Price determination in a competitive market
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
What factors shift the demand curve?
Population
Advertising
Substitutes Price
Income
Fashions/Tastes
Interest rates
Complements price
What is the price elasticity for a price elastic good?
PED>1
What is the price elasticity for a price in elastic good?
PED<1
What is the price elasticity of a unitary elastic good?
PED=1
What is the price elasticity of a perfectly price inelastic good?
PED=0
What is the price elasticity of a perfectly elastic good?
PED=Infinity
What factors affect PED?
Substitutes (no of)
Percentage of income
Luxury/Necessity
Addictive/Habit forming
Time period
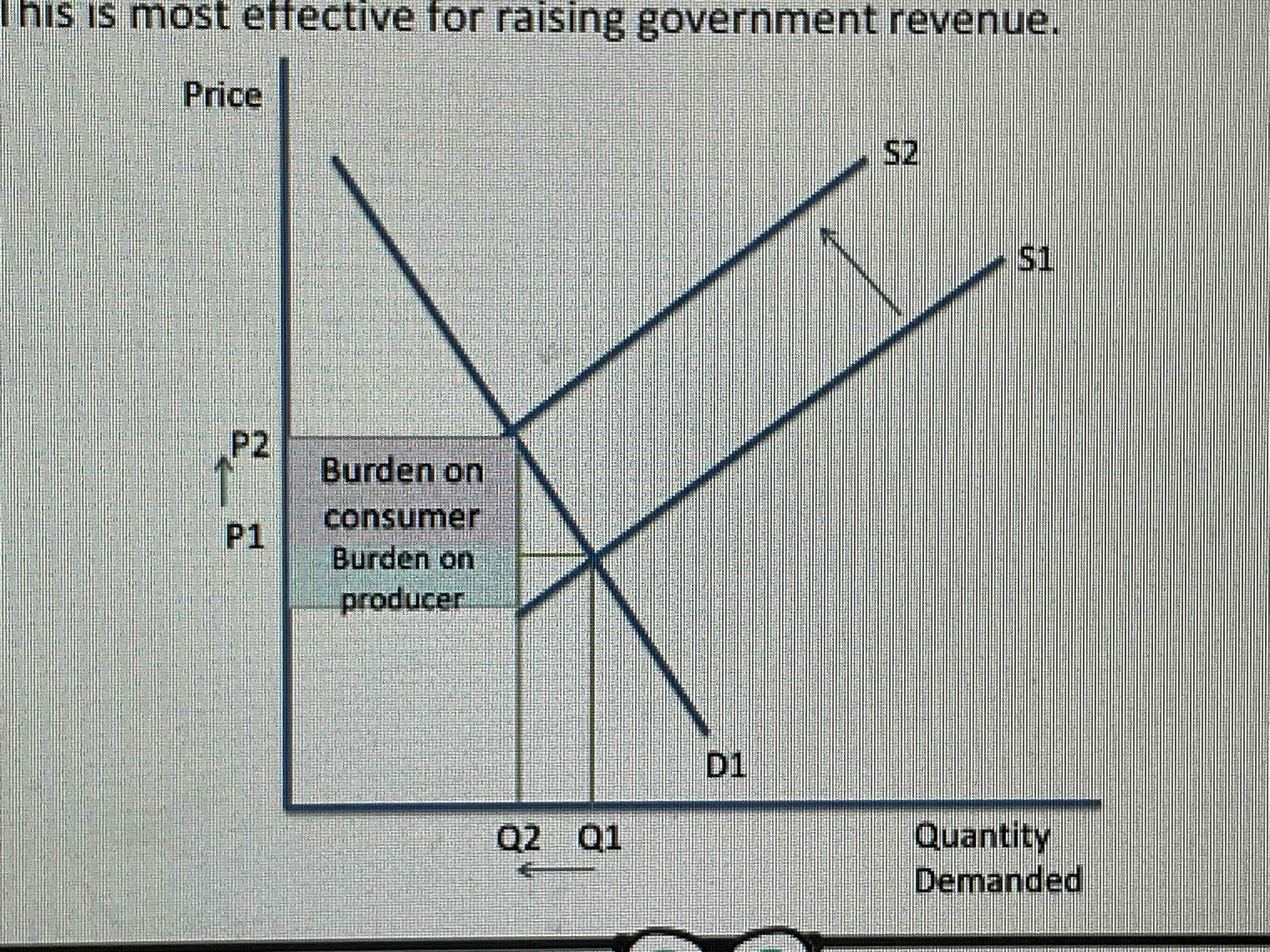
What happens when an inelastic good is taxed indirectly?
The burden falls on the consumer as the producer knows that the price increase will not lead to a large change in demand
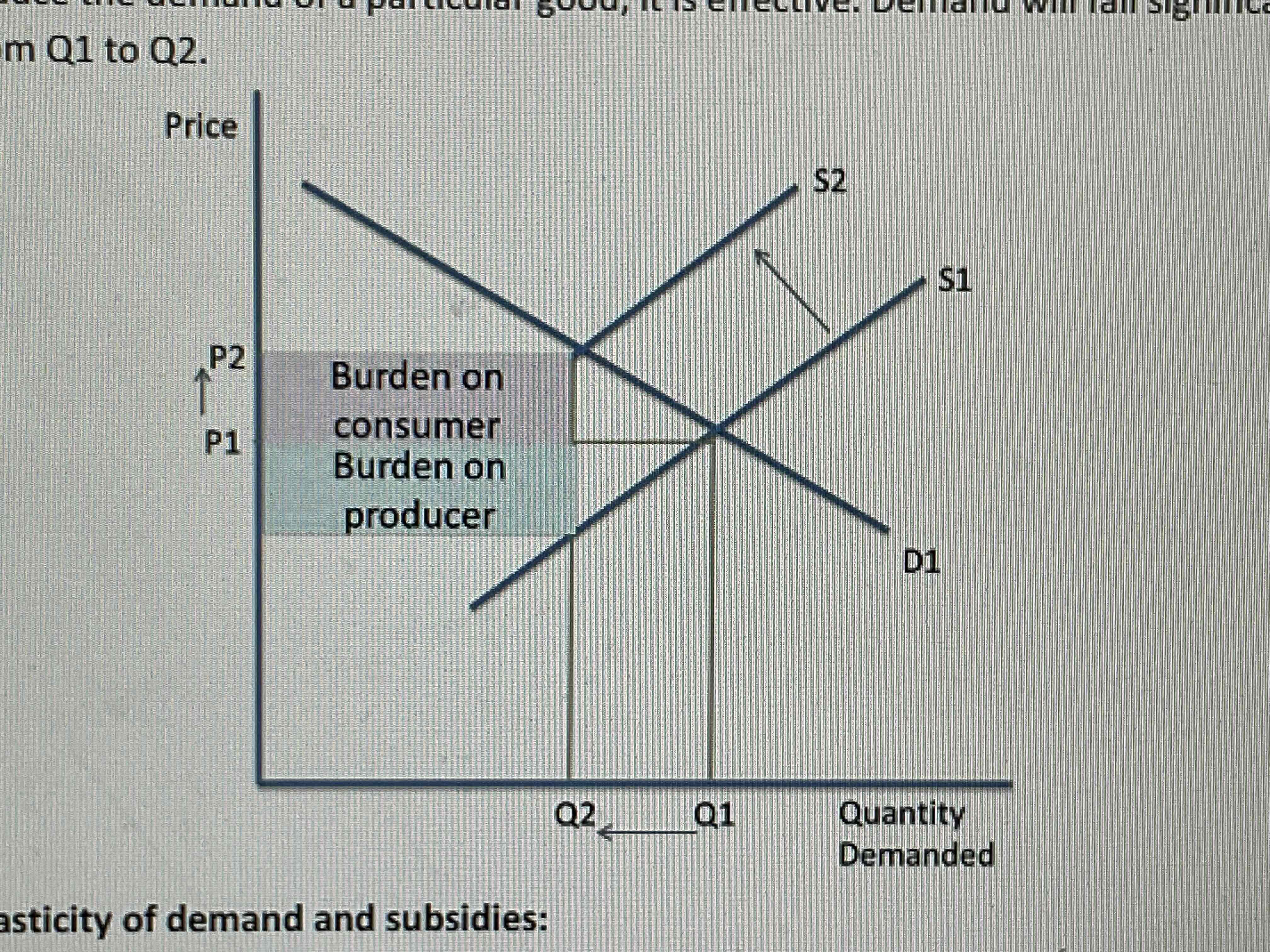
What happens when an elastic good is taxed indirectly?
The firm will burden most of the tax themselves as they don’t want demand to fall and lose revenue
How does a subsidy benefit consumers and producers?
Producers benefit from increased revenue whilst consumers benefit from lower prices
What happens to revenue if you increase the price of a good?
If demand is inelastic total revenue will increase
If demand is elastic total revenue will decrease
What are inferior goods? YED<0
Those which see a fall in demand as income increases e.g value options at supermarkets
What are normal goods?
Goods where demand increases with an increase in income YED>0
What are luxury goods?
An increase in income leads to an even bigger increase in demand YED>1 they are also normal goods
What XED do complementary goods have?
A negative XED as if one good becomes more expensive then the Qd for both goods will fall

What is a close complementary good?
A small fall in price X causes a large increase Qd for Y
What is a weak complementary good?
A large fall in the price of X leads only to a small increase in QD of Y
What is a substitute?
Something that can replace another good so XED is positive so demand curve is upwards slowing for price of X vs quantity of Y
What is a close substitute?
A small increase in the price of good X leads to a large increase in Qd of Y
What is a weak substitute?
A large increase in the price of good X leads to a smaller increase in quantity demanded of Y
What causes the supply curve to shift?
Productivity
Indirect taxes
Number of firms
Technology
Subsidies
Weather
Costs of production
When is supply elastic?
PES>1
When is supply inelastic?
PES<1
When is supply fixed?
PES = 0
When is supply perfectly elastic?
PES = Infinity
What are the factors influencing PES?
Production lag
Stocks
Spare capacity
Substitutability of FOPs
Time
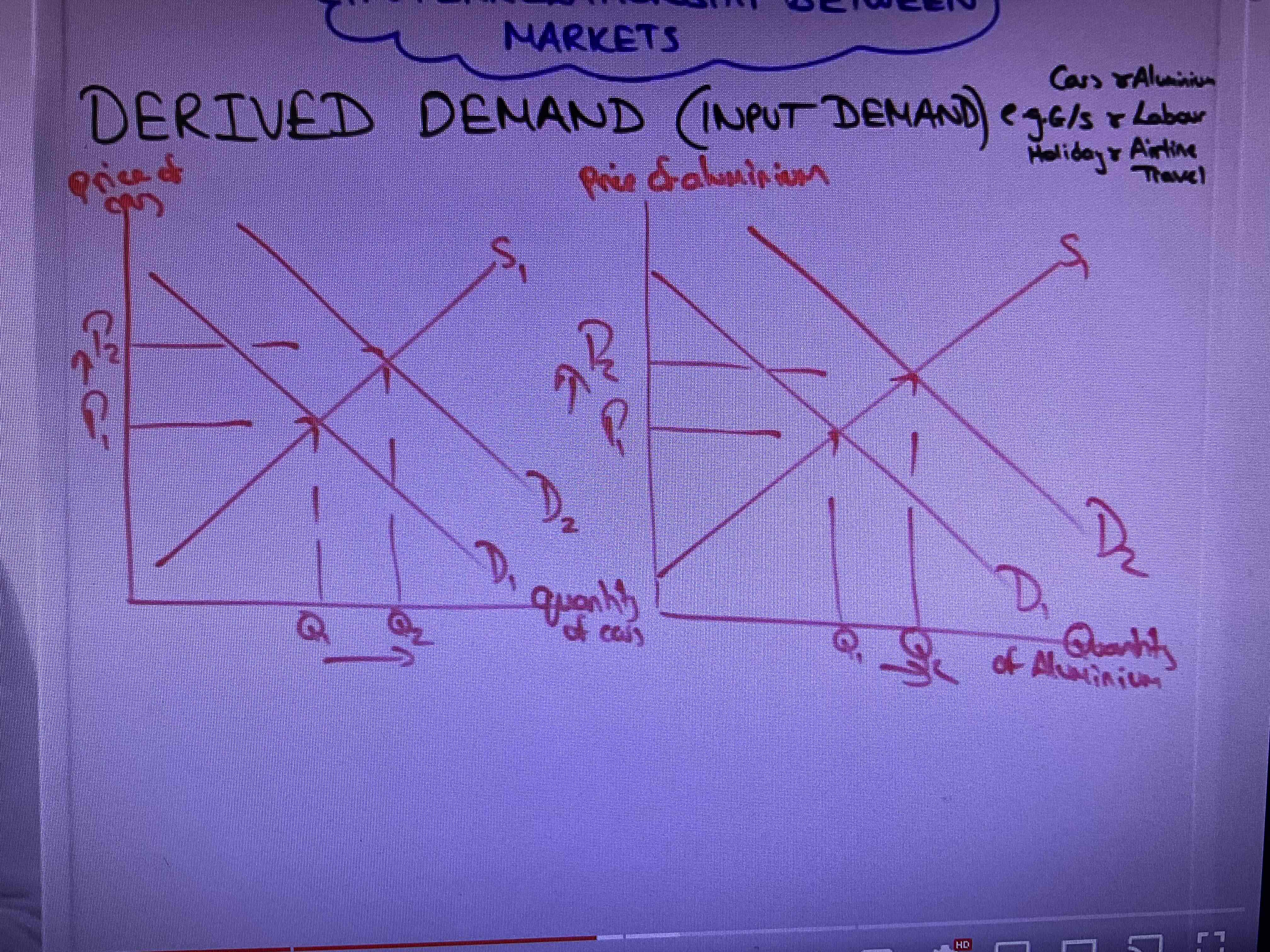
What is derived demand?
Demand of a good is linked to the demand of another good such as cars and aluminium
What is composite demand?
When the good demanded has more than one use like milk and cheese
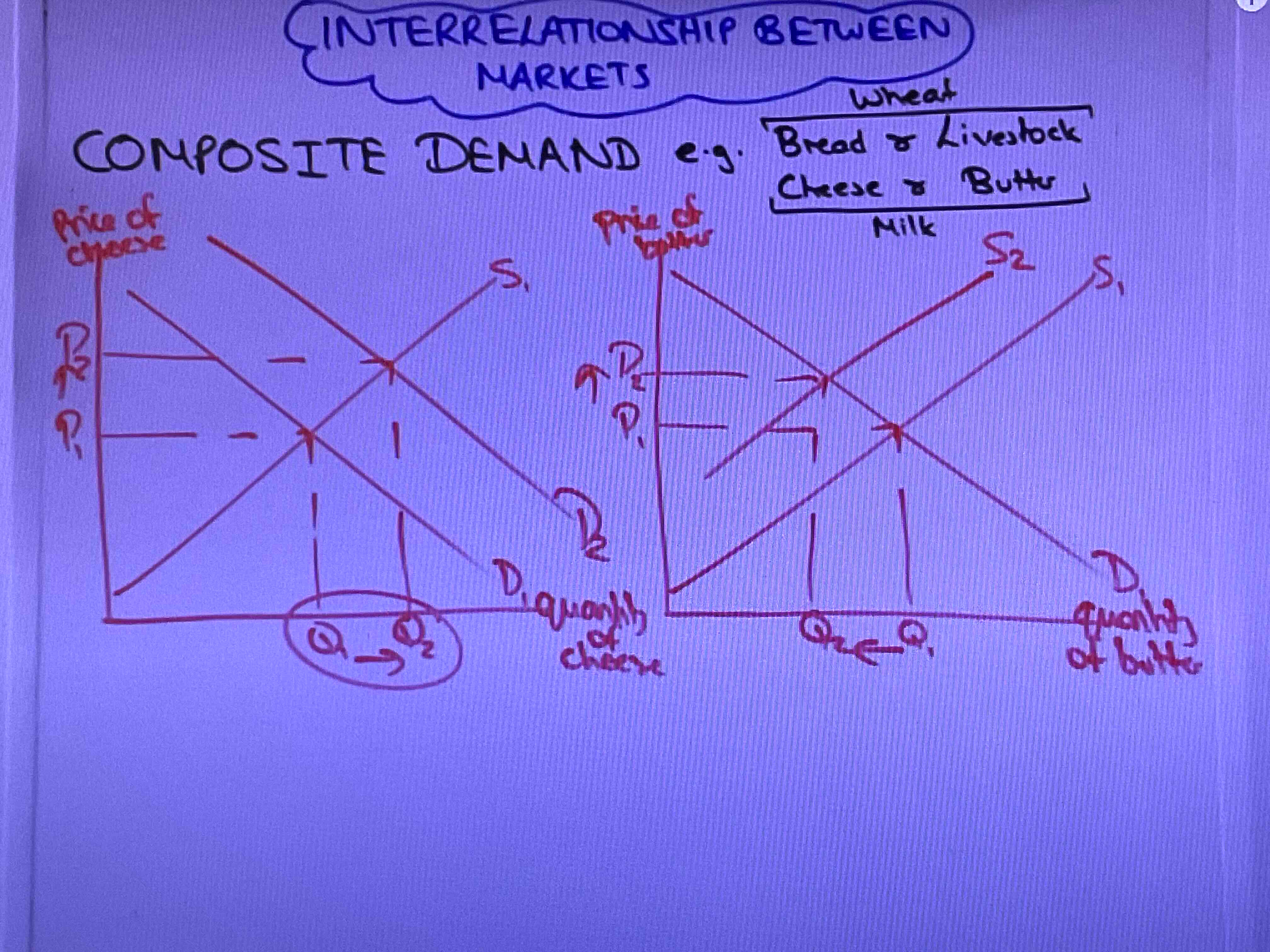
What is joint demand?
When goods are bought together such as cameras and memory cards
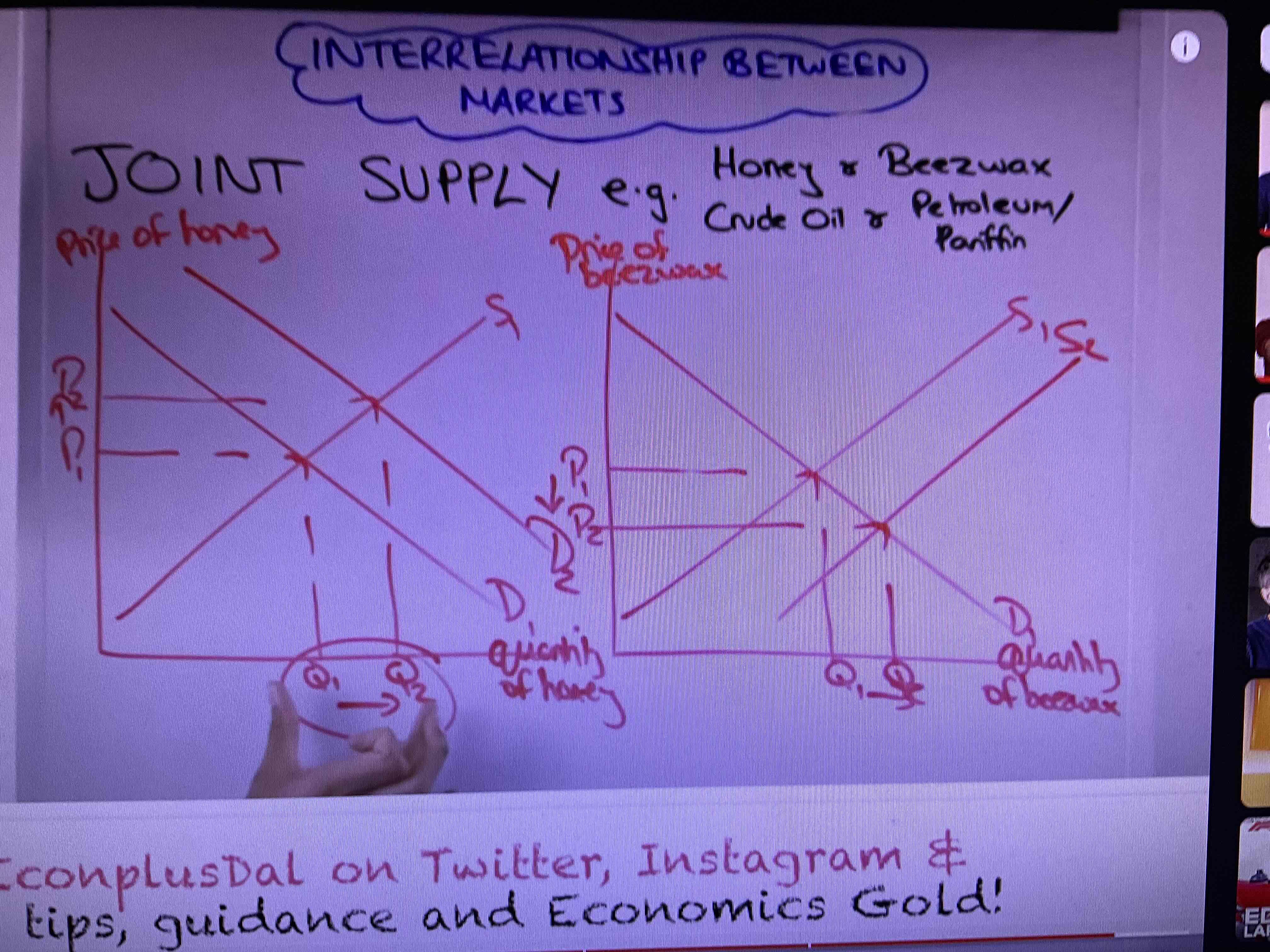
What is joint supply?
Increasing the supply of one good will decrease the other e.g lamb and wool