mechanisms of early normal growth of the craniofacial skeleton
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
1
New cards
define isometric growth?
* progressive proportional increase in all organs and systems with time
2
New cards
define allometric growth?
describes the differences in the relative rates of growth between one part of the body and another
3
New cards
where is allometric growth shown?
is clearly demonstrated in the changes of body proportion between fetuses, neonates, children and adults.
4
New cards
describe the head at 6-7 weeks post-fertilisation
the head is nearly half of the total length of the embryo.
grows until the head is 1/8th of body size in adults
grows until the head is 1/8th of body size in adults
5
New cards
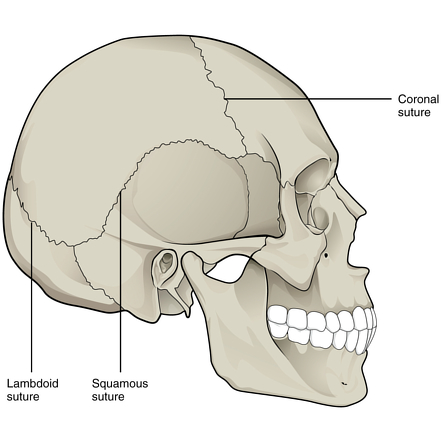
What bones of the skull are derived from mesoderm and ectomesenchyme?
- The skull posterior to the coronal suture is derived from mesoderm
- The bones anterior to this suture are derived from ectomesenchyme from neural crest
- The bones anterior to this suture are derived from ectomesenchyme from neural crest
6
New cards
What is the process of condensation?
Coalescence of mesodermal or ectomesenchymal cells into dense groups
This is the START of the 2 types of bone formation
This is the START of the 2 types of bone formation
7
New cards
What are the 2 types of bone formation?
**Endochondral Ossification (ECO)** - condensed cells differentiate into chondroblasts - forms cartilage template. Then cartilage replaced by bone
**Intramembranous Ossification (IMO)** - bone formed directly from condensed cells
**Intramembranous Ossification (IMO)** - bone formed directly from condensed cells
8
New cards
what do most organs grow by?
**Interstitial growth** - results from cell division and matrix proliferation throughout their structure
9
New cards
what prevents interstitial growth in bones?
therefore what does bone do in order to grow?
therefore what does bone do in order to grow?
* the mineralised matrix of bones,
* Therefore, bones grow by addition of new material onto existing surfaces. = APPOSITIONAL GROWTH
* Therefore, bones grow by addition of new material onto existing surfaces. = APPOSITIONAL GROWTH
10
New cards
why do bones developing from ECO not have the limitations of appositional growth?
cartilage is growing during this process and cartilage can grow by interstitial growth
11
New cards
How are the adult size and proportion of bone achieved?
Process of remodelling - combination of surface deposition (osteoblasts) and resorption (osteoclasts)
12
New cards
What bone surfaces undergo remodelling during growth periods too?
all internal and external bone surfaces undergo remodelling
13
New cards
describe growth sites
are surfaces or cartilages where large amounts of growth take place
14
New cards
What general factors Affect Growth of the Craniofacial Skeleton?
* hormonal influences
* nutritional influences
* genetic influences
* socioeconomic influences - links to nutrition
* nutritional influences
* genetic influences
* socioeconomic influences - links to nutrition
15
New cards
What localised factors affect Growth of the Craniofacial Skeleton?
1) Growth Patterns
* Somatic (bones whose growth is in relation to the rest of the body)
* Neural (growth of the bones surrounding the brain follows the pattern of growth of the brain).
2) Capsular Matrices- bone around enclosed soft tissues need to be remodelled in relation to soft tissue e.g bones around the eye, the brain
3) Periosteal Matrices- Joints, Muscular Attachments and Teeth a have an influence on the bones of the craniofacial skeleton
16
New cards
describe the skull and facial skeleton at birth?
skull = proportionally large •
facial skeleton = relatively small compared with an adult - due to early stages of development of the mandible and maxillae
facial skeleton = relatively small compared with an adult - due to early stages of development of the mandible and maxillae
17
New cards
Based on looking at skull at birth what reflects early cerebral maturation?
* the large size of the calvaria (top of skull)
* ossification is incomplete in many sites
* ossification is incomplete in many sites
18
New cards
when is there the biggest growth of the facial skeleton?
during childhood and puberty.
19
New cards
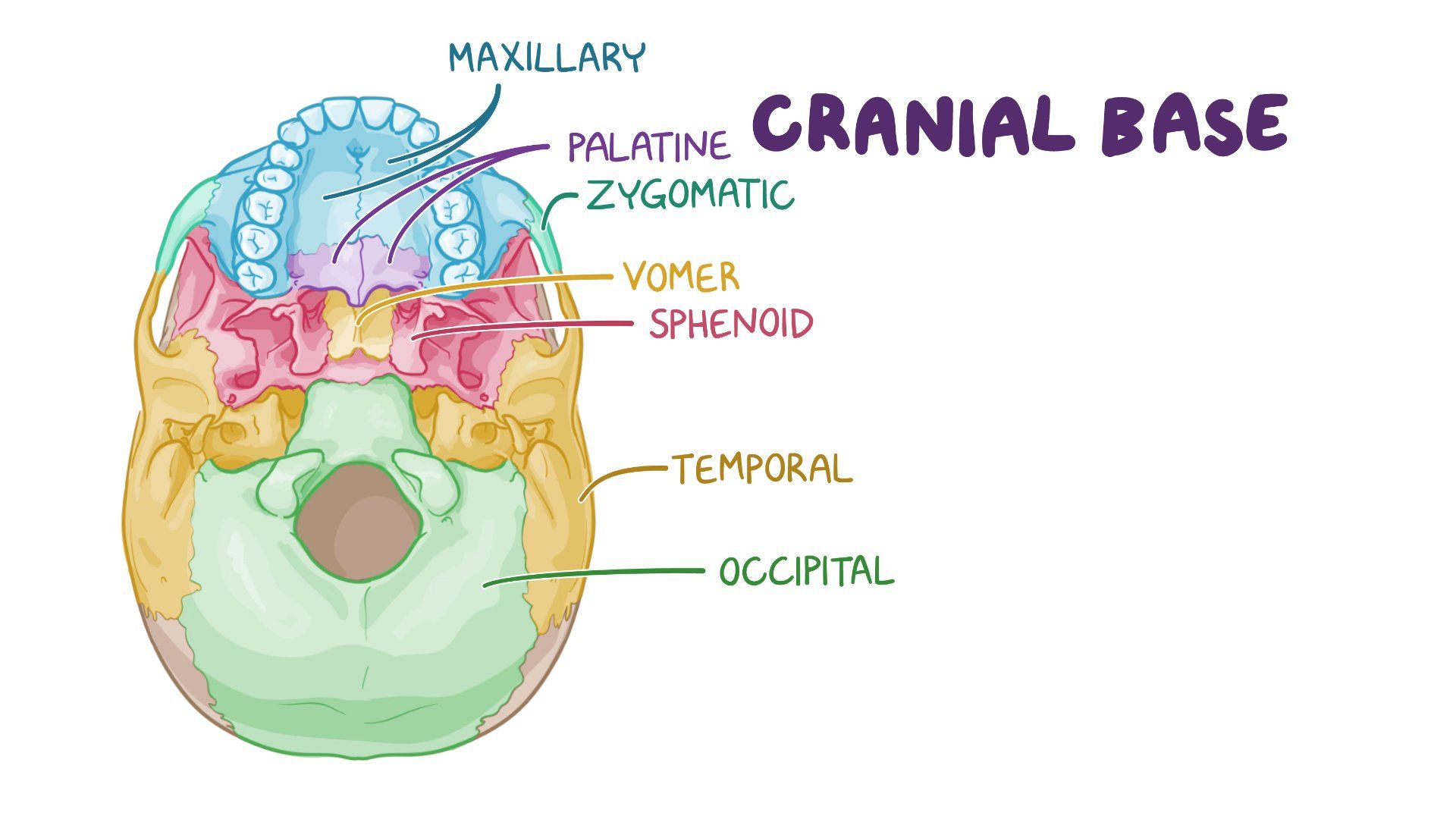
What is cranial base?
Bones at bottom of skull
20
New cards
How is cranial base formed?
Bones of cranial base formed from cartilaginous precursors therefore via ECO
In between the bones of the cranial base are **cartilaginous joints** (remnants of the precursors) known as **synchondroses**
In between the bones of the cranial base are **cartilaginous joints** (remnants of the precursors) known as **synchondroses**
21
New cards
What does growth of cranial base result in?
* Cranial lengthening
* Important site of growth : spheno-occipital synchondrosis -continues until \~18 years old
* Elongation of the cranial base allows room for elongation of the maxillae to accommodate the 2nd and 3rd permanent molars.
* Important site of growth : spheno-occipital synchondrosis -continues until \~18 years old
* Elongation of the cranial base allows room for elongation of the maxillae to accommodate the 2nd and 3rd permanent molars.
22
New cards
What is cranial vault?
Part of the Skull Overlying the Brain
23
New cards
How are bones of cranial vault formed?
* Via IMO (no cartilage precursor)
* Follows neural growth pattern - this is rapid prenatally
* Grows from 1-7 yrs starts rapidly but slows down
* Grows via appositional growth (bone onto bone) and remodelling in 1st year
* fontanelles gradually fuse by ossification
* Follows neural growth pattern - this is rapid prenatally
* Grows from 1-7 yrs starts rapidly but slows down
* Grows via appositional growth (bone onto bone) and remodelling in 1st year
* fontanelles gradually fuse by ossification
24
New cards
what are the facial bones formed by?
* IMO
* Occurs over long period (well into adulthood)
* Orbital and upper nasal cavity growth is achieved by **deposition of bone at sutures**
* More deposition occurs on the **facial aspect** of sutural junctions -resulting in the maxilla being carried **downwards and forward**
* Occurs over long period (well into adulthood)
* Orbital and upper nasal cavity growth is achieved by **deposition of bone at sutures**
* More deposition occurs on the **facial aspect** of sutural junctions -resulting in the maxilla being carried **downwards and forward**
25
New cards
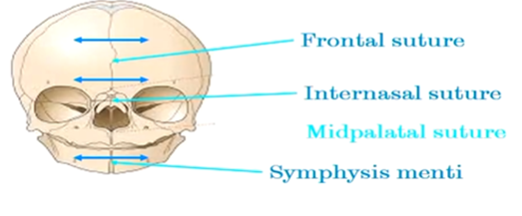
what are some of the post natal sites of growth
* Frontal suture
* Internasal suture
* Symphysis menti - joins 2 halves of mandible together
\
Deposition of bone at the sutures is associated with an increase in width of the facial skeleton.
* Internasal suture
* Symphysis menti - joins 2 halves of mandible together
\
Deposition of bone at the sutures is associated with an increase in width of the facial skeleton.
26
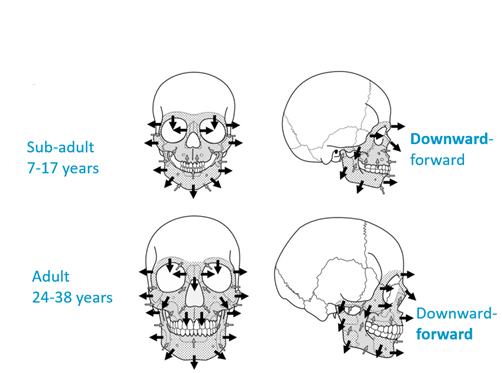
New cards
What direction does facial skeleton always form?
downwards and forwards
27
New cards
How does the maxilla grow forwards?
Arrow in pic shows direction of growth
* deposition = on the palate and rapid on the tuberosities
* resorption = labial area
\
Deposition posteriorly is greater than resorption anteriorly = forward growth
* deposition = on the palate and rapid on the tuberosities
* resorption = labial area
\
Deposition posteriorly is greater than resorption anteriorly = forward growth
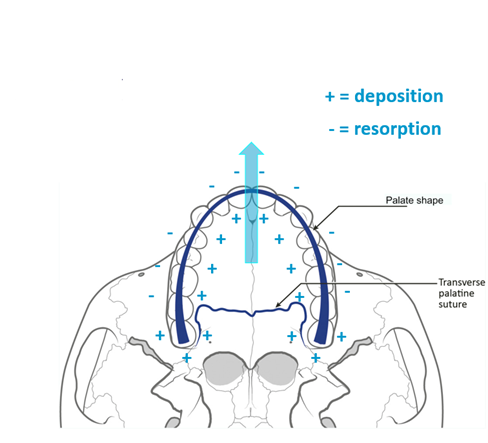
28
New cards
What causes downward growth of maxilla?
* Resorption of bone in upper aspect of nasal cavity
* Deposition of bone on palate
* Deposition of bone on palate
29
New cards
How does mandible form embryologically?
forms by IMO - bone forms around nerve canal (IAN,incisive,mental) and ramus formed by backward spread
\
After bone is formed secondary cartilages appear in mandible
Secondary cartilages = growth sites - produce bone by ECO
\
After bone is formed secondary cartilages appear in mandible
Secondary cartilages = growth sites - produce bone by ECO
30
New cards
How does the mandible grow?
Condylar cartilage is one of the main sites of bone deposition in the mandible:
* active throughout the growth period to maturity
* as cartilages grows it is replaced inferiorly by bone
Narrow zone of growth cartilage persists beneath the articular surface of the condylar head.
* means that changes in the mandible and condyle can occur throughout life.
* active throughout the growth period to maturity
* as cartilages grows it is replaced inferiorly by bone
Narrow zone of growth cartilage persists beneath the articular surface of the condylar head.
* means that changes in the mandible and condyle can occur throughout life.
31
New cards
How do teeth influence growth of mandible?
* Eruption of primary dentition enables infant to chew food
* Stimulates development of muscles of mastication
* Increases size of their attachment sites to mandible
* Angle of mandible must be altered so that occlusal surfaces of upper and lower teeth are parallel
* Stimulates development of muscles of mastication
* Increases size of their attachment sites to mandible
* Angle of mandible must be altered so that occlusal surfaces of upper and lower teeth are parallel
32
New cards
what is the position of the TMJ altered by?
The position of the TMJ is altered by growth in the lateral cranial base:
As skull widens, underside of glenoid fossa moves outwards
So condylar process of mandible needs to widen so that they align
\
This is done by selective resorption and deposition in ramus
As skull widens, underside of glenoid fossa moves outwards
So condylar process of mandible needs to widen so that they align
\
This is done by selective resorption and deposition in ramus
33
New cards
How is length of ramus increased and what for?
* increased by bone deposition along posterior border
* resorption along the anterior border
* accommodates for eruption of permanent teeth
* resorption along the anterior border
* accommodates for eruption of permanent teeth
34
New cards
Summary for why mandible growth needed
occurs to accommodate eruption of the permanent dentition, to maintain alignment of the TMJ and to keep upper and lower teeth aligned.
35
New cards
When is there the most change in growth of facial soft tissues?
* most change occurs around puberty
* They may mask or enhance hard tissue changes
* They may mask or enhance hard tissue changes
36
New cards
What change happens in nose?
grow in a downward and forward direction at least until early adulthood.
yearly increase of 1–1.3 mm in overall length
yearly increase of 1–1.3 mm in overall length
37
New cards
describe the growth of the lower lips
lower lip grows more than the upper lip
Increase in lip thickness at the vermillion border is proportional to increase in lip length
Increase in lip thickness at the vermillion border is proportional to increase in lip length
38
New cards
Why is there increased chin projection in males?
due to mandibular growth rather than soft tissue change.