1 2 Fixed Proths Midterm: Introduction + Gypsum/Alginate
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
74 Terms
replacement and/or restoration of teeth by artificial substitutes that cannot be removed by the patient
What is the purpose of Prosth. treatment?
single crown
ID the type of fixed prosth.:
inlays and onlays
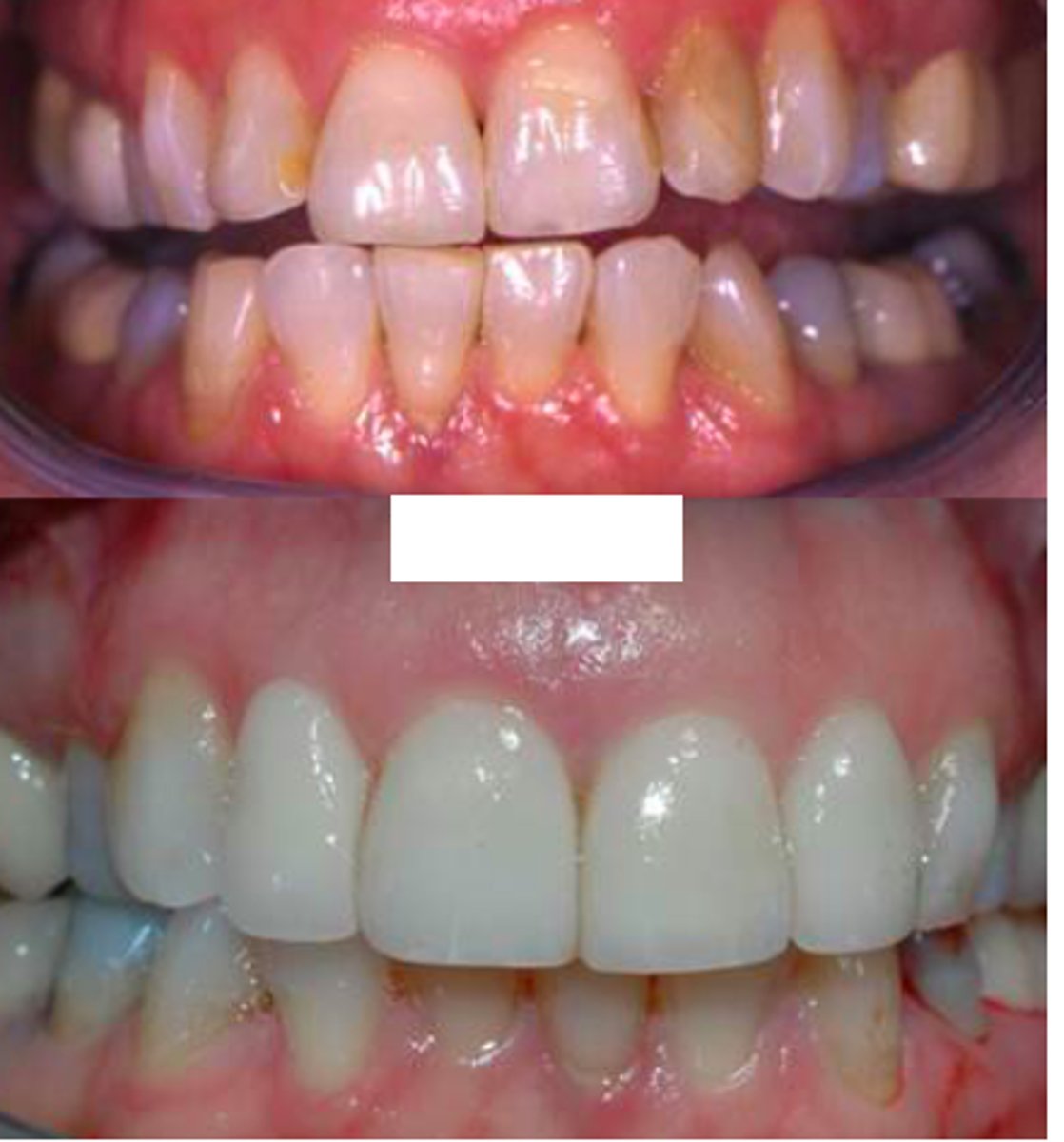
ID the type of fixed prosth.:
veneers
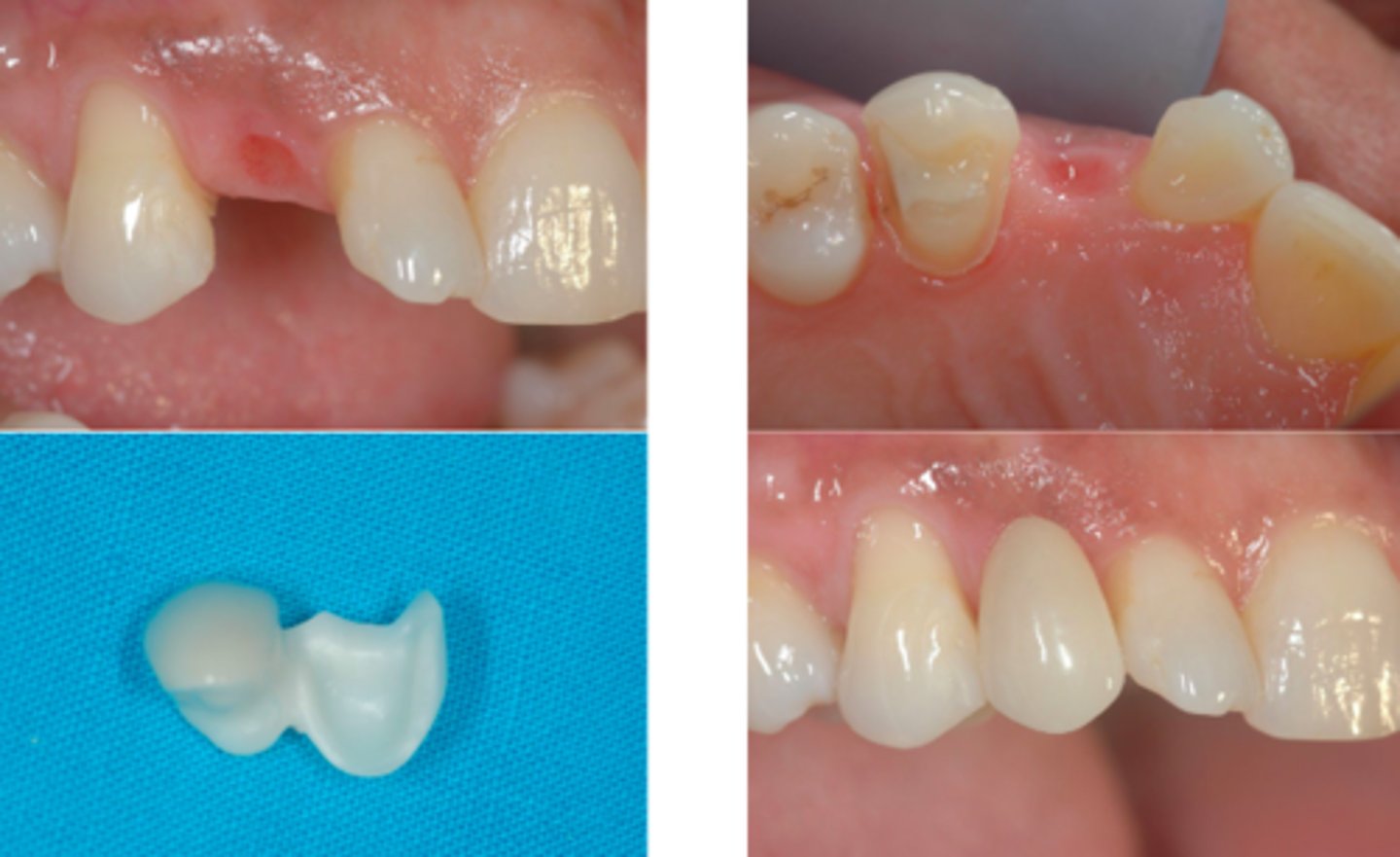
ID the type of fixed prosth.:
resin bonded FPD
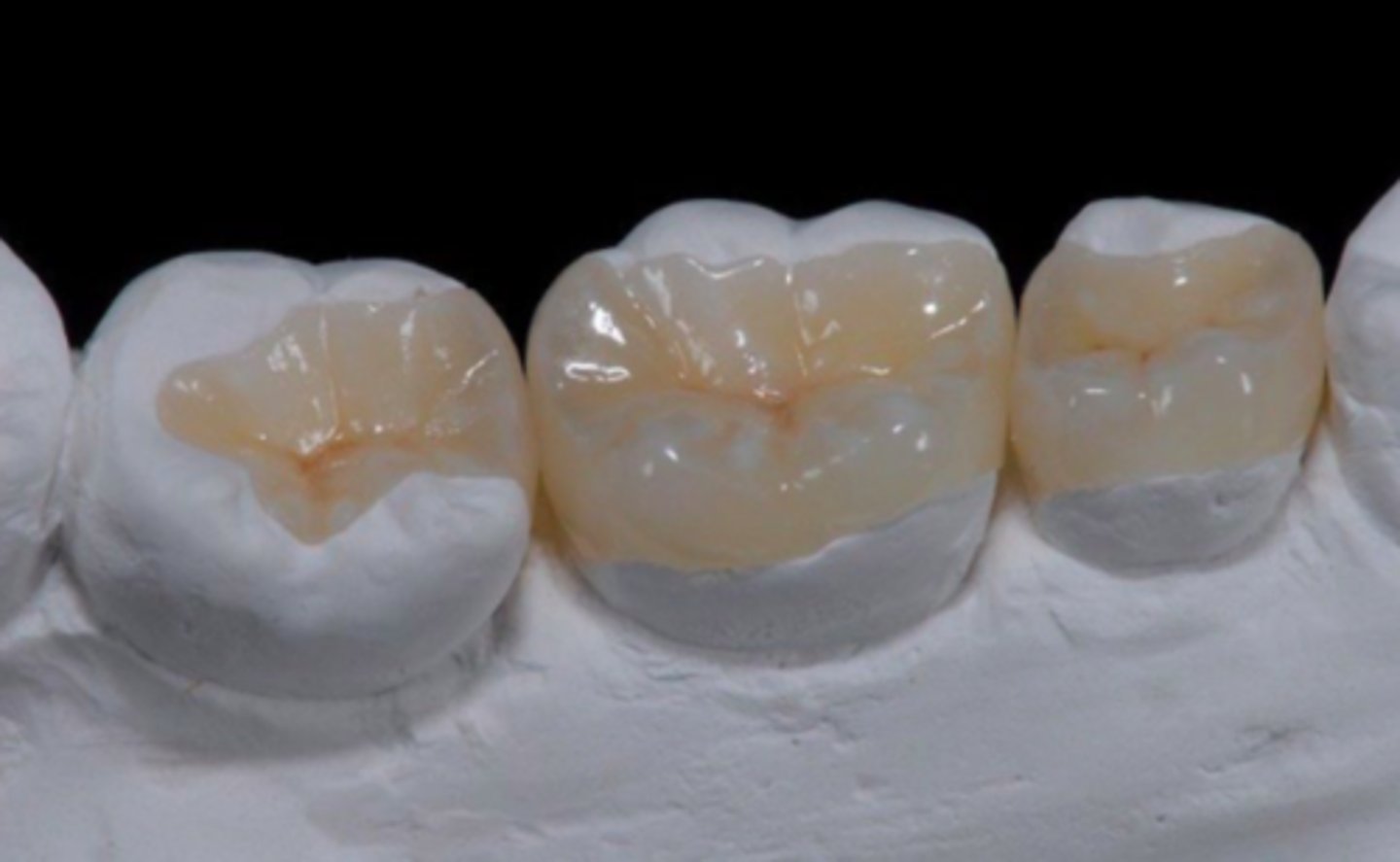
ID the type of fixed prosth.:
3- unit FPD
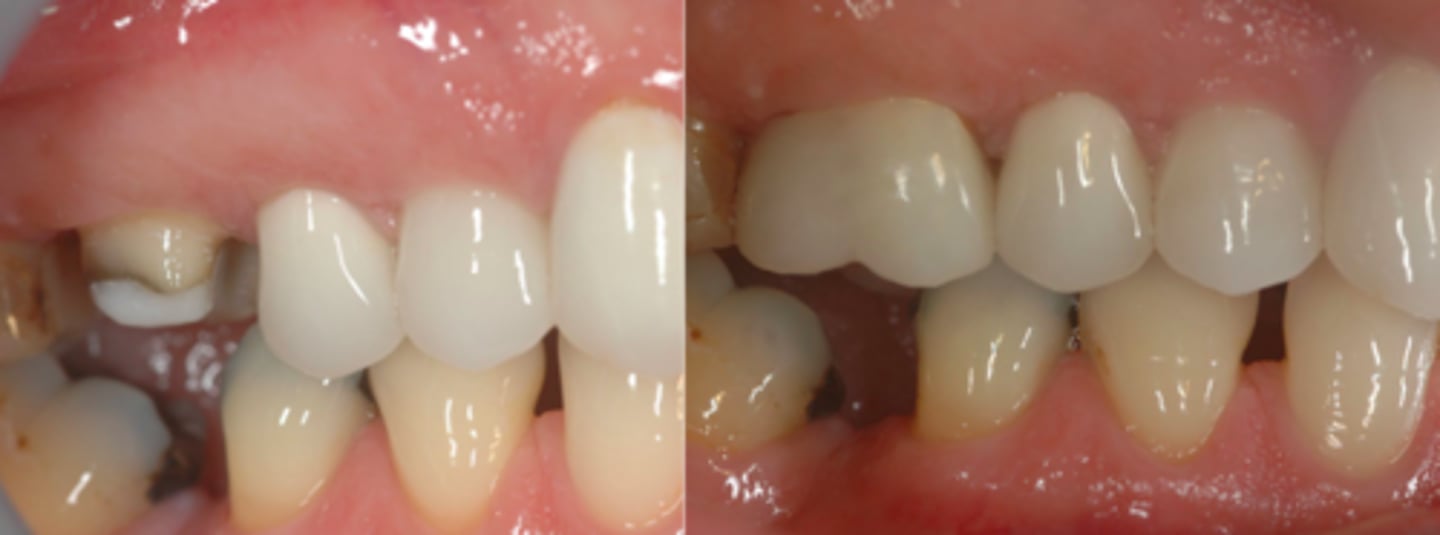
ID the type of fixed prosth.:
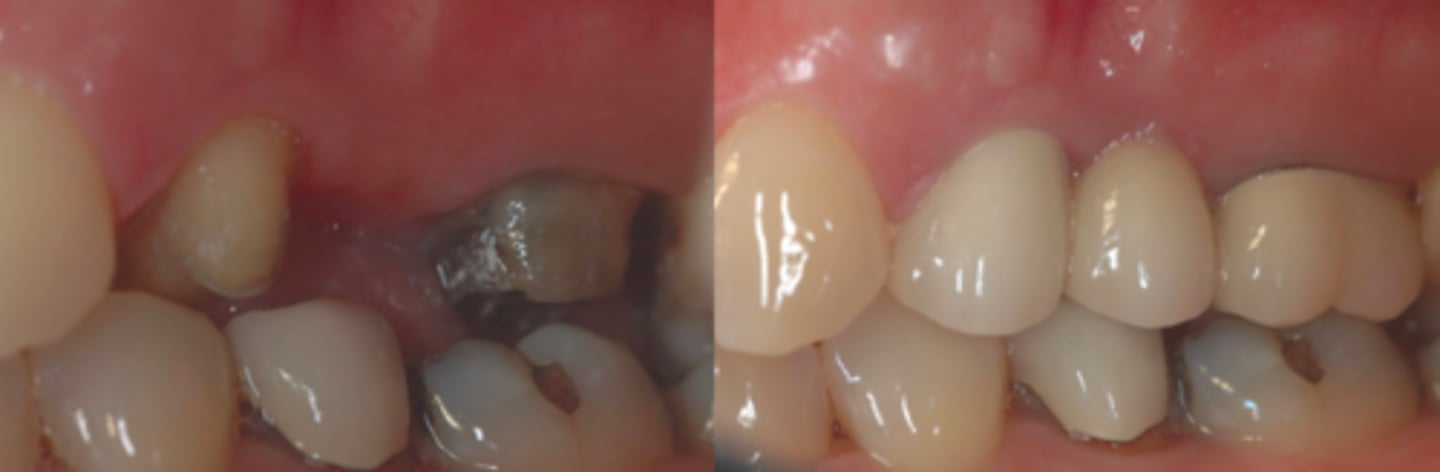
foundation restoration/post and core
ID the type of fixed prosth.:
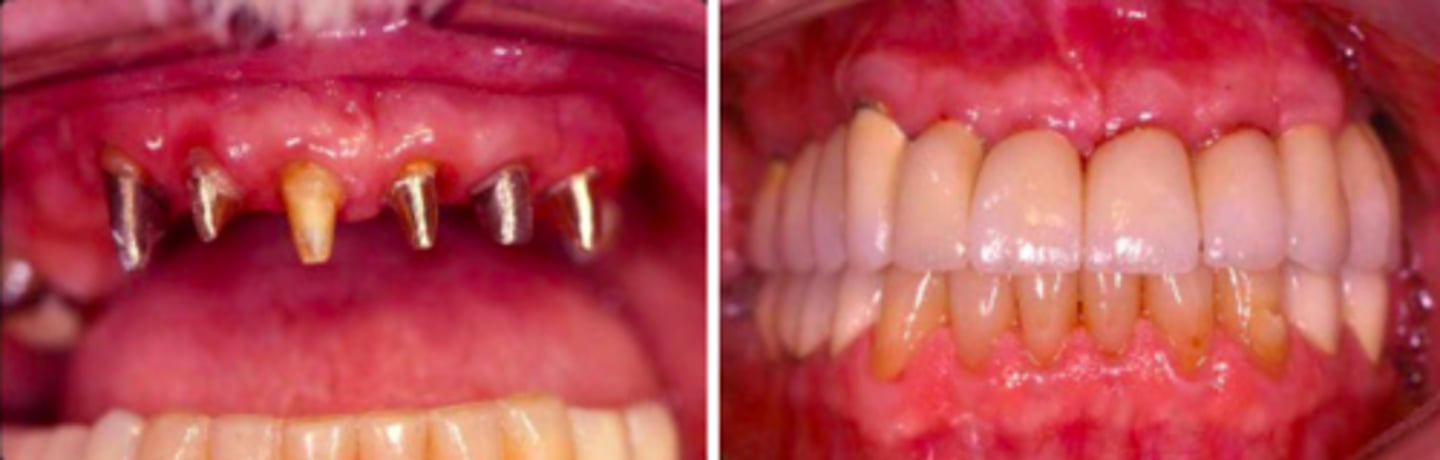
8%
What is the % incidence of complication for an all ceramic crown?
10%
What is the % incidence of complication for a post/core?
11%
What is the % incidence of complication for a conventional single crown?
27%
What is the % incidence of complication for a conventional fixed partial denture?
26%
What is the % incidence of complication for a resin bonded fixed partial denture?
fracture
What is the most common complication for all ceramic crowns?
-fracture
-need for endo tx
-loss of retention
Post Loosening
What is the most common complication for a post/core?
-Post Loosening
-Root Fracture
-Caries
Need for Endodontic Tx
What is the most common complication for a single crown?
-Porcelain Veneer Fracture
-Need for Endodontic Tx
-Loss of Retention
Caries on abutment
What is the most common complication for a Fixed Partial Denture (FPD)?
-Caries on abutment
-Need for Endodontic Tx
-Loss of Retention
Debonding
What is the most common complication for a Resin Bonded Fixed Partial Denture (FPD)?
-Tooth Discoloration
-Caries
-Debonding
-Serve as a complement tool in addition to clinical examination
-Provide a legal proof of pt's current occlusion
-Allow clinician to modify occlusal pre-treatment plan prior to establish a definitive TxPlan
-Allow clinician to evaluate pt's occlusion in centric and eccentric positions
-Allow clinician to determine inter arch distance, relationship between the teeth and alveolar ridge and allow clinician to make as many alteration to as clinician's desire w/ absence of the patient.
What are 5 purposes for Mounted Diagnostic Casts on an articulator?
irreversible hydrocolloid
What type of material is alginate?
negative
If you are working with alginate, your goal is to make a _______ impression of the patients oral tissues
positive
If you are working with dental stone, your goal is to make a _______ impression of the patients oral tissues
-Inexpensive
-Easymanipulation
-Pleasant taste
-Able to displace blood and body fluids
-Hydrophilic
-Easily poured
-Can be used with stock trays
-Accurate if handled properly
What are some advantages of alginate hydrocolloids?
-Low tear resistance
-Must be poured immediately
-Limited detail reproduction
-Dimensionally unstable(syneresis vs imbibition)
-Can only be used for single casts
-Incompatible with epoxy resin die materials
What are some disadvantages of alginate hydrocolloids?
sodium alginate
What is the alginate we use made of?
2Na3PO4
What is the "retarder" of the alginate reaction?
3CaSO4
What is the "accelerator" of the alginate reaction?
1:1
what is the water to powder ratio for alginate?
1 minute
If you want a regular setting time, how long should you mix the alginate for?
45 seconds
If you want a quick setting time, how long should you mix the alginate for?
3.5 minutes
After mixing, how long does it take for an alginate impression to set?
increase
a lower water/powder ratio of alginate will result in a _____ in strength
increase
a lower water/powder ratio of alginate will result in a _____ in tear strength
better
a lower water/powder ratio of alginate will result in a _____ consistency
decrease
a lower water/powder ratio of alginate will result in a _______ in working time
decrease
a lower water/powder ratio of alginate will result in a _______ in setting time
decrease
a lower water/powder ratio of alginate will result in a _______ in flexibility
decrease
a higher water/powder ratio of alginate will result in a ______ in strength
decrease
a higher water/powder ratio of alginate will result in a ______ in tear strength
runny
a higher water/powder ratio of alginate will result in a ______ consistency
increase
a higher water/powder ratio of alginate will result in a ______ in working time
increase
a higher water/powder ratio of alginate will result in a ______ in setting time
increase
a higher water/powder ratio of alginate will result in a ______ in flexibility
increase
using cold water for mixing alginate impressions will ______ you working and setting times
decrease
using warmer water for mixing alginate impressions will ______ you working and setting times
syneresis
Loss of water due to dehydration that causes shrinkage:
imbibition
Tendency to absorb water that results in swelling:
100%
if you can't pour your stone in an alginate impression right away, you can store it in ____% humidity for 30 mins
calcium sulfate
what is the base of all gypsum powder made of?
calcination
Gypsum products are manufactured by the ______ of calcium sulfate dihydrate
type 2
what ISO type is white plaster that we use to pour up alginate impressions?
type 3
what ISO type is micro-stone?
Differences in properties result from differences in the physical nature of the powders, and how they are processed
Both plaster and stone are products of partial dehydration of gypsum. How are they different?
dry
Traditional hemihydrate plaster is produced by _____ calcination
wet
medium and high strength plaster (stones) is produced by _____ calcination
decrease
When using slurry water instead of regular tap water, it will _______ the setting time
decrease
When using slurry water instead of regular tap water, it will _______ the compressive strength
increase
When using slurry water instead of regular tap water, it will _______ the dimensional change
more
The different water requirements of plaster, stone, and high-strength stone are mainly the result of differences in the apparent density of the powders. ISO 2 lab plaster requires ____ water than higher ISO stones, like Die-keen ISO 4
-fluid
-plastic
-friable
-carvable
What are the 4 stages of the stone setting process?
decrease
when mixing stone, an increase in spatulations will result in a _____ in the setting time
inversely
Setting expansion is _______ proportional to the water-powder ratio
inversely
Strength is _______ proportional to the water-powder ratio
increase
An Increase water/ powder ratio will result in a ______ in the setting time
increase
An Increase water/ powder ratio will result in a ______ in the consistency
decrease
An Increase water/ powder ratio will result in a ______ in the setting expansion
decrease
An Increase water/ powder ratio will result in a ______ in the compressive strength
decrease
An Increase in the rate of spatulation will result in a ______ in the setting time
decrease
An Increase in the rate of spatulation will result in a ______ in the consistency
increase
An Increase in the rate of spatulation will result in a ______ in the setting expansion
no effect
An Increase in the rate of spatulation will result in a ______ in the compressive strength
decrease
An Increase in the water temperature will result in a ______ in the setting time
decrease
An Increase in the water temperature will result in a ______ in the consistency
increase
An Increase in the water temperature will result in a ______ in the setting expansion
no effect
An Increase in the water temperature will result in a ______ in the compressive strength