Lecture 13: Linking Biodiversity to Ecosystem Functioning
1/18
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Gonzalez
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
How much biodiversity do grasslands need?
200 plant species
How much biodiversity do North American lakes need?
80 algae species
How much biodiversity do deciduous forests need?
53 tree species
How much biodiversity to tropical forests need?
2000+ plants
How much biodiversity do North American streams need?
120 algae
How much biodiversity does the open ocean need?
500 phytoplankton
Biodiversity-Ecosystem Functioning (BEF)
Old paradigm: Environmental variation drives biodiversity and ecosystem functioning
New paradigm: Biodiversity and environmental variation jointly drive biodiversity and ecosystem functioning
Ecosystem functioning
Stocks of biomass, flow of nutrients, or fluxes of gases
Ecosystem multifunctionality
When biodiversity promotes the supply, persistence, and stability of multiple ecosystem functions above a certain level
Ecosystem services/ nature’s contributions to people
Subset of functions of relational value to humans
Ecosystem
Combined plant and animal communities and physical environment
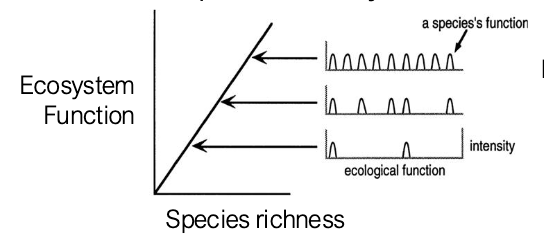
“Complementarity” model of ecosystem diversity and function
Species functionally complement each other because each niche has a function
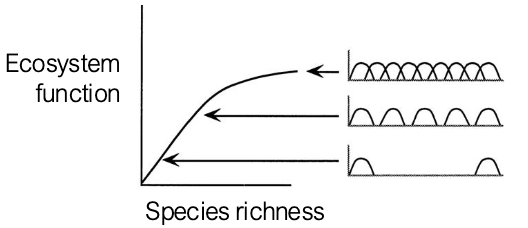
“Rivet” model of ecosystem diversity and function
After a certain amount of species, there is redundancy
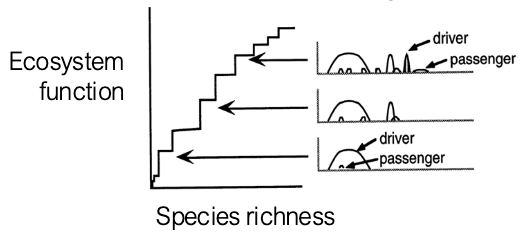
“Drivers and passengers” model of ecosystem diversity and function
Some species are drivers and contribute strongly to ecosystem function
Some species are passengers and contribute only to species richness
Functional traits
Influence ecosystem properties (effect traits)
Influence species response to environmental conditions (response traits)
These can be used to group species
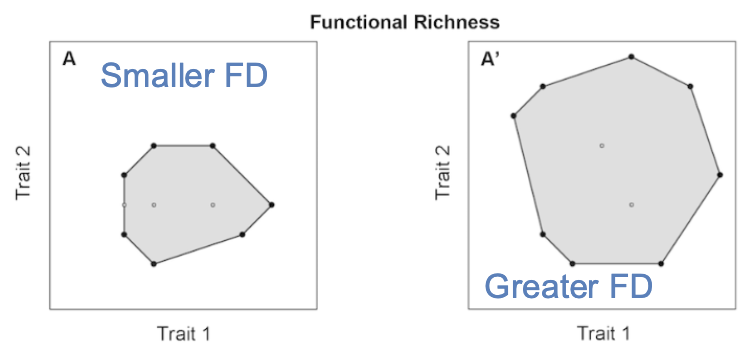
Functional diversity, plotted
Area corresponds to functional diversity
2 mechanisms by which adding a species can promote function
Complementarity: Increased function due to resource partitioning or facilitation
Selection: Greater likelihood of diverse communities being dominated by a competetively superior, high-performing species
Selection effect
When species with higher-than-average yields when grown alone dominate the functioning of a multispecies community
Complimentarity
Species yields are higher on average that expected based on average monoculture yield