Chapter 15 (GVSU BMS 208)
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
65 Terms
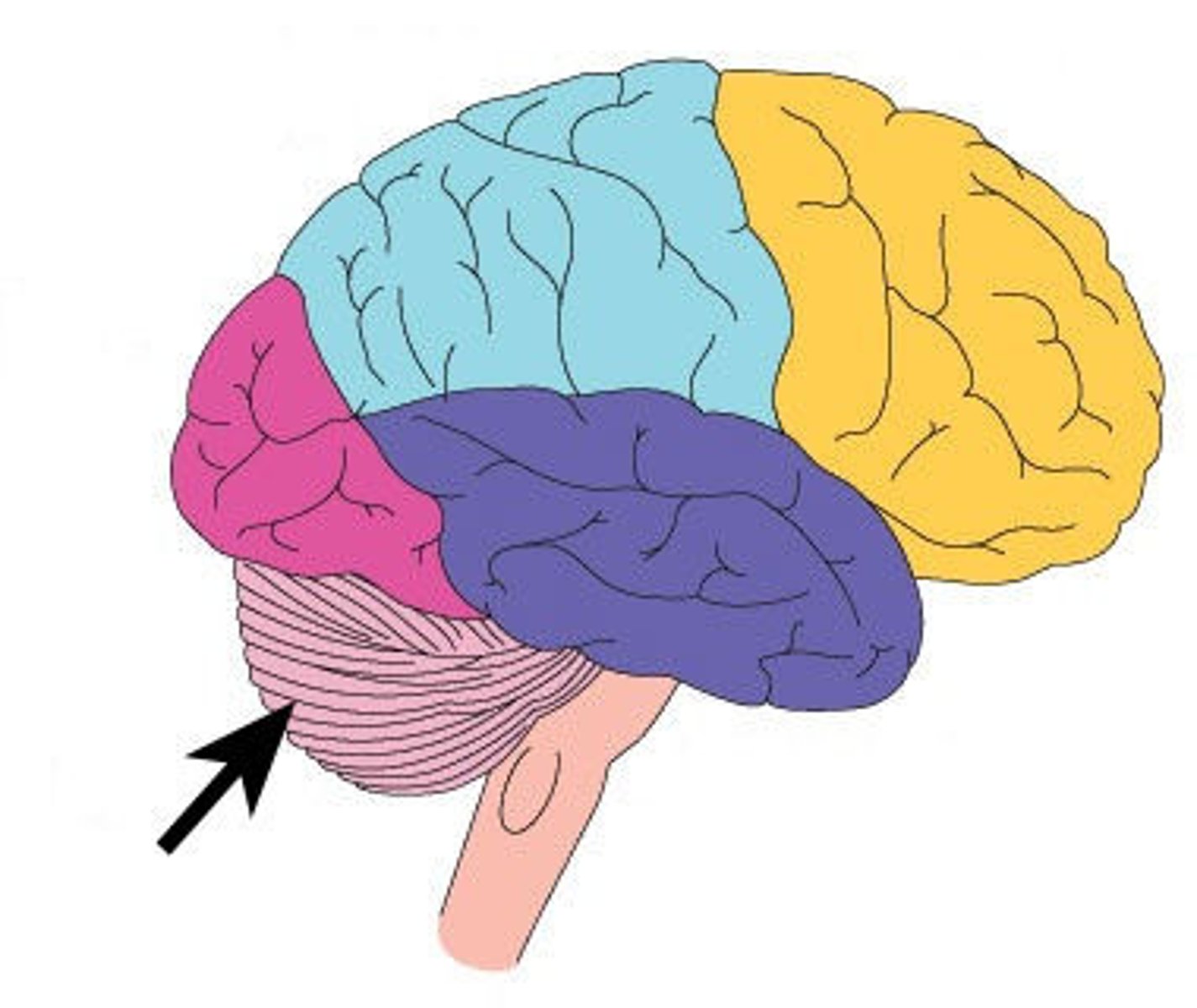
What are the four regions of the brain?
cerebrum, diencephalon, brainstem, cerebellum
cerebrum function
thinking, personality, sensations, movements, memory
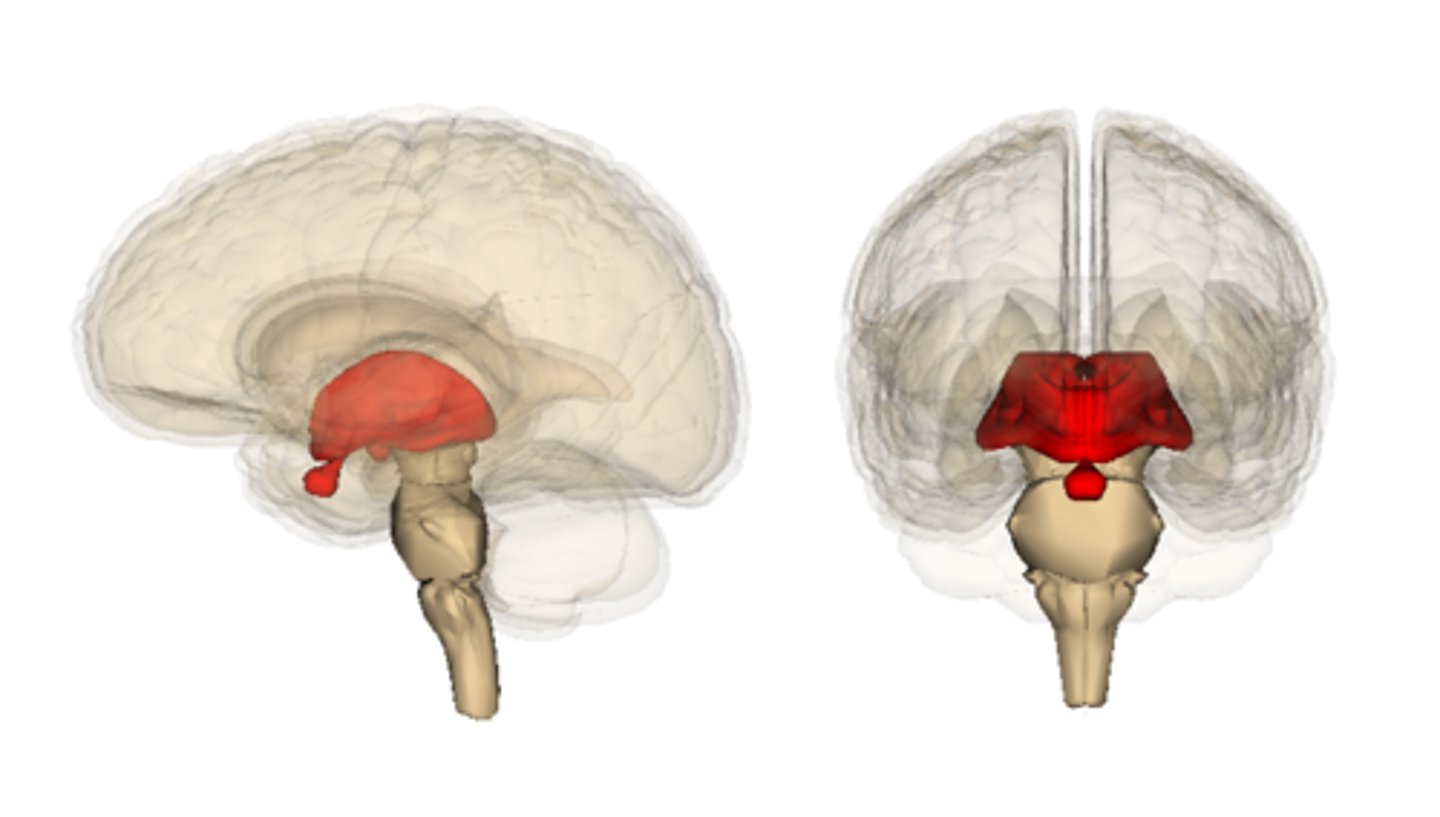
diencephalon
thalamus, hypothalamus, epithalamus
cerebrum
largest part of the brain

brainstem
responsible for automatic survival functions
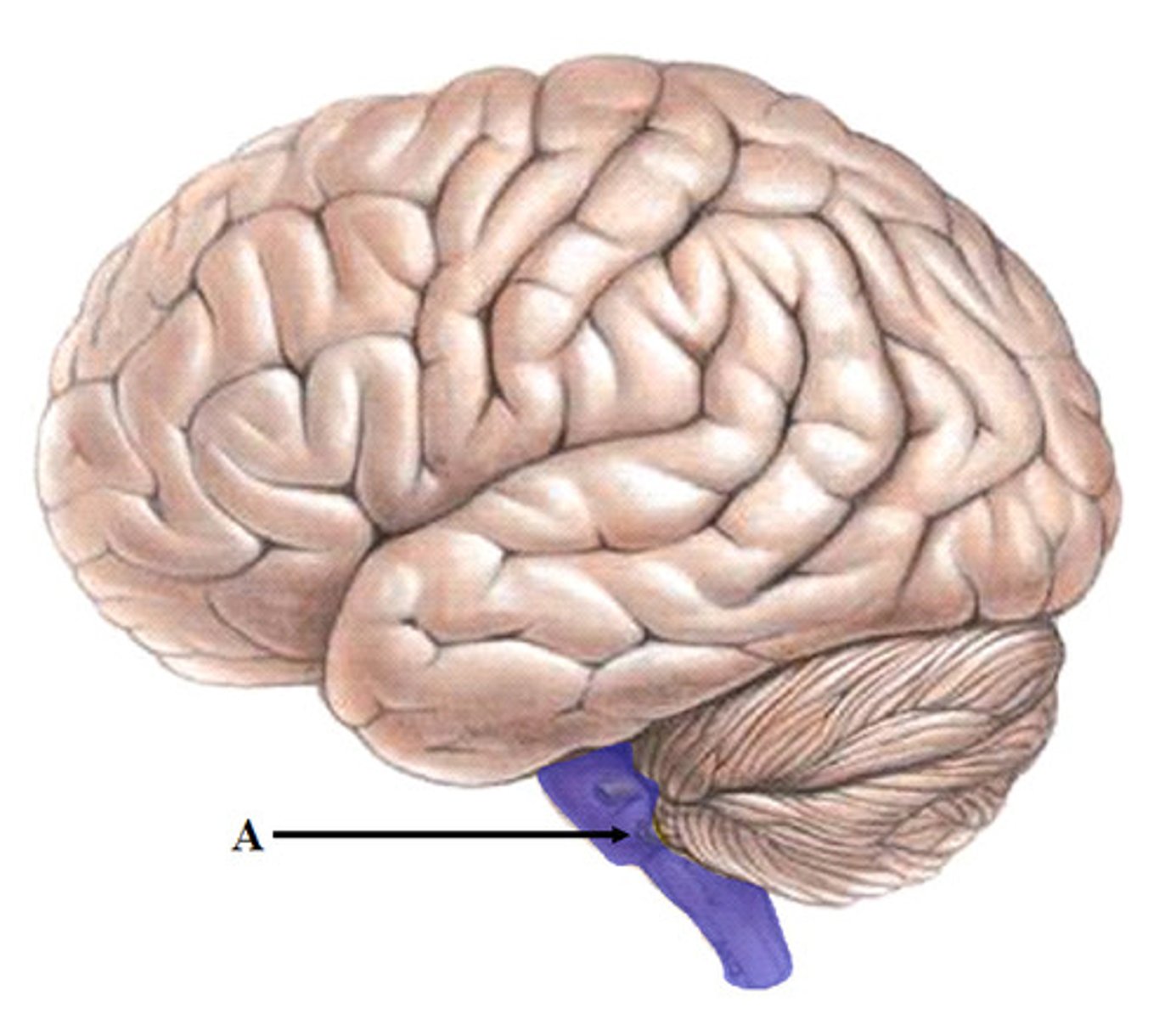
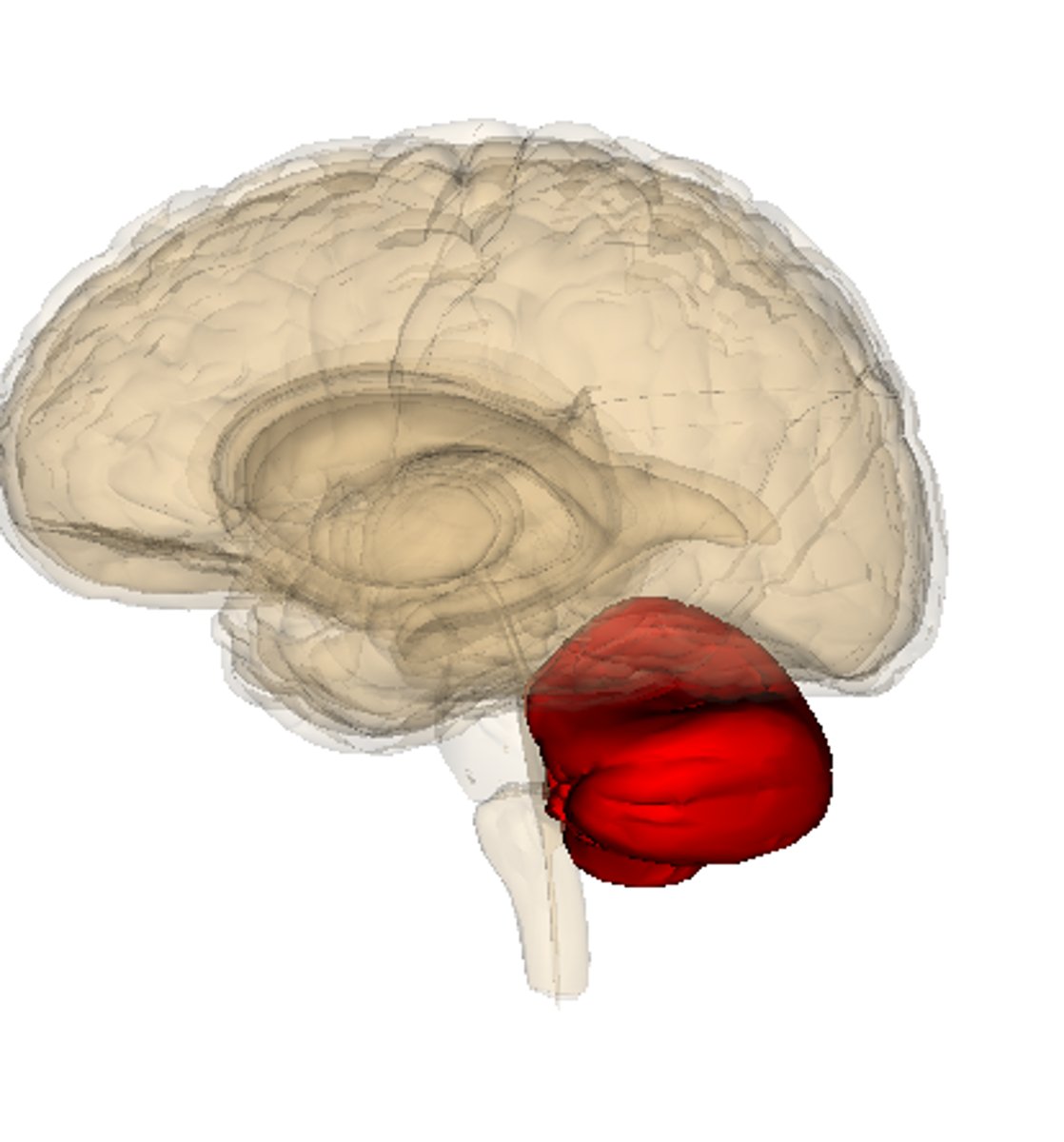
cerebellum
Balance and coordination
ganglia
cluster of neuronal cell bodies in the PNS
white mater
myelinated axons
gray mater
nerve cell bodies and branching dendrites.
cerebral nuclei
internal clusters of gray matter embedded within masses of white matter
gyrus
folds or bumps on the surface of the cerebrum
increases surface area
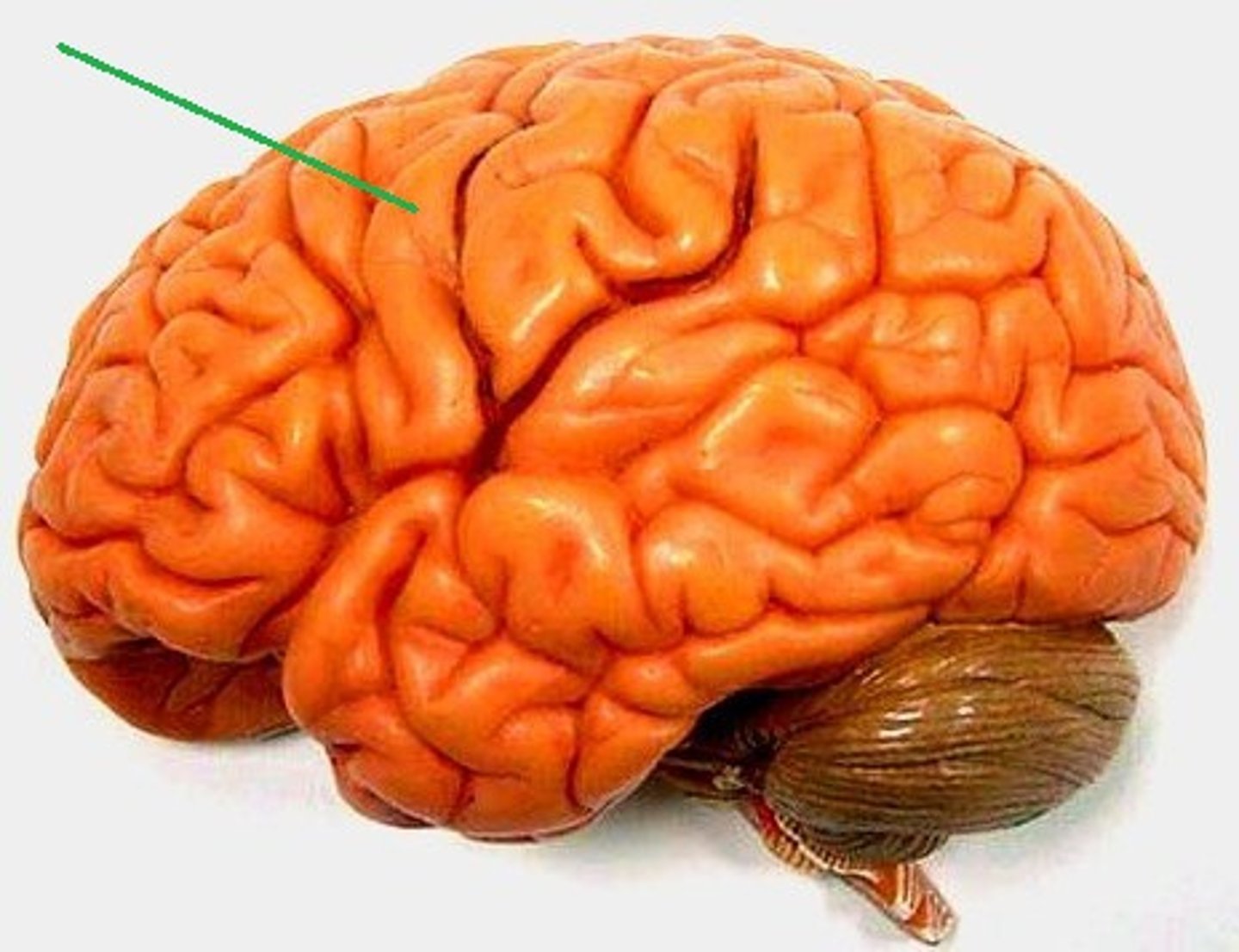
sulcus
narrow groove on the surface of the brain in the cerebral cortex
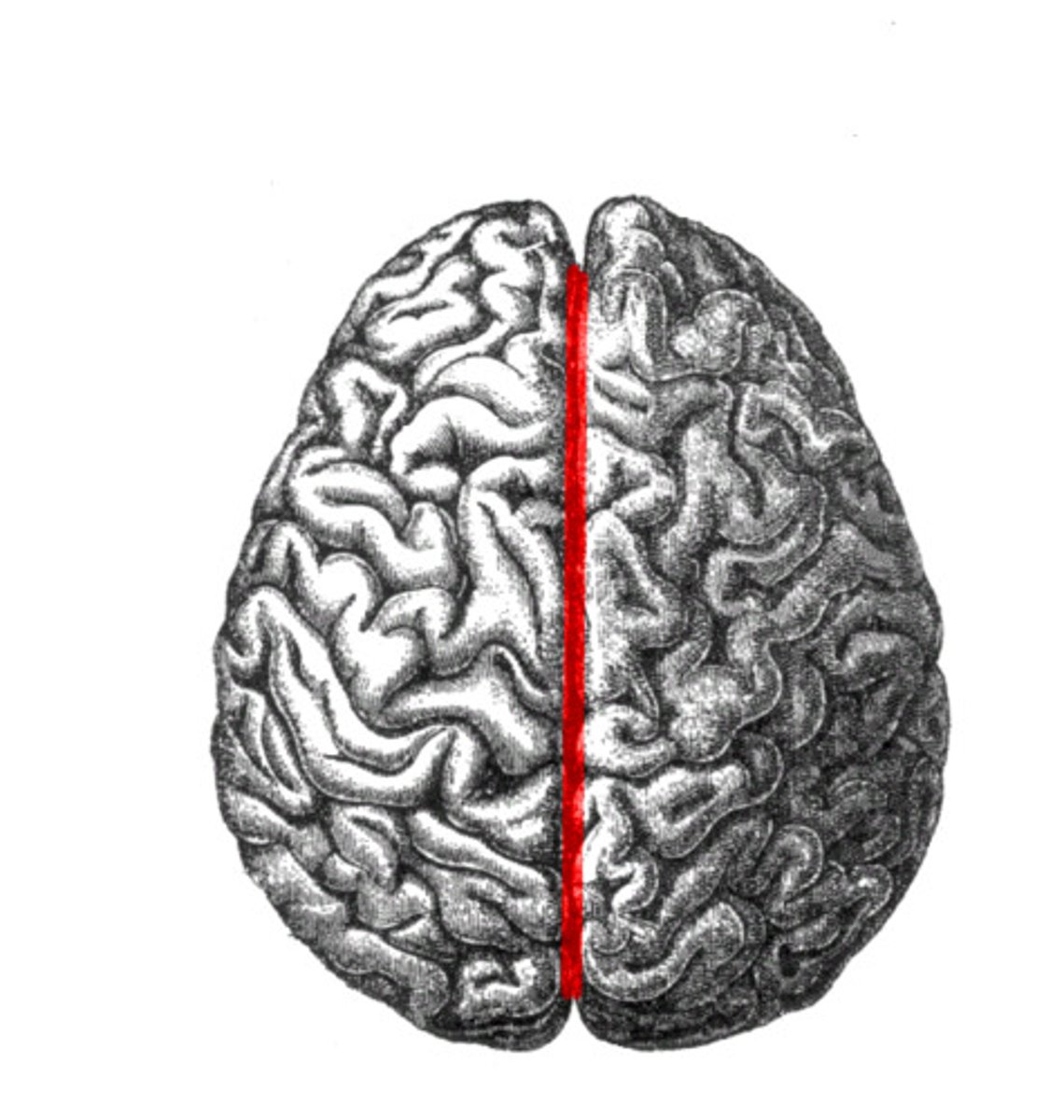
longitudinal fissure
separates left and right hemispheres
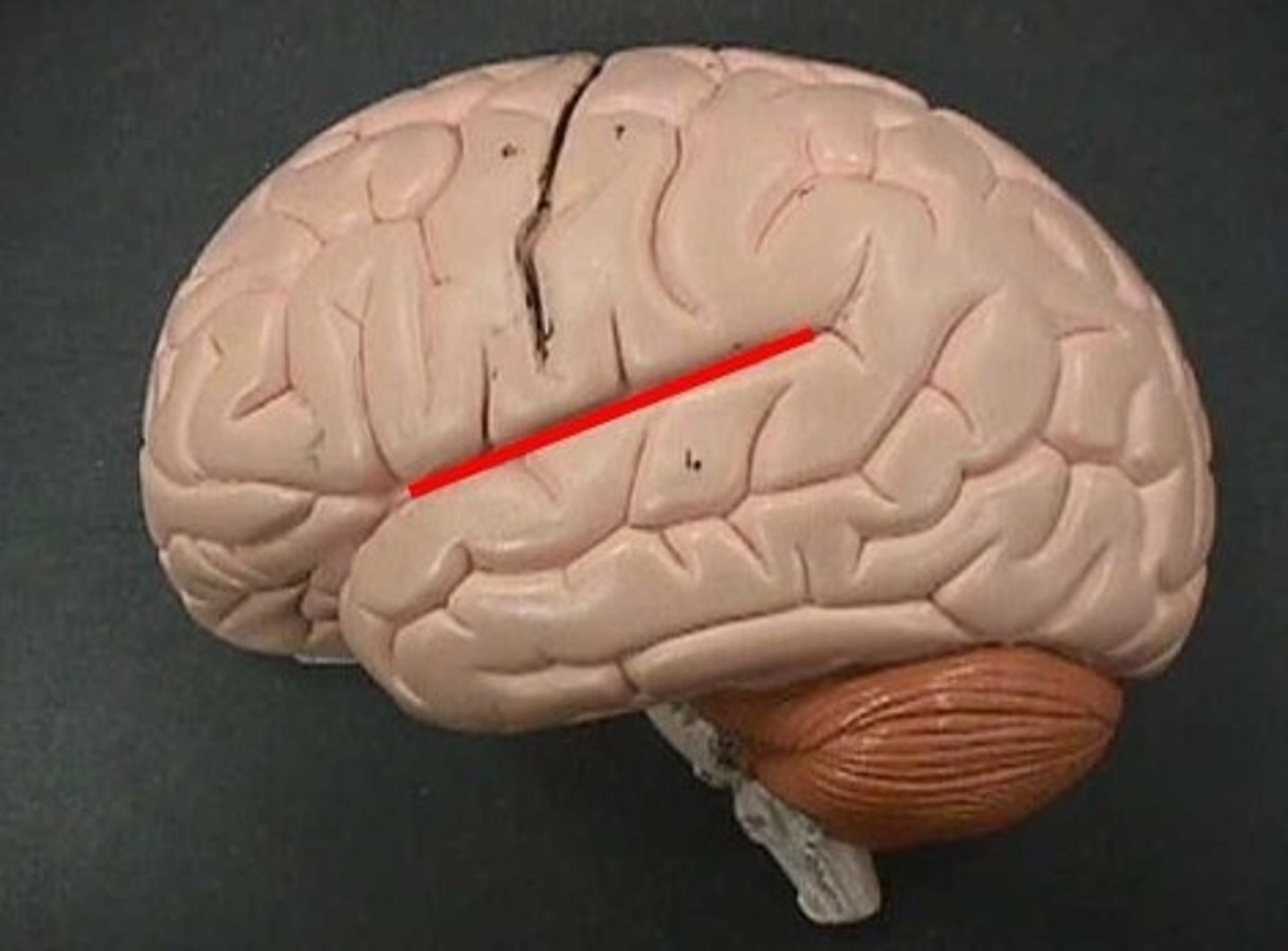
central sulcus
separates frontal and parietal lobes
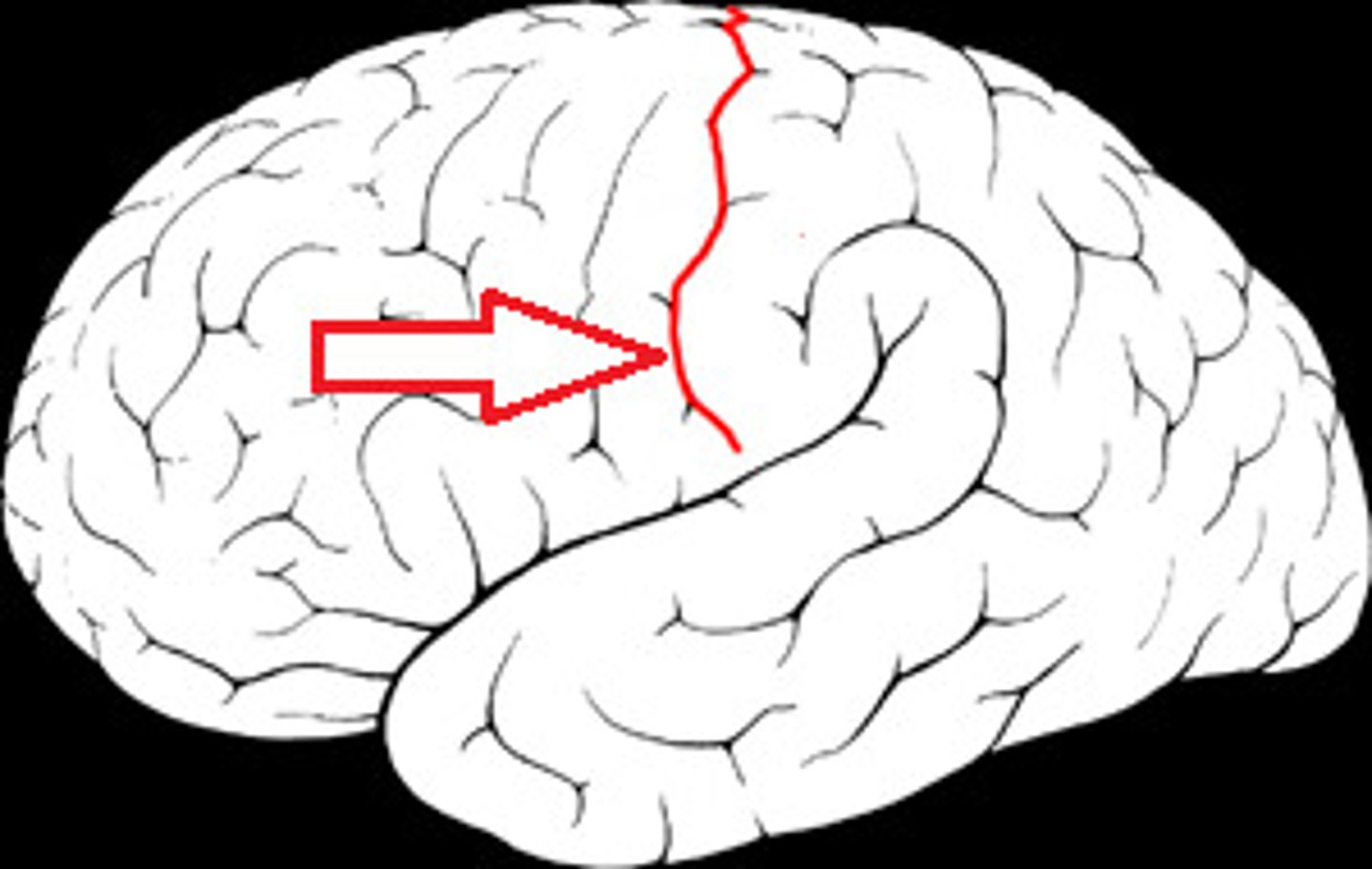
lateral sulcus
Separates temporal lobe from parietal and frontal lobes
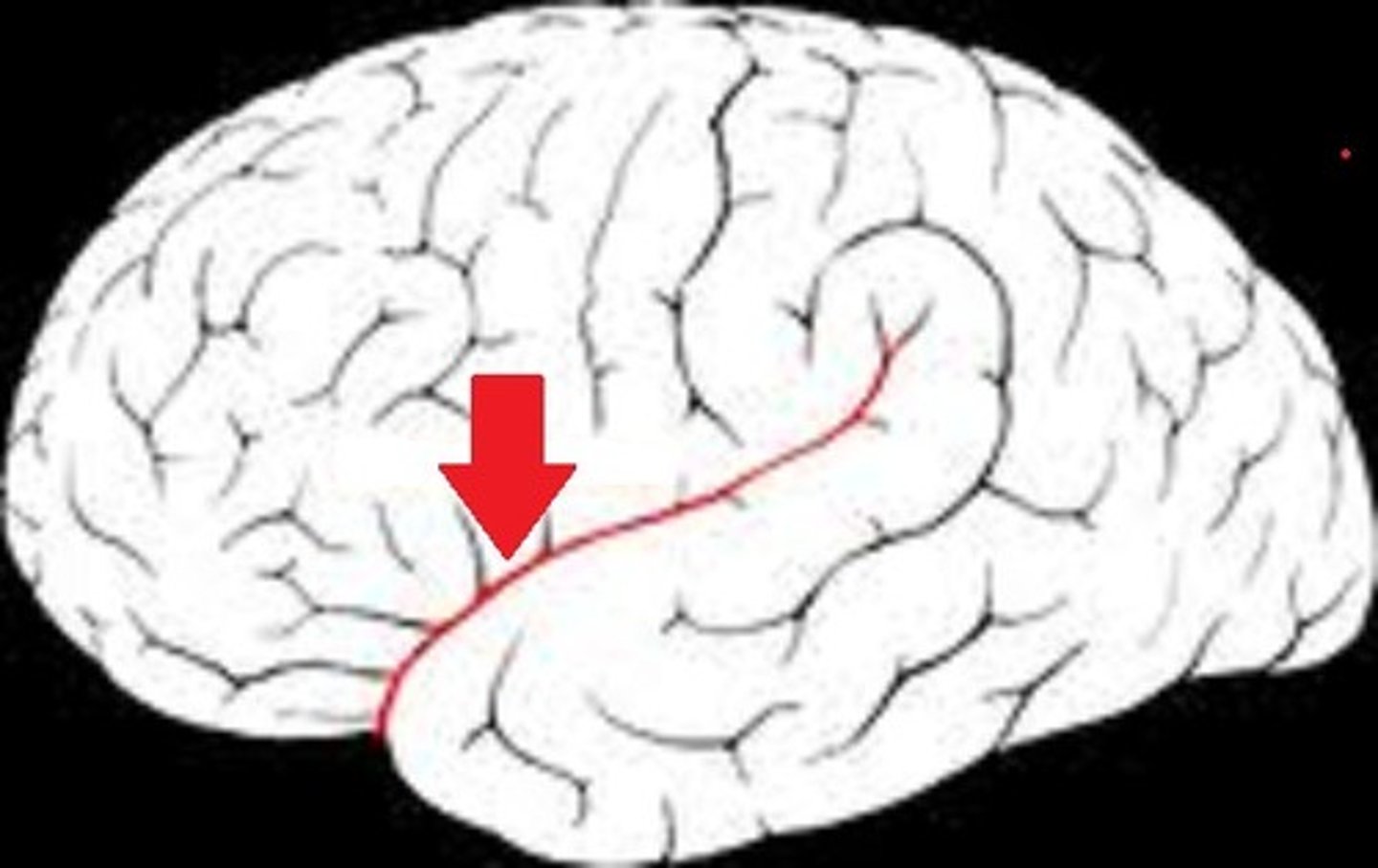
fissue
deep groove
frontal lobe function
higher intellectual functions (concentration, decision making, planning), personality, verbal communication, voluntary motor control of skeletal muscles
parietal lobe function
sensory interpretation of textures and shapes, understanding speech and formation of words to express thoughts and emotions
temporal lobe function
interpretation and storage of auditory and olfactory sensations, understanding speech
occipital lobe function
conscious perception of visual stimuli,
integration of eye-focusing movements, correlation of
visual images with pervious visual experiences
insula function
memory and interpretation of taste
pre-central gyrus function
primary motor cortex
post-central gyrus function
primary somatosensory cortex
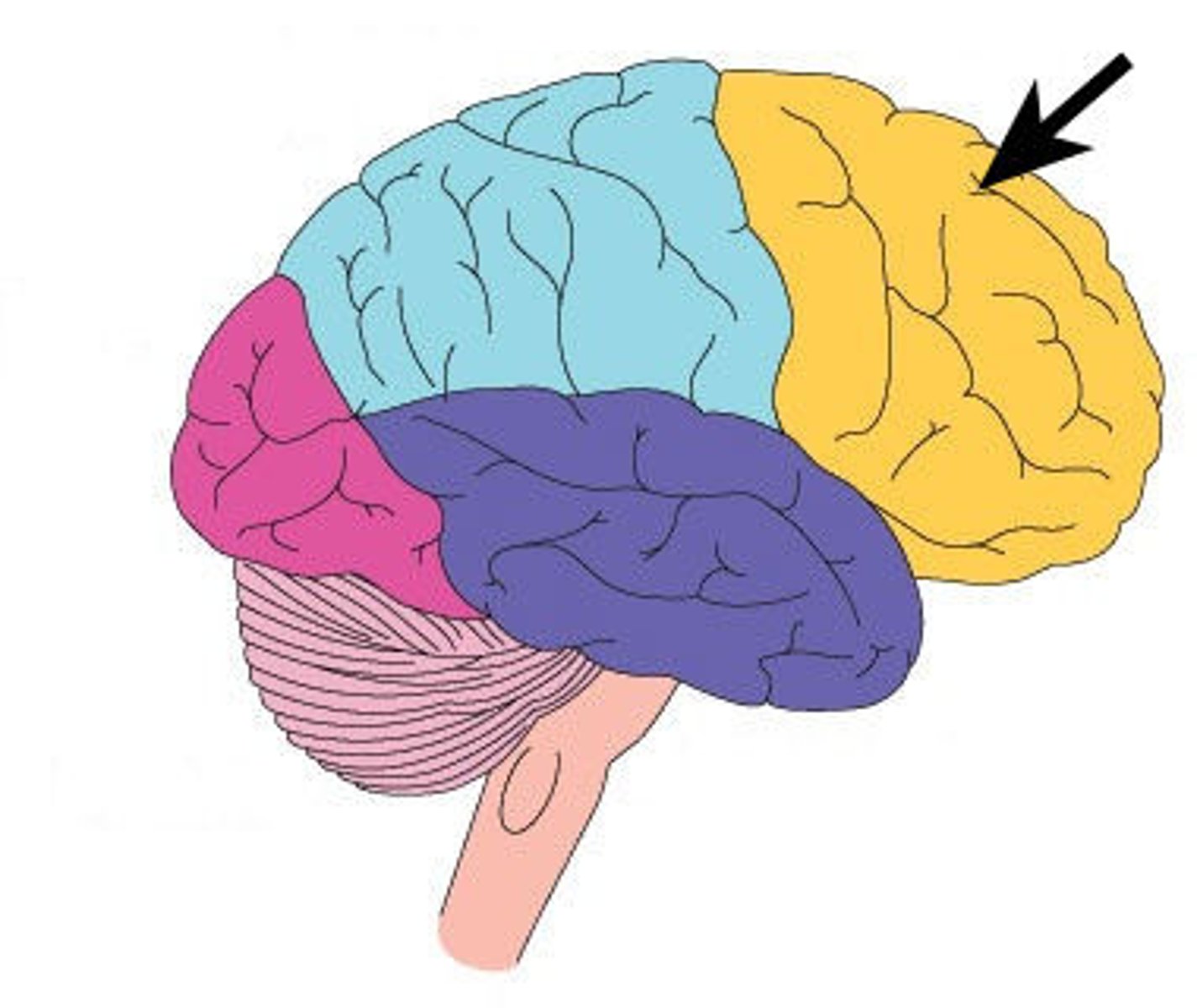
frontal lobe location
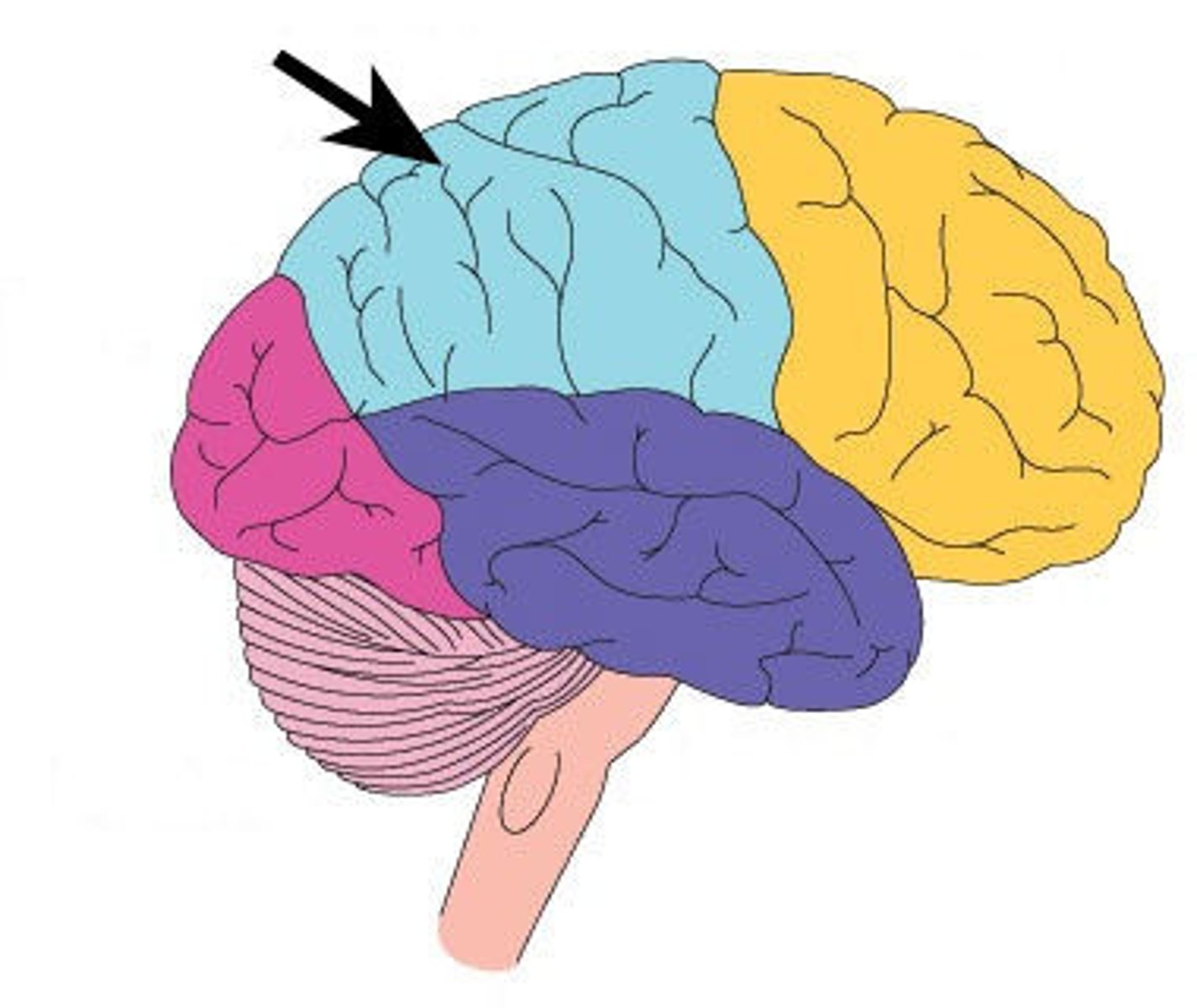
parietal lobe location
temporal lobe location
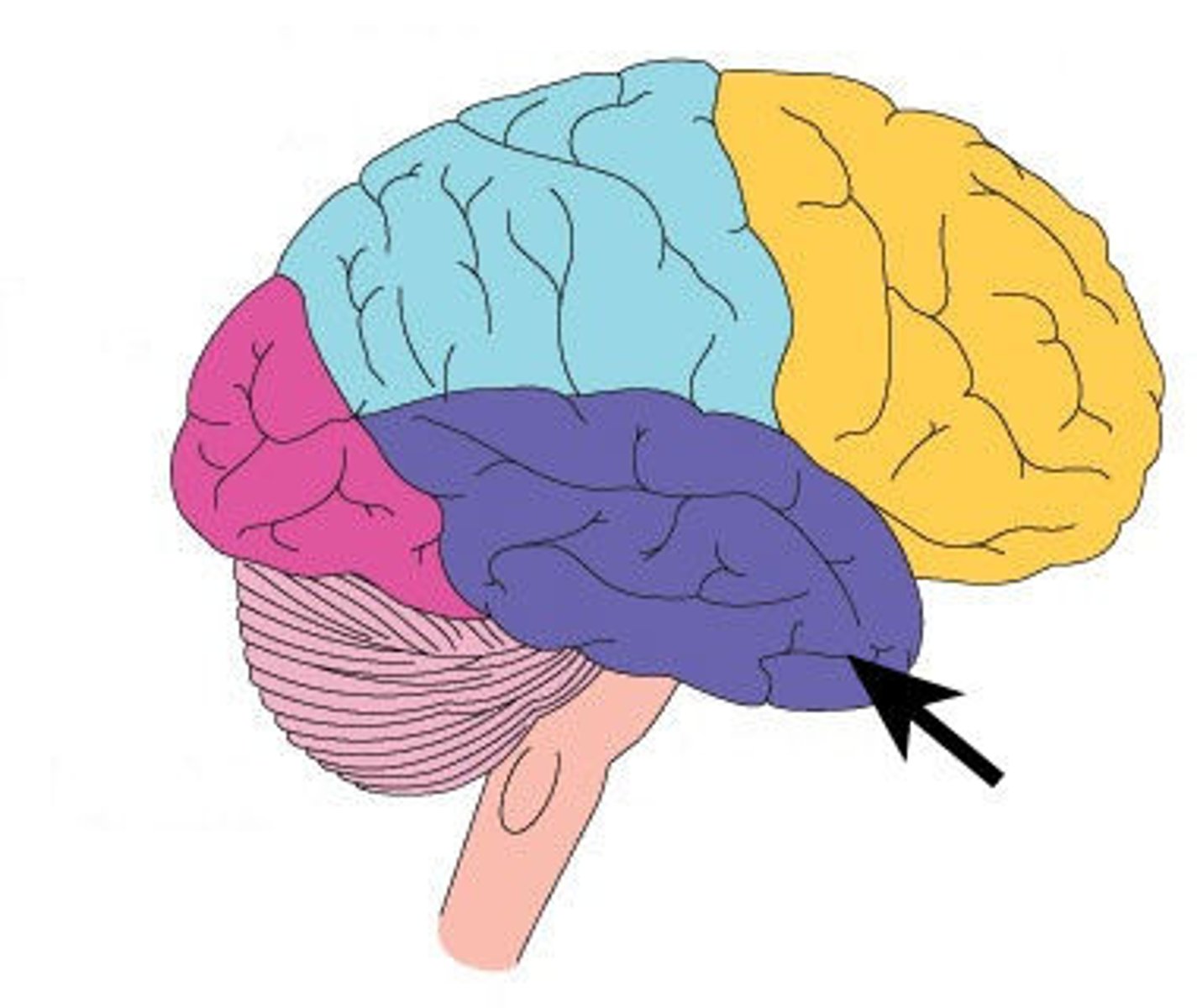
occipital lobe location
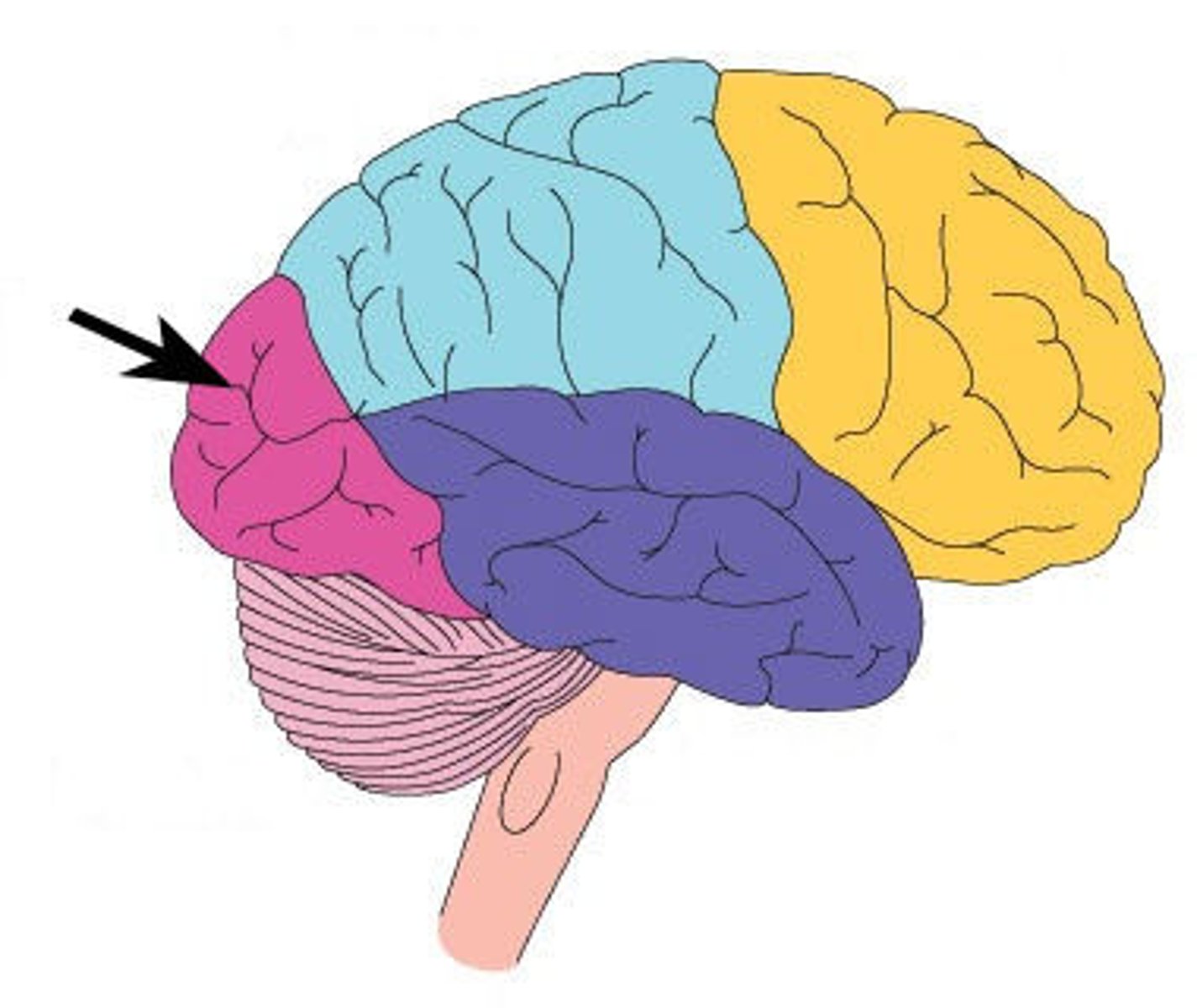
insula lobe location
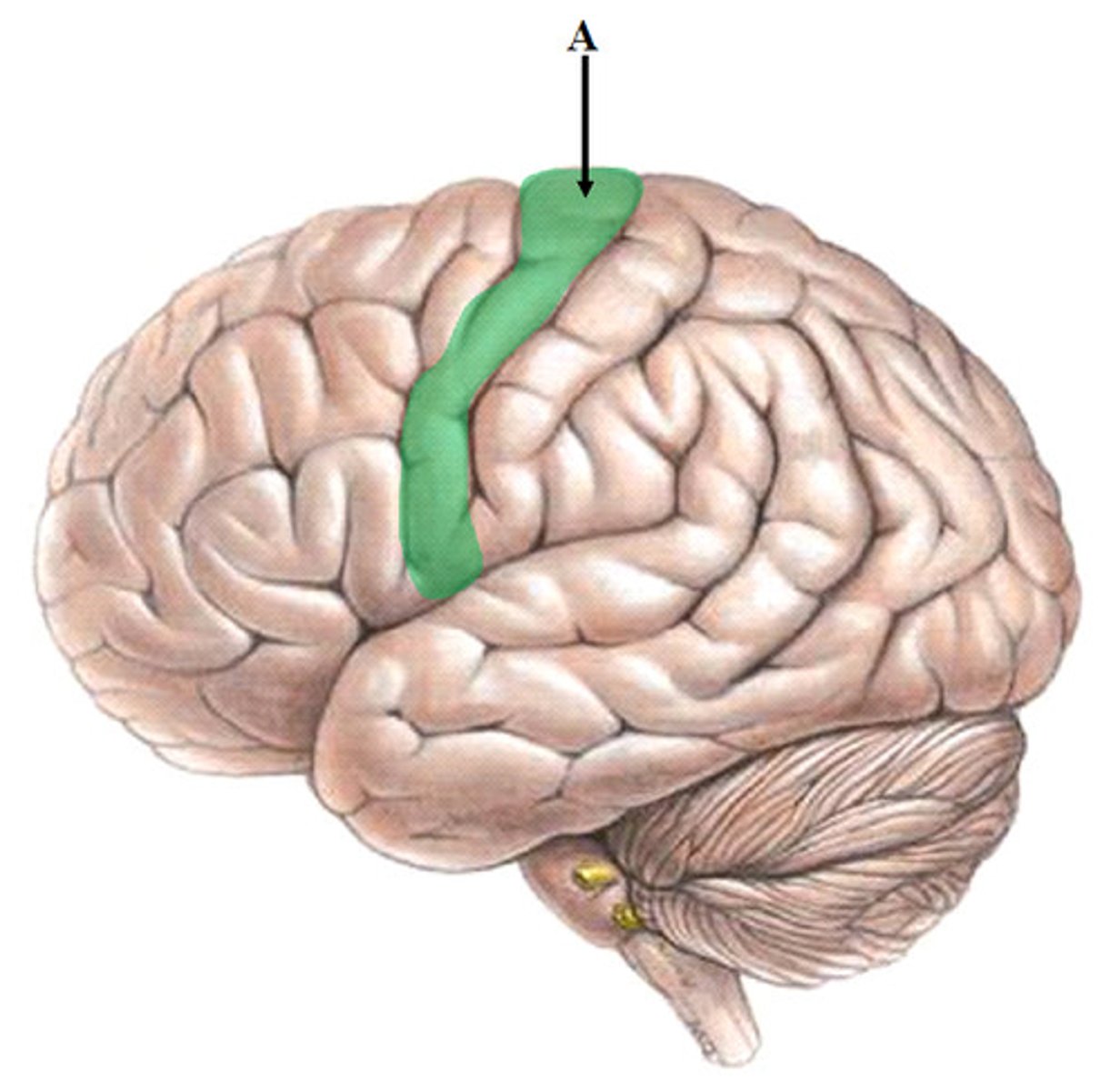
pre-central gyrus location
in frontal lobe
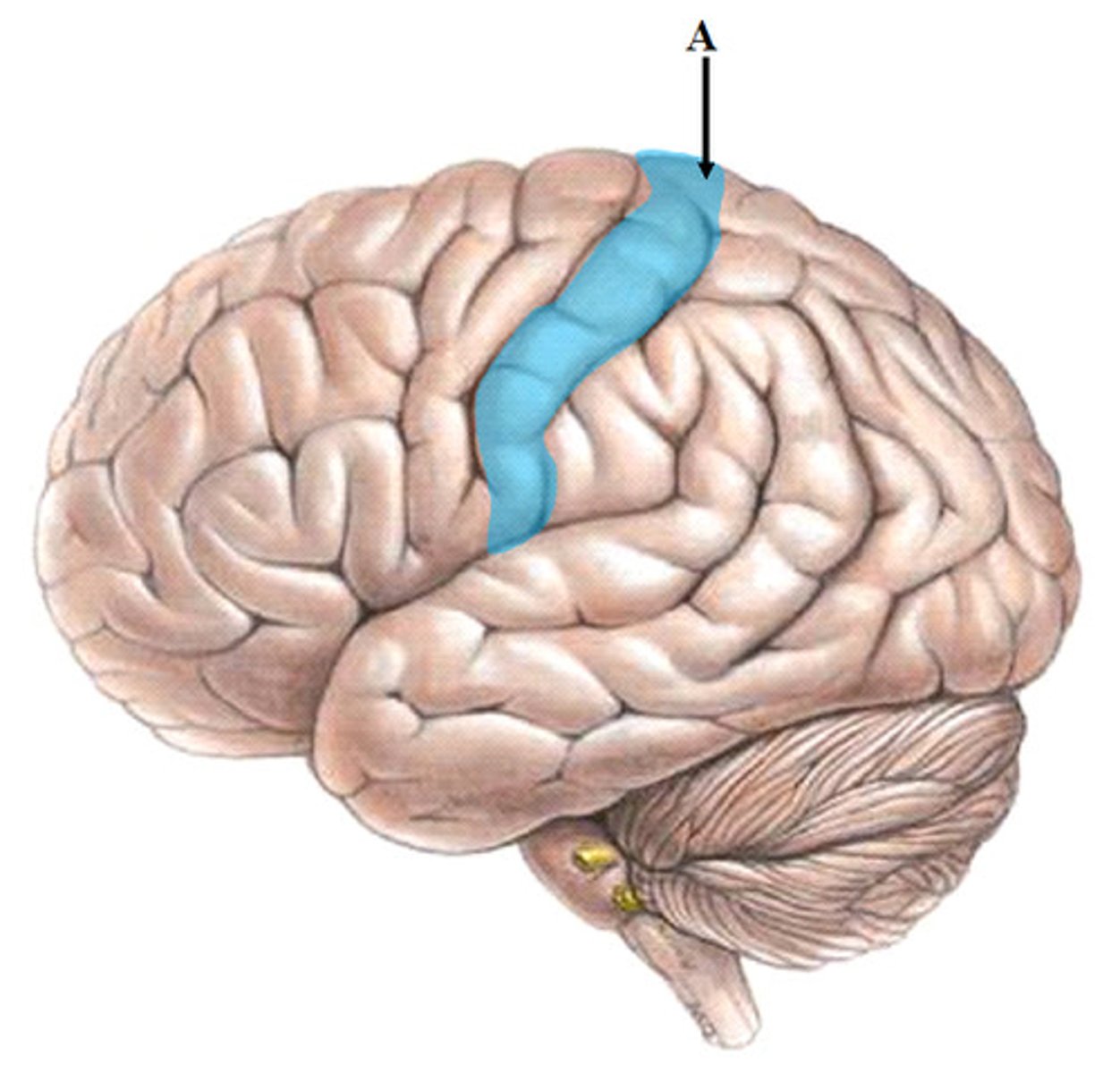
post-central gyrus location
in parietal lobe
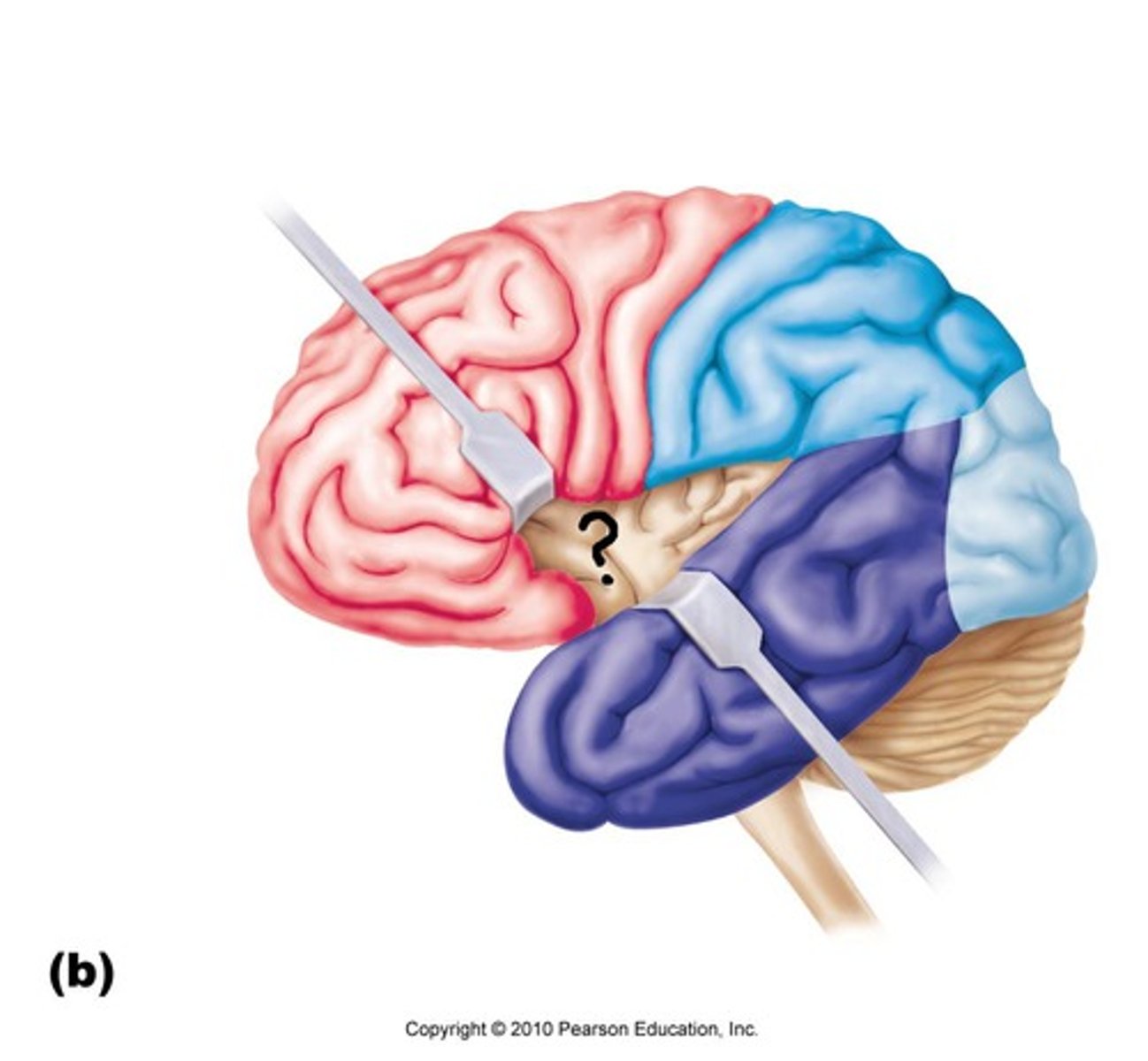
cerebral nuclei function
gives us our muscle rhythm, subconsciously regulates contractile activity
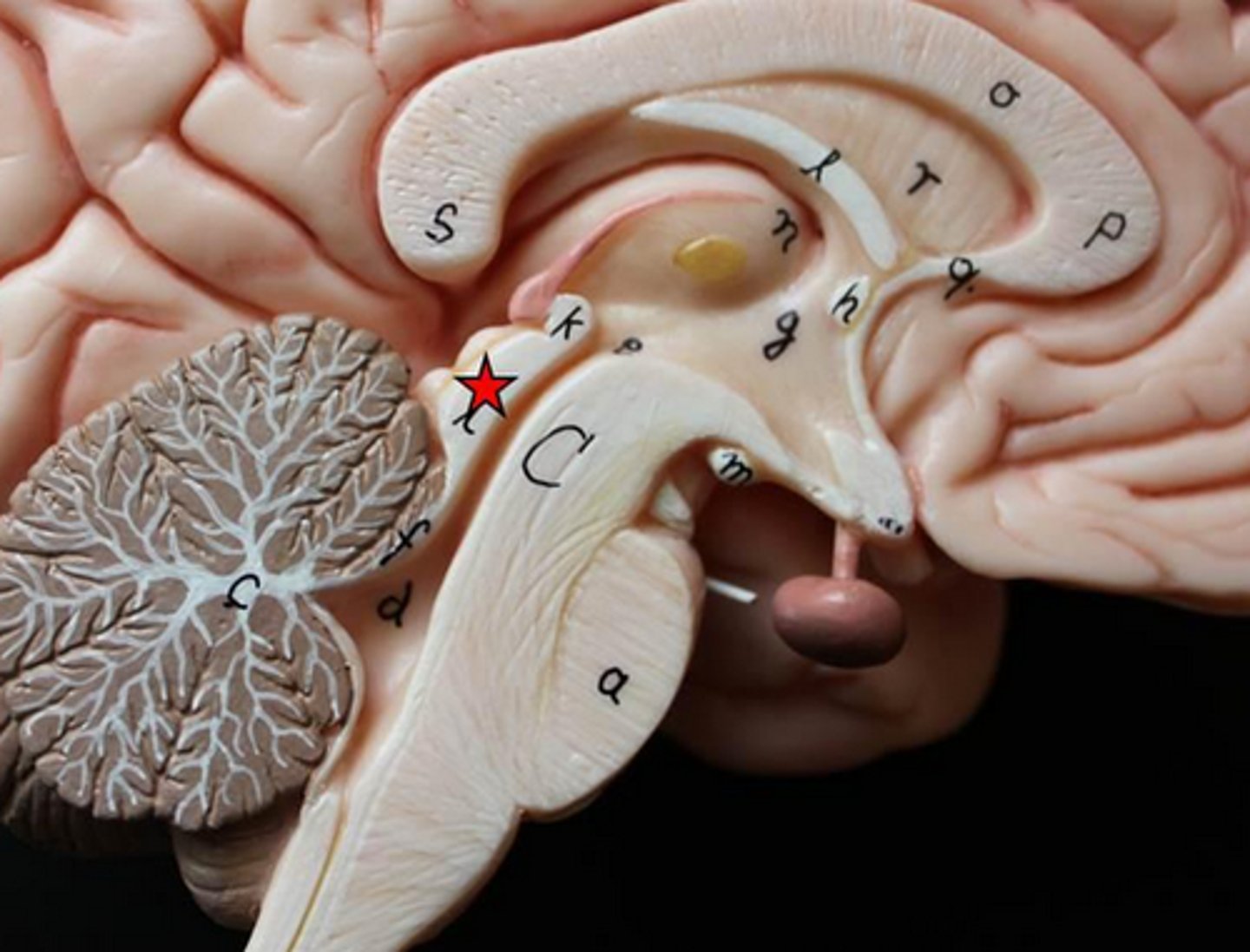
corpus callosum location
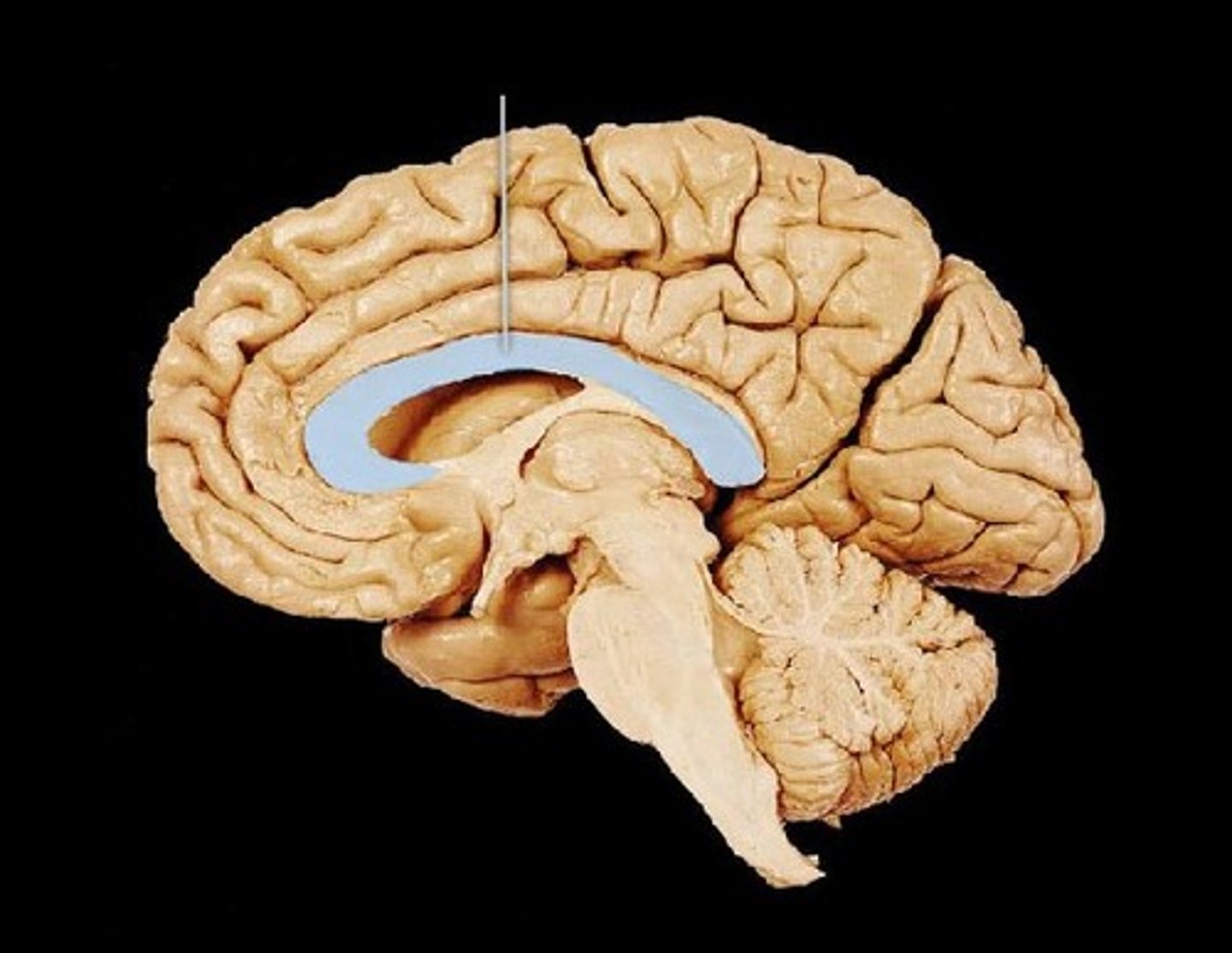
corpus callosum function
Connects the right and left hemispheres of the brain, how action potential travel between hemispheres
thalamus location
pair of oval masses of gray matter
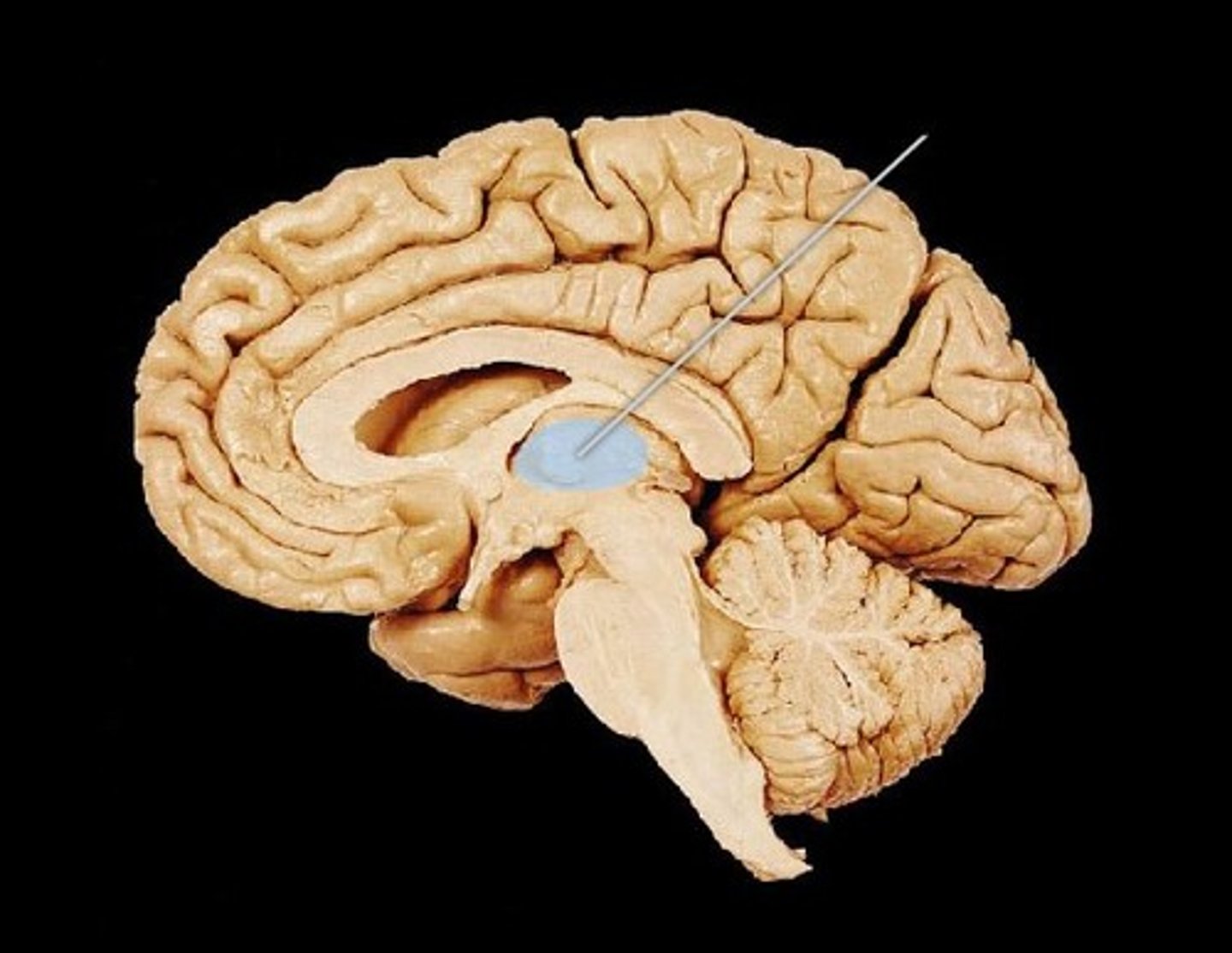
thalamus function
relay station for sensory impulses, pain
Hypothalamus location
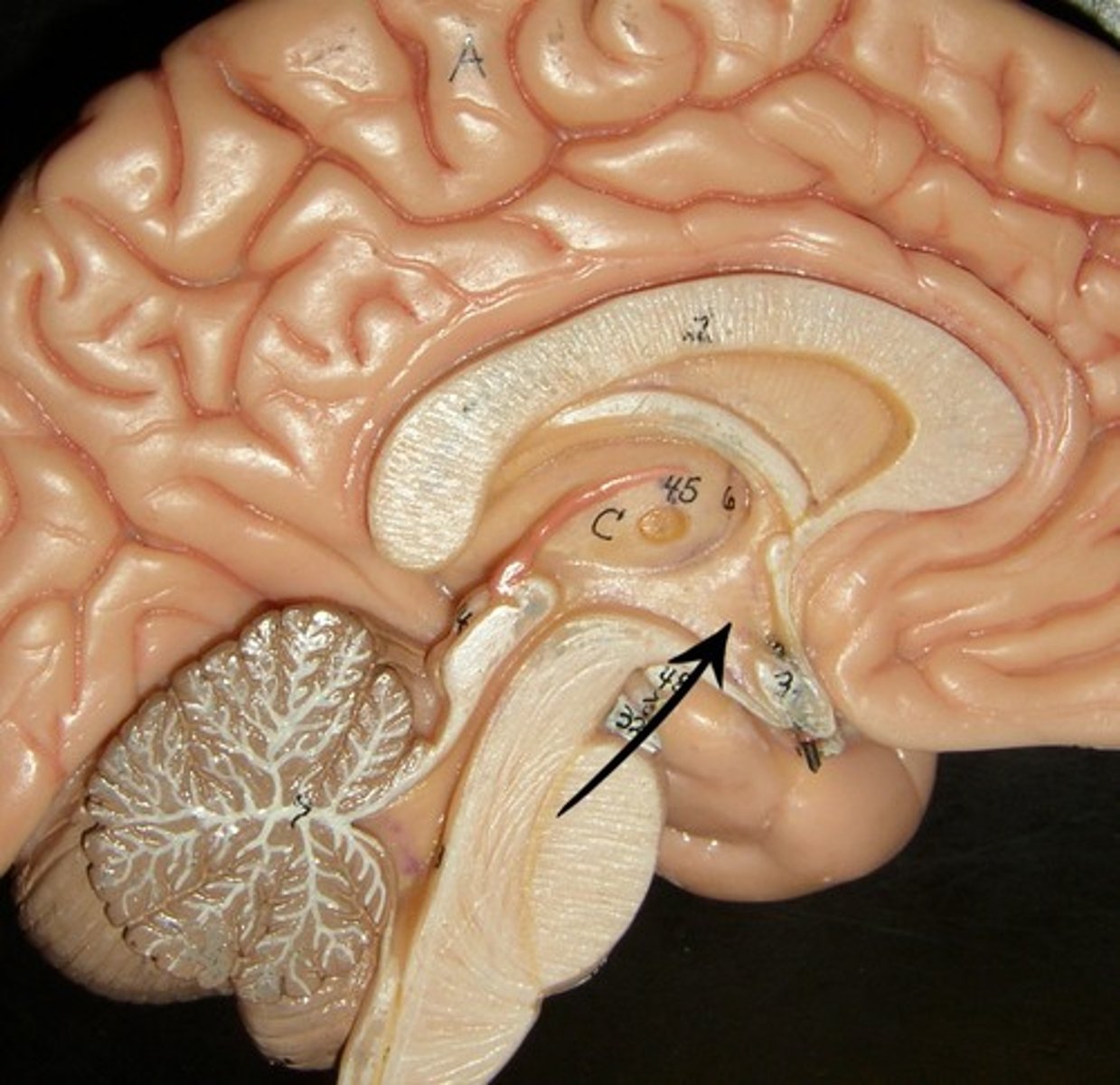
hypothalamus function
autonomic control (heart rate, blood pressure, digestion)
emotions/behavioral drives (aggression, fear, content, sex drive, thirst center)
endocrine (hormones)
body temperature
Epithalamus location
contains the pineal gland
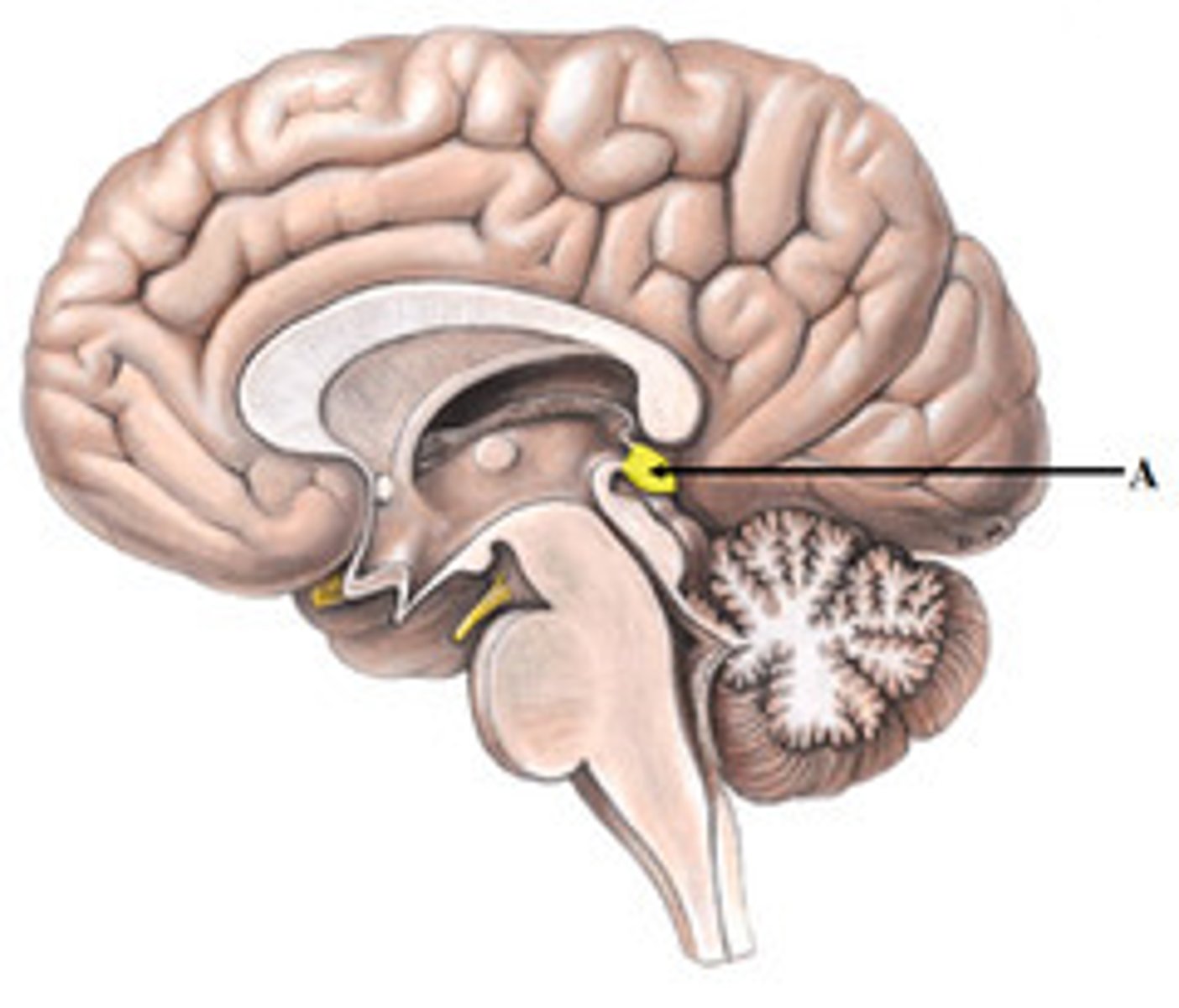
epithalamus function
secretes melatonin
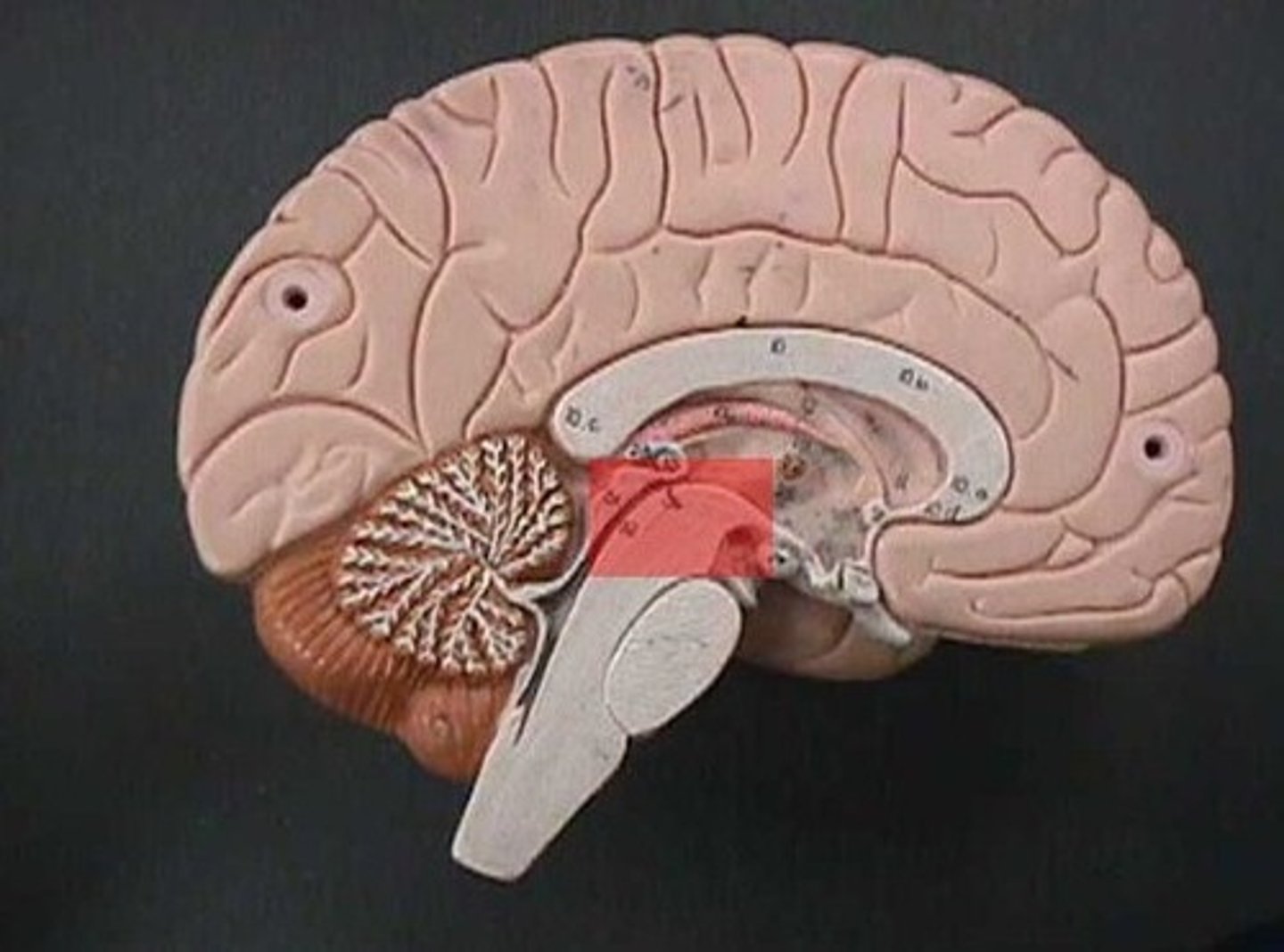
midbrain
A small part of the brain above the pons that integrates sensory information and relays it upward.
corpora quadrigemina of midbrain
coordinates visual and auditory reflexes
superior colliculus of midbrain
receives visual sensory input
inferior colliculus of midbrain
receives auditory sensory input
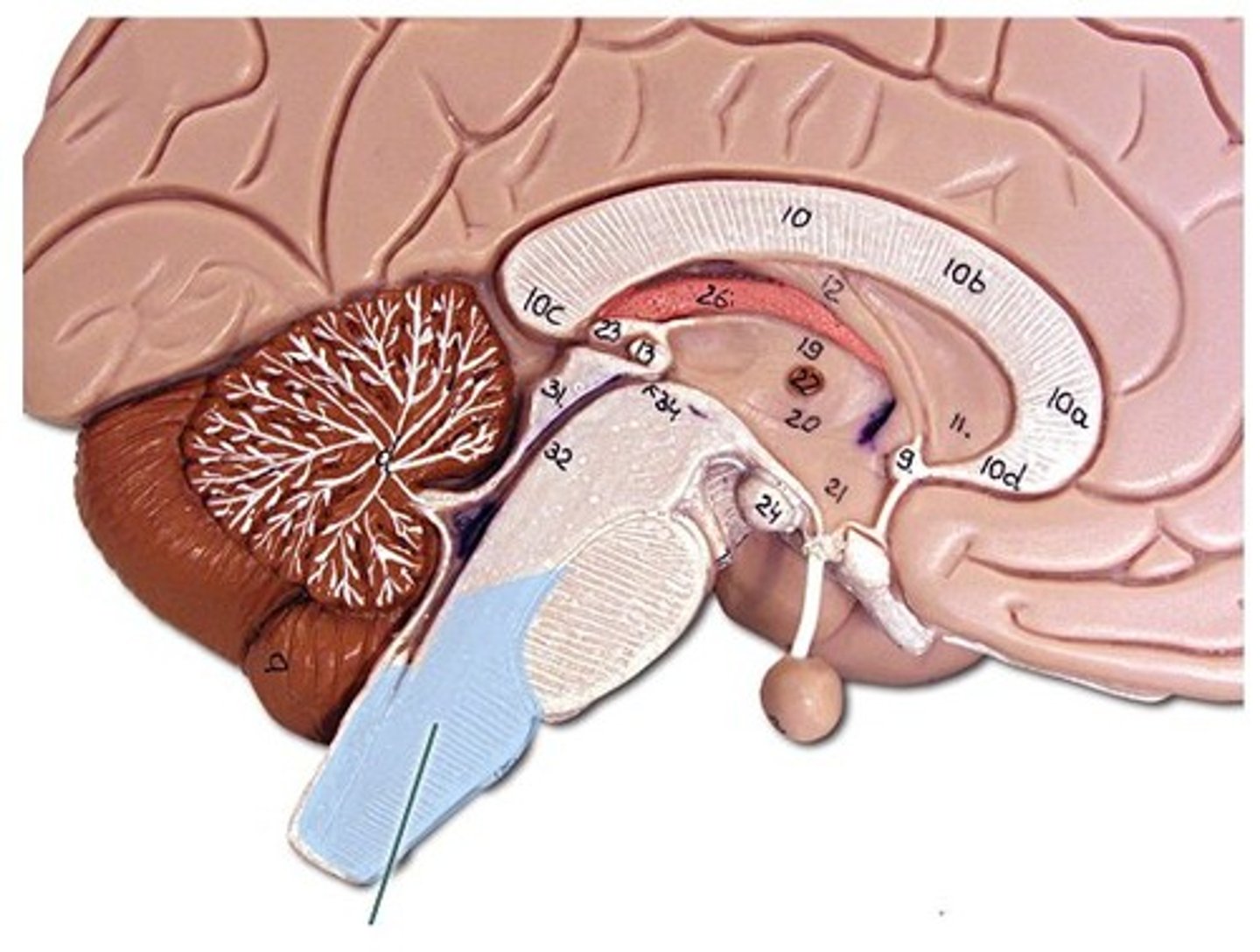
pons
contains sensory and motor tracts that connect brain to spinal cord
brainstem nuclei, respiratory muscles (rhythm)
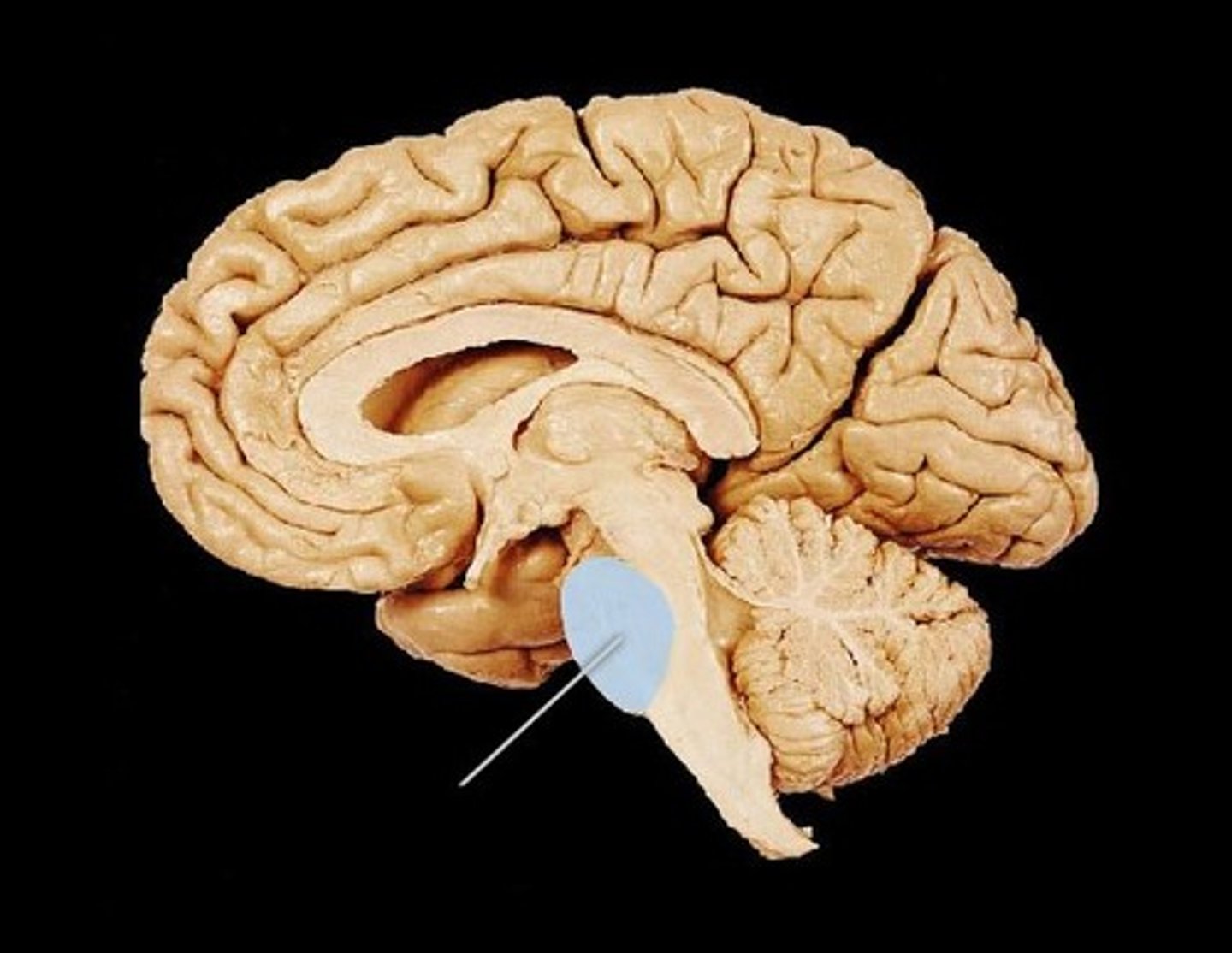
medulla oblongata
brainstem nuclei, vital centers for control
of respiratory rate and cardiac function (heart rate/strength)
has sensory and motor tracts
gagging and vomiting center
cerebellum function
fine tuning of skilled voluntary motor activity to produce smooth, accurate movements
balance, equilibrium, and skilled movement
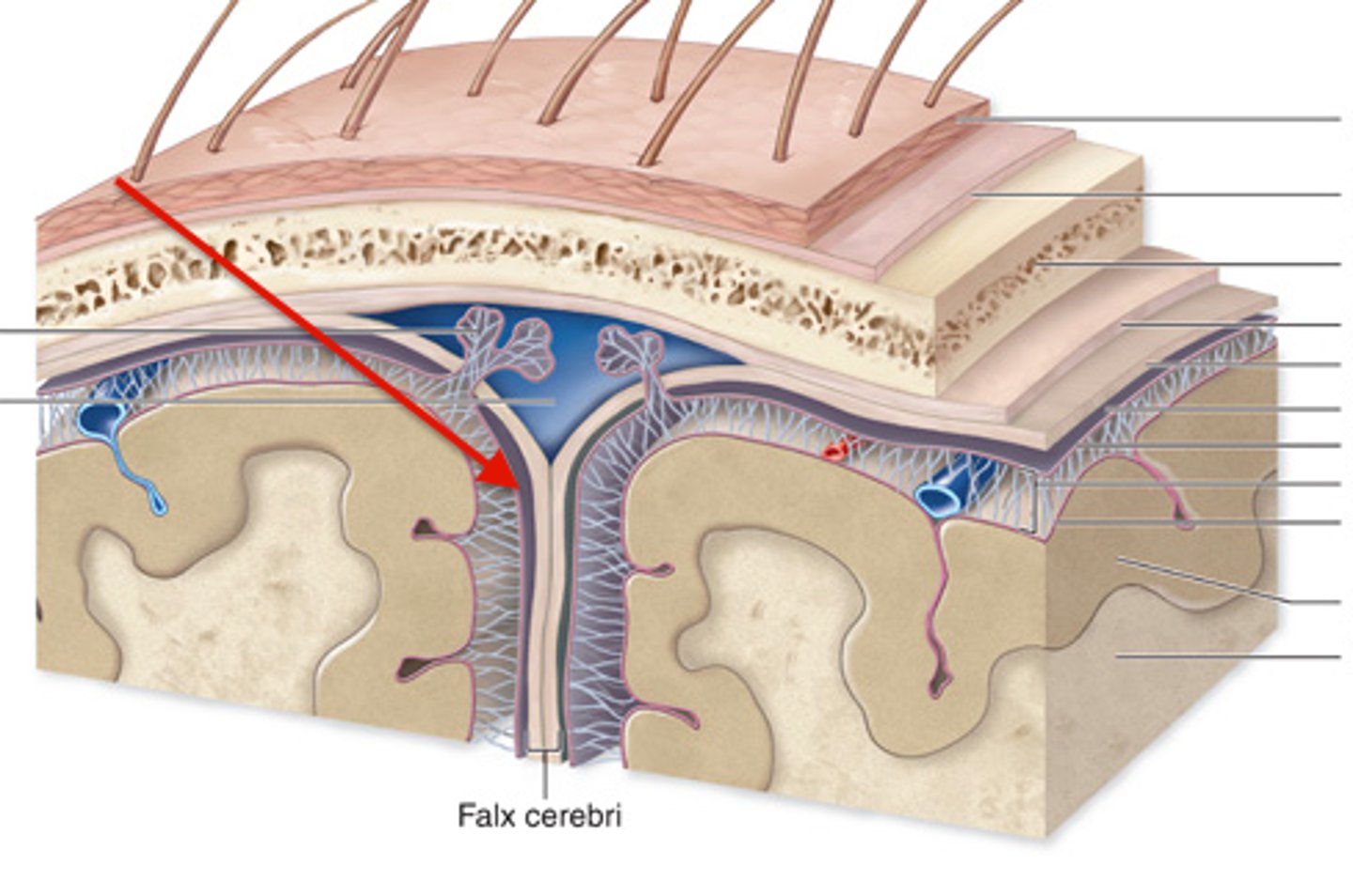
meninges function
protect brain and spinal cord
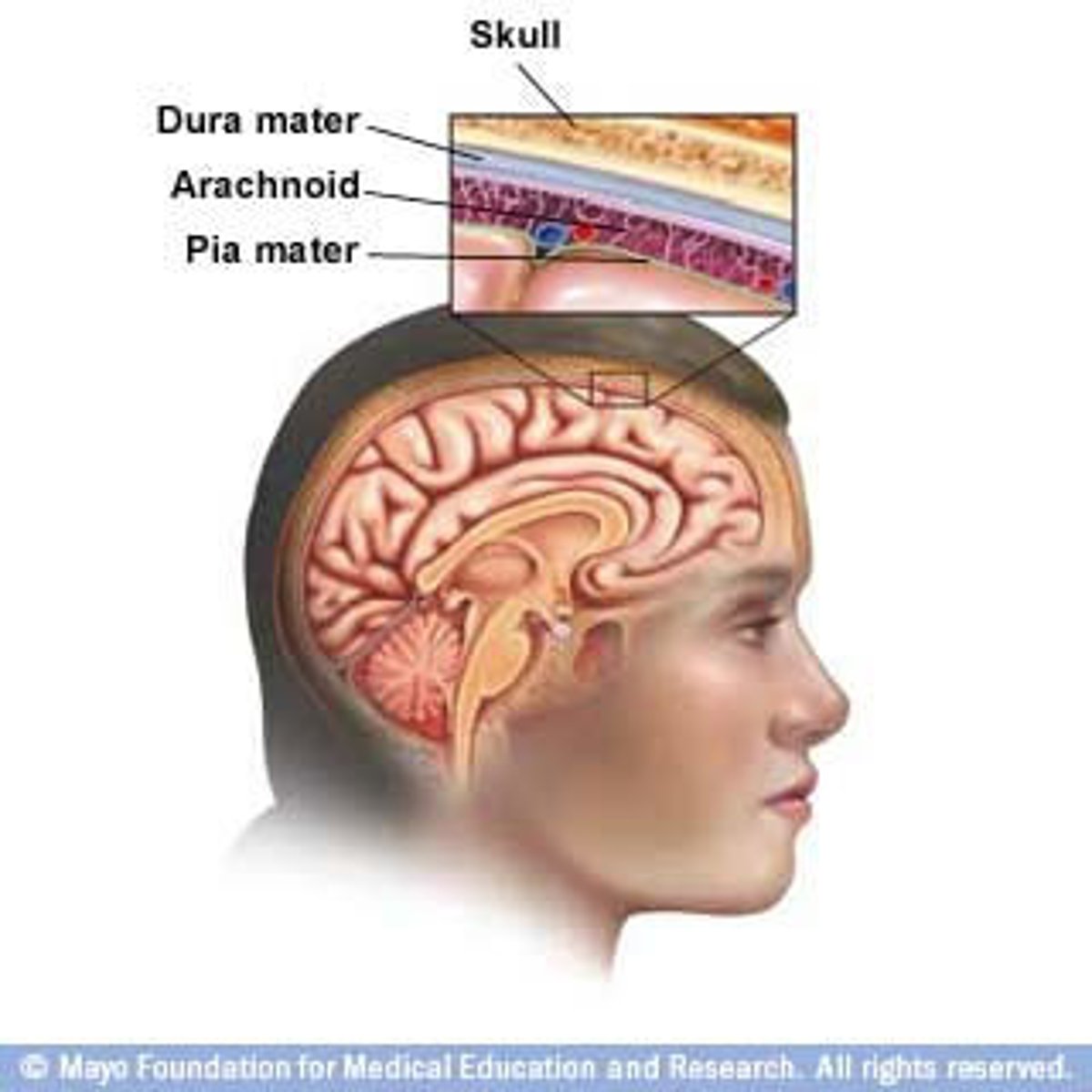
pia mater
deepest meninge, follows every contour of the brain
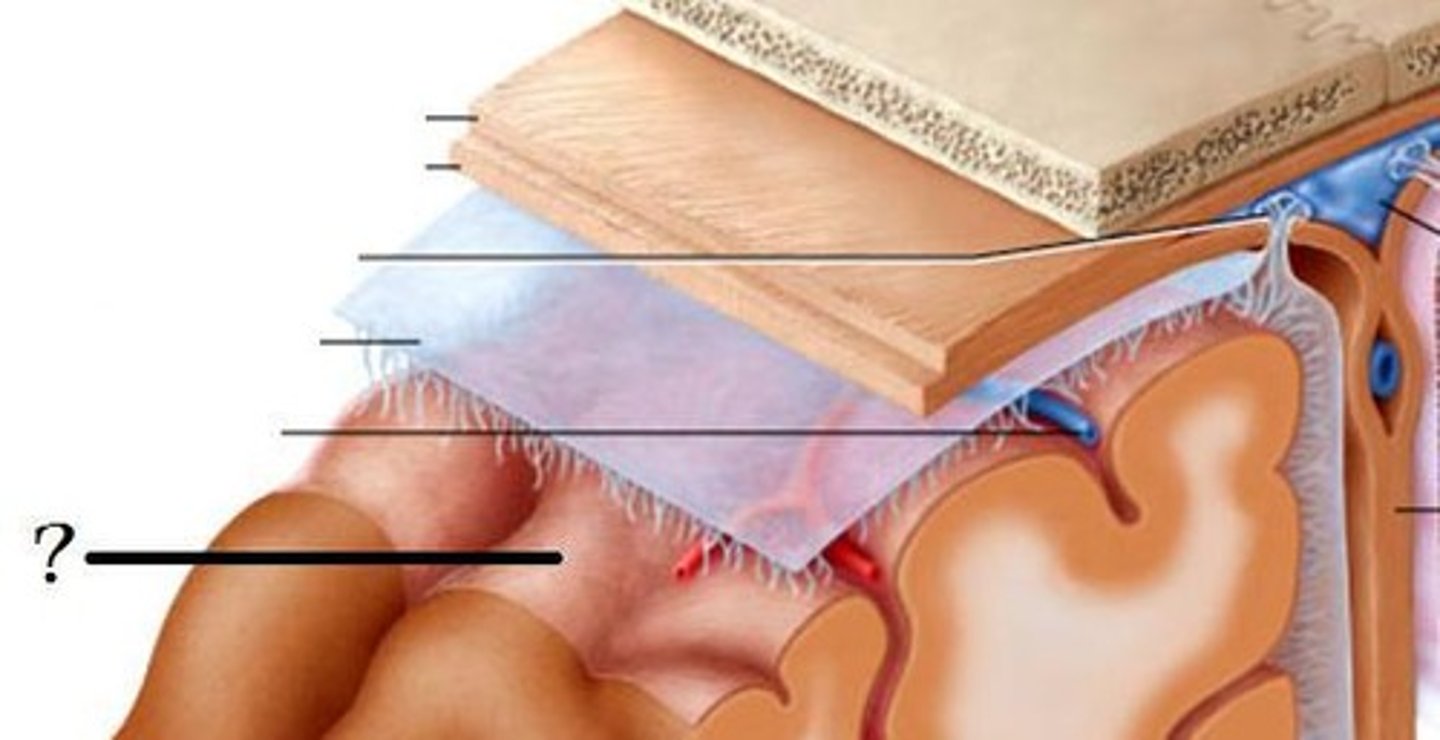
arachnoid mater
middle meninge, collagen and elastin fiber, spider web look
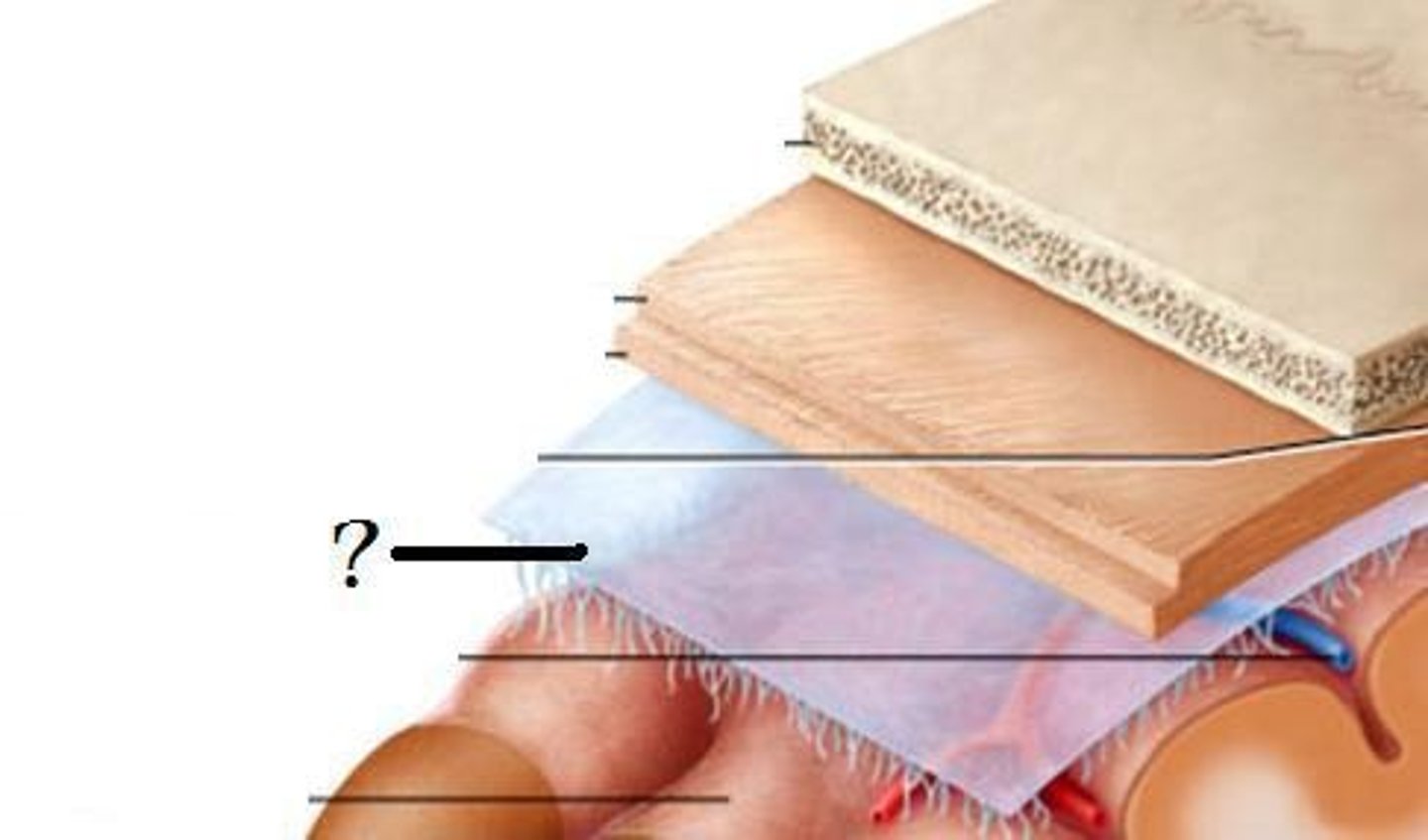
dura mater
made up of tough fibrous connective tissue, made up of the periosteal layer (creates periosteum of skull bone)
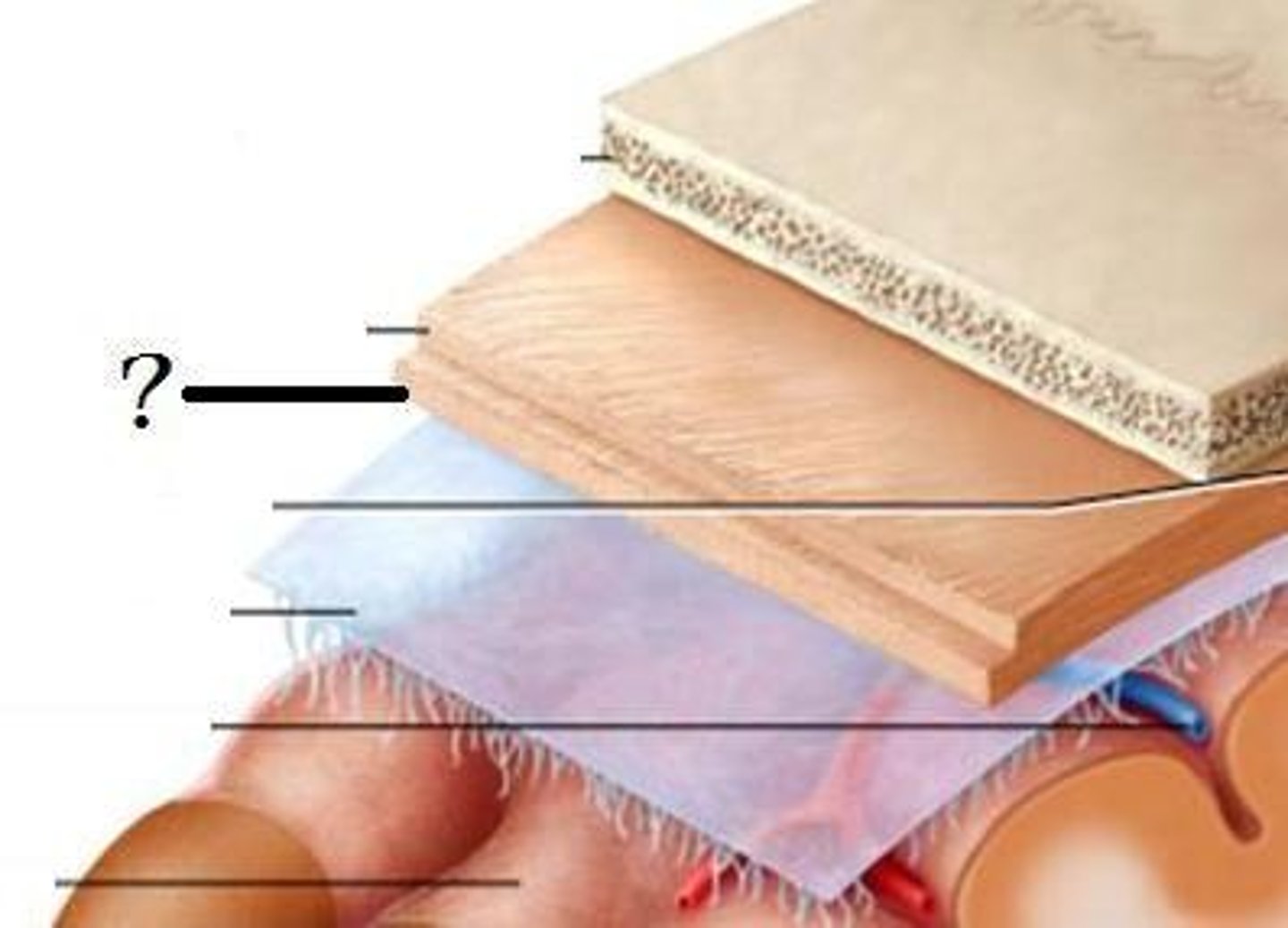
subarachnoid space
filled with cerebrospinal fluid
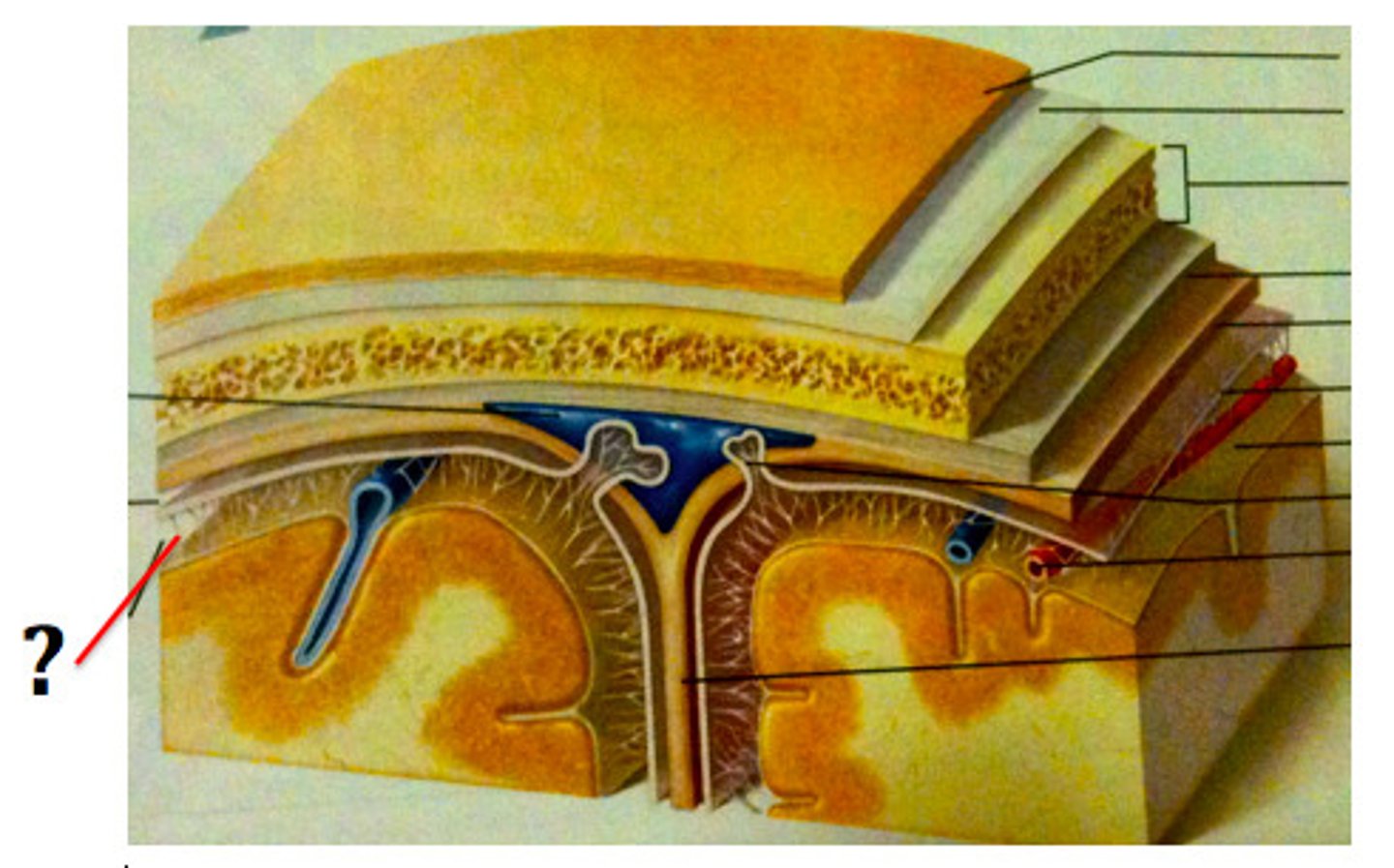
dural folds
Folded inner layer of dura mater
Extend into cranial cavity
Stabilize and support brain
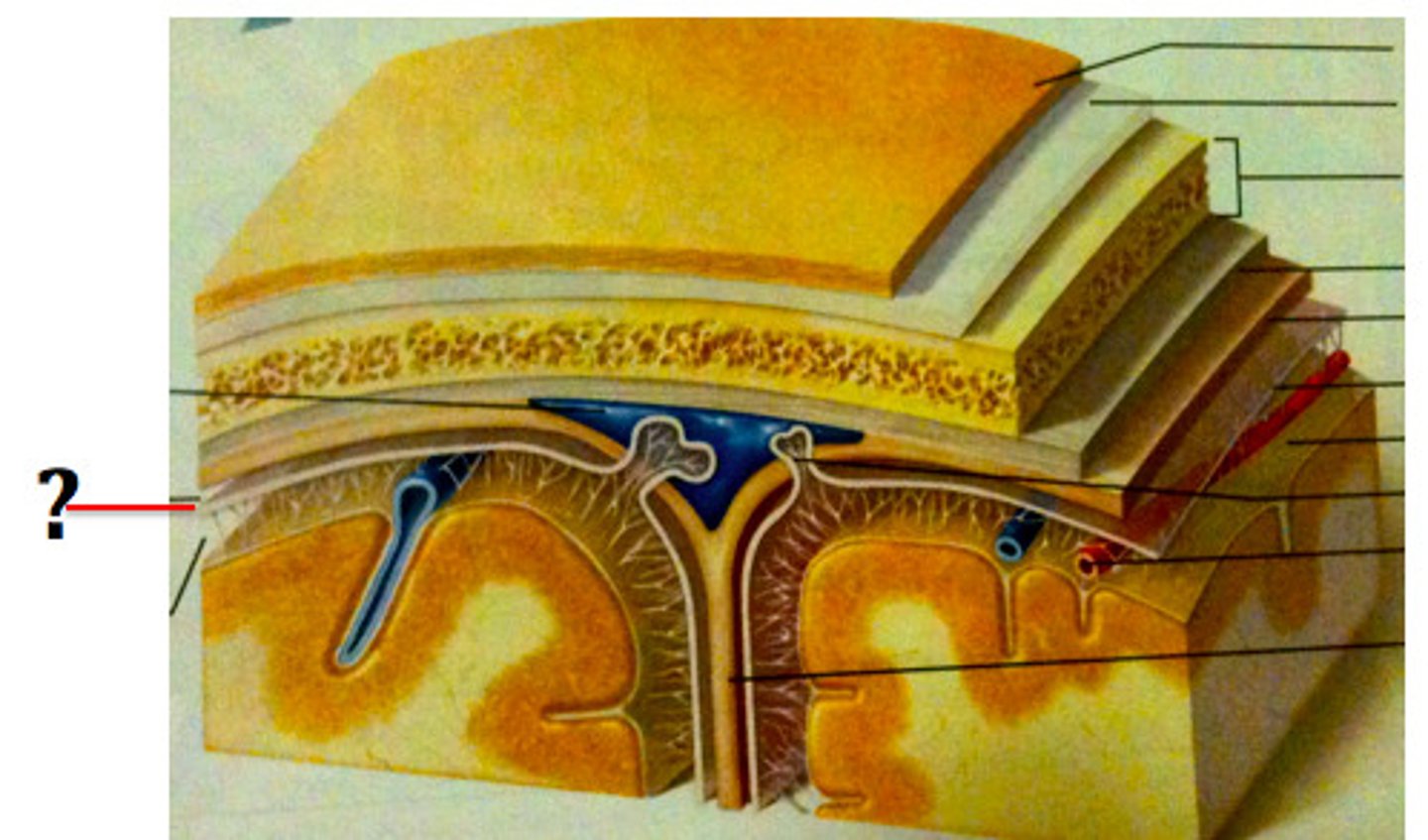
subdural space
below the dura mater
potential space (if you have a head injury
the blood goes into the subdural space)

falx cerebri
separates the two hemispheres of the cerebrum
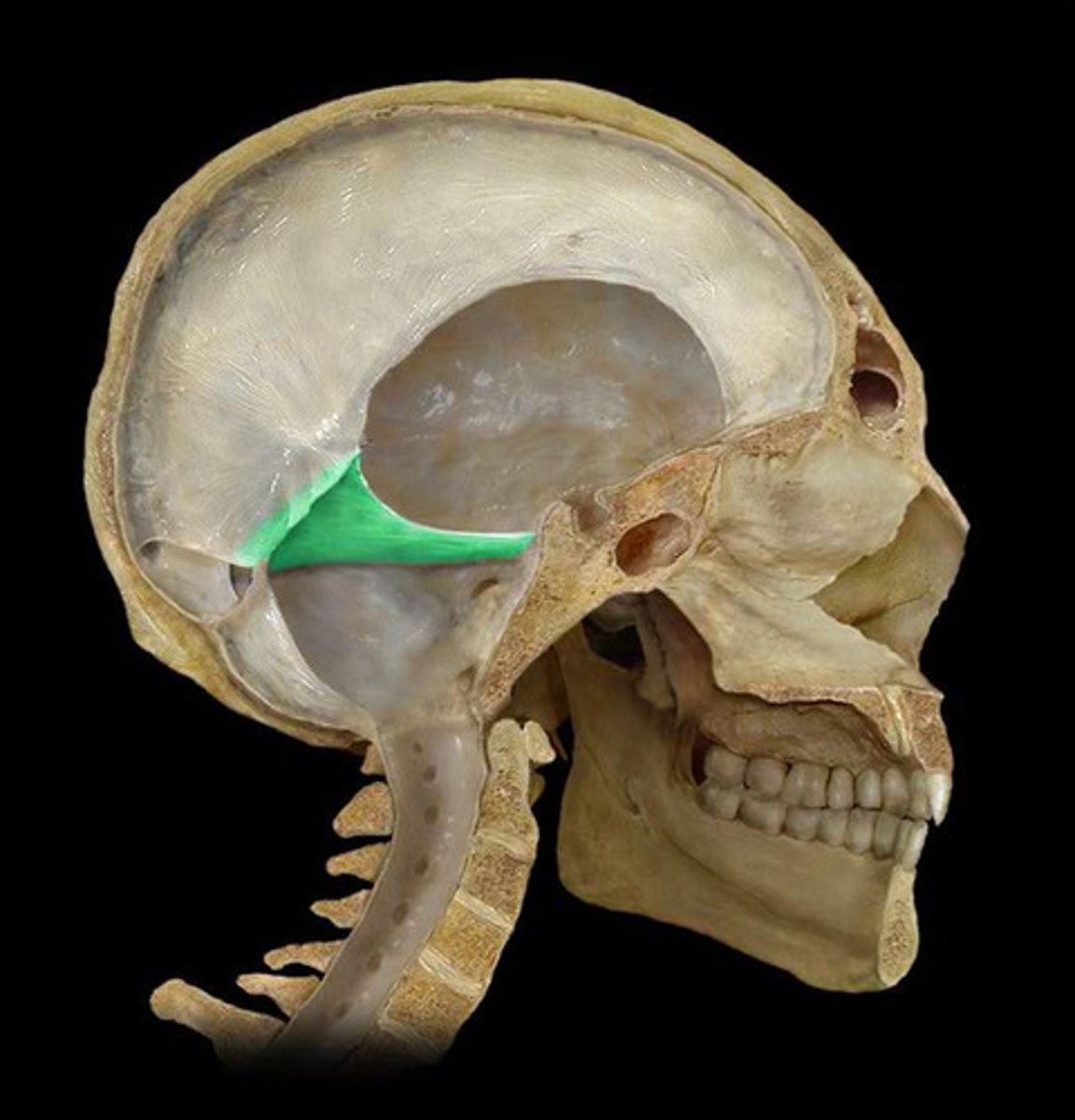
tentorium cerebelli
horizontal dural fold over cerebellum and in transverse fissure
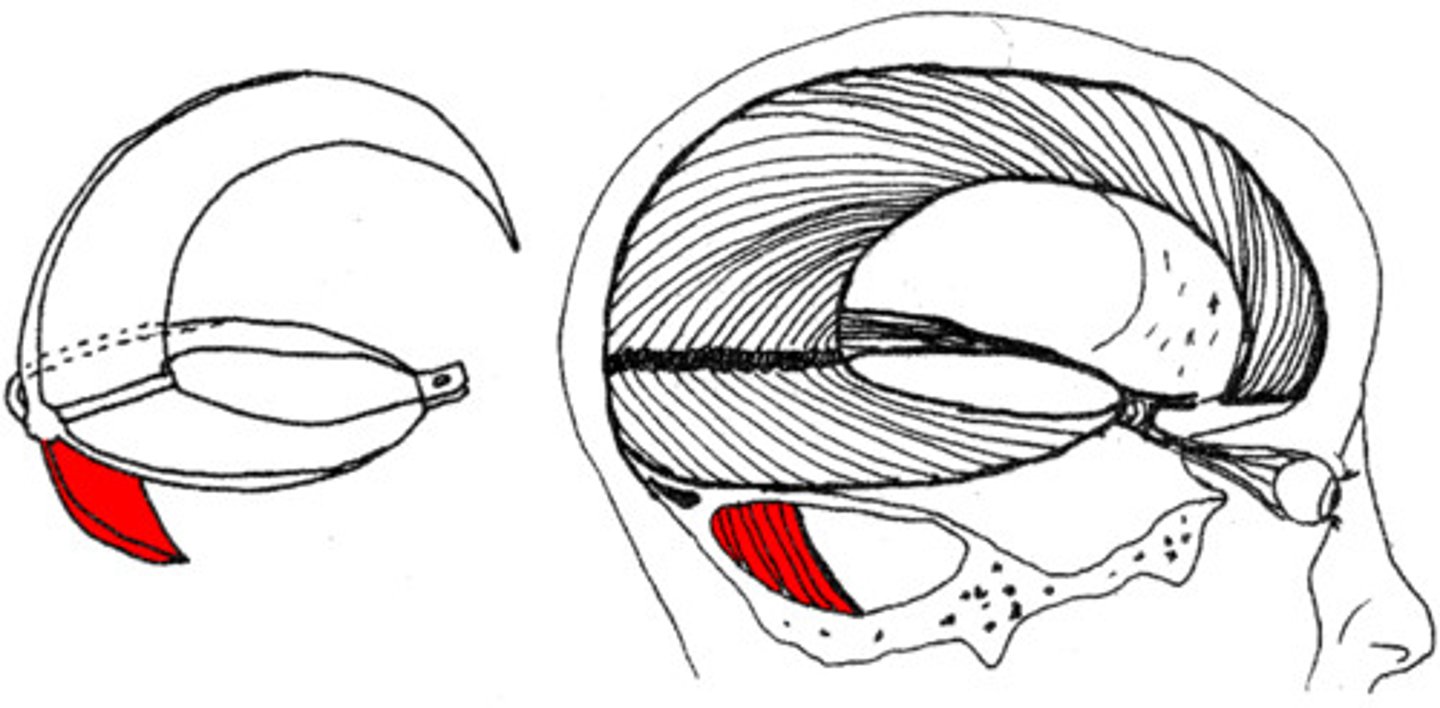
falx cerebelli
separates the two hemispheres of the cerebellum
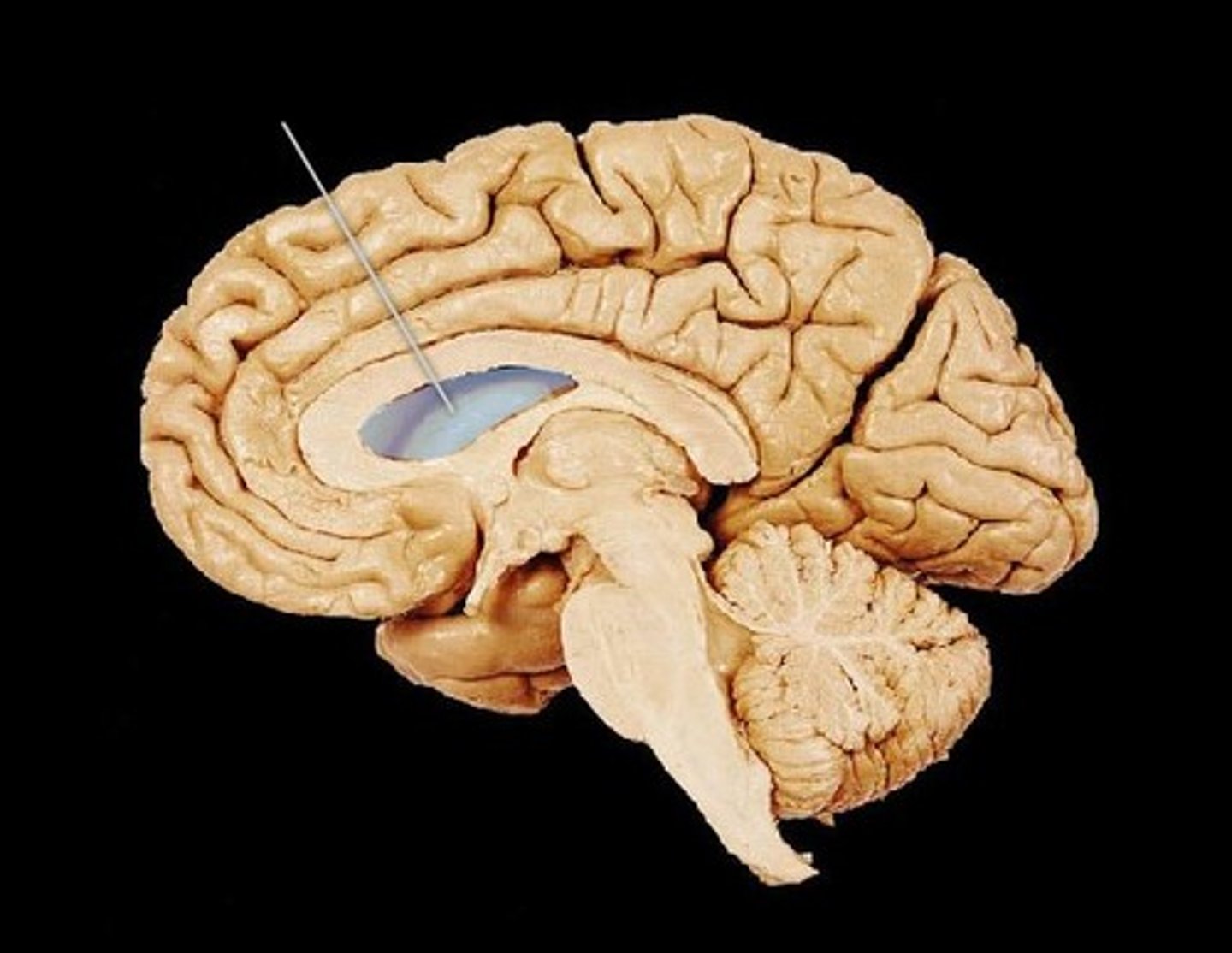
ventricles of the brain
canals in the brain that contain cerebrospinal fluid
lateral ventricles
Ventricles located in each cerebral hemisphere
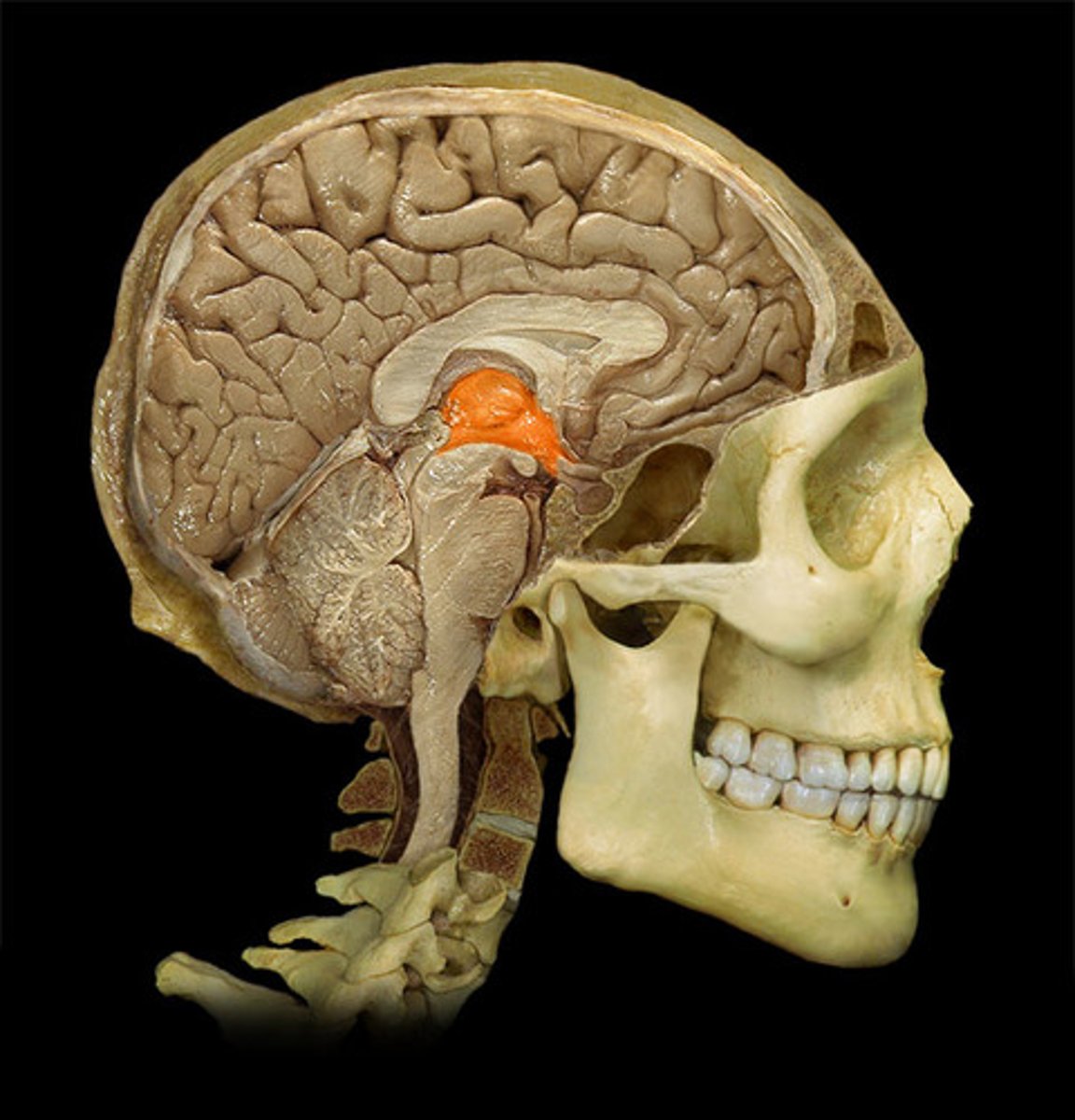
third ventricle
the ventricle located in the center of the diencephalon
fourth ventricle
between pons and cerebellum
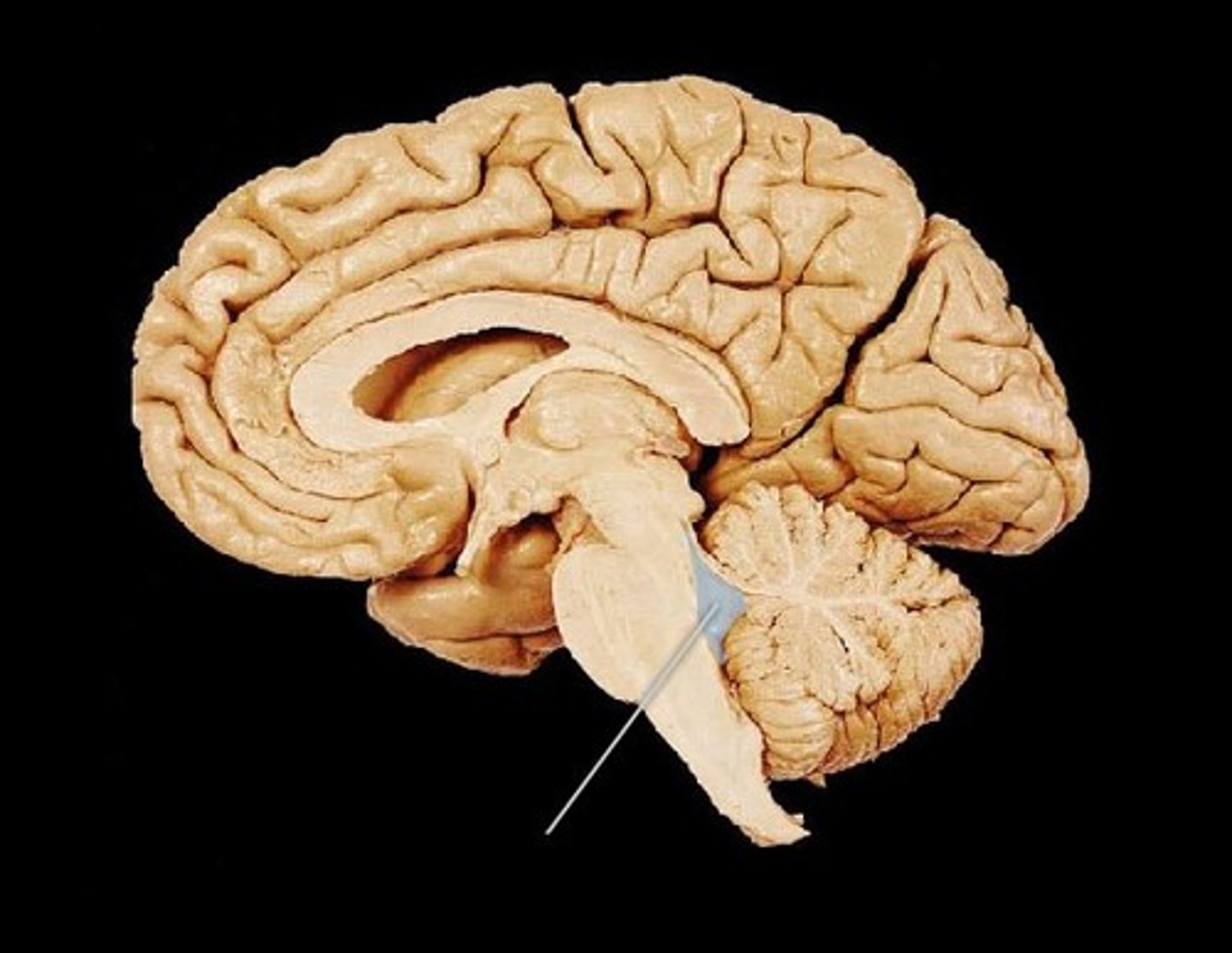
interventricular foramen
opening that connects the lateral ventricles and 3rd ventricle
cerebral aqueduct
connects the third and fourth ventricles
cerebral spinal fluid
made by choroid plexus
CSF function
buoyancy (supports 95% of the weight of the brain), protection (liquid cushion for brain tissue), chemical stability (transports nutrients to brain and waste away from brain)
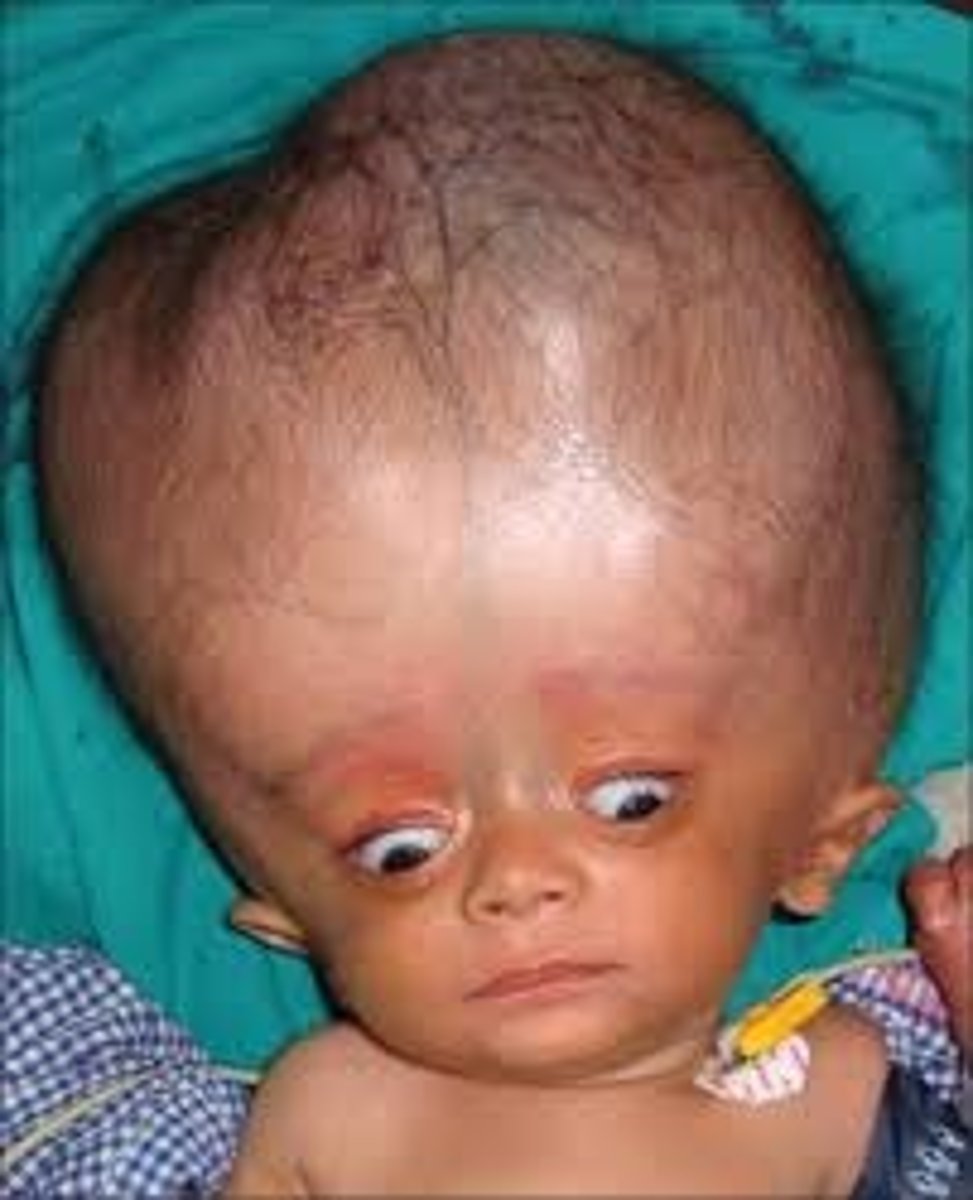
Hydrocephalus
accumulation of CSF in the spaces of the brain