AQA A LVL Physics - Waves
1/142
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
143 Terms
2 main types of wave
Transverse and Longitudinal
Progressive waves transfer ______, not ______
Energy, matter
Waves are produced by...
particles (of a medium) or fields oscillating at the source
Evidence showing that waves carry energy:
Heating, physical vibration, loss of energy from the source, electricity generation, ionisation
Longitudinal waves - the direction of particle/field oscillations is ________ to the direction of energy propagation.
Parallel
Longitudinal waves contain ____________ and ____________
compressions, rarefactions
what are longitudinal waves made up of
compressions
rarefactions
on a regular wave that represents a longitudinal wave, where are the compressions, and where are the rarefactions
peaks = compressions
troughs = rarefactions
Transverse waves - the direction of particle/field oscillations is _____________ to the direction of energy propagation.
Perpendicular
Wavelength symbol
definition
what is its units
lamda
the length of one whole oscillation (e.g the distance between successive peaks or troughs)
measured in m
Displacement
Distance and direction from equilibrium (rest) position
Amplitude symbol
definition
what is it measured in?
A
Maximum displacement from equilibrium position
measured in m
Time period symbol
definition
what is it measured in
T
Time taken for one full oscillation
units are s
frequency symbol
definition
what are its units
what is the SI base unit of this unit
f
the number of complete oscillations passing through a point per second
measured in Hz (hertz)
SI of Hz = s-1
speed symbol
definition
what are its units
c
distance travelled by the wave per unit time
ms-1
What is intensity proportional to
the amplitude squared
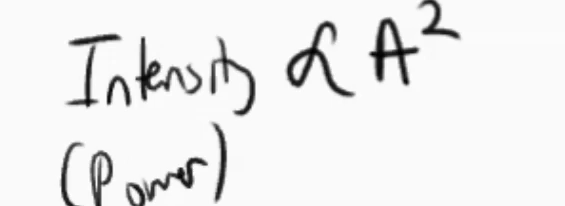
give some examples of what I mean by applications of intensity
e.g hint intensity, light intensity….
(In terms of time and displacement) V =
s/t
T =
1/f
(In terms of waves) V =
f x λ
c =
f x λ
Examples of longitudinal waves
Sound waves, P waves
Examples of transverse waves
S waves, EM waves, water, waves on string
Examples of both transverse and longitudinal waves
Mechanical waves, L waves
Sound wave properties
Longitudinal, produced by the vibration of particles in a medium
What waves do polaroid sunglasses involve?
EM waves
EM wave properties
transverse, have oscillating electric and magnetic fields at right-angles to eachother and the direction of propagation
A wave is unpolarised when...
transverse oscillate in more than 1 plane
how do polaroid sunglasses reduce glare?
they block partially polarised light, (e.g thats reflected from water or tarmac)
they only allow oscillations in the plane of the filter, making it easier to see
Can transverse waves be polarised?
Yes
How can transverse waves be polarised?
by using a polarising filter, which only lets oscillations in one plane through
Can longitudinal waves be polarised?
no
Why can't longitudinal waves be polarised?
Only have 1 plane of oscillations (they oscillate in the same direction as they travel)
can longitudinal waves travel in a vacuum?
no
How are TV signals polarised?
By the orientation of the rods on the transmitting aerial (which have to be aligned)
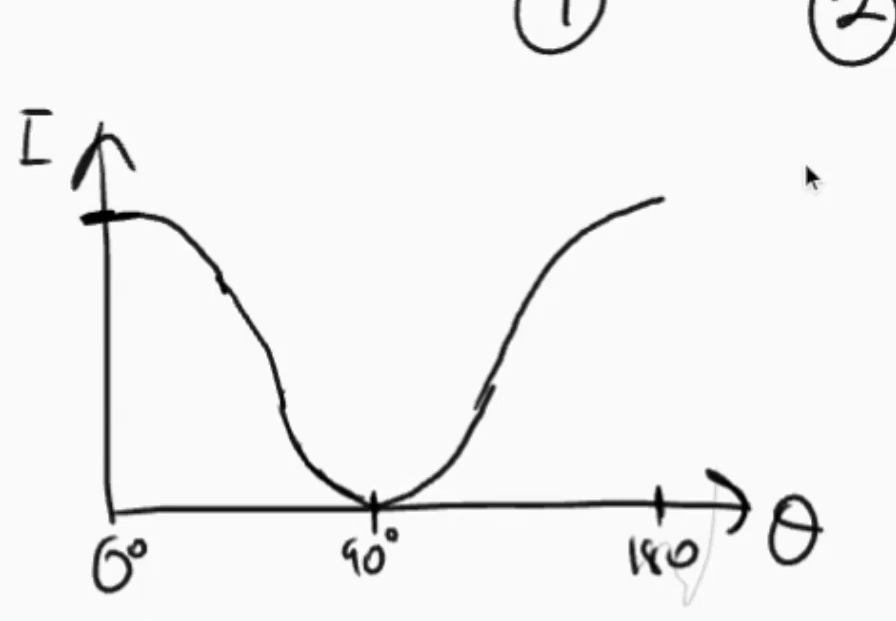
on the graph of Intensity against theta (for polarisation / rotation of a polarising filter), what graph is it?
a cos2 graph (a cos graph but where -1 is the x axis)
wave front
leading edge of a moving wave
rays
lines drawn through the wavefronts at 90 degrees
phase definition
what units does it have
A measure of how far through a wave’s cycle a given point on the wave is
units are radians, degrees, or fractions of a cycle
phase difference definition
what units is it measured in
how much a particle / wave lags behind another particle / wave.
what 2 things are needed for 2 points on a wave to be in phase?
if they are the same point of the wave cycle
need the same frequency and wavelength
how can u find the phase difference using the wavelength (eqtn)
phase diff =
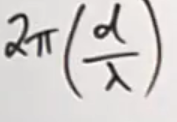
how can u find the phase difference using the Time period (eqtn)
phase diff =
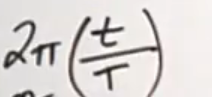
path difference
A measure of how far ahead a wave is compared to another wave. (the difference in distance travelled by 2 waves)
usually expressed in terms of wavelength
90 degrees phase difference in radians
0.5π
180 degrees phase difference in radians
π
monochromatic definition
1 wavelength/frequency
coherent (light source) definition
same frequency and wavelength, and a fixed/constant phase difference
give an example of a source of light which is coherent and monochromatic
a laser
superposition
when waves meet, pass through eachother and combine
principle of superposition
when 2 waves meet, the total displacemenet at a point is equal to the total sum of the individual displacemenets at that point
constructive interference
when waves reinforce, creating supercrests and supertroughs
destructive interference
when waves cancel eachother out
constructive interference occurs when:
waves meet in phase, phase difference = 0 or 360, path difference = n*wavelength
destructive interference happens when:
waves meet in anti phase, phase difference = 180, path difference = (n+0.5)*wavelengths
interference examples
sound waves using 2 loudspeakers, wavter waves in a ripple tank, mircrowave with chocolate buttons
stable interference patterns form when...
the wave sources are coherent
stationary (standing) wave
superpostion of 2 coherent progressive waves moving in opposite directions
when is a stationary wave formed
its formed from the superposition of 2 progressive waves travelling in opposite directions, with the same freq, wavelength and amplitude
what are the necessary conditions for a stationary wave to happen
the progressive waves need to be travelling in opposite directions
the progressive waves must have the same frequency, amplitude, wavelength
what 3 things need to be the same for the progressive waves that make a standing wave
frequency
amplitude
wavelength
nodes definition
points of 0 amplitude/displacement in a stationary wave
antinodes definition
points of maximum amplitude/displacement in a stationary wave
Standing waves have:
nodes, antinodes, no energy transferred
Standing waves have the ability to..
be formed in sound waves (in tubes), microwaves and on a string (using a driving oscillator)
where will constructive interference occur on a standing wave?
where will destructive interference occur on a standing wave?
constructing interference = antinode
destructive interference = node
the number of_____________represents which harmonic it is
anitnodes
First harmonic (fundamental frequency) length
½ Wavelength
2nd harmonic Length
Wavelength
3rd harmonic Length
3/2 Wavelength
To calculate the frequency of harmonics:
Recicopral of wavelenth fraction fitted in to V/L (eg. λ of 2/3L would be 3V/2L, which = 3f0)
how can u calculate the frequency of second and third harmonics based on the frequency of 1st harmonic
Frequency (of first harmonic) x 2 = freq of 2nd harmonic
Frequency (of first harmonic) x 3 = freq of 3rd harmonic
this continues for nth harmonic
mathematical equation that links wavelength, length (e.g of string) and nth harmonic
L = n/2 wavelength
how are stationary microwaves formed?
how can nodes and antinodes of a stationary microwave be found
formed by reflecting a microwave beam at a metal plate.
nodes and antinodes can be found using a microwave probe
how can a stationary sound wave be formed?
what happens to the antinodes and nodes
place a speaker at 1 end of a glass tube
put powder at bottom of tube
antinodes will be shaken, and nodes will be settled
Mathmatical equation linking speed, tension and mass per unit length
v = square root(tension/mass per unit length)
how do you calculate mass per unit length, µ =
Mass (kg) / Length (m)
how do you calculate Tension (T) if the harmonic is done by a string attached to masses over a pulley
m*g
for any wave: f =
(n/2L) * square root(T/mass per unit length)
what is the first harmonic equation to find frequency, and what does every term mean
L = length of the vibrating string
T = tension
μ = mass per unit length
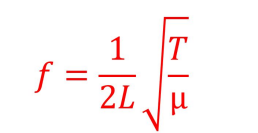
in a tube, when talking about harmonics, what is formed at an open end?
an antinode
in a tube, when talking about harmonics, what is formed at a closed end?
a node
When does maximum diffraction occur?
when gap = wavelength
(roughly)
when does minor/unnoticeable diffraction occur?
when gap > wavelength
when are waves mostly reflected back?
when gap < wavelength
what happens when a wave meets an object/obstacle
you get diffraction around the edges
what happens to the diffraction when the obstacle gets wider, compared to the wavelength
less diffraction happens
what 4 safety precautions must you do when dealing with lasers
wear laser safety goggles
dont shine the laser at reflective surfaces
display a warning sign
never shine the laser at a person
when doing a double slit experiment, how can u get a coherent and monochromatic light, without depending on a monochromatic and coherent light source.
use a single slit to make it have a fixed path difference,
and use a filter to make the light monochromatic
then send it through the double slit
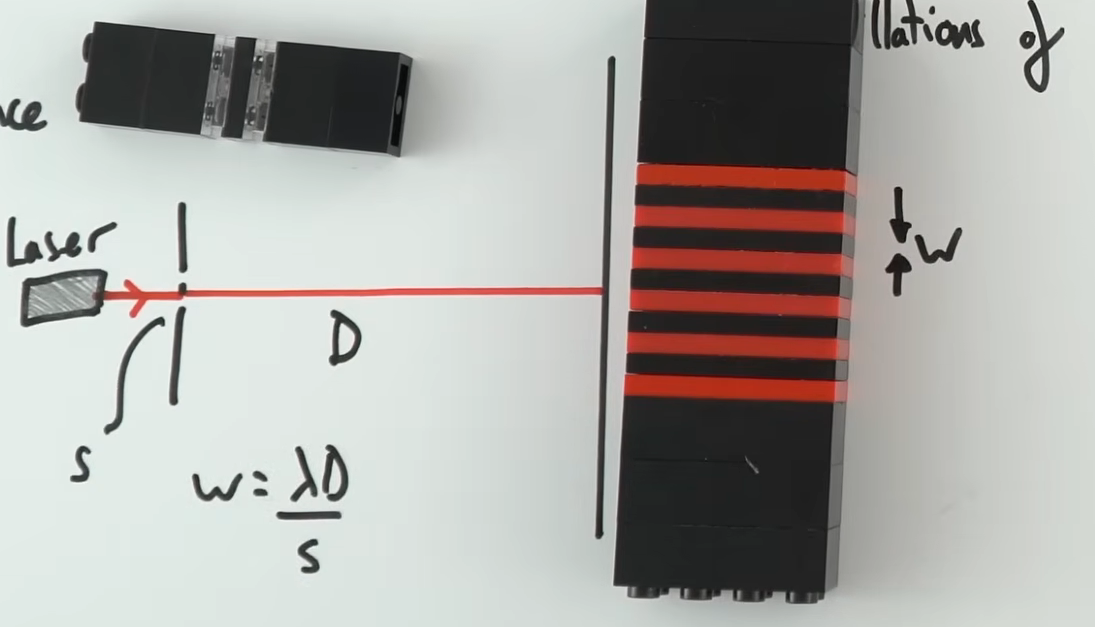
what is young’s double slit fringe spacing equation, and what does each term represent?
w = fringe width / spacing
s = slit separation
D = distance from slit to screen
λ = wavelength
using white light (for YDS) instead of monochromatic laser light gives _________maxima and a _________ intense diffraction pattern
wider, less
if we use white light with for any diffraction experiment, what will the diffraction pattern look like
a central white fringe, with alternating bright fringes (which are spectra), violet is closest to central maxima, and red furthest
when using white light for any diffraction experiment, what colour is closes to white central max, and which is furthest
closest = violet light
furthest = red light
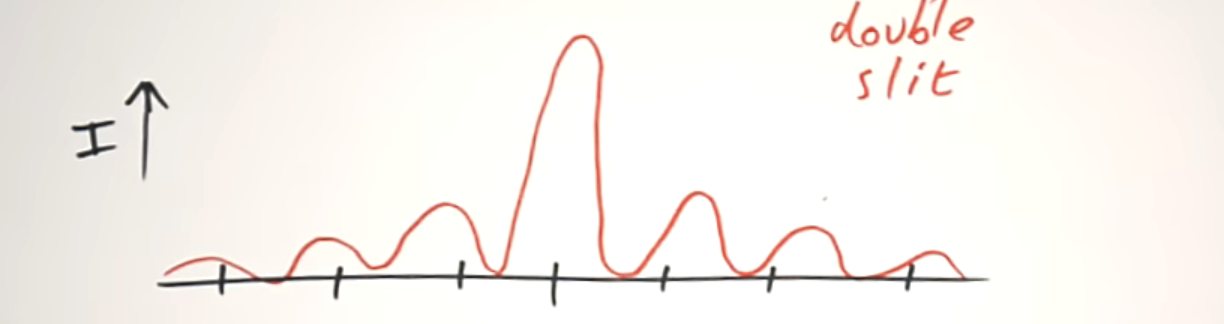
what does the double slit intensity graph look like?
what are the 2 accepted ways of drawing this graph?
the intensity of the fringes gradually decrease from the central maxima on both sides
OR
the intensity of the fringes stay the same as the central maxima
(experiment 1) Monochromatic light through one slit: type of interference
destructive at minima
constructive at maxima
for single slit diffraction, what does the diffraction pattern look like for monochromatic light?
describe it
has a bright central fringe which is double the width of all other fringes
alternating bright and dark fringes on either side of central maxima

(experiment 2) White light through 1 slit: observations
central fringe white, then others 'rainbow fringes', different colours in white light diffracted by different amounts, dark fringes still present between rainbow fringes.
larger wavelength further away from white central maxima

what does the graph of intensity of maximas look like for a single slit?
describe 2 key features of it
the central maxima is very bright compared to the rest of the fringes
the width of the central maxima is double the width of the other fringes
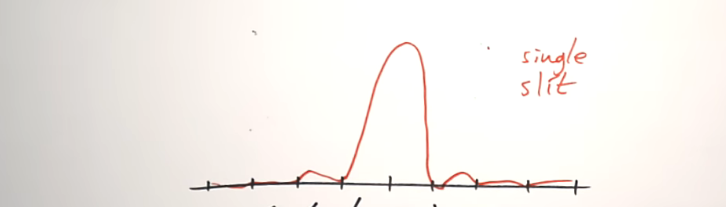
for both single and double slit intensity graphs, what has to happen for it to be drawn correctly
must touch the “x axis” —> shows dark fringe
what should the diffraction grating/slit size roughly be equal to
the laser light wavelength