AP Comp Sci A Final mc
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
How many times will the following code print “X”?
String var = “X”;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i ++) {
System.out.println(var);
}
10 times
What is method abstraction?
Breaking down a complicated task into smaller, simpler methods
Consider the following code segment:
Int a = 3 + 2 * 3;
Int b = 4 + 3 / 2;
Int c = 7 % 4 + 3;
Int d = a + b + c;
20.0
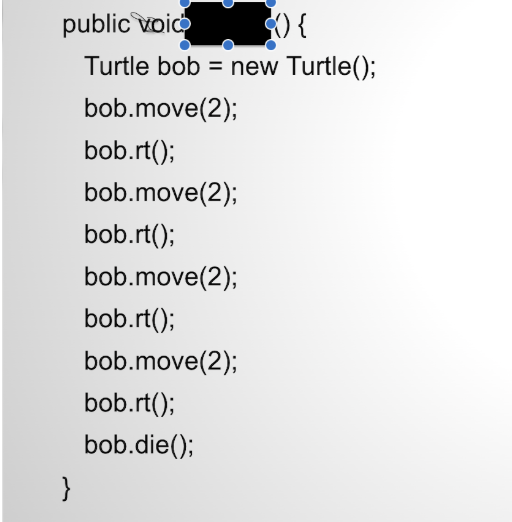
What shape does this draw??
Square
Java _____
Is a high-level coding language.
True or False: The following code executes without error: int c = (int) 1.5;
double d = Math.sqrt(c);
d /= c - d;
d++;
System.out.println(d);
True, prints Infinity.
What does “out” equal after the code runs:
int out = 0;
for (double i = 0; !(i > 10 || i > 11); i += i) {
out += (double) i++;
}
System.out.println("out = " + out);
out = 8;
What will the value of x be after this code is executed.
int y = 0;
int x = y;
for (x++; x < 10; x++) {
y--;
}
10
What will the value of y be after this code is executed.
int y = 0;
int x = y;
for (x++; x < 10; x++) {
y--;
}
-9
After this code runs, the value of z will be greater than 50
int y = 0;
int z = 1000000;
int x = y;
for (x++; x < 10; x++) {
y--;
}
True, the value will be 1,000,000
What is NOT a part of a method declaration?
Object
Read through the code below.
ArrayList list = generateSampleList();
// Assume that this creates an ArrayList usable for this problem
double a = 0;
Double n;
for(int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
n = (Double)list.get(i);
if(n.doubleValue() > a) {
a = n.doubleValue();
}
}
System.out.println("Result: " + a);
What does this code do?
Finds the largest number in the list
For String s and int x>=0, what does “s.charAt(x)” do?
Gives the character in string s which is at the index of int x.
True or False: The following method declaration is valid.
public int RunCode(double num) {
//code
}
True because method names can start with capital letters
What does the following code do?
public void exampleCode(ArrayList l) {
int size = l.size()-1;
for(int n = 0; n<=size; n++) {
Object a = l.get(n);
if(a instanceof String) {
System.out.println((String) a);
}
}
}
Goes through the arraylist and only prints the strings it contains.
What does the following code do?
ArrayList words = new ArrayList<String>();
words.add("pen");
words.add("pinneaple");
words.add("apple");
for (String w : words)
{
System.out.println(w.toUpperCase());
}
Prints PEN PINNEAPLE APPLE (one per line, in uppercase)

What does this code do?
Accepts any angle and hypotenuse and creates a right triangle based on those variables
What does the code add(int index, Object object) do?
Adds an object to an ArrayList at the given index
Where should the values of instance variables be initially set?
In the constructor
A While loop in Java continues running as long as its condition is true
True because while loops will repeat until the condition becomes false
What is wrong with this loop below?
a = 0;
while(a < 10) {
t.move();
t.rt();
t.move();
}
The condition is always met creating an infinite loop
How do you declare a primitive variable in Java?
VariableType VarName = VarValue;
What does super() do?
super() is a call to the constructor of the superclass
Write an expression that will do each of the following: Find the remainder upon dividing 35 by 11.
35 % 11
True or false: You cannot make modifications to an array or arraylist with a for : each loop
True, because attempting to modify a list that is being iterated through will throw a ConcurrentModificationException
Why won’t the following method work properly?:
public void removeStartingWith(ArrayList<String> arr, char char) { // Removes all items in a list that start with the specified character
for (int i = 0; i >= arr.length(); i++) {
String item = arr.get(i);
if (item.startsWith(char)) {
arr.remove(i);
i--;
}
}
}
The variable ‘char’ won’t work because ‘char’ is a reserved keyword
Which of the following Java primitive data types can store decimal numbers with the highest precision?
double
True or False: The == operator compares primitive values, while .equals() compares the contents of objects.
True because == checks raw values and .equals() compares object content
What is the output of the following Java code?
int x = 4;
int y = 7;
int z = x + y / 2;
System.out.println(z);
7
True or false: once an array has been created, you can change its size
False, because the array length is fixed after creation
What is the result of executing this code if w = 8?
public static void sm(int w) {
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= w; i++) {
sum += i;
}
System.out.println(sum);
}
36
What is the format for an if statement that results true when x = 5
if(x >3 && x < 6){}
What will this function do?
public int nameFunction(int i){
for(int j = 0; j < 3; j++){
i++;
}
return(i);
}
Return 3
True or False, does the following bit of code get the number of characters in a string: “x.characters”?
False, because the correct function is x.length
How many times will the following code print “X”?
int var = 6;
for (int i = 0; i <Math.pow(var) ; i ++) {
System.out.println(var);
if( var == 10){
i++;
}}
35 times
True/False: It is possible to create a method in Java without a return value.
True, if your method is void, it doesn’t need to return a value
What is the difference between an array and an arraylist?
an array has a fixed size, defined at the time of creation, while an ArrayList is dynamic and can grow or shrink as elements are added or removed.