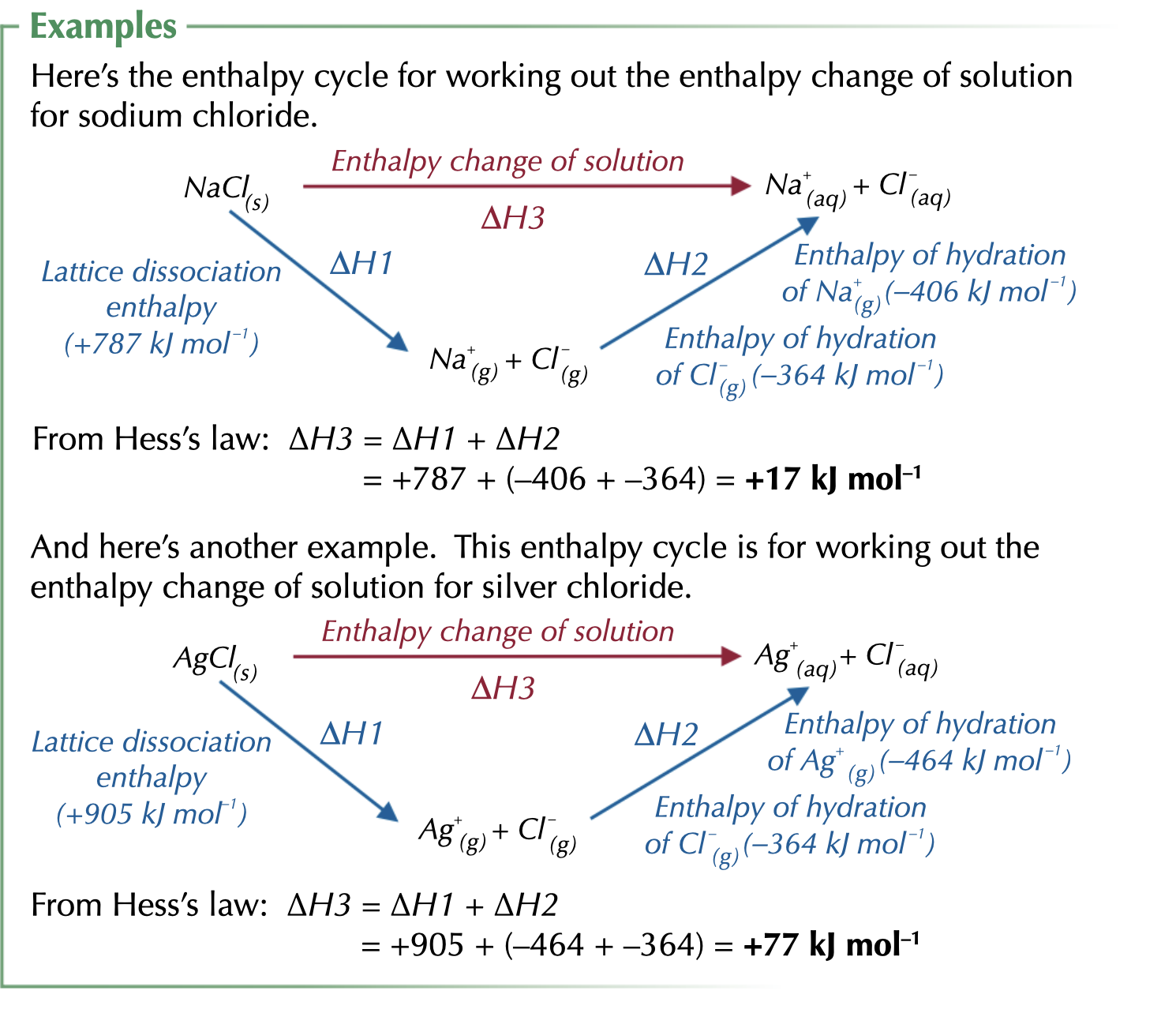
enthalpy change of solution
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
recap of bonding what are the type of inter/intramolecular ?
Inter: hydrogen, permeant dipole - dipole, Van Der Waals
Intra: Ionic, covalent, metallic
def of enthalpy change of solution
enthalpy change when one mole of an ionic solid dissolves in a amount of water large enough so that dissolved ions are well separated and do not interact with each other. its an endothermic reaction
def of enthalpy change of hydration
enthalpy change when one mole of gaseous ions become hydrated ( dissolved in water ). its an exothermic reaction
what does charged molecules dissolved in ?
polar solvent eg H2O
what does non - charged molecules dissolved in ?
non polar solvent
how can we work out the enthalpy change of solution ?
using the hess law cycle
Dissolved ionic lattice -
what are the 2 steps in dissolving an ionic lattice ?
1) the lattice breaks to form gaseous ions therefore is opposite to lattice enthalpy. lattice enthalpy of dissociation, endothermic.
2) The gaseous ions are attracted to polar, water to become hydrated aqueous ions. lattice enthalpy of hydration, exothermic
E.g. NaCl
1) ionic crystal dissolved in water
Na+ + Cl- (s) → Na+ (aq) + Cl- (aq)
🔺H le : -776 kj mol -1
2) ion have to be hydrated
Na+ (g) → Na+ (aq) 🔺H hyd = -407 kj mol1
Cl- (q) → Cl- (aq) 🔺H hyd = -304 kj mol-1
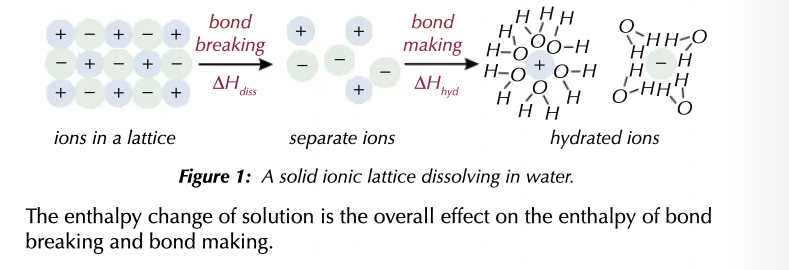
Oxygen is more electronegative than hydrogen, so it draws the bonding electrons toward itself, creating a dipole. Consequently, positive ions form weak bonds with the partial negative charge on the oxygen atom and negative ions form weak bonds with the partial positive charge on the hydrogen atoms.
draw an example of enthalpy change of solution

enthalpy change of hydration
hydration enthalpies of the ions are inversely proportional to the ionic radii
as you do down group 1 / 7 , the exothermic enthalpy hydration increase or decreases ?
as you do down group 1 / 7 , the exothermic enthalpy hydration decrease
as you go across period 3 does the enthalpy change of hydration increases or decreases and why >
as you go across period 3 the enthalpy change of hydration increases, because of the increase of ionic charge and decrease in the ionic radii → leading to a increase of attraction to polar substance such as H2O molecules.
does larger or smaller ions attract to polar molecules easier ?
Smaller ions attract to polar molecules easier as the smaller ions have smaller ionic charge, higher charge density → easier to attract to water / polar molecules. \
Known as exothermic enthalpy change of hydration
draw and calculate the lattice enthalpy. of KCl dissolve in water
K+ hydration = -322
Cl- hydration = - 363
enthalpy change of solution = +26

calculating enthalpy change of solution - formula
solution = hydration of cation and onion + lattice dissociation of enthalpy
solution = hydration of cation and onion + lattice formation of enthalpy ( -🔺Hf )
using hess law cycle to calculate enthalpy change of solution