The Chemistry of Life
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
47 Terms
…….. is anything that has mas and takes up space
matter
The different forms of matter are the….., of which there are about 114 examples of.
elements
Six of these make up about 97 percent of compounds found in living things: they are………….
carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen, phosphorus, sulfur
An individual building block of any of those examples is a(n) …………, which are the smallest componet of matter that still retains the properties of that kind of matter.
atom
When two or more atoms bond together, they form a(n) ………..
Molecule
If the two atoms are different kinds of atoms, we
can call this a(n)………..
Compound
Atoms are made up of three different
subatomic particles: the first is………., which are positively charged particles in the ……… of the atom:…………, are negatively charged particles that float around in a energy levels around the nucleus, and finally there are ………., which have no charge and are in the nucleus as well.
proton, nucleus, electrons, neutrons
Atoms of the
same element that have different numbers of neutrons are called………., which cause the atoms to have different ………..
isotopes, mass numbers
When an atom gains or loses
an electron, it becomes a(n)…………. because it now has a(n) …………
ion , charge
Put the following in order from smallest to largest
Atom
Molecule
Nucleus
Proton
Proton =1
Nucleus =2
Atom =3
Molecule =4
In hydrogen peroxide (H,02), how many elements are there?
2
In hydrogen peroxide (H,02), how many atoms?
4

How many protons
4

How many neutrons
5

How many electrons
4

The 4 represents the …………. of beryllium
atomic number

What subatomic particle(s) does atomic number represent?
protons / electrons

The 9 represents the ……….. of beryllium
mass number

What subatomic particle(s) does mass number represent?
protons plus neutrons

According to the table, which substance has the most basic pH?.
ammonia

How many times more basic is the pH of ammonia than baking soda?
100x

Which substance contains the most hydrogen ions (H+)?
egg whites

Which substance contains the most hydroxide ions (OH-)?.
ammonia

What would you expect to happen to the pH of egg whites if small amounts of acid were added to them? Explain why.
Because egg whites are living material, they contain buffers, so adding acid only slightly lowers the pH.

What is a buffer? How do you know if a solution is buffered? Why is a buffer important to living things?
A buffer keeps the pH of a system, organism, or cell stable when small amounts of acid or base are added.
A solution is buffered if its pH does not change much when acid or base is added.
Living things must stay at a certain pH to survive.
Explain how a buffer words in an acid? In a base?
When a strong base is added, a weak acid donates H⁺ to neutralize it.
When a strong acid is added, a weak base absorbs H⁺, preventing big pH changes.
Whats so special about carbon?
Carbon is small and stable, so it forms stable compounds.
It has four valence electrons, allowing it to form four covalent bonds.
Carbon is abundant and found in all living things.'
It bonds easily with itself and with many other atoms.
Carbon can form single, double, or triple bonds.
Its bond angles allow many different shapes.
Using the following chemical equation: 2H2 + 1 02 → 2 H, to answer the questions below.
What is happening in this reaction? Use the correct vocab to describe it.
two molecules of hydrogen gas react with one molecule of oxygen gás to produce two molecules of water
Using the following chemical equation: 2H2 + 1 02 → 2 H, to answer the questions below.
How many total molecules are involved in the reaction?
5
Using the following chemical equation: 2H2 + 1 02 → 2 H, to answer the questions below.
How many total atoms are involved in the reaction?
12
Using the following chemical equation: 2H2 + 1 02 → 2 H, to answer the questions below.
Why is water polar?
Water is polar because oxygen is more electronegative than hydrogen, so electrons are shared unequally and stay closer to oxygen.
Using the following chemical equation: 2H2 + 1 02 → 2 H, to answer the questions below.
Describe how hydrogen bonds form between water molecules
hydrogen bonds form between the partially negative oxygen and the partially positive hydrogens → opposites attract
Using the following chemical equation: 2H2 + 1 02 → 2 H, to answer the questions below.
Name and describe the seven characteristics of water due to its polarity/hydrogen bonds.
Cohesion: Water sticks to itself due to hydrogen bonds.
Adhesion: Water sticks to other polar or charged surfaces.
Surface tension: Cohesion creates a skin-like surface.
Capillary action: Water moves up small spaces using cohesion and adhesion.
High specific heat: Water resists temperature changes.
High heat of vaporization: Water needs lots of energy to evaporate.
Lower density as ice: Ice is less dense because hydrogen bonds spread molecules apart.
Draw a Bohr model of a Nitrogen atom below.
What would change about your model if you were told that the atomic mass was 15?
Be sure to label where the protons, neutrons, & electrons are in your model.

Draw a lewis dot structure for ethanol, CH,CH,OH and acetic acid, CH,COOH
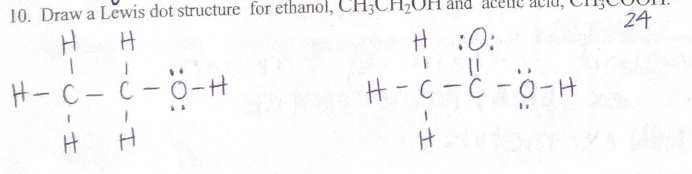
Differentiate between ionic & covalent bonding. Be able to define an ion.
ion is a charged particle.
ionic bond, electrons are transferred.
covalent bond, electrons are shared.
What is an organic compound? Name some examples & some compounds that are NOT examples.
compound containing carbon ex: DNA, table sugar
NON ex: metals
What is the process that makes polymers from monomers? Describe this process
Dehydration synthesis forms polymers by joining monomers and releasing water.
What is the process that breaks up polymers into monomers? Describe this process.
Hydrolysis breaks polymers into monomers by adding water and releasing energy (exothermic).
Most lipids contain what type of molecule? Describe the structure of this molecule. How does it behave in water and why? Explain the difference between saturated and unsaturated fats.
Lipids are nonpolar and hydrophobic, so in water they form bilayers or micelles.
Unsaturated fats have one or more double bonds.
Saturated fats have only single bonds.
Describe the 4 levels of protein folding.
Primary: sequence of amino acids
Secondary: twists and folds of the chain (alpha helix or beta sheet)
Tertiary: complex 3D folding of the protein
Quaternary: two or more folded proteins joined together
DNA
double helix
adenine, thymine
cytosine, guanine nitrogen bases
deoxyribose is a sugar
found in nucleus of a cell
RNA
Single strande
adenine, cytosine, guanine, uracil, nitrogen bases
ribose is sugar
found in nucleus
Macromolecule Protein
Name of monmer:
Name of polymer:
Examples:
Descripton:
Functions:
Name of monomer: Amino acid
Name of polymer: polypeptide
Examples: actin hemoglobin
Description: protein building block with an amino group, carboxyl group, and an R group.
Functions: speed up enzymes
structural
component of cell membrane and transport
Macromolecule Nucleic Acid
Name of monomer:
Examples:
Description:
Functions:
Name of monomer: nucleotide
Examples: DNA/RNA
Description:the building block of nucleic acids, made of a sugar, phosphate group, and nitrogen base
Functions: Structure of genetic information
determine sequence of amino acids when proteins are formed
Macromolecule lipid
Name of monomer:
Examples:
Description:
Functions:
Name of monomer: Fatty acid chains and glycerol
Examples: fats oils
Description: basic parts that make up lipids
Functions: Long term energy storage
important signaling molecules
used as insulation in some organisms
Macromolecule Carbohydrate
Name of monomer:
Name of Polymer:
Examples:
Description:
Functions:
Name of monomer: monosaccharide
Name of polymer: polysaccharide
Examples: sugar , startch, cellulose, glycogen
Description: a simple sugar and the building block of carbohydrates
Functions: Short term energy source
act as receptors for chemical messengers
structural molecules