Organisms and their Environment
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
ecology
the branch of biology that deals with the relations of organisms to one another and to their physical surroundings.

biosphere
It is the sum of all ecosystems on Earth

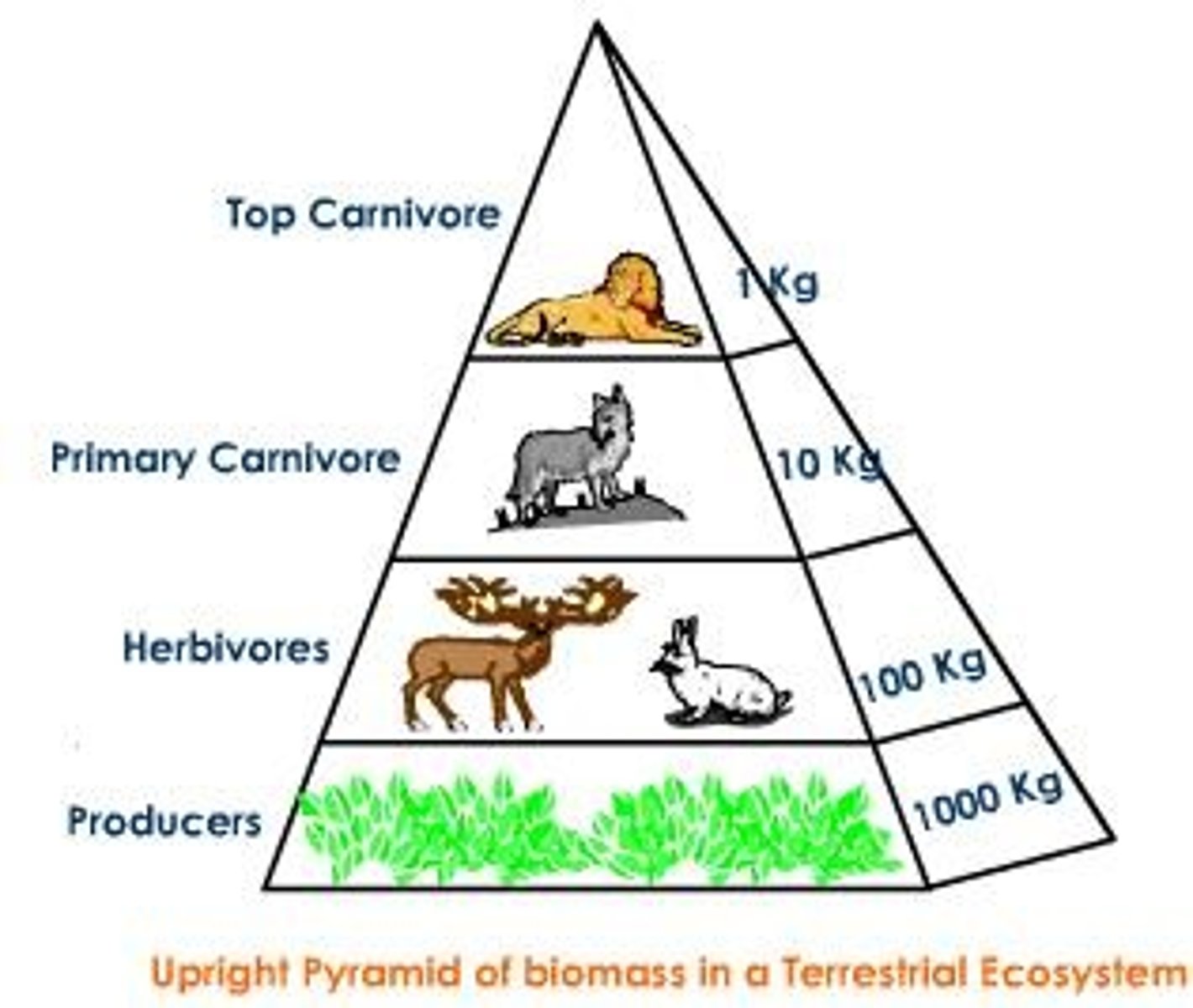
trophic level
made up of organisms that share the same function in the food chain and the same nutritional relationship to the primary sources of energy
abiotic factor
part of the ecosystem that is NON living (examples: air, soil, weather, temperature, pH, etc.)

biotic factor
the parts of the world's ecosystem that are livings (examples: plants, animals, bacteria, etc.)
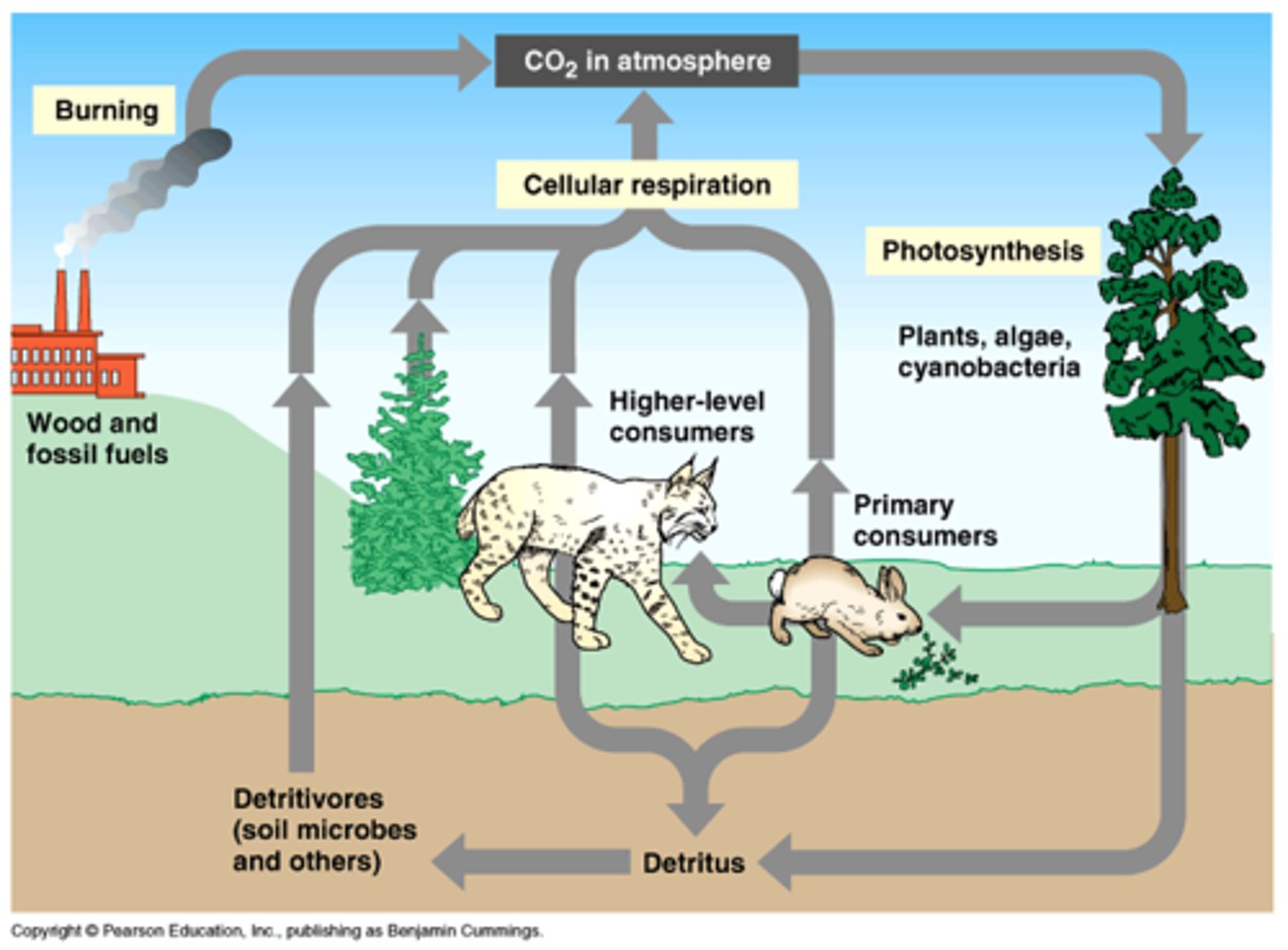
cycles in nature (biogeochemical cycles)
is the flow of chemical elements between living organisms and the environment
species
a group of related individuals that resemble one another and are able to breed among themselves
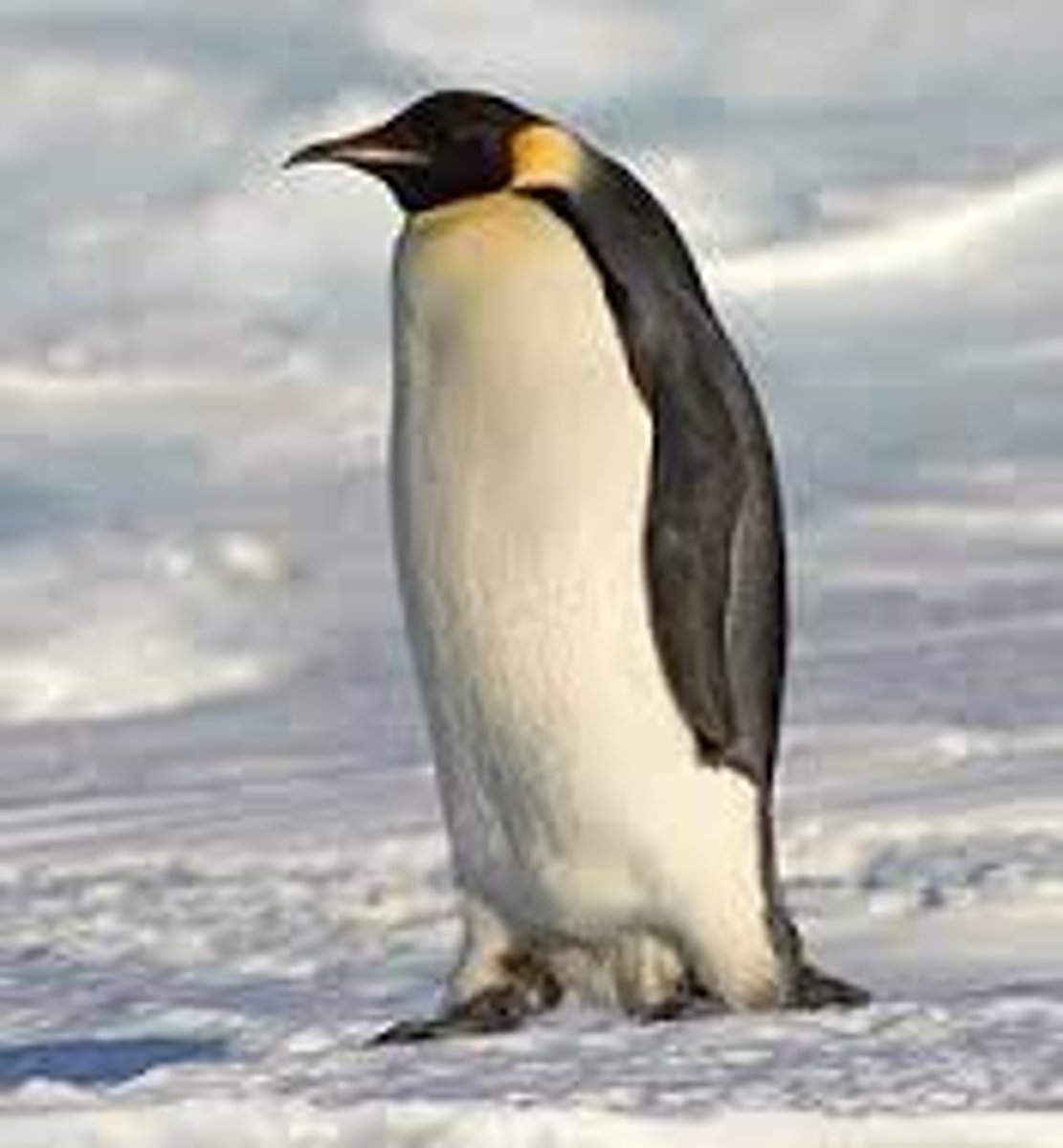

population
A group species that interbreed and live in the same place at the same time (e.g. Emperor Penguin population).

herbivore
Plant eater

carnivore
Meat eating

community
a group of interdependent organisms inhabiting the same region and interacting with each other

ecosystem
a system formed by the interaction of a community of organisms with their physical environment

habitat
the type of environment in which an organism or group normally lives or occurs

niche
(ecology) the status of an organism within its environment and community (affecting its survival as a species)

symbiosis
the relation between two different species of organisms that are interdependent

commensalism
the relation between two different kinds of organisms when one receives benefits from the other without damaging it

biomass
the total mass of living matter in a given unit area

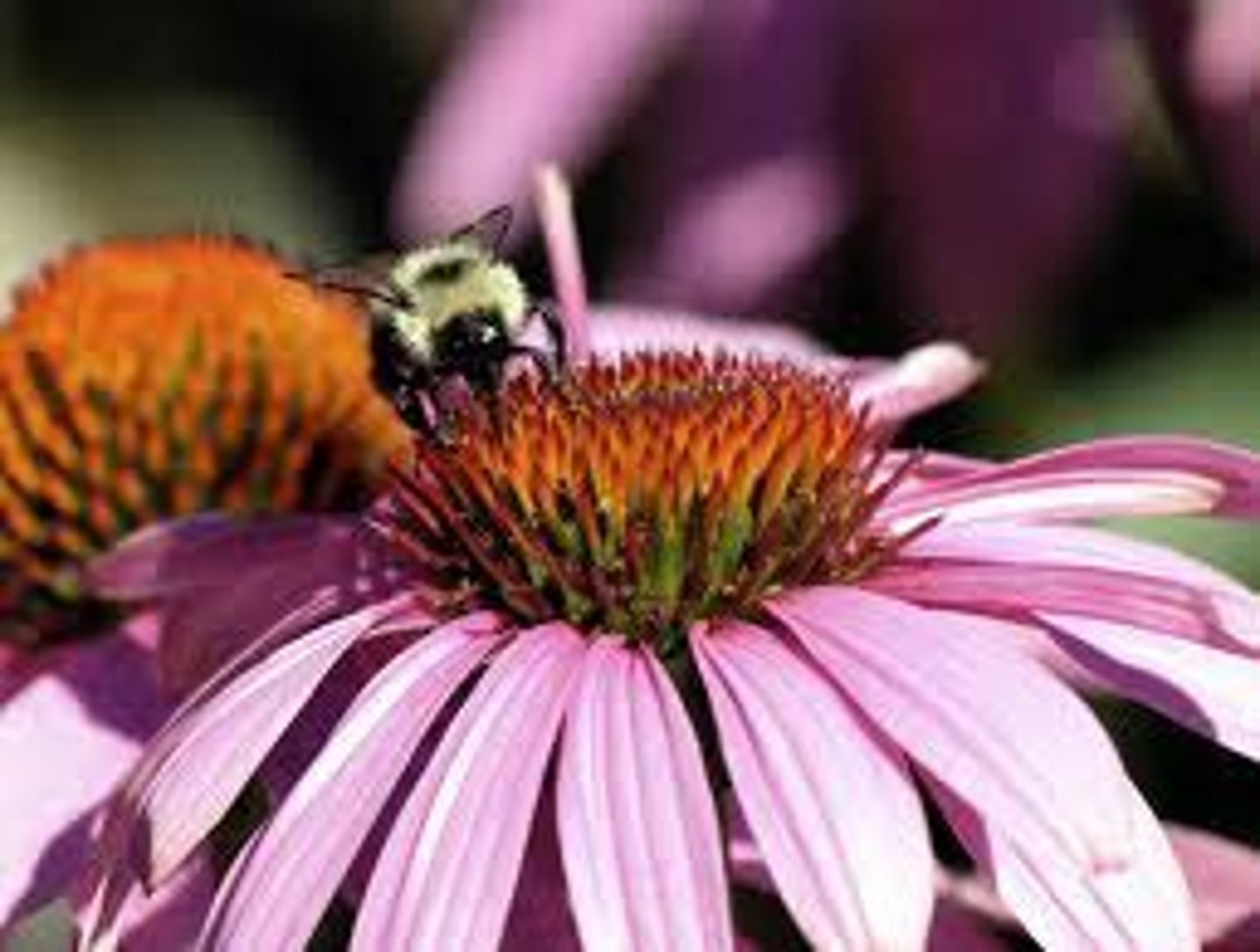
mutualism
A type of symbiosis where two individuals are able to benefit from each other (ex. bees pollinating flowers)

parasitism
the relation between two different kinds of organisms in which one receives benefits from the other by causing damage to it (usually not fatal damage)

photosynthesis
The means by which plants obtain their energy (or food)
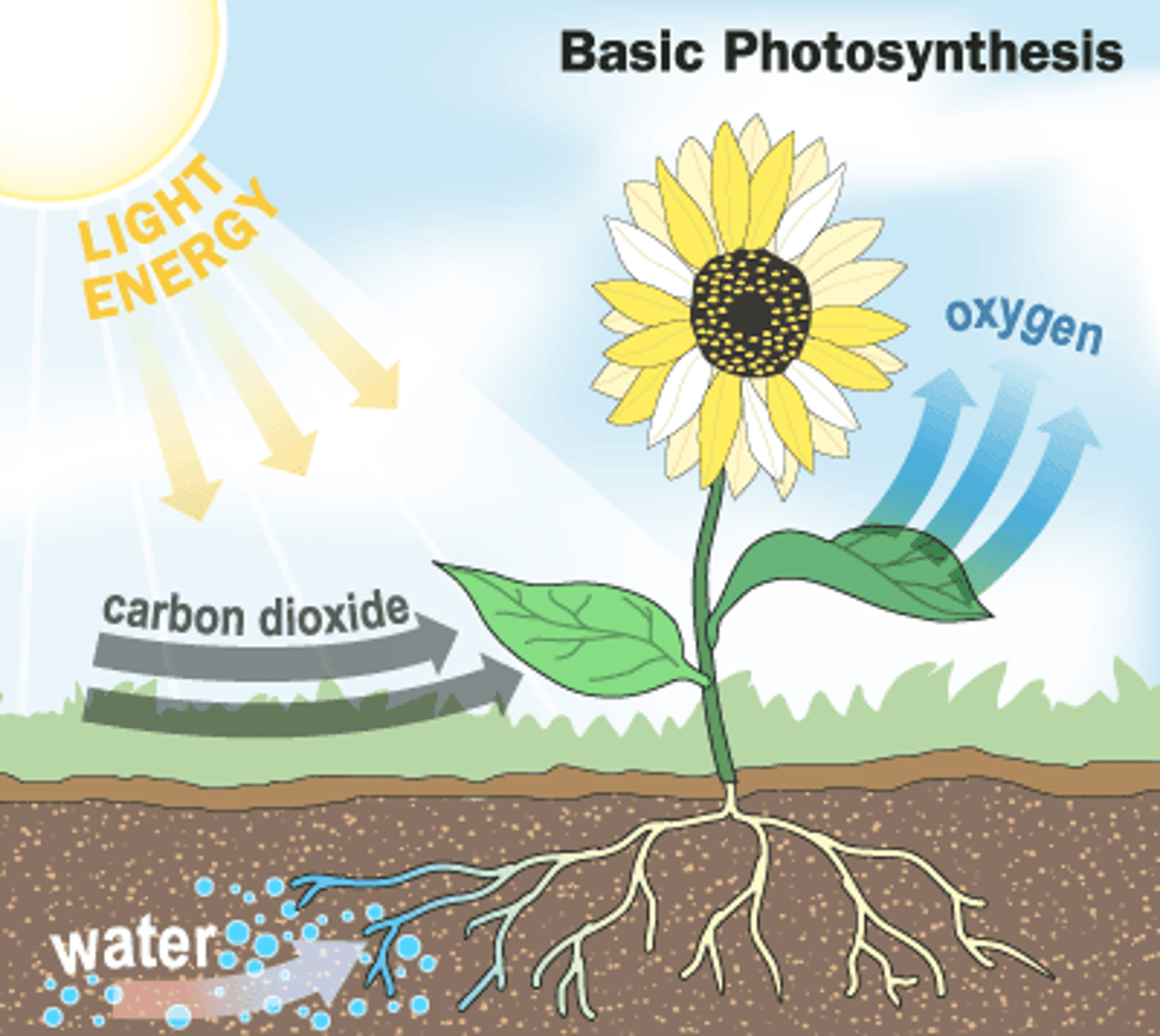
autotroph
an organism that is able to form nutritional organic substances from simple inorganic substances such as carbon dioxide.

heterotroph
an organism that obtains its energy (food) by consuming organic matter (i.e. deers eating grass or a mushroom decomposing plant matter)
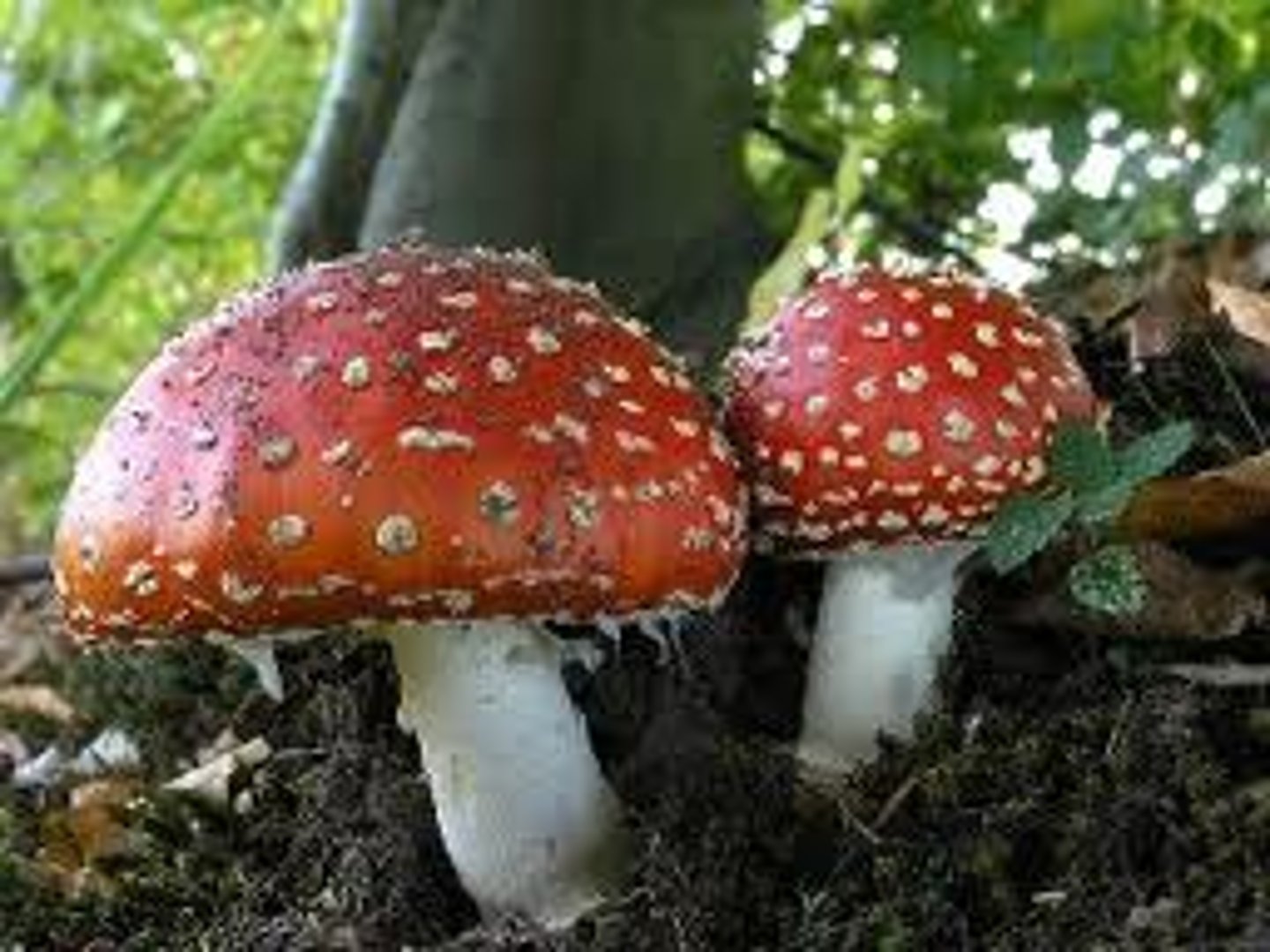

primary consumer
The first trophic level where organisms obtain their energy by eating plants
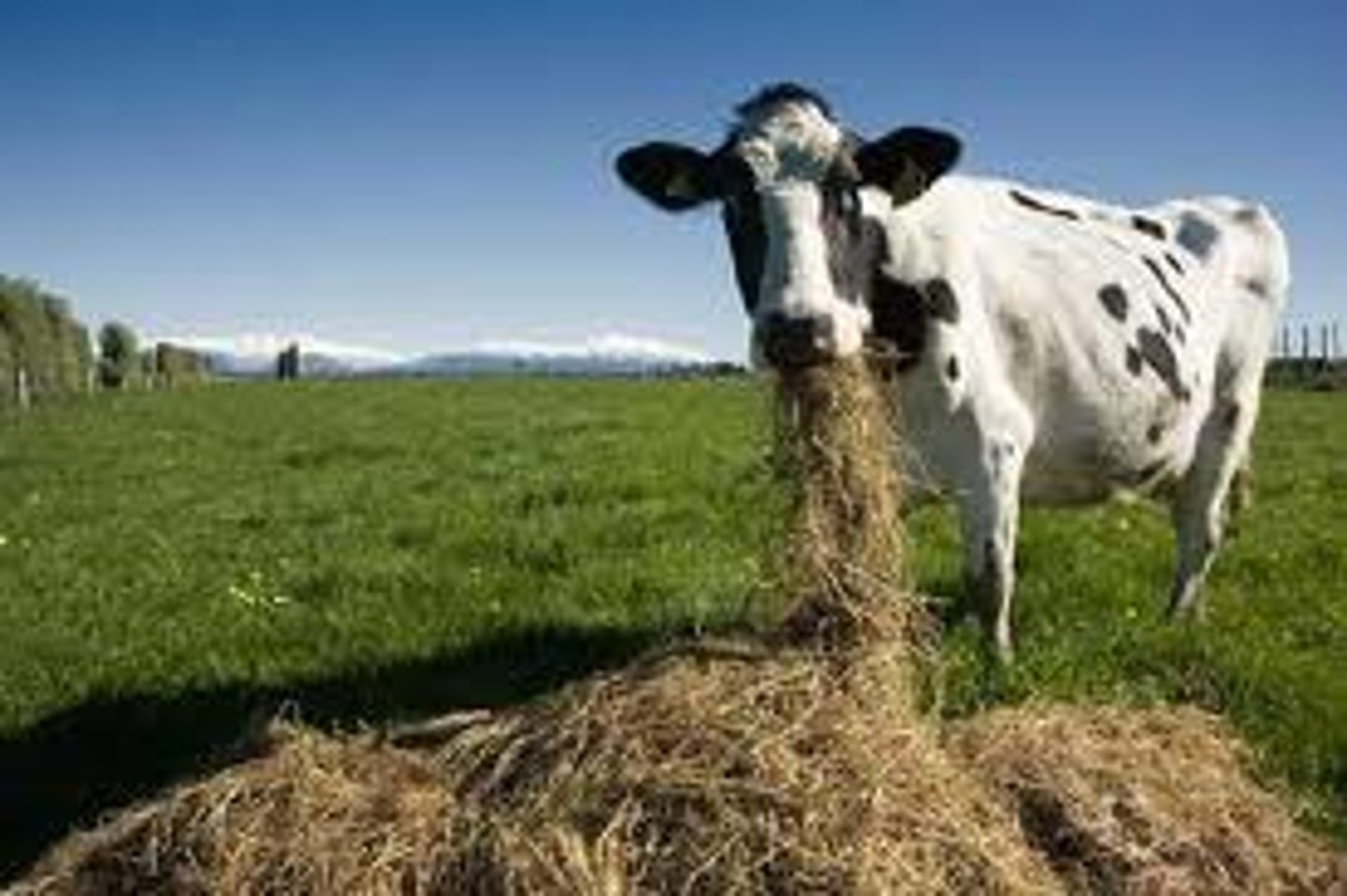

scavenger
any animal that feeds on refuse and other decaying organic matter (example: buzzard)

decomposer
an organism that is able to break down or disintegrated organic matter (example: bacteria breaking down a dead carcass)
secondary consumer
The second trophic level where organisms obtain their energy by consuming herbivores
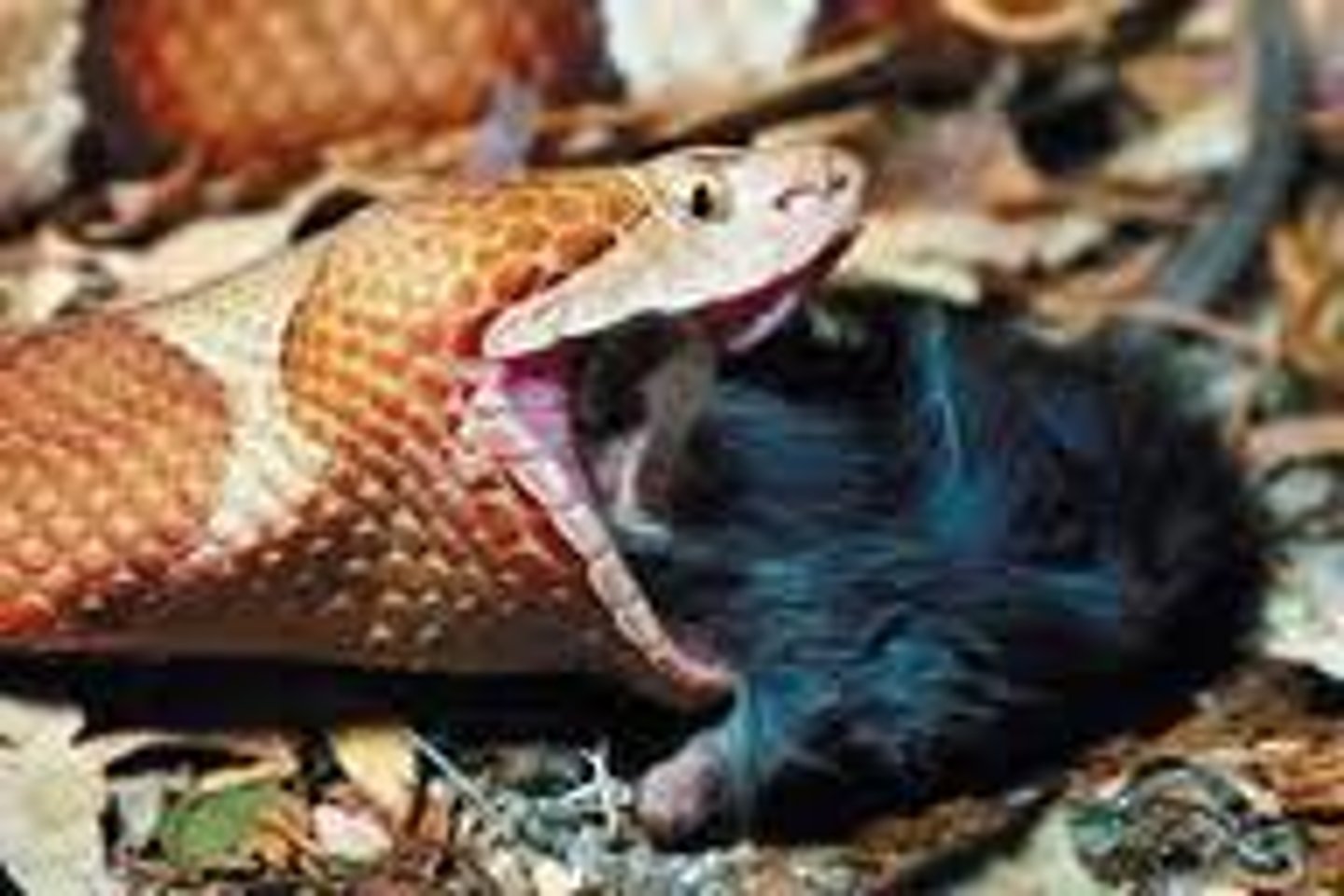

food chain
a simple representation that shows how energy is passed from one organism to the next

food web
a complex representation showing the various and complex ways in which energy is passed through an ecosystem
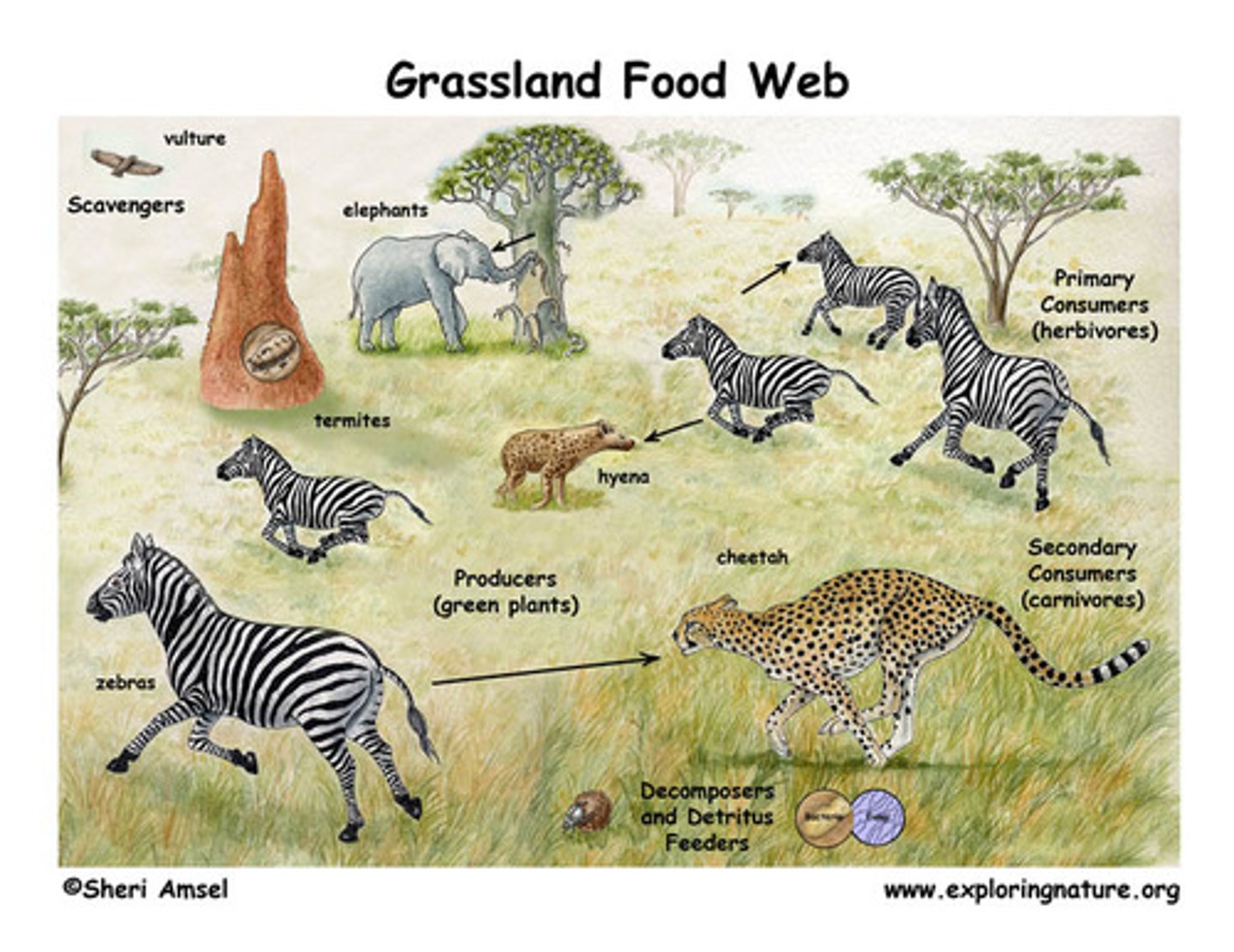
tertiary consumer
the top consumer

Omnivore
an animal or person that eats food of both plant and animal origin.
