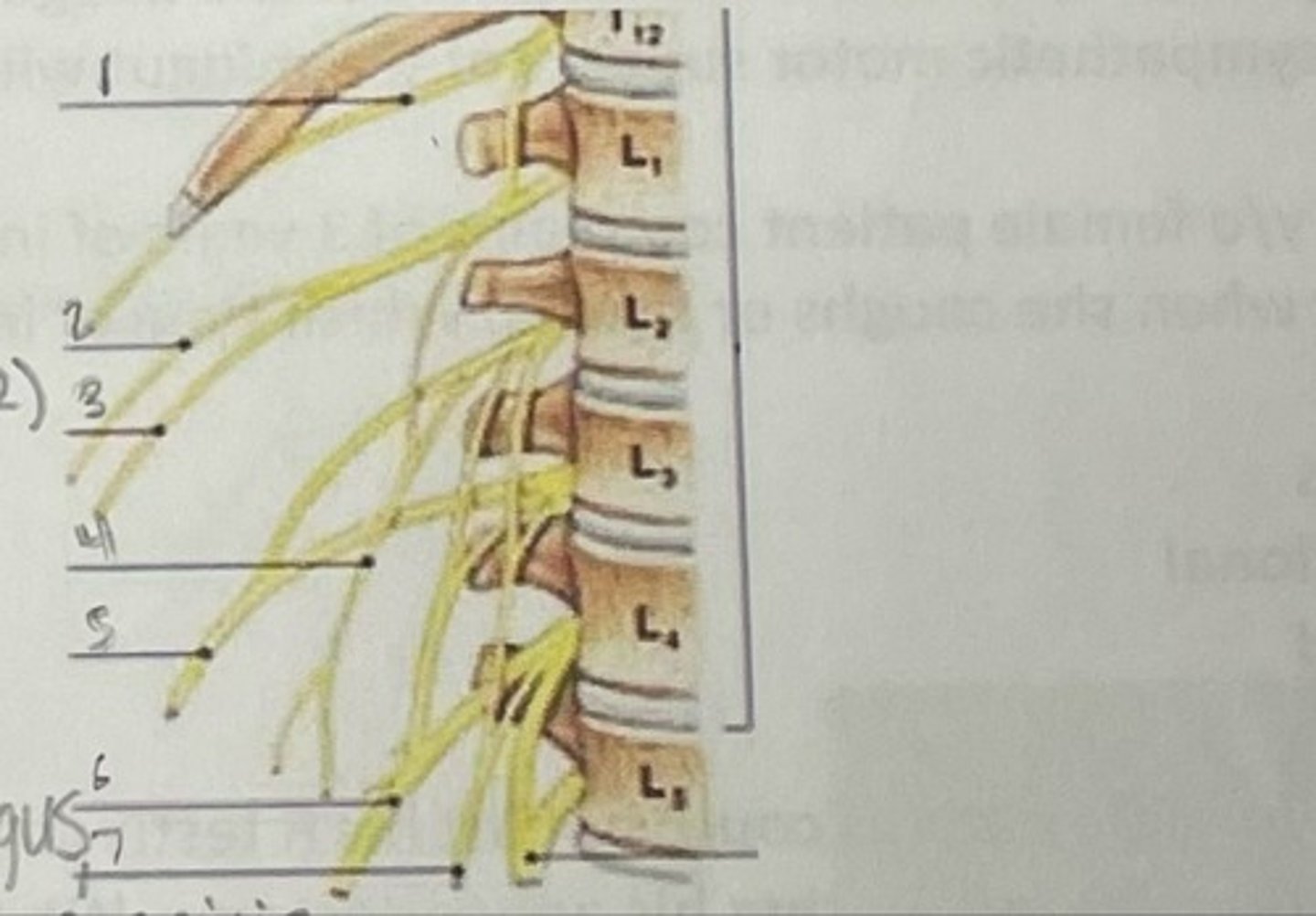
Illioinguinal nerve (L1)
What is 3
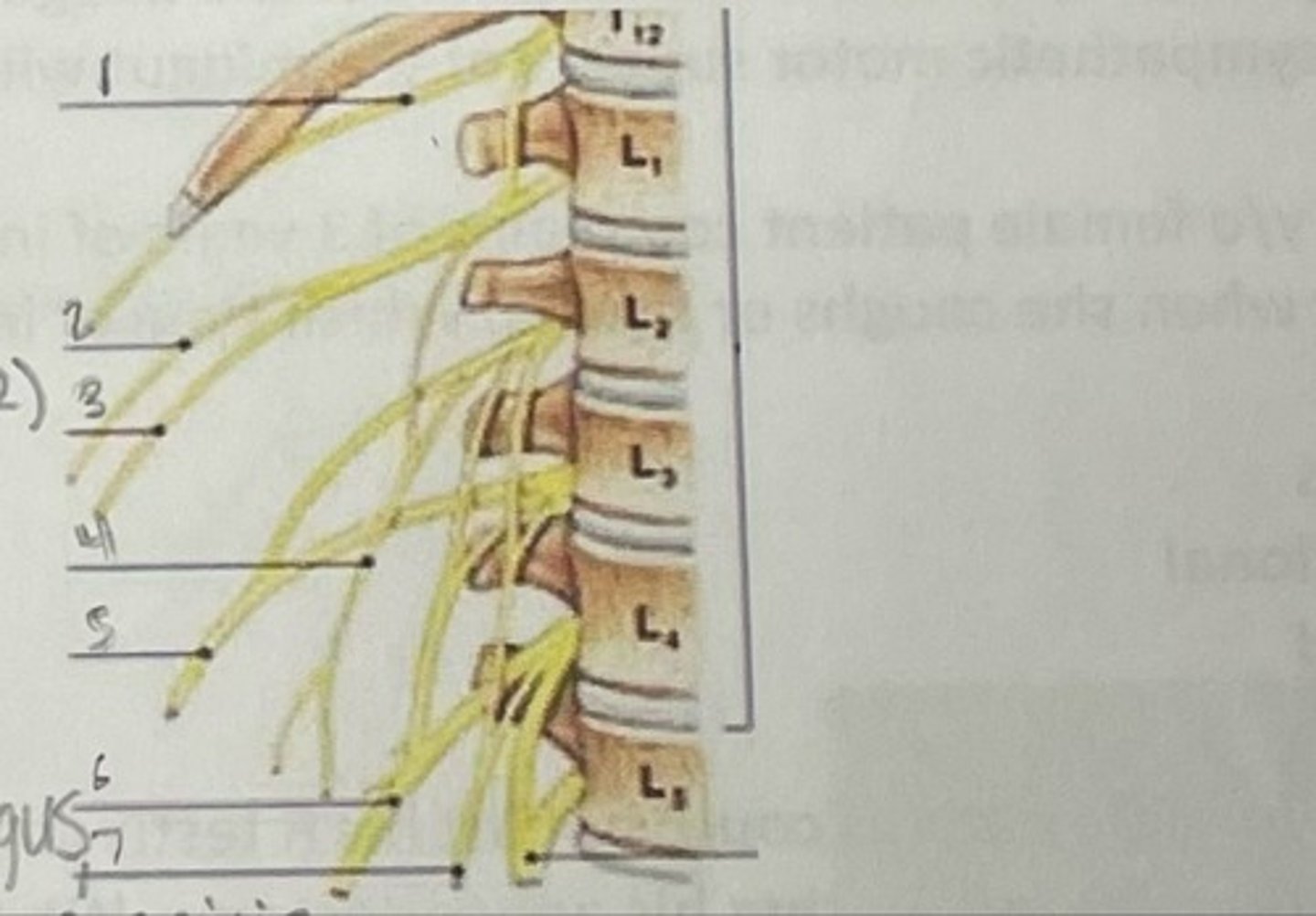
Genitofemoral nerve (L1-L2) ; on top of psoas
What is 4
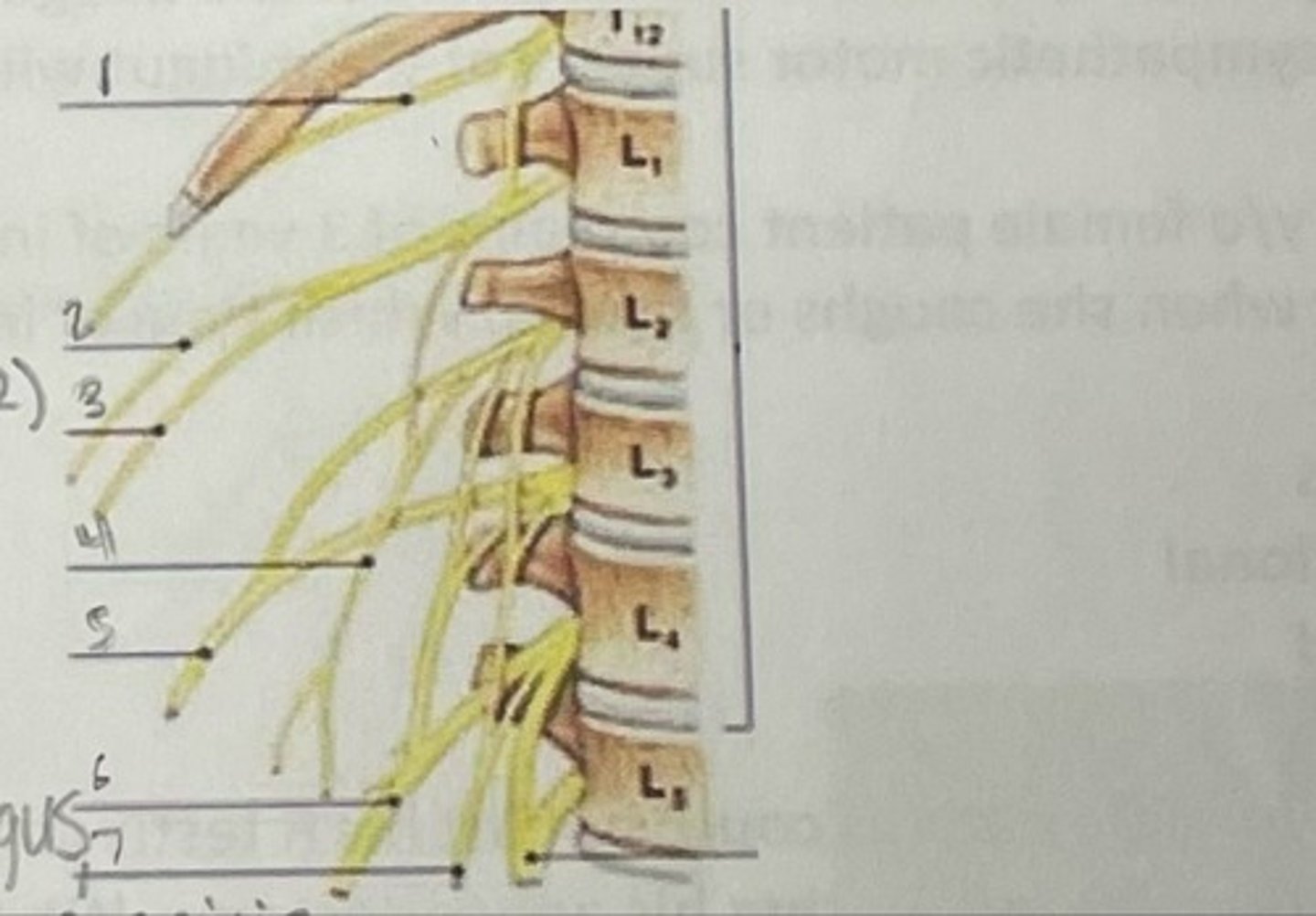
lateral femoral cutaneous nerve (L2-L3)
What is 5
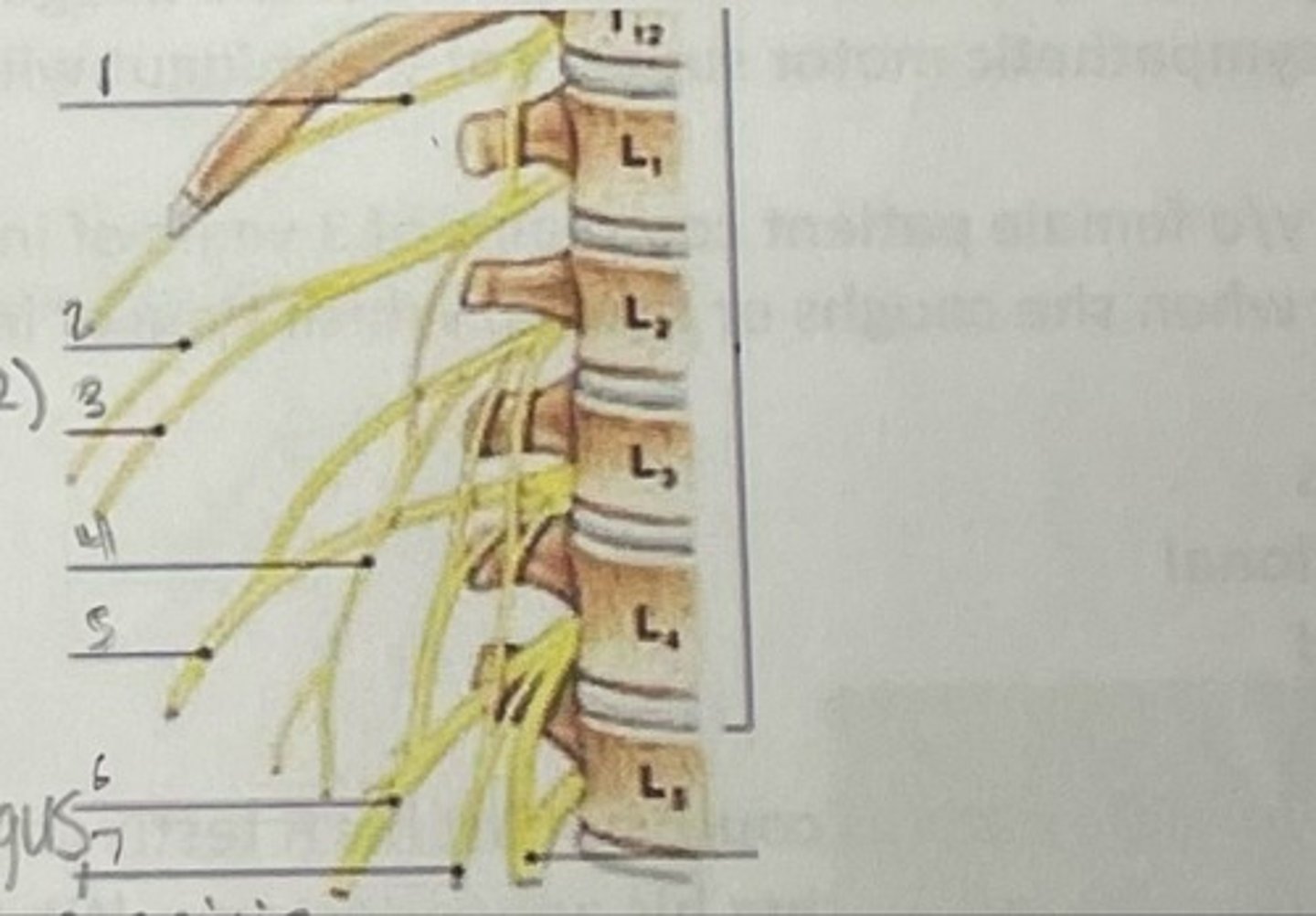
Femoral Nerve (L2-L4)
What is 6
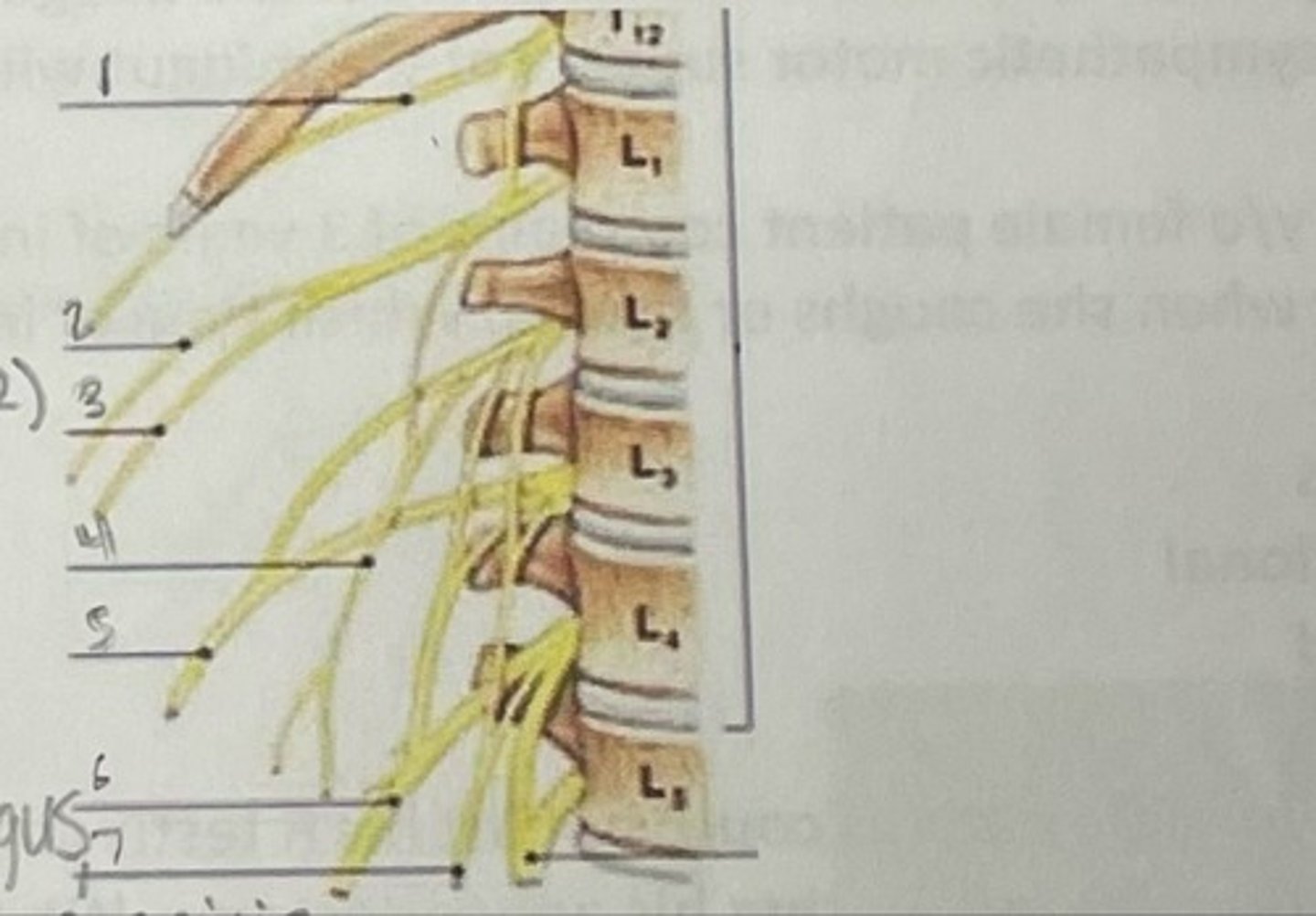
Obturator nerve (L2-L4)
What is 7
Renal artery
What is the 1st one
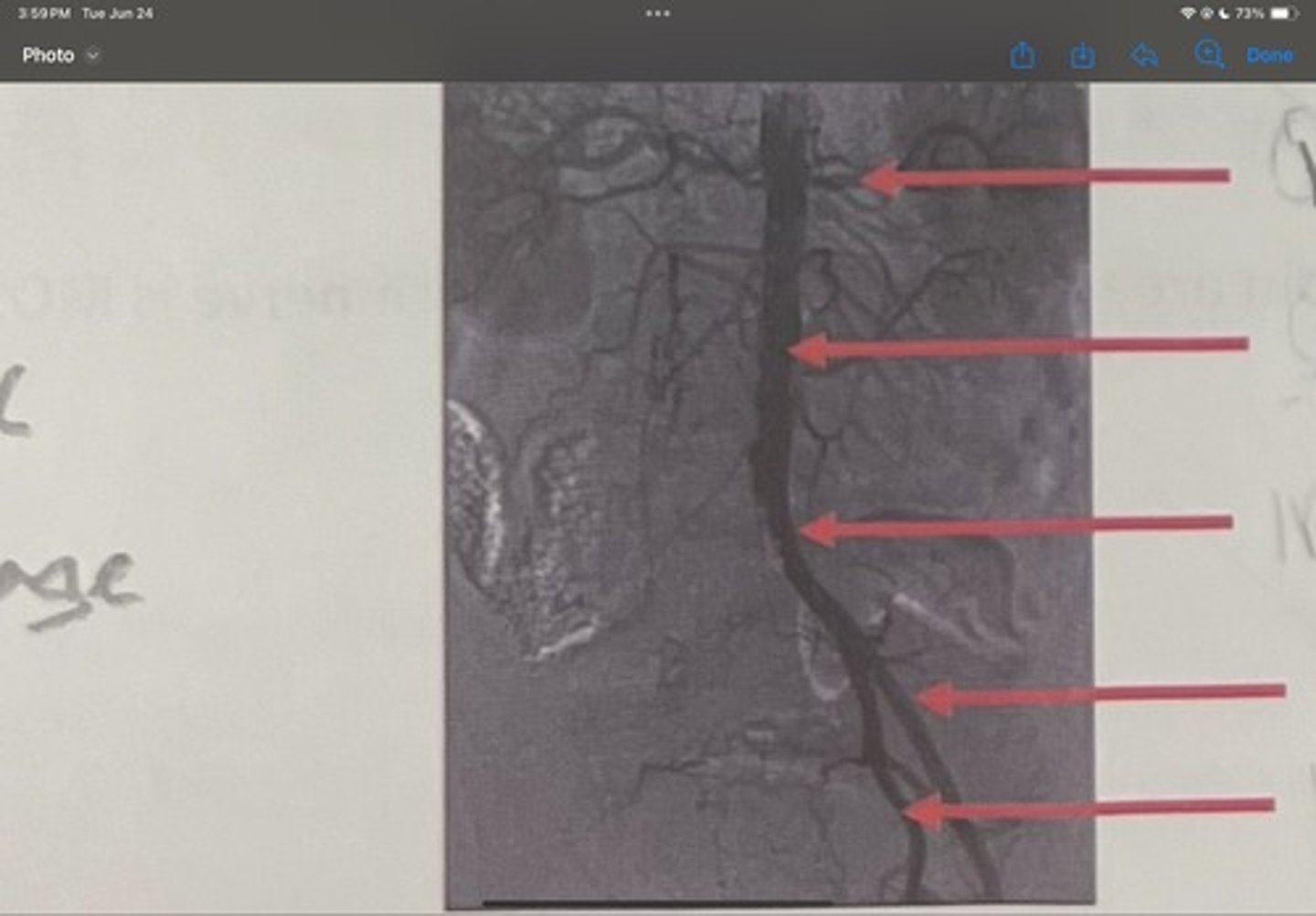
Abdominal aorta
What is the 2nd one
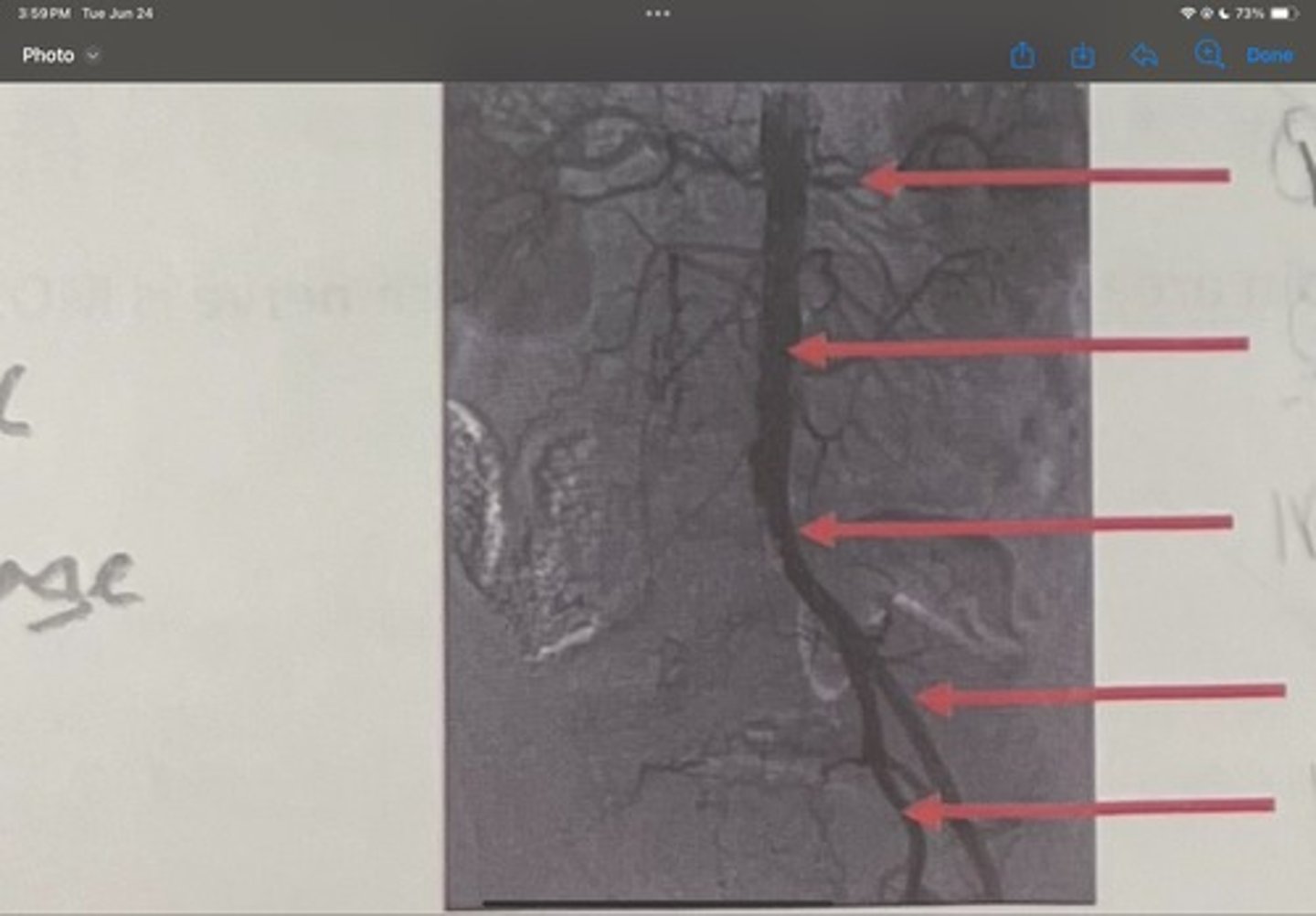
Common iliac artery
What is the 3rd one
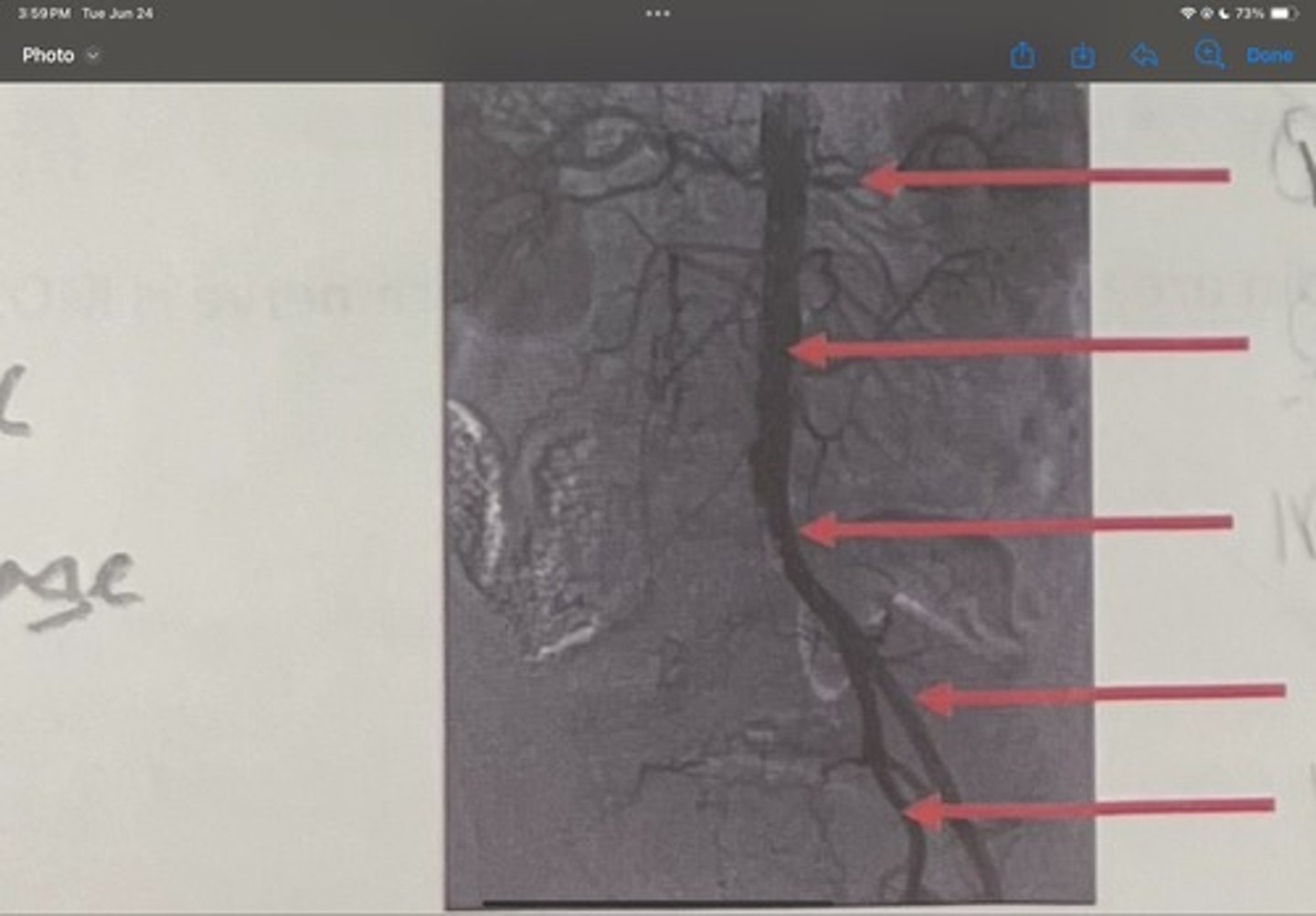
External iliac artery
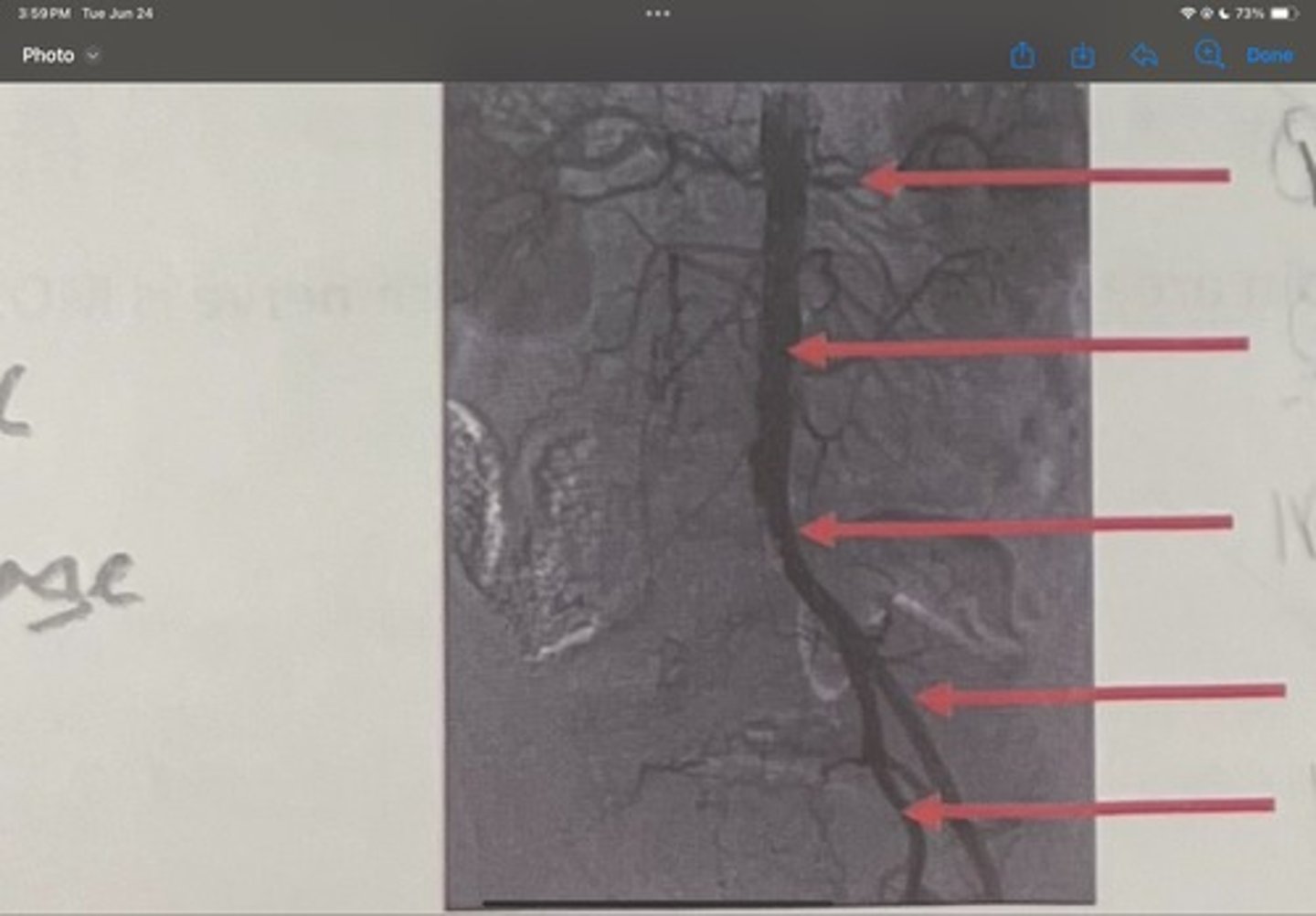
What is the 4th one
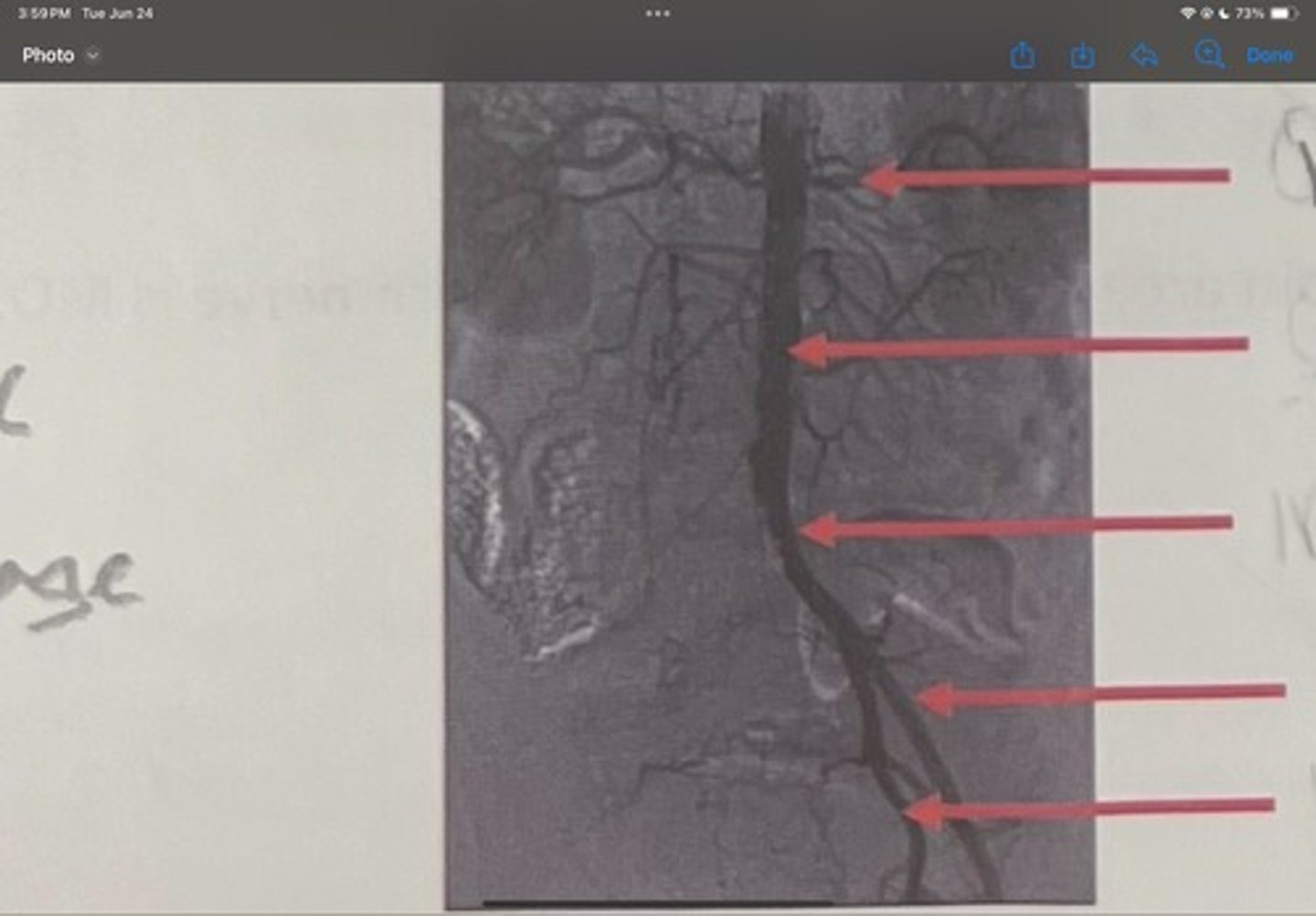
Internal iliac artery
What is the 5th one
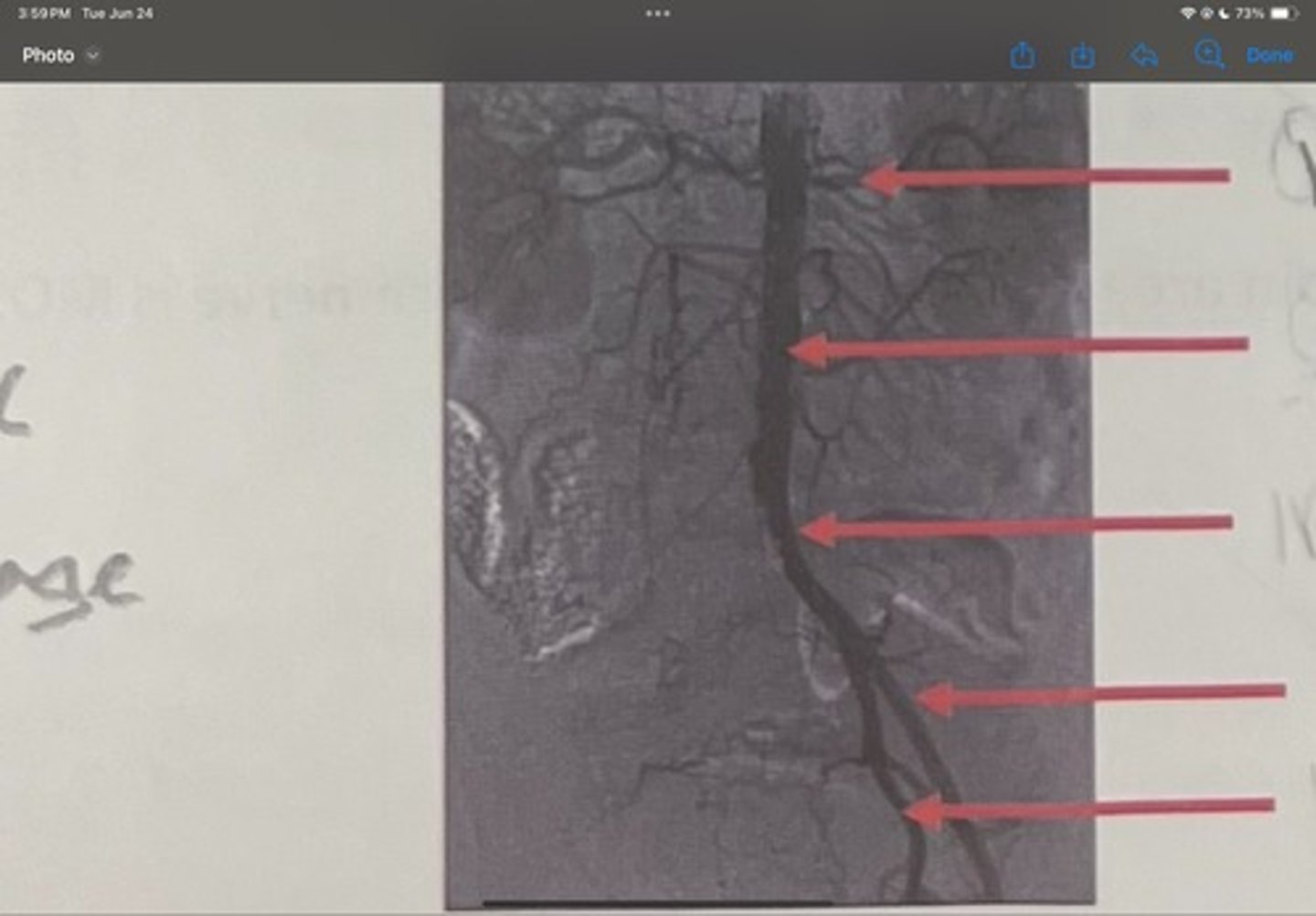
right common iliac artery blockage
What is the pathology of the image
9. Which visceral functions will be affected by A 40 y/o female patient with multiple sclerosis with lesions in the conus medullaris?
A) The parasympathetic motor support of the pelvic organs will be affected.
B.) The sympathetic motor support of the pelvic organs will be affected.
C) The parasympathetic motor support of the midgut will be affected.
D) The sympathetic motor support of the midgut will be affected.
A. ) The parasympathetic motor support of the pelvic organs will be affected
A 25 y/o female patient complains of 3 years of incontinence since giving birth to her 1st child, which happens when she coughs or squats. Which type of incontinence does the patient have?
A) Urge
B) Stress
C)Functional
D) Mixed
D. Mixed
A 38 y/o male patient could not lift his R testis voluntarily. The physician believed that this patient had one nerve injured during his appendectomy. Which nerve roots contribute to that nerve?
A.) L1/L2
B) L2/L3
C) L3/L4
D) L4/L5
A.) L1/L2
During the urinary micturition/urination phase, what are the functions of sympathetic and parasympathetic components?
A) Sympathetic nerve inhibits detrusor muscles and activates the internal sphincter.
B) Sympathetic nerve activates detrusor muscles and inhibits the internal sphincter.
C.) Parasympathetic nerve inhibits detrusor muscles and activates the internal sphincter.
D.) Parasympathetic nerve activates detrusor muscles and inhibits the internal sphincter.
D.) Parasympathetic nerve activates detrusor muscles and inhibits the internal sphincter.
Which of the following muscles attaches to the tendinous arch of the obturator internus?
A) Puborectalis
B) Piriformis
C) Pubococcygeus
D) lliococcygeus
D. lliococcygeus
A biker complains of numbness in the groin area and incontinence. Which nerve is MOST likely injured?
A) Pelvic splanchnic nerve
B) Sacral splanchnic nerve
C) Pudendal nerve
D) Superior gluteal nerve
D. Superior gluteal nerve
Which planes divides the abdominal cavity into 4 quadrants?
a. Midclavicular and supracristal planes
b. Median sagittal and midclavicular planes
C. Transumbilical and median sagittal planes
d. Intertubercular and subcostal planes.
C. Transumbilical and median Sagittarius planes
16. A patient complains of pain around McBurney's point. Which of the following structure is MOST likely involved?
a. Duodenum
b. Jejunum
c. lleum
d. Appendix
D. Appendix
Where does the left adrenal gland drain its venous blood to?
a. Inferior vena cava
b.Hepatic portal vein
C.) Left renal vein
d. Left common iliac vein
C. Left renal vein
Which organ has higher mobility due to its intraperitoneal location?
a. Transverse colon
b. Descending colon
c. Kidney
d. Abdominal aorta
A. Transverse colon
19. A female patient suffers from pelvic inflammatory disease with fluid accumulating in the peritoneal cavity. Where will the fluid drain to when the patient stands up?
a. Vesicouterine pouch
b. Uterine triangle
c. Rectouterine pouch
d. Anal triangle
C. Rectouterine pouch
Which sympathetic nerve innervates the foregut?
A.Greater splanchnic nerve
b.Lesser splanchnic nerve
c. Lumbar splanchnic nerve
d. Vagus nerve
A. Greater splanchnic
22. Which internal organ is in the right lumbar region?
a.Ascending colon
b. Descending colon
C. lleum
d. Jejunum
A. Ascending colon
Where is intrinsic factor synthesized to facilitate the absorption of vitamin B12?
a. Liver
b. Duodenum
c. lleum
d.) Stomach
Stomach
If the superior mesenteric artery is blocked, which organ will be compromised?
a. Stomach
b. Liver
C.Spleen
D. Jejunum
D. Jejunum
What are the primary retroperitoneal organs
Rectum, testes, anus, kidneys
What are the secondary retroperitoneal organs
duodenum, pancreas, ascending and descending colon
What are intraperitoneal organs
Esophagus, jejeunum, ileum, cecum, appendix, transverse colon, sigmoid colon, uterus
What is the portal triad
Proper hepatic artery, hepatic portal vein, common bile duct
CT Sagittal
What type of image is this
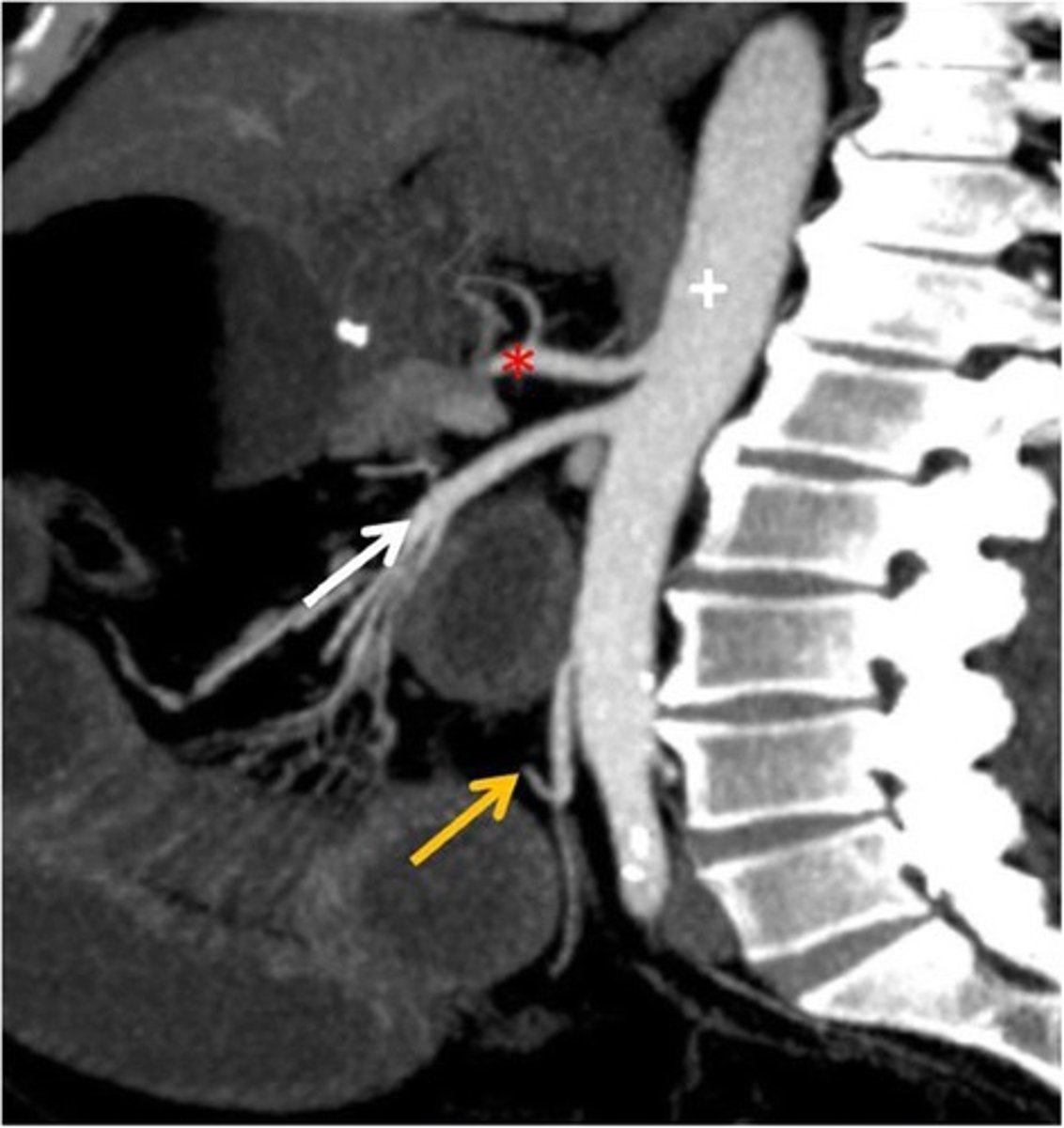
Celiac trunk
What is the red star artery
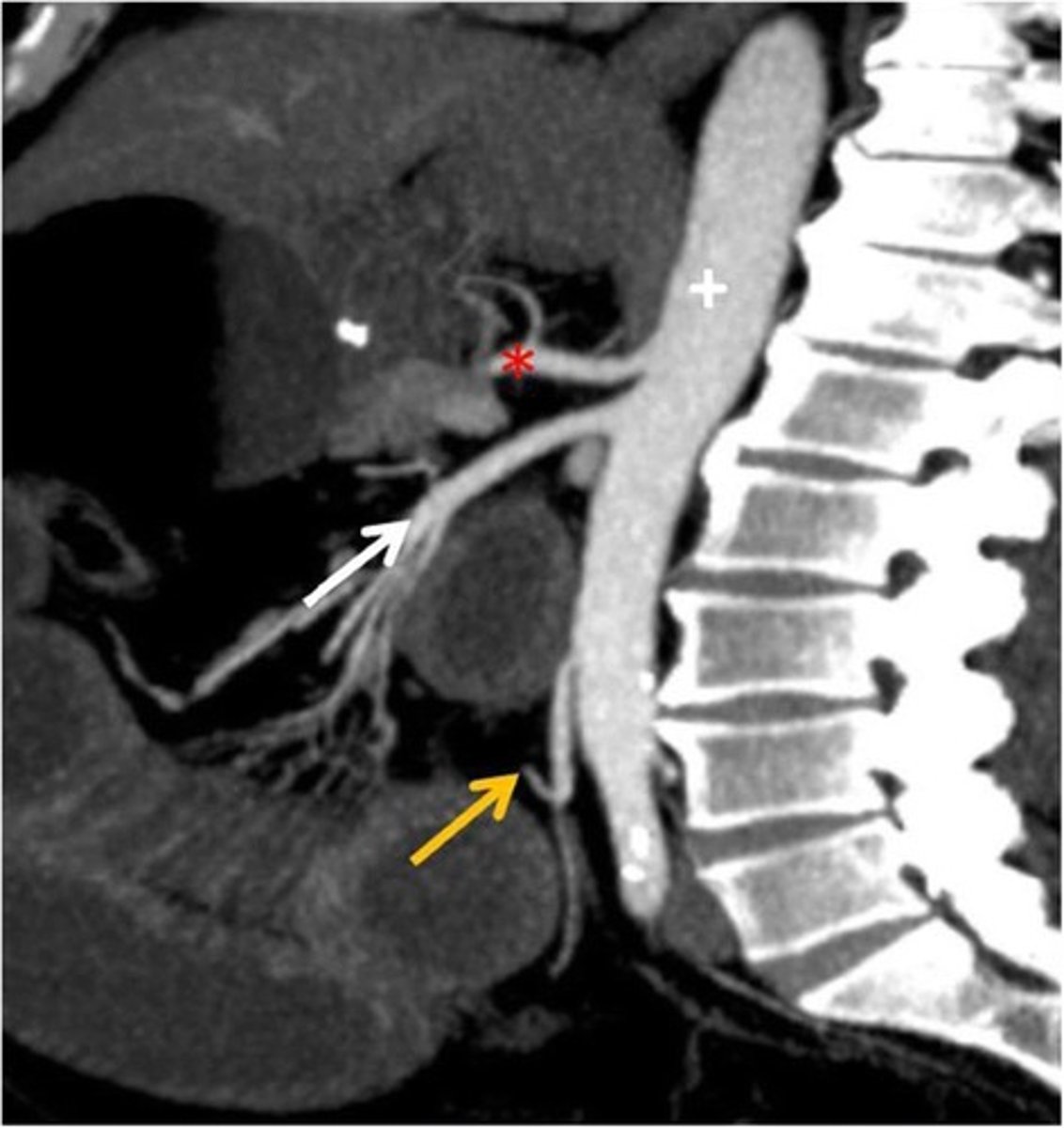
What are the contents of the digestive tract in the foregut
Abdominal esophagus, stomach, 1/2 duodenum
What is the sympathetic innervation of the celiac trunk: foregut
Greater splanchnic nerve T5-T9
superior mesenteric artery: midgut
What is the white arrow artery
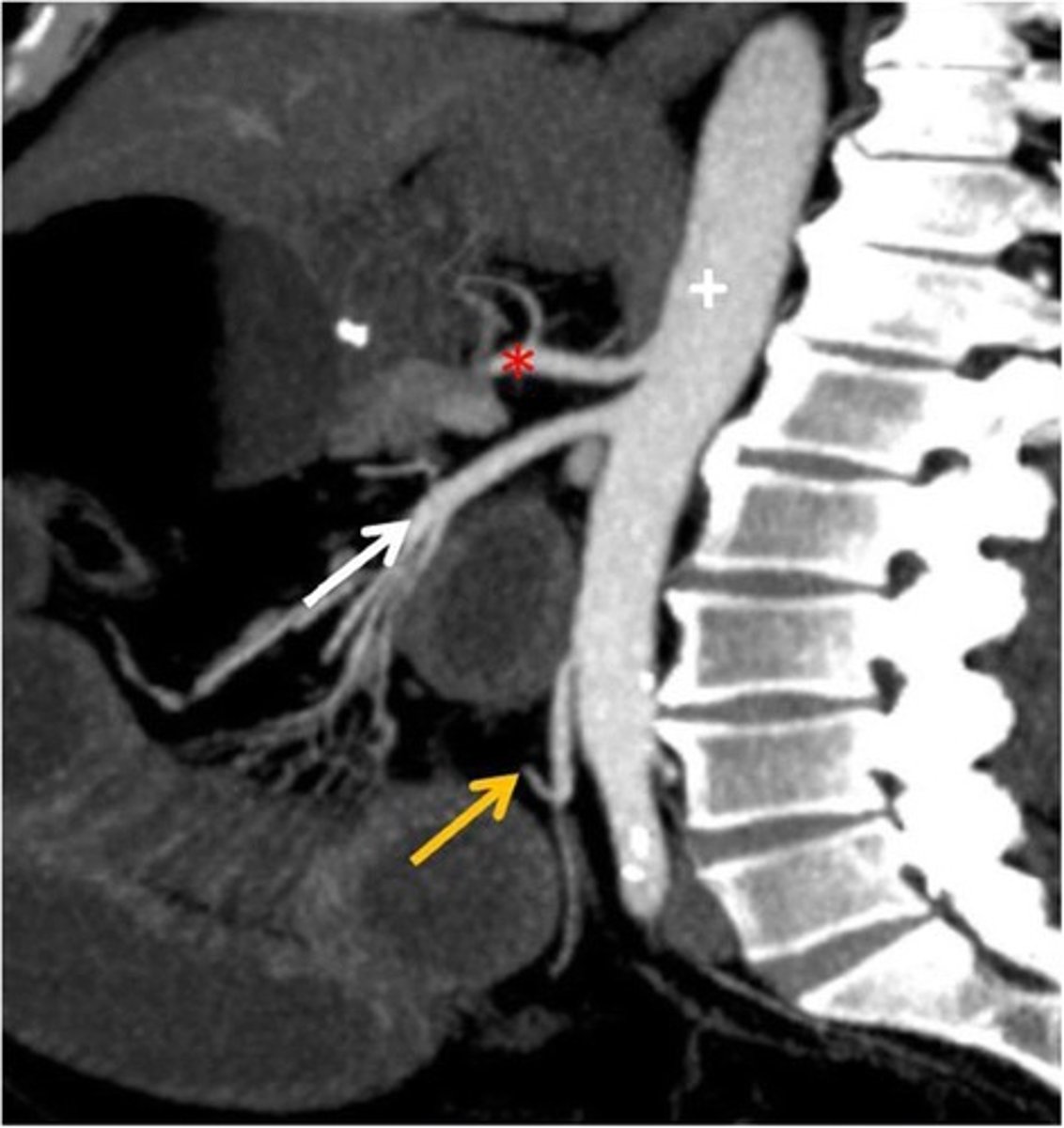
What are the contents of the digestive tract in the midgut
1/2 duodenum, jejunum, ileum, cecum, appendix, ascending colon, 2/3 transverse colon
What is the sympathetic nerve for the mid gut; superior mesenteric artery
Lesser splanchnic nerve T10-T11
Inferior mesenteric artery; hindgut
What is the yellow arrow artery
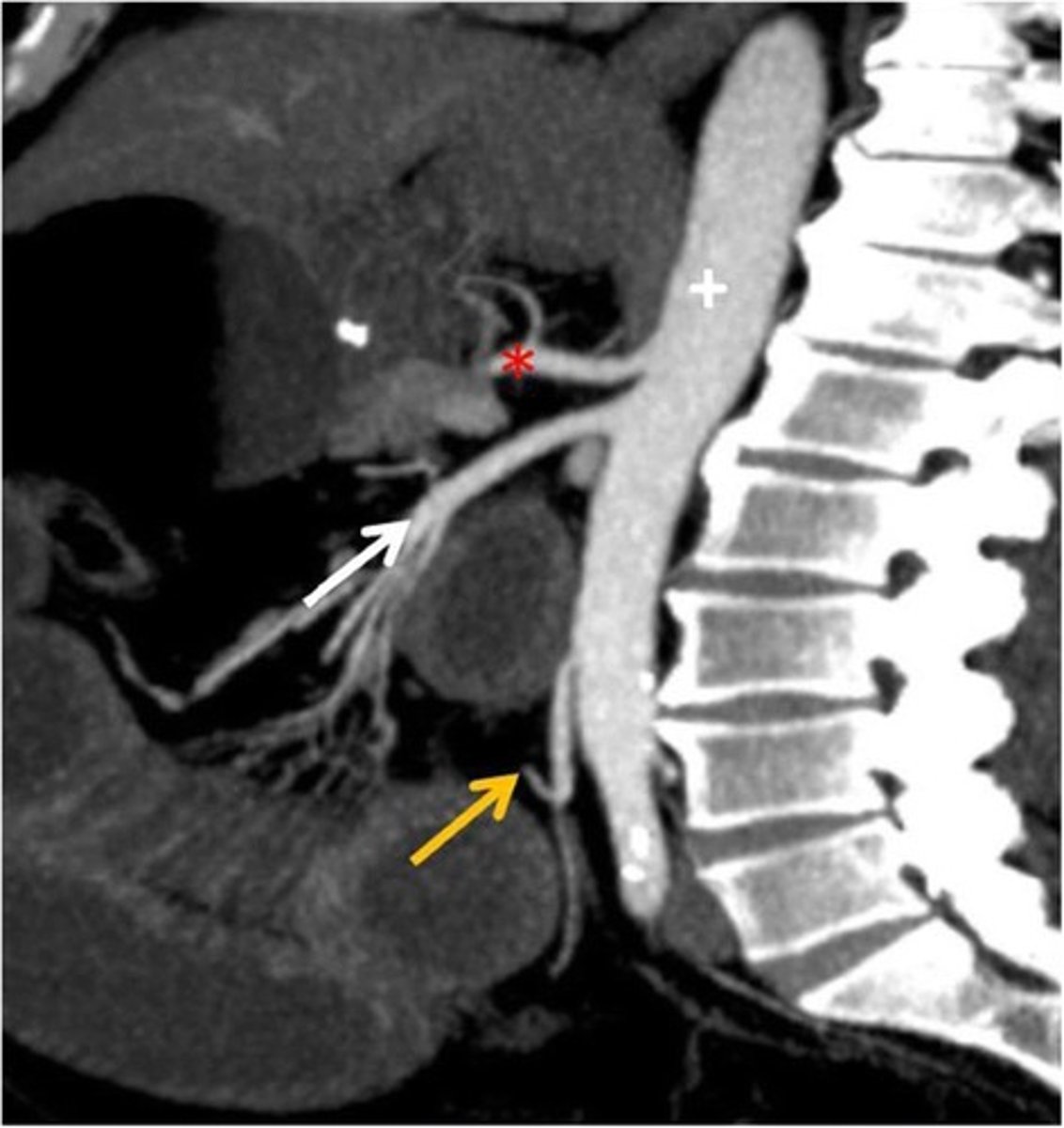
What are the contents of the hindgut
Distal 1/3 transverse colon, descending colon, sigmoid colon, rectum
What is the sympathetic nerves for the hindgut; inferior mesenteric artery
Lumbar splanchnic nerve L1-L2
What might you be afraid of if the celiac trunk is impinged
Eating, idk drlei had it on the slides
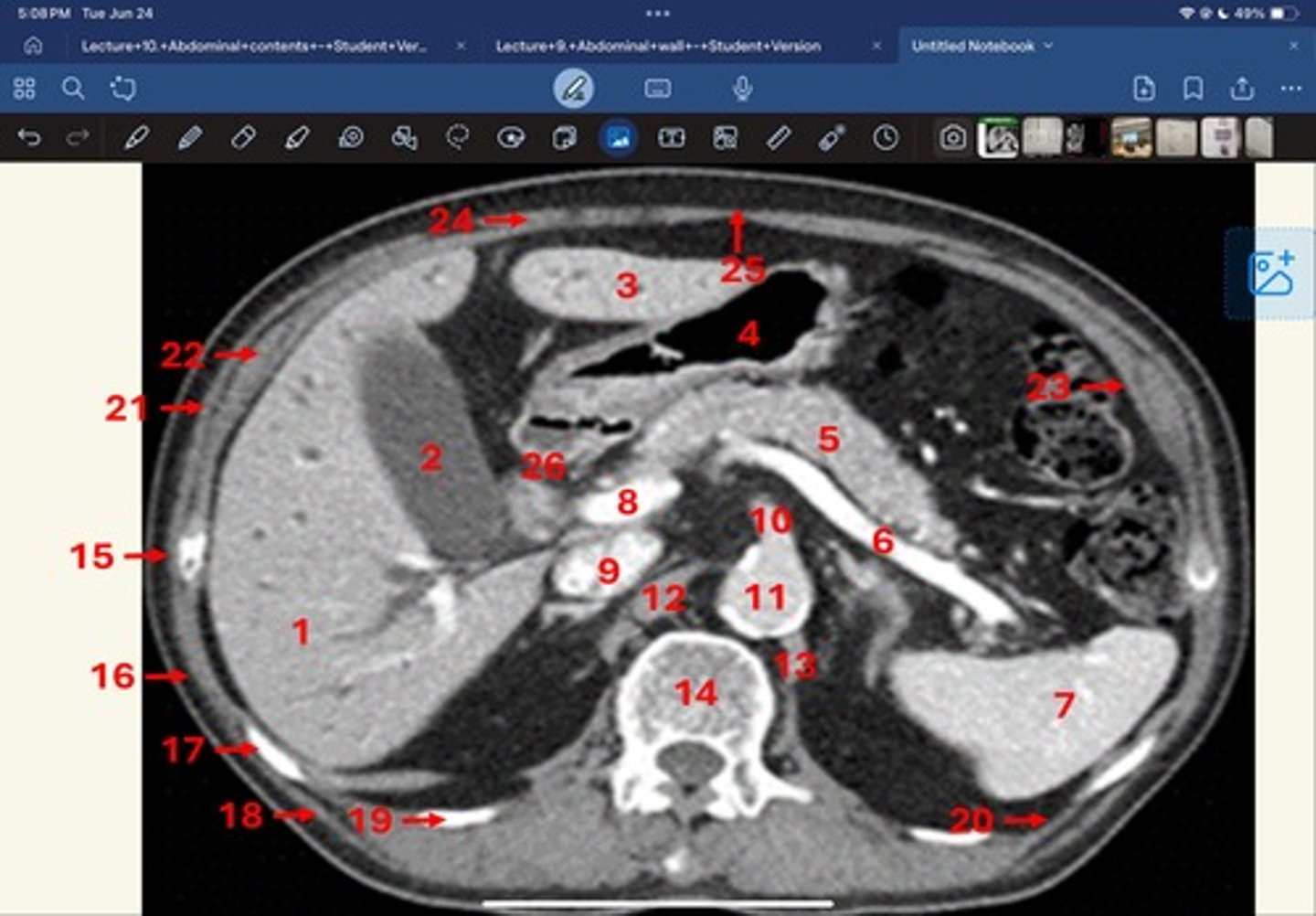
Right lobe of liver
What is 1
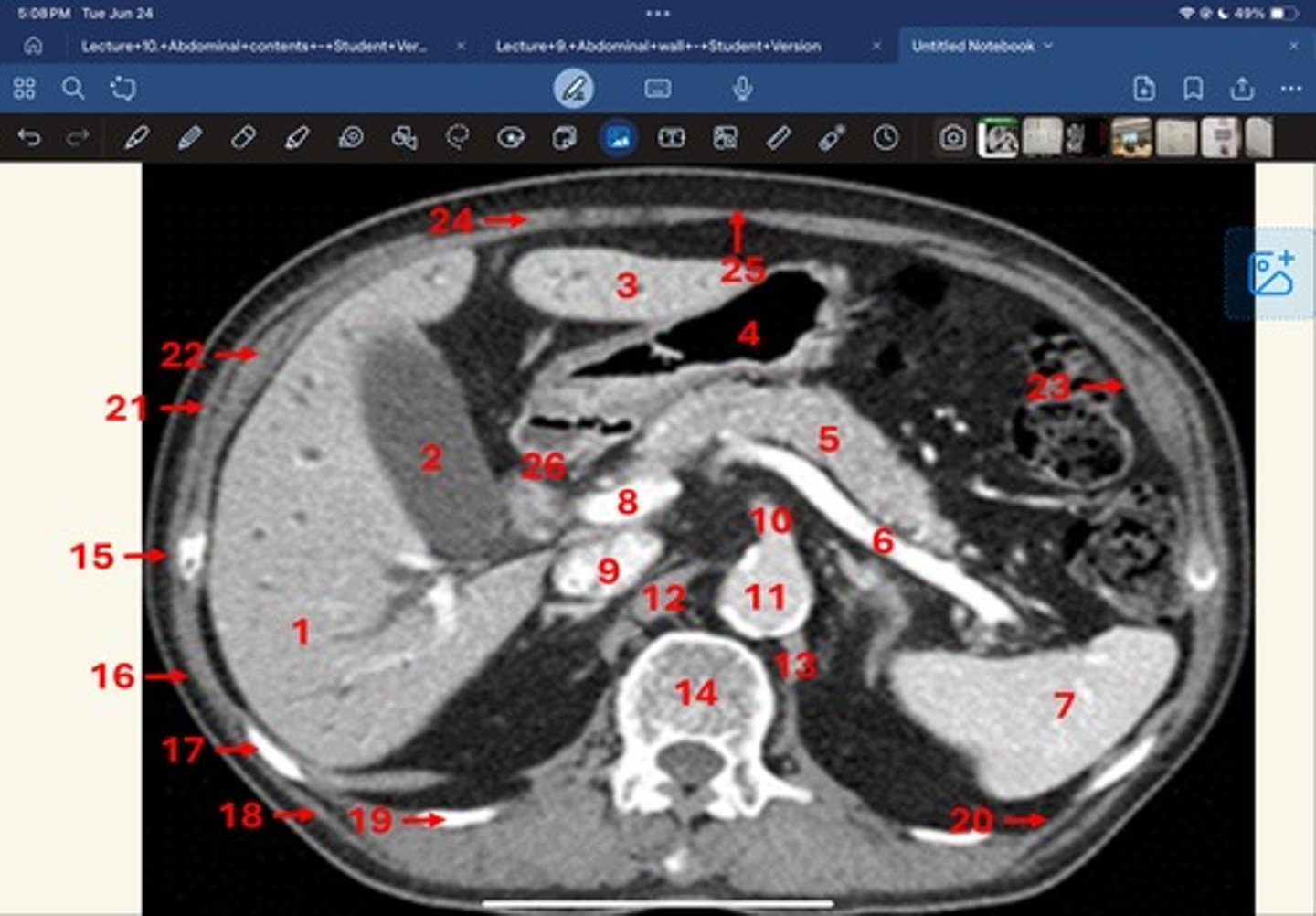
Gallbladder
What is 2
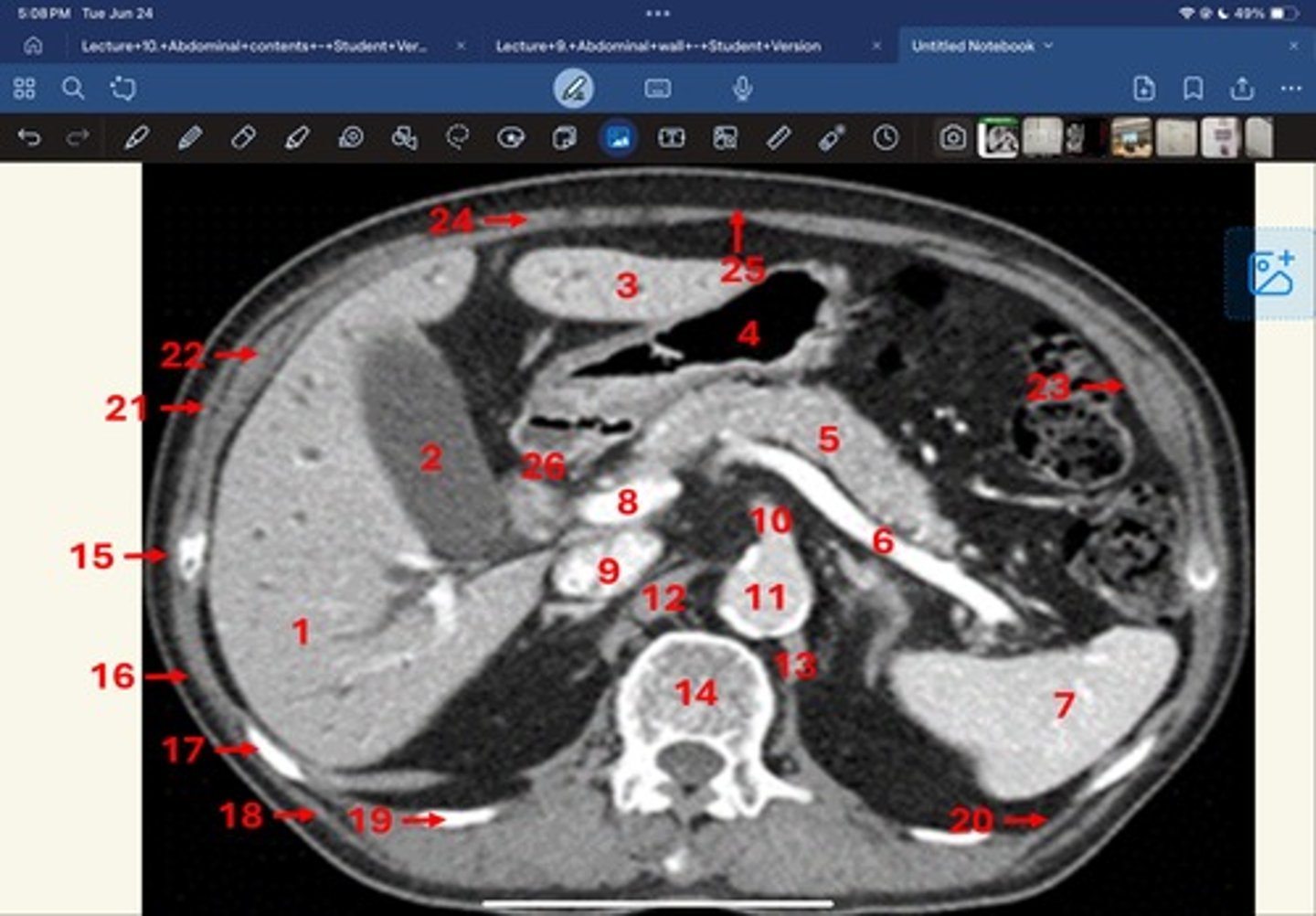
Left lobe of liver
What is 3
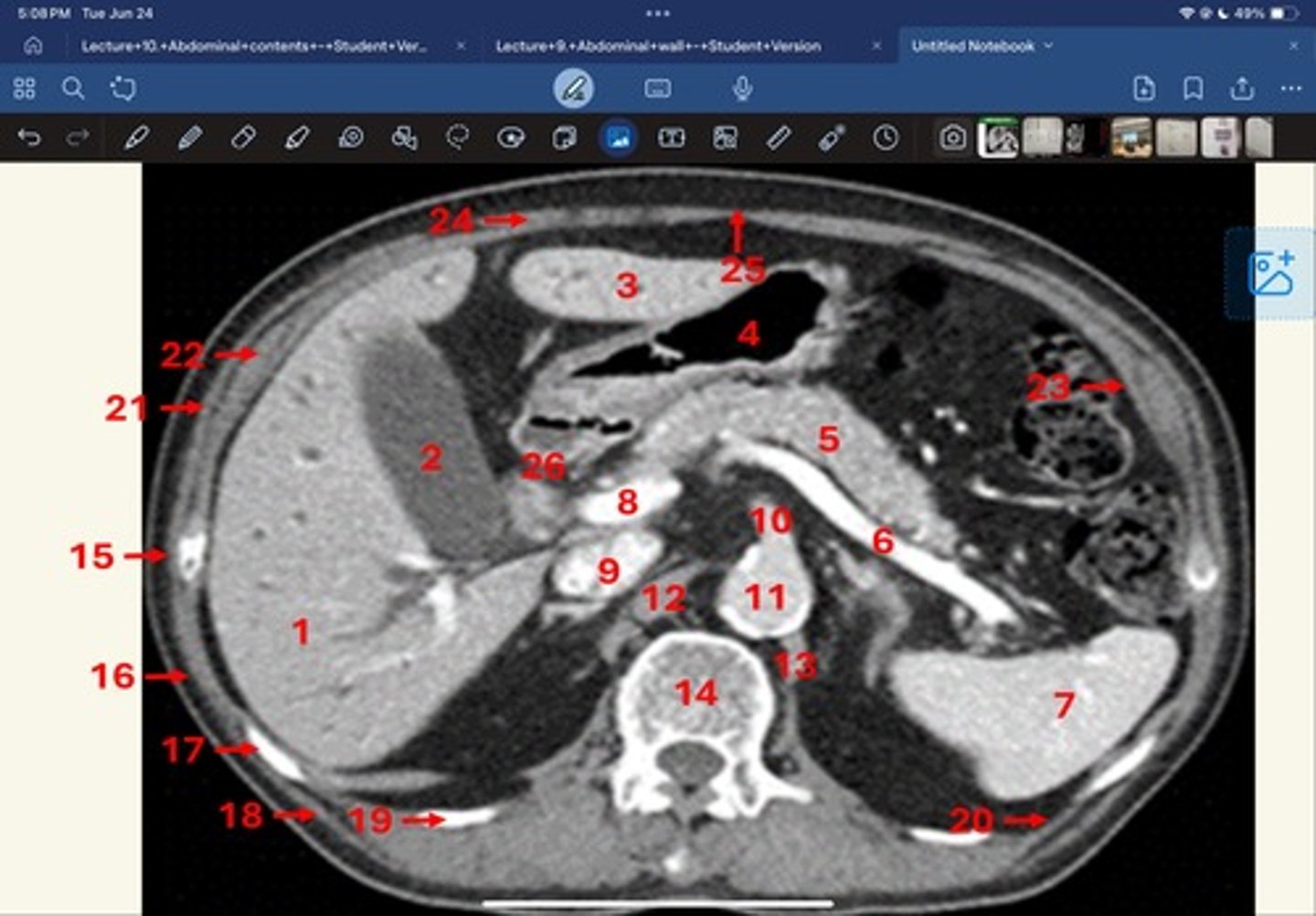
Stomach, pylorus
What is 4
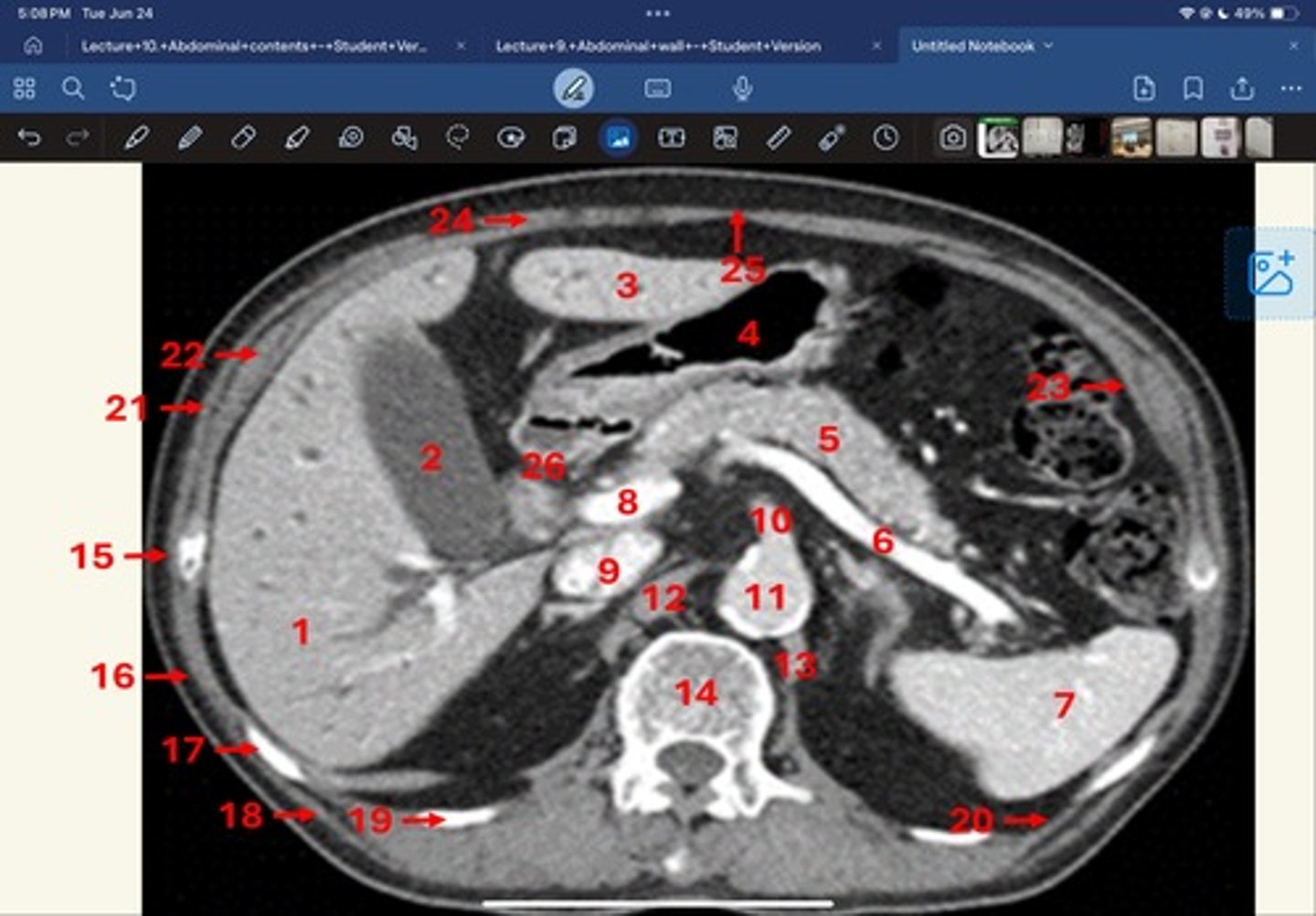
Pancreas
What's 5
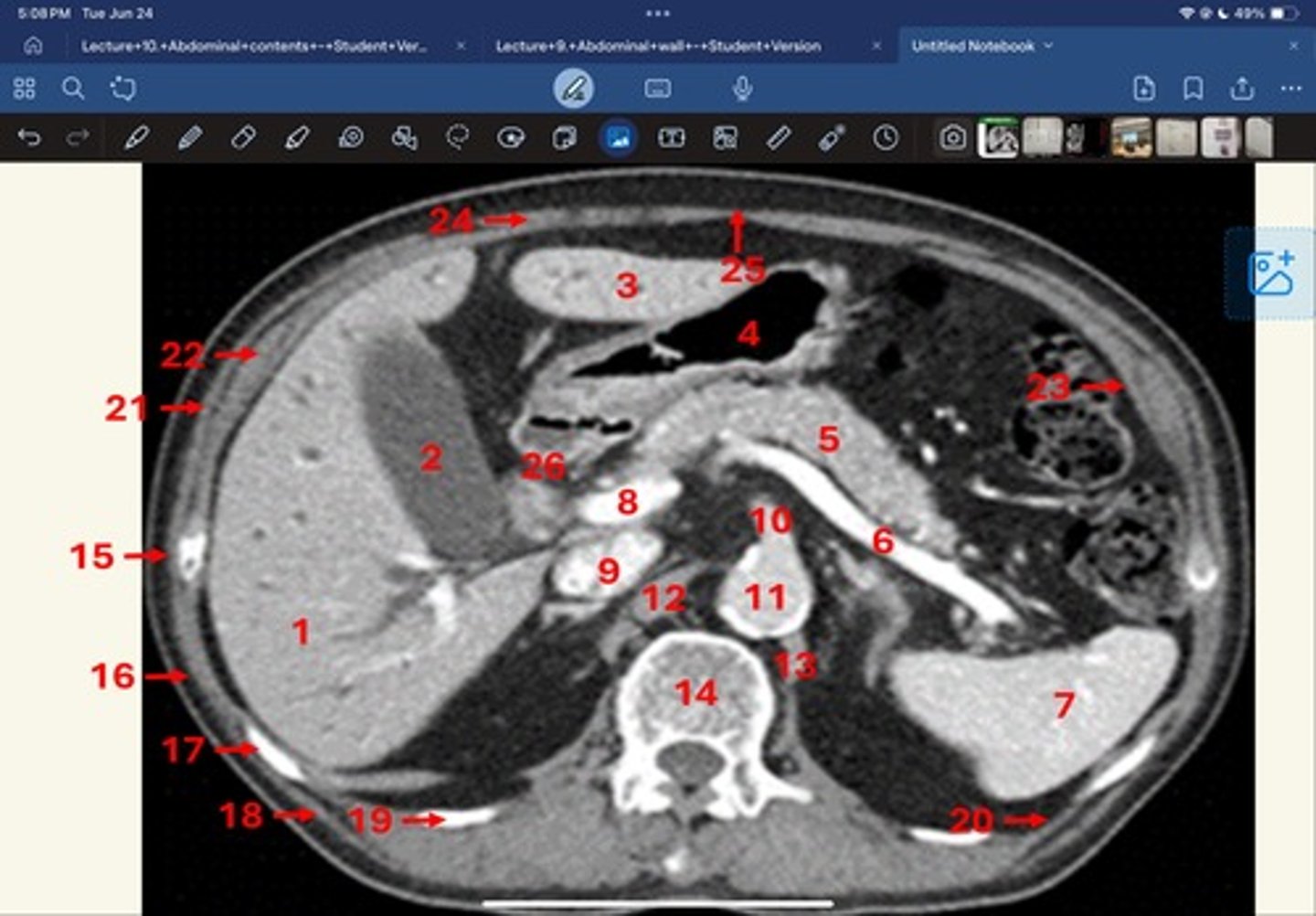
Splenic vein
What's 6
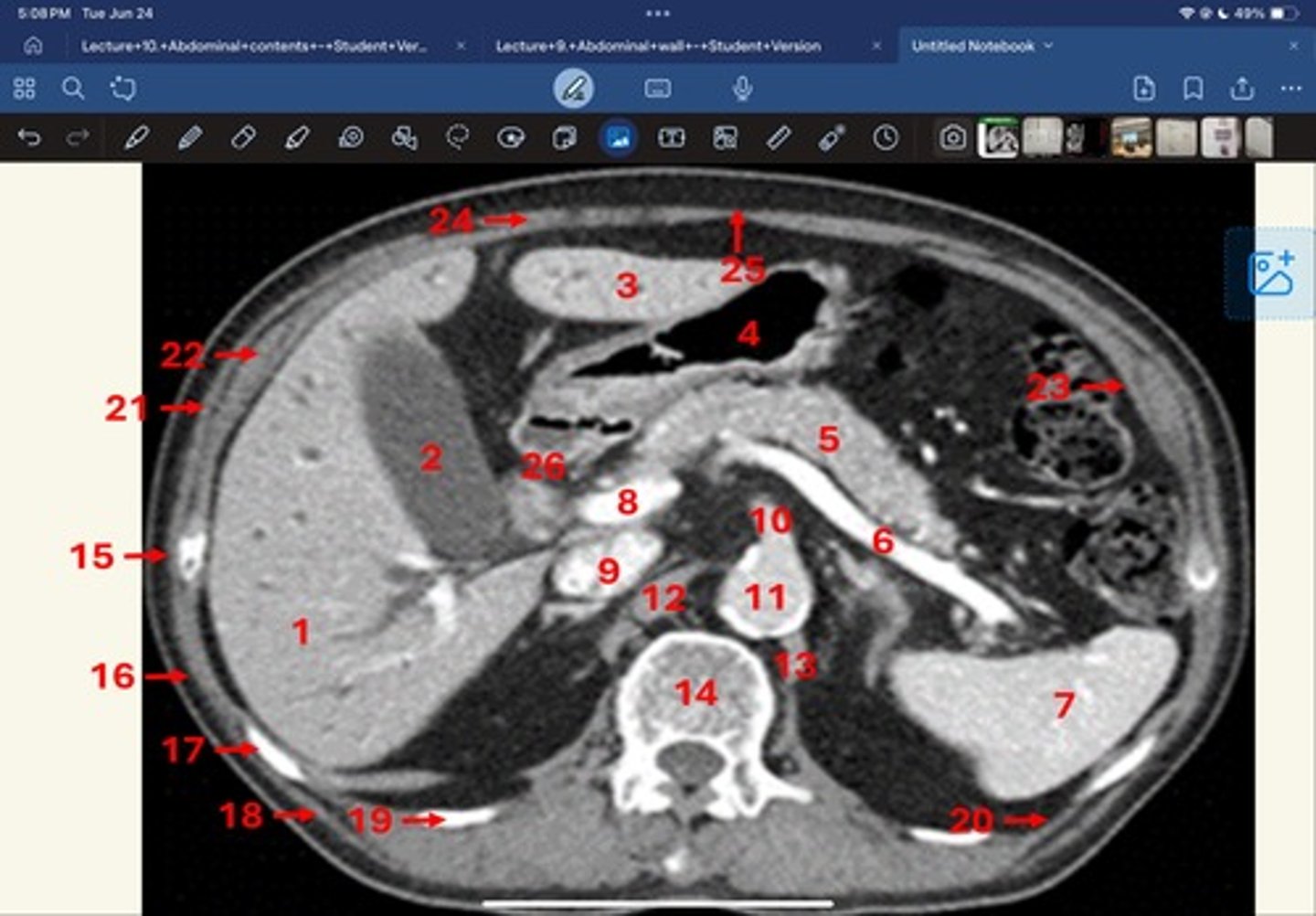
Spleen
What's 7
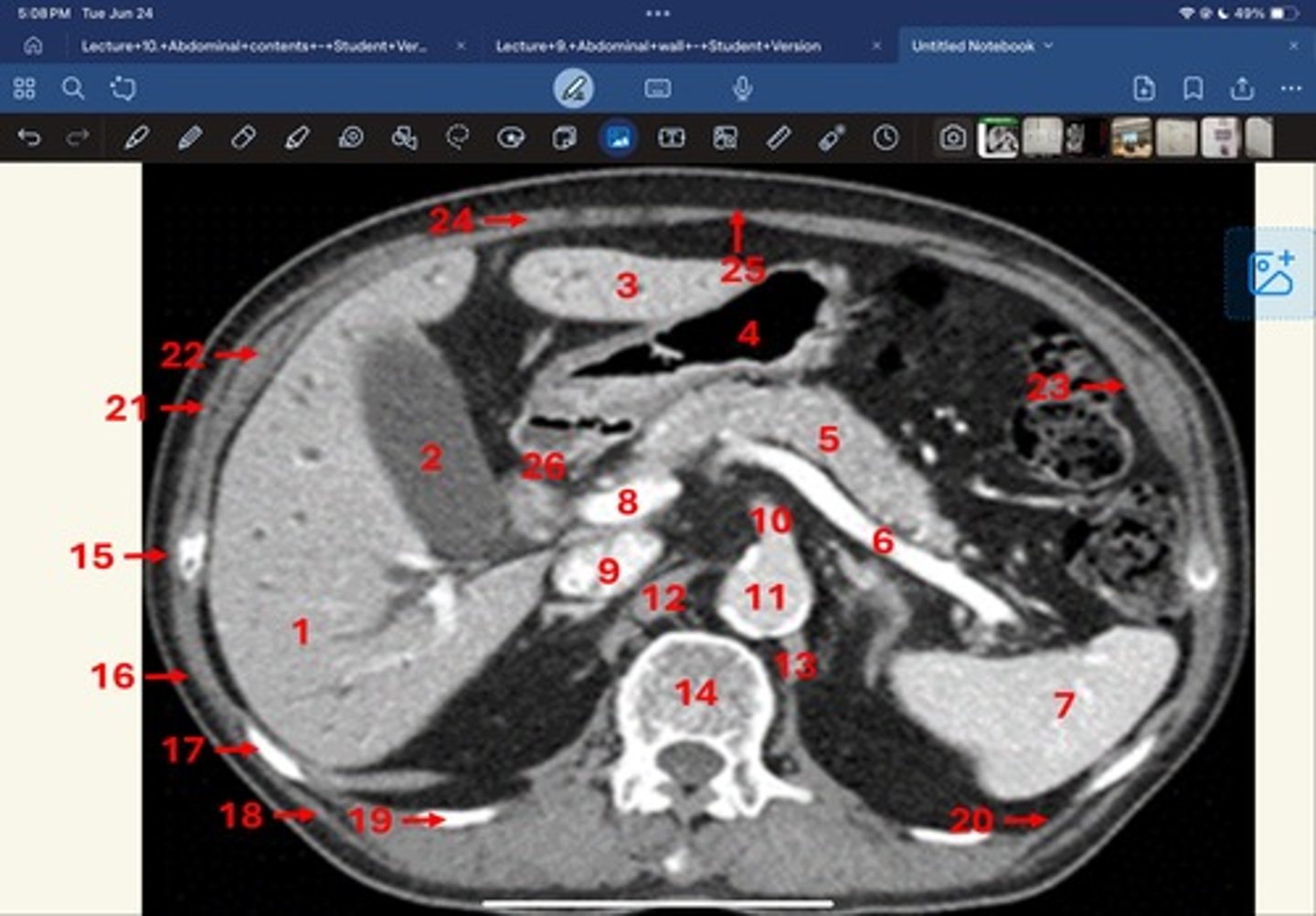
superior mesenteric vein
What's 8
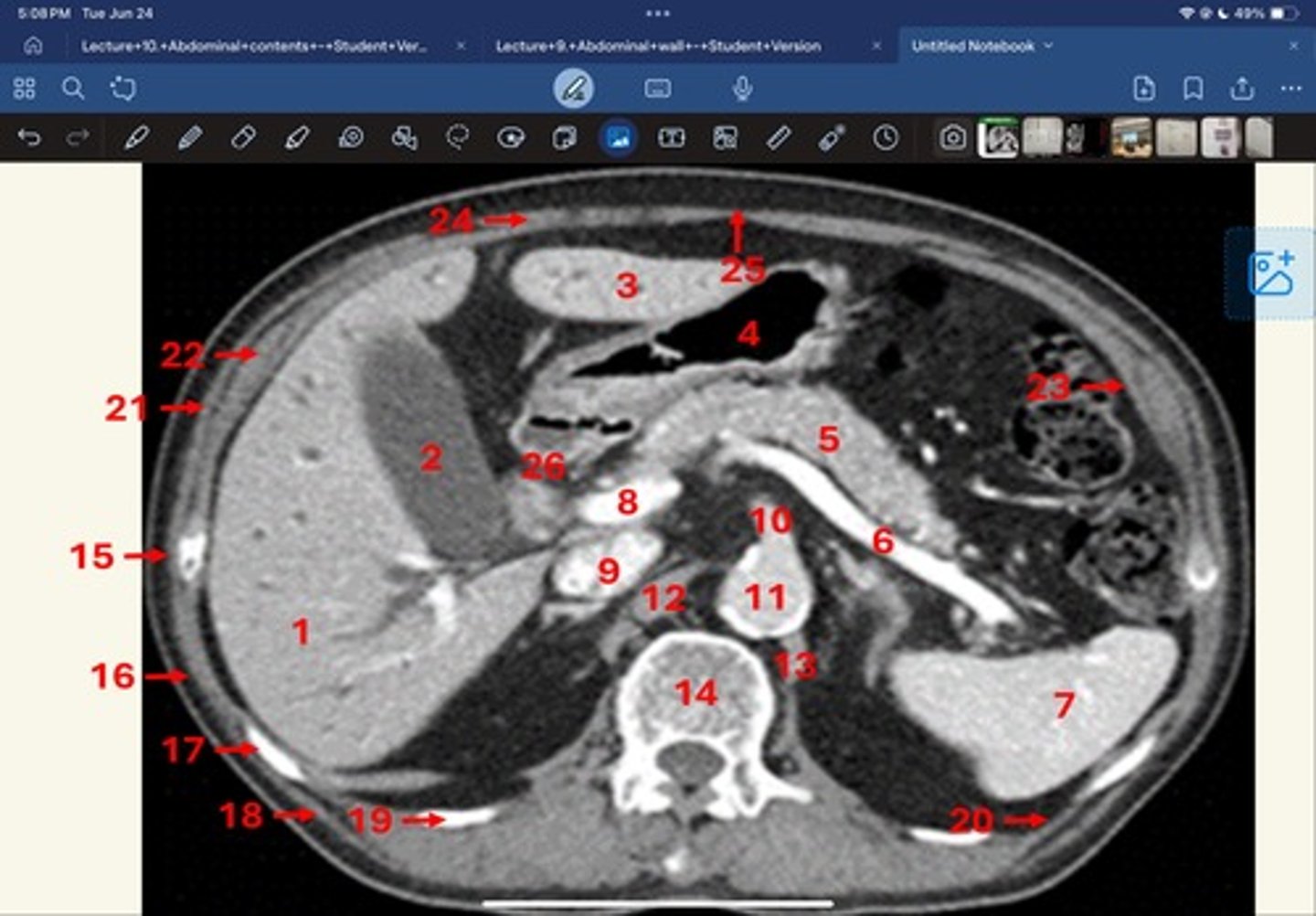
Inferior vena cava
What's 9