Nursing Care of Clients with Disturbances in Sexuality and Reproduction
1/129
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
130 Terms
Who are the candidates for pap smears?
Sexually-active women
Clinical manifestations of TSS involve 3 or more of:
Increased/Elevated | Decreased |
|
|
What are the s/sx that should be reported after brachytherapy? (Hint: A-BBB-D-E-F)
Abdominal pain
heavy vaginal Bleeding
urethral Burning for more than 24 hours
Blood in urine
severe Diarrhea
Extreme fatigue
Fever (T > 38C)
X-ray of the cervix, fallopian tubes, and uterus; this test is used to evaluate tubal anatomy and patency
Hysterosalpingography (HSG)
What are the 3 endoscopic studies?
Colposcopy - cervix and vaginal wall
Laparoscopy - pelvic cavity
Hysteroscopy - uterus
Infertility refers to a couple’s inability to achieve pregnancy after _____ of unprotected intercourse
1 year
What are the 3 female factors that affect infertility?
Ovarian and ovulation factors (PCOS, hyperprolactinemia, premature ovarian failure)
Tubal factors (endometriosis)
Uterine factors (polyps, fibroids, congenital malformations)
What is an adverse effect of clomiphene?
Multiple gestation
In women with PCOS, what is their serum progesterone level during:
Pre-ovulation?
Mid-cycle?
Less than 1 ng/mL
5-20 ng/mL
What hormone is excessive in women with PCOS?
Progesterone (mimics pregnancy)
Treatment: clomiphene
A. Polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS)
B. Hyperprolactinemia
C. Premature ovarian failure
A
Diagnostic study: ovulation index
A. Polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS)
B. Hyperprolactinemia
C. Premature ovarian failure
A
What are the 3 components in Rotterdam’s criteria?
Menstrual disorders
High levels of androgenic hormones
Enlarged ovaries upon UTZ
Treatment: dopaminergic drugs (e.g., Intropan, Inovan, Revivan, Dopastat)
A. Polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS)
B. Hyperprolactinemia
C. Premature ovarian failure
B; these will decrease the prolactin levels
Manifestation: hirsutism and acne
A. Polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS)
B. Hyperprolactinemia
C. Premature ovarian failure
A, B, and C
In premature ovarian failure, the ovaries stop working before _____ years of age
40
Hypergonadotropic hypogonadism
A. Polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS)
B. Hyperprolactinemia
C. Premature ovarian failure
C
Treatment: oocyte donation
A. Polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS)
B. Hyperprolactinemia
C. Premature ovarian failure
C
Manifestation: absent menstrual periods
A. Polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS)
B. Hyperprolactinemia
C. Premature ovarian failure
C
Manifestation: symptoms of low estrogen levels (e.g., hot flashes, night sweats, and vaginal dryness)
A. Polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS)
B. Hyperprolactinemia
C. Premature ovarian failure
C
What are the major manifestations of endometriosis? (Hint: 4D)
Dyspareunia
Dysuria
Dysmenorrhea
Dyschezia
What is the treatment for polyps?
Surgery
Methods: intracervical, interauterine, intratubal/intrafallopian
A. Artificial insemination
B. In vitro fertilization (IVF)
C. Gamete intrafallopian transfer (GIFT)
D. Intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI)
A
The male should not have ejaculated ____ hours prior to artificial insemination
24
Indication: inability of male to deposit semen in the vagina, inability of semen to be transported from vagina to uterine cavity (e.g., erectile dysfunction), single woman who desires to have a child
A. Artificial insemination
B. In vitro fertilization (IVF)
C. Gamete intrafallopian transfer (GIFT)
D. Intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI)
A
Treatment of choice for women with ovarian failure
A. Artificial insemination
B. In vitro fertilization (IVF)
C. Gamete intrafallopian transfer (GIFT)
D. Intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI)
C
Single sperm is injected through the zona pellucida and into the cytoplasm of oocyte
A. Artificial insemination
B. In vitro fertilization (IVF)
C. Gamete intrafallopian transfer (GIFT)
D. Intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI)
D
Treatment of choice in severe male factor infertility
A. Artificial insemination
B. In vitro fertilization (IVF)
C. Gamete intrafallopian transfer (GIFT)
D. Intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI)
D
In patients with endometriosis, GSCS is done to rule out _____ caused by chlamydia or gonorrhea
Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID)
True or false? Calcium and magnesium can treat endometriosis
False; these are only used for muscle relaxation
What is the side effect of the laparoscopic removal of endometrial implants and adhesions?
Temporary postoperative pain
Possibly caused by retrograde menstruation
A. Endometriosis
B. Toxic shock syndrome (TSS)
C. Uterine prolapse
D. Endometrial cancer
E. Ovarian cancer
F. Pelvic inflammatory disease
A
Management: oral contraceptives
A. Endometriosis
B. Toxic shock syndrome (TSS)
C. Uterine prolapse
D. Endometrial cancer
E. Ovarian cancer
F. Pelvic inflammatory disease
A
Manifestation: peeling of skin, abrupt onset of high fever, sunburn-like rashes, severe hypotension
A. Endometriosis
B. Toxic shock syndrome (TSS)
C. Uterine prolapse
D. Endometrial cancer
E. Ovarian cancer
F. Pelvic inflammatory disease
B; pag toxic, PASS (creds to ley)
Affects the heart, kidneys, liver, and respiratory system
A. Endometriosis
B. Toxic shock syndrome (TSS)
C. Uterine prolapse
D. Endometrial cancer
E. Ovarian cancer
F. Pelvic inflammatory disease
B
Management: IV antibiotics and corticosteroids
A. Endometriosis
B. Toxic shock syndrome (TSS)
C. Uterine prolapse
D. Endometrial cancer
E. Ovarian cancer
F. Pelvic inflammatory disease
B
Management: platelet transfusions
A. Endometriosis
B. Toxic shock syndrome (TSS)
C. Uterine prolapse
D. Endometrial cancer
E. Ovarian cancer
F. Pelvic inflammatory disease
B
True or false? Super-absorbent tampons should be used to prevent TSS
False
Causes: neuromuscular damage of childbirth, increased intra-abdominal pressure, weakening of pelvic support
A. Endometriosis
B. Toxic shock syndrome (TSS)
C. Uterine prolapse
D. Endometrial cancer
E. Ovarian cancer
F. Pelvic inflammatory disease
C
Common in multiparous women
A. Endometriosis
B. Toxic shock syndrome (TSS)
C. Uterine prolapse
D. Endometrial cancer
E. Ovarian cancer
F. Pelvic inflammatory disease
C
Grade of uterine prolapse in which the uterus bulges into the vagina, but the cervix does not protrude through the entrance to the vagina
Grade I
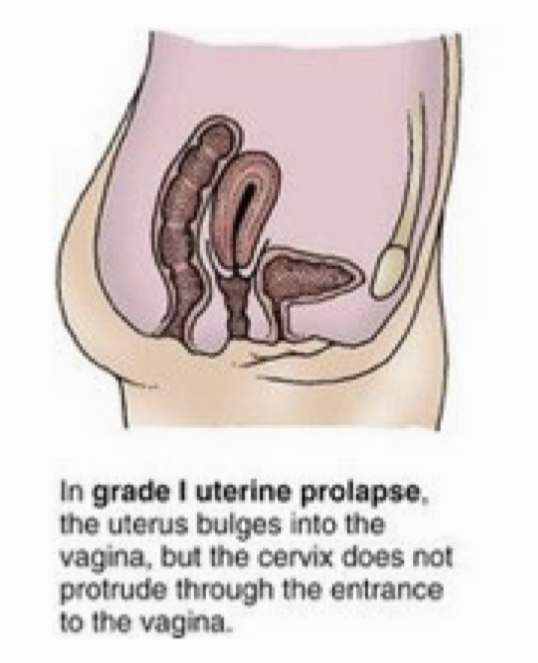
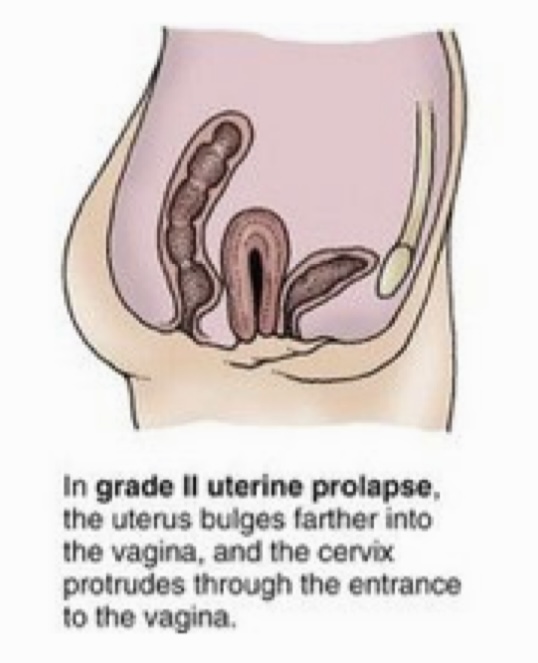
Grade of uterine prolapse in which the uterus bulges farther into the vagina, and the cervix protrudes through the entrance to the vagina
Grade II
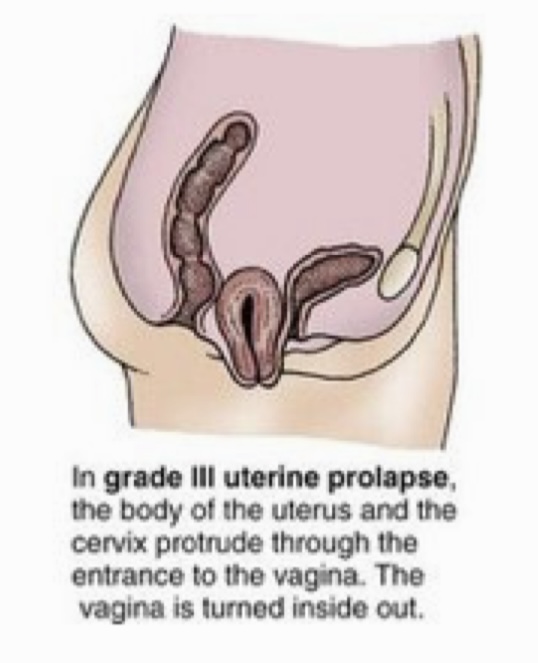
Grade of uterine prolapse in which the body of the uterus and the cervix protrude through the entrance to the vagina. The vagina is turned inside out.
Grade III
Manifestation: feeling as if “something is falling out”
A. Endometriosis
B. Toxic shock syndrome (TSS)
C. Uterine prolapse
D. Endometrial cancer
E. Ovarian cancer
F. Pelvic inflammatory disease
C
Management: Kegel exercises, space-filling devices, and bladder training
A. Endometriosis
B. Toxic shock syndrome (TSS)
C. Uterine prolapse
D. Endometrial cancer
E. Ovarian cancer
F. Pelvic inflammatory disease
C
Management: intravaginal estrogen therapy
A. Endometriosis
B. Toxic shock syndrome (TSS)
C. Uterine prolapse
D. Endometrial cancer
E. Ovarian cancer
F. Pelvic inflammatory disease
C
Management: transvaginal repair and anterior/posterior colporrhaphy
A. Endometriosis
B. Toxic shock syndrome (TSS)
C. Uterine prolapse
D. Endometrial cancer
E. Ovarian cancer
F. Pelvic inflammatory disease
C
True or false? Any woman can have a vaginal hysterectomy
False; pwede lang kapag hindi na magbubuntis at all o kapag na-achieve na ‘yung desired family size
What is the most common type of endometrial cancer?
Adenocarcinoma
What are the 4 stages of endometrial cancer?
I: confined in the endometrium
II: cervix
III: vagina or lymph nodes
IV: spread beyond the pelvis
Risk factors: late menopause, nulliparity
A. Endometriosis
B. Toxic shock syndrome (TSS)
C. Uterine prolapse
D. Endometrial cancer
E. Ovarian cancer
F. Pelvic inflammatory disease
D and E
Risk factors: DM, HTN, obesity
A. Endometriosis
B. Toxic shock syndrome (TSS)
C. Uterine prolapse
D. Endometrial cancer
E. Ovarian cancer
F. Pelvic inflammatory disease
D and E
Risk factor: taken Tamoxifen
A. Endometriosis
B. Toxic shock syndrome (TSS)
C. Uterine prolapse
D. Endometrial cancer
E. Ovarian cancer
F. Pelvic inflammatory disease
D
Manifestation: postmenopausal bleeding
A. Endometriosis
B. Toxic shock syndrome (TSS)
C. Uterine prolapse
D. Endometrial cancer
E. Ovarian cancer
F. Pelvic inflammatory disease
D
Manifestation: palpable uterine mass or uterine polyp
A. Endometriosis
B. Toxic shock syndrome (TSS)
C. Uterine prolapse
D. Endometrial cancer
E. Ovarian cancer
F. Pelvic inflammatory disease
D
Treatment: hysterectomy
A. Endometriosis
B. Toxic shock syndrome (TSS)
C. Uterine prolapse
D. Endometrial cancer
E. Ovarian cancer
F. Pelvic inflammatory disease
C and D
Treatment: brachytherapy
A. Endometriosis
B. Toxic shock syndrome (TSS)
C. Uterine prolapse
D. Endometrial cancer
E. Ovarian cancer
F. Pelvic inflammatory disease
D; for stage II and III endometrial cancer
True or false? Heavy vaginal bleeding is expected in brachytherapy
False; report this s/sx
True or false? A woman on brachytherapy for endometrial cancer is radioactive between treatments
False; hence, there are no restrictions on her interactions with others
Treatment: chemotherapy (Doxorubicin, Ciplatin, Paclitaxel)
A. Endometriosis
B. Toxic shock syndrome (TSS)
C. Uterine prolapse
D. Endometrial cancer
E. Ovarian cancer
F. Pelvic inflammatory disease
D
Disordered growth in response to excessive exposure to estrogen
A. Endometriosis
B. Toxic shock syndrome (TSS)
C. Uterine prolapse
D. Endometrial cancer
E. Ovarian cancer
F. Pelvic inflammatory disease
E
Risk factor: family history of hereditary nonpolyposis colon cancer (HNPCC)
A. Endometriosis
B. Toxic shock syndrome (TSS)
C. Uterine prolapse
D. Endometrial cancer
E. Ovarian cancer
F. Pelvic inflammatory disease
D and E
Risk factor: colorectal cancer and breast cancer
A. Endometriosis
B. Toxic shock syndrome (TSS)
C. Uterine prolapse
D. Endometrial cancer
E. Ovarian cancer
F. Pelvic inflammatory disease
E
Manifestation: vague GI disturbances, urinary frequency/incontinence, unexpected weight loss, abdominal mass
A. Endometriosis
B. Toxic shock syndrome (TSS)
C. Uterine prolapse
D. Endometrial cancer
E. Ovarian cancer
F. Pelvic inflammatory disease
E
Manifestation: abdominal pain
A. Endometriosis
B. Toxic shock syndrome (TSS)
C. Uterine prolapse
D. Endometrial cancer
E. Ovarian cancer
F. Pelvic inflammatory disease
D, E, F
Diagnostic study: CA-125
A. Endometriosis
B. Toxic shock syndrome (TSS)
C. Uterine prolapse
D. Endometrial cancer
E. Ovarian cancer
F. Pelvic inflammatory disease
A, D, E
Management: total abdominal hysterectomy, bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy (TAHBSO)
A. Endometriosis
B. Toxic shock syndrome (TSS)
C. Uterine prolapse
D. Endometrial cancer
E. Ovarian cancer
F. Pelvic inflammatory disease
E
Treatment: chemotherapy (Cisplatin, Carboplatin, Taxanes)
A. Endometriosis
B. Toxic shock syndrome (TSS)
C. Uterine prolapse
D. Endometrial cancer
E. Ovarian cancer
F. Pelvic inflammatory disease
E
The nurse should instruct patients with ovarian cancer to avoid tampons, douches, and sexual intercourse for at least _____ or as instructed after surgery
6 weeks
Complex infectious process in which organisms from lower genital tract migrate from endocervix upward through the uterine cavity into the fallopian tubes
A. Endometriosis
B. Toxic shock syndrome (TSS)
C. Uterine prolapse
D. Endometrial cancer
E. Ovarian cancer
F. Pelvic inflammatory disease
F
What is the most common site of PID?
Fallopian tubes
Leading cause of infertility
A. Endometriosis
B. Toxic shock syndrome (TSS)
C. Uterine prolapse
D. Endometrial cancer
E. Ovarian cancer
F. Pelvic inflammatory disease
F
Cause: STIs
A. Endometriosis
B. Toxic shock syndrome (TSS)
C. Uterine prolapse
D. Endometrial cancer
E. Ovarian cancer
F. Pelvic inflammatory disease
F
Manifestation: vaginal discharge has a foul smell
A. Endometriosis
B. Toxic shock syndrome (TSS)
C. Uterine prolapse
D. Endometrial cancer
E. Ovarian cancer
F. Pelvic inflammatory disease
F; indicates infection
Manifestation: may possibly experience no symptoms
A. Endometriosis
B. Toxic shock syndrome (TSS)
C. Uterine prolapse
D. Endometrial cancer
E. Ovarian cancer
F. Pelvic inflammatory disease
F
What is the diagnostic criteria for PID?
Sexually active woman and at risk for STIs
Pelvic or lower abdominal pain
No other causes for illness can be found; AND
Uterine tenderness, or
Adnexal tenderness, or
Cervical motion tenderness (chandelier sign)
The antibiotic therapy for women with PID lasts for how many days?
14 days (1 shot lang for males unfair!!!!!)
Management: maintain rest in a semi-Fowler’s position
A. Endometriosis
B. Toxic shock syndrome (TSS)
C. Uterine prolapse
D. Endometrial cancer
E. Ovarian cancer
F. Pelvic inflammatory disease
F; para mawala ‘yung pressure sa abdomen
True or false? Women on antibiotic therapy for PID can still have sexual intercourse
False; avoid sexual intercourse hangga’t hindi ka pa cleared ng doktor
Exact cause is unclear
A. Benign prostatic hyperplasia
B. Erectile dysfunction
C. Priapism
A
Pathophysiology: increased dihydrotestosterone (DHT) levels
A. Benign prostatic hyperplasia
B. Erectile dysfunction
C. Priapism
A
_____ is the most common cause of hematuria among men
A. Benign prostatic hyperplasia
B. Erectile dysfunction
C. Priapism
A
How is the specimen for urine GSCS obtained?
Via a straight/foley catheter
Management: 5-alpha reductase inhibitor (5-ARI) and alpha-1 selective blocking agents
A. Benign prostatic hyperplasia
B. Erectile dysfunction
C. Priapism
A
After TURP, the patient should have an indwelling urinary catheter for at least _____
24 hours
Also known as impotence
A. Benign prostatic hyperplasia
B. Erectile dysfunction
C. Priapism
B
What are the 2 major types of erectile dysfunction?
Organic ED: gradual deterioration of function
Functional ED: psychological cause; onset is usually sudden and follows a period of high stress
Diagnostic study: nocturnal penile tumescence test
A. Benign prostatic hyperplasia
B. Erectile dysfunction
C. Priapism
B; differentiates urogenic from psychogenic cause
During deep sleep, men can have ____ erections
3-5
Management: PDE-5 inhibitors (e.g., sildenafil, vardenafil, tadalafil)
A. Benign prostatic hyperplasia
B. Erectile dysfunction
C. Priapism
B
PDE-5 inhibitors should be taken at least _____ prior to sexual intercourse
1 hour
Intracorpeal injections (e.g., alprostadil, paverine, phentolamine) should be done at least _____ prior to sexual intercourse
30 minutes
True or false? Priapism affects the 2 corpora cavernosa, while corpus spongiosum and glans penis are unaffected
True
Management: prostatic massage, sedation, ice packs, bed rest, meperidine, urinary catheterization
A. Benign prostatic hyperplasia
B. Erectile dysfunction
C. Priapism
C
Management: aspiration of corpora cavernosa with large-bore needle
A. Benign prostatic hyperplasia
B. Erectile dysfunction
C. Priapism
C
Urologic emergency
A. Benign prostatic hyperplasia
B. Erectile dysfunction
C. Priapism
C
It is a cytologic study that is effective in detecting precancerous and cancerous cells from the cervix
Pap smear
How are specimens obtained via Pap smear?
A speculum is inserted into the vagina and several cell samples from the cervix are obtained with a small brush or spatula.
Specimens are placed on a glass slide and sent to the laboratory for examination.
When should a Pap smear be scheduled?
Between menstrual periods so that the menstrual flow does not interfere with the test interpretation
What should be included in the health teaching before a Pap smear?
Teach women not to:
douche,
use vaginal medications or deodorants, and
have sexual intercourse for at least 24 hours before the test