Chp 6 Bones and Tissue
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/112
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 6:36 AM on 11/15/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
113 Terms
1
New cards
hyaline, elastic, fibrocartilage
3 types of cartilage
2
New cards
hyaline cartilage
most common cartilage, provides support, flexibility, and resilience, contains collagen fibers only
3
New cards
articular (joints), costal (ribs), respiratory (larynx), nasal cartilage (nose tip)
where is hyaline cartilage usually found?
4
New cards
elastic cartilage
similar to hyaline cartilage but contains elastic fibers
5
New cards
external ear and epiglottis
where is elastic cartilage usually found?
6
New cards
fibrocartilage
thick collagen: great tensile strength
7
New cards
menisci of knee; vertebral discs
where is fibrocartilage cartilage usually found?
8
New cards
support: body and soft organs
protection: brain, spinal chord, vital organs
movement: levers for muscle action
mineral and growth factor storage: calcium and phosphorus and growth factors reservoir
blood cell formation: hematopoiesis occurs in red marrow cavitites of certain bones
triglyceride (fat) storage: fat, used as energy source stored in bone cavities
hormone production: osteocalcin helps to regulate insulin, secretion, glucose levels, and metabolism
protection: brain, spinal chord, vital organs
movement: levers for muscle action
mineral and growth factor storage: calcium and phosphorus and growth factors reservoir
blood cell formation: hematopoiesis occurs in red marrow cavitites of certain bones
triglyceride (fat) storage: fat, used as energy source stored in bone cavities
hormone production: osteocalcin helps to regulate insulin, secretion, glucose levels, and metabolism
7 functions of the bones
9
New cards
Hematopoiesis
blood cell formation
10
New cards
206
how many named bones in the human skeleton is there?
11
New cards
axial and appendicular
2 main groups bones are broken into
12
New cards
axial skeleton
Long axis of body
Skull, vertebral column, rib cage
80 bones
Skull, vertebral column, rib cage
80 bones
13
New cards
appendicular skeleton
bones of upper and lower limbs
girdles attaching limbs to axial skeleton
girdles attaching limbs to axial skeleton
14
New cards
tissues
bones are organs because they contain different types of _______
15
New cards
nervous tissue, cartilage, fibrous connective tissue, muscle cells, epithlelial cells in its blood vessels
osceous tissue (is main thing in a bone)
osceous tissue (is main thing in a bone)
what do bones contain? (6 things)
16
New cards
compact bone
dense outer layer on every bone that appears smooth and solid
17
New cards
spongey
made up of a honeycomb of small, needle-like or flat pieces of bone called trabeculae
18
New cards
trabeculae
supporting bundles of bony fibers in cancellous (spongy) bone
19
New cards
red or yellow bone marrow
open spaces between trabeculae are filled with...
20
New cards
hematopoietic tissue
red bone marrow
21
New cards
red marrow
found in cavities of spongy bone
22
New cards
medullary cavity, and all spongy bone
in newborns, contains red marrow
23
New cards
heads of femur and humerus, most active areas of hematopoiesis: flat bone, and some irregular bones (hip bone)
in adults where is red marrow located?
24
New cards
anemic
When a person becomes _____ yellow marrow can convert to red
25
New cards
22, sutures
the skull is made up of ____ bones joined together by ______
26
New cards
cranal cavity
cranial bones surround the _____ ______ and are in contact with the meninges
27
New cards
eight
the cranial cavity is made up of ____ bones
28
New cards
meninges
wrappings of the brain
29
New cards
calvaria
skull cap
30
New cards
teeth, nasal cavity, orbit
facial bones support _____ and form ______ _____ and ______
31
New cards
14
how many bones make up the facial?
32
New cards
no
do the facial bones have direct contact with the brain or meninges?
33
New cards
attachement of facial and jaw muscles
what do the facial bones attach?
34
New cards
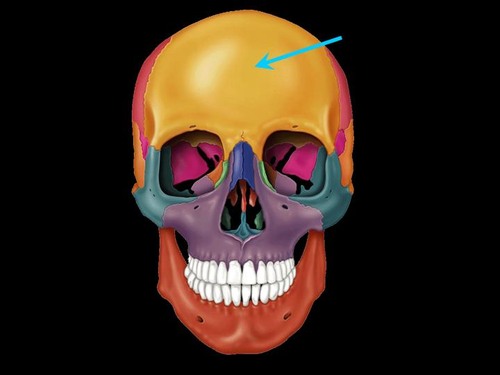
frontal bones, frontal
forms forehead and part of roof of cranium
forms roof of the orbit
contains ______ sinus
1 bone
forms roof of the orbit
contains ______ sinus
1 bone
35
New cards
orbit
bones around the eye
36
New cards
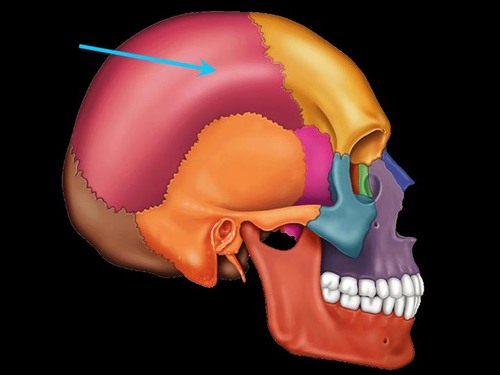
parietal bones
forms cranial roof and part of its lateral walls
marked by temportal lines where temporalis muscle attaches
2 bones
marked by temportal lines where temporalis muscle attaches
2 bones
37
New cards
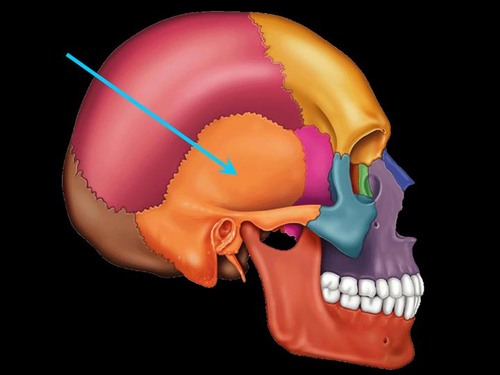
temporal bones
forms part of cranial floor
part of tmj: temporal mandibular joint
houses middle and inner ear cavities
2 bones
part of tmj: temporal mandibular joint
houses middle and inner ear cavities
2 bones
38
New cards
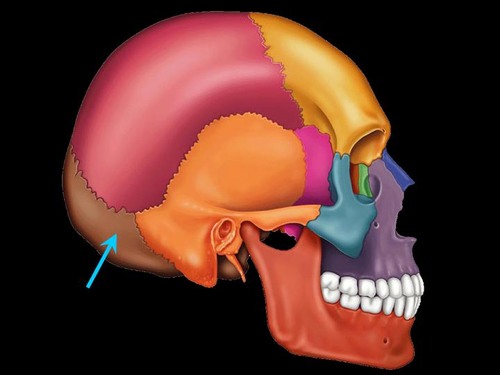
occipital bone, occipital
rear and much of base of skull
foramen magnum holds spinal chord
skull rests on atlas at _______ condyles
nuchal lines mark neck muscles (hold head upright)
1 bone
foramen magnum holds spinal chord
skull rests on atlas at _______ condyles
nuchal lines mark neck muscles (hold head upright)
1 bone
39
New cards
foramen magnum
great hold
40
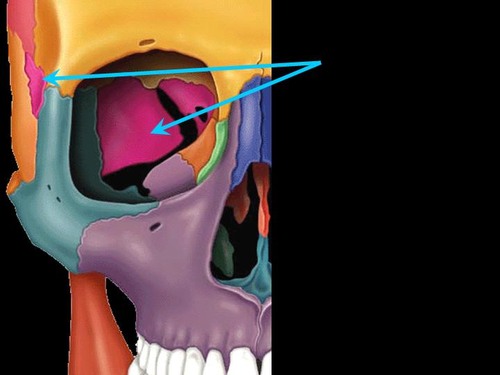
New cards
sphenoid bone
houses pituitary gland
protection for optic nerve
1 bone
protection for optic nerve
1 bone
41
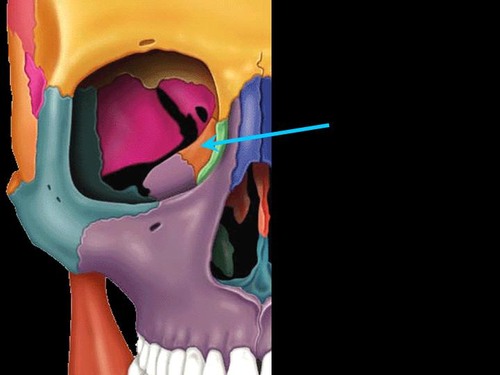
New cards
ethmoid bone
found between orbital cavities
forms lateral walls and roof of nasal cavity
perpendicular plate forms part of nasal septum
smell cells
1 bone
forms lateral walls and roof of nasal cavity
perpendicular plate forms part of nasal septum
smell cells
1 bone
42
New cards
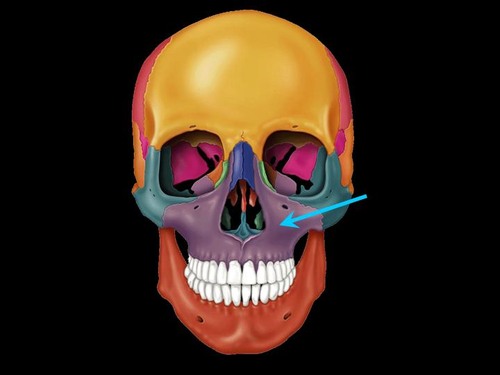
maxillary bones
forms upper jaw- sockets hold teeth
helps form wall of orbit
forms anterior 2/3's of hard palate
2 bones
helps form wall of orbit
forms anterior 2/3's of hard palate
2 bones
43
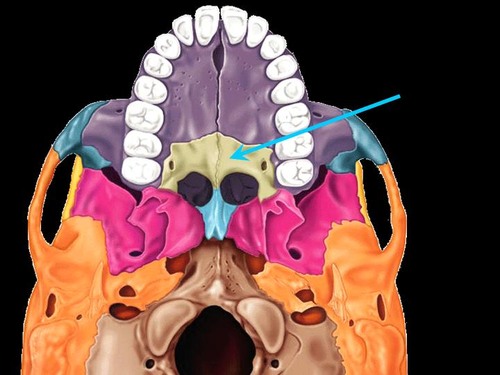
New cards
palatine bones
posterior 1/3 of hard palate
part of lateral nasal wall
part of orbital floor
separates oral and nasal cavity
2 bones
part of lateral nasal wall
part of orbital floor
separates oral and nasal cavity
2 bones
44
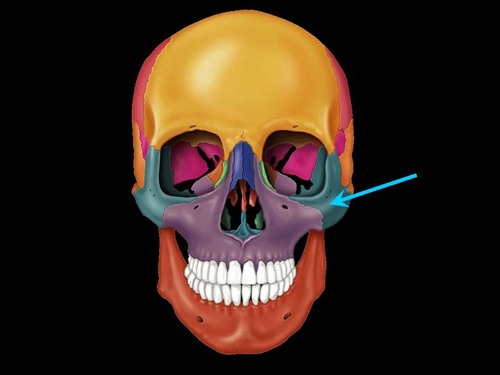
New cards
zygomatic bones
forms angles of the cheekbones and part of lateral orbital wall
2 bones
2 bones
45
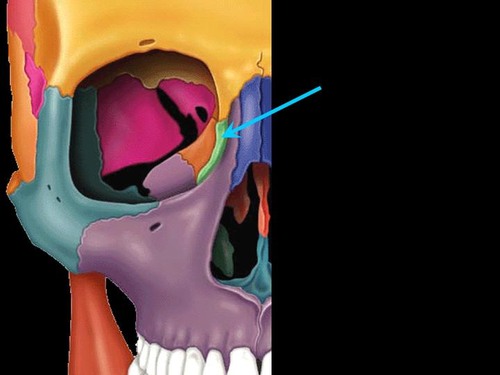
New cards
lacrimal bones
form part of medial wall of each orbit
houses lacrimal sac
2 bones
houses lacrimal sac
2 bones
46
New cards
lacrimal sac
tears collect here and drain into nasal cavity
47
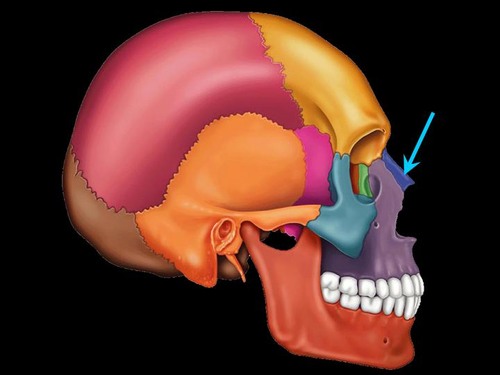
New cards
nasal bones
forms bridge of nose and supports cartilages of nose
often fractured by blow to the nose
2 bones
often fractured by blow to the nose
2 bones
48
New cards
inferior nasal conchae
separates bones
2 bones
2 bones
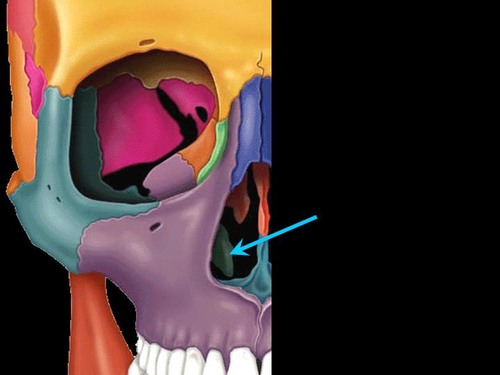
49
New cards
vomer
inferior half of nasal septum
supports cartilage of nasal septum
1 bone
supports cartilage of nasal septum
1 bone
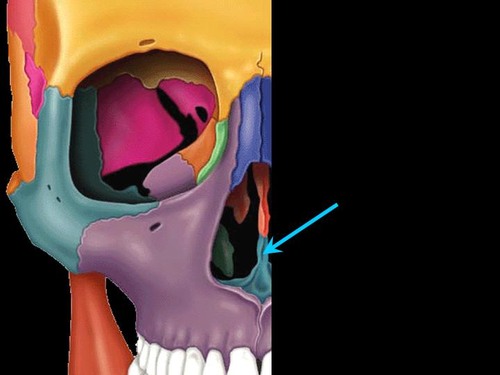
50
New cards
mandible
only bone of skull that can move
articulates with the temporal bone
holds lower teeth
attachment of muscles of mastication (chewing)
foramen
1 bone
articulates with the temporal bone
holds lower teeth
attachment of muscles of mastication (chewing)
foramen
1 bone
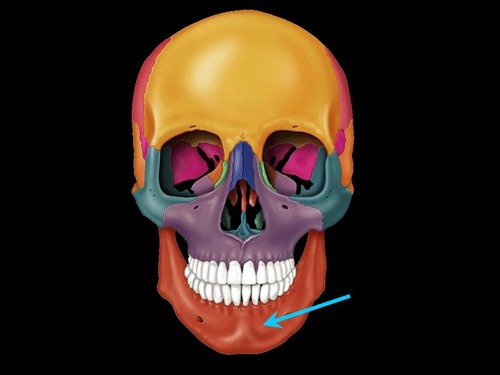
51
New cards
foramen
holes for blood vessels and nerves
52
New cards
malleus- hammer
incus- anvil
stapes- stirrup
incus- anvil
stapes- stirrup
auditory ossicles
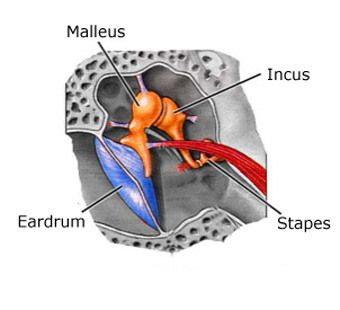
53
New cards
hyoid bone
between chin and larynx
tongue muscles for swallowing and chewing
forensics
tongue muscles for swallowing and chewing
forensics
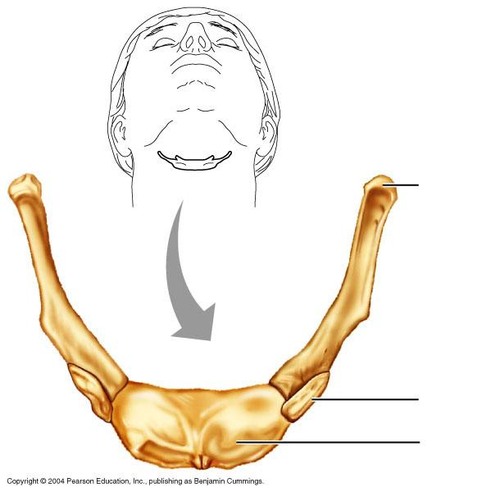
54
New cards
fontanels
spaces between unfused skull bones that allow shifting of bones during birth and growth of brain in infancy
55
New cards
2 years
When do your fontanels fuse together?
56
New cards
6 years
When do your 2 frontal bones fuse together?
57
New cards
8 or 9
what age does the skull reach adult size? This causes the heads of children to be larger in proportion to the trunk
58
New cards
33
how many vertabrae and discs of fibrocartilage between them are there?
59
New cards
5
how many vertabral groups are there?
60
New cards
7
number of cervical vertabrae in the neck
61
New cards
12
number of thoracic vertebrae in the chest
62
New cards
5
number of lumbar vertabra in the lower back
63
New cards
5
number of sacral fused vertabra into the sacrum
64
New cards
4
number of coccygeal vertabrae fused into the coccyx
65
New cards
coccyx
tailbone; single small triangular bone
4 small vertebrae fused by age of 30
Co1 to Co4
4 small vertebrae fused by age of 30
Co1 to Co4
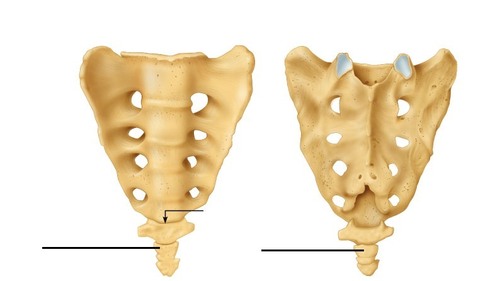
66
New cards
c- shaped curve, primary curvature
what shape is a newborn's spine, and what is this called?
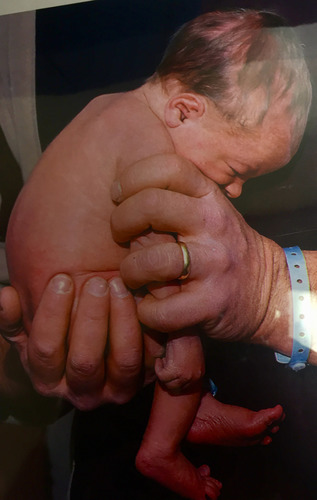
67
New cards
S, 4
adults have ____ shaped vertebral columns with ___ curvatures
68
New cards
secondary curvature
_______ curvature develops after birth
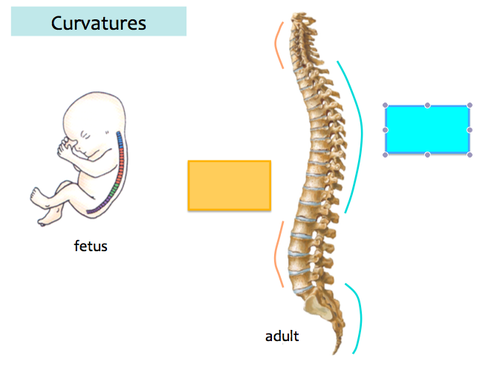
69
New cards
cervical
when the child starts lifting its head as it begins to crawl it develops a _______ curvature
70
New cards
lumbar
when a child starts walking upright it develops a __________ curvature
71
New cards
abnormal spinal curvatures
resutls from disease, posture, paralysis, or congenital defect
72
New cards
scoliosis
from lack of proper development of one vertebrae; left to right curve
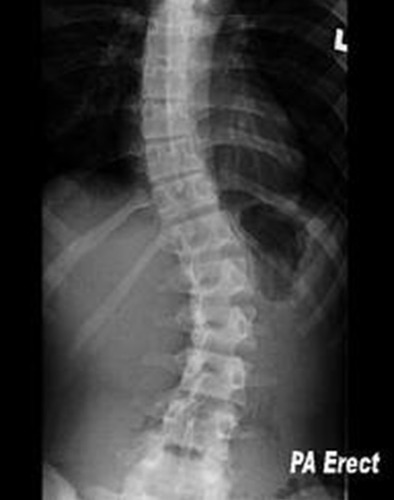
73
New cards
kyphosis
hunchback; from osteoporosis, in your upper back
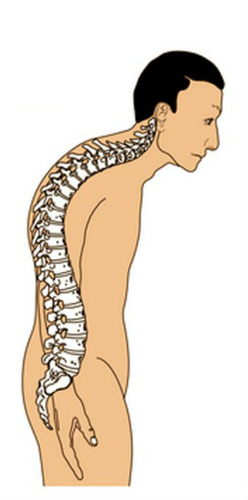
74
New cards
osteoporosis
A condition in which the body's bones become weak and break easily
75
New cards
lordosis
from weak abdomincal muscles, lower back
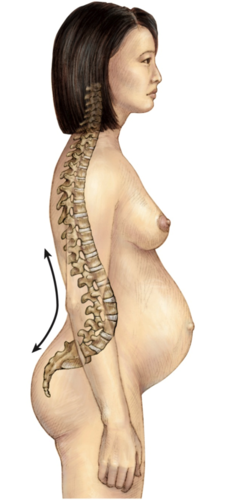
76
New cards
they all have the same body, all have a vertebral foramen, and have same processes
what do all general vertebral structures have in common?
77
New cards
spongy bone, red marrow, weight bearing, irregular shaped bones
what kind of body do general vertebral structures have?
78
New cards
passage of the spinal chord (in cervical vertebrae's they have three foramen-holes- the two on teh sides let blood vessels go through them)
what is the vertebral foramen for?
79
New cards
spinous process- what you feel when you press on someone's spine
transverse process- the parts that stick out to the side
articular process- (superior and interior) they grip on to what's above/below, hard to see
transverse process- the parts that stick out to the side
articular process- (superior and interior) they grip on to what's above/below, hard to see
List and explain the three different processes general vertebral structures have
80
New cards
small body and larger vertebral foramen
3 holes
3 holes
what are 2 characteristics of typical cervical vertabrae?
81
New cards
atlas (C1)
supports the skull, flat profile, concave superioe articular facet, nod head "yes"
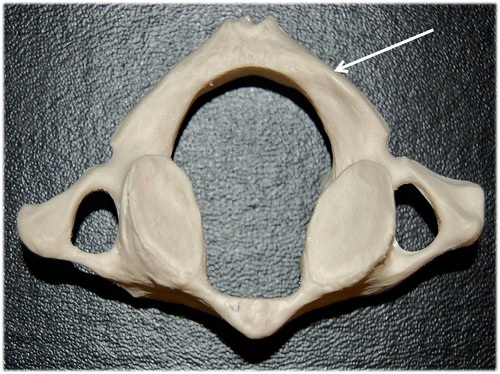
82
New cards
axis (C2)
dens or ondontoid process is held in place inside the vertebral foramen of _____ by ligaments, allows rotation of the head "no"
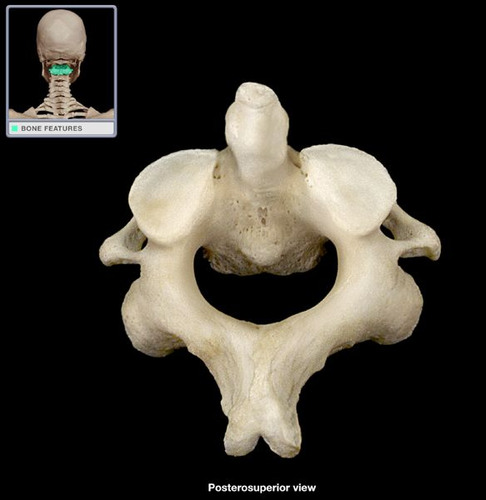
83
New cards
dens (odontoid process)
acts as pivot for rotation of atlas and the skull
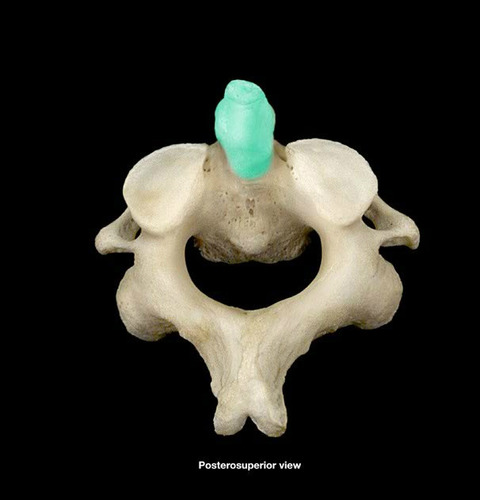
84
New cards
more massive body than cervical but smaller than lumbar
spinous processes are pointed and angled downward
rib attachment (costal facets for articulation of ribs)
spinous processes are pointed and angled downward
rib attachment (costal facets for articulation of ribs)
characteristics of the typical thoracic vertebrae
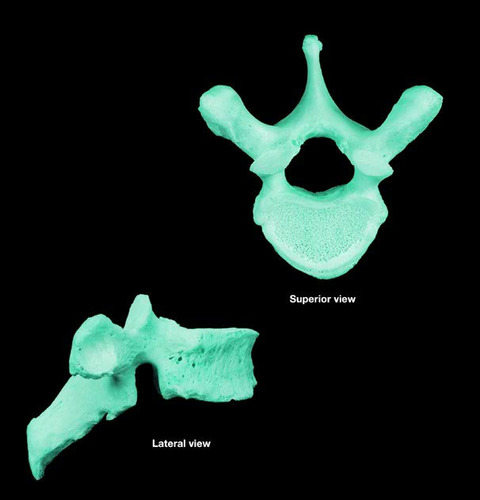
85
New cards
lumbar vertebrae
thick stout body and blunt, squarish spinous process
superior articular processes face medially
resists twisting movements
superior articular processes face medially
resists twisting movements
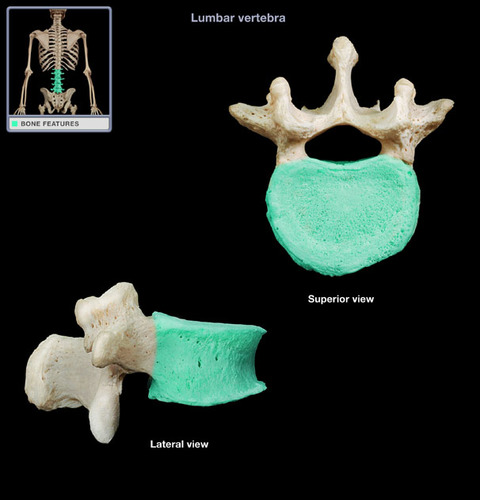
86
New cards
articulate
to form a joint
87
New cards
sacrum (anterior view)
5 separate sacral vertebra fuse by age 26
anterior surface: smoothe and concave, 4 transverse lines indicate line of fusion in vertebrae
anterior surface: smoothe and concave, 4 transverse lines indicate line of fusion in vertebrae
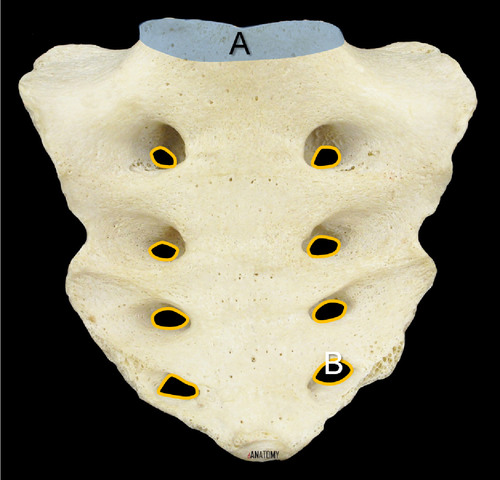
88
New cards
sacrum (posterior view)
rough surface of sacrum, spinous and transverse processes have fused into sacral crests
sacrioliac joints (SI)
sacrioliac joints (SI)
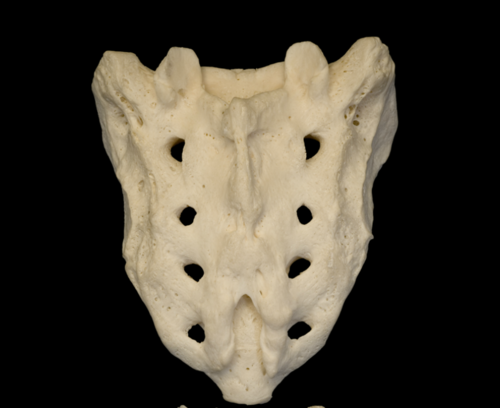
89
New cards
Coccyx
provides attachment site for muscles of pelvic floor
fractured by fall or during childbirth
fractured by fall or during childbirth
90
New cards
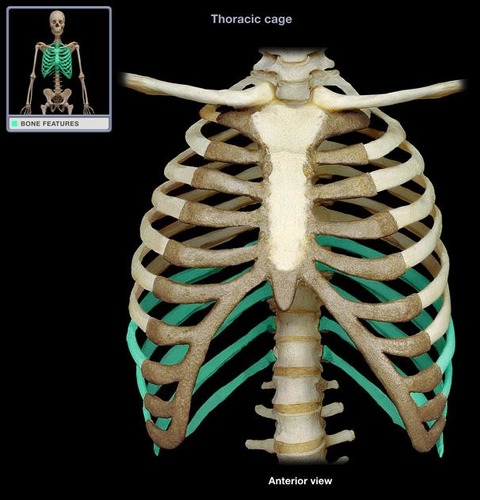
thoracic cage
consists of thoracic vertebrae, sternum, and ribs
attachment site for pectoral girdles and many limb muscles
protects many organs
expanded by respiratory muscles to draw air into lungs
attachment site for pectoral girdles and many limb muscles
protects many organs
expanded by respiratory muscles to draw air into lungs
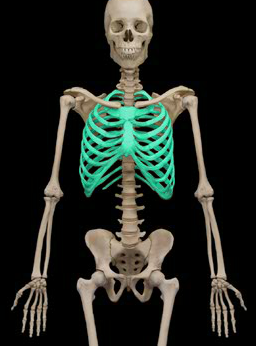
91
New cards
24; 12 pairs
how many ribs are there in total? and how many pairs?
92
New cards
straight line connects to cartilage
smoothe superior (smoothe side up)
rough part connects to the vertebrae
underside of the rib has a groove and that goes downward
smoothe superior (smoothe side up)
rough part connects to the vertebrae
underside of the rib has a groove and that goes downward
how can you tell which rib is the right and which is the left?
93
New cards
true ribs (1-7)
attach directly to sternum with hyaline
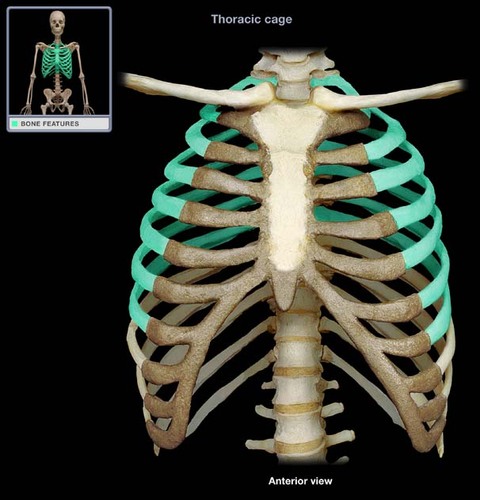
94
New cards
false ribs (8-12)
aren't directly attached to sternum
95
New cards
they're floating and not attached to sternum
why are 11 and 12 ribs special?
96
New cards
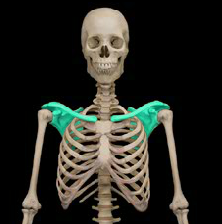
pectoral girdle
attaches upper extremity to the body
scapula and clavicle
clavicle attaches medially to the sternum and laterally to the scapula
scapula and clavicle
clavicle attaches medially to the sternum and laterally to the scapula
97
New cards
sternoclavicular joint and acromioclavicular joint
What 2 joints involve the clavicle?
98
New cards
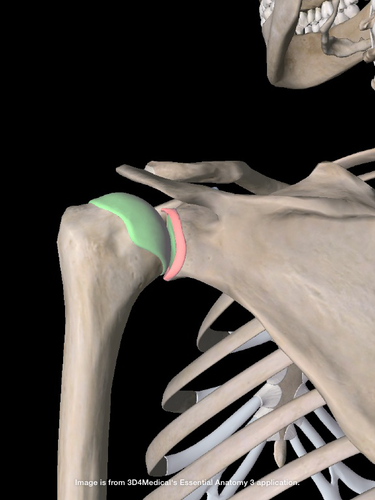
humeroscapular joint
scapula articulates with humerus
(shoulder joint)
easily dislocated bec of its loose attachment
(shoulder joint)
easily dislocated bec of its loose attachment
99
New cards
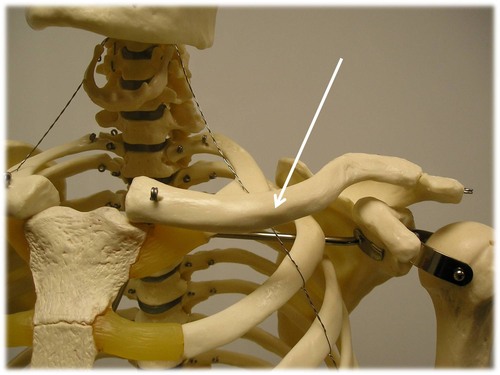
clavicle
s-shaped bone
sternal end is rounded, acromial end is flattened
aka collar bone
sternal end is rounded, acromial end is flattened
aka collar bone
100
New cards
superior side is smoother, groove is on botton
chunky end towards the middle and the flat end is out
curves OUT from the sternum
chunky end towards the middle and the flat end is out
curves OUT from the sternum
how do you know your left clavicle from your right?