BIOL100 Ch. 17: Animals and Human Evolution
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
Animals
Multicellular ingestive heterotrophs; that is, complex organisms (eukaryotes) that obtain energy and carbon by ingesting food into their bodies and digesting it internally
Chordates
A large phylum that encompasses all animals with backbones. such as fishes, birds, and mammals (dorsal nerve cord)
Vertebrates
Animals that have a backbone
Invertebrates
Animals without backbones
Radial symmetry
An animal body plan in which the body can be sliced symmetrically along any number of planes and pass through the animal, such as cnidarians
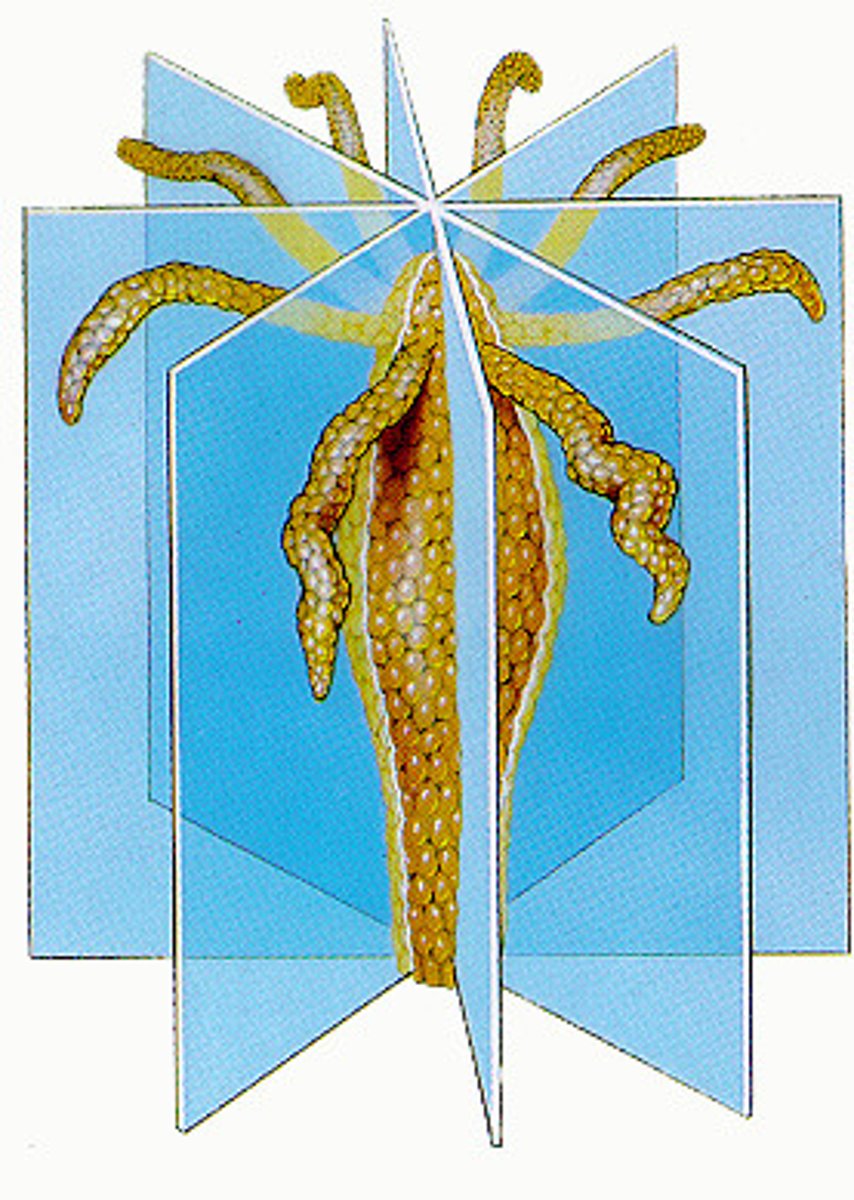
Bilateral symmetry
An animal body plan in which the body can be divided by just one plane passing vertically from the top to bottom of the animal into two halves that mirror each other.
Notochord
In chordates, a flexible yet rigid rod along the length of the body is critical for development
Nerve cord
A solid strand of nervous tissue that we call the spinal cord in humans.
Cartilage
A dense tissue of the skeleton that combines strength with flexibility. It is found almost everywhere that two bones meet and prevents them from grinding together
Segments
Repeated identical units that make up the body plan of arthropods, annelids, and vertebrates
Appendages
Body parts with specialized functions that develop in pairs from particular segments of an animal's body
Mammals
A large class of animals that are defined by:
Body hair
Sweat Glands
Milk is produced by mammary glands
Eutherians
One of the 3 main groups of mammals, whose members have a placenta and produce offspring that are born in a relatively well-developed state. Humans are eutharians.
Marsupials
One of three main groups of mammals, whose members have a simple placenta and produce offspring that complete development in their mothers couch, such as a kangaroo or koala
Monotremes
One of three main groups of mammals, whose members lack a placenta and lay eggs, such as platypi
Primates
The order of mammals to which humans belong. All primates have flexible shoulder and elbow joints, five functional fingers and toes, opposable thumbs, flat nails, and large brains in relative size to their body
Opposable
Able to be placed opposite other digits of the hand or foot. For example, opposable thumbs can be placed opposite each other of the other four fingers
Bipedal
the ability to walk upright on two legs
Hominids
The ape family, which includes humans and chimpanzees. All hominids are capable of tool use, symbolic language, and deliberate acts of deception
Hominins
The "human" branch of hominids, including modern humans and extinct relatives such as Neanderthals
Australopiths
(3-3.5 mya) A colloquial name referring to a diverse group of Plio-Pleistocene African hominins. Australopiths are the most abundant and widely distributed of all early hominins and are also the most completely studied.
Homo lineage broke off from Australopithecus about 2 million years ago
Other lineages, such as Homohabilis, Homoerectos, Neanderthals, (Modern & archaic) Homosapiens began to separate (All members of the Homo genus).
Modern humans are a mix of these
Mitochondrial DNA inheritance
The passing down of DNA from the mitochondria in an egg cell to a new generation. mitochondrial DNA passes virtually unchanged from mother to child, so it can be tracked from one generation, or species, to another. Sequencing of mitochondrial DNA can determine how related an individual is to its female ancestors on its mother's side.
Nuclear DNA inheritance
The passing down of DNA from the nucleus in an egg or sperm cell to a new generation. Sequencing of nuclear DNA an determine how related an individual is to all of its ancestors, both male and female.